L3 Population Growth and Regulation
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
What is exponential growth?
Exponential growth is any change in numbers with time that occurs at a constant per capita(per individual) rate
What is per capita?
per individual
Why does population size have the capacity for exponential increase?
Because living organisms self replicate
When does the exponential growth rate mean the yearly population is proportional to?
Exponential growth means yearly population growth is proportional to population size: arises from a birth rate per female that remains constant over time
What does the exponential model assume?
The exponential model assumes no competition among the members of a species (intra-specific) for the available resources (density independent, no carrying capacity)
What are the 2 types of exponential growth?
• Discrete growth: change happens at specific intervals
• Continuous growth: change happens at every instant
In Exponential growth in discrete generations (semelparous life history), instead of absolute numbers of births and deaths, what do we use?
we often talk in terms of rates per individual (per capita):
b = per capita birth rate
d= per capita death rate
What is the difference between b and d?
The difference between b and d becomes one parameter: R net growth rate (remember that for semelparous species, this is equivalent to R0 basic reproductive rate)
How do you work out Exponential growth in discrete generations (semelparous life history)?
Nt+1 = Nt (b-d) = Nt R
b = per capita birth rate
d= per capita death rate
R = net growth rate
How can you predict the size of a population at any given time?
Nt+1 = NtR OR Nt = N0Rt
t = time
What can Continuous exponential growth (iteroparous life history) be determined by?
Exponential continuous growth can be determined by dividing the change in population size (ΔN) by the time interval (Δt) for a certain population size (N):
𝑑𝑁/𝑑𝑡 =B-D
𝑑𝑁/𝑑𝑡 = population growth rate
What does 𝑑𝑁/𝑑𝑡 mean?
'dN/dt' is a single term (differential) meaning the rate of change over time, t, in numbers N (i.e. how fast it's growing). Here, changes happen constantly over time rather than in discrete jumps
What can you substitute B-D for?
bN-dN
Total births per time =bN
Total deaths per time =dN
So equation becomes: 𝑑𝑁/𝑑𝑡 =bN-dN
What does b-d equal?
r = rate of increase
what happens when you substitute the rate of increase into the equation?
𝑑𝑁/𝑑𝑡 =rN
How do you predict the size of the population at any given time t?
Nt = N0ert
What does exponential growth look like on a log scale?
Exponential growth looks linear on a log scale
It remains approximately constant (linear) overtime, indicating exponential growth.
What is a linear equation?
This is a linear equation:
• Slope (m) is r or R
• X is time
• Intercept (b) is log(N₀)
y=mx+b
When does population growth exponentially?
- Following protection from persecution, recovery is often exponential
- Establishment of invadingspecies is often exponential
Can any environment support limitless growth indefinitely?
no
What does density dependence imply?
Density dependence implies population regulation
How is a population regulated?
• A regulating mechanism (e.g. predation) brings the population towards equilibrium.
• Regulating mechanisms are always density-dependent processes
• Population limiting mechanisms may be density-independent processes
What are different regulatory mechanisms? Which are limiting or regulation mechanisms?
Limiting:
- Climate
- Human disturbance
- Natural disasters
Regulating:
- Competition for water resources
- Food competition
- Competition for living space
- Disease
- Parasitism
- Predation
What is the logistic growth model?
Logistic model includes competition within a species for resources (density dependent)
What is density dependence?
Density dependence: population growth that depends on population size
Density-dependence as a process of population regulation:
▪ density-dependent births
▪ density-dependent deaths
What is K?
Carrying Capacity
What is carrying capacity?
Maximum number of organisms in a population that can survive within the same habitat
What does logistic growth look like?
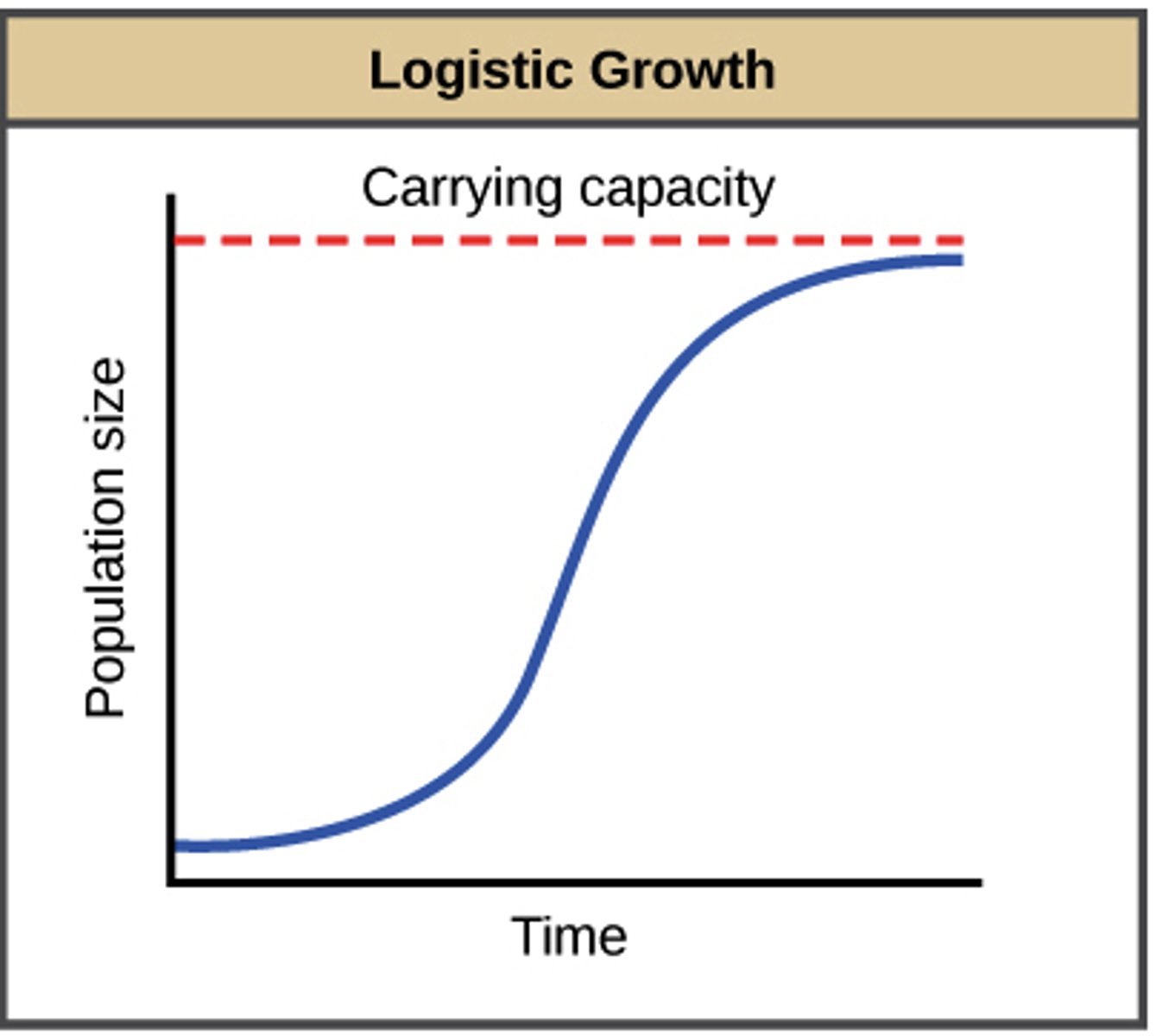
What is the equation for the logistic model of discrete growth?
Nt+1 = NtR/1 + ((R−1)Nt/K)
Nt+1 = NtR/
1 + aNt
"a" measures the per capita susceptibility to crowding: the larger the value of "a", the greater the effect of density on the actual rate of increase in the population
What does exponential growth look like?
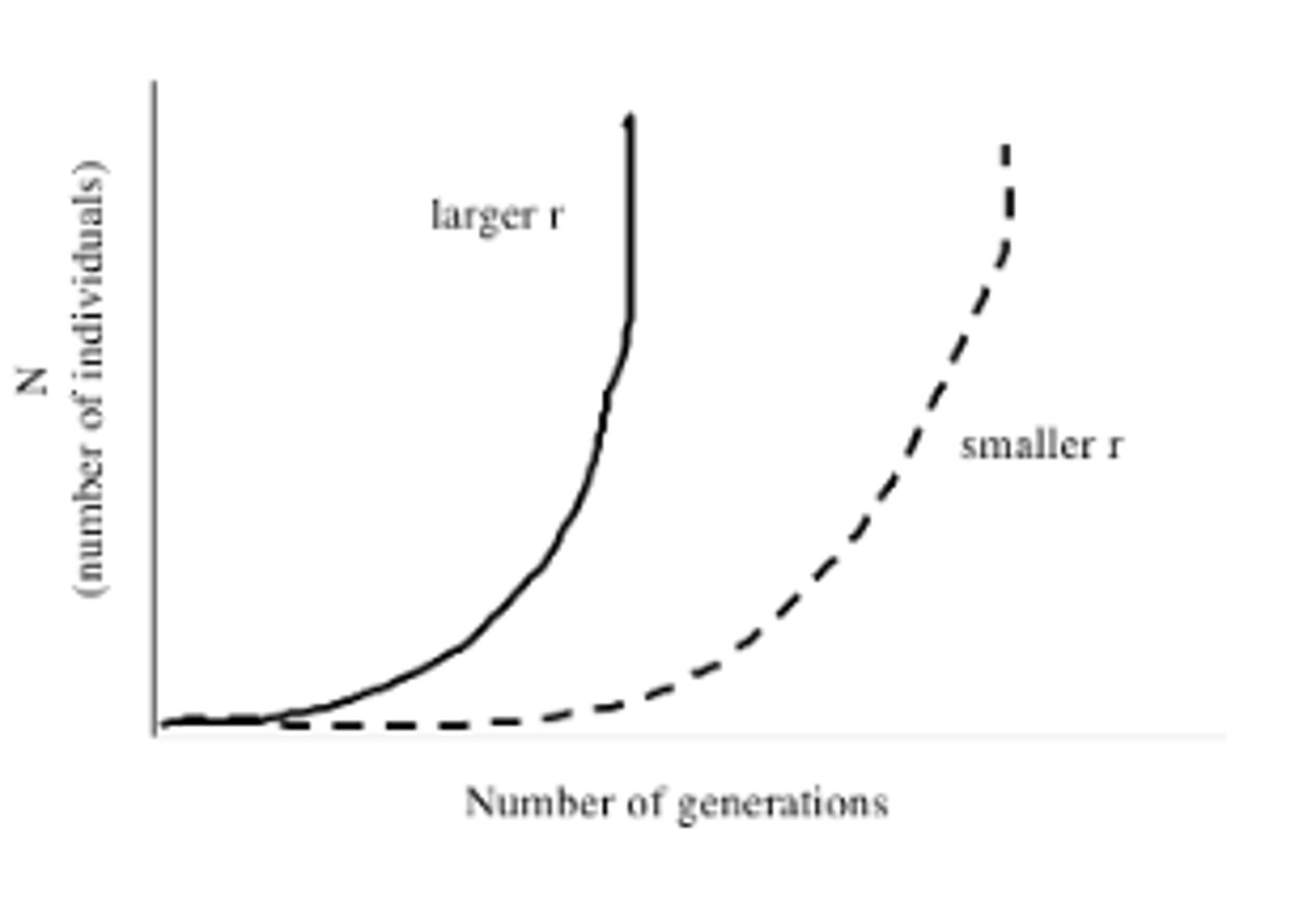
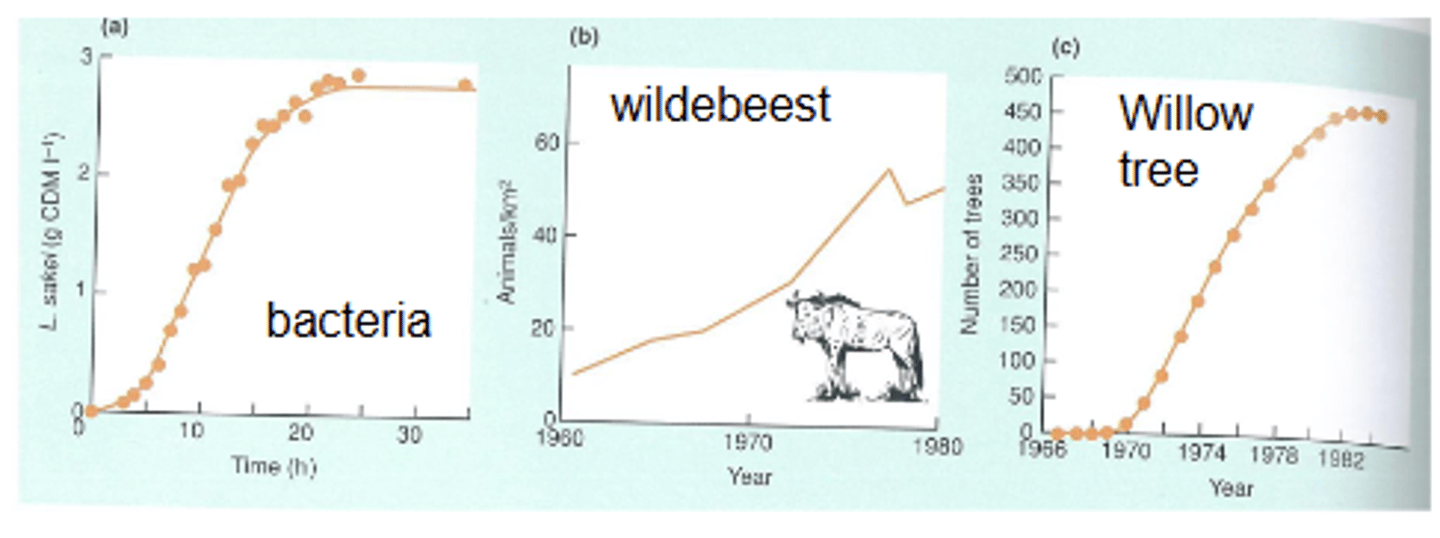
What are examples of S shape logistic growth?
- Bacteria
- Wildebeest
- Willow tree
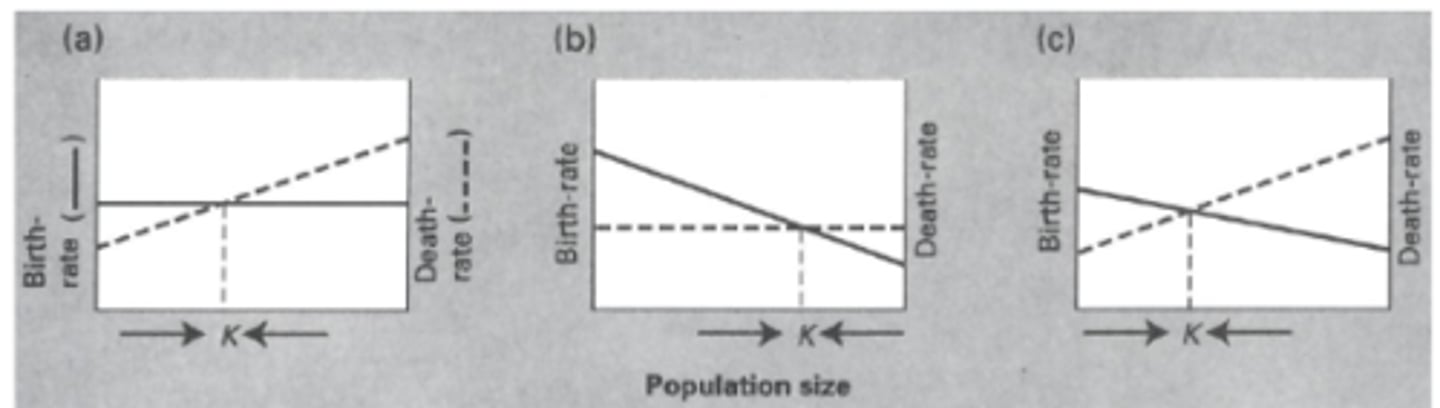
What are examples of population regulation?
a) Density-independents birth
Density-dependent death
b) Density-dependents birth
Density-independent death
c) Density-dependents birth
Density-dependent death
What is intraspecific competition?
• Individuals do not leave isolated
• Individuals from the same species have similar requirements so they must "compete" for shared resources to survive and reproduce
Involves exploitation and interference
What is exploitation competition?
individuals are affected by the amount of resources remaining after exploitation by other individuals
What is interference competition?
individual directly interact with each other (i.e. aggression,territory defence, etc.)
What are the 3 characteristics of intraspecific competition?
1. Result of competition is a decreased contribution of individuals to the next generations.
2. Resources for which the individuals are competing must be limited.
3. Reciprocity, all individuals are equivalent (contrary to predator-prey interactions).
What is density dependent mortality?
as population density increases, the rate of mortality increases
What is density dependent fecundity?
as population density increases, the rate of fecundity decreases
What is fecundity?
the number of female offspring produced by each female in the population
What is density dependent net recruitment?
• Number of birth minus number of deaths over a period of time
• Humped or dome-shaped curve