Mexico Notes
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/136
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 6:12 PM on 4/18/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
137 Terms
1
New cards

What is the official name of Mexico?
United Mexican States (Estados Unidos Mexicanos)
2
New cards
Explain how a diverse geography shaped Mexico
* Deserts, mountains and jungles encouraged %%different regional cultures%%
* %%Natural barriers%% discouraged communication and integration while encouraging %%regionalism%%
* Natural resources encouraged resource-extraction
* Warm climate and nutritious plants encouraged %%agriculture and large populations%%
* %%Natural barriers%% discouraged communication and integration while encouraging %%regionalism%%
* Natural resources encouraged resource-extraction
* Warm climate and nutritious plants encouraged %%agriculture and large populations%%
3
New cards
Explain how Mexico was shaped by its location
* Between North America and Latin America
* USA to the north; Guatemala to the south
* %%Proximity to USA%% encouraged %%economic and military domination%% and %%drug trade%%
* USA to the north; Guatemala to the south
* %%Proximity to USA%% encouraged %%economic and military domination%% and %%drug trade%%
4
New cards

Explain how Mexico’s cultural diversity makes it unique
* True mélange of different cultures and ethnic groups
* Mesoamerican civilizations (aboriginals)
* Spanish settlers
* Mixed race
* Anglo-American Influence
* Mesoamerican civilizations (aboriginals)
* Spanish settlers
* Mixed race
* Anglo-American Influence
5
New cards

Explain how Mexico was shaped by its legacy of colonialism
* Controlled by a European empire for centuries
* Spanish extracted as much profit as possible
* Killed 90% of aboriginal population
* Colonial authorities did not invest in development
* Feudal-like “Encomienda” system and hierarchical society imposed by Spanish discouraged innovation and economic diversification
* Spanish extracted as much profit as possible
* Killed 90% of aboriginal population
* Colonial authorities did not invest in development
* Feudal-like “Encomienda” system and hierarchical society imposed by Spanish discouraged innovation and economic diversification
6
New cards
Summarize patterns and themes that make Mexico unique
* Top-down, %%elite-driven reforms%% and %%irregular transitions of power%%
* Populist, grassroots, bottom-up %%protests and revolutions%%
* %%Instability%% and violent upheavals, bloody %%rebellions%%, assassinations and brutality
* %%Regionalism%% and ethnic fragmentation
* %%Authoritarian military strongmen as leaders%%
* Ongoing %%struggle to industrialize%% and improve standard of living
* %%Great disparities%% in wealth and opportunity creating %%instability%%
* Zigzagging %%periods of socialist and free-marked approaches%% to development
* Managing power through %%corporatism%% and %%patron-clientism%%
* Populist, grassroots, bottom-up %%protests and revolutions%%
* %%Instability%% and violent upheavals, bloody %%rebellions%%, assassinations and brutality
* %%Regionalism%% and ethnic fragmentation
* %%Authoritarian military strongmen as leaders%%
* Ongoing %%struggle to industrialize%% and improve standard of living
* %%Great disparities%% in wealth and opportunity creating %%instability%%
* Zigzagging %%periods of socialist and free-marked approaches%% to development
* Managing power through %%corporatism%% and %%patron-clientism%%
7
New cards
When did the Spanish Conquistadors arrive in Mexico?
1500s
8
New cards
Who conquered the Aztec Empire and established Spanish dominance
Cortez
9
New cards
1801-1821
Series of rebellions ends with Conservatives ejecting Spanish authorities
10
New cards
1833-1848
Military strongmen fight destructive wars with the USA
11
New cards
1857-1876
* Liberal revolution followed by French-imposed monarchy
* Military strongmen Diaz emerges as dictator
* Military strongmen Diaz emerges as dictator
12
New cards
Who emerged as a dictator in 1876?
* Diaz
* Conservative
* Rules with iron fist
* Conservative
* Rules with iron fist
13
New cards
Describe Diaz’s rule
* 1876-1910
* Ignored demands for economic reform and political liberalization
* Gap between rich and poor grows
* Ignored demands for economic reform and political liberalization
* Gap between rich and poor grows
14
New cards
How and when does Diaz’s rule end?
* 1910
* Overthrown by rebels
* Strongmen seize power in coups, turn on each other
* 5-way civil war
* US forces vainly attempt to restore order
* Overthrown by rebels
* Strongmen seize power in coups, turn on each other
* 5-way civil war
* US forces vainly attempt to restore order
15
New cards
1917
* Moderate revolutionaries triumph
* United Mexican States are established with liberal, secular presidential system
* One six-year term to avoid dictatorship
* United Mexican States are established with liberal, secular presidential system
* One six-year term to avoid dictatorship
16
New cards
Which party is formed in the late 1920s and why
* PRI formed by different groups of politicians, soldiers, peasant leaders to promote stability in response to failed rebellion by conservative Catholics
17
New cards
Describe the early PRI
* Introduces State Corporatism supported by massive patron-client network based on rewards (camarillas)
* Reduces power of Catholic church
* Party of power
* Other parties exist but cannot compete, like the conservative, Catholic PAN
* Reduces power of Catholic church
* Party of power
* Other parties exist but cannot compete, like the conservative, Catholic PAN
18
New cards
Camarillas
* PRI’s patron-client networks based on rewards
* Allows them to stay in power (party of power)
* Allows them to stay in power (party of power)
19
New cards
PAN
Conservative, Catholic party
20
New cards
When was the PRI the dominant party
1930s to 1980s
21
New cards
Who was elected as president in 1934
Cardenas
22
New cards
Describe Cardenas’ policies
* Socialist president elected in 1934
* Introduced mixed economy
* Land redistributions
* Nationalization of oil industry into state-run “Pemex”
* Introduced mixed economy
* Land redistributions
* Nationalization of oil industry into state-run “Pemex”
23
New cards
Pemex
State-run oil industry
Nationalized by Cardenas
Nationalized by Cardenas
24
New cards
Mexican Miracle
* 1970s
* Optimistic belief that good times will continue
* Rising oil prices
* Government overspending
* Growing gap between rich and poor
* Optimistic belief that good times will continue
* Rising oil prices
* Government overspending
* Growing gap between rich and poor
25
New cards
When did Mexico’s economic bubble burst?
1980s
26
New cards
1980s
* Oil price drops
* Currency devalues
* Government unable to afford its debt
* Austerity measures
* Privatization of state-owned industries
* Economy begins to recover
* Frustration with PRI grows
* Currency devalues
* Government unable to afford its debt
* Austerity measures
* Privatization of state-owned industries
* Economy begins to recover
* Frustration with PRI grows
27
New cards
When and why do people begin to be frustrated with the PRI
* 1980s
* Reasons
* Crackdowns of protests
* State interference in private businesses
* Economic instability
* Electoral fraud
* Austerity measures
* Reasons
* Crackdowns of protests
* State interference in private businesses
* Economic instability
* Electoral fraud
* Austerity measures
28
New cards
List factors that led to the end of PRi dominance
* Forced by public to reform elections, they began to lose opposition parties. With fewer officials in power, access to money for patron-client bribes began to dry up
* Poorly regulated banks collapse; many lose savings
* Socialists break away to form own party, PRD
* Zapatista uprising in Chiapas demonstrated aboriginal anger with regime
* Top PRI officials assassinated
* Public fed up with corruption
* Poorly regulated banks collapse; many lose savings
* Socialists break away to form own party, PRD
* Zapatista uprising in Chiapas demonstrated aboriginal anger with regime
* Top PRI officials assassinated
* Public fed up with corruption
29
New cards
Who is elected as president in 1999
* Vincente Fox
* PAN
* PAN
30
New cards
What is the significance of the election of Vincente Fox (PAN) as president in 1999?
* Signals end of PRI dominance
* PRI’s grip on power through patron-clientism shattered
* Mexico transitions increasingly toward liberal democracy
* PRI’s grip on power through patron-clientism shattered
* Mexico transitions increasingly toward liberal democracy
31
New cards
Explain Fox’s reforms - what did and didn’t change
* Liberalized economy and politics
* Critical and independent media emerges
* Civil society becomes more active with end of corporatism
* Legislatures and courts begin to check executive
* Corruption remains rampant
* Critical and independent media emerges
* Civil society becomes more active with end of corporatism
* Legislatures and courts begin to check executive
* Corruption remains rampant
32
New cards
Which party continued steady liberalization after winning contested 2006 election
PAN
33
New cards
How many major parties are in congress, and how does this impact policy-making?
* Three
* Policy-making is slow and contentious
* Policy-making is slow and contentious
34
New cards
Which president launched the war on drugs?
Calderon
35
New cards
Who is elected in 2012 and why?
* Enrique Pena Nieto (PRI)
* Public wants change; tired of drug violence
* Public wants change; tired of drug violence
36
New cards
Describe Pena Nieto’s policies
* Reduce corruption
* Calm drug war
* Further liberalize the economy
* Tackle powerful unions
* Calm drug war
* Further liberalize the economy
* Tackle powerful unions
37
New cards
Who won the 2018 election?
Andrés Manuel López Obrador (socialist)
38
New cards
Describe Andrés Manuel López Obrador’s policies
* Raise low salaries
* Cut high spending on infrastructure
* Increase social programs
* Curb corruption
* Strengthen economy
* Cut high spending on infrastructure
* Increase social programs
* Curb corruption
* Strengthen economy
39
New cards
Mexico is structured as a:
Federation
40
New cards
Describe Mexico’s structure as a federation
* One central national/federal government
* 31 state-level governments
* 1 federal district of Mexico city
* 31 state-level governments
* 1 federal district of Mexico city
41
New cards
Each state has a governor (elected for ? years) and ? legislature
1. 6-year terms
2. unicameral
42
New cards
Is the legislature in each state in Mexico unicameral or bicameral?
Unicameral
43
New cards
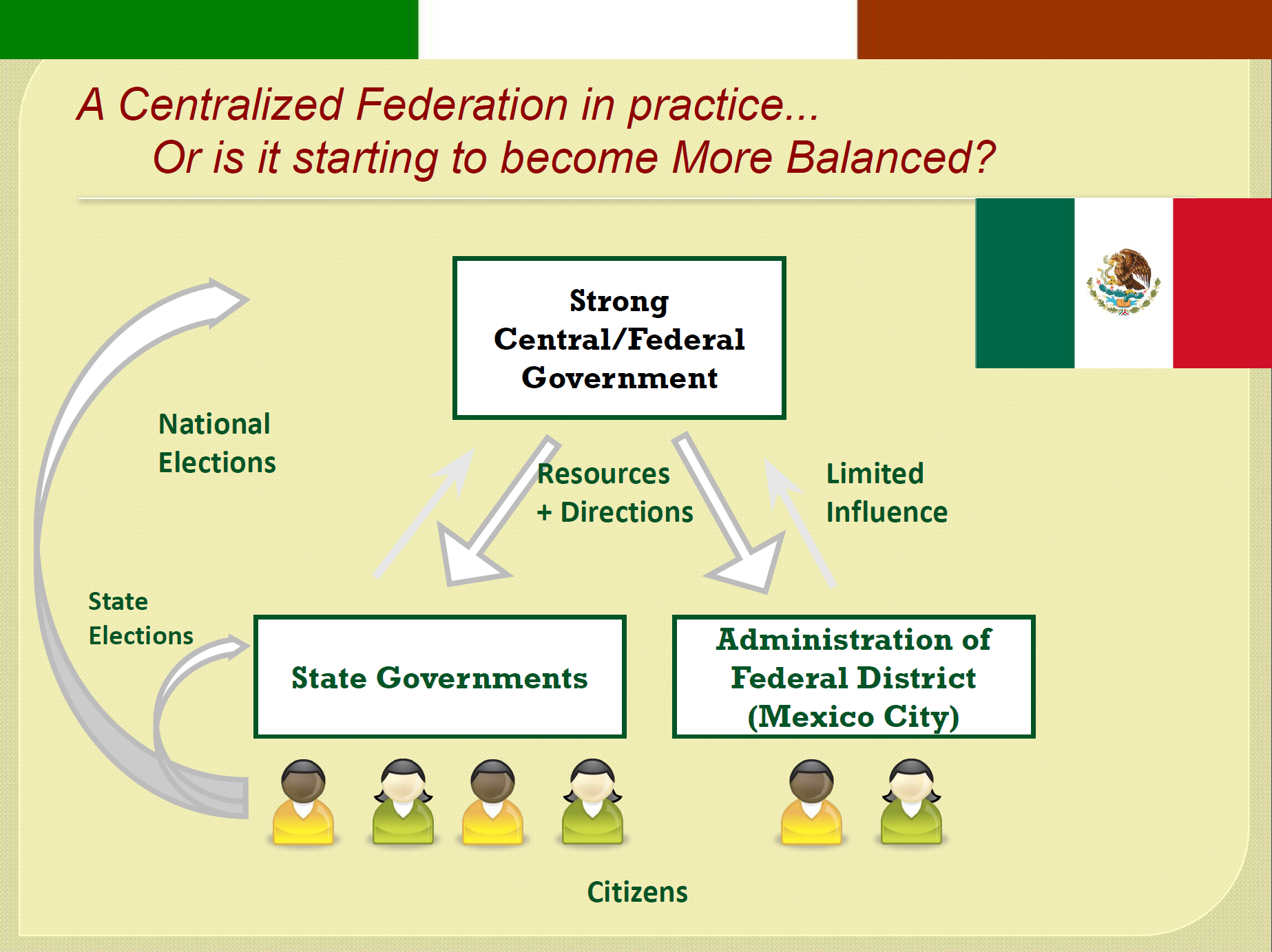
Explain why power, in practice, has been centralized or decentralized in Mexico?
* __Centralized__
* State governments have few resources
* Funded mainly by federal government
* PRI dominance meant state governments were controlled by leaders friendly to central government (rewarded for going along with federal policies)
* However, with end of PRI dominance and states split between PRI, PRD and PAN control, state leaders are likely to
* Exercise formal powers more frequently
* Take on more active role in advocating for their state or opposing federal policies they dislike
* State governments have few resources
* Funded mainly by federal government
* PRI dominance meant state governments were controlled by leaders friendly to central government (rewarded for going along with federal policies)
* However, with end of PRI dominance and states split between PRI, PRD and PAN control, state leaders are likely to
* Exercise formal powers more frequently
* Take on more active role in advocating for their state or opposing federal policies they dislike
44
New cards
45
New cards
46
New cards
Mexico’s constitution from ? was modeled on the constitution of ?
1. 1917
2. USA
47
New cards
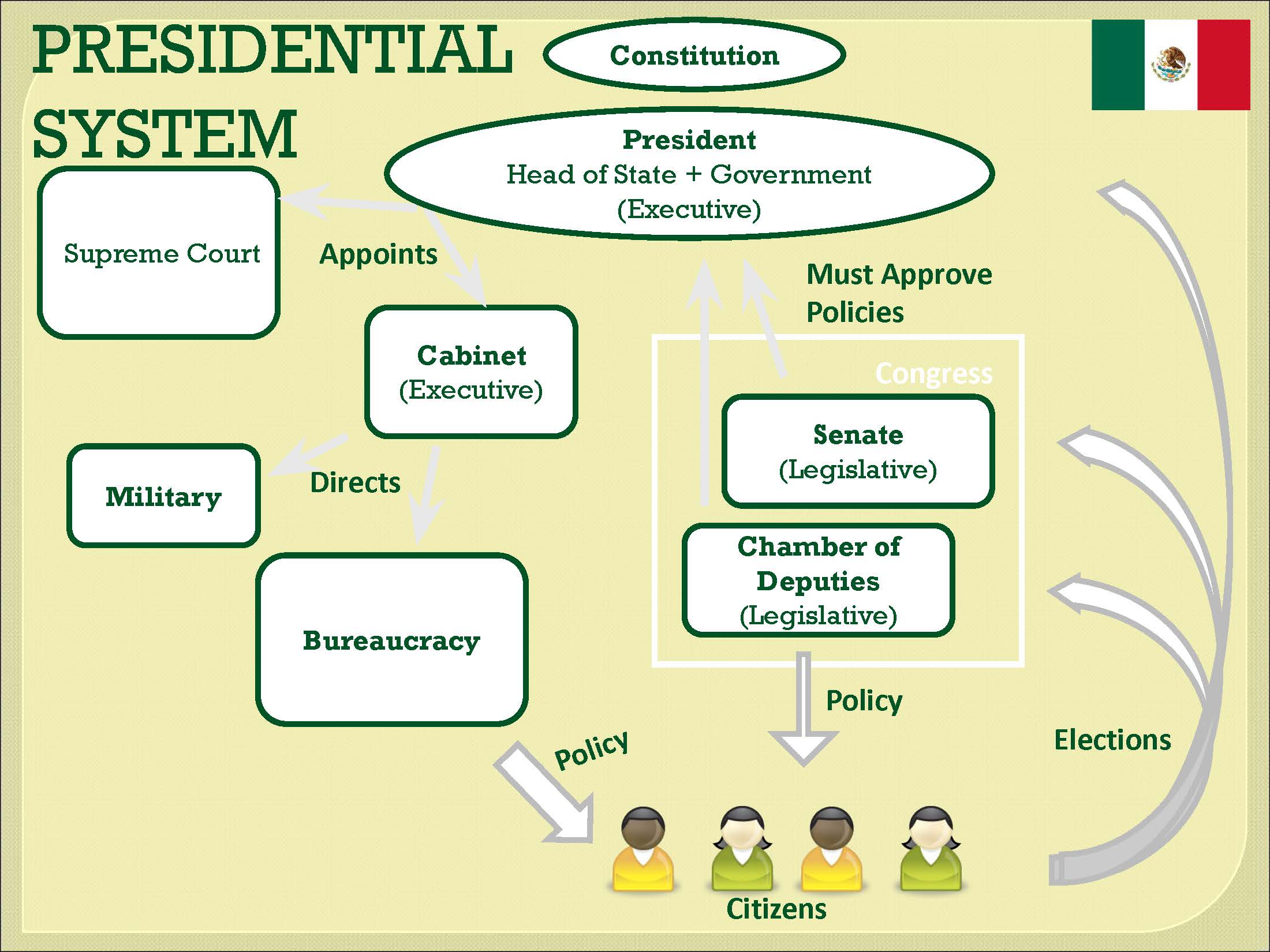
Strong presidential system
* Before 2000
* President dominant
* Legislature rubber-stamps president’s policies
* Supreme court does not challenge them
* Concentration of power helped by
* Long tradition of dictatorial presidents
* Dominance of PRI
* President dominant
* Legislature rubber-stamps president’s policies
* Supreme court does not challenge them
* Concentration of power helped by
* Long tradition of dictatorial presidents
* Dominance of PRI
48
New cards
The constitution is long and easily amended, \[reducing/increasing\] its legitimacy
reducing
49
New cards
Is Mexico’s congress unicameral or bicameral?
bicameral
50
New cards
What is Mexico’s bicameral congress made of?
Senate and Chamber of Deputies
51
New cards
Describe the Senate
* 128 seats
* Represents states equally
* 6-year terms
* Elected by mix of SMD and PR
* Represents states equally
* 6-year terms
* Elected by mix of SMD and PR
52
New cards
Describe the Chamber of Deputies
* Lower house
* 500 seats
* Represents population equally
* 3-year terms
* Elected by mix of SMD and PR
* 500 seats
* Represents population equally
* 3-year terms
* Elected by mix of SMD and PR
53
New cards
Who has to approve legislation proposed by the executive?
Both the Senate and the Chamber of Deputies
54
New cards
Between the 1920s and the 1990s the houses of congress were dominated by which party with a massive majority?
PRI
55
New cards
What allowed opposition parties to make steady gains in representation in the houses of congress from 1988 on?
Electoral reforms
56
New cards
When were electoral reforms introduced that allowed opposition parties to become more influential?
1988
57
New cards
Since 2000, no party has had more than a ? in either house
plurality
58
New cards
Which party holds a plurality in the Chamber of Deputies and which in the Senate?
* Senate: PAN
* Chamber of Deputies: PRI
* Chamber of Deputies: PRI
59
New cards
Mexico’s legal system is based on ? rather than “common” law
Code/civil law
60
New cards
Are state or federal level court more important and why?
Federal courts are more important because most laws are federal
61
New cards
The top federal court is the:
Federal court
62
New cards
In practice, was there judicial review during the PRI’s dominance?
* No, presidents appointed PRI-loyal judges that never overruled executive
63
New cards
Prior to the emergence of the PRI, Mexican presidents were traditionally ? who ruled as ?
1. military strongmen
2. authoritarian rulers
64
New cards
Under the PRI, presidents were extremely ?
* __powerful__
* Controlled all appointments to positions of power
* Patron-client pyramid
* Party control of all government institutions
* Controlled all appointments to positions of power
* Patron-client pyramid
* Party control of all government institutions
65
New cards
Following the end of the PRI’s dominance, presidents had to become ? to secure majority and avoid gridlock
coalition-builders
66
New cards
Describe Mexico’s Cabinet
* 20 Secretaries responsible for different portfolios and departments
* All appointed by president
* Many other lower-level cabinet positions
* All appointed by president
* Many other lower-level cabinet positions
67
New cards
Describe a recent change in the way Mexico’s governments are formed and what this suggests
* Emergence of fragmented, multi-party system has forced presidents to build coalitions to get policies approved
* To help earn support, they have begun inviting opposition politicians into cabinet
* 7 out of 20 current Cabinet members are not from PAN
* Suggests that the influence of the cabinet may be increasing
* To help earn support, they have begun inviting opposition politicians into cabinet
* 7 out of 20 current Cabinet members are not from PAN
* Suggests that the influence of the cabinet may be increasing
68
New cards
Describe Mexico’s bureaucracy
* Long tradition of large and sophisticated bureaucracy
* Federal bureaucracy has about 1.5 million employees and there are hundreds of thousands at state and local levels
* Underpaid
* Receptive to patron-client corruption
* Federal bureaucracy has about 1.5 million employees and there are hundreds of thousands at state and local levels
* Underpaid
* Receptive to patron-client corruption
69
New cards
Describe the military before the PRI period
* Often involved in coups
* Installed strongmen
* Installed strongmen
70
New cards
Describe the current state of Mexico’s military
* Little fear of a military coup
* Considered of of Mexico’s less corrupt institutions
* Since 2006, more active role in support (and often replacing) incapable or corrupt police forces in crackdown on drug cartels
* Considered of of Mexico’s less corrupt institutions
* Since 2006, more active role in support (and often replacing) incapable or corrupt police forces in crackdown on drug cartels
71
New cards
At which levels do competitive elections occur
Local, state and federal
72
New cards
What do citizens vote for?
* Governor of state
* Representatives to Senate
* Representatives to Chamber of Deputies
* President
* Representatives to Senate
* Representatives to Chamber of Deputies
* President
73
New cards
What electoral system are the congressional elections?
Mixed PR
74
New cards
Who could vote during the 1800s?
The rich elite
75
New cards
When was the right to vote extended to other section of society?
Mid-1950s
76
New cards
Describe Mexico’s early elections
* Leaders developed political parties as tools to secure and maintain election victories
* Unscrupulous but effective techniques
* Holding parties and giving free food to supporters on election day
* Bribing voters with favours
* Coercing voters with treats
* Stuffing ballot boxes with fraudulent ballots from fictional voters (known as “Tacos”)
* “Independent” electoral officials bribed to ignore fraud
* Unscrupulous but effective techniques
* Holding parties and giving free food to supporters on election day
* Bribing voters with favours
* Coercing voters with treats
* Stuffing ballot boxes with fraudulent ballots from fictional voters (known as “Tacos”)
* “Independent” electoral officials bribed to ignore fraud
77
New cards
Describe the role of the PRI in election from 1920s to 2000s
* So effective that it ruled uninterrupted from 1920s to 2000
* PRI candidates often won with 70-95%
* As late as 2000, PRI candidates were caught bribing voters with offers and favours
* Rampant fraud became national embarrassment
* Public anger forced massive reforms in 1986
* PRI candidates often won with 70-95%
* As late as 2000, PRI candidates were caught bribing voters with offers and favours
* Rampant fraud became national embarrassment
* Public anger forced massive reforms in 1986
78
New cards
Federal Electoral Institute
* Created in 1990 as truly independent agency
* Monitors campaign donations
* Fraud investigated and prosecuted more effectively
* Monitors campaign donations
* Fraud investigated and prosecuted more effectively
79
New cards
Describe the end of the PRI’s dominance
* Elections became more competitive and smaller parties began to prosper
* 1990: opposition parties
* 1997: PRI loses majority in Congress
* 2000: PRI presidential candidate defeated
* 1990: opposition parties
* 1997: PRI loses majority in Congress
* 2000: PRI presidential candidate defeated
80
New cards
When do presidential election occur?
Every 6 years (in sync with congressional elections)
81
New cards
What electoral system is used for presidential elections?
* Single round
* No run-off
* Winner just needs plurality
* No run-off
* Winner just needs plurality
82
New cards
Describe the 2006 election crisis
* Calderon (PAN) vs. Obrador (PRD)
* Calderon wins by razor-thin margin (0.5%)
* Obrador refused to concede, publicly accused Calderon of fraud and demanded recount
* Calderon sworn in
* Fraud allegations refuted
* Crisis threatened legitimacy, but successful resolution good sign for future
* Federal Electoral Institute respected by citizens
* Calderon wins by razor-thin margin (0.5%)
* Obrador refused to concede, publicly accused Calderon of fraud and demanded recount
* Calderon sworn in
* Fraud allegations refuted
* Crisis threatened legitimacy, but successful resolution good sign for future
* Federal Electoral Institute respected by citizens
83
New cards

Felipe Calderon
Son of PRI’s founder
* Devout catholic
* Middle class upbringing
* Calm, sensible management
* Compromiser and consensus-builder
* Unlike more fiery Fox
* Had to form coalitions in congress to get policies approved
* Pro-business, not socialist, but tries to cooperate with workers and peasants
* Devout catholic
* Middle class upbringing
* Calm, sensible management
* Compromiser and consensus-builder
* Unlike more fiery Fox
* Had to form coalitions in congress to get policies approved
* Pro-business, not socialist, but tries to cooperate with workers and peasants
84
New cards

Enrique Peña Nieto
* Mexico’s old guard, PRI claimed back power in 2013 after a 12-year hiatus
* Peña Nieto won about 38% of the vote
* Promotes strong economy over drug war
* Pledges to embody democratic values
* Peña Nieto won about 38% of the vote
* Promotes strong economy over drug war
* Pledges to embody democratic values
85
New cards
Since the electoral reforms of ?, elections have become ?
1. 1986
2. highly competitive
86
New cards
Describe how the Senate is elected
* 128 senators for 6-year terms
* 96 senators chosen in single-member district plurality elections across Mexico’s 31 states
* 32 senators allocated from party list by proportional representation
* According to each party’s vote share
* Mixed PR system at the same time as presidential election
* 96 senators chosen in single-member district plurality elections across Mexico’s 31 states
* 32 senators allocated from party list by proportional representation
* According to each party’s vote share
* Mixed PR system at the same time as presidential election
87
New cards
Describe how the Chamber of Deputies is elected
* 500 deputies for 3-year terms
* 300 deputies chosen in single-member district plurality elections across Mexico
* 200 deputies allocated from party list by proportional representation
* According to each party’s vote share
* At the same time as presidential/senate elections and “mid-term elections”
* 300 deputies chosen in single-member district plurality elections across Mexico
* 200 deputies allocated from party list by proportional representation
* According to each party’s vote share
* At the same time as presidential/senate elections and “mid-term elections”
88
New cards
Today, ? are essential, as no party controls a majority
Coalitions
89
New cards
What party system does Mexico have?
Multiparty system
90
New cards
Why or why not is a legislative gridlock between president and congress now a distinct possibility?
It is because of the multiparty system (no party/president has a majority)
91
New cards

PRI (Institutional Revolutionary Party)
* Centrists
* Was one ideologically diverse
* Used to be party of power created by elites to control government and manage peaceful transition of power between powerful presidents
* Dominated Mexican local, state, federal government from 1920s to 2000 using electoral fraud, patron-client rewards system and corporatism (co-opting potential conflicting interests)
* Rampant corruption turned many against it
* Leading to PAN victories
* Socialist wing broke off to form PRD
* Regained some ground since stunning defeat of 2000
* Was one ideologically diverse
* Used to be party of power created by elites to control government and manage peaceful transition of power between powerful presidents
* Dominated Mexican local, state, federal government from 1920s to 2000 using electoral fraud, patron-client rewards system and corporatism (co-opting potential conflicting interests)
* Rampant corruption turned many against it
* Leading to PAN victories
* Socialist wing broke off to form PRD
* Regained some ground since stunning defeat of 2000
92
New cards

PAN (National Action Party)
* Catch-all party
* Unites more conservative Catholics, pro-business opponents of PRI
* Long existed but only became competitive following electoral reforms of 1986
* Benefited from public anger over PRI corruption
* Promote:
* Law and order
* Limiting government involvement in economy
* Some devolution of power
* Unites more conservative Catholics, pro-business opponents of PRI
* Long existed but only became competitive following electoral reforms of 1986
* Benefited from public anger over PRI corruption
* Promote:
* Law and order
* Limiting government involvement in economy
* Some devolution of power
93
New cards

PRD (Party of the Democratic Revolution)
* Socialists that broke away from more centrist PRI in 1988, believing it was too business-friendly
* Ideological party
* Benefited from PRI’s corruption scandals and shift towards more centrist policies
* Very populist
* Lead by fiery former mayor of Mexico City, Andrés Manuel Lopez Obrador
* Disorganized and quarreling
* Recent spit between those who supported and opposed Obrador’s election antics
* Advocate:
* Workers rights
* Greater government involvement in economy
* Redistribution of wealth and land to poor
* Anti-NAFTA
* Ideological party
* Benefited from PRI’s corruption scandals and shift towards more centrist policies
* Very populist
* Lead by fiery former mayor of Mexico City, Andrés Manuel Lopez Obrador
* Disorganized and quarreling
* Recent spit between those who supported and opposed Obrador’s election antics
* Advocate:
* Workers rights
* Greater government involvement in economy
* Redistribution of wealth and land to poor
* Anti-NAFTA
94
New cards

Ecologist Green Party of Mexico
* Minor party
* Aliances with PRI and PAN
* Aliances with PRI and PAN
95
New cards

Labour Party
* Minor party
* Often allied with PRD
* Often allied with PRD
96
New cards

Convergence
* Minor party
97
New cards

New alliance
* Minor party
* Formed by largest teacher’s union
* Formed by largest teacher’s union
98
New cards

Morena
* Began in 2011 as a non-profit organization and turned into an official political party
* Established and led by Obrador until he because president in 2018
* Described as left-wing and even socialist
* Open to ethnic, religious, cultural and sexual diversity
* Advocates crackdown on:
* Political corruption
* Overspening
* Gap between rich and poor
* Established and led by Obrador until he because president in 2018
* Described as left-wing and even socialist
* Open to ethnic, religious, cultural and sexual diversity
* Advocates crackdown on:
* Political corruption
* Overspening
* Gap between rich and poor
99
New cards
Describe Mexico’s voting patterns
* Ideology is key
* Social class, education and location also factors
* Religion less so
* Socially conservative
* Pro-free market
* More educated
* Middle/upper income
* Devout Catholics
* From richer north
* Centrist
* From traditional rural strongholds where patron-client system still effective
* Socialist
* Pro-government intervention
* Less educated
* Middle/lower income
* Younger
* From poorer south
* Social class, education and location also factors
* Religion less so
* Socially conservative
* Pro-free market
* More educated
* Middle/upper income
* Devout Catholics
* From richer north
* Centrist
* From traditional rural strongholds where patron-client system still effective
* Socialist
* Pro-government intervention
* Less educated
* Middle/lower income
* Younger
* From poorer south
100
New cards
Assess the role of women in Mexican politcs
* Proportion of female politicians risen to 22% since 1996
* Law requiring minimum 30% minimum of female candidates for each party
* PRI has committed to running 50% female candidates
* Women have won state governorships and seats in congress but have not yet won presidency
* Law requiring minimum 30% minimum of female candidates for each party
* PRI has committed to running 50% female candidates
* Women have won state governorships and seats in congress but have not yet won presidency