Muscle Physiology Lab
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
Define muscle twitch
A single contraction-relaxation cycle in a skeletal muscle fiber in response to adequate stimulation.
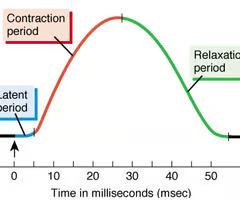
What are the phases of muscle twitch?
latent period, contraction phase, and relaxation phase.
What are the two ways that the force of a muscle contraction can increase?
Change the stimulation frequency or change the intensity of the stimulation.
Summation
When two muscle contractions fuse due to frequency and muscle not fully relaxing.
recruitment
When multiple motor units fire at the same time.
motor unit
composed of many muscle fibers that are connected by a motor neuron.
Describe the relationship between an increase in intensity of a stimulus and the strength of contraction.
Increase of stimulus will mean a stronger contraction due to increase in motor units.
Define slow twitch fibers
are resistant to fatigue, develop tension the slowest, and are weakest. Slow twitch fibers are able to sustain a lower amount of tension for a longer period of time.
Define fast twitch fibers
Fatigue more easily, develop tension more quickly, and produce more force.
Describe the sequence of recruitment of motor units
Slow twitch motor units are recruited first, then intermediate twitch motor units, then fast twitch motor units. Slow twitch motor units activate first due to lower threshold.
electromyography
The process in which the electromyogram is recorded.
electromyogram
The recording of increased motor unit activity and its corresponding electrical activity on the sarcolemma of the muscle fibers.
Compare and explain the electrical activity of an unfatigued muscle vs fatigued muscle
Has a normal amount of electrical activity, when contracted there is an increase in electrical activity (larger requirement of motor units), but when muscle fatigues, there is less electrical activity.
describe the clinical use of electromyograms
Diagnose the cause of muscle weakness, also used in studies for kinesiology and exercise physiology.
state the various uses of handgrip dynamometers
1. Measure the strength of the hand and forearm muscles. 2. Measure a person's strength during an illness or injury. 3. Provide dr. reason for loss in strength. 4. Compare right and left strength.
Define the term calibration and state the importance of calibration
Comparison of measurements using a measurement of known accuracy as a standard to a measurement of unknown accuracy. Important to affirm we know the reading is accurate.
Describe the relationship between graded contractions (increase strength of contractions) and the amount of electrical activity.
There is more electrical activity due to there being a stronger contraction.