Gene replication
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
Monomers of Nucleic Acids
Nucleotides:
1. nitrogenous bases
2. Organic phosphate group
3. Pentose sugar (deoxyribose for DNA, ribose for RNA)
How does phosphate attach to the ribose sugar?
Carbon prime 1 in the sugar attaches to the nitrogenous base, carbon prime 5 attaches to the phosphate.
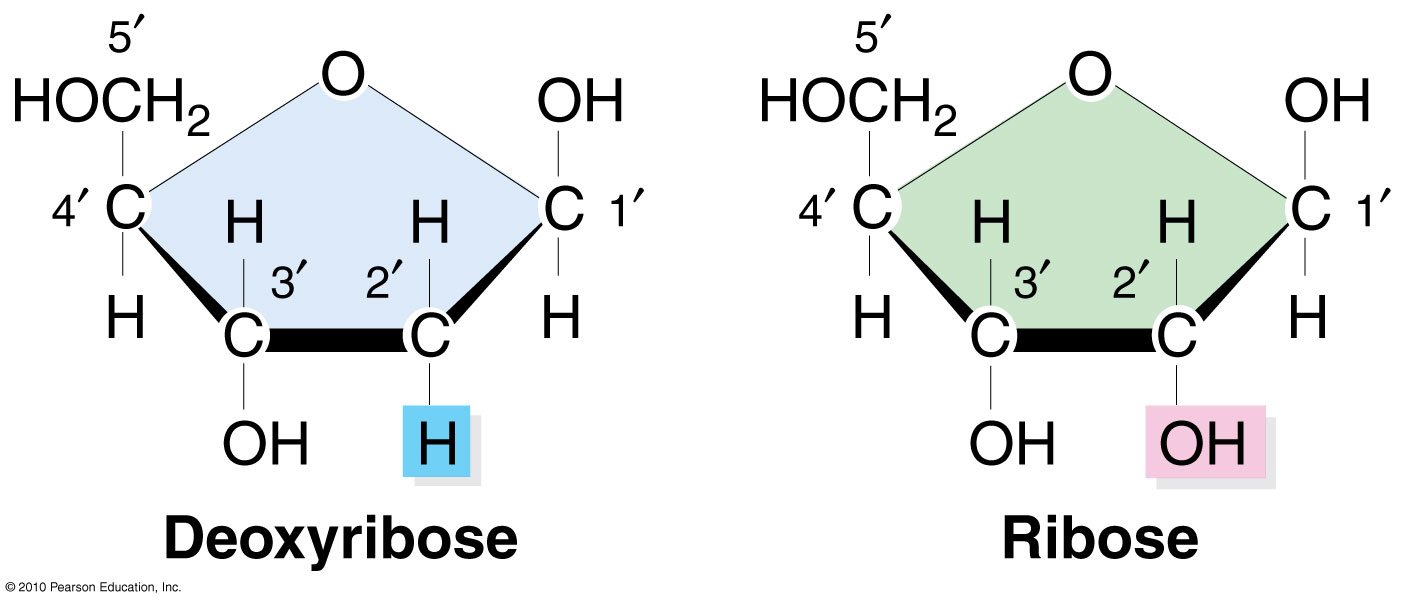
Pyrimidines
1 ring nitrogenous base
Thymine, Cytosine, Uracil
Purines
2 ring nitrogenous base
Guanine, Adenine
Chargaff’s law
Nitrogenous bases are always complimentary
C=G
T=A
Order of DNA
5’ = Phosphate end, 3’= Hydroxyl end
G1
Cell prepares for replication
1. It must grow in size
2. It must receive a stimuli (signal) to initiate replication
Synthesize phase
DNA replication
G2
Cell prepares for mitosis
1. Ensure that DNA replication was done properly, look for errors in replicated code
Direction that enzymes read
3’-5’
Origin
Portions of DNA indicating where enzymes can bind (special sequences of DNA). Eukaryotes have many origin sites, bacteria only have one.
Helicase
Unzips your genes, creates a replication bubble
Topoisomerase
Alleviates the strain caused by the replication fork, breaks one strand, lets it unwind, then seals it again.
Single stranded binding proteins
Prevent re-annealing of complementary strands near the replication fork
DNA polymerase 3
Attaches to primer set by primase and adds complementary DNA by reading 3’-5’, creating a 5’-3’ strand for leading, opposite for lagging.
Adds deoxynucleotide triphosphates to the 3’ (hydroxyl). Energy comes from the nucleus itself
Primase
Sets down an RNA primer for DNA polymerase 3 to dock onto. Adds nucleotides 5’-3’, while reading 3’-5’ off of the conservative strand.
Lagging strand
Primer gets deposited multiple times
DNA polymerase 3 attaches to a primer, builds until it reaches another primer, drops off, and attaches to the next primer, thus making okazaki fragments.
Leading strand
Only one primer is deposited, DNA polymerase 3 works steadily along
DNA polymerase 1
Binds to regions just upstream to the primer and removes ribose and uracil with deoxyribose and thymine. Ligase, distributed via DNA ligase, will seal these nucleotides together via phosphodiester bonds
Mutations
Every million base pairs that DNA polymerase 3 replicates, it creates a mistake, leading to a mutation that can be corrected by other enzymes. However, most of DNA is non-coding (introns), therefore there is rarely a phenotypic mutation
Erosion
Primase adds to the end, but polymerase 1 can’t bind to regions upstream of it (if it is at the very end bit of DNA), so each replication gets shorter due to a couple of nucleotides not being replicated.
Telomeres
Special end bits of non-coding DNA regions (introns) that are meant to be eroded to combat DNA erosion to protect coding DNA.
Produced by telomerase, found in gametes, stem cells, and tumour cells
Telomerase activity
In muscle or brain cells (cells that don’t divide), telomerase is turned off, but tumour cells actively turn on telomerase to divide nonstop
How to count chromosomes
Count centrosomes! Chromosomes can be single or double copied
Haploid
1N=23, a cell with 1 complete set of chromosomes of the entire genome
Diploid
2N=46, a cell with two complete sets of chromosomes (entire genome)
Diploid or haploid?
Count (odd is 1N, even is 2N)
Pairs (absent= 1N, present= 2N)
Double/single copy (count centromeres)
Homologous pairs of chromosomes
Chromosomes that code for the same genes, but have possible differing alleles.