Ch 6- Bone Tissue
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
72 Terms
components of skeletal system
bones, cartilage, ligaments, and tendons
functions of the skeletal system
support, protection, assist in movement, mineral homeostasis, blood cell production, and triglyceride storage
diaphysis
bone shaft or body of bone
epiphyses
distal and proximal ends of bone
metaphysis
located between epiphysis and diaphysis
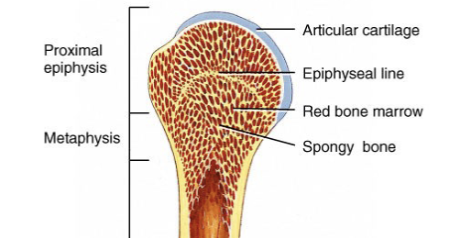
epiphyseal plate
a layer of hyaline cartilage found in the epiphysis of growing long bones that is responsible for their longitudinal growth
epiphyseal line
bony structure that replaces the epiphyseal plate when bone stops growing
medullary cavity
space within diaphysis that makes long bones lighter; contains yellow bone marrow
red bone marrow
located in spaces within epiphyses; site of homeopoiesis
homeopoiesis
the production of blood cells (RBCs, WBCs, platelets)
yellow bone marrow
located in medullary cavity of long bone; stores triglycerides
periosteum
connective tissue covering the outside of the bone
endosteum
connective tissue covering the inside of the bone
what arteries supply bone
periosteal, nutrient, metaphyseal, and epiphyseal arteries
periosteal arteries
supply periosteum and bone tissue of diaphysis
nutrient artery
travels through nutrient foramen to medullary cavity; supplies bone tissue of diaphysis and part of red marrow of epiphyses
metaphyseal artery
enter metaphyses and supplies bone tissue and red marrow of matephyses
epiphyseal arteries
enter epiphyses and supplies bone tissue and red marrow of epiphyses
extracellular matrix of bone tissue
bone ECM consists of mineral salts (mainly hydroxyapatite) and collagen fibers
calcification
the process by which the extracellular matrix becomes hardened by mineral salts; only occurs when collagen fibers are present
what gives a bone its hardness
mineral salts
what gives a bone its flexibilty
collagen fibers that provide tensile strength (resistance to stretching and pulled apart)
types of bone cells
osteogenic cells, osteoblasts, osteocytes, and osteoclasts
osteogenic cells
the only bone cells that divide; they are stem cells and form osteoblasts
osteoclasts
large cells that breakdown bone; they secrete lysosomal enzymes and acids that breakdown the extracellular matrix
osteocytes
main cells in bone tissue; maintain bone tissue by exchanging nutrients and wastes with blood
osteoblasts
cells that build bone; secrete collagen and other substance to form extracellular matrix
compact bone tissue
dense; forms the exterior of all bone and most of the diaphysis of long bone- protects, supports, and resists stress
microscopic structure of compact bone
osteons with concentric lamellae around a central canal, connected by perforating canals, containing osteocytes housed in lacunae linked by canaliculi, plus interstitial and circumferential lamellae
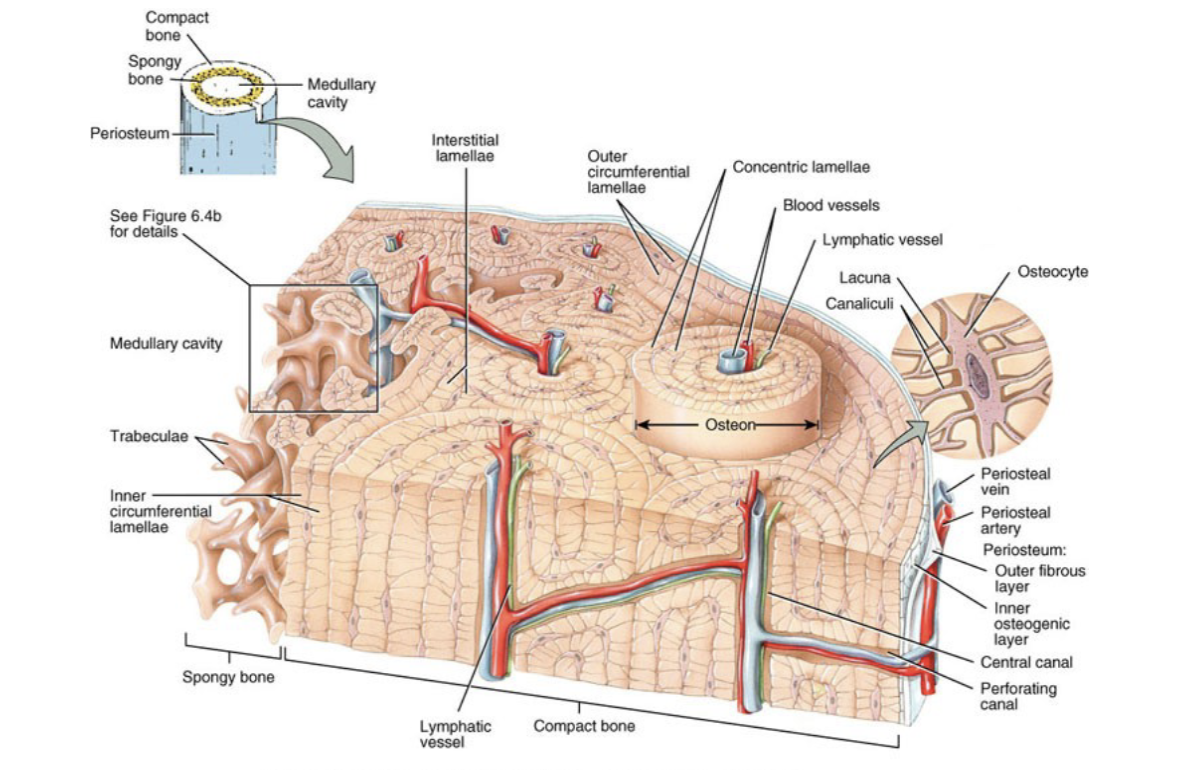
lacunae
small spaces between lamellae that contain osteocytes
canaliculi
connect lacunae with each other and with central canal; provides routes of oxygen, nutrients, and wastes
osteons
repeating structural units of compact bone; aligned along lines of stress and determine strength of bone
what does an osteon consist of
a central canal, its concentrically arranged lamellae, lacunae, osteocytes, and canliculi
interstitial lamellae
area between osteons that contains lacunae, osteocytes, and canaliculi
circumferential lamellae
encircle bone beneath periosteum or encircle medullary cavity
spongy bone tissue
contains trabeculae, is lighter, and house red marrow
microscopic structure of spongy bone
trabeculae composed of lamellae with osteocytes in lacunae and spaces filled with red marrow
microscopic difference between compact and spongy bone
compact bone is dense and organized into osteons with central canals for strength, while spongy bone has porous trabeculae without osteons, allowing lightness and red marrow storage
osteogenesis/ossification
bone formation that occurs during: embryonic and fetal development, infancy, childhood, adolescence, remodeling of bone, and repair of fractures
intramembranous ossification
bone develops from mesenchymal membrane and forms flat bones of skull and mandible
endochondrial ossification
bone replaces hyaline cartilage; used to form most bones of body
intramembranous vs. endochondrial ossification
intramembranous ossification forms bone directly from mesenchyme, while endochondrial ossification replaces a cartilage model with bone
appositional growth
growth in thickness that occurs by growth at outer surface of bone
interstitial growth
growth in length by division of cartilage on epiphyseal side of epiphyseal plate
interstitial growth vs appositional growth
interstitial growth lengthens bone at the epiphyseal plate (closing after adolescence), while appositional growth increases bone thickness
osteoclast resorption
osteoclasts secrete enzymes and acids that dissolve bone matrix and release minerals
factors affecting bone growth/ remodeling
minerals, vitamins, hormones
fracture
a break in a bone
types of fractures
open (compound) fracture, closed (simple) fracture, comminuted fracture, greenstick fracture, impacted fracture, and stress fracture
open fracture
broken ends of bone protrude through the skin
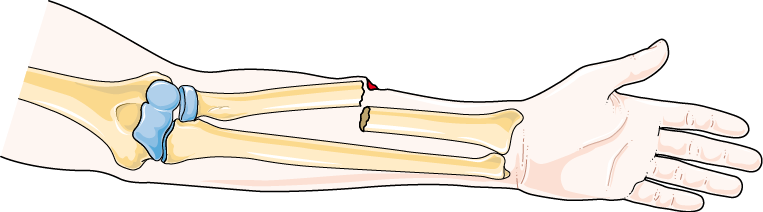
closed fracture
broken ends of bone do not break through skin

comminuted fracture
bone is broken into pieces

greenstick fracture
partial fracture that occurs in children; one side of bone is broken, other
side is bent
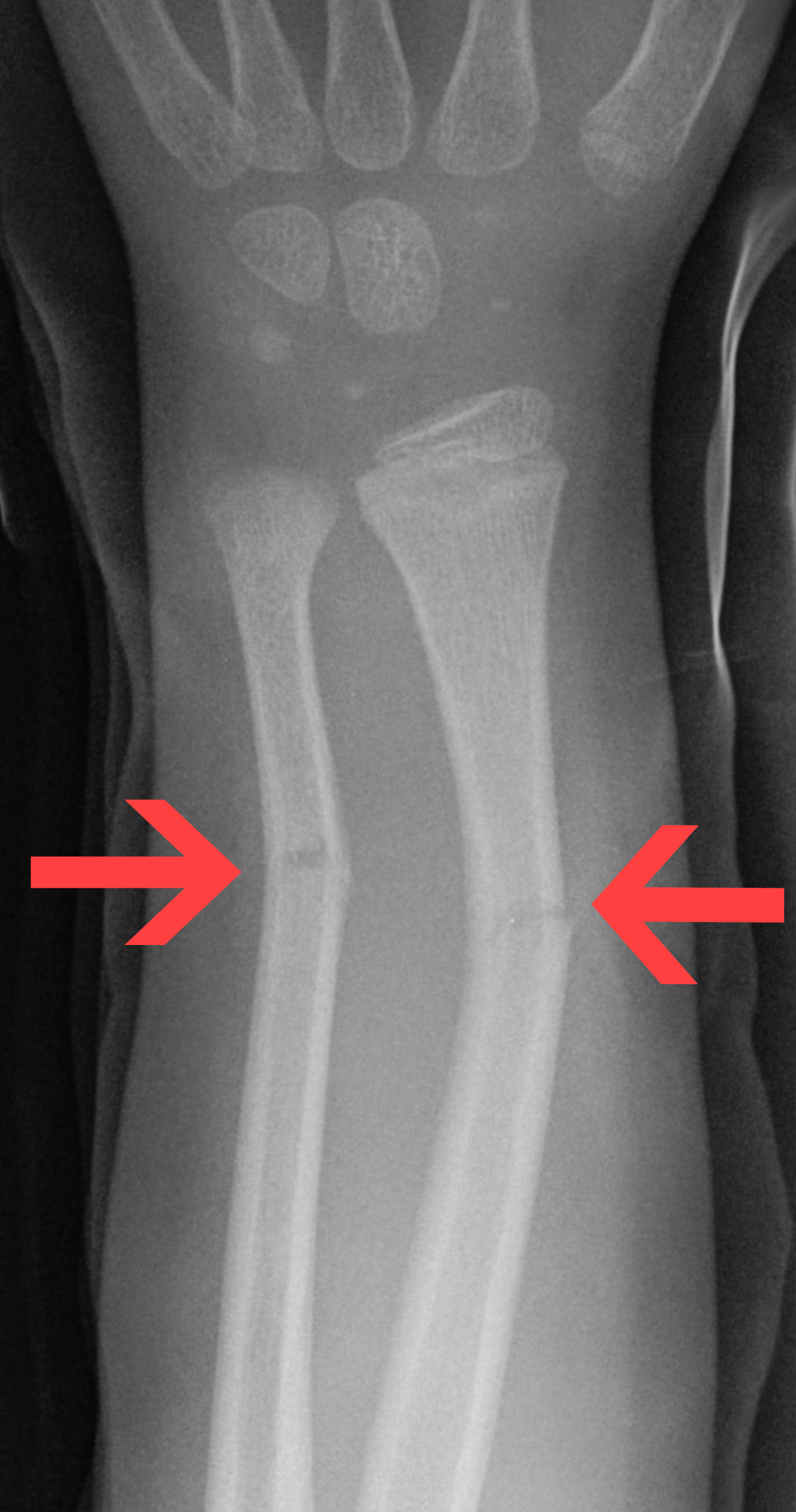
impacted fracture
one broken end of bone driven into the other broken end of bone
stress fracture
microscopic fissures in bone but no visible break due to repeated, strenuous activities such as running, jumping , or aerobic activities
repair of fracture
hematoma formation
fibrocartilaginous callus formation
bony callus formation
bone remodeling
hematoma formation
blood leaks from damaged vessels, forming a clot that brings cells for inflammation and healing to the fracture site
fibrocartilaginous callus formation
a soft callus of collagen and cartilage bridges the broken bone ends to stabilize the fracture
bony callus formation
the fibrocartilaginous callus is replaced by spongy bone, forming a hard bony bridge between the broken bone ends
bone remodeling
osteoclasts remove old or excess bone and osteoblasts deposit new bone, restoring the bone’s original shape and strength
function of blood calcium
neuron function, muscle contraction, enzyme regulation, blood clotting
calcium homeostasis
bones act as the calcium reservoir, releasing or storing Ca²⁺ as needed
PTH
produced by parathyroid gland and is secreted when blood calcium levels are low; stimulates osteoclasts and bone resorption
calcitonin
produced by thyroid gland and is secreted when blood calcium levels are high; stimulates osteoblasts and inhibits osteoclasts
exercise effects on bones
increases bone density
aging effects on bones
causes bone loss due to decreased osteoblast activity and hormone levels
osteoporosis
caused by a decrease in blood calcium levels- more calcium is lost from the body than absorbed from the diet
osteomalacia
adult form of inadequate calcification of the extracellular matrix, usually caused by a deficiency of vitamin D; results in pain and tenderness and increased risk of bone fracture
rickets
childhood form of inadequate calcification of the extracellular matrix, usually caused by a deficiency of vitamin D; results in pain and tenderness and increased risk of bone structure
gigantism
the oversecretion of growth hormone prior to puberty
dwarfism
the undersecretion of growth hormone prior to puberty
acromegaly
oversecretion of growth hormone during adulthood; the bones of the hands, feet, and jaws enlarge as well as the nose