AUgh midterm self reflection
1/37
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
Pauli Exclusion Principle
no 2 electrons in an atom can have exactly the same energy
Hund’s Rule
For degenerate orbitals (same energy), the lowest energy is attained when the number of electrons in the same spin direction are maximized
Aufbau Principle
As protons are added one by one to the nucleus to build up the elements, electrons are similarly added to hydrogen-like orbitals
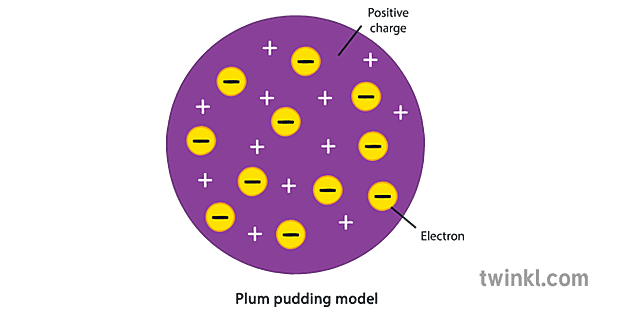
Plum Pudding Model
J.J. Thomson, 1897. All atoms contain electrons. Conducted the cathode-ray experiment and discovered electrons.
John Dalton
1800s
All elements consist of atoms
All atoms of the same elements are identical
Atoms cannot be created or destroyed
Neils Bohr
Explained why atoms only emit light of fixed wavelengths
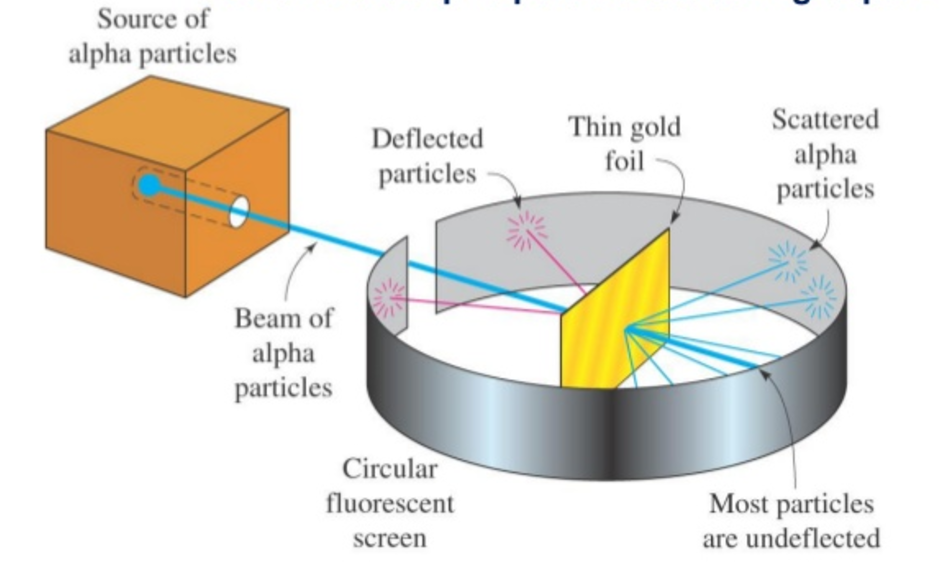
Rutherford
Conducted the gold foil experiment. Discovered the location of electrons and the existence of the nucleus.
Shrodinger
Electrons paths cannot be predicted. Electron cloud discovery
Hess’s Law
In gaining from a particular set of reactants to a particular set of products, the change in enthalpy is the same whether the reaction takes place in one step or in a series of steps.
Alkali/Alkaline-Earth metals + H2O →
Metal_Hydroxide (MetalOH) + H2 (g)
Active metals + Acid →
Salt of acid + H2 (g)
Metal_Carbonates + Acid →
CO2, H2O, Salt of acid
Metal_Sulfites + Acid →
SO2 + H2O + Salt of acid
Carbonate Decomposition
Metal_Oxide + CO2
Chlorate decomposition
Metal_Chloride + O2 (g)
Ammonium Hydroxide
NH3 + H2O
Gas Laws: As Temperature Increases,
Volume Increases and Pressure increases
Gas Laws: As particles are added
volume increases and Pressure increases
Gas Laws: As volume increases
pressure decreases
Water vapor eq
P(total) = P(atmosphere) + P(H2O)
Graham’s Law of Effusion
Determines how fast a gas will travel.
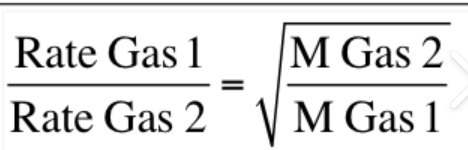
Pgas > Patm
Pgas = Patm + H
Pgas < Patm
Pgas = Patm + H
Kinetic Molecular Theory
The ideal gas. These laws are not true when applied to extreme conditions.
Gases are tiny gas particles. Their volume is zero
Gases always move in straight lines
There are no attractive forces
Kinetic energy depends on K temp.
Properties of Ionic Compounds
Soluble in water
Charged ions
Not conductible in a solid state
Solid at room temperature (Except Hg)
<= 1.7 electronegativity
High melting points
Metal + Nonmetal
Total transfer electrons
Properties of Covalent Compounds
Polar & Nonpolar determines solubility
Low melting point
No/partial charge
Nonmetal + Nonmetal
Low En difference
Properties of Metallic Substances
Mobile ions
Rigid solids
High boiling point (like, really high.)
Luster
Ductile
Malleable
High Ionization energy
There are 2 bonds and 0 unused e pairs. Qu’est-ce que c’est?
Linear, 180 bond angle, sp hybridization
There are 3 bonds and 0 unused e pairs. Qu’est-ce que c’est?
Trigonal Planar, 120 bond angle, sp2 hybridization
There are 4 bonds and 0 unused e pairs. Qu’est-ce que c’est?
Tetrahedral, 109.5 bond angle, sp3 hybridization
There are 3 bonds and 1 unused e pairs. Qu’est-ce que c’est?
Pyramidal, 90-109.5 bond angle, sp3 hybridization
There are 2 bonds and 2 unused e pairs. Qu’est-ce que c’est?
Angular, 90-109.5 bond angle, sp3 hybridization (like H2O)
There are 5 bonds and 0 unused e pairs. Qu’est-ce que c’est?
Trigonal Bipyramidal, 90 and 120 bond angles, sp3d hybridization
There are 6 bonds and 0 unused e pairs. Qu’est-ce que c’est?
Octrahedral, 90 bond angle, sp3d2 hybridization
Network Covalent Bonds
Insoluble
Hard
High melting point
Arrangement affects properties
Found in large covalent compounds
Poor conductors of heat and energy
Ex. carbon, silicon
Coordinate Covalent Bonding
When two particles, one that is positively charged and one has a lone pair of electrons, bond and one shares both of the lone electron pairs. That’s the best i can explain it.
[NH3-] + [H+]
N has a lone pair of electrons. [H+] has no electrons. N shares both electrons with [H+] to bond.
Sigma Bonds
Single bonds. Stronger than Pi bonds
Pi bonds
Double bonds. Weaker than Sigma Bonds.