History Test 2
1/62
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
63 Terms
French:
Commercial interests
Colonial settlements organized directly by the Crown
90% French Catholic
Feudal System/Aristocracy
British:
Religious interests/flee persecution & commercial
More refugees
Early government intervention inconsistent, less Crown intervention
Direct forms of local government with elected governor's and legislatures
More religious diversity, but mostly protestant
What were the differences between the French and British Colonial Governments?
Created 1670
York Factory, Northern Manitoba, established 1684
Merged with Northwest Company 1821
Fur Trade was key to the company.
Indigenous interconnection; "Country Wives"
Dependence; Swampy Cree
HBC had its own army, navy, minted coins, and military forts
What was the Hudson’s Bay Company?
2 French Explorers, Medard Chouart des Groseilliers & Pierre-Esprit Raddison discovered the region.
French officials uninterested, so they went to British instead
1668 first trading ships
1670 Hudson's Bay Company created
French discovery, British company
Describe the origins of the Hudson’s Bay Company.
Renewed alliances with indigenous nations
French = Economical
Indigenous = Cultural Exchange
What did French “gift giving” grant?
Huron-Petun
Odawa
Ojibwa
Fox
Winnebago
Potawatomi
Wabanaki Confederacy
Miami
Kickapoo
Sulk
Illinois
Mascouten
Nippissing
What were some of the French-Indigenous Alliances at the Turn of the 18th Century?
Also known as War of Spanish Succession
1702 - 1713
Importance of North American colonies in global power dynamics
1710: British Capture Port Royal, Acadia
What were some key details of Queen Anne's War?
5 Nation Iroquois Confederacy (Haudonausansee):
Mohawk
Oneida
Onondaga
Cayuga
Seneca
Extra notes:
Remained Neutral as per the Great Peace of Montreal
"Four Kings" Visit to Queen Anne
What were some of the British-Indigenous Alliances in Queen Anne's War?
1713
The end of Queen Anne’s War
Iroquois Confederacy considered British subjects; not consulted.
France recognized Hudson's Bay territory as British holding
British took control of Acadia
Want French out. Oath of Allegiance issues.
France kept Cape Breton Island
Construction began on Louisbourg
What was the Treaty of Utrecht?
1716 = 600 people
1740s = 600 soldiers, 2,000 administrators, clerks, innkeepers, artisans, fisherman, and families.
Defensive line to Quebec
What were some details of the Louisbourg Fortress?
Also known as the War of Austrian Succession
1744-1748
France & Britain use the European conflict to continue battle for power in colonies.
June 16th, 1745: Britain captures Louisbourg
BRITISH REALIZE THE POWER THE FRENCH HAVE IN ACADIA
1749 Halifax, Nova Scotia founded. 2,544 British immigrants (Scottish) brough to the province
Acadians becoming outnumbered
What were some key details of King George's War?
Officially dated 1756-1763; Really began 1754
War against France and Britain for imperial control of North America
Considered first global military conflict
West Indies, Asia, India, Africa, Europe, North America
In North America, military theatres mainly the Ohio Valley & Quebec
British outnumbered French 20:1. French indigenous allies important.
Battle of Jumonville
May 28th, 1754
Begins the War
George Washington's first battle
Cultural differences in war; Indigenous allies of Britain kill French captives
What were some key details of the Seven Year’s War?
July 1755: Executive Council of Nova Scotia demand Acadian deputies take the Oath of Allegiance.
Many Refused. Council took back the offer. Announced the expulsion of Acadians from Nova Scotia.
6,000 Acadian lands, homes, money, cattle, and farming goods confiscated
Mass chaos. Families separated. Ships taken to New England, Britain, France, and New Orleans
1755-1763: 10,000 Acadians forced to leave Maritimes
What happened around the time of the Expulsion of the Acadians in the Seven Year's War in 1755?
Britain lays siege to Quebec City. General James Wolfe
7,000 men & 200 naval ships
15,000 cannon balls bombard the city
Lucky British. Gain password to scale to the Plains of Abraham.
French forced to a set battle.
Both General James Wolfe and Governor Louis-Joseph Montalm die.
EXTREMELY IMPORTANT IN HISTORY OF CANADA! Fuels Quebecois sentiment to this day.
What happened during The Battle on the Plains of Abraham, as part of the Seven Year’s War?
Augustine nurses; Hopital General. Set up mobile aid station.
Brought 271 horse drawn carts filled with food and provisions.
Elenor Job: British field nurse. On the battlefield. "Good Mother Job." Embalmed General Wolfe on his death.
What role did women play in the Battle on the Plains of Abraham?
Ends Seven Year's War
France loses all of New France in North America
British take the land
Cape Breton Island, Quebec, and the Great Lakes Basin
British relations with Indigenous: WASP mentality
British settlers push into the interior.
British immigration on the rise.
Costly War. Higher taxes in the British colonies.
Articles of capitulation
What was the Treaty of Paris (1763)?
1763-1766
Most successful First Nation Resistance to European invasion.
Great Lake's Region.
Indigenous relations strained with British since the fall of New France. Ended gift giving.
White settlers pushing into Indigenous Territory
Odawa Chief Obwandiyag (Pontiac) created confederation of forces: Wyandot, Potawatomi, Odawa, Ojibwe
Attacked Fort Detroit
British won, but had to make concessions to indigenous nations
1763 Royal Proclamation
What were some key details of Pontiac's War?
1775-1783
Seven Year's War created big problems for British colonies:
Increased colonial control
Raised funds through colonial administration
Increased taxes
British troops brought to North America
June 1775: Continental Congress created an Army
June 1776: Declaration of Independence
What were some key details of the American Revolutionary War?
Plantation slavery system in colonial south
Revolution offered paths to freedom
November 7th, 1775, Earl of Dunmore Proclamation
80,000-100,000 enslaved individuals of African descent escaped slavery
Black British regiments
At war's end: 3,500 Black Loyalists taken to Nova Scotia and Amherstburg/Sandwich
White loyalists also brought 2,000 enslaved individuals of African descent.
What were some British tactics in the Revolution?
Ended the Revolutionary War
United States declared a new nation
British Canada still a colony
Beginning of modern boundaries between US and Canada
Article 2d
1794 Jay Treaty
Evolution of identity between Americans and Canadians
What was the Treaty of Paris (1783)?
1812-1815
Post-revolution: British and American governments uneasy neighbors
Detroit River Region: Not much changed, family networks.
Unclear reasons for the cause of the war. Official reasons: British limit American trade. British impressment.
Ended in a draw.
Historians say no policy changes, no boundary changes, but EVERYTHING IN THE DETROIT RIVER REGION CHANGED BECAUSE OF THIS WAR.
War brewing in the region before it began
Fort Amherstburg (Fort Malden) headquarters for the Department of Indian Affairs in the Western District
Held gift giving ceremonies
US suspicious. Thought British were rallying indigenous forces.
British definitely courting the favor of indigenous nations.
British "Tree Trunk" Theory. Sir Isacc Brock.
What were some key details of the War of 1812?
Shawnee Chief Tecumseh & Prophet
Pan-Indian Movement 1783-1795
Confederation of indigenous nations; as many as 5,000
1811: Chief Tecumseh holds council with British at Fort Amherstburg. Offered an alliance.
Indigenous nations promised a Native state in the Ohio country.
FIGHTING THE WAR FOR DIFFERENT REASONS
Tecumseh and Brock's scheme
Hull Surrender's Fort Detroit August 16th, 1812
September 10th, 1813: America Brigadier-General William Henry Harrison invaded Amherstburg. Battle of Lake Erie.
Marched on Sandwich.
British Colonel Henry Procter retreated up the River Thames.
Battle of the River Thames October 5th, 1813.
Chief Tecumseh killed
Sandwich occupied by Americans until the end of the war.
What were some MORE key details of War of 1812?
William Hull, Governor of Michigan territory
July 12th, 1812: landed in sandwich (modern Walkerville distillery)
Marched to Francois Baby House, made his headquarters.
Worried about supply lines
Retreated to Fort Detroit August 1812
What were some key details of the Willum Hull's Invasion of the War of 1812?
Modern Monroe, MI
Watershed battle. Cemented Candian, Indigenous, and American identities.
January 17th, 1813: Americans win small battle at Frenchtown.
Get comfy
January 22nd, 1813: British and Indigenous forces counterattack.
January 23rd, 1813: Burning of sick houses. Indigenous looting.
"REMEMBER THE RIVER RAISIN!"
What were some key details of The Battle of the River Raisin/Battle of Frenchtown?
Slash and burn tactics used by both armies.
The region is devestated.
Tilly Buttrick travel diary 1814: he was "struck by the devestation which had been made by the late war...provisions of all kind very scarce; where once peace and plenty had abounded, poverty and destruction now struck the land."
Estwick Evans travel diary 1818 Detroit visit: Detroit needed "a system of education, laws, customs, and manners of the territory such as to outweigh the counter influence of those of the British in its neighborhood."
Immigration tactics used on both sides of the border as protection
How were the Detroit River Borderlands forever changed?
African Canadian militia War of 1812
"Colored Corps"
1820: British crown gifts African Canadians land in Essex County
Many Wyandot of Michigan move to the Anderdon Reserve in Essex County.
Ethnic people loyal to the crown granted land by government. Culturally, not accepted in the British identity.
So... Across this century of conflict: who was in and who was out of the Candadian identity?
How were ethnic communities in Canada affected?
After War of 1812, economy becomes the focus
RESOURCE ECONOMY
Immigration needed for the economy to grow
What was British Canada’s primary focus after 1815?
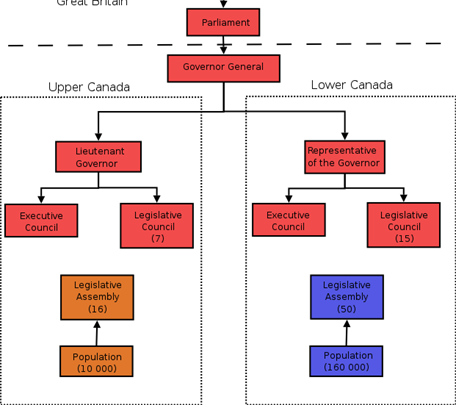
Canada Act of 1791
Created Upper and Lower Canada
Goals of the Canada Act:
Guarantee same rights as British subjects
Colonial assemblies right to levy taxes
Justify separation of Quebec
Strengthen political dependency of the colonies to the motherland
What was the political structure of Upper and Lower Canada?

a nationalist economic policy that is designed to maximize the exports and minimize the imports for an economy. In other words, it seeks to maximize the accumulation of resources within the country and use those resources for one-sided trade.
What is ‘mercantilism’?
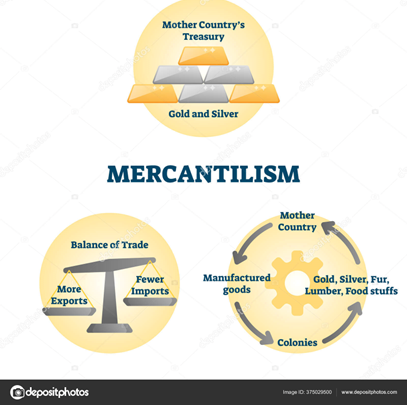
Mercantilism = Economic theory
Fixed amount of wealth in the world; a country must sell more exports than buy imports.
Risk passed to colonial entrepreneurs
What was the mercantile system of economics?
Newfoundland Cod major resource until 1815
Cod 1/3 value of exports by 1831
History of overfishing; modern reflections
Describe what fisheries were like in the Maritimes.
1820s timber the leading export of British Canadian colonies
New Brunswick the leader in export
Ship building
Describe what the export of timber was like.
Fur trade not as important economically
“Fur provided the means by which Great Britain retained its claim to sovereignty over much of the northern half of the province.”
This was done by the Hudson's Bay Company
Describe what Canadian fur trade was like in the mid-19th century.
Increased immigration was necessary to the growth of the resource economy.
1815: Upper and Lower Canada exclude American immigration
British homeland: overpopulated; Colonies act as a release valve
Scottish and Irish immigration
Four patterns of immigration:
British public Assistance
Settlement by large land companies
Private companies transport immigrants
Leaving it to chance
Describe what immigration was like from 1815 - the 1830’s.
Created by Royal Charter 1826
Bought land from Colonial Government, paid annual loans to the Provincial Government.
Founder: John Galt. Founded Guelph 1827
Credit system of the 1830s
Loan payments to Provinces lead to grievances.
What was The Canada Land Company?
“Women were placed on a pedestal as keepers of culture and as civilizing influences.”
Women were non-legal entities
Without women’s labor, there would be no frontier life.
The home economy:
Food stores, tending subsistence gardens, foraging, canning, candle making, maple-syrup making, child rearing, children’s educator, cooking, preserving meat, cleaning, and assisting in tending farms.
Women relegated to the domestic sphere
Some worked outside the home
Domestic positions in the economy:
Domestic Servant
Laundress
School Mistress
Describe what the domestic economy was like.
The Slavery Abolition Act of 1833
The Underground Railroad
Harriet Tubman; 300 individuals saved
Andrew the Runaway Slave
The Blackburn Riots of 1833
What was society like from 1815 - the 1840’s?
1830s: Indigenous administration placed into the hands of “civil authorities” in the colonies of Upper and Lower Canda
"Civilize and settle"
New, harmful era of Indigenous policy
What was society like for Indigenous peoples from 1815 - the 1840s?
Treaty of Ghent (1814): British and US agree to share the waterways
1817: Rush-Bagot Agreement
Mrs. Hector Scott’s Young Ladies’ Institute in Sandwich, Essex County
Girl's school taught: “spelling, reading, writing, arithmetic, geography, history, delineations definitions, composition, astronomy, use of globes, natural history, rhetoric, botany, chronology, mythology, natural philosophy, and history.”
Describe key pieces of local history and the economy from 1814 - 1817.
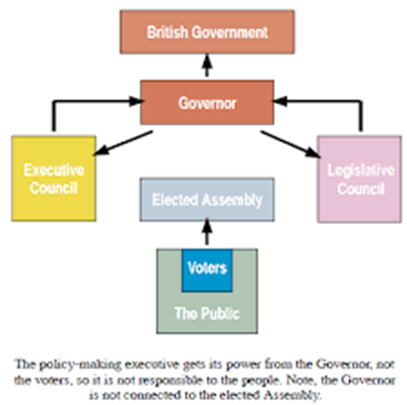
Lack of Representative Government; no "Responsible Government"
Family Compact & the Chateau Clique
Reform movements
Petition in Support of Reform Upper Canada, 1818
What were some brewing political issues of the 1820s-1830s?
Radical and moderate reformers
Moderates align with British political systems
Rebels align with American political systems
Major reformers in the 1830s:
William Lyon Mackenzie, Upper Canada
Louis-Joseph Papineau, Lower Canada
Joseph Howe, Nova Scotia
William Cooper, Prince Edward Island
How were reformers vying for power at this time?
Louis-Joseph Papineau leader of Parti Patriote
Lower Canada suffering economic decline
Francophone culture threatened
92 Resolutions 1834
November 23rd, 1837 battle; Papineau flees
What did the 1837 Rebellion in Lower Canada (Quebec) look like?
William Lyon Mackenzie leader
December 4th, 1837 plan to attack militia of York (Toronto)
Battle December 5th, 1837
Mackenzie flees to United States
1838 seize Navy Islands within Lake Ontario and Lake Erie
What did the 1837/1838 Rebellion in Upper Canada (Ontario) look like?
1838
Invasion of American Rebels December 11th, 1838
Spurred by rebel rhetoric against the tyrannical British government
"The Ferry" and Sandwich attacked
Colonel John Prince
Killing order
The City of Windsor gets its name
What were some key details of The Battle of Windsor?
Lord Durham "Report on the Affairs in British America"
Two solutions:
Responsible Government
Unification of Upper and Lower Canada
The Act of the Union 1840
Created Canada East and Canada West
Voters = white men who owned property
Responsible government created 1848 under Lord Elgin, Governor of Canada
Prince Edward Island; 1851
New Brunswick; 1854
Newfoundland; 1855
1850s were a messy time for politics
Ideological views created political parties:
The Conservative Party (British Tories)
The Reformers
The Clear Grits
1860s: The Reformers--> The Liberal Conservative Party; Clear Grits--> Liberal party
What were some key details of road to confederation?
Canada East (Quebec)- Concerned with Francophone issues and threat of Protestant Anglophones
Canada West (Ontario)- Pushing Confederation forward; focus on economic goals
Maritimes- Did not want to join Confederation
Major Political Actors in Confederation:
John A. Macdonald
George Brown
George-Etienne Cartier
Created the Great Coalition in 1864
What did confederation look like for different areas of Canada?
September 1864
Meeting to get the Maritimes to agree to Confederation
Proposed to create a strong central government consolidating all provincial legislatures into one large parliament
General unity during this conference
What were some key details of Charlottetown Conference?
October 1864
Pivotal meeting in the process of Confederation
72 Resolutions; Quebec Resolutions
Legislative sovereignty
French Canada and the Maritimes pushed for provincial governments
PEI and Newfoundland refused to join
What were some key details of Quebec Conference?
December 1866
Canada East, Canada West, New Brunswick and Nova Scotia the original provinces that agreed to Confederation
72 Quebec Resolutions reviewed and amended; became the basis of Constitution
British North America Act/ Constitution Act of 1867
Enacted July 1st
Created the Dominion of Canada
What were some key details of London Conference?
The Canadian Constitution=Constitutional Conventions
The Queen of Canada
Head of state
Delegates power to Governor General
Ceremonial role
Parliamentary system
John A. Macdonald 1st Prime Minister
Senate; region not population
24 from Quebec
24 from Ontario
30 Maritimes
24 Western Canada
What did the structure of the Government of the Dominion of Canada look like?
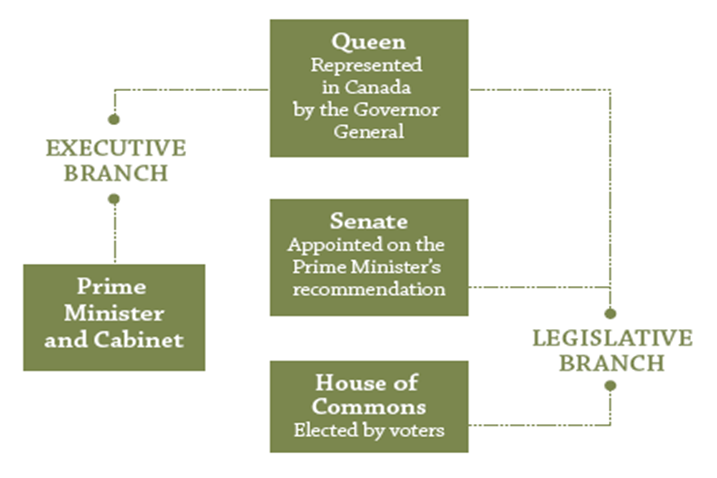
What did Canada’s parliamentary system look like?
Parliamentary Resolutions December 1867: Transcontinental expansion
1868: Hudson's Bay cedes territory to Canada
1857 Act for the Gradual Civilization of Indian Tribes in the Canadas
Social Darwinism; "Noble Savage"
What did Indigenous policy look like Post-Confederation?
11 treaties signed in the Prairie and Western Provinces between 1871-1929
Indigenous nations ceded territory to Canada
Treaty provisions:
Farm equipment
Medicine
Food
Treaties 1 - 7:
Enacted between 1871-1877 with indigenous groups in Manitoba, Saskatchewan, and Alberta
Sought out by the indigenous groups
1870: Buffalo herds near extinction
Smallpox epidemic
What were the Numbered Treaties?
1878: John A. McDonald back in power as Prime Minister
Railroads central focus
Intensified government action to remove indigenous peoples
1882-188 Macdonald government reduced aid to treatied indigenous groups
1882 McDonald ordered the Nakoda and Plains Cree be forcefully removed
What factors contributed to rising tensions in the late 1870’s to the early 1880’s?
Created to police, monitor, and control indigenous peoples
"Pass System" 1885-1940
What were The Northwest Mounted Police?
a segregationist policy by the Canadian Department of Indian Affairs (DIA), first initiated on a significant scale in the region that became the three prairie provinces in the wake of the 1885 North-West Rebellion—as part of a series of highly restrictive measures—to confine Indigenous people to Indian reserves—newly-established through the numbered treaties.
What was the Pass System?
1876
Amalgamated all the previous indigenous treaties and made a stauncher legalized system
Control; not assimilation
Defined "Indian"
Men versus women
Granted federal government control over reserve lands
Federal government controlled indigenous governments on reserves
Indigenous peoples not citizens
What was the Indian Act?
"Cultural Genocide"
Secluded children from language and culture; purposeful assimilation
Origins in the Western Numbered Treaties
1883 federal government responsible for education of indigenous children
Partnered with Christian organizations
Underfunded; children used as laborers
Major centers of disease
Older buildings; no infirmaries
Large dormitories; poor sanitation
Lack of funding=low quality food and malnourishment
Forced attendance even when Sick
What were residential schools?
Although new evidence has recently been uncovered, it will never properly reflect the numbers.
When a child was dying, the residential school would often send the child home to die there with their parents meaning that there would be no record of their death and there will be no body to recover upon the residential school grounds.
To date approximately 2,300 unmarked graves of children found on residential school grounds and indigenous hospitals
Why will never know the actual number of children who died in the residential school system?
Under Louis Riel
1869-1870 Metis Uprising in Red River region
Louis Riel leader October 1869
Educated man
November 1869, Riel and followers took over Fort Garry (former HBC headquarters)
Headquarters to form government and policies
December 7th, 1869 took 49 prisoners to Fort Garry
December 8th, 1869, "Declaration of the People"
Created provisional government; Riel president
Thomas Scott
What was the Metis Resistance Movement?
Three Metis delegates go to Ottawa
1870 Manitoba Act
Provincial status to a province that encompassed the old Red River settlement
Manitoba set aside for the Metis
May 1870: Federal government sends "peaceful military expedition"
Riel and his associates forced to flee
What was the Manitoba Act?
By 1885: white settlers had flooded into Manitoba outnumbering the Metis five to one
Riel settled in Montana; American citizen1884 Metis delegation from Saskatchewan urged him to fight; he agreed
•March 1885: Gabriel Dumont, military leader, faced off against NWMP
Canadian force of 800 men arrived and defeated Riel and arrested
Charged with high treason; faced death penalty
Found guilty; jury urged for mercy
Canadian government ignored this. Louis Riel hanged in Regina on November 16th, 1885
What was the 1885 Northwest Resistance?
Changing class structure
Business class and working class born from industrialization
Stronger middle class
Mostly stratified by gender and ethnicity
Women, Indigenous people, individuals of Asian Descent and African Canadians outside of social class structure
Chinese immigration
Immigration Act of 1869
Political allegiances were not as important to Canadian individuals as was family, religion, and fraternal commitments
Catholic Church in Quebec
Ontario Protestantism
Describe society, religion, and regional differences from this time.
This issue continues to plague Canadian politics today
Federal system that acknowledges the rights of provinces and allows provincial legislatures to continue to exist
Process of identity negotiated through politics, culture, art, and education
Describe the issue of Regional vs National identity.