COMSCI 2201 (MAM ISAY) 1ST SEM
1/89
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
90 Terms
Complex organizational process
Used to develop and maintain computer-based information systems
Used by a team of business and systems professionals
Information Systems Analysis and Design
Computer software designed to support organizational functions or processes
Application Software
Organizational role most responsible for analysis and design of information systems
Systems Analyst
What are the organizational approach to system analysis and design
methodologies
techniques
and tools
In __ , focus on efficient automation of existing processes
1950
In __ , advent of procedural third generation languages (3GL) faster and more reliable computers
1960
In __, system development becomes more like an engineering discipline
1970
In__ major breakthrough with 4GL, CASE tools, object-oriented methods
1980
In__ , focus on system integration, GUI applications, client/server platforms, internet
1990
The__, Web application development, wireless PDAs and smartphones, component-based application services
The New Century
a standard process followed in an organization to conduct all the steps necessary to analyze, design, implement, and maintain information systems.
System Development Methodology
Traditional methodology used to develop, maintain, and replace information systems.
System Development Life Cycle (SDLC)
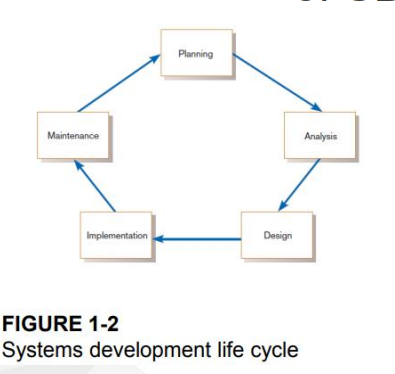
What are the Phases in SDLC
Planning
Analysis
Design
Implementation
Maintenance
What are the two views of SDLC?
System Development Life Cycle
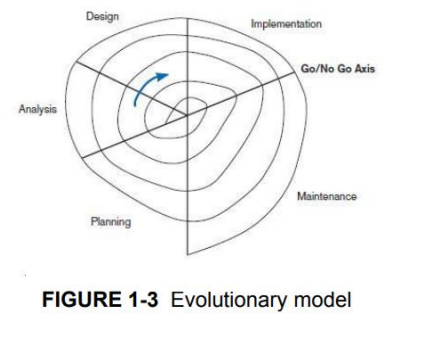
Evolutionary model
System Development Life Cycle View
Evolutionary model View
an organization’s total information system needs are identified, analyzed, prioritized, and arranged.
Planning
system requirements are studied and structured.
Analysis
a description of the recommended solution is converted into logical and then physical system specifications
Design
Two types of Design
Logical Design
Physical Design
all functional features of the system chosen for development in analysis are described independently of any computer platform.
Logical design –
the logical specifications of the system from logical design are transformed into the technology-specific details from which all programming and system construction can be accomplished.
Physical design
the information system is coded, tested, installed and supported in the organization.
Implementation
an information system is systematically repaired and improved.
Maintenance
System Development Life Cycle
Product of SDLC
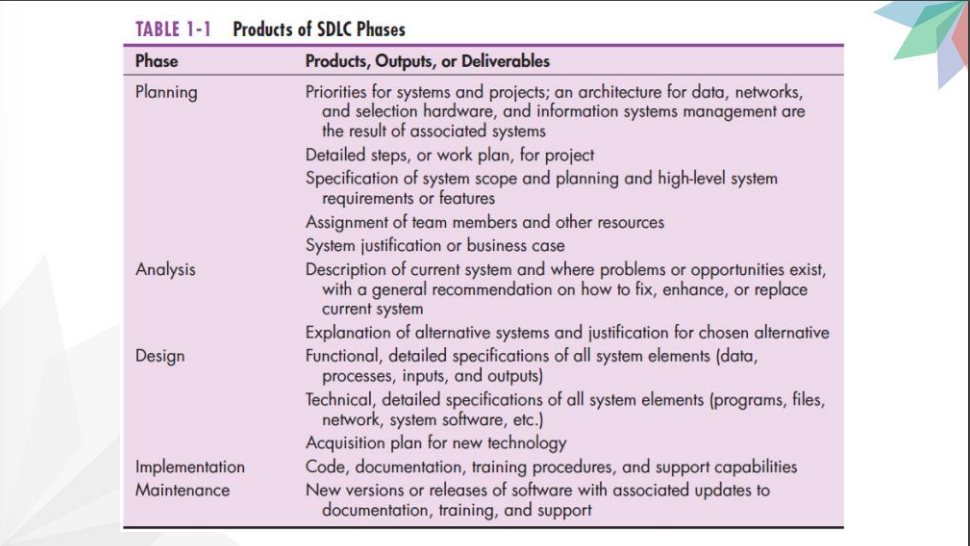
Microsoft’s Security Development Lifecyle (SDL)
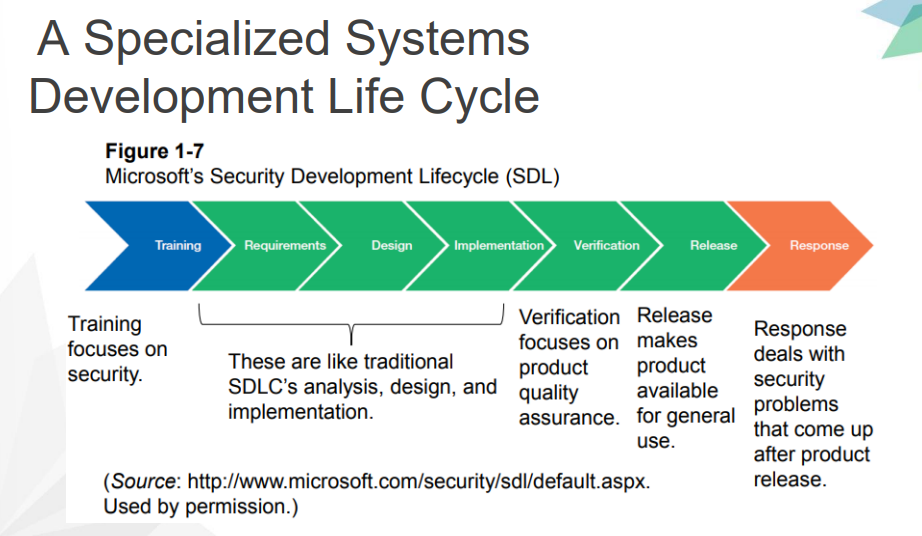
The Heart of the Systems Development Process
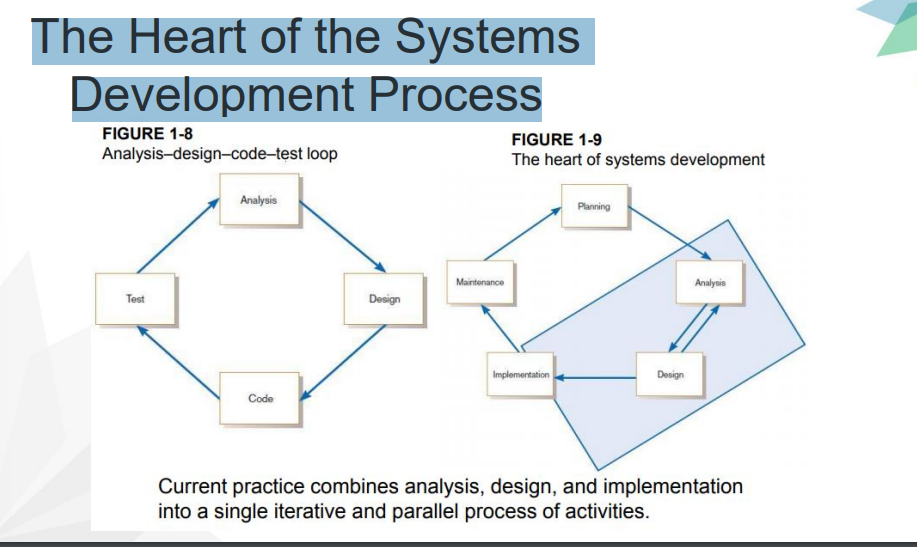
One phase begins when another completes, with little backtracking and looping
Traditional Waterfall SDLC
Problems with Waterfall Approach
Feedback ignored, milestones lock in design specs even when conditions change.
Limited user involvement (only in requirements phase).
Too much focus on milestone deadlines of SDLC phases to the detriment of sound development practices.
Different Approaches to Improving Development
CASE Tools
Agile Methodologies
eXtreme Programming
CASE Tools stands for?
Computer Aided Software Engineering ( CASE Tools)
are used to automate some task in system development of information systems e.g. generating documentation and diagrams. CASE tools can also be used for code generation
CASE Tools
Types of CASE Tools
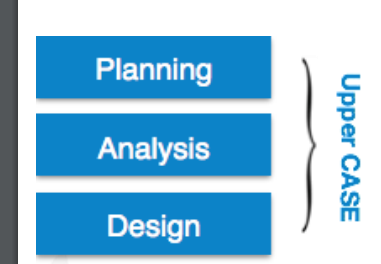
Upper Case tools
Lower Case tools
It is Also known as Analyst’s workbench
UPPER CASE TOOLS
it is also known as Programmer’s workbench
Lower Case tooos
Product of CASE Tools

it enable graphical representation.
Diagramming tools
it s help prototype how systems “look and feel”.
Computer displays and report generator
automatically check for consistency in diagrams, forms, and reports.
Analysis tools
it provides integrated storage of diagrams, reports, and project management specifications.
central repository
standardize technical and user documentation.
Documentation generators
it enables automatic generation of programs and database code directly from design documents, diagrams, forms, and reports.
Code generators
what are the CASE TOOLS
Diagramming tools
Computer displays and report generators
Analysis tools
central repository
Documentation generators
Code generators
Example of CASE Usage within the SDLC
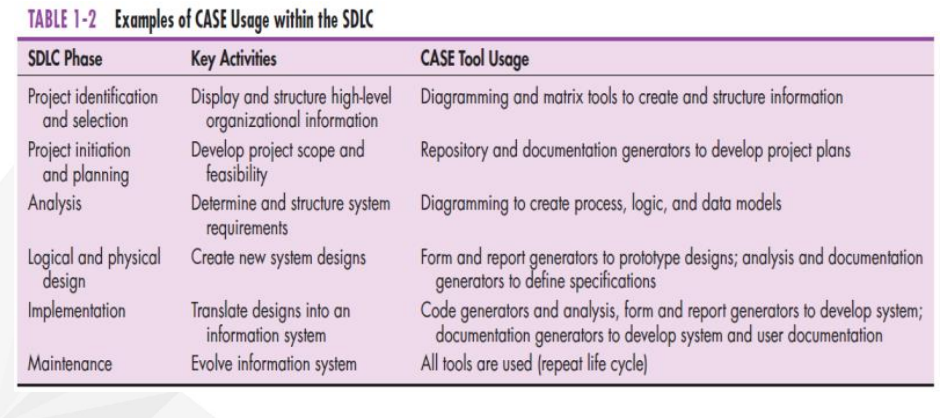
Motivated by recognition of software development as fluid, unpredictable, and dynamic
Agile Methodologies
What are the 3 key Principle of Agile Methodologies
Adaptive rather than predictive
Emphasize people rather than roles
Self-adaptive processes
Agile Methodology
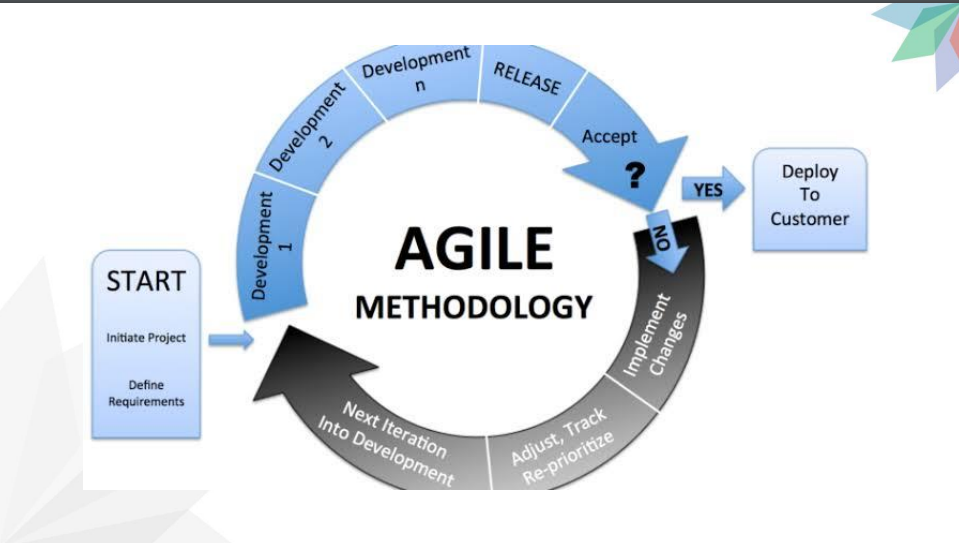
Agile Methodology Sample
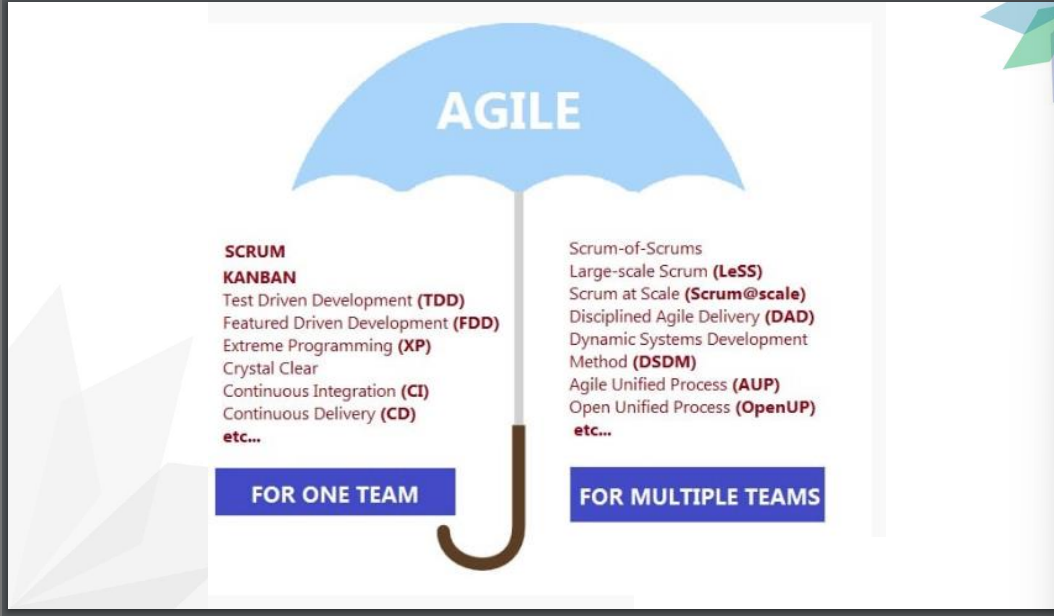
Kanban Card
Scrum
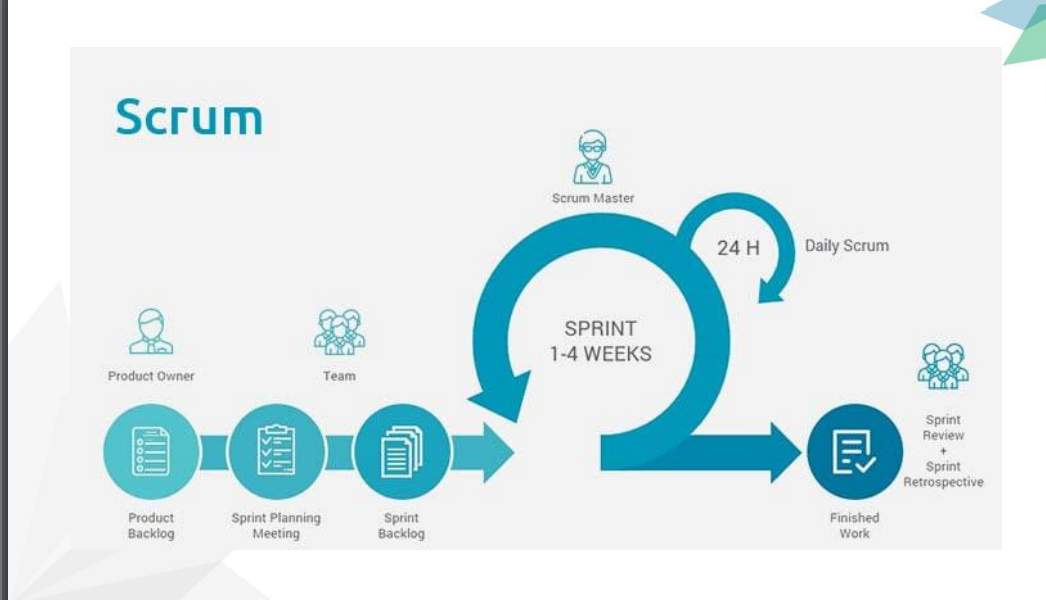
Agile Manifesto
We are uncovering better ways of developing software by doing it and helping others do it.

When to Use Agile Methodologies
If your project involves:
Unpredictable or dynamic requirements
Responsible and motivated developers
Customers who understand the process and will get involved
What are the five critical factors that distinguish agile and traditional approaches to system development
Size
Criticality
Dynamism
Personnel
Culture
Short, incremental development cycles
Focuses on automated tests
Two-person programming teams
Coding, testing, listening, designing
eXtreme Programming
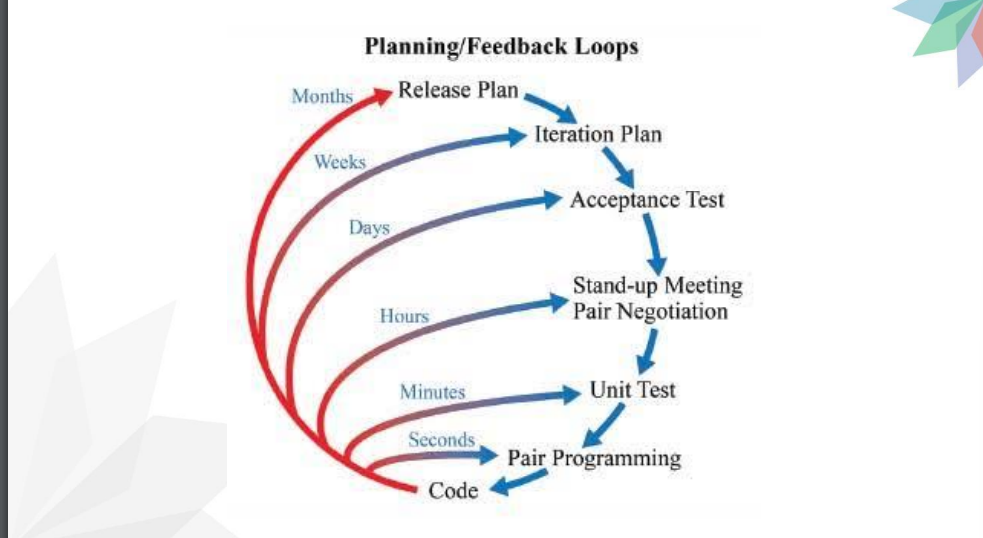
Planning/Feedback Loops
It combines data and processes (called methods) into single entities called __
objects.
Its goal is to make systems elements more reusable, thus improving system quality and the productivity.
Object-Oriented Analysis and Design
allows the creation of new classes that share some of the characteristics of existing classes.
Inheritance
ORIGINS OF SOFTWARE
The first source considered is __, in which all or part of an organization’s information systems, their development, and their maintenance are given over to another organization.
outsourcing
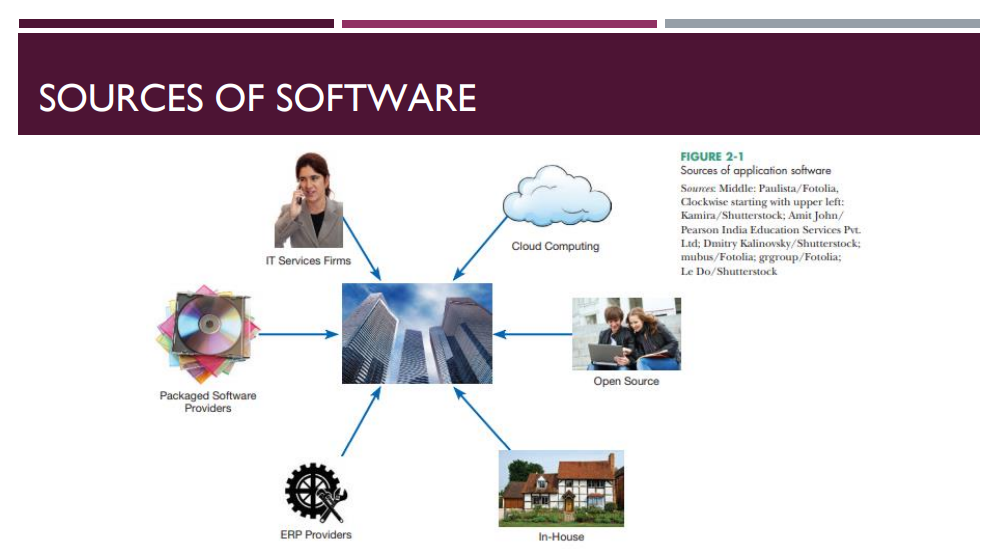
six different sources of software:
1) Information technology services firms;
2) Packaged software providers;
3) Vendors of enterprise-wide solution software;
4) Cloud-computing;
5) Open-source software;
6) The organization itself when it develops software in-house.
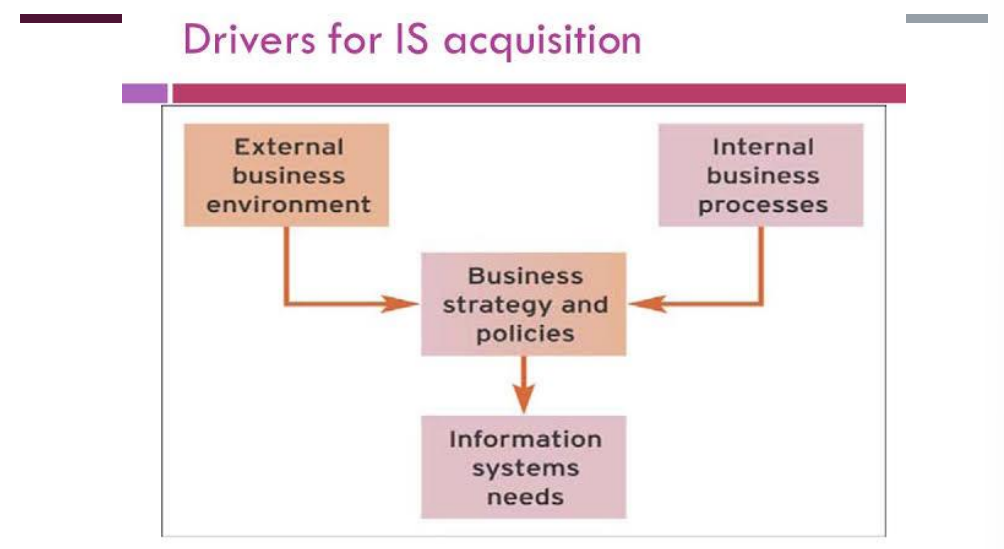
Driver for IS acquisition
If one organization develops or runs a computer application for another organization, that practice is called ___
outsourcing
The practice of turning over responsibility for some or all of an organization’s information systems applications and operations to an outside firm.
Outsourcing
Why would an organization outsource its information systems operations?
cost-effectiveness
freeing up internal resources
increasing the revenue potential of the organization
reducing time to market
increasing process efficiencies,
outsourcing noncore activities.
Outsourcing Companies

If a company needs an information system but does not have the expertise or the personnel to develop the system in-house, and a suitable off-the-shelf system is not available, the company will likely consult an___
information technology services firm
it help companies develop custom information systems for internal use, develop, host, and run applications for customers, or they provide other services.
INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY SERVICES FIRMS
Outsourcing Companies

PACKAGED SOFTWARE PRODUCERS
INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY SERVICES FIRMS
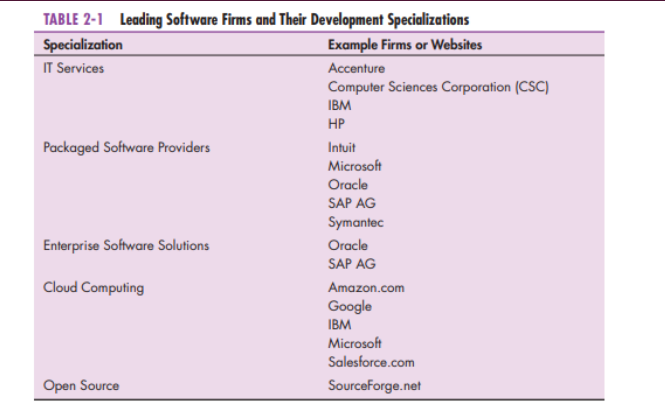
Some of the largest computer companies in the world are companies that produce software exclusively.
PACKAGED SOFTWARE PRODUCERS
Software companies develop what are sometimes called___
prepackaged or off-the-shelf systems
Also known as enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems
ENTERPRISE SOLUTIONS SOFTWARE
It consists of a series of integrated modules which support an individual, traditional business function.
ENTERPRISE SOLUTIONS SOFTWARE
It refers to the provision of applications over the Internet, where customers do not have to invest in the hardware and software resources needed to run and maintain the applications.
CLOUD COMPUTING
BENEFITS ON USING CLOUD COMPUTING
Freeing internal IT staff;
Gaining access to applications faster than via internal development;
Achieving lower cost access to corporate-quality applications.
It is freely available, not just the final product but the source code itself.
OPEN SOURCE SOFTWARE
it performs the same functions as commercial software, such as operating systems, e-mail, database systems, web browsers, and so on.
OPEN SOURCE SOFTWARE
OPEN SOURCE SOFTWARE

it has become a progressively smaller piece of all systems development work that takes place in and for organizations.
IN-HOUSE DEVELOPMENT
__ involving some purchased and some in-house software components are common.
Hybrid solutions
– comparing the cost of developing the same system in-house with the cost of purchasing or licensing the software package.
Cost
– tasks the software can perform and the mandatory, essential, and desired system features.
Functionality
CHOOSING OFF-THE-SHELF SOFTWARE

– A document provided to vendors that asks them to propose hardware and system software that will meet the requirements of a new system.
Request for proposal (rFP)
two different development technologies
object-oriented development
component-based development
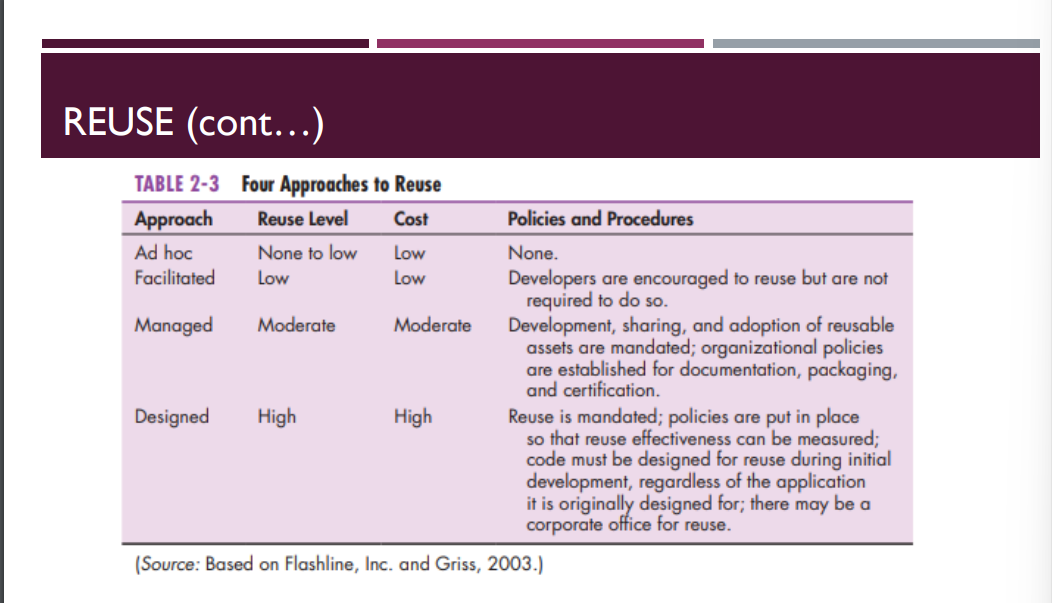
REUSE
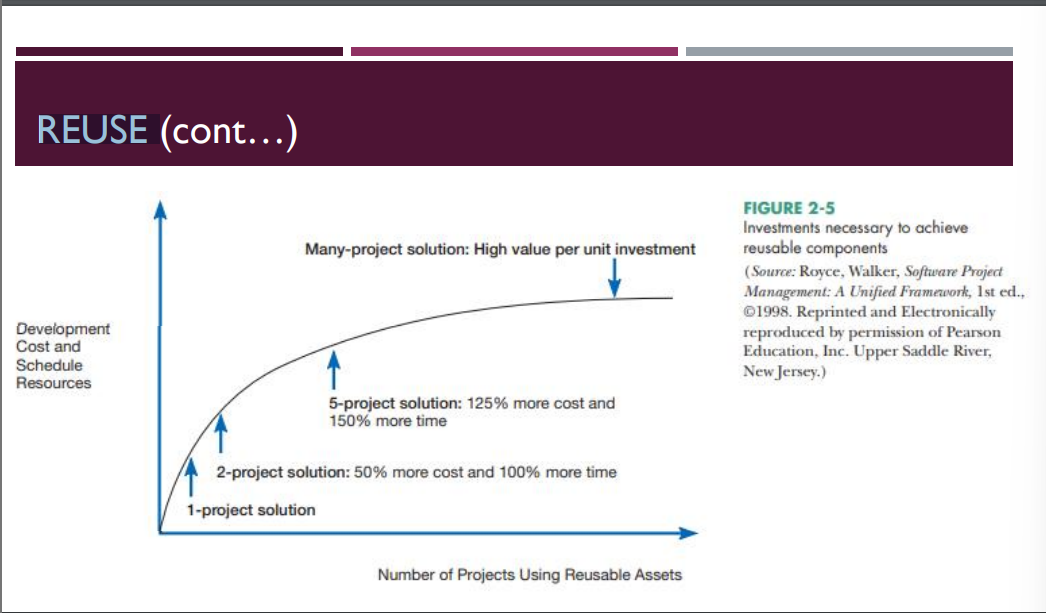
FOUR APPROACHES TO REUSE