endocrine system
1/114
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
115 Terms
what are hormones ?
chemical messengers secreted by ductless glands that travel in blood to target cells
what brain region controls the pituitary gland ?
hypothalamus
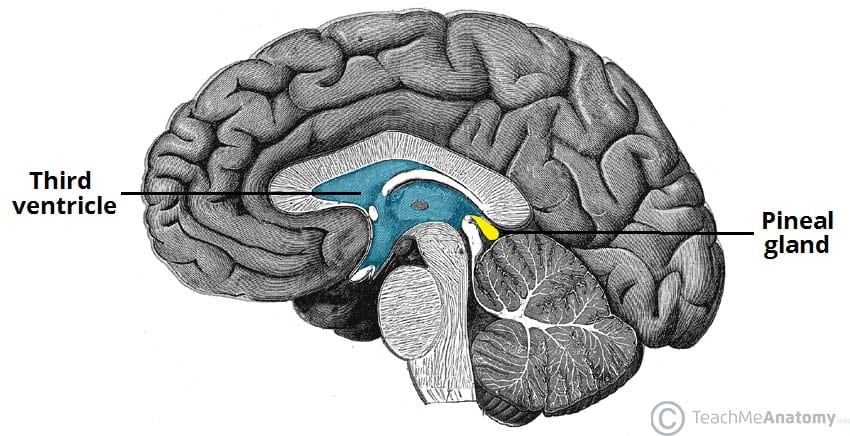
the pineal gland secretes
melatonin
the hypothalamus secretes
TRH, GnRH, CRH
the pituitary secretes
hormones that act on other glands - master gland
ATCH, TSH, FSH, prolactin, ADH
the thyroid secretes
thyroxine
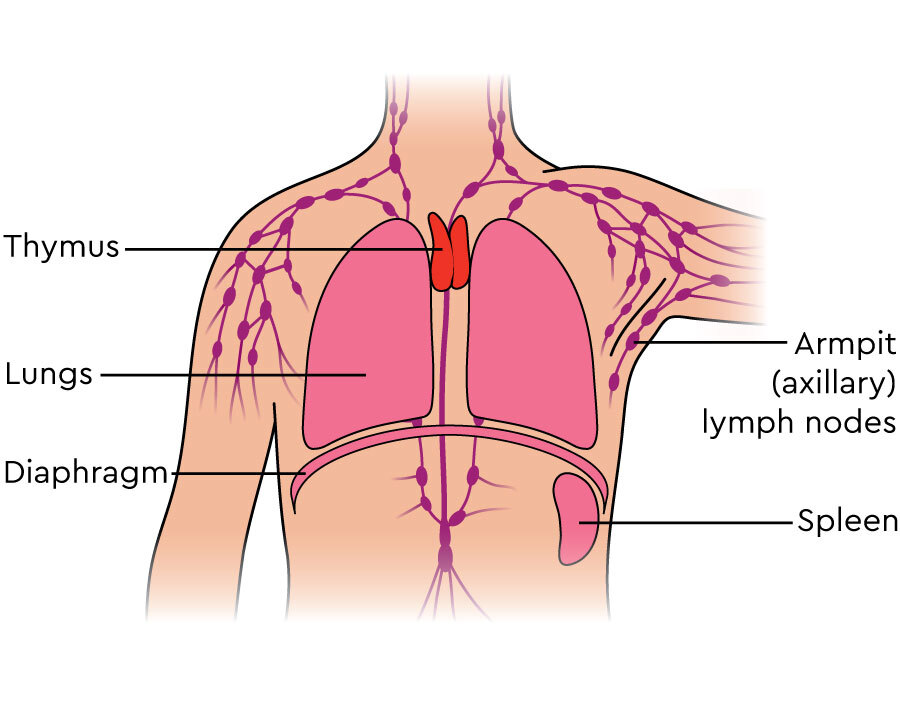
the thymus secretes
thymosin
role of thymosin
essential for development and maturation of T cells
the pancreas secretes
insulin and glucagon
the adrenal glands secrete
adrenaline, cortisol, aldosterone
the gonads secrete
sex hormones - androgens (testosterone), progesterone and oestrogen
endocrine glands control what major processes ?
osmolarity of blood
cellular metabolism
reproduction
why are endocrine glands referred to as “regulators” ?
alter magnitude of existing system - no de novo production
what are the 3 hormone classes
amino acid based
steroids
eicosanoids
most hormones are what class ?
amino acid based
insulin and glucagon are what hormone class
amino acid based - peptide
eicosanoids
not technically hormones
active lipids that illicit response
hormone-like activity
leukotrienes, prostaglandins
3 mechanisms of hormone action
direct
paracrine - autocrine
endocrine
direct signalling can be
juxtacrine
through gap junctions or plasmodesmata

autocrine signalling
specialised type of paracrine signalling where cell releases chemicals that act on same cell
specialised types of paracrine signalling
autocrine
neuronal
the vast majority of cell signalling is
endocrine
hormones alter target cell activity via what 2 mechanisms ?
secondary messengers
direct gene activation
secondary messengers are what hormone class
amino acid based
how do secondary messenger systems work
hormone = first messenger
binds to receptor
activates G protein
cAMP cascade (2nd messenger)
activates PK - leads to response
direct gene activators are what hormone class
steroid hormones
how do steroid hormones illicit change in target cell ?
lipid soluble
bind to intracellular receptor
binds to dna of nucleus
transcriptional change - increase or decrease transcription of certain protein
3 mechanisms of hormone release
hormonal, humoral and neural
hormonal hormone release
secretion of one hormone stimulates release of another
humoral hormone release
triggered by changes in the levels of non-hormone chemicals in bodily fluids, like blood eg. ions or nutrients
neuronal hormone release
direct nervous stimuli signals to gland
calcium homeostasis mechanism
high calcium levels causes calcitonin release
increased deposition into bones
decreased uptake in intestines and reabsorption from urine
returns levels to normal
role of ADH
regulates water reabsorption in kidneys
excess salt in the body triggers
brain to increase fluid intake
ADH secreted posterior pituitary
epinephrine can bind to how many receptors and illicit how many effects ?
2 receptors 3 effects
acromegaly
too much growth hormone later in life
Cushing’s Syndrome
prolonged exposure to high levels of cortisol
often caused by steroid use
Diabetes Insipidus
excess ADH
increased thirst and production of large amounts of dilute urine
Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis
autoimmune disease that attacks thyroid
effects metabolism
hypogonadism
reduction of reproductive hormones
hypothalamic pituitary axis
neuroendocrine system that regulates the body's response to stress and stress-related functions (fight or flight)
communicates hypothalamus, pituitary and adrenal glands
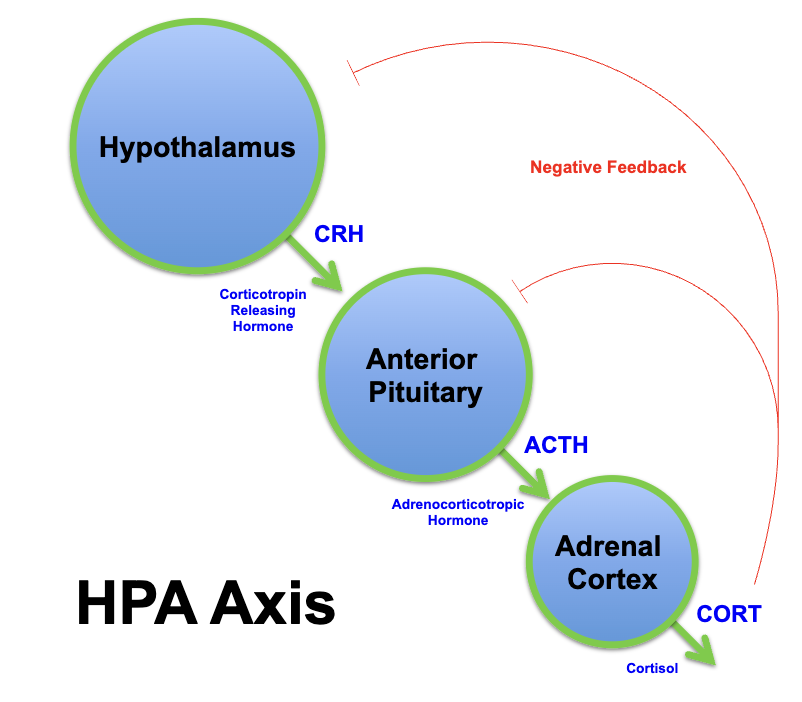
oxytocin and ADH are transported from hypothalamus to posterior pituitary via
hypothalamic-hypophseal tract
anterior vs posterior pituitary
anterior is larger and produces and secretes own hormones
posterior - produced by hypothalamus
what 3 hormones do the adrenal glands secrete
adrenaline
aldosterone
cortisol
adrenal cortex produces
steroid hormones - androgens, glucocorticoids, mineral corticoids
adrenal medulla produces
catecholamines and peptides
cortisol is a
glucocorticoid
aldosterone is a
mineralcorticoid
epinephrine and norepinephrine are
catecholamines
stress is regulated short term by what system
neural - sympathetic NS
fight or flight
how does the sympathetic NS respond to stress ?
adrenal medulla releases epinephrine and norepinephrine
cause glycogen to break down into glucose, increased BP etc.
(chronic) stress is regulated long term by what system ?
HPA axis
HPA axis
neuroendocrine system
regulates the body's response to stress
hypothalamus, pituitary, adrenals
how does the HPA axis respond to stress ?
ATCH released from anterior pituitary into blood
adrenal cortex releases:
mineralcorticoids - retention of Na+ and water by kidneys
glucocorticoids - protein and fats broken down and converted into glucose
expected values for normal fasting BG
3.5 - 6.5 mmol/L
high blood sugar promotes
insulin release from pancreas
formation of glycogen from glucose in liver (glycogenesis)
stimulates uptake of glucose from blood
low blood sugar promotes
glucagon release from pancreas
formation of glucose from glycogen (glycogenolysis)
raises BG
gluconeogenesis
metabolic process of producing glucose from non-carbohydrate sources like amino acids, glycerol, and lactate
how does insulin allows for the uptake of glucose ?
signals to cell to insert GLUT4 transporters into mem allowing glucose into cell
what is diabetes ?
chronic disease characterised by raised BG levels - hyperglycaemia
pancreas unable to produce or respond to insulin
results in abnormal metabolism of carbohydrates
symptoms of diabetes
polyuria, polydipsia and fatigue
sign vs symptom
sign = measurable
signs of diabetes
hyper-glycemia and diabetic ketoacidosis
diabetic ketoacidosis
break down of fats and proteins as alternative source (to glucose)
build up of ketones in blood lowering pH - acidosis
what 4 tests can be used for diabetes ?
fasting BG, random BG, oral glucose tolerance, HbA1c
oral glucose tolerance test
pt given 75g of liquid glucose and test 2hrs later for reaction
HbA1c (glycosylated haemoglobin)
measure of glucose control over past 2-3 months
quantity of glucose that has been glycosylated - attached to haemoglobin
higher HbAC1 = higher BG level
type I diabetes
beta cells do not produce enough insulin
autoimmune disease
selective destruction of B-cells of pancreas by T cells
peak incidence in childhood
treatment of diabetes I
exogenous insulin via pump or injection
short acting insulin is given
before meals
intermediate long acting insulin is given
once daily - acts as background insulin
hybrid closed loop systems (HCL)
link continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) with insulin pump technology to manage blood sugar levels in people with type 1 diabetes
“artificial pancreas”
type II diabetes
insulin deficiency and resistance (desensitisation)
similar osmotic symptoms to type 1 - frequent urination etc.
but no weight loss as some insulin present
who is at risk of type II diabetes and why ?
individuals with metabolic syndrome
increased BMI, LDLs and triglycerides
decreased HDLs
hypertension
disrupted BG levels
what glucose lowering drugs are used to treat diabetes II
SGLT2
sulphanyle ureas (SU)
glitazones (TZD)
GLP-1 - analogues
DPP-4 - inhibitors
basal inhibitors
what are 5 diabetes associated complications
microvascular - retinopathy, nephropathy, neuropathy
macro - cardiovascular and cerebrovascular disease
how is retinopathy treated ?
anti-VEGF injections into eye or laser treatment
neuropathy
damage to blood vessels that supply nerves
stop nutrients reaching them
nerve fibres become damaged
cardiovascular disease
blood vessels of heart
glucose sticks to RBCs causing blockage and damage
risk factors - high HbA1c, smoking and obesity
artherosclerosis
buildup of fats, cholesterol and other substances in and on the artery walls
how many pregnancies result in gestational diabetes ?
5 - 10%
macrosomia
baby has significantly higher birth rate
(high BG of mother during pregnancy so more glucose to baby)
gestational diabetes treatment
metformin or insulin injections
hyperthyroidism
over active
thyroid produces increased amount of thyroid hormone
but lower levels of TSH
under active thyroid
decreased thyroid hormone production
high TSH
diseases of the thyroid
Hashitmoto’s, cancer, nodules
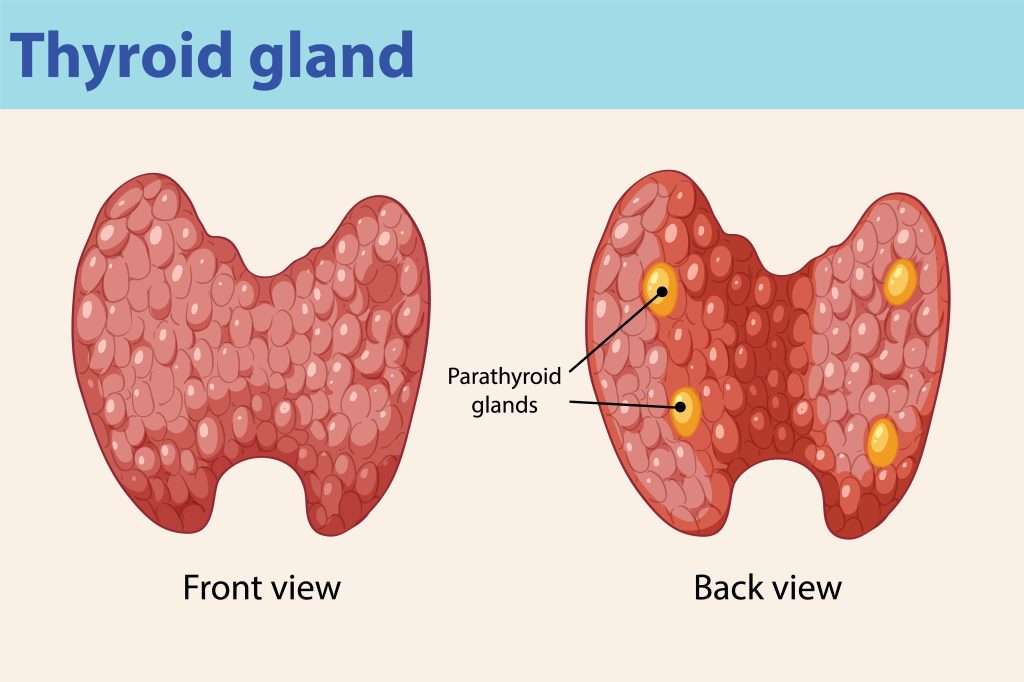
where is the thyroid gland located ?
saddles trachea just below larynx
anatomy of thyroid gland
butterfly shape
right and left lobes joined by isthmus
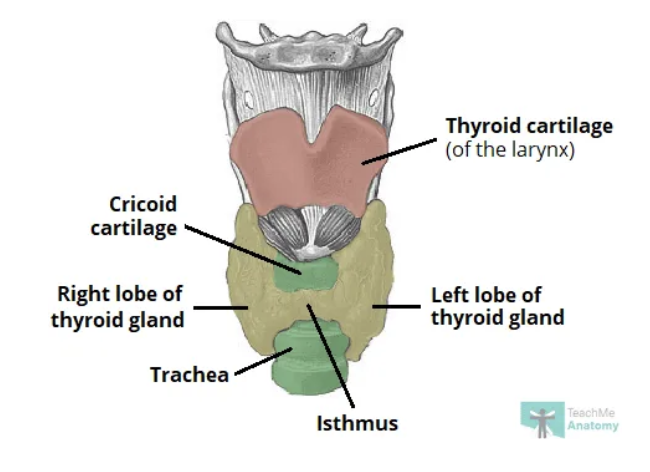
which lobe of the thyroid is larger ?
right lobe
what is the functional unit of the thyroid gland ?
spherical thyroid follicles - lined with follicle cells
how many parathyroid glands are there ?
4 - lie between 2 layers of capsule at base of lobes
function of thyroid
produces hormones that aid in regulating metabolism
thyroid hormones
thyroxine (T4)
triiodothyronine (T3)
calcitonin - peptide hormone
thyroid hormones contain what elements
iodine and tyrosine
what is the biologically active thyroid hormone
T3 - triiodothyronine
metabolic effects of thyroid hormone
increase basal metabolic rate and gut absorption
stimulates lipolysis
decrease cholesterol levels - promotes its conversion and excretion into bile.
cardiovascular effects of thyroid hormone
increases HR, respiration, oxygen use, mitochondrial activity and blood flow
developmental effects of thyroid hormones
increase growth rate
role in brain maturation during foetal development
role of thyroid in cognitive function
regulates sleep and thought patterns
increased levels of thyroid hormones associated with faster speed of thought but decreased focus - adhd
how does high iodine affect the thyroid ?
can inhibit activity (Wolff-Chaikoff effect)