Biology Keystone
The Cell
The Cell Theory
All living things are made up of cells
All living things function through the activities of their cells (metabolism)
Cells come only from pre-existing cells
“Cell People”
Schleiden: Plants are made of cells
Schwann: Animals are made of cells
Virchow: Cells come only from cells
Hooke: Named the cell
van Leeuwenhoek: Invented a crude microscope; first to see living cells
Brown: Discovered the nucleus
Structure and Function
Nerve cells have long processes to transmit information over long distances
Epithelial Cells (Skin)
Epithelial cells are flat and platelike in order to form a protective covering over the organism
Prokaryotic Cells
Lack an organized nucleus
Lack membrane-bound organelles
Usually have a cell wall
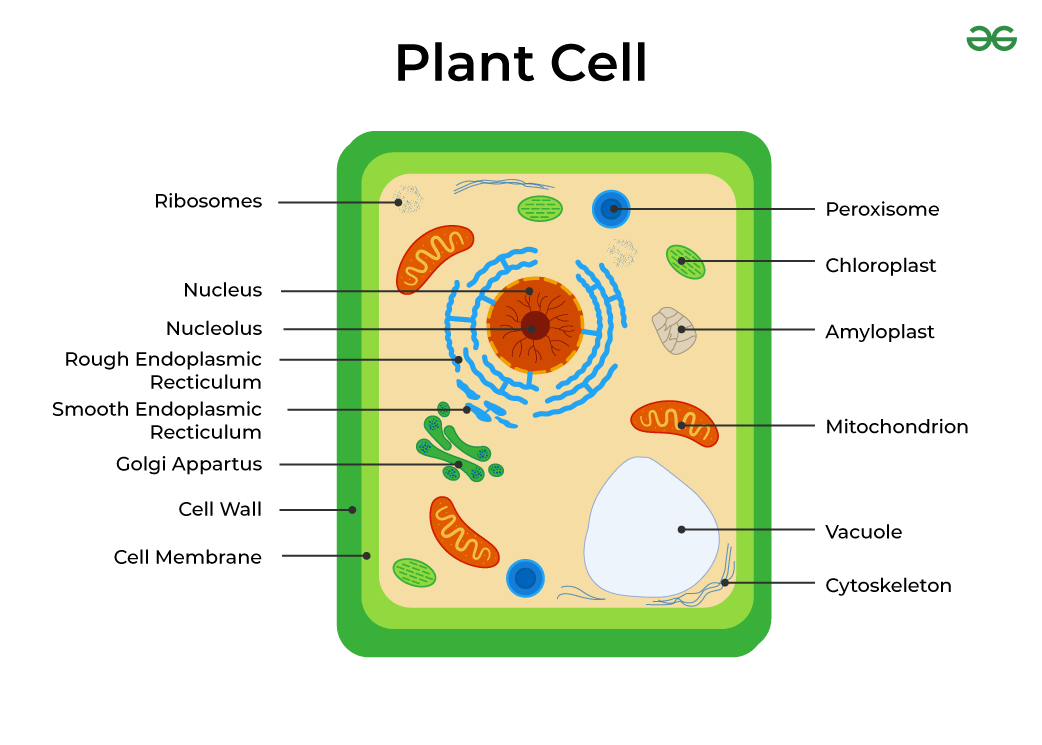
Plant Cells
Have a cell wall
Contain a large central vacuole
Usually contain chloroplasts
Animal Cells
Do not have a cell wall
Have centrioles
Have smaller vacuoles
Have lysosomes
The Cell Wall
Made of cellulose
Gives support to the plant cell
Gives strength to the plant cell
Is permeable
Plasma Membrane
Controls what enters and leaves the cell
Made of a phospholipid bilayer
Found in all types of cells
Cytosol
The area of the cytoplasm outside of the individual organelles is called the cytosol
The cytosol contains thousands of enzymes
The cytosol takes molecules and breaks them down, so that the individual organelles can use them
The Nucleus
Contains the cell’s DNA
Is surrounded by its own nuclear envelope
Often referred to as the “control center” of the cell
DNA
The genetic material in the nucleus
Double helix
Forms chromatin (working DNA) and chromosomes (nonworking DNA)
Nucleolus
The nucleolus is an approximately spherical region within the nucleus of eukaryotic cells
It stores RNA and ribosomal subunits
Mitochondria
Mitochondria generate the cell’s energy through cellular respiration
Usually they are rod-shaped, however, they can be round
The inner membrane is thrown into folds or shelves called cristae
Mitochondria have their own DNA and ribosomes
They are capable of reproducing themselves
Humans inherit mitochondrial DNA only from the mother
Powerhouses of the cell
Site of cellular respiration
Breakdown of food to release energy and generate ATP
Chloroplasts
Chloroplasts are the site of photosynthesis, the process by which autotrophs make food
Chlorophyll is the light-trapping pigment in the chloroplast
Stroma is the semi-fluid filled space that contains enzymes
Thylakoids are hollow sacs that provide membrane for photosynthetic reactions
Grana are stacks of thylakoids
Lamellae connect the grana
Like mitochondria, chloroplasts have a double membrane, their own DNA, and ribosomes
Chloroplasts can reproduce themselves
Ribosomes
Granular organelles
Site of protein synthesis
Attached to the rough ER or located in the cytoplasm
Manufactured in the nucleolus
Made of RNA and protein subunits
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
A complex network of membranes
Bears the ribosomes during protein synthesis
Processes and transports polypeptides to the Golgi complex
Hollow interior is known as the “lumen”
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum
Smooth ER is associated with the production and storage of lipids, especially steroids
Releases calcium in cardiac and skeletal muscle cells so that contraction can occur
Detoxifies alcohol and poisons in the liver and kidney cells
Golgi Apparatus
Receives proteins from the rough ER
Processes, packages, and delivers the proteins
Packaging occurs via vesicles
Responsible for packaging proteins for the cell
Proteins produced by the rough ER pass into the Golgi cisternae
These proteins are then squeezed off into vesicles (small vacuoles) for transport out of the cell
Lysosomes
Found in animal cells
Contains hydrolytic enzymes to digest almost everything in the cell
Manufactured by the Golgi Apparatus
Autophagy
Digestion of worn organelles
Autolysis
Digestion of damaged or extra cells
Peroxisomes
Not from the Golgi apparatus
Neutralize free radicals (Oxygen ions that damage cells) in the liver and kidneys
Detoxify alcohol and drugs
Break down fatty acids for the mitochondria to use for energy
Glyoxysomes
Found in some seeds
Break down stored fats to provide energy for the developing plant embryo
Vacuole
Large fluid-filled vesicle surrounded by a membrane
Can store water, nutrients, wastes, and pigments
Larger in plant cells
Help plant cells create turgor, internal water pressure
Contractile Vacuoles
Membrane-bound sac
Plays roles in release of excess water from protists that live in watery environments
Other Vacuoles
Amyloplasts
Store starch in plant cells
Chromoplasts
Store pigments other than chlorophyll; give color to petals and leaves
Cytoskeleton
For mobility and stability
Primary types of fibers comprising the cytoskeleton are microfilaments, microtubules, and intermediate filaments
Centrioles
In animal cells only
Two cylinders at right angles to one another
Close to the nucleus
Help to form the spindle fibers for cell division
Flagella and Cilia
Flagella are long and whiplike
Cilia are short and hairlike
Both are used for locomotion
Cilia are also used internally to sweep cells or particles
Animal Cell
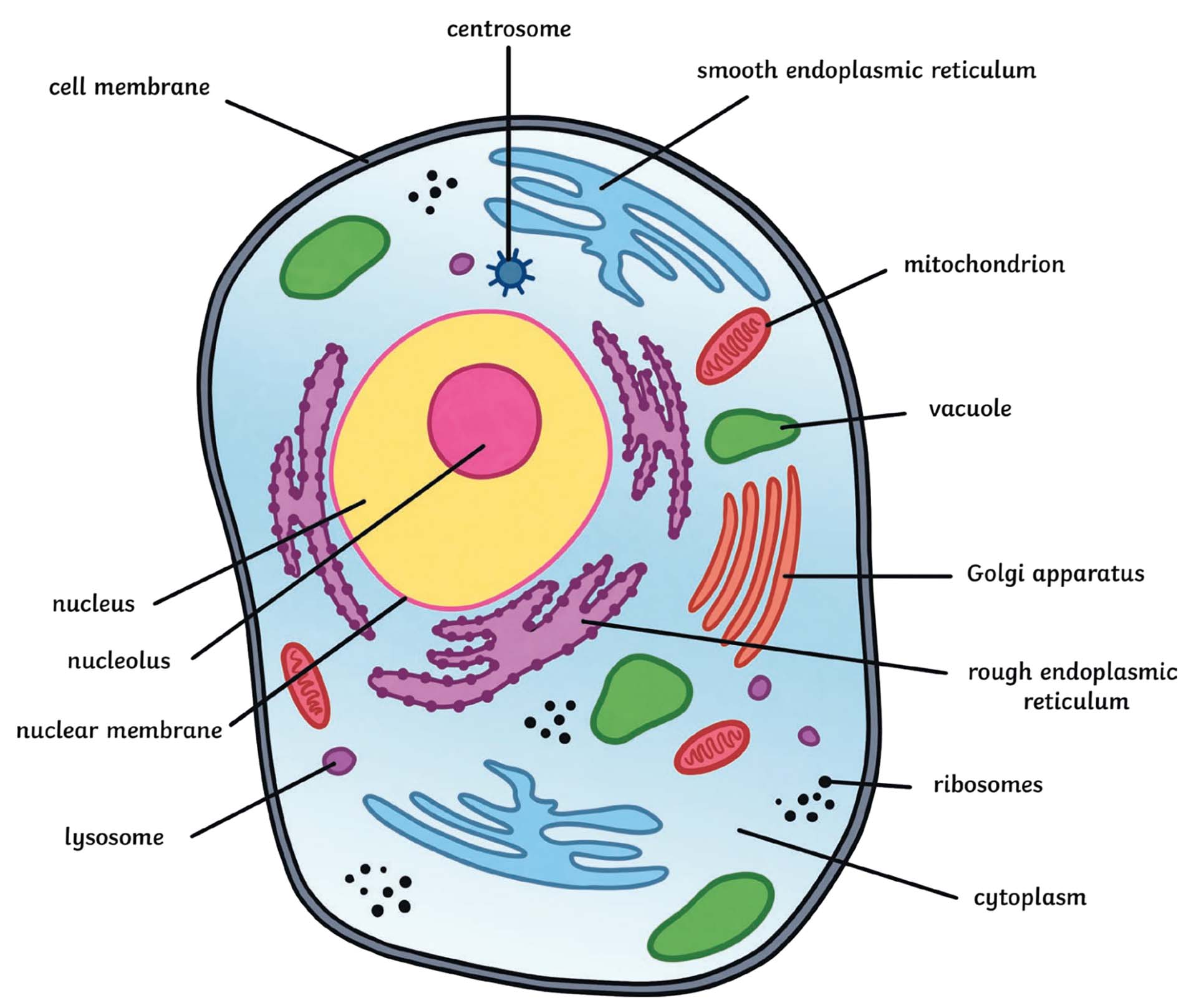
Plant Cell
Organic Compounds
Organic Compounds
The Molecules of Life
Made of
Carbon
Hydrogen
Usually Oxygen
Sometimes:
Nitrogen
Phosphorus
Sulfur
The Carbon Atom
Has four valence electrons
Forms strong covalent bonds
Can form single, double, and triple bonds
Likes to bond to itself
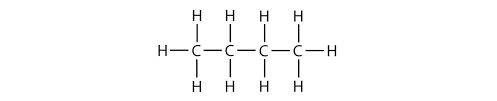
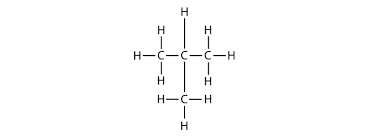
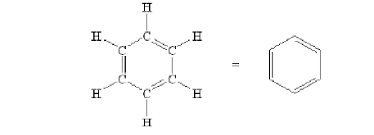
Carbon compounds take many shapes such as:
Chains
Branched Chains
Rings
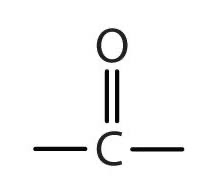
Functional Groups
Groups of atoms sometimes bond to carbon chains
These “functional” groups give the carbon compound unique properties
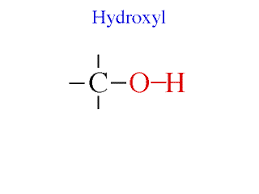
Hydroxyl: OH
Carbonyl: CO
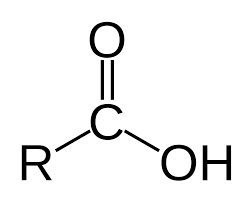
Carboxyl: CO2H
(R is a placeholder)
Amino: NH2
Methyl: CH3
Phosphate: PO4H2
Building Organic Compounds
Monomers are single units of an organic compound that have all the properties of the compound
Polymers are large organic compounds consisting of several monomers bonded together
Macromolecules refer to extremely large polymers
Glucose is the monomer of starch, glycogen, chitin, and cellulose
Organic Compounds
The four categories of Organic Compounds found in living things
Carbohydrates
Lipids
Proteins
Nucleic Acids
Carbohydrates
Sugars
Used for energy
Produced by plants through photosynthesis
Simple sugars
Made of Carbon, Hydrogen, and Oxygen
The ratio of C:H:O is 1:2:1
Monosaccharides are the monomers of carbohydrates
C6H12O6 is the formula for a monosaccharide
Glucose: blood sugar
Fructose: fruit sugar
Galactose: found in milk
Disaccharides
Are built from two monosaccharides
C12H22O11 is the general formula
Sucrose: table sugar; sweet
Lactose: milk sugar; nourishment for young mammals
Maltose: sugar in seeds; nourishment for embryo plants
Glucose + Glucose = Maltose + H2O
Glucose + Fructose = Sucrose + H2O
Glucose + Galactose = Lactose + H2O
Polysaccharides
Large molecules (polymers)
Made of many monosaccharides bonded together
Starch: energy storage in plants
Glycogen: energy storage in animals
Cellulose: cell wall construction
Chitin: cell walls in fungi and exoskeletons in arthropods
Isomers
Compounds that have the same molecular formula but different structures are called isomers
Each isomer has its own properties because the shape of the molecule determines its characteristics
Shape determines properties
Condensation Reaction (Dehydration Synthesis)
Building a large organic molecule from two smaller organic molecules by removing a molecule of H2O through a process called condensation reaction
The water is produced by removing an OH group from one molecule and a H from a hydroxide group in the other molecule
Hydrolysis
The breaking of polymers into monomers through the addition of water
Lipids
Made of Carbon, Hydrogen, and Oxygen
Monomers are glycerol and fatty acids
The high Carbon:Hydrogen ratio enables the molecules to store more energy than carbohydrates
Fatty Acids
Made of long hydrocarbon chains
Attached to a carboxyl functional group
Saturated Fatty Acids
Have only single Carbon to Carbon bonds
Fatty acid tails are straight
Can cause Cardiovascular disease
The bad fat
Unsaturated Fatty acids
Have one or more double Carbon to Carbon bonds
Fatty acid tails are “kinked”
Less likely to cause cardiovascular problems
The good fat
Unsaturated fats are liquid at room temperature
Olive oil and corn oil are unsaturated fats
Most saturated fats are solid at room temperature
Butter and lard are saturated fats
Coconut oil is an exception
Trans Fat
The new health threat
Types of Lipids
Triglycerides
3 fatty acids:1 glycerol
Used for insulation under the skin and around organs
Store energy for future use
Phospholipids
Composed of
Two fatty acids
One glycerol
One phosphate group
Phospholipid Structure
Hydrophilic head
Hydrophobic tails
The unsaturated fatty acid tails create kinks that enable the phospholipid to spin freely
Allow our membranes to be fluid
Steroids
Chemical messengers
Composed of four fused Carbon rings
Cholesterol
Keeps membrane’s fluid at low temperatures
Stabilizes membranes at high temperatures (keeps them together)
Estrogen and Testosterone
Responsible for the development of secondary sexual characteristics
Waxes
Waterproof
Form a protective coating on plants
Form protective layers in animals
Earwax prevents bacteria from entering the ear
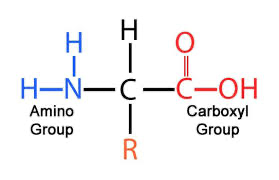
Proteins
Made of Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen, and Nitrogen
Monomers are called amino acids
Amino acids are help together by peptide bonds
Amino Acids
Essential
Cannot be made by the body
Must be supplied in the diet
Nonessential
Can be made by the body
Ex:
The alpha carbon is in the center
A hydrogen atom, a carboxyl group (acid group), and an amino group are bonded to the alpha carbon in all amino acids
The rest of the amino acid referred to as the “R” group is unique to each of the 20 amino acids
Condensation Reaction
Polypeptide is the name given to protein polymers
They can be built by removing a molecule of water from every two amino acids bonded together
Peptide Bonds
H is removed from the amino group of one amino acid, and the OH is removed from the carboxyl group of the other amino acid
Hydrolysis
Polypeptides can be broken down into amino acids by adding back the H2O
Structural Proteins
Uniquely made in each person
Used for skin, hair, nails, muscles, bones
Examples: collagen and keratin
Transport Proteins
Found in the cell membrane to bring molecules in and out
Some are unique to particular cells
Example: Hemoglobin- carries oxygen
Messenger Proteins
Hormones are chemical messengers
Example: Insulin- regulates blood sugar
Motile Proteins (Mobility)
Found in cytoskeleton and muscles
Examples: actin and myosin
Storage Proteins
Proteins that remain in supply for growth and development
Example: egg white
Defense Proteins
Antibodies fight specific infections
Enzymes
Controls every activity in the cell
Speed up reactions at least one-million times
Examples: lactase and sucrase
Heat can change protein structure
Other agents that denature proteins are:
Extreme pH
Exposure to Lead (Pb) and Mercury (Hg)
Nucleic Acids
Made of monomers called nucleotides
One 5-Carbon sugar
One phosphate group
One Nitrogen base
DNA
Transmits genetic information from one generation to the next
Contains the information necessary to tell the cell how to make proteins
The genetic material in the nucleus
Double Helix
Forms chromatin and chromosomes
Sugar in DNA is deoxyribose
Always in a double strand called a helix
Has four bases:
Adenine
Thymine
Guanine
Cytosine
Watson and Crick
Used the research of many people
Put together the double helix model of DNA
Won the Nobel Prize with Wilkins for the model
Rosalind Franklin
Took the x-ray pictures of DNA that enabled Watson and Crick to figure out the double helix model
Died before the Nobel Prize was awarded
RNA
Copies the DNA genetic code
Controls protein synthesis according to directions from DNA
Sugar in RNA is ribose
Exists as a single strand
Has four bases:
Adenine
Uracil
Guanine
Cytosine
ATP
Adenosine Triphosphate
Composed of
Adenine- a nitrogen base
Ribose- a five carbon sugar
Three phosphate groups
The molecule is the energy storage mechanism for all living things
Recycling ATP
When energy is needed, the cell breaks down ATP molecules
ATP → Energy + ADP + Phosphate
During cellular respiration, energy is released and used to replace the phosphate
ADP + Energy + Phosphate → ATP
Embedded Proteins
The Cell Membrane
Regulates what goes in and out of the cell
Protects the cell
Communication (with other cells)
Fluid Mosaic Model
Proteins embedded in the cell membrane:
Enzymes are chemicals that catalyze biochemical proteins
Receptor proteins: The receptor proteins are always found on the outer cell membrane surface. This is where hormones and neurotransmitters and other chemicals attach (binding site) to the surface of the cell. We know hormones affect the activity of the cells.
Ex: Insulin regulates glucose
Ion Channels: ion channels are a very narrow tube-shaped protein that help establish a tiny pore in the cell membrane. They are only large enough to allow an ion to go through. Each ion channel is for specific ions. They can open and close and are very important in understanfing the rest of physiology.
Ex: “Calcium channel blockers” are important in regulating blood pressure
Transport/Carrier Proteins are embedded in the cell membrane to help transport glucose and amino acids across the membrane. These molecules are too large to go through ion channels.
Glycoproteins have carbs attached to the protein which are used as cell surface markers. Key in transplantation.
Sodium-Potassium Pump (carrier protein) is a pump which moves 3 sodium ions out of the cell for every 2 potassium ions that enter the cell
Aquaporin: small proteins that allow for osmosis to occur
Cholesterol helps maintain the cell’s firmness and integrity
Functions of Receptor Proteins
Changes in Permeability
The binding of a signal molecule to the receptor protein causes an ion channel to open, allowing specific ions to cross the cell membrane
Second Messengers
The receptor protein may cause the formation of a second messenger inside the cell. The second messenger acts as a signal molecule and amplifies the signal of the first messenger, that is, the original signal molecule
Enzyme Action
The receptor protein may act as an enzyme. When a signal molecule binds to the receptor protein, the receptor protein may speed up chemical reactions inside the cell
Easiest type of molecule to cross the cell membrane: Small, Nonpolar
Cell Transport
Diffusion
One way cells maintain homeostasis is by controlling the movement of substances across their cell membrane
Cells must use energy to transport some substances across the cell membrane
Other substances move across the cell membrane without any use of energy by the cell
Random Motion & Concentration
Passive Transport
Movement across the cell membrane that does not require energy from the cell
Concentration Gradient
A difference in the concentration of a substance, such as the balls, across a space
Equilibrium
A condition in which the concentration of a substance is equal throughout a space
Diffusion
The movement of a substance from an area of high concentration to an area of lower concentration caused by the random motion of particles of the substance
Many substances, such as molecules and ions dissolved in the cytoplasm and in the fluid outside cells, enter or leave cells by diffusing across the cell membrane
Osmosis
The diffusion of water through a selectively permeable membrane
Like other forms of diffusion, osmosis involves the movement of a substance, water, down its concentration gradient
Osmosis is a type of passive transport
Hypertonic solution
Water moves out. When water diffuses out of the cell, the cell shrinks.
Hypotonic solution
Water moves in. When water diffuses into the cell, the cell swells.
Isotonic solution
No net water movement. A solution that produces no change in cell volume.
Diffusion Through Ion Channels
An ion channel is a transport protein with a polar pore through which ions can pass
The pore of an ion channel spans the thickness of the cell membrane
An ion that enters the pore can cross the cell membrane without contacting the nonpolar interior of the lipid bilayer
Electrical Charge and Ion Transport
The movement of a charged particle, such as an ion, across the cell membran is also influenced by the particle’s positive or negative electrical charge
A more positively charged ion located outside the cell is more likely to diffuse into the cell, where the charge is negative
A more negatively charged ion located inside the cell is more likely to diffuse out of the cell
Facilitated Diffusion
Most cells also have a different kind of transport protein, called carrier proteins, that can bind to a specific substance on one side of the cell membrane, carry the substance across the cell membrane, and release it on the other side
Definition: when carrier proteins are used to transport specific substances, such as amino acids and sugars, down their concentration gradient
Movement Against a Concentration Gradient
Active Transport
The transport of a substance across the cell membrane against its concentration gradient
Unlike passive transport, active transport requires the cell to use energy because the substance is being moved against its concentration gradient
Most often, the energy needed for active transport is supplied directly or indirectly by ATP
Sodium-Potassium Pump
One of the most important membrane pumps in animal cells is this carrier protein
In a complete cycle, the Na-K pump transports three sodium ions, Na+, out of a cell and two potassium ions, K-, into the cell
The Na-K pump has four steps:
Three sodium ions inside the cell bind to the sodium-potassium pump
The pump changes shape, transporting the three sodium ions across the cell membrane and releasing them outside the cell
Two potassium ions outside the cell bind to the pump
The two potassium ions are transported across the cell membrane and are released inside the cell
Movement in Vesicles
Many substances, such as proteins and polysaccharides, are too large to be transported by carrier proteins. These substances are moved across the cell membrane by vesicles
Endocytosis is the movement of a substance into a cell by a vesicle
Exocytosis is the movement of a substance by a vesicle to the outside of a cell
Membrane Receptor Proteins
Cells must also respond to important information and filter out unimportant information
Cells can receive the messages carries by certain signal molecules because the cell membrane contains specialized proteins, called receptor proteins, that bind these signal molecules
Receptor protein is a protein that binds to a specific signal molecule, enabling the cell to respond to the signal molecule