Unit 1 Textbook/Slide definitions
1/32
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Scientific method, Molecules of life, Atoms, Chemical bonds, Water, Carbon, Organic Molecules
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
Observation
- The act of viewing the world around us
- Using your senses to notice things
Experimentation
To test the hypothesis
Scientific literature
Published information about experiments/observations that others have done
EX: Articles, papers
Hypothesis
A statement to test
(What you think will happen in an experiment/study)
Hypotheses
More than one hypothesis
(plural form of hypothesis)
Prediction
The expected outcomes of an experiment
Controlled experiment
A test where only one thing is changed to see its effect, while everything else stays the same
Variable
Something that can change or be changed in an experiment
Test (experimental) group
The experimental group thats is exposed to a variable in the experiment
The group in an experiment that gets the change or treatment being tested.
Control group
The group that is not exposed to the variable in an experiment
The group in an experiment that doesn’t get the treatment—used for comparison.
Elements
Basic/pure substances (can’t be broken down into simpler ones)
EX: Copper, Gold, Oxygen, etc.
Atom
Basic unit of matter
Atomic Number
The number of protons (also equals number of electrons)
Atomic mass
Total mass of an atom
(# of protons + # of nuetrons)
Isotopes
Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons, but the same number of protons.
Ions
An electrically charged atom/molecule
EX: An atom that has lost an electron is positively charged. An atom that gained an electron is negatively charged.
Independent variable
The cause
What you control or change in the experiment.
Dependent variable
The effect
What changes because of the independent variable (what you measure)
Qualitative data
Observations
Cannot be graphed
Goes in a table
Quantitive data
Numbers
Can be graphed
Orbital
The area where an electron is likely to be found
(Orbitals closer to nucleus have less energy)
atomic mass - atomic # =
# of neutrons
Molecule
Two or more atoms joined together (by covalent bonds)
Compound
Two or more DIFFERENT elements (atoms) joined together
(All compounds are molecules, but not all molecules are compounds)
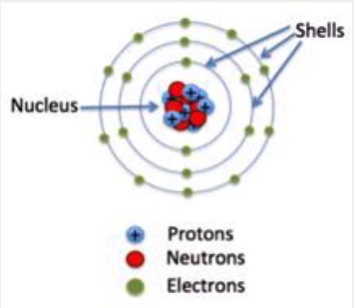
Shells
The energy levels around an atom’s nucleus where electrons are found.
Rings around an atom’s center where electrons live.
FACT: Each ring can hold a certain number of electrons.
ring 1: 2
ring 2: 8
ring 3: 8
(The farther away a shell is the more potential energy it holds)
Chemical bond
An attraction between atoms that holds them together
Valance electrons
Electrons farthest from the nucleus (in the outermost orbitals of an atom)
(Highest energy level of the atom)
Molecular orbital (aka merged orbital)
A molecular orbital is like a merged orbital, formed when atomic orbitals from different atoms combine during bonding.
Covalent bond
A bond that holds merged orbitals together by sharing electrons between atoms
They are strong and stable, requirring more energy to break compared to Ionic bonds)
remember these are bonds between atoms
Covalent bond structural formula
A line connecting two chemical symbols

Ionic bonds (aka non-covalent bonds)
Explanation: A bond formed when one atom gives away electrons and another takes them, so they stick together because of opposite charges.
🧠 How It Works:
One atom loses electrons
→ becomes positive (called a cation)One atom gains electrons
→ becomes negative (called an anion)Opposites attract
→ They stick together like magnets 🧲
(Electrons are transferred compared to covalent bonds which SHARE electrons)
remember these are bonds between atoms
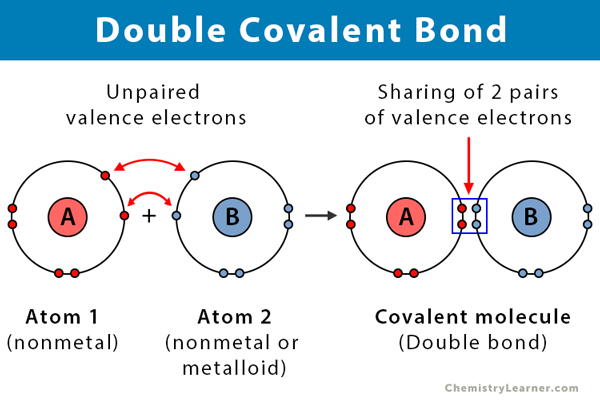
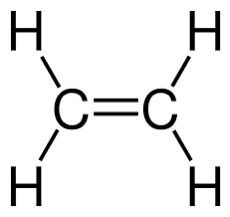
Double bond
When two atoms share two pairs of electrons (4 elhappens when two atoms link up by sharing four outer electrons (two pairs) to stay together
remember these are bonds between atoms
Double bond structural formula
A double line connecting two chemical symbols for the atoms