Dr. Wood Mammalogy Tracking
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
47 Terms
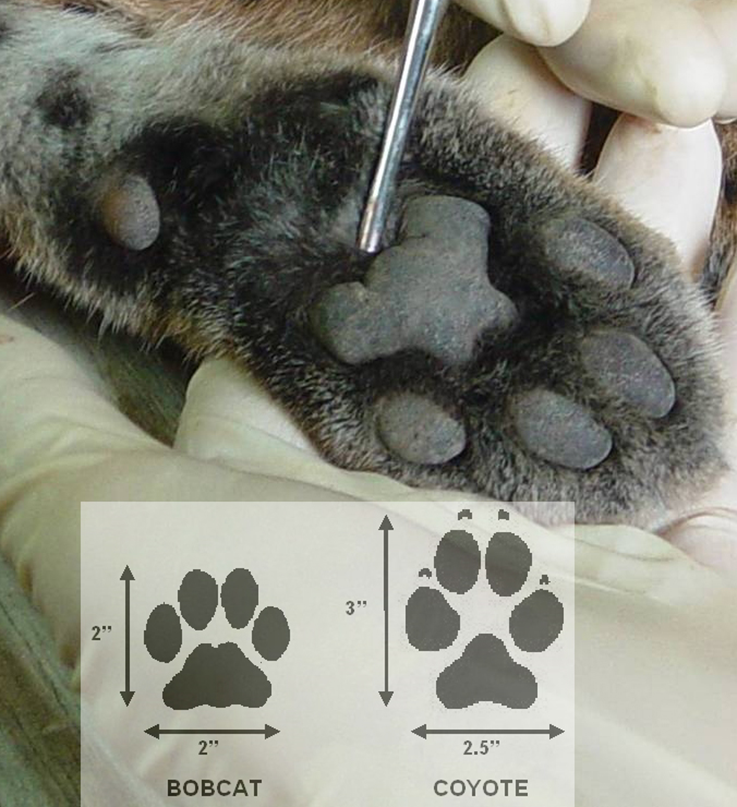
the footprints or imprints left by mammals on a substrate like mud, snow, or sand. The study of these tracks, along with other animal signs
Tracks
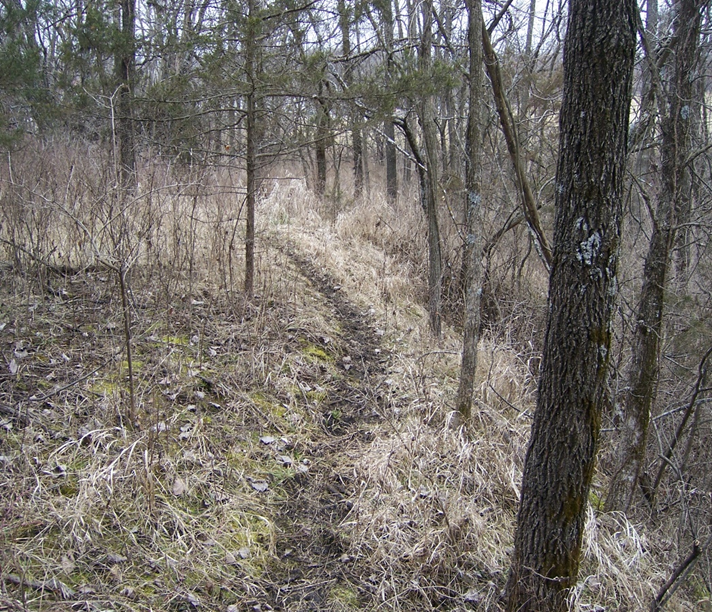

a distinct, worn-down path or trail created by the repeated travel of small animals through dense undergrowth.
Run
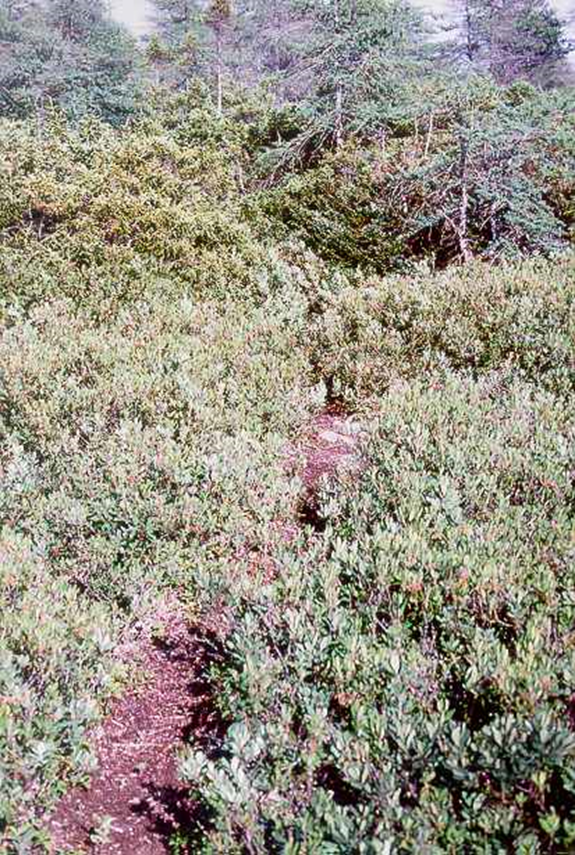

a distinct, worn-down path or trail created by the repeated travel of small animals through dense undergrowth.
Run
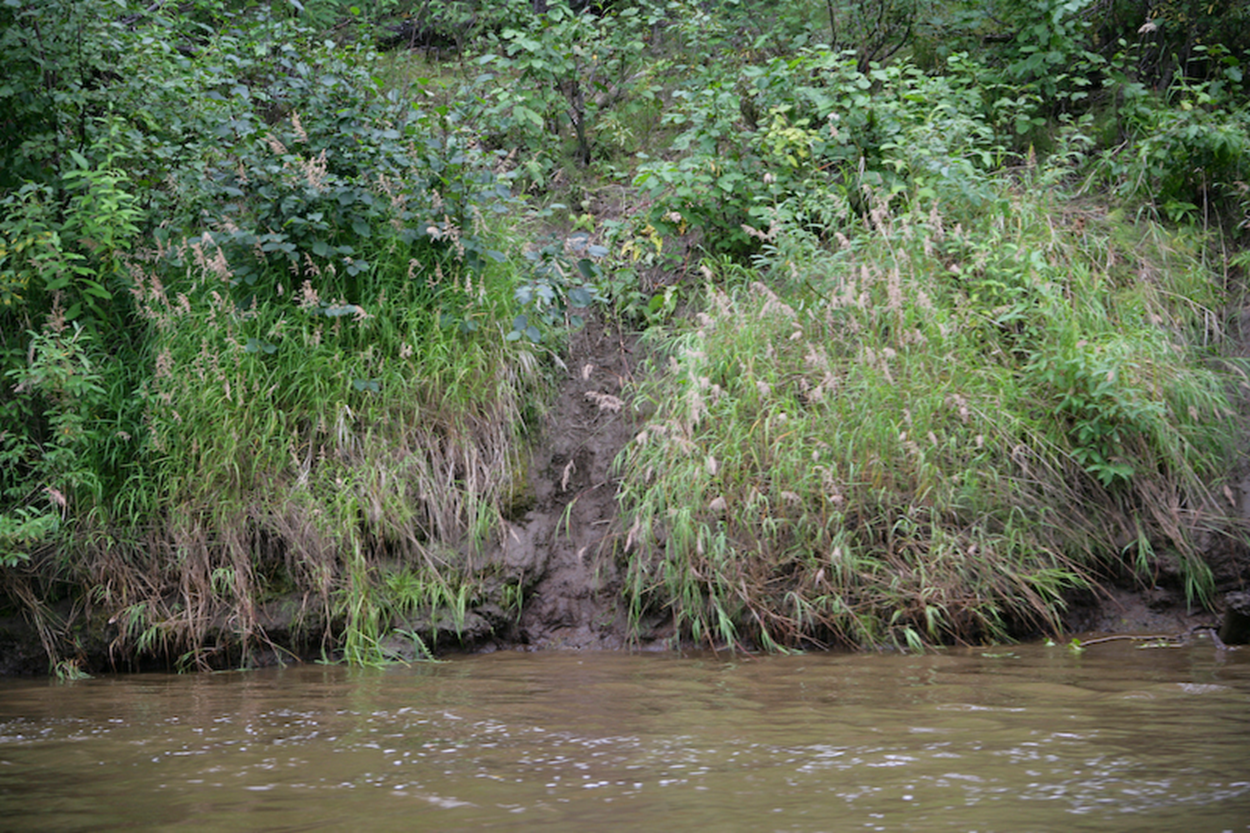

a distinct, worn-down path or trail created by the repeated travel of small animals through dense undergrowth.
Run

A travel corridor or underwater path used by muskrats in a marsh, pond, or other wetland environment.
Channel

for small animals to escape and travel while hidden
Tunnel
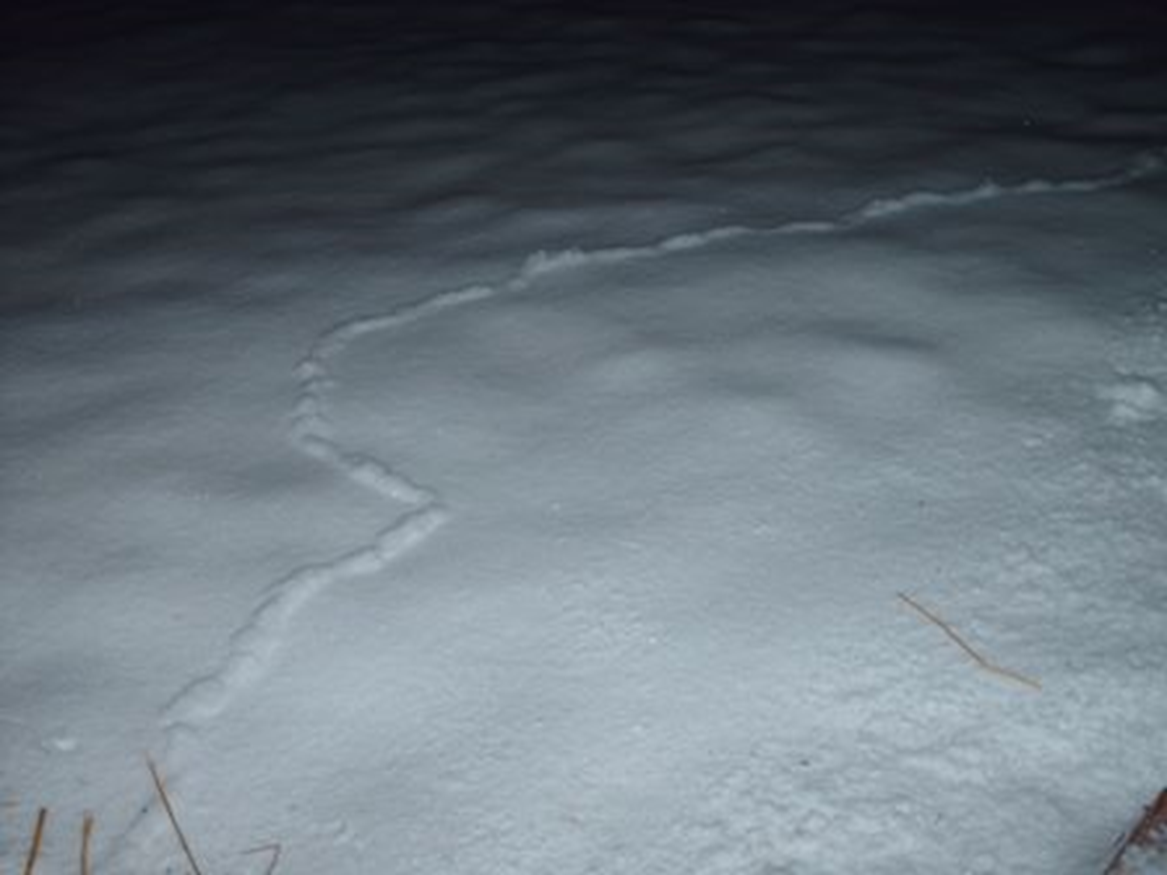

A under snow tunnel for rodents
Esker
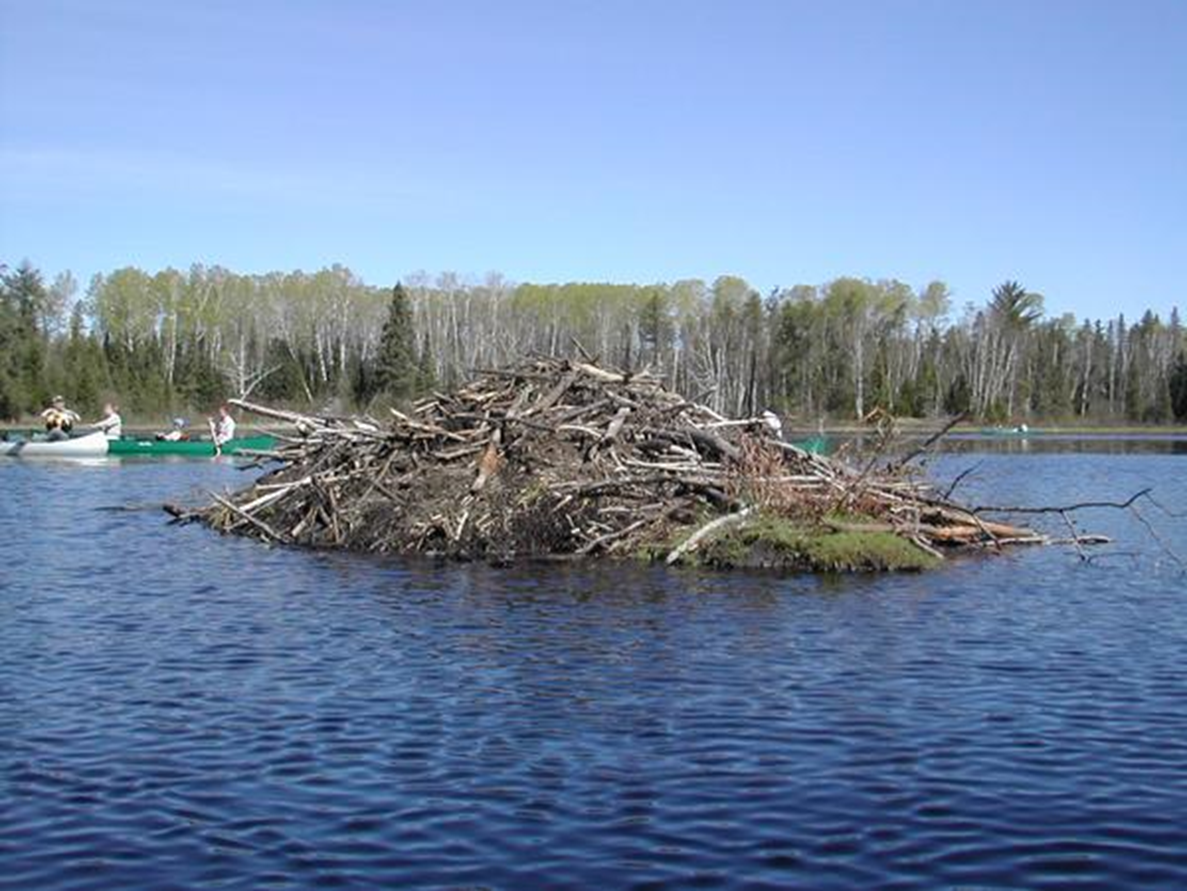

An extensive, above-ground shelter constructed by certain species of rodents, primarily for protection and nesting. Beavers are the most famous lodge-building mammals.
Lodge
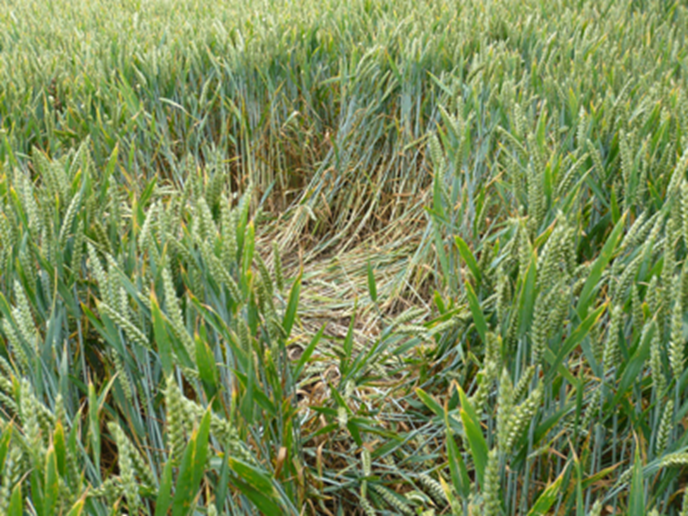

The specific resting place or nesting site used by a mammal.
Bed/Lay
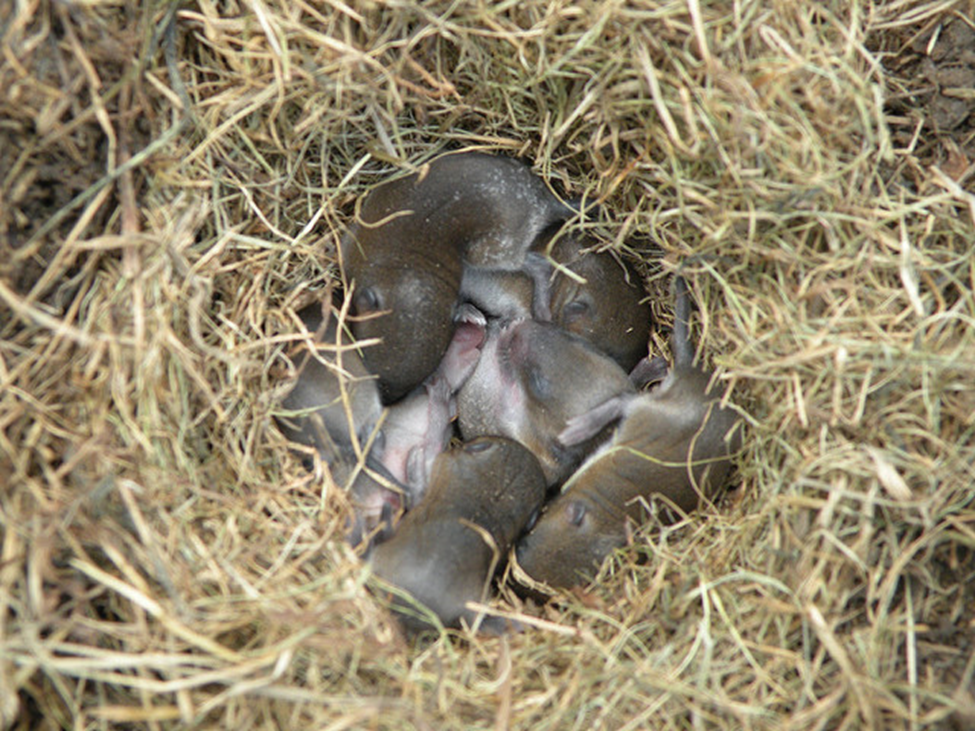

A shelter or structure built by an animal to protect itself and its young from the elements and predators. While most people associate nests with birds, many mammals, particularly smaller ones, also construct them for various purposes, including maternity, resting, and protection from the environment.
Nest
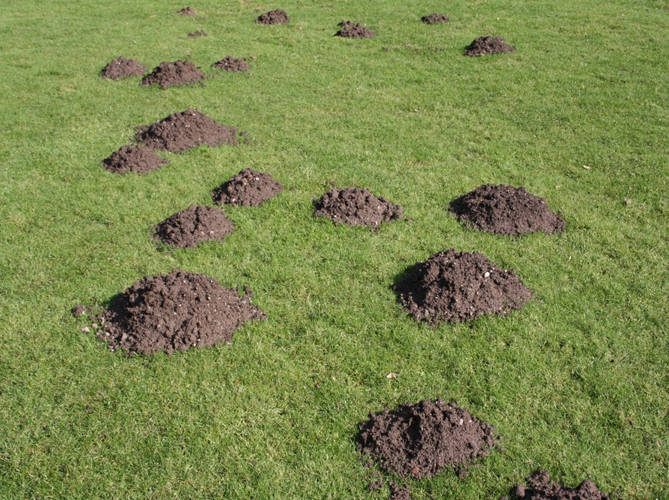

Created by animals, the result of burrowing activity and serve various critical functions for survival and reproduction. Different species, such as moles and pocket gophers, create distinct types of mounds, and studying these structures
Dirt Mound

A hole or tunnel excavated by a mammal into the ground to create a space for habitation, temporary refuge, or as a byproduct of locomotion.
Burrow
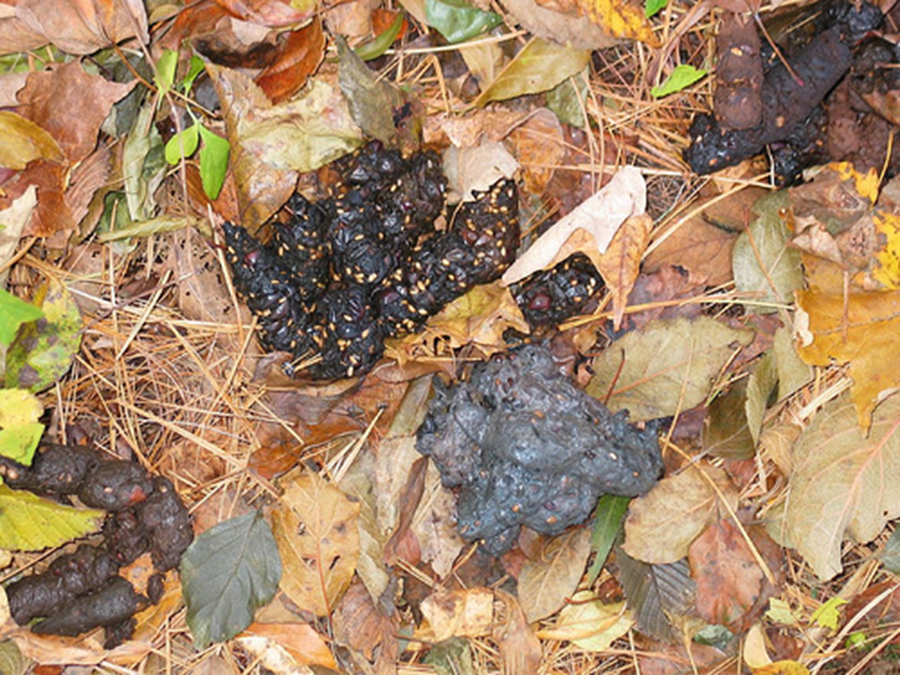

A tubular shape, dark brown to black color, and contents from its omnivorous diet like seeds, fruit, fur, and insect exoskeletons
Racoon Scat
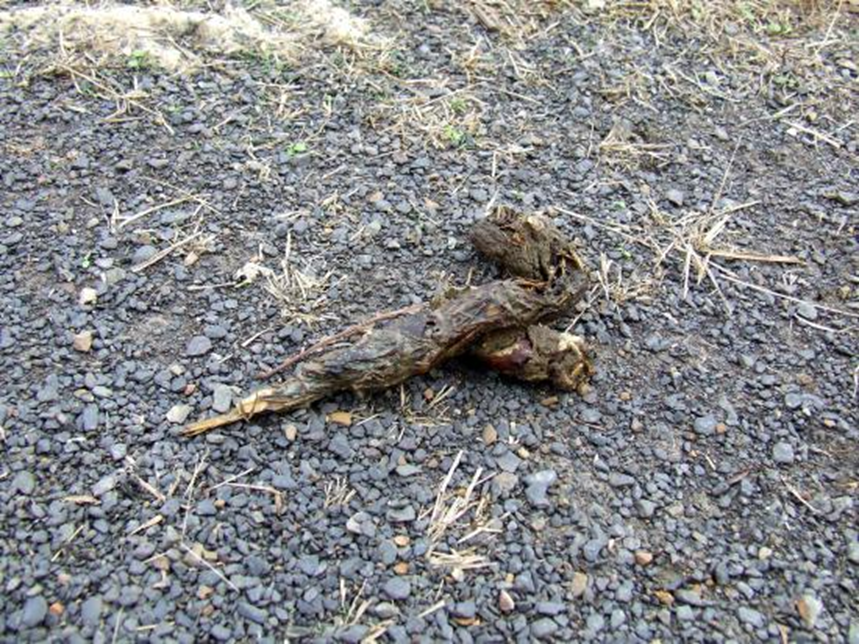

The form of an animal's feces, and it is a key characteristic used for species identification. This specific shape is most commonly associated with carnivorous mammals, especially canids (dogs, foxes) and mustelids (weasels, martens, otters).
Twist and Tapered
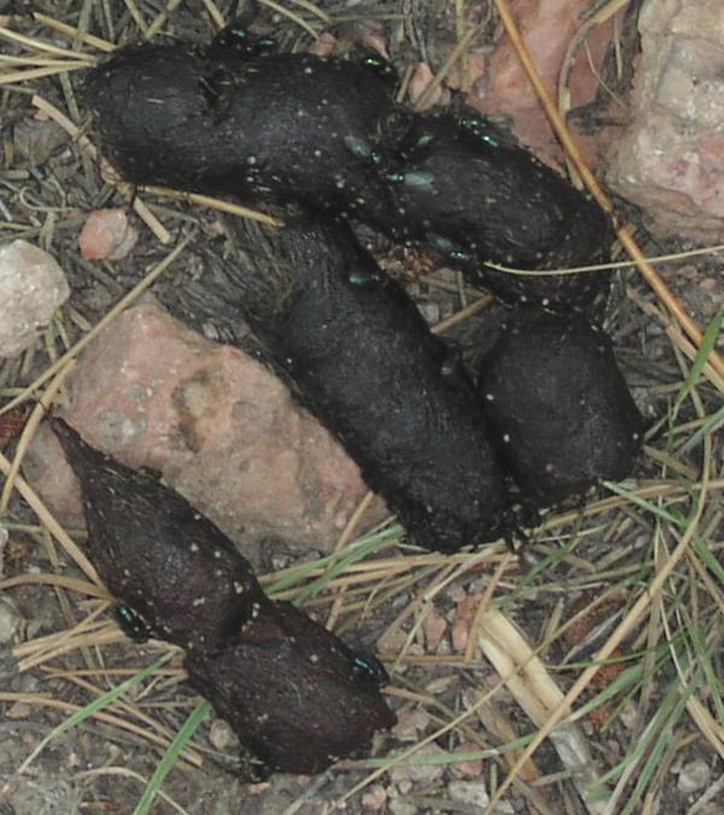

The distinctive, rope-like feces of a cougar (also called a mountain lion or puma) that has broken into multiple, distinct pieces.
Segmented Cougar Scat
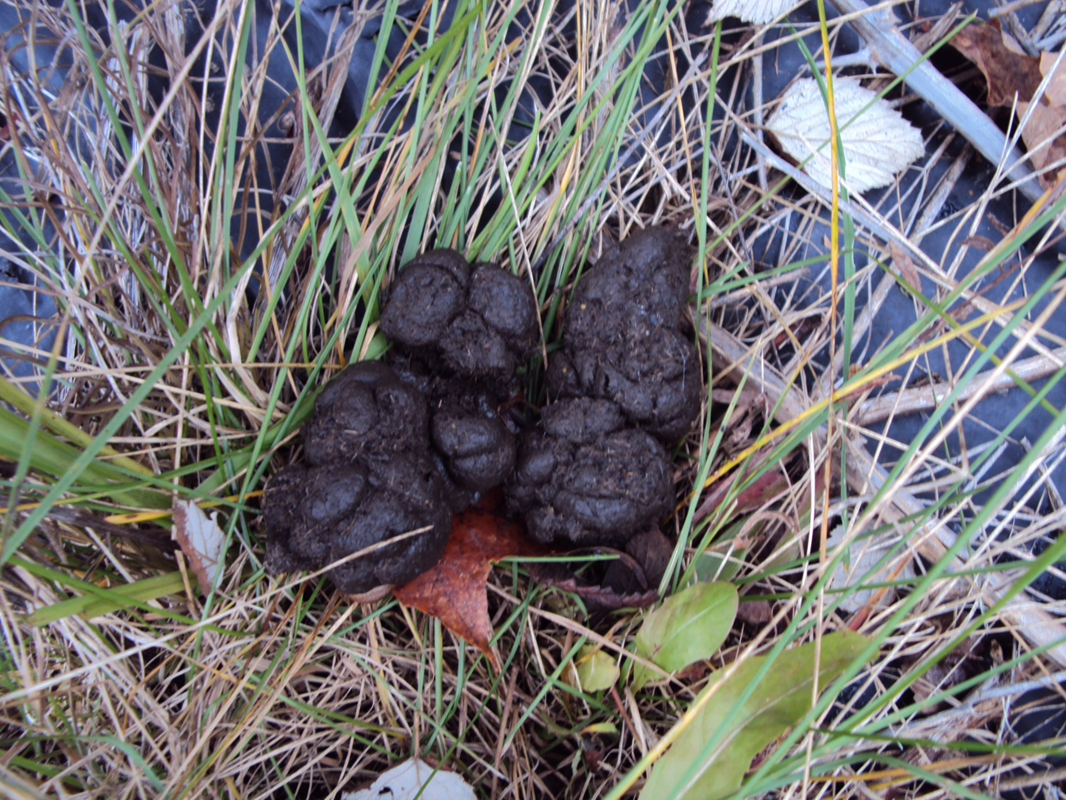

The rodent behavior of repeatedly defecating and urinating in the same location, which creates a concentrated pile of droppings called a latrine
Raised Scat
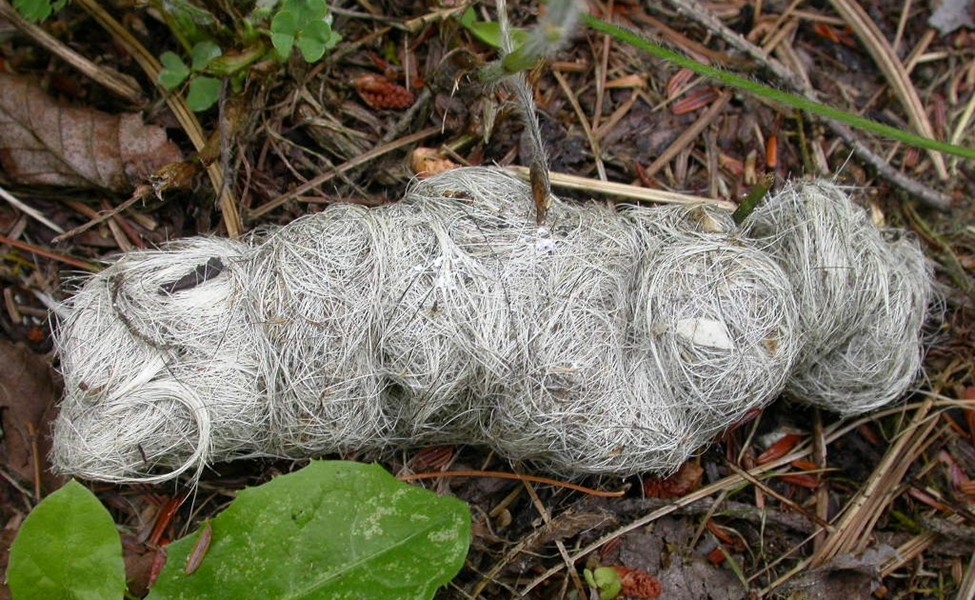

Aged ______droppings that have turned a light color due to sun bleaching and decomposition
Whitened Coyote Scat
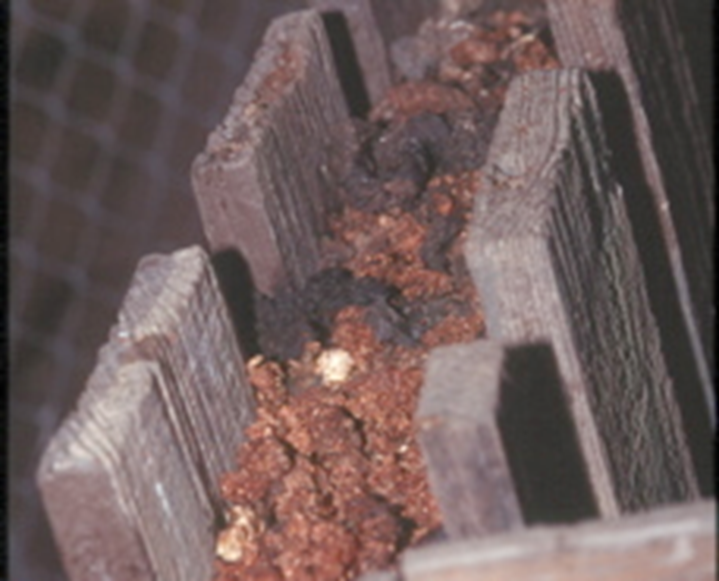

feces and urine deposited by animals in a specific, repeated location, forming a "communal bathroom" for a species. In mammalogy, this behavior is a form of scent marking used for communication, territorial defense, and social bonding
Latrine Raccoon
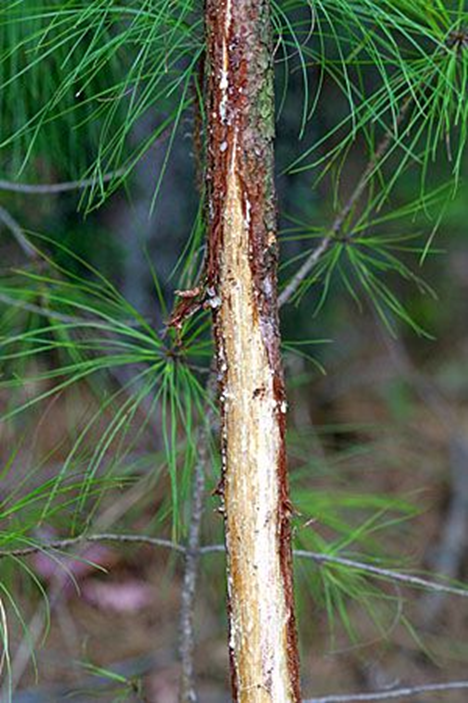

Distinct forms of non-vocal, scent-based communication primarily used by male ungulates, such as deer and elk, to announce their presence, dominance, and reproductive readiness. Rubs and scrapes act as "signposts" or communication hubs that other animals in the area can read and interpret.
Rub
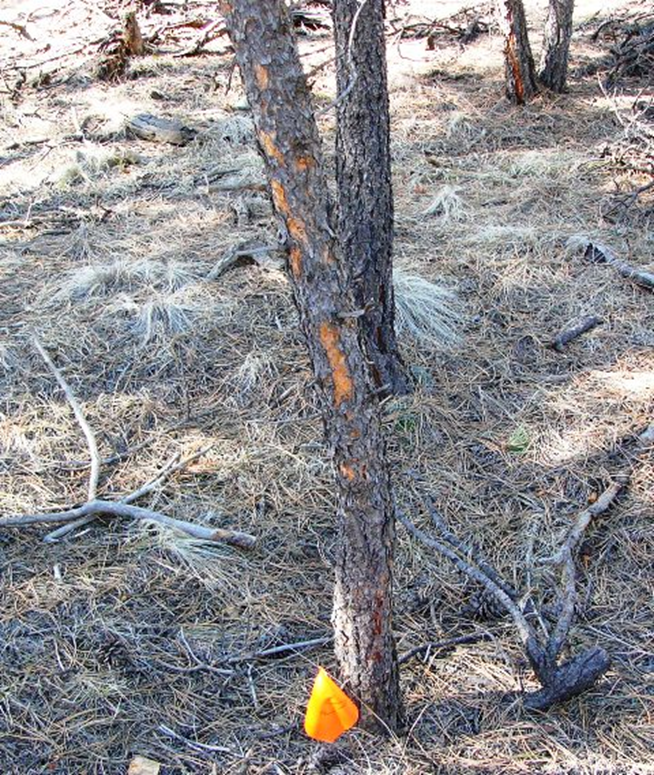

Distinct forms of non-vocal, scent-based communication primarily used by male ungulates, such as deer and elk, to announce their presence, dominance, and reproductive readiness. Rubs and scrapes act as "signposts" or communication hubs that other animals in the area can read and interpret.
Scrape
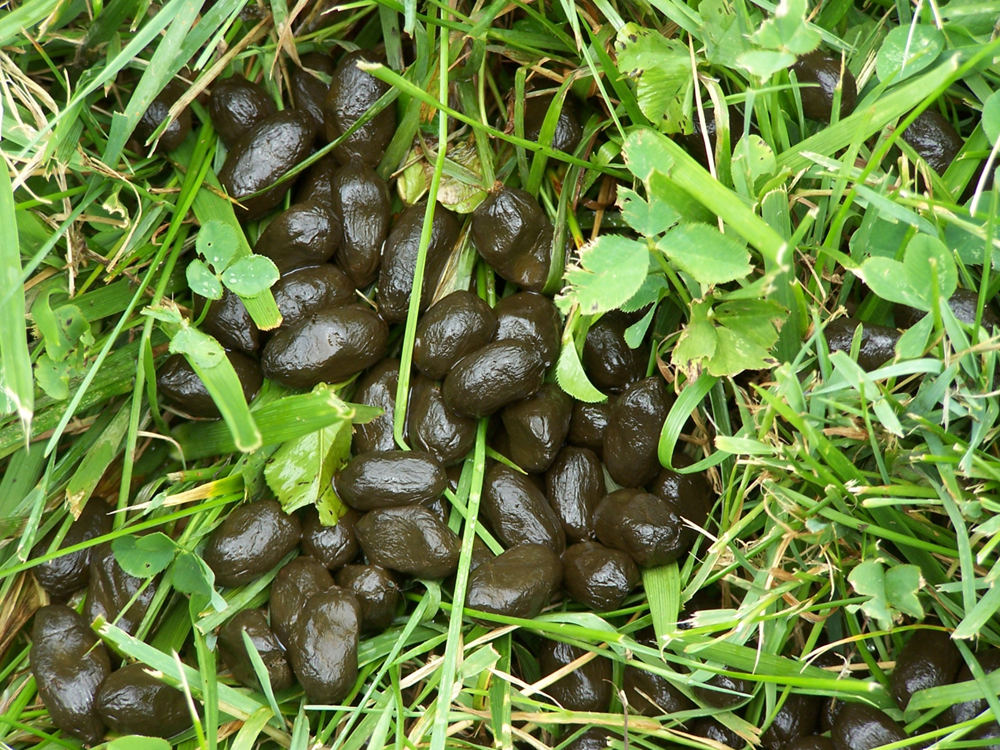

The distinctive, pellet-shaped feces produced by many herbivorous mammals, such as rabbits, deer, and goats
Pellets
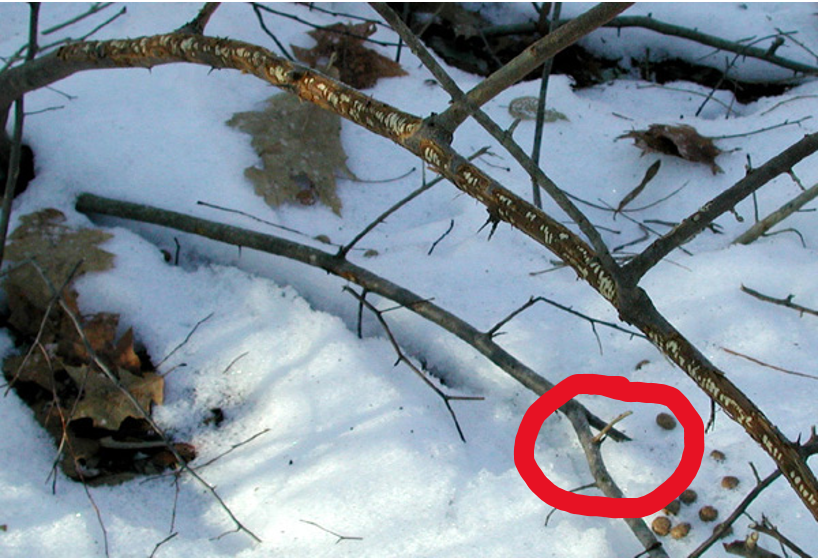

A type of rodent chews on wood because their teeth grow continuously throughout their lives, and chewing on tough, fibrous material like wood is necessary to wear them down and prevent overgrowth.
Rabbit Chew
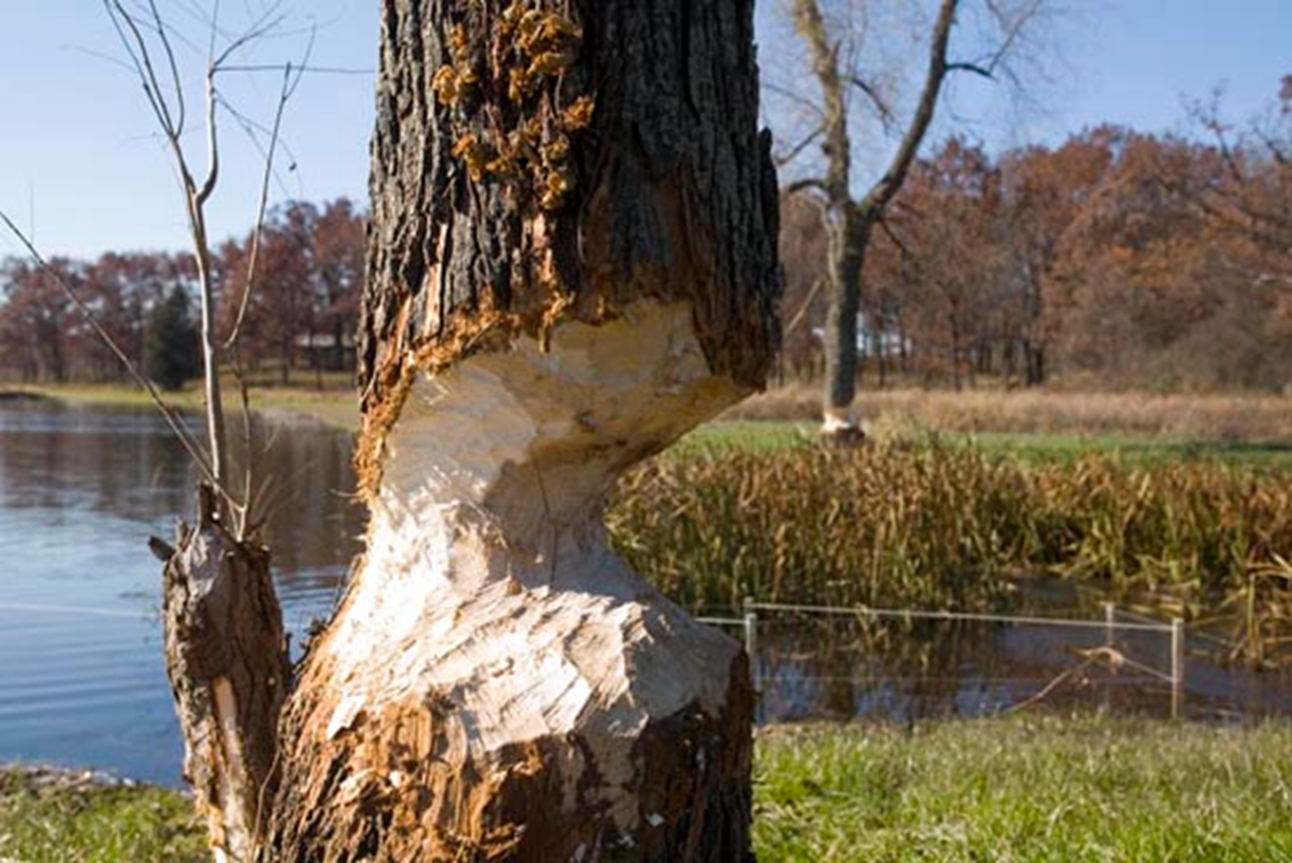

Bears, beavers, porcupines, rabbits, squirrels, and some rodents ______ on trees for nutrition or to wear down their teeth. This behavior is a normal feeding strategy, especially during winter when other food sources are scarce.
Bark Chew
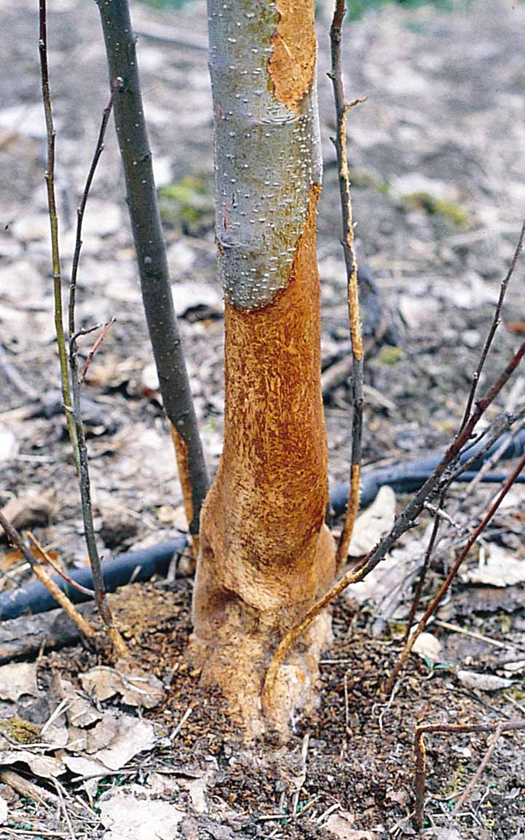

The act of a mammal chewing a continuous ring of bark from around the circumference of a tree or shrub. This behavior, which is most often seen in rodents and deer, can kill the tree by severing the vascular tissues that transport water and nutrients.
Beavers, rabbits, voles, and deer are known to girdle trees by stripping or gnawing the bark.
Girdling
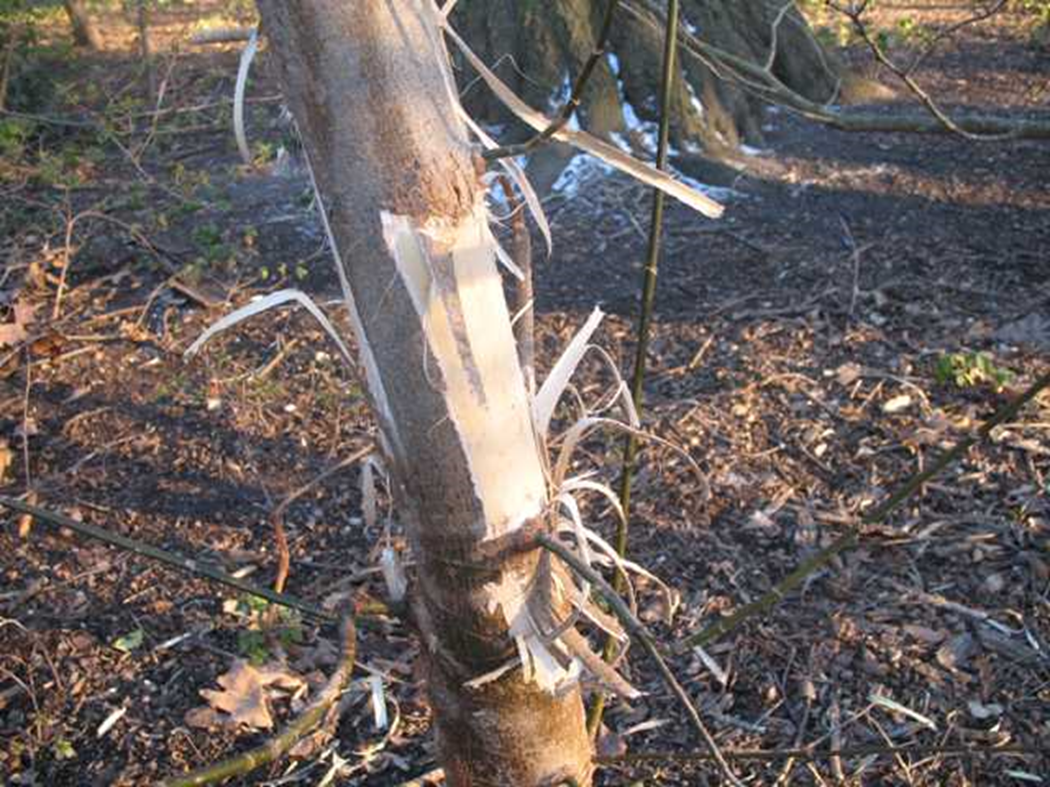

The act of an animal removing bark from trees and other vegetation. This behavior leaves behind a visible, identifiable sign—or "spoor"
Stripping
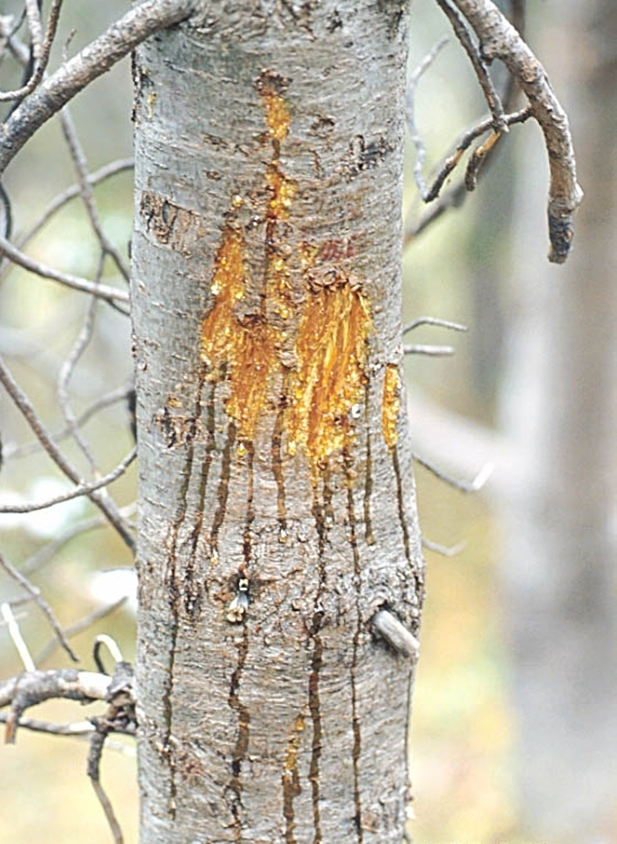

A specific type of marking left on trees by bears, which serves as a form of communication. These markings, along with rubbing and biting, act as a "bulletin board" for bears, indicating their presence to other bears in the area.
Bear Scratch
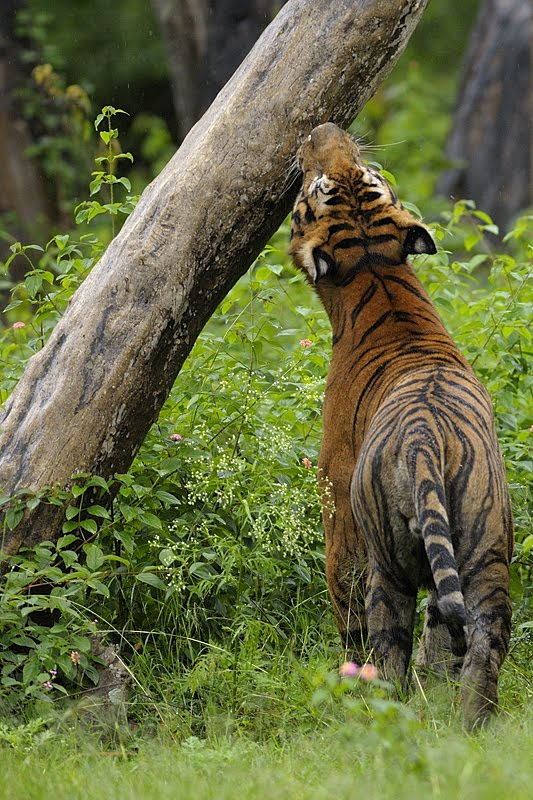

A chemical signal left by an animal on a surface in its environment to communicate messages to other animals of the same species
Scent Mark
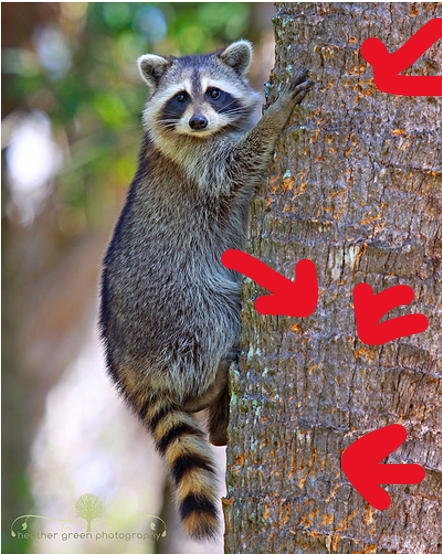

A physical markings that indicate an animal has been in a tree, on a rock, or on other elevated surfaces. The types of signs you can find depend on the species and its climbing technique.
Climbing Sign
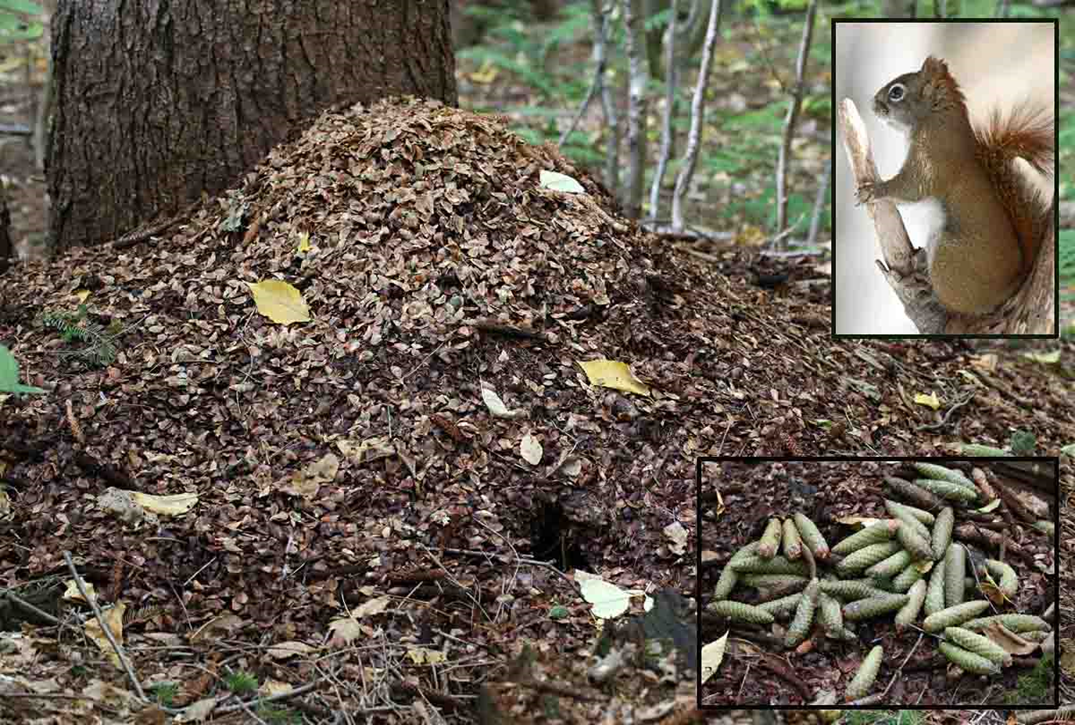

An animal's waste disposal or storage area, which can provide valuable clues about the animal's identity, diet, and behavior. The contents of a midden can include feces, food scraps, or other discarded items.
Midden

Coyote

Woodchuck

Whitetail Deer

Mink

Dog

Opossum

Cottontail Rabbit

White footed mouse

House Cat

Muskrat

Beaver

Racoon

Otter

Striped Skunk

Grey Squirrel

Red Fox

Black Bear

Porcupine