chemistry - chemical changes: acids (3.1 - 3.21)
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
3.1 acids in solution
produce hydrogen ions (H+)
3.1 alkalis in solution
produce hydroxide ions (OH-)
3.2 neutral solution pH
pH 7
3.2 acidic solutions pH
lower than pH 7
3.2 alkaline solutions pH
higher than pH 7
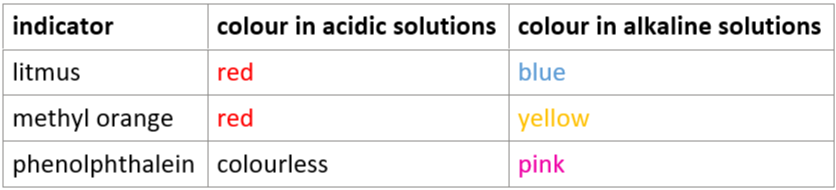
3.3 indicators in acidic & alkaline solutions: litmus, methyl orange, phenolphthalein
3.4 concentration of hydrogen ions effect on pH
higher conc. H+ ions in acidic solution = lower pH
3.4 concentration of hydroxide ions effect on pH
higher conc. OH- ions in alkaline solution = higher pH
3.5 factors of hydrogen ion concentration effect on pH
H+ conc. in solution increases by factor of 10 = pH of solution decreases by 1
e.g. HCl (pH 0) is 104 = 10000x more acidic than vinegar (pH 4) & its H+ ions conc. is 10000x greater than vinegar
3.6 core practical: investigate change in pH on adding powdered calcium hydroxide or calcium oxide to fixed volume of dilute hydrochloric acid
use measuring cylinder to add 50cm3 dilute HCl to beaker
estimate & record pH of contents of beaker
put piece of universal indicator paper onto white tile
dip end of glass rod into liquid, tap onto indicator paper
wait 30s, match colour to appropriate pH on pH colour chart
rinse glass rod with water
measure 0.3g calcium hydroxide powder onto ‘weighing boat’
add calcium hydroxide powder to beaker & stir
estimate & record pH of mixture
repeat steps 2 & 3 seven times so you add total of 2.4g calcium hydroxide to acid
plot graph with pH on y-axis & mass of calcium hydroxide on x-axis
3.7 dilute vs concentrated solutions
dilute: contains small amount of dissolved solute per unit volume
concentrated: contains lots of dissolved solute per unit volume
3.8 weak vs strong acids
weak: molecules do not dissociate completely into ions in solution - low concs. of H+ ions
strong: molecules dissociate completely into ions in solution - high concs. of H+ ions
3.9 base definition
any substance that reacts with acid to form salt & water only (neutralises acid)
3.10 alkalis definition
soluble bases
3.11 metal + acid (aq)
metal + acid → salt + hydrogen
3.11 metal oxide + acid (aq)
metal oxide + acid → salt + water
3.11 metal hydroxide + acid (aq)
metal hydroxide + acid → salt + water
3.11 metal carbonate + acid (aq)
metal carbonate + acid → salt + water + carbon dioxide
3.12 chemical test for hydrogen
place lit splint near end of test tube containing gas
hydrogen present: squeaky pop heard
3.12 chemical test for carbon dioxide
bubble gas through limewater
carbon dioxide present: limewater turns cloudy
3.13 neutralisation reaction
reaction between acid & base
3.14 acid-alkali neutralisation
reaction in which H+ ions from acid react with OH- ions from alkali to form H2O
3.15 preparing soluble salts from acid & insoluble reactant
excess reactant added - ensure all acid used up
excess reactant removed - ensure prepared salt is pure (mixture filtered)
solution remaining only salt & water - no excess reactant present
3.16 preparing soluble salts from acid & soluble reactant
titration used - lets you see what volume of reactant needed to react completely with certain volume of other reactant
acid & soluble reactant mixed in correct proportions - reactant added in excess, difficult to separate from products; end with solution containing only water & desired salt
solution remaining only salt & water - exact volume of acid added to alkali
3.17 core practical: investigate preparation of pure, dry, hydrated copper sulfate crystals starting from copper oxide
measure 20cm3 of dilute sulfuric acid using measuring cylinder into small conical flask
warm acid in water bath at 50°C, measure temp. with thermometer
add a little copper oxide powder to acid & stir
if all copper oxide reacts & disappears, add more; stop when copper oxide in excess & no longer reacts
filter mixture & transfer filtrate to evaporating basin
heat evaporating basin by placing over beaker of water heated with Bunsen burner, stop heating when crystals start to form
pour solution into watch glass, leave for few days to let all water evaporate
3.18 how to carry out acid-alkali titration to prepare pure, dry salt?
measure fixed volume of alkali into conical flask using pipette
add few drops of indicator to alkali
add acid from burette to alkali in small amount at a time
stop when indicator changes colour (end-point)
record exact volume of acid needed to neutralise alkali
use burette to add correct volume of acid to alkali without indicator
evaporate water from solution formed - leaves pure, dry salt
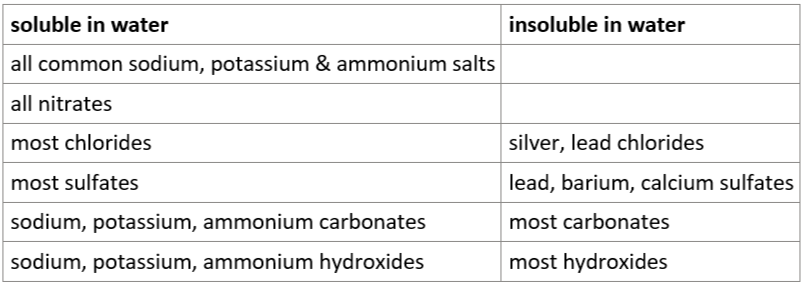
3.19 solubility rules (salts, nitrates, chlorides, sulfates, carbonates, hydroxides)
precipitation reaction
soluble substances in solutions form insoluble precipitate
3.20 named solutions mixed together - predict if precipitate will be formed
check solubility of products
both products soluble - no precipitate forms
e.g. potassium sulfate soluble - doesn’t form precipitate, copper carbonate insoluble - forms precipitate
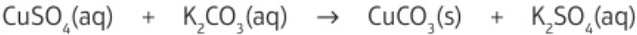
3.20 named solutions mixed together - name precipitate formed
2 solutions containing soluble salts react together - ions from salts swap

3.21 how to prepare pure, dry sample of insoluble salt?
pure, dry sample of insoluble salt prepared from two soluble salts
mix two solutions in beaker
filter mixture
rinse beaker with a little distilled water & pour through funnel
pour a little distilled water over precipitate in funnel
remove filter paper containing precipitate & dry in warm oven