AP Human Geo Unit 6
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
47 Terms
site vs. situation factors
characteristics that are at a specific location vs. locations surrounding a place
urban sprawl
expansion of an urban/suburban area into the surrounding countryside
urbanization
migration of people from rural areas to urban areas
types of cities
megacity: 10 million+ residents
metacity: 20 million+ residents
→ both in developed & developing countries
core/semi-periphery/periphery countries
core countries: industrialized & have most advanced economies
semi-periphery countries: emerging economies that are industrializing
periphery countries: still rely on exporting raw resources & less economically developed
informal settlements
housing & residential areas that are built without legal authorization
boomburb, exurb, edge city
boomburb: rapidly growing suburban city that has developed its own unique identity
exurb: settlement that exists outside of a suburban area, but remains connected to the metro area
→ low population density
edge city: settlement that has its own economic district and is located on the outskirts of a city/near a major highway
→ lots of businesses
urban decentralization
movement of a population away from an urban area’s core to peripheral areas
world city
city that is connected to other cities around the world through a series of networks
impacts people in the world
does hierarchical diffusion from world cities~suburban cities
NewYork, London, Paris, Tokyo
primate city
city that has twice the population of the next largest city
has significant political, economic, social control over the rest of the city
unequal wealth, power
Mexico City, Seoul
rank-size rule
the population of a settlement ranked n will be population of largest city/n
gravity model
flow between locations based on population and distance
larger the city, more “pull” power it has
larger, closer locations interact more
Christaller’s central place theory
hexagons that indicate business’s threshold & range
smaller settlements depend on major urban areas to access service/goods
→ because smaller settlements can’t meet the threshold for businesses, they don’t operate there
threshold and range
threshold: minimum number of people that are required to support any good or service
range: maximum distance that a consumer is willing to travel for a certain good or service
burgess concentric model
circular model that shows decreasing density from center→ periphery
central business district
zone of transition
zone of independent workers’ homes
zone of better residences
commuter’s zone
Hoyt sector model
with CBD in the center and kinda like pie chart
cities develop in sectors radiating out from the central business district (CBD) circles.
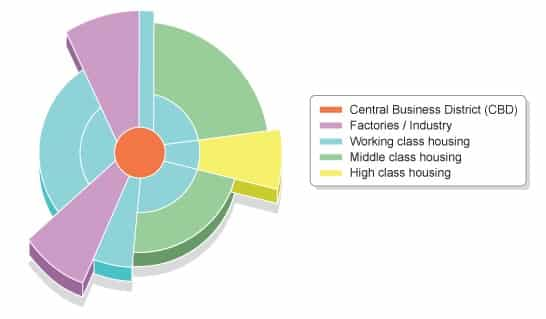
multiple nuclei model
cities do not grow around a single central business district (CBD) but rather develop multiple, specialized, independent nodes (nuclei) or centers
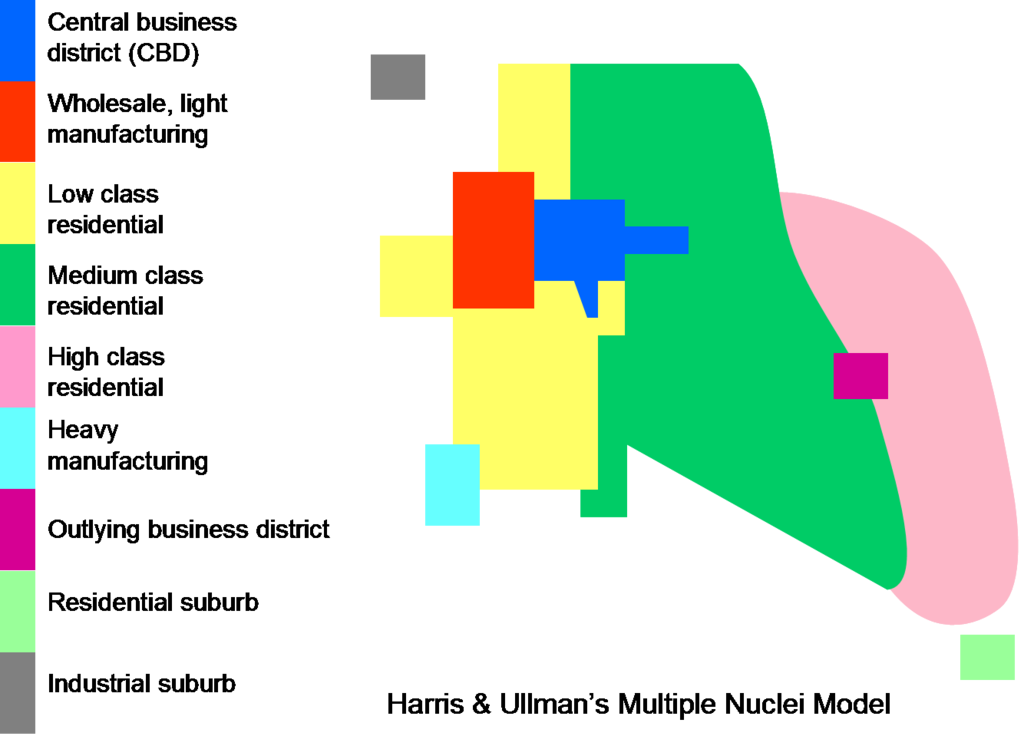
galatic model
the structure of urban areas that develop and distributes around a central city
latin american city model
centered around “plaza”
impacted by European colonization
sub-saharan african city model
colonial CBD & traditional CBD
impacted by European colonization
southeast asian city model
based around port
impacted by colonial trading ports
density gradient
a change in the population density of an urban area
people move from the center to the periphery
impact of infrastructure
internet allows working at home, purchasing service/goods, get education…
roadways allow people to live away from central cities
not CBD→ more reliance on automobiles→ traffic, pollution→ electric cars?
sustainability
use of Earth’s resources in a way that ensures those will be available in the future
mixed used areas, zoning can encourage…
walkable cities
transit-oriented development
urban planning that strategically locates public transit stations to reduce dependence on automobiles
smart growth policies
urban policies that seek to reduce urban sprawl and protect farmland surrounding the city
promotes mixed-use development, public transportation, green areas
Greenbelt (acts as buffer)
new urbanism
urban planning that seeks to create compact and walkable cities that are sustainable and socially connected
more focus on architecture & community design
building local communities
de facto segregation
separation of people along racial, ethnic, or socioeconomic lines that is not officially enforced by laws or regulations
increasing rent→ original resident have to move out
genterificaiton
process of renovating, rebuilding, or revitalization an urban area, resulting in lower-income residents to become displaced and more wealthy residents to move into the area
result of smart growth policies
can disrupt unique communities
slow-growth cities
urban areas that promote sustainable growth by limiting new development in the periphery of the city
lower population growth rate, lower economic expansion, or more stable infrastructure development
growth boundary
boundary that control urban sprawl, only allowing development to occur inside the boundary
infill development
building within an existing developed area on land that is unused or underdeveloped
brownfield
abandoned property that was previously been used for industrial or commercial use and is contaminated with hazardous pollutants
smart cities
cities that utilize technology to reduce inefficiencies & improve quality of life
officials use quantitative & qualitative data, census for
crime rates
pollutions
amount of diseases
need of infrastructure
redlining
discriminatory practice where banks refuse to provide loans to people who live in certain neighborhoods
high risk= black, hispanic people
prevented accumulating generational wealth for certain races
blockbusting
discriminatory practice where real estate agents use misinformation about minority communities moving into a neighborhood to motivate white homeowners to sell their home at a lower price so they can resell to minority buyer who was previously excluded from the area
white flight
phenomenon in which white residents migrate out of an urban area to a suburban area is large numbers
urban blight
homes that hold close to no value to being abandoned, vandalized
environmental injustice
disproportionate distribution of environmental hazards among different social groups
food desert
urban/rural community that lacks access to affordable, healthy, and fresh food
can cause obesity, diabetes, heart disease
disamenity zone
area within a city that lacks public services, infrastructure, and have high crime, poverty, informal settlement rate
inclusionary zones
areas where affordable housing is encouraged with local policies in place
bureaucracy
an organization that has multiple levels which all seek to carry out a specific task
eminent domain
right of the government to take private property to use it for public use
ecological footprint
amount of land and resources that are used to support the population of a city