AP Biology Unit One
1/80
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
81 Terms
What 4 elements make up 96% of all living things?
Hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and carbon. (HONC)
What 6 elements make up the macromolecules?
Sulfur, phosphorus, oxygen, nitrogen, carbon, hydrogen. (SPONCH)
What three elements does each macromolecule ALWAYS have in common?
Oxygen, carbon, and hydrogen.
Which of the six SPONCH elements is found only in protein?
Sulfur (in cysteine)
Which is the only macromolecule that always has phosphorus?
Nucleic acids. (Lipids can have phosphorus as well, but only in phospholipids)
Which macromolecules always contain nitrogen?
Proteins and nucleic acids. Lipids and carbons can have nitrogen, just not always.
What happens when the valence electrons from two different atoms interact?
Chemical bonding.
What is electronegativity?
An atoms ability to attract electrons.
What are the two most electronegative SPONCH elements?
Oxygen and Nitrogen.
What is an ionic bond?
When electrons transfer from a less electronegative atom to a more electronegative atom.
What is an ion?
An atom with a charge. (can be + or -)
There are cations and anions, which one is negative and which one is positive?
Cation is positive, and anions is negative.
What is a covalent bond?
A pair of electrons being shared between two atoms.
What is the difference between a polar and non-polar covalent bond?
Polar covalent bonds are between two atoms that have different electronegativities (unequal sharing of electrons). Non-polar covalent bonds are between two atoms that have similar electronegativies (equal or near equal sharing).
What do hydrophobic and hydrophilic mean?
Hydrophobic means that a molecule will not interact with, mix, or dissolve with water. Hydrophilic simply means the opposite.
What is a hydrogen bond?
A weak chemical bond between a partially negative charged atom of one molecule, and a partially positive charged hydrogen atom of another.
What shape is H2O?
Bent, with polar covalent bonds between the O and the 2 H’s.
Water is a polar molecule. How does this dictate its function?
Because of the high electronegativity of oxygen, and low electronegativity of hydrogen, the hydrogen’s electrons are drawn closer to the oxygen, giving the oxygen a slightly negative charge, and the hydrogen a slightly positive charge. (You need to be able to represent this in a drawing). These charges are what allows water to hydrogen bond.
What gives water all of its unique properties?
Hydrogen bonds. Remember that hydrogen is always attracted to the oxygen of another water molecule, and vice versa. Also water can maintain a total of 4 hydrogen bonds.
What are the four very important and unique properties of water?
High specific heat, universal solvent, less dense as a solid than a liquid, and cohesion.
What is specific heat, and why is having a high specific heat such an essential aspect of water?
Specific heat is the amount of heat required to raise one gram of a substance one degree Celsius. The fact that it takes a lot of heat to change the temperature of water, makes it so that its temperature hardly fluctuates. This is good for aquatic plants and animals.
What substances dissolve in water?
“Like dissolves like” Anything that’s polar or ionic, would be hydrophilic, and would therefore dissolve in water.
True or false? If water is poured in a negative solution, the oxygen molecules in the water would be attracted to the negatively charged molecules of the solvent. Also, if water was poured into a positively charged solvent, then the hydrogen atoms would be attracted to the positive molecules of the solvent.
False, it would be the other way around. Since the oxygens in water are negatively charged, they would be attracted to a positive solvent. Hydrogens in water are positively charged, so they would be attracted to the negative solvent.
Why is it important that water is denser as a liquid than a solid?
It keeps large bodies of water from freezing solid. It also makes it so that ice floats in water, which helps to insulate bodies of water, so aquatic life can survive very cold outside temperatures.
What is the difference between cohesion and adhesion?
Cohesion is when something sticks to itself (hydrogen bonding in water), and adhesion is when something sticks to something else.
Why are cohesion and adhesion important?
Cohesion creates surface tension in water, and both cohesion and adhesion assist in transpiration.
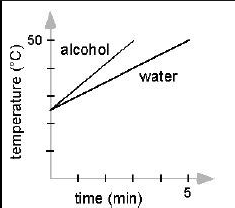
Not a question, but remember how to draw a temperature graph over time for alcohol and water. (alcohol changes temperature and phase much faster) (image is on the answer)
I should probably be charging people money for these flashcards.
Water moves from ___ to ___ concentration
high to low concentration
Windy and sunny environments will ______ evaporation rates, and dark and humid environments will _____ evaporation rates.
increase, decrease
What is transpiration, and why does it work?
Transpiration is the movement of water from the bottom of a plant, up through the xylem, and then out through the stomata. This works due to evaporation. When water evaporates, it is still hydrogen bonded to other water molecules, so they get pulled upwards along with the water that is being evaporated. Adhesion also assists, because it allows water to stick to the walls of the xylem.
What regulates how much water the stomata lets out?
Guard cells (whatever those are)
What is the pH scale?
A scale that measures from 0-14, that details the amount of H+ in a solution.
A solution has more H+ than OH-, and is below a 7 on the pH scale. What is this called?
An acid.
A solution has more OH- than H+, and is above a 7 on the pH scale. What is this called?
A base.
In terms of pH, water is…?
Neutral, because it is at a 7 on the pH scale. This means that the amount of H+ and OH- is equal.
How do buffers regulate pH?
They “donate” H+ to bases, and “steal” H+ from acids.
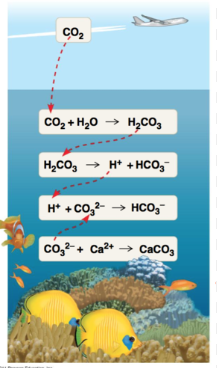
How does ocean acidification work?
Carbon dioxide (CO2) dissolves in the ocean to become carbonic acid (H2CO3). The carbonic acid (H2CO3) then dissasociates, and releases an H+. This H+ reacts with carbonate ions (CO3²-). These carbonate ions are needed for the calcification of coral. Essentially the H+ from the carbonic acid “takes the bricks away” from coral, taking away needed material to make it grow.
What property of carbon makes it so important?
It has four valence electrons, so it can make four bonds. This makes it a great base, and makes it able to form very large molecules (chains, branched, or rings).
What is an isomer?
Where two molecules have the same molecular formula, but have different shapes, so they have different functions. Ex. Methamphetamine has two different isomers. One is used in nasal decongestant spray, and the other is the street drug.

What did the Miller-Urey experiment conclude?
They showed that you could abiotically form organic molecules (amino acids and RNA) from inorganic molecules that existed before life on earth (NH3, CH4, H20, H2).
What is the carbon cycle?
Cellular respiration from animals and decomposition of organic materials releases CO2 into the air, which the plants then convert to oxygen. Animals then breath the oxygen, continuing the cycle.
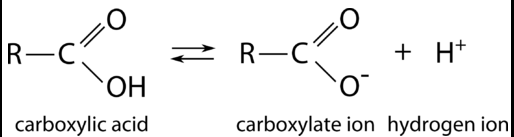
What does the functional carboxyl group look like, and what is its function?
“C double-bond O, single-bond OH” (Unless ionized). Since carboxyl groups are often ionized, they can act as acids.
What does the functional amino group look like, and what’s its function?
NH2, but often changes because it accepts an H+ (becoming NH3-) Because of this, it acts as a base.
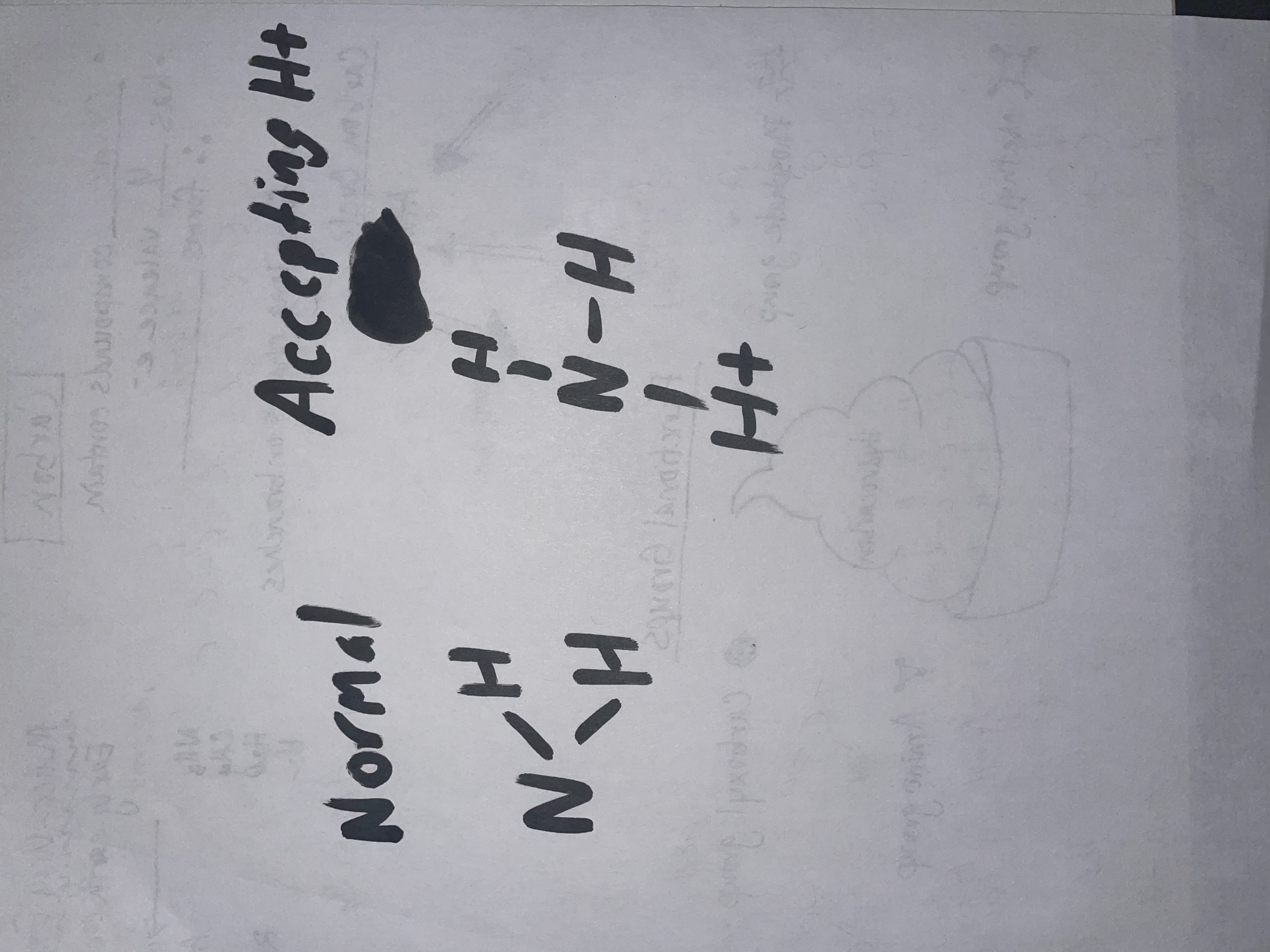
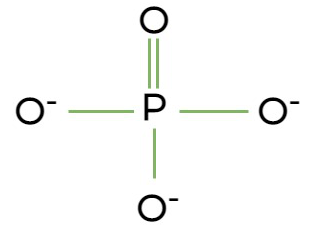
What does a functional phosphate group look like, and what makes it special?
It is negatively charged, due to the high polarity of the molecule.
What functional groups are always found in amino acids?
Amino and carboxyl. (carboxyl acts as an acid, so it is literally amino and acid)
What are polymers?
Long chains of monomers.
What are macromolecules?
Polymers. The monomers that the polymer is made out of determines the macromolecule’s classification, structure, characteristics, and function.
What monomers make up carbohydrates?
Sugars.
What monomers make up lipids?
Fatty acids. (but not really)
What monomers make up proteins?
Amino acids.
What monomers make up nucleic acids?
Nucleotides.
What does dehydration synthesis (also called a condensation reaction) do?
Bonds monomers together, and forms water in the process.
What does hydrolysis do?
Adds water to break the bonds between monomers.
What are the functions of carbohydrate polymers?
Storage (starch which is stored energy for plants and glycogen which is stored energy in animals), and structure (cellulose in plants and chitin in fungi and arthropods).
What is a monosaccharide? And what is its general formula?
One monomer of a carbohydrate. CH2O
What is the monomer for carbohydrates?
Sugar
What is a disaccharide?
Two sugar monomers bonded together.
What is a polysaccharide?
Several sugar monomers bonded together (typically hundreds).
Starch and cellulose are both polymers comprised of glucose. Why do they have different functions?
They have different structures.
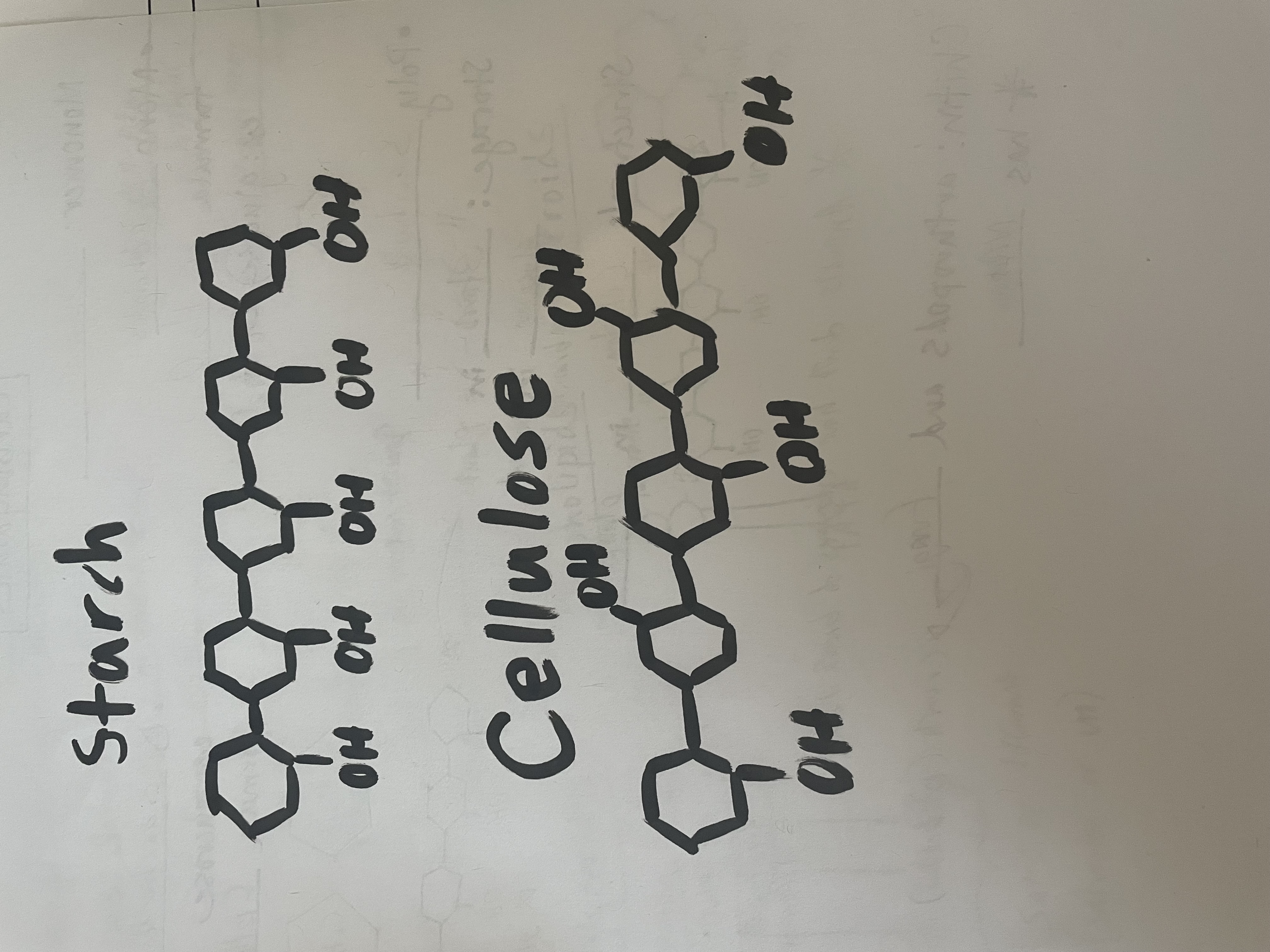
What makes chitin a special carbohydrate?
It has nitrogen in it.
What are characteristics of lipids?
They are non-polar and hydrophobic.
What is the purpose of lipids?
Long-term energy storage (more than double the amount of carbohydrates) (triglycerides), making certain hormones (steroids), and regulating cell membranes (phospholipids). However, the only one that you will probably need to know for this unit is the long-term energy storage one.
Are lipids polymers?
No, since they lack a specific single type of monomer.
What are fatty acids?
Hydrocarbon chains with carboxyl groups on the end, which allow it to bond with glycerol through dehydration synthesis.
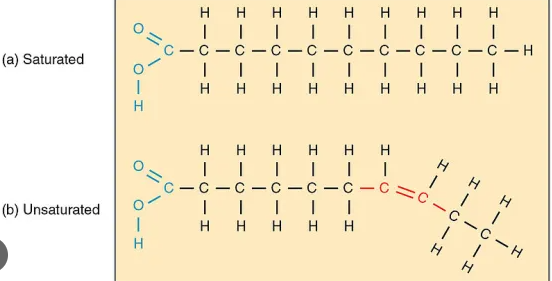
What is the difference between saturated and unsaturated fats?
Saturated fats have no double bonds in them, are produced by animals, and are solid at room temp. Unsaturated fats have double bonds, are produced by plants, and are liquid at room temp.
What are triglycerides made up of?
Glycerol and three fatty acids.
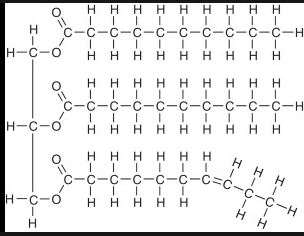
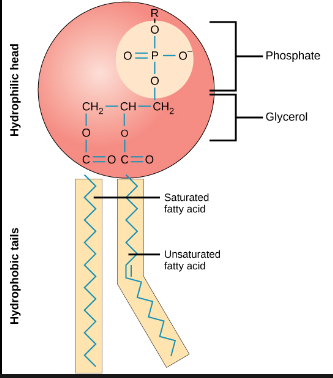
What are phospholipids made up of?
1 phosphate, 1 glycerol, 2 fatty acids. (Also remember that the phosphate head is hydrophilic, while the fatty acid tails are hydrophobic).
What is the monomer of nucleic acids?
nucleotides
What are nucleotides made of?
Sugar, phosphate, and nitrogen base.
What are three major differences between RNA and DNA?
DNA has deoxyribose as a sugar, while RNA has ribose instead. DNA is a double-stranded helix, while RNA is single stranded. DNA and RNA both have guanine, cytosine, and adenine, yet only DNA has thymine, and only RNA has uracil.
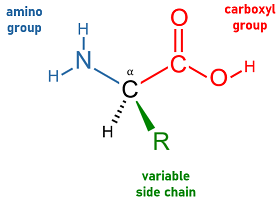
What are the monomers for proteins, and what do they look like/are made of?
Amino acids. Made of central carbon, hydrogen, carboxyl group, amino group, and the variable r-group.
What is a peptide bond?
The covalent bond formed between amino acids through a dehydration reaction.
What is the primary structure of a protein?
A long chain of amino acids bonded together.
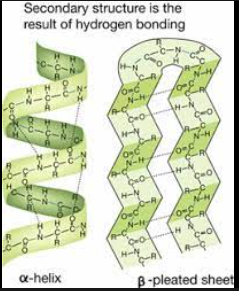
How does the secondary structure of a protein form, and which two shapes does it make?
The secondary structure is formed through hydrogen bonds between atoms of the polypeptide backbone. (Not r-groups)
How does the tertiary structure of a protein form?
Interactions between r-groups such as disulfide bridges, hydrophobic interactions, hydrogen bonds, and ionic bonds.
What is the quarternary structure of a protein?
Two or more polypeptide chains interacting with one another. Examples are hemoglobin and collagen.
Why are the different structures of protein significant?
Shape dictates function.
What determines the structure of a protein?
The outside environment, namely pH, and heat.
What is denaturing?
When influences from the outside environment break down a proteins’ structure. Only primary structure is unaffected.
Why is the specific order of amino acids in a protein so important?
The specific order determines how the protein will form and interact with itself. For example, the difference between a normal red blood cell and sickle cell anemia, is only one amino acid in its primary structure. This small change completely changes the shape of the molecule, and therefore the function.
Why is directionality important in DNA and proteins?
It determines shape, which determines function. DNA replication works the way it does, only because the two sides of DNA run opposite of each other. In a peptide chain, one end is always carboxyl, and another is always amino, which determines how proteins are broken down by enzymes.