DRAFT Chapter 8 - Intelligence & Cognitive Development
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
What is intelligence according to the psychometric, multiple intelligences and successful intelligence views?
Psychometric View: measurable cognitive abilities through standardized testing
Multiple Intelligences: diverse forms of intelligence across different domains
Successful Intelligence: practical application of analytical, creative, and practical abilities
What is Spearman’s General Intelligence theory?
general Intelligence (g)
single underlying factor across all cognitive tasks
What is Thurstone’s Primary Mental Abilities?
seven distinct abilities including verbal, spatial and numerical reasoning
What is Carroll’s Hierarchical Model?
three-tier structure bridging general and specific theories
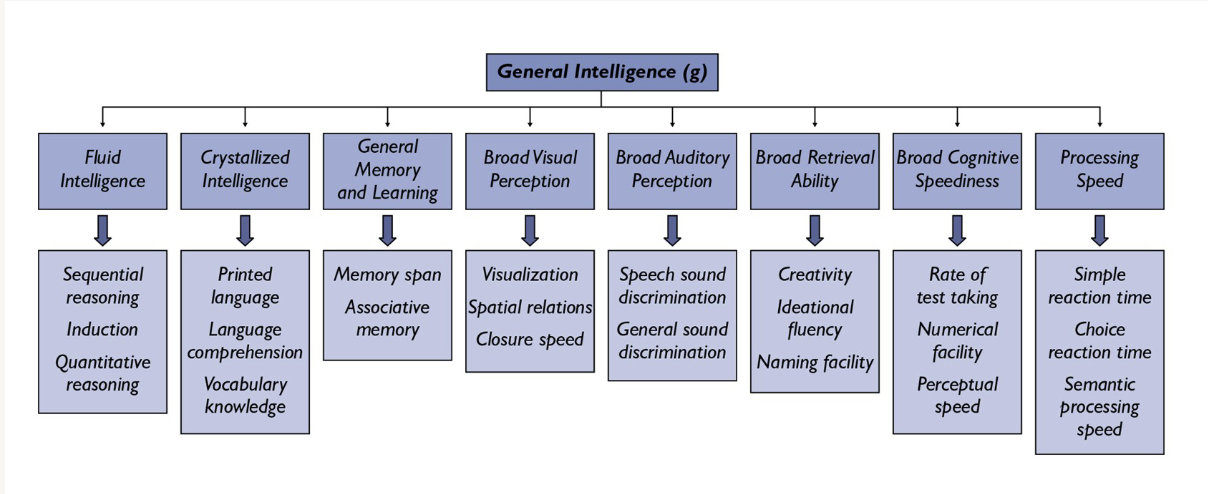
What are the 2 types of intelligences?
fluid
crystallized
What is fluid intelligence?
ability to think logically and solve novel problems
pattern recognition
abstract reasoning
problem-solving in new situations
What is crystallized intelligence?
accumulated knowledge and skills from experience
vocabulary and language
cultural knowledge
learned strategies
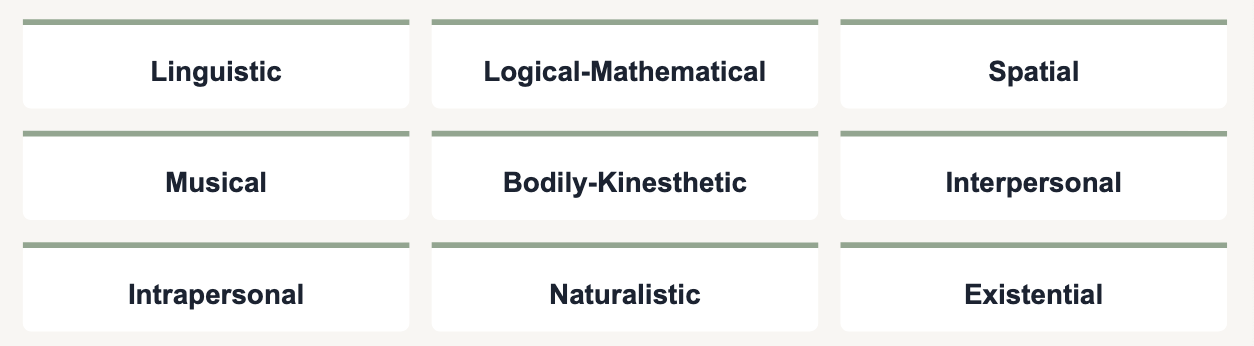
What are Gardner’s Multiple Intelligences?
9 distinct forms of intelligences and solve novel problems
LIES MILK No one
What is emotional intelligence?
ability to understand and manage emotions
perceive emotions accurately
understand emotional patterns
regulate emotions effectively
What does strong emotional intelligence help with?
better relationships and self-esteem
more effective leadership and teamwork
greater life satisfaction
What is Sternberg’s Theory of Successful Intelligence and what are its components?
using abilities skillfully to achieve personal goals
analytical: analyzing problems and generating solutions
creative: dealing flexibly with novel situations
practical: knowing what will actually work
What is the history of IQ testing?
began with Binet’s pioneering work
now we have modern assessments
What were Binet’s assessments for intelligence?
1905
French government asked Binet and his colleague Théodore Simon to develop a way to identify children who needed extra help in school/needing support
‘mental age’ concept
If a 7-year-old child performs like the average 9-year-old, their mental age is 9
What was Stanford-Binet’s methods for measuring intelligence?
intelligence quotient (IQ) score
average of 100
series of tasks organized by age level or difficulty
standardized test
What are modern tests that we use now?
e.g. WISC assesses multiple cognitive domains
verbal scale
INFORMATION: child is asked questions that tap their factual knowledge of the world
COMPREHENSION: child is asked questions that measure their judgment and common sense
SIMILARITIES: child is asked to describe how words are related
performance scale
PICTURE ARRANGEMENT: pictures are shown and the child is asked to place them in order to tell a story
PICTURE COMPLETION: child is asked to identify the part that is missing from the picture
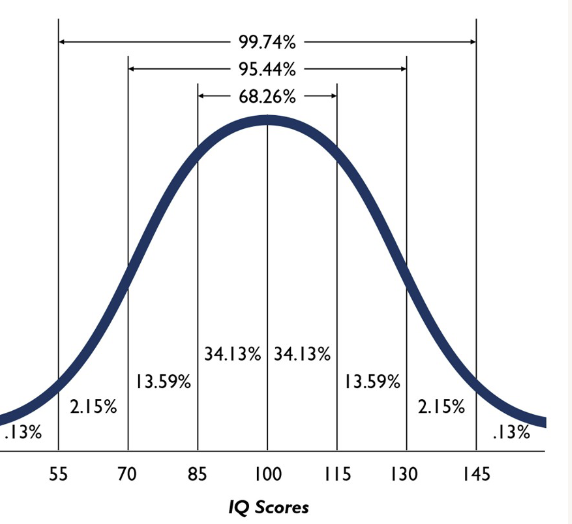
What is the mean IQ score and standard distribution?
mean = 100
SD = 15
What do IQ scores predict?
academic success
reasonable predictor of school performance
job performance
especially for complex occupations
stability over time
reliable after age 6
What are limitations of IQ score prediction?
self-discipline may better predict school success
infants tests poorly predict later IQ
How do nature vs. nurture shape intelligence?
both heredity and environment shape intelligence
heredity: twin studies, genetic links
environment: home stimulation, Flynn effect
Flynn effect: steady rise in average IQ scores over generations
What are some environmental influences on intelligence?
home environment
books, materials, engagement
education quality
resources, methods, class size
nutrition and health
prenatal care, childhood nutrition
4, socioeconomic status
access to resources
cultural exposure
language, experiences
interventions
early programs show effects
What are cultural considerations for IQ testing?
the challenge: linguistic and cultural differences affect test performance
the solution: use non-verbal patterns and visual reasoning
e.g. Raven’s Matrices
most widely used tests for assessing general intelligence (g) because it minimizes language and cultural bias
What is the influence of stereotypes on IQ testing?
how awareness of stereotypes affects performance
the challenge: knowledge of negative stereotypes creates anxiety and reduces test performances
the solution: activities boosting self-worth improve scores and reduce the threat effect
What are the 4 special populations of people?
exceptional abilities (above-av