NPB 130: L28 Ovary/testes
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
Why are gonads special endocrine glands?
Ovary + testes make steroids AND gametes
Sex hormones critical for 3x things
reproduction
-growth
metabolism
What controls reproduction? x3 categories
Steroids
Androgens (androstenedione, testosterone, dihydrotestosterone)
• Estrogens (estradiol, estrone, estriol) – follicle development, ovulation
• Progesterone – uterine environment for early embryo development
Eicosanoids
Prostaglandins (PGE, PGF2α) – responsible for “killing” or lysing the Corpus luteum
Proteins
GnRH
• Pituitary gonadotropins (FSH, LH)
• Inhibin
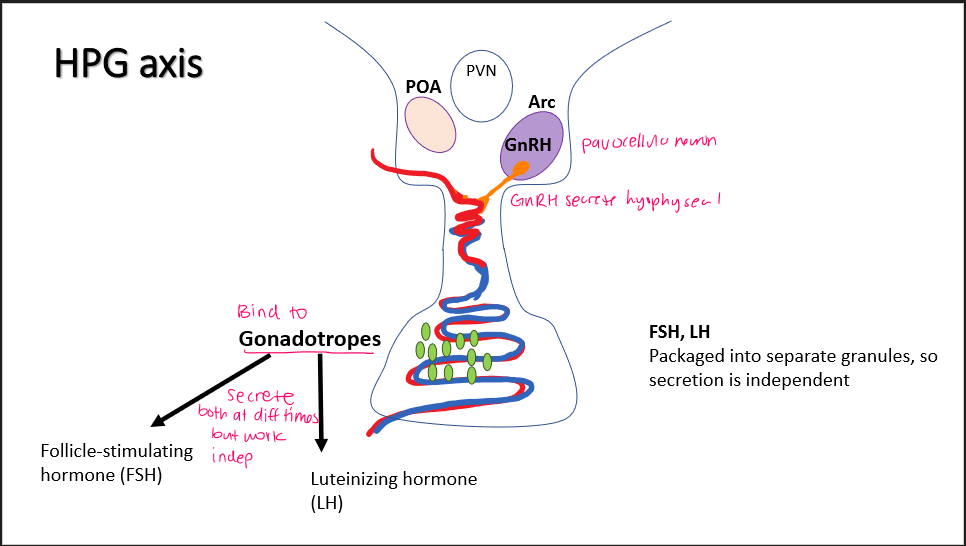
HPG axis
Arc parvocellular neuron → GnRH → gonadotropes → FSH + LH
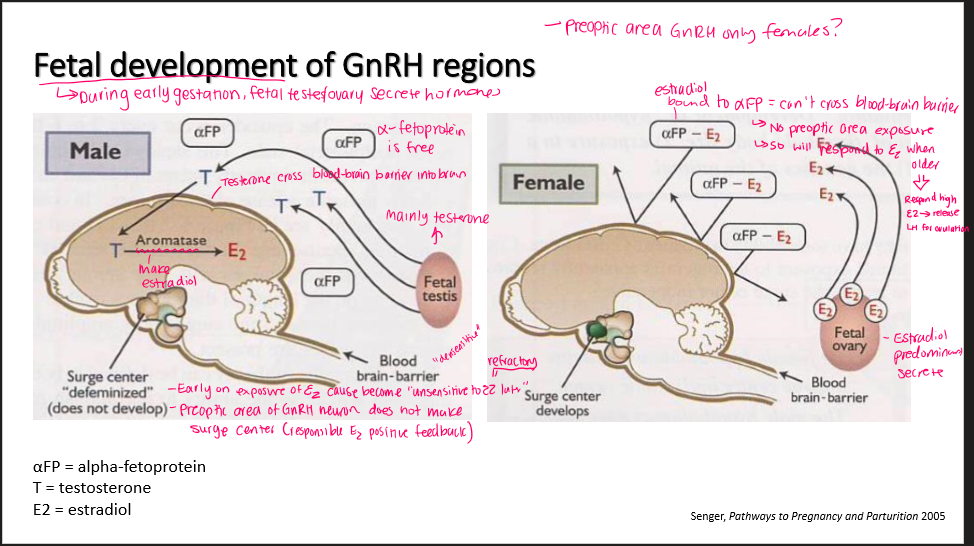
How do male and female GnRH regions develop?
Male testes: secrete testerone → cross blood-brain barrier → aromatase into E2
E2 exposure= desensitize to estrogen later (refractory)
No surge center develop (defeminine)
Female ovary: secrete E2 → binds to aFP (alpha-fetoprotein) → can’t cross blood-brain barrier
Surge center develops
LH production in male
M: LH make testerone in cyclic pattern
F: this is covered so idk if need know, but high LH right before preovulatory surges
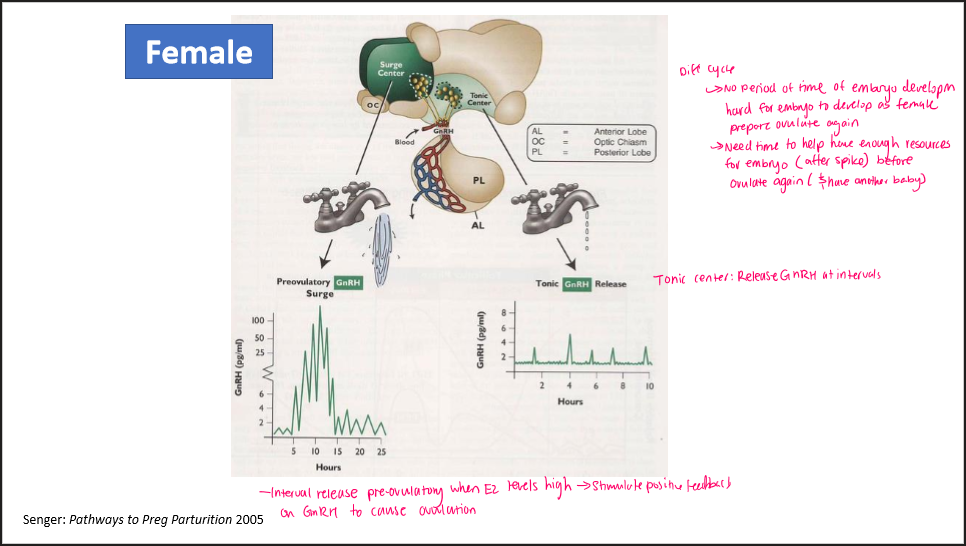
GnRH release in females… 2 phases
Tonic phase: release GnRH at intervals
Pre-ovulatory GnRH surge: Release when E2 levels high → positive feedback on GnRH to cause ovulation
IDK what this corresponds, but: need time for embryo to develop before ovulate again (after spike)
HPG axis in females + males REGULATION
Kisspeptin neurons in POA + Arc: Receive positive/neg feedback (NOT GnRH neurons)
→ Then stimulate GnRH neurons
make GnRH → anterior pituitary make FSH/LH
Inhibition:
FSH/LH neg feedback → ovary/testes → testerone - (CYP19A1)—> estrogen
estrogen inhibit kisspeptin
Progesterone (ovary) inhibit kisspeptin
Important to prevent early ovulation while embryo develop
Inhibin: From ovary/testis: inhibit FSH
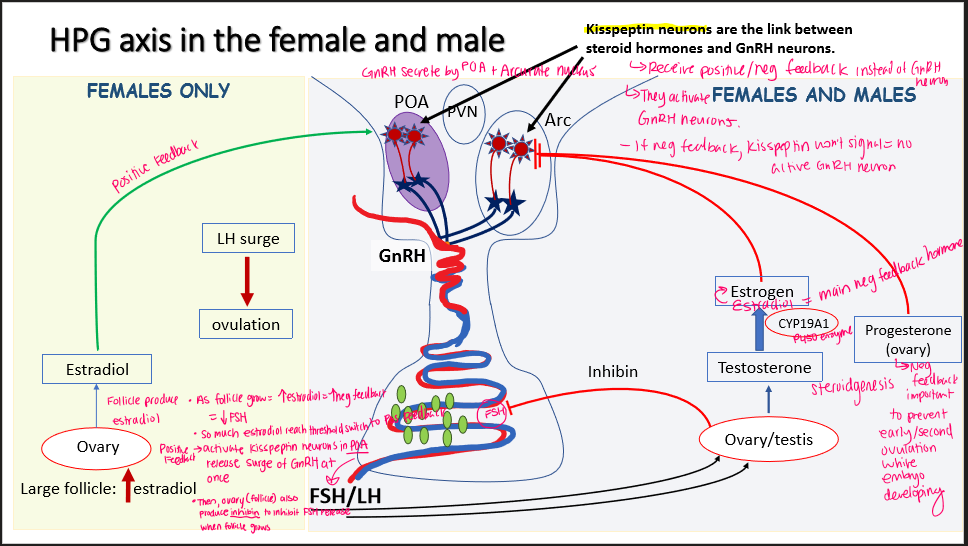
HPG axis in females ONLY regulation
Large follicle= estradiol
Low levels: neg feedback FSH
High level: positive feedback on kisspeptin in POA —→ GnRH surge
Ovary also make inhibin
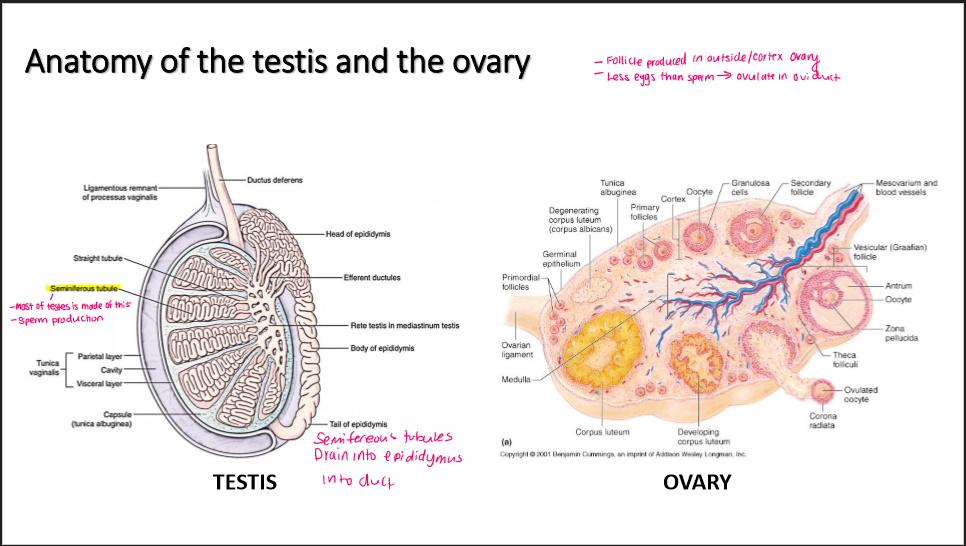
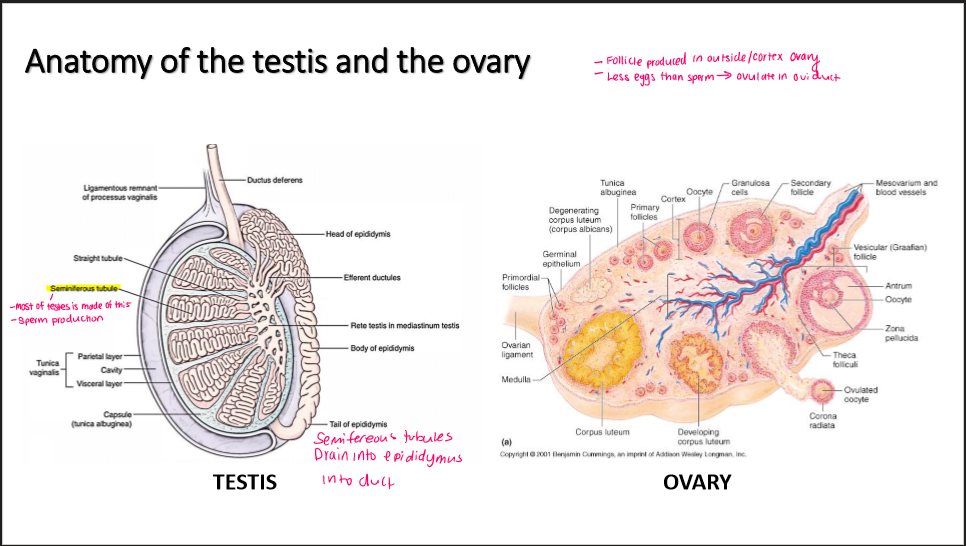
Testis anatomy
-where sperm made
seminferous tubule
→ drain into epididymis
Ovary anatomy
-where follicle made
-ovulate where
follicle made in cortex ovary
Ovulate in oviduct
Testis cell types
Leydig cells
Sertoli cells
Peritubular myoid cells → contract semiferous tubule make sperm
Germ cells (sperm)
tunica albuginae: connective tissue protect semiferous tubule
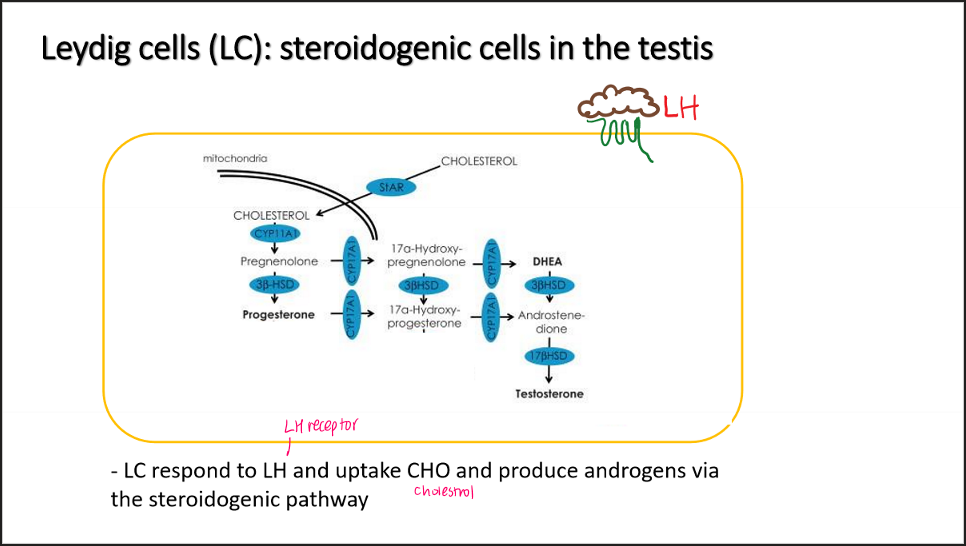
Leydig cells (LC)… what do they respond to?
do?
Respond to LH → cause uptake cholestrol (StAR) → cholestrol
→ make progesterone, DHEA, testerone =ANDORGENS
*pic for pathway memorize
Sertoli cells
-purpose x2
-barrier?
-respond to?
-produce 2 things
-”nurse cell”= nourish + adequate environment germ cell
-help w/ sperm maturation
-has blood testes-barrier
-Respond to FSH → convert androgen → estrogen
Also testerone + 5-alpha-reductase → Dihydrotesterone
Blood testes barrier
Mitosis → haploid to diploid
Barrier protect haploid (sperm) from human immune system, which doesn’t recognize it
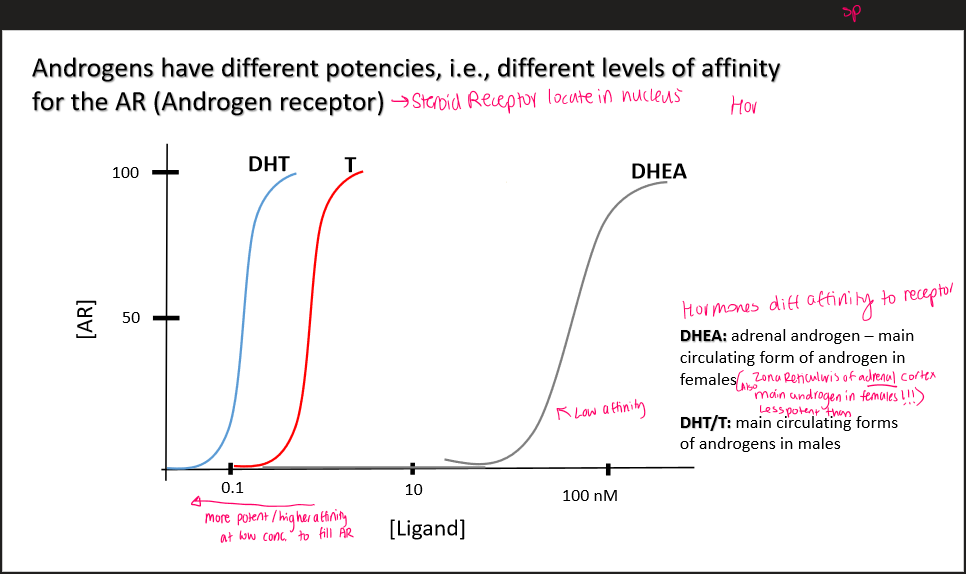
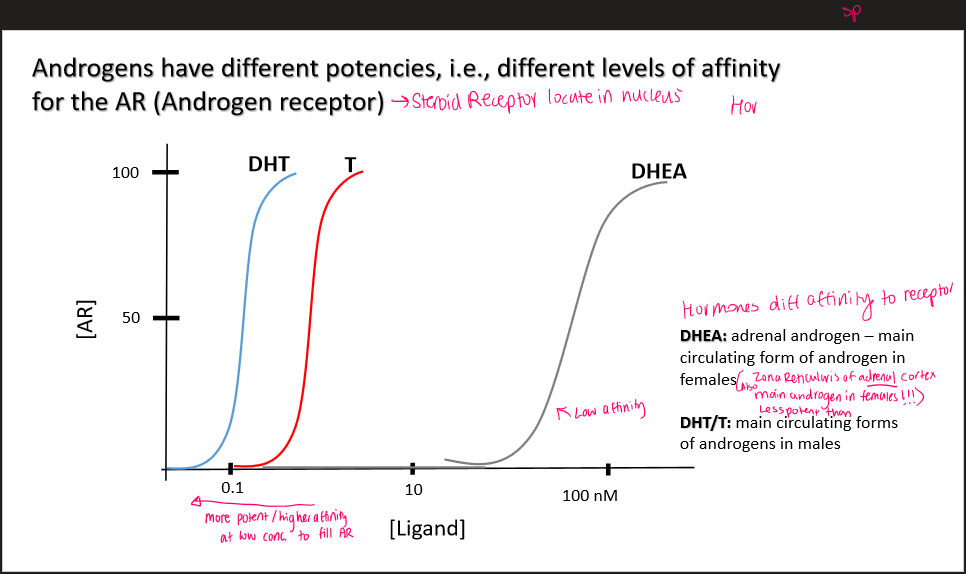
Dihydrotesterone (DHT)
more potent androgen
→used in secondary sexual characteristics
-main form of androgen in males
DHEA
adrenal androgen
main androgen form in females
Zona reticularis of adrenal cortex, main androgen in females
Less potent form
Androgen receptor
DHT has 30x greater affinity for AR
What is main steroid hormone produced by testes
testerone
Male reproductive organs are made from?
DHT