AP Bio Parts of the Cell Diagram | Quizlet
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
Four things homologous characters between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells
1) cell membrane
2) ribosomes
3) DNA
4) cytosol/cytoplasm
Cell membrane (plasma membrane)
Outer boundary of the cell which separates the internal environment of the cell from the external environment and regulates the passage of materials into and out of the cell.
Cytosol
The thick solution portion of cytoplasm
Cytoplasm
Everything inside the cell membrane minus the nucleus
Ribosome
cellular machine made of protein and rRNA (ribosomal RNA) which cells use to make proteins; found throughout the cytoplasm and on the rough ER
prokaryotic cell
The simpler, smaller type of cell that lacks a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles; all are unicellular
Two types of prokaryotes
Bacteria and Archaea
nucleoid region
Region in a prokaryotic cell's cytoplasm where the circular DNA chromosome is located
capsule
outer coating on some prokaryotes which allows them to stick to things
Pili
Hairlike structures on bacteria surfaces which can allow them to attach to other surfaces
eukaryotic cell
More complex, larger type of cell which contains a nucleus and membrane bound organelles; can be unicellular or multicellular
endomembrane system
network of membranes that includes the nuclear envelope, the endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, lysosomes, vacuoles, and plasma membrane
Nucleus
organelle in eukaryotic cells which houses and protects the cells DNA
nuclear envelope
lipid bilayer membrane which surrounds the nucleus
nuclear pores
openings in the nuclear envelope to allow materials in and out of the nucleus
nucleolus
region of the nucleus which is responsible for building the different parts of ribosomes out of proteins and rRNA
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
A highly folded membrane structure outside the nucleus which takes in proteins and lipids to modify and sort them
Rough Endoplasmic reticulum
The portion of the endoplasmic reticulum which has ribosomes attached to it and modifies proteins
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum
The portion of the endoplasmic reticulum which does not have ribosomes attached to and deals primarily with lipid synthesis and modification
Golgi apparatus
A series of stacked, flattened membranes which takes material from the ER and further modifies and sorts it
Examples of modifications made to proteins in the ER and Golgi
1) help proteins fold correctly
2) chemically modifying them by cutting them or adding other molecules like carbohydrates to them
3) packaging them to be transported to their intended destinations
glycosylation
addition of carbohydrate chains to proteins as they pass through the ER and Golgi apparatus to determine cellular destination
Vacuole
membrane-enclosed sac which stores and releases materials within the cell
Vesicle
Small membrane-enclosed structure which transports materials in the cell
secretory pathway
route taken by materials made by the cell and released outside the cell
Rough ER --> Golgi ---> Cell membrane
Materials move from place to place using vesicles which bud off of one structure and fuse with the next one
Lysosome
Membrane-enclosed sac which gets rid of or recycles waste by using digestive enzymes to break down molecules (hydrolyzes macromolecules)
autophagy
process which maintains cellular homeostasis through recycling selective intracellular organelles and molecules
apoptosis
process which maintains organismal homeostasis by killing damaged or unneeded cells; programmed cell death
If a lysosome leaks into the cell, why does that not cause a lot of damage?
Enzymes in lysosomes function in the acidic environments but denature in neutral pH range like in the cell
peroxisome
breaks down toxic molecules such as hydrogen peroxide which constantly accumulate in our cells and would otherwise be toxic
semi-autonomous organelles
organelles which have their own DNA and divide on their own but which still must rely on other parts of the cell to function; examples mitochondria and chloroplasts
Mitochondria
Site of cellular respiration which converts chemical energy from food into the energy molecule ATP; found in all eukaryotic cells
Chloroplast
Site of photosynthesis in plants where they capture light energy and use it to make food (i.e. glucose); found only in plant cells
Central Vacuole
Large vacuole filled with water (and other things) and supports plant cell structure by exerting pressure on the cell wall
Cell Wall
Found on the outside of the cell membrane which provides a cell with structure and protection; found only plant and fungal cells in eukaryotes and most prokaryotic cells
cellulose
polysaccharide that makes up plant cell walls
chitin
polysaccharide that makes up fungal cell walls
peptidoglycan
a compound made of polysaccharide and peptide chains which forms cell wall of bacteria
cytoskeleton
A network of fibers that holds the cell together, helps the cell to keep its shape, and aids in movement
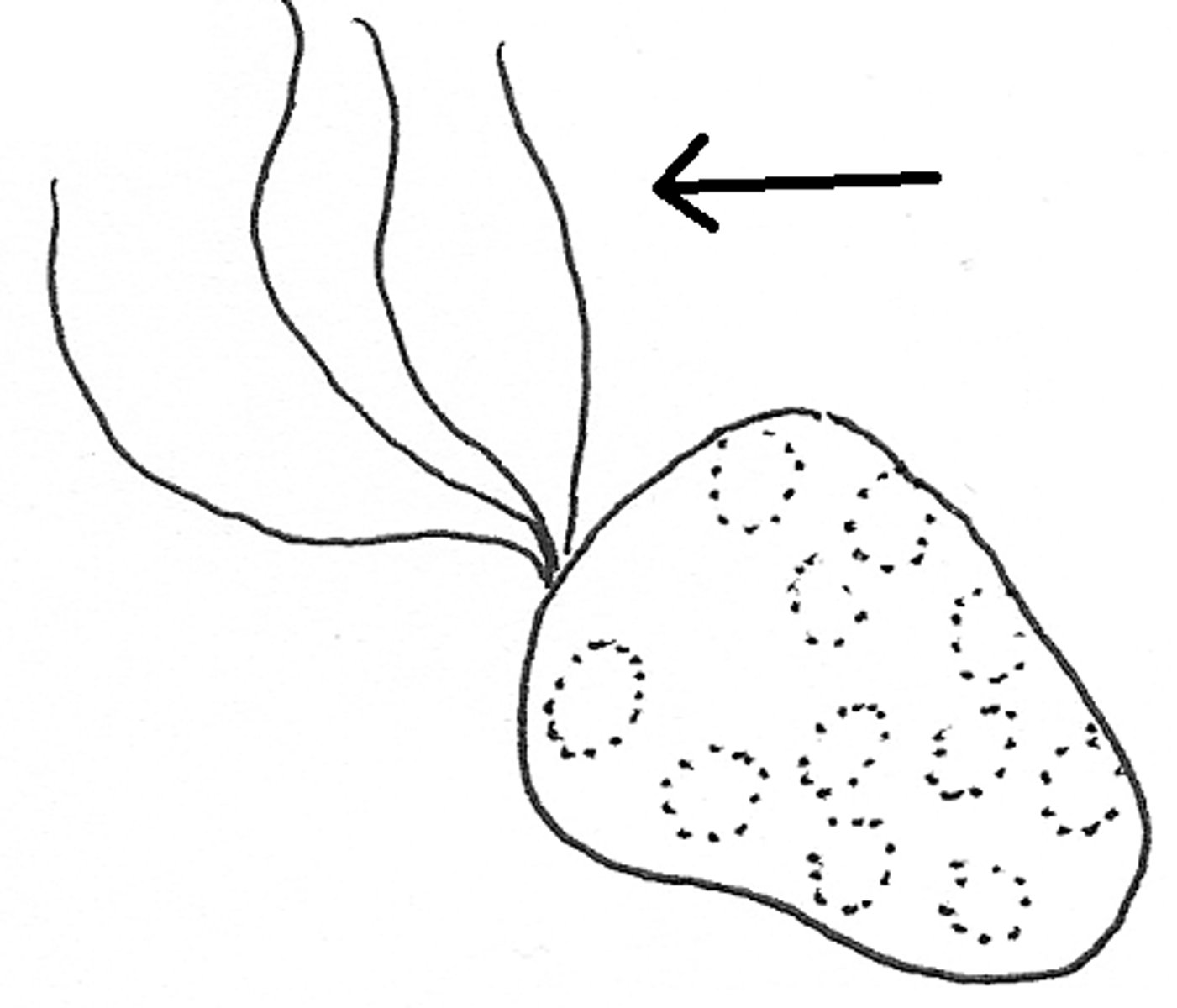
cilium (pl. cilia)
short hairlike projections found all around the surface of a cell that produces movement of cell or materials around the cell
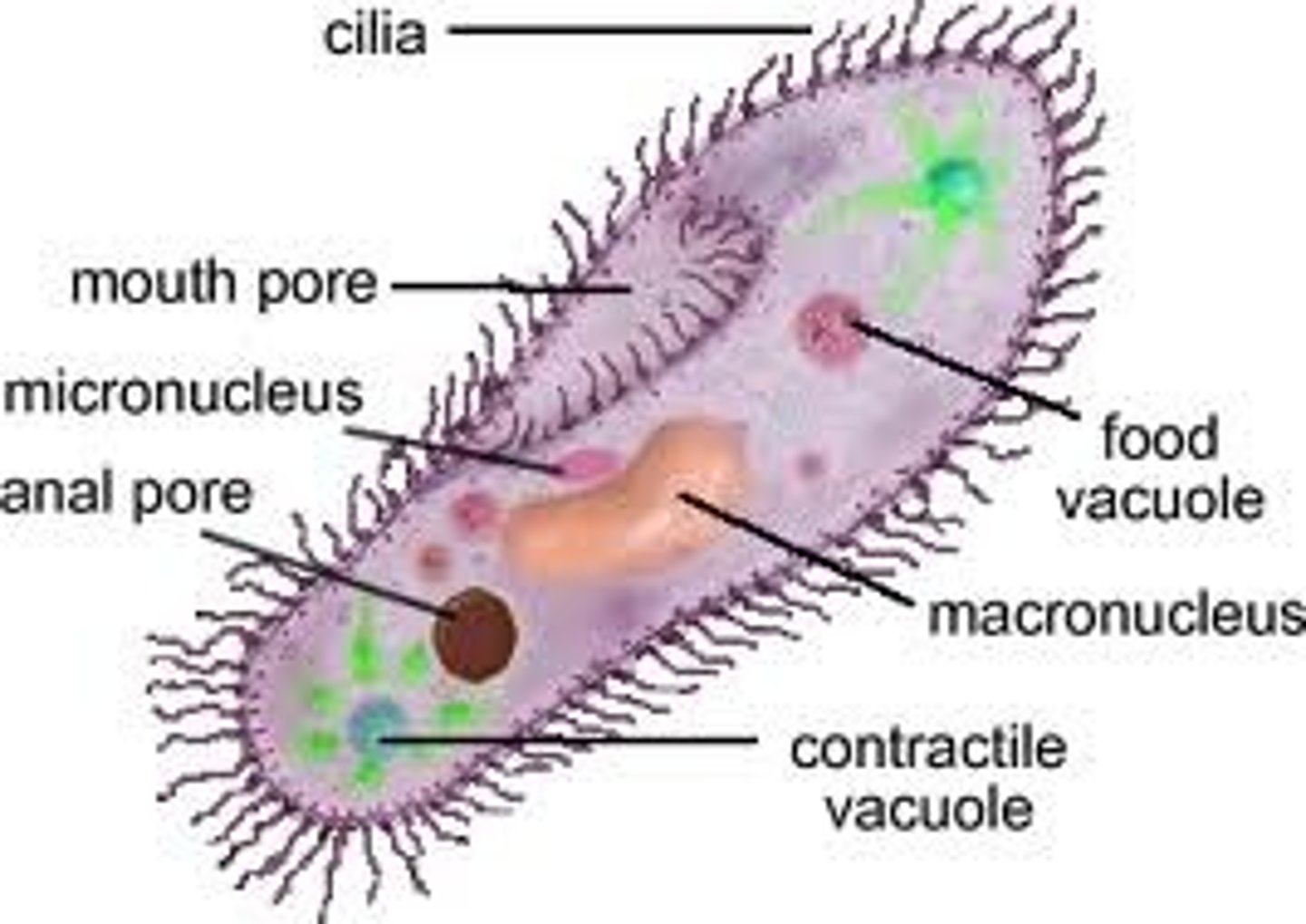
flagellum (pl. flagella)
long cellular extension(s) on one side of the cell that rotates, enabling that cell to move