IMED1001 - ANS 1 (Week 12)
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
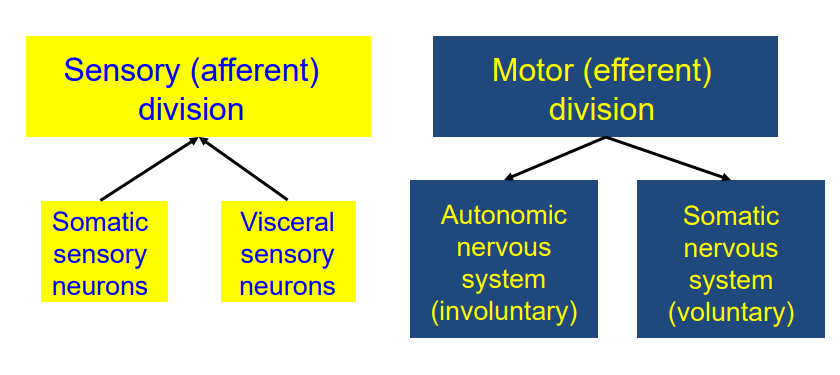
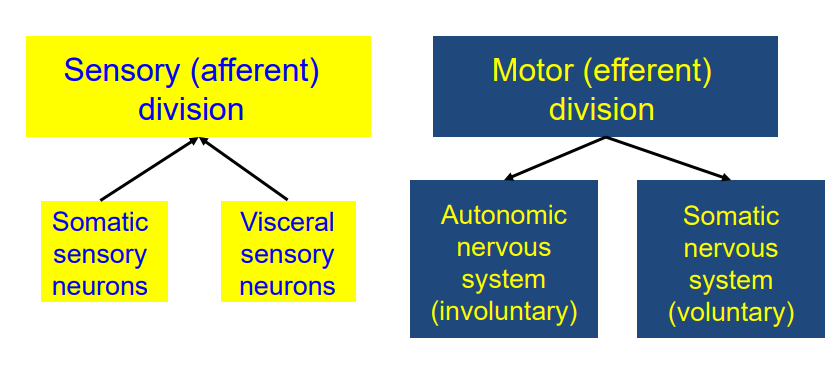
Peripheral Nervous System
- Sensory (Afferent) Division is split into Somatic Sensory and Visceral Sensory Neurons
- Motor (efferent) division is split into autonomic NS (involuntary) and Somatic NS (Voluntary)
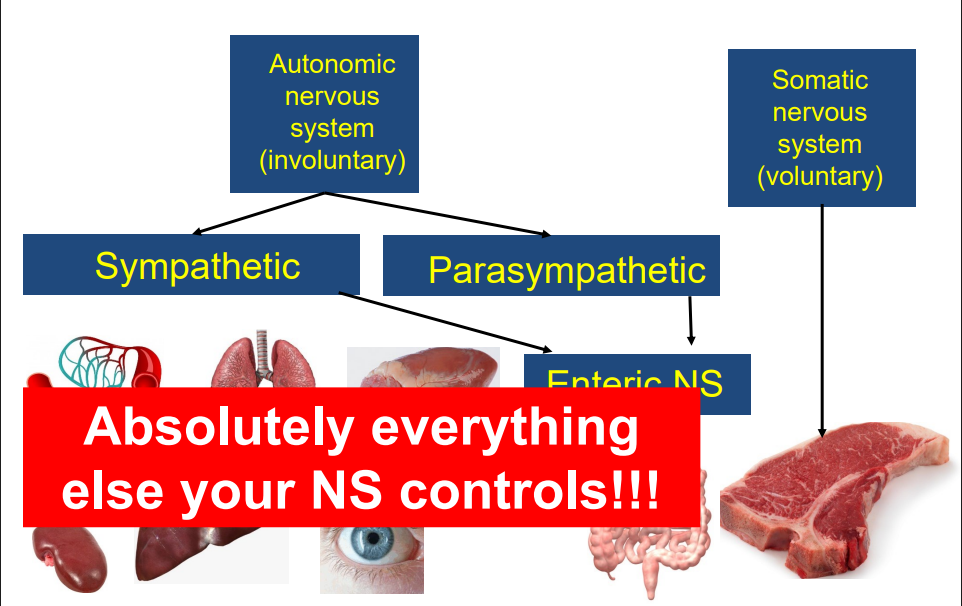
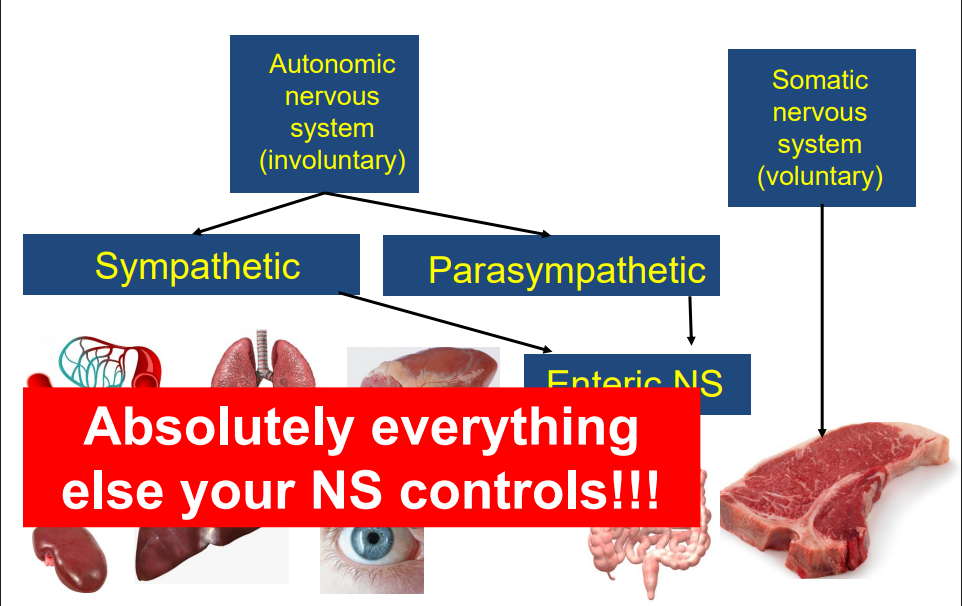
Peripheral NS Diagram
- somatic NS controls muscle, Autonomic NS controls everything else
- sympathetic NS has enteric NS
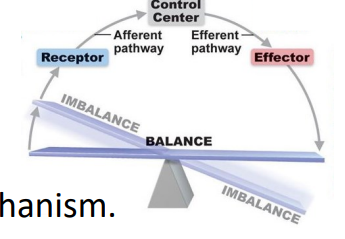
Role of ANS in vegetative functions
- essential homeostatic control mechanism
- regulates fundamental states and life processes (known as vegetative functions)
- examples of vegetative functoins: Heart rate, BP, body temp, digestion etc.
- animals with their ANS blocked cannot survive on their own (have to be kept warm and stress-free)
- we have drugs that can block "ganglia" (processing centres of NS) which renders you useless
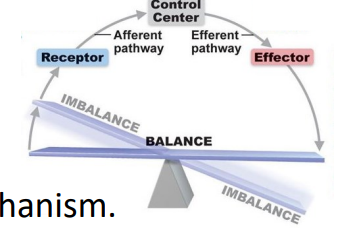
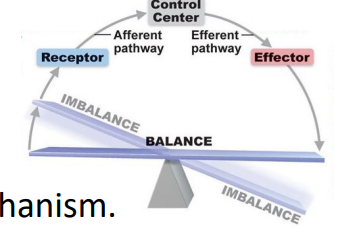
Features of Autonomic Reflex
- visceral reflex arc
- Unconscious, automatic, stereotyped responses to stimulation involving visceral receptors and effectorsX
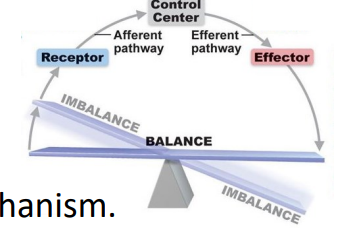
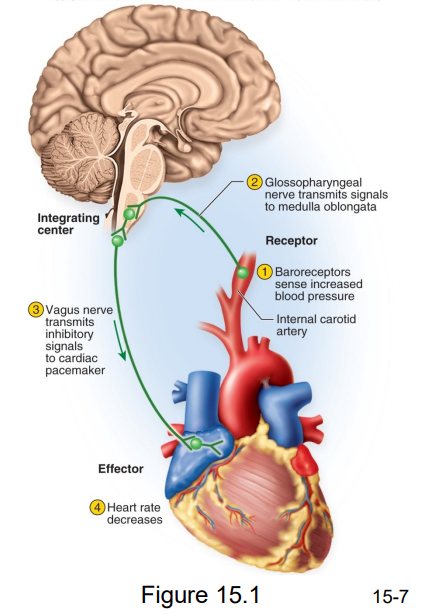
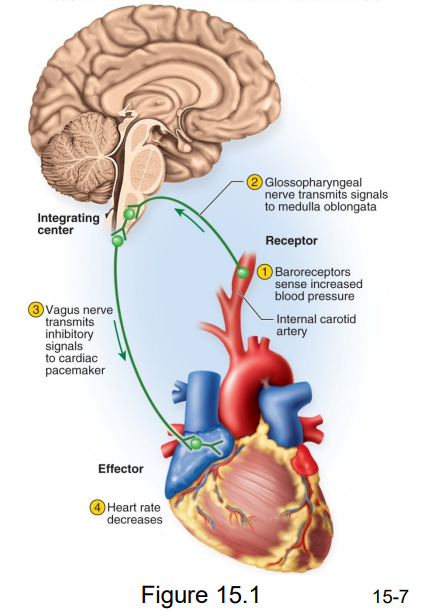
Baroreceptor Reflex
- for blood pressure
1. blood pressure detected by arterial stretch receptors
2. afferent neuron carries signal to CNS
3. efferent signals travel to the heart;
4. heart then slows, reducing blood pressure
- example of homeostatic negative feedback loop
- its parasympathetic because its slowing down the heart (thats why vagus nerve is used)
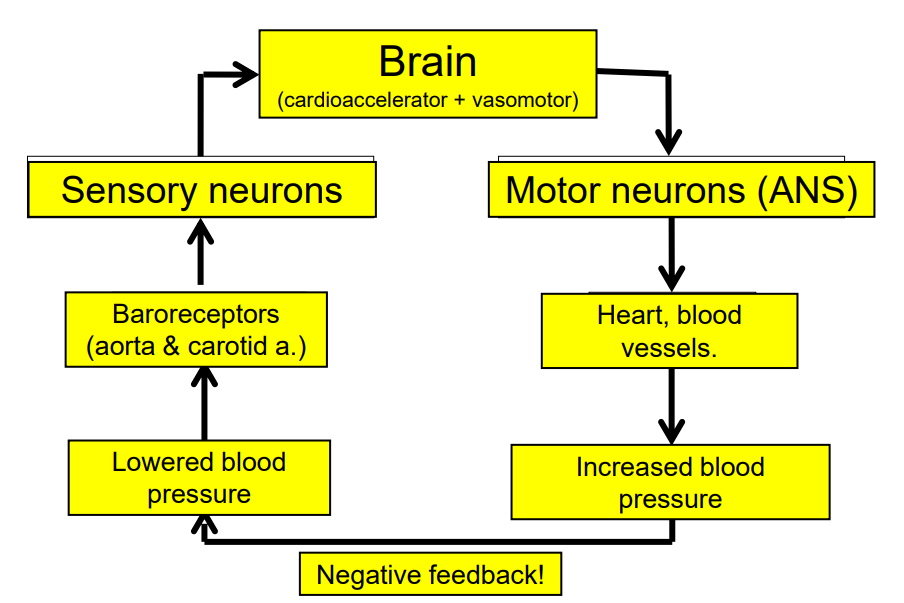
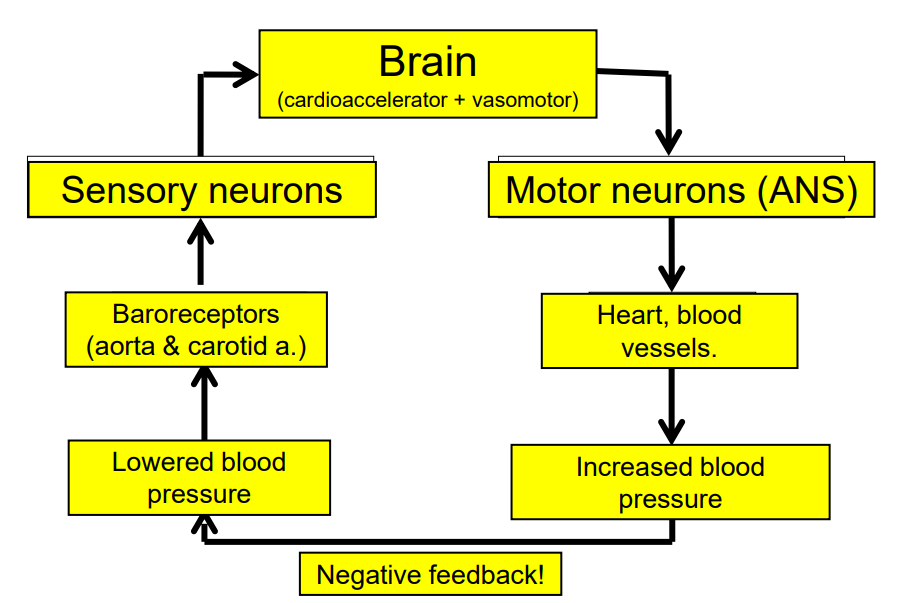
Feedback Loop for Baroreceptor
DIAGRAM ON SLIDE 8
Autonomic vs Conscious (Examples)
- Purely autonomic: blood pressure, kidney function, digestion
- Linked to consciousness: temperature, hunger, thirst, defecation, urination
Autonomic Reflexes with conscious control
TWO POINTS OF CONTROL:
- AFFERENTs go to both conscious and subconscious centres
- EFFERENTS (ANS controls automatic functions (secretion, smooth muscle and somatic NS controls behavioural override (skeletal muscle)
Spinal Cord Reflexes:
- defecation and micturition reflexes are integrated in spinal cord
- We control these functions because of our control over skeletal muscle sphincters; if the spinal cord is damaged, the smooth muscle of bowel and bladder is controlled by autonomic reflexes built into the spinal cord
- its kind of like an override. if we didnt have it for urination and defecation we would never have control. the body just stuck a skeletal muscle in these areas so we can control it
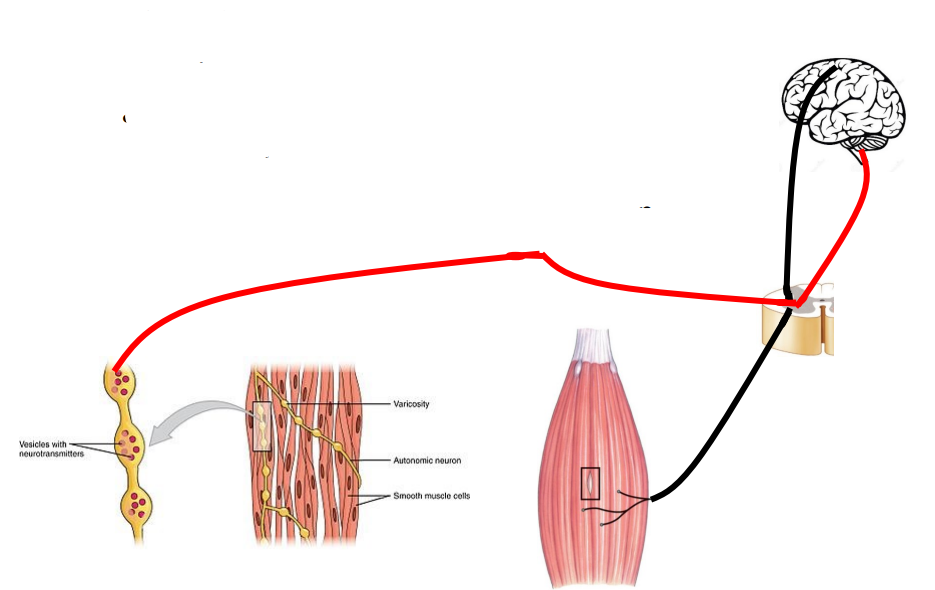
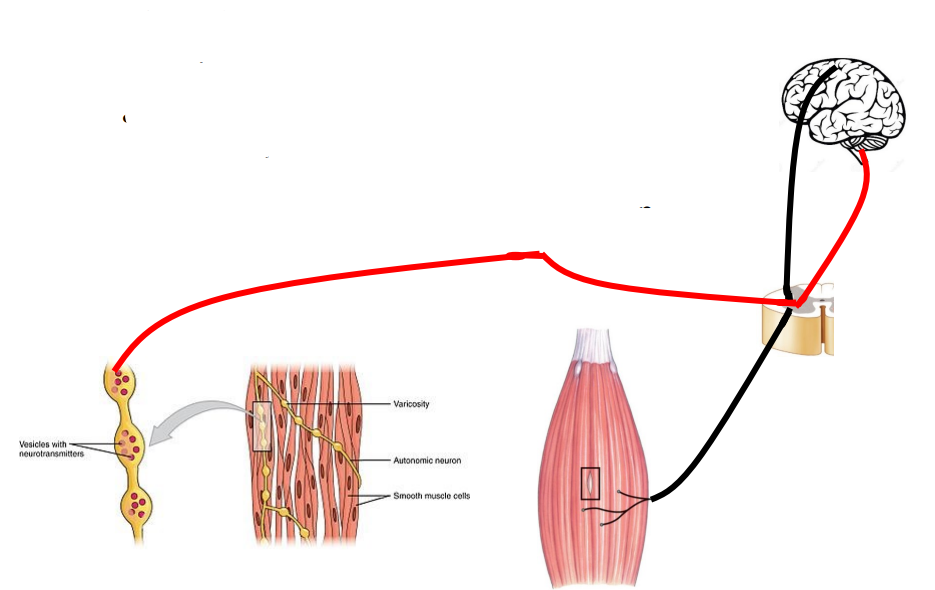
Autonomic reflexes with conscious control (examples)
spinal cord reflexes in urination and defecation:
- Internal sphincter: smooth muscle - Autonomic Control
- External sphincter: skeletal muscle - Somatic Motorneuron Control
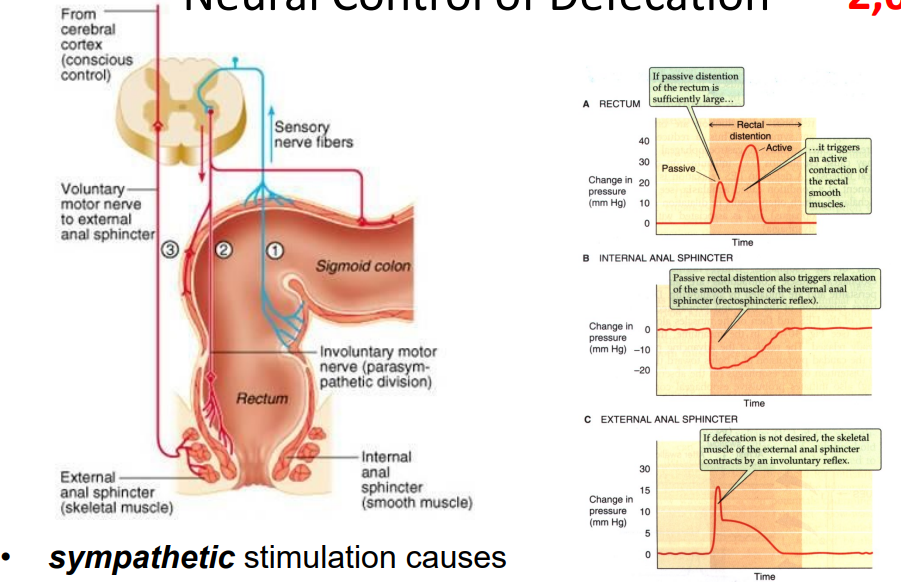
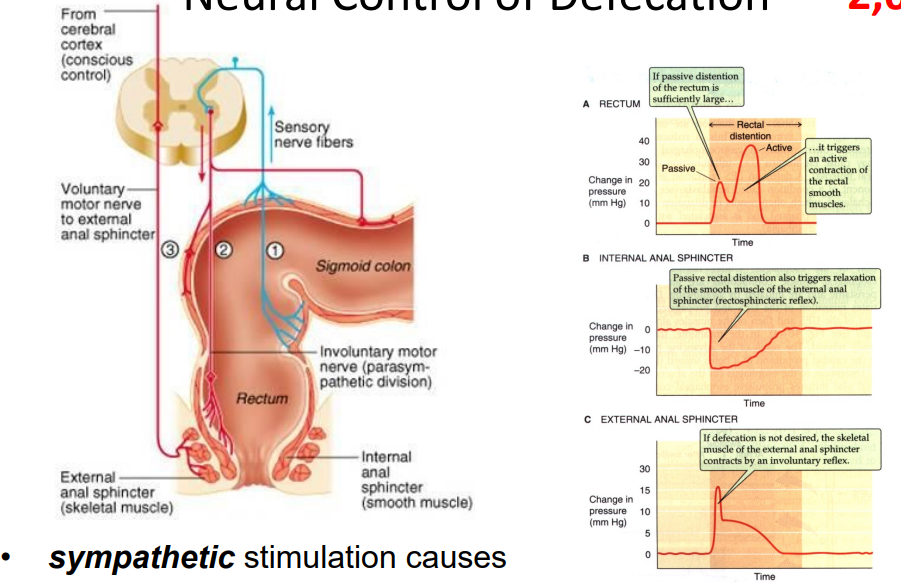
Neural Control of Defecation
- sympathetic stimulation causes contraction, parasympathetic stimulation causes relaxation
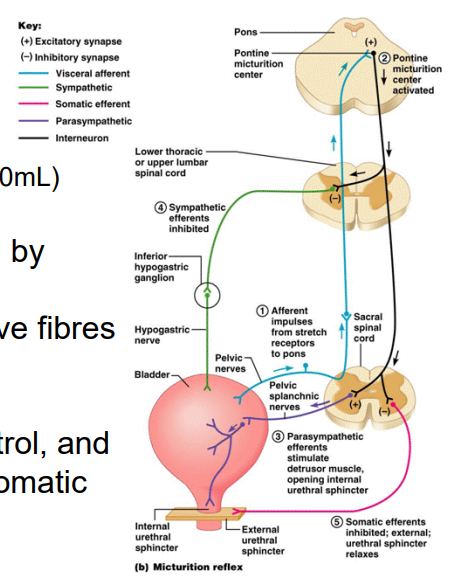
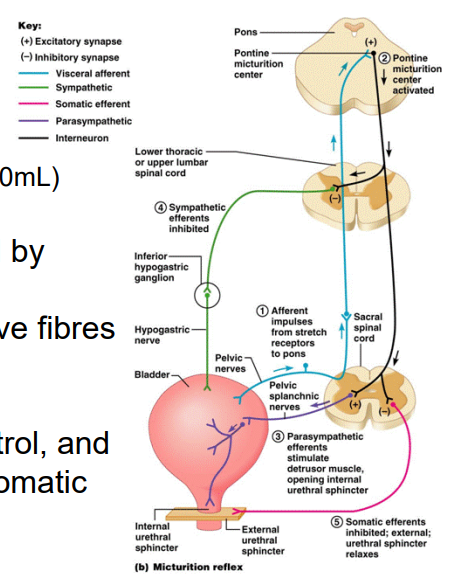
Neural Control of Urination
- micturition reflex
- afferents sense stretch (300-400mL)
- detrusor and internal urethral sphincter muscle is innervated by the sympathetic (storage) and parasympathetic (to urinate) nerve fibres from spinal cord
- external urethral sphincter muscle is under voluntary control, and as such is innervated by the somatic nervous system
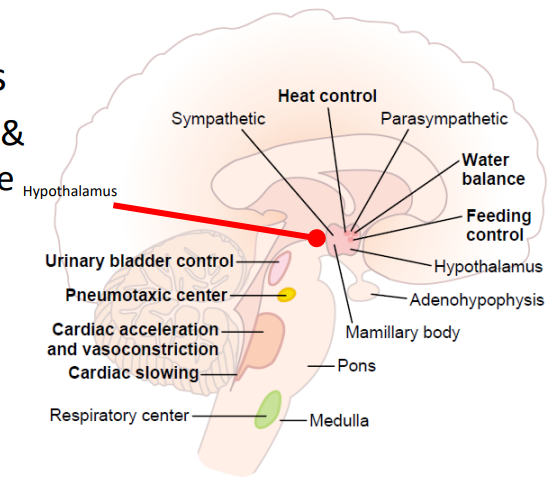
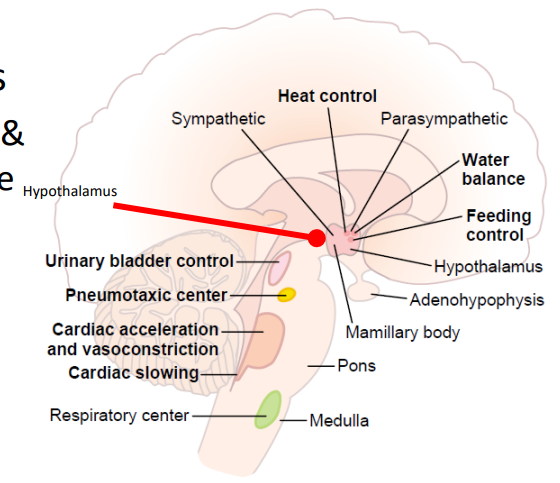
Control of Autonomic Function
ANS REGULATED BY SEVERAL LEVELS OF CNS
- Hypothalamus (major visceral motor control centre): nuclei for primitive functions - hunger, thirst, sex (master gland)
- Midbrain, pons and medulla: nuclei for cardiac and vasomotor control, salivation, swallowing, sweating, bladder control, and pupillary changes
- Cerebral cortex has an influence (anger, fear, anxiety): powerful emotions influence the ANS because of the connections between our limbic system and the hypothalamus.
- we sort of have a conscious control of the unconscious
Respiratory and Cardiac Centres and Blood Vessels
RESPIRATORY CENTRES: respiratory centre and pneumotaxic centre
CARDIAC CENTRES: cardioacceleratory and cardiac slowing
BLOOD VESSELS (BP): Vasomotor
- dont need to know how to label the diagram, just need to know that they exist
Tone
we refer to someone as having a sympathetic or parasympathetic tone
Fight or Flight Response
GET MORE OXYGEN AND FUEL TO YOUR MUSCLES (PREPARING FOR FLIGHT):
- bronchodilation, increased HR and Cardiac Output, vasodilation at muscles, breakdown of stored glucose (liver, muscle) and fat (adipose tissue) increases plasma [glucose] and [fats], blood vessel constriction (increased BP drives blood to where you need it)
- shuts down renal/hepatic/gastrointestinal tract blood flow and function, peripheral and visceral vasoconstriction
COOL DOWN:
- lots of sweat
PREPARING FOR FIGHT:
- Same as flight, plus you:
- see beter (dilate pupils)
- Increased strength and skill (increased muscle tone, increased mental activity)
- Lose less blood (peripheral vasoconstriction, increased clotting response)
Parasympathetic System - Rest and Digest
- slows down heart rate
- increased glandular (secretion) and muscular (peristalsis) activity in the gut, increased blood flow to the gut to pick up all the goodies
- increased sexual arousal, eye ciliary muscle constriction (all the better to see nearby faces)
- pupillary constrictions (sleep easier)
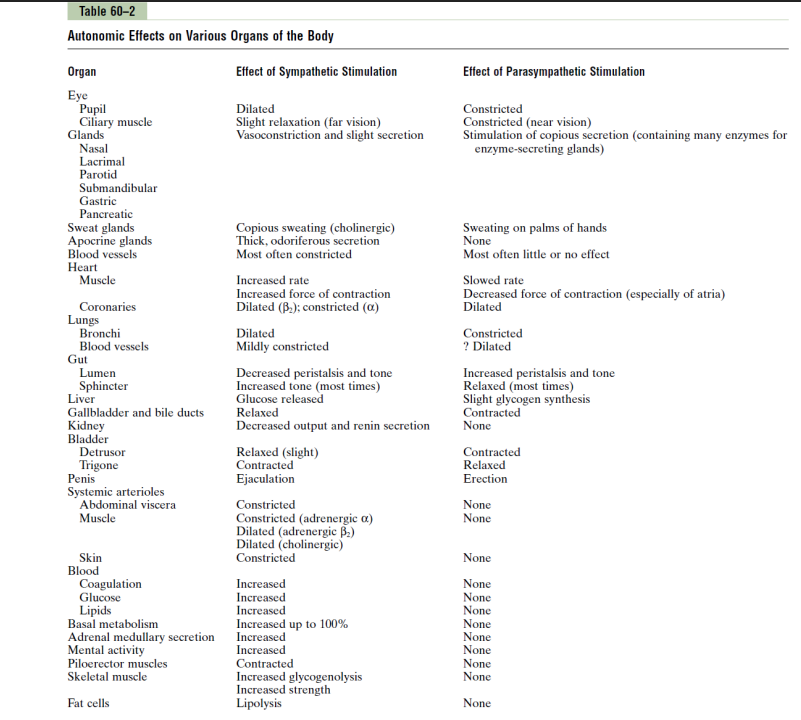
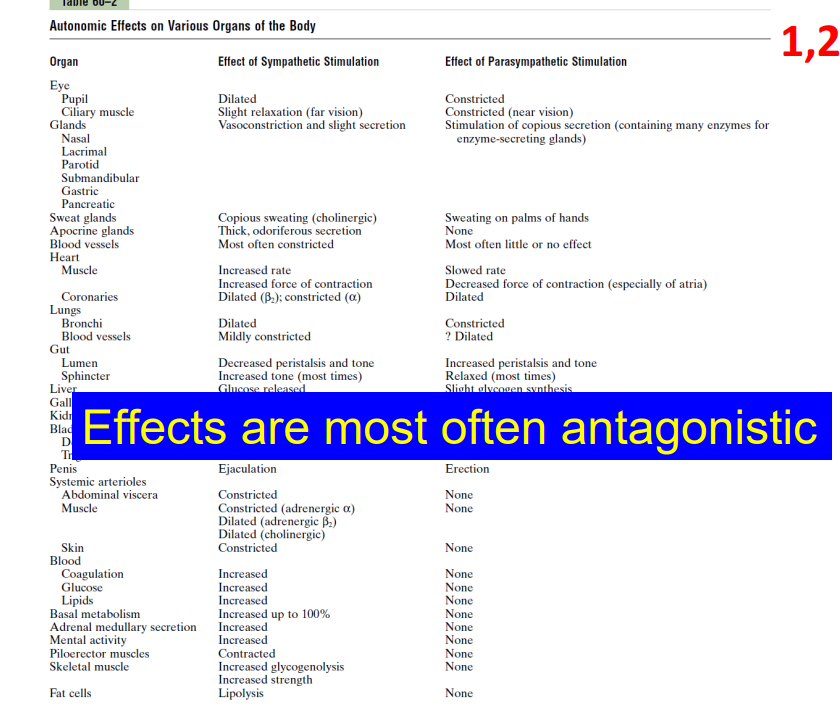
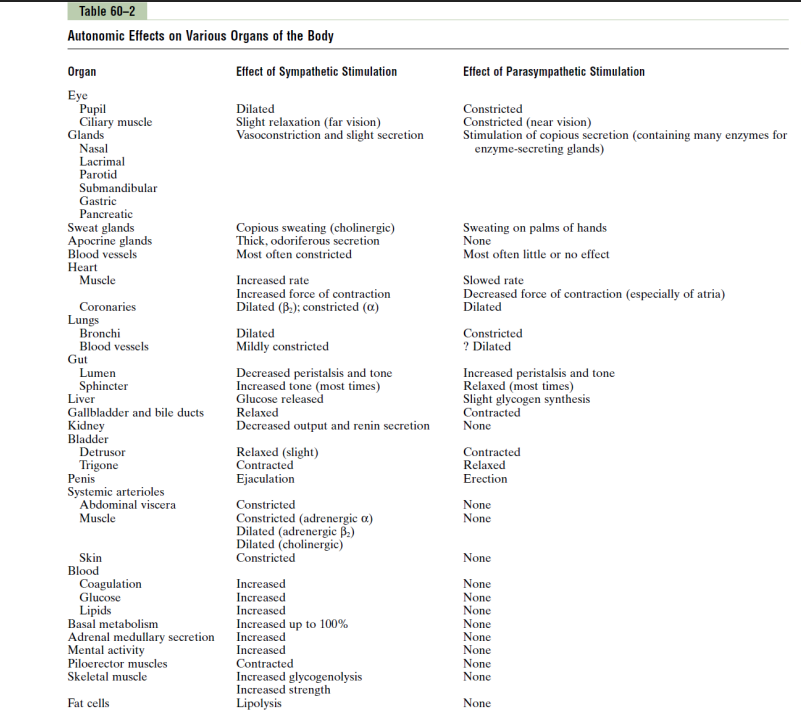
Easiest Way to Antagonise - Dual Innervation
- organs innervated by both parasympathetic and sympathetic divisions (antagonistic effect: oppose eachother)
- however some of them arent dual innervated
- Autonomic tone: normal background firing rate -> balance between the two divisions (Parasympathetic tone maintains smooth muscle tone in intestines and holds resting heart rate down to around 70-80 beats per minute. Sympathetic tone keeps most blood vessels partially constricted and maintains blood pressure
- e.g if we increase sympathetic tone, we get vasoconstriction, if we decrease sympathetic tone we get vasodilation. its not dual innervation, its the same nerve that is like a "switch"
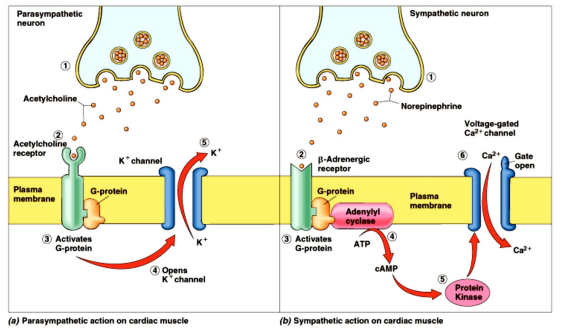
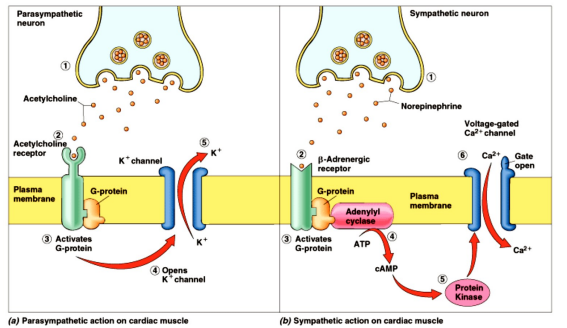
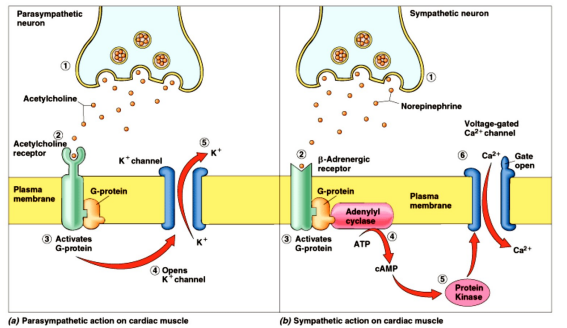
Heart Rate - Dual Innervation
- antagonistic effects - oppose eachother
- May be exerted through dual innervation of same effector cells (heart rate decreases (parasympathetic) or heart rate increases (sympathetic)
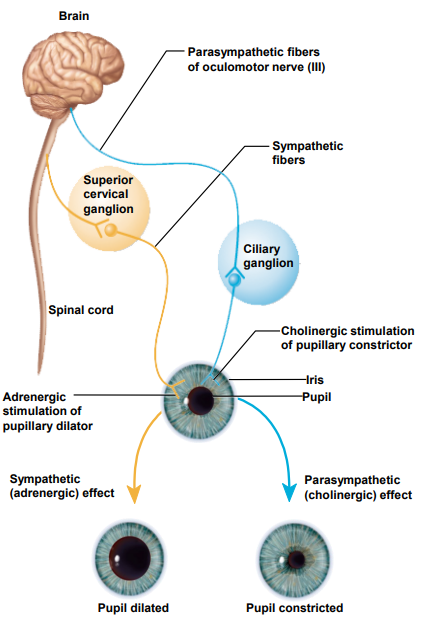
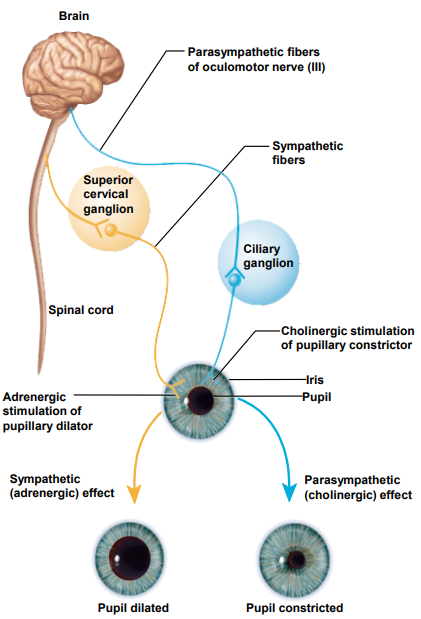
Eyesight - Dual Innervation
- exerted because each division innervates different cells
- Pupillary dilator muscle (sympathetic) dilates pupil
- Constrictor pupillae (parasympathetic) constricts pupil
- stereotyped = both eyes dilate or constrict at once (dilation of one eye is indicative of CNS trauma)
Some exceptions to dual innervation
- synergistic effects: two divisions act on different effectors to produce a unified overall effect (Parasympathetic NS increase salivary serous cell secretion, Sympathetic NS increase salivary mucous cell secretion)
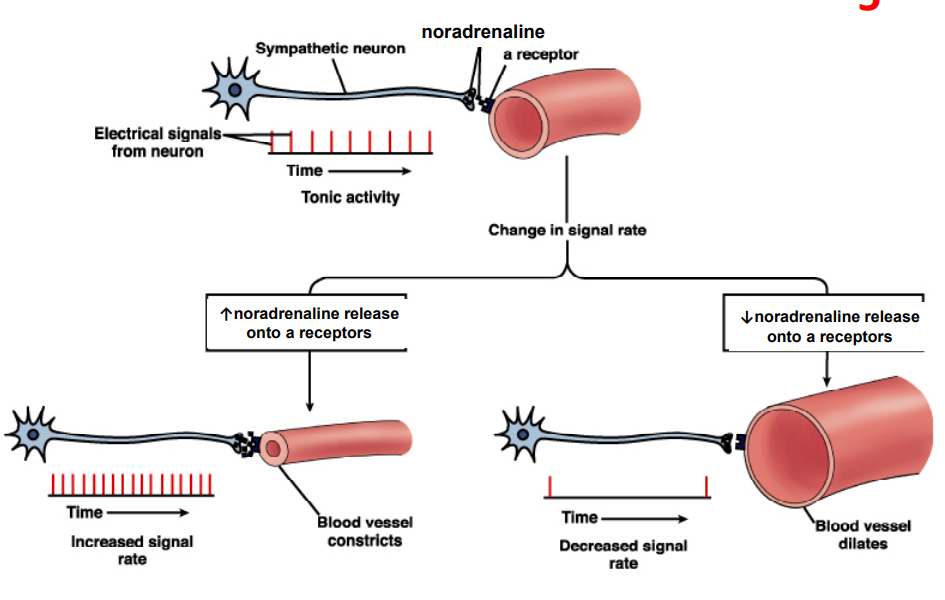
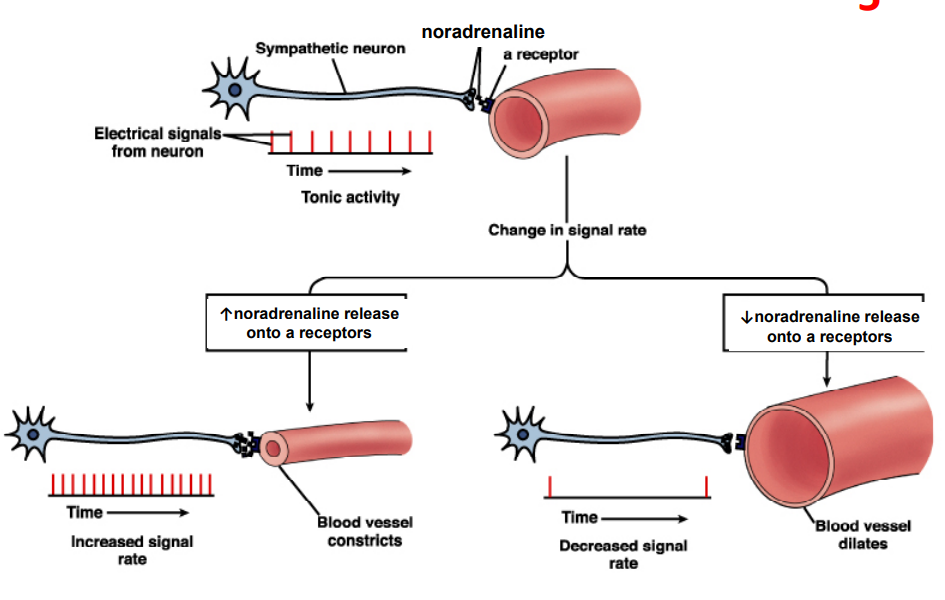
- Not all organs receive dual innervation:
- sweat glands receive only sympathetic neurons
- blood vessels (arterioles and veins) receive only sympathetic nerve fibres, except penis and clitoris
- sympathetic tone (vasomotor tone): increase in firing frequency means vasoconstriction, decrease in firing frequency means vasodilation
- needs alpha receptors, otherwise effect won't happen in blood vessels
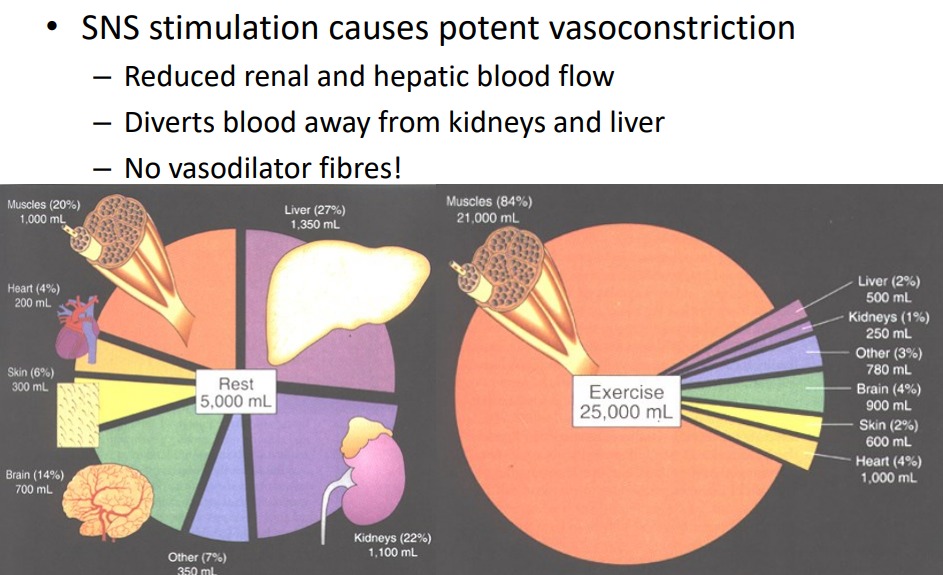
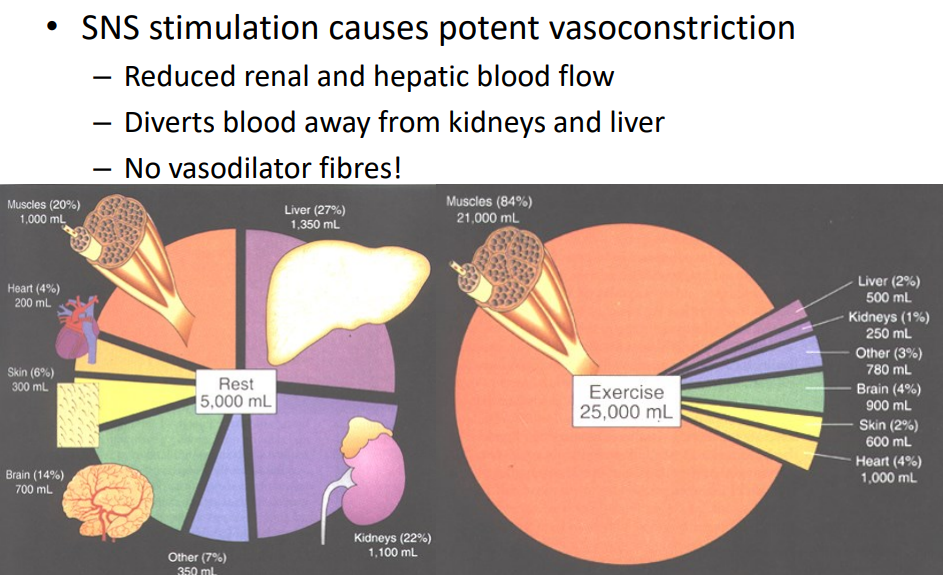
Kidney and Liver Bloodflow Control
- SNS stimulation causes potent vasoconstriction
- reduced renal and hepatic blood flow
- diverts blood away from kidneys and liver
- no vasodilator fibres

Summary
DIAGRAM ON SLIDE 31
