Molecular Genetics Chapter 9 - Molecular Structure of DNA and RNA
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
What four criteria must genetic material meet?
Information - blueprint for determining the inherited traits of an organism.
Transmission - genetic material must be passed from parents to offspring.
Replication - must be copied because genetic material is passed from parents to offspring.
Variation - genetic material varies in ways that account for the known phenotypic differences within each species.
What was the purpose of adding RNase or protease to a DNA extract?
it rules out the possibility of RNA or protein contaminating type R bacteria, which converts it into S bacteria.
In the experiment of Avery, McLeod, and McCarty, the addition of RNase or protease to a DNA extract
A. prevented the conversion of type S bacteria into type R bacteria
B. allowed the conversion of type S bacteria into type R bacteria
C. prevented the conversion of type R bacteria into type S bacteria
D. allowed the conversion of type R bacteria into type S bacteria
D. allowed the conversion of type R bacteria into type S bacteria
Nucleic acid
large biomolecules that play essential roles in all cells and viruses; storage and expression of genomic information.
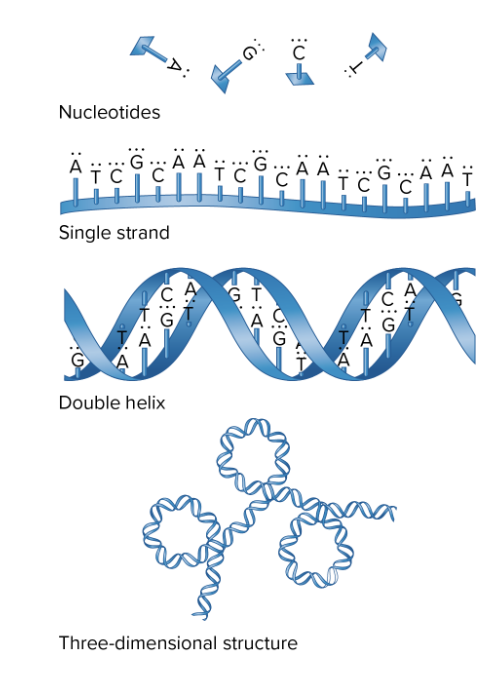
The four levels of complexity of DNA
Nucleotides form the repeating structural unit of nucleic acids
Nucleotides are linked together in a linear manner to form a strand of DNA or RNA
Two strands of DNA interact with each other to from a double helix
The 3-D structure of DNA results from the folding and bending of the double helix
Going from simple to complex, which of the following is the proper order for the structure of DNA?
A. Nucleotide, double helix, DNA strand, chromosome
B. Nucleotide, chromosome, double helix, DNA strand
C. Nucleotide, DNA strand, double helix, chromosome
D. Chromosome, nucleotide, DNA strand, double helix
C. Nucleotide, DNA strand, double helix, chromosome
Structure of a nucleotide
A pentose (5) sugar, a nitrogenous base, and at least one phosphate group. The bases are categorized as purines (adenine and guanine) and pyrimidines (thymine, cytosine, and uracil)
Which of these components of nucleotides are not found in DNA?
Ribose and uracil are not found in DNA
What are the two types of sugars?
Deoxyribose and ribose
What are the purine bases?
Adenine and guanine and they have double ring structures
What are the pyrimidine bases?
Thymine, cytosine, and uracil and they have single ring structures
Which bases occur in both RNA and DNA?
Adenine, guanine, and cytosine
Which of the following could be the components of a single nucleotide found in DNA?
A. deoxyribose, adenine, and thymine
B. ribose, phosphate, and cytosine
C. deoxyribose, phosphate, and thymine
D. ribose, phosphate, and uracil
C. deoxyribose, phosphate, and thymine
A key difference between the nucleotides found in DNA and those in RNA is that
A. those in DNA have phosphate, and those in RNA do not
B. those in DNA have deoxyribose, and those in RNA have ribose
C. those in DNA have thymine, and those in RNA have uracil
D. Both B and C are correct
D. those in DNA have deoxyribose and those in RNA have ribose and those in DNA have thymine, and those in RNA have uracil
What are the structural features of a DNA strand?
a phospate group connects two sugar molecules via two ester bonds (phosphodiester bonds)
The phosphates and sugar molecules form the backbone of the strand
A phosphodiester linkage involves attachment of a phosphate to the 3’ carbon in one nucleotide and to the 5’ carbon in the next nucleotide
Which components of nucleotides form the backbone of a DNA strand?
Deoxyribose and phosphate
In a DNA strand, a phosphate connects a 3’ carbon atom in one deoxyribose to
A. a 5’ carbon in an adjacent deoxyribose
B. a 3’ carbon in an adjacent deoxyribose
C. a base in an adjacent nucleotide
D. none of the above
A. a 5’ carbon in an adjacent deoxyribose
Evidence that led to the discovery of the DNA double helix included
A. the determination of structures using ball-and-stick models
B. the X-ray diffraction data of Franklin
C. the base composition data of Chargaff
D. All of the above
D. the determination of structures using ball-and-stick models, the X-ray diffraction data of Franklin, and the base composition data of Chargaff
Chargaff’s analysis of the base composition of DNA is consistent with base pairing between
A. A and G, and T and C
B. A and A, G and G, T and T, and C and C
C. A and T, and G and C
D. A and C, and T and G
C. A and T, and G, and C
What holds the DNA strands together?
hydrogen bonding between bases and base stacking
Major and minor grooves
Major and minor grooves are indentations in the outer surface of DNA double helixes
What are the strucural differences between B DNA and Z DNA?
B DNA is a right-handed helix and the backbone is helical while Z DNA is left-handed and the backbone appears to zigzag slightly. Z DNA has bases tilted relative to the central axis and B DNA is perpendicular to the central axis
Which of the following is not a feature of the DNA double helix?
A. it obeys the AT/GC rule
B. the DNA strands are antiparallel
C. the structure is stabilized by base stacking
D. all of the above are features of the DNA double helix
D. it obeys the AT/GC rule, the DNA strands are antiparallel, and the structure is stabilized by base stacking
A groove in a DNA double helix refers to
A. the indentations where the bases are in contact with the surrounding water
B. the interactions between bases in the DNA
C. the spiral structure of the DNA
D. all of the above
A. the indentations where the bases are in contact with the surrounding water
A key difference between B DNA and Z DNA is that
A. B DNA is right-handed, whereas Z DNA is left handed
B. B DNA obeys the AT/GC rule, whereas Z DNA does not
C. Z DNA allows ribose in its structure, whereas B DNA uses deoxyribose
C. Z DNA allows uracil in its structure, whereas B DNA uses thymine
A. B DNA is righthanded, whereas Z DNA is lefthanded (zebra bakes)
What types of bonds hold nucleotides together in an RNA strand?
Covalent bonds within phosphodiester linkages
What are the base pairing rules for RNA?
A bonds with U and G bonds with C (RNA got U)
A double-stranded region of RNA
A. forms a helical structure
B. obeys a helical structure
C. may result in the formation of a structure such as a bulge loop or a stem-loop
D. does all of the above
D. forms a helical structure, obeys a helical structure, may result in the formation of a structure such as a bulge loop or a stem-loop