Electrical and Automation Technology - Exercise 1a
1/78
Earn XP
Description and Tags
DC Circuits key objectives
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
79 Terms
What is scientific notation? Give an example
A method of expressing a number with a decimal number between 1 and 10 multiplied by a power of 10. 12,345 becomes 1.2345 × 10^4
What is engineering notation? Give an example
A method of expressing a number with a decimal number between 1 and 1000 multiplied by a power of 10 that is a multiple of 3. 12,345 becomes 12.345 × 10³
List 8 most common metric prefixes associated with engineering notation that are used extensively for electrical measurements in order of smallest to largest?
pico, nano, micro, milli, kilo, mega, giga, tera
What property of an atom makes it a good conductor?
Few valence electrons (1-3)
List the 4 most common single element conductors in order of best to worst.
Silver , Copper, Gold, Aluminum
What property of an atom makes it a good insulator?
Full valence shell
List 4 common electrical insulators.
Traditionally - mica, glass, Teflon, paper, rubber, Bakelite, oils, porcelain, air, phenolic
Most newer equipment uses GPO (fiberglass reinforced thermoset polyester)
List the symbol and units for electrical charge.
Symbol is the letter “Q”
Unit - Coulomb(C)
How many electrons in one standard unit of electrical charge?
1 Coulomb = 6.24 × 10^18
What is the standard SI unit of energy or work?
Joule(J)
List the symbol, units, and formula in terms of work and charge for Electrical Potential.
Symbol - letters V for Volts or E for Electro-motive Force
Unit - Volts(V) named after Alessandro Volta
Formula - 1V = 1 Joule / 1 Coulomb
List the symbol, units and formula in terms of charge and time for Electrical Current.
Symbol - letter I
Unit - Amps (A) named after Andre-Marie Ampere
Formula - 1A = 1 Coulomb / 1 Second
Explain in detail the key characteristics and specifications required for selecting a battery for a particular application.
The voltage required by the load
The current required by the load and the time the load needs to run on battery power which determine the amp-hour rating
The peak current required by the load (cold cranking amps)
How can battery system voltage be increased?
By combining cells in series within the battery (zinc-carbon 1.5V/cell, lithium 3V/cell, NiMH 1.2V/cell, lead-acid 2.1V/cell)
By combining batteries in series
How can battery system current be increased?
By making cells with greater surface area within the battery - this is the preferred method
By combining batteries in parallel and understanding that when batteries are combined in parallel they must be perfectly matched or they will discharge one another.
What factors affect battery life (amp-hours)?
Ambient temperature - room temperature (68F) is typically best
Discharge rate - a faster than C20 discharge rate will generally result in fewer amp-hours
What is the proper method of testing batteries?
Connect a load to the battery, monitor the voltage, and compare to the published discharge curve
The output voltage of a dead battery with no load connected will be very close to the battery nominal voltage
What are primary cells and secondary cells as they relate to batteries?
Primary cells are disposable (Zinc, Carbon, Alkaline, Lithium)
Secondary cells are rechargeable (Lead-Acid, NiCd, NiMH, Li-Ion, etc)
What term is used for opposition to DC current flow?
Resistance - represented by the letter “R”
List the symbol, units, and formula in terms of energy, time, and charge for Electrical Opposition to current flow.
Symbol - “R” for resistance
Unit - Ohm named after Georg Simon Ohm - German Physicist
Formula - 1 Ohm = 1 Joule-second / Coulomb2
List the formula for calculating the resistance of a conductor.
R = ρ(1/A) = resistivity (length/area)
R = 1(σA) = (length/conductivity*area)
Explain circular mil conductor size.
The cross-sectional area of a conductor calculated by squaring the diameter measured in mils (thousandths of an inch)
A 0.707” diameter cable would be 707mils2 = 500,000 CM or 500kCM
Explain how to interpret the color codes on a standard 4 band resistor.
The first two bands represent the first 2 significant digits of the resistance, the third band represents the number of zeros after the significant digits, and the forth band represents the tolerance.
List color codes used to determine a resistor’s nominal value in order from smallest to largest.
Black, brown, red, orange, yellow, green, blue, violet, gray, white.
List the color codes used to determine resister’s tolerance in order from smallest to largest.
1% - Brown, 5% - Gold, 10% - Silver
How does temperature affect resistance?
Positive temp coefficient - Conductors and resistors, and heating elements.
Negative temp coefficient - Semiconductors, thermistors, photo conductive cells
What is the component found in most surge suppressors?
Varistor - high resistance up to the firing voltage then low resistance - rated in joules
List the two most common types of variable resistor with the typical application.
Rheostat (only two leads) for varying circuit current.
Potentiometer (three leads) for varying reference voltage. Can be used as a rheostat.
Define conductance.
The reciprocal of resistance represented by the letter “G” were G = 1/R
Units are mhos or Siemens where 1Mho = 1Siemen
List the three forms of Ohm’s Law.
I = E/R, E=IR, R=E/I
List the memory aids that can be used to remember Ohm’s Law for the rest of your electrical career.
Eagle flies over the Indian and the Rabbit, Ohms Law Wheel, Ohms Law Triangle
What is the unit of electrical power?
Watt
List the symbol, units, and formula in terms of work and time for Electrical Power.
Symbol - letter “P” for Power is a rate of energy delivery
Unit - Watts “W” named after James Watt
Formula - 1W = 1 Joule / 1 Second
List the three forms of the power formula.
P = IE, P = I2R, P = E2/R
List the most common memory aid that can be used to retain the power formula.
P = IE as in Blueberry PIE
What units of measure are we billed for by the electric utility company?
Kilowatt-Hours
What is the significance of the units that we are billed for by the power company?
A kilowatt-hour is a unit of energy not a unit of electricity or power
1 kilowatt - hour = 1000 Joules/sec x 3,600 seconds = 3,600,000 Joules = 3.6MJ
What is 1kW-hr in terms of BTU?
1kWHr = 3,412 BTU
List the efficiency formula.
Efficiency (η) = (Pout/Pin) x 100%
How is electrical power related to mechanical power?
Mechanical power is typically rated in Horsepower (HP)
The HP rating of a motor is the Output Power of the motor
1HP = 746Watts
When are two resistors considered to be connected in series?
When they share only one connection point in common.
What is the formula for the total resistance of resistors in series?
RTotal = R1 + R2 + R3 …
What is the formula for total current in a series circuit?
ITotal = ESource / RTotal
What is the same everywhere in a series circuit?
Current
Explain Kirchhoff’s Voltage Law.
The sum of the voltages around a closed loop must equal zero
Explain the electrical circuit polarity conventions for sources and passive components when using “conventional current flow”.
Conventional current exits the positive terminal and enters the negative terminal of all voltage sources.
Conventional current enters the positive terminal and exits the negative terminal of all passive components.
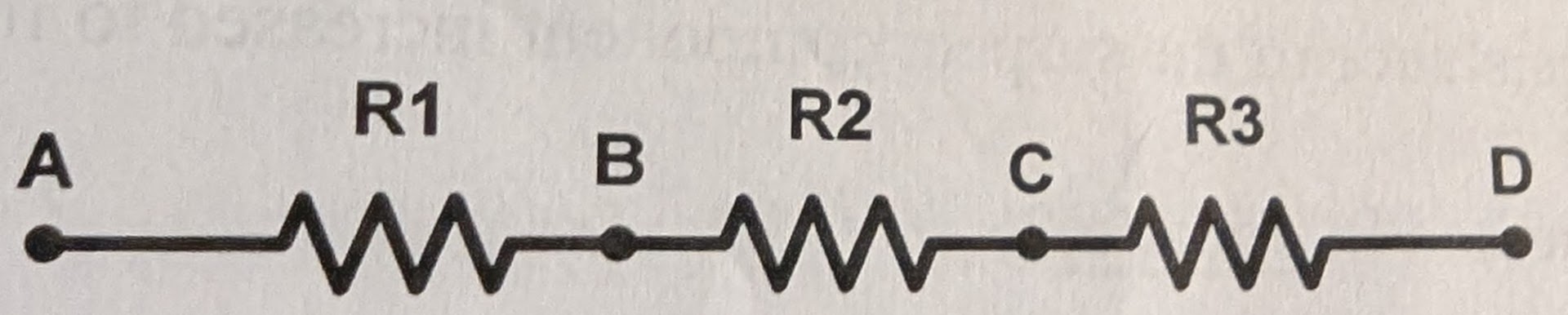
Write the KVL equation using conventional current flow for the circuit below given VA = +10V and VD = -20V.
Draw the voltage sources at points A and D with their proper polarity.
Define the direction of current I1 to flow clockwise (left to right) through the circuit which defines the polarity of the voltage across each resistor to be “+” on the left and “-” on the right .
The KVL equation becomes +10 - I1R1 - I1R2 - I1R3 + 20 = 0
If you knew the values of R1, R2, R3, you could solve for I1
If I1 turned out to be a negative number that would tell you that the current is actually flowing CCW and you would have to change the resistor voltage polarities.
What is the voltage divider formula?
VRx = Vtotal(RX/RTotal)
Explain subscript notation.
Single subscript notation as in Va is measured at point “a” wrt common
Double subscript notation as in Vab is measured at point “a” wrt point “b”
Vab can be calculated as Va - Vb
(wrt - with respect to)
Explain voltage regulation and the effects of source loading.
Most electrical sources have some form of internal opposition to current flow
When a load is connected to a source the output voltage at the terminal of the source will decrease due to the voltage dropped across the internal opposition to current flow
Voltage regulation is a measure of the drop where %Vreg = [(VNL - VFL)/VFL] x 100%
How is the modern DMM designed so that it will not affect circuit values?
The internal resistance is very high >10MOhms when measuring voltage
The internal resistance is very low < 1Ohm when measuring current
How would you calculate the voltage across a shorted component?
The voltage across a shorted component is always zero
Resistors typically do not short but a drop of solder or loose wire can accidentally shot them
If contacts in a sealed switch or relay are closed the voltage across them will be zero
How would you calculate the current through a shorted component?
When a short exists the circuit current will always be higher than the expected current
Recalculate the circuit current with the resistance of the suspect component reduce to zero
How do you calculate the voltage across an open component?
The voltage across an open component will always be higher than the expected voltage
For series circuits the voltage across the open component will be the source voltage
If contacts in a sealed switch or relay are open the voltage across them will be the source voltage
How do you calculate the current through an open component?
The current through an open component or open branch will always be zero
When an open exists the circuit component with the resistance of the suspect component increased to infinity
When are two resistors considered to be connected in parallel?
When they have two points in common.
What are the two formulas for the total resistance of resistors in parallel?
RTotal = 1/(1/R1 + 1/R2 + 1/R3 …)
RTotal = (R1 x R2) / (R1 + R2) referred to as product over sum and only works for two resistors
What is the formula for total current in a parallel circuit?
ITotal = IR1 + IR2 + IR3 this only works if all three resistors are in parallel
ITotal = Sum of the Branch Currents - this is true for all parallel circuits
What is the same everywhere in a parallel circuit?
Branch circuit voltage
The sum of the currents entering the node must equal the sum of the currents exiting the nodeW
Explain Kirchhoff’s current law.
The sum of the currents at any node must equal zero
The sum of the currents entering the node must equal the sum of the currents exiting the node
What is the current divider formula?
IRx = ITotal(RTotal/Rx)
What is meant by the expression “increasing load”?
Increasing load means increasing total current
This is because all homes and power distribution systems are wired in parallel. When any load is added in parallel the total resistance of the system decreases and the total current increases.
List the steps in order that you would use to completely solve a series parallel circuit?
1) Reduce by creating an orderly series of redraws that combine series and parallel components until total resistance is found
2) Solve for the total resistance and total current for the final redraw
3) Return using Ohm’s Law to fully label all voltages and currents on each redraw
Explain Thevenin”s theorem with the steps required to Thevenize a circuit.
A complex circuit can be replaced by an equivalent voltage source (VTH) with an equivalent series resistance (RTH)
Remove the load and determine the voltage that would exist across the open terminals
a. This will be the Thevenin voltage
Short all voltage sources, open all current sources, and determine the resistance that would be measured by an Ohmmeter placed across the output terminals
a. This will be the Thevenin resistance
Explain Norton’s theorem with the steps required to Nortonize a circuit.
A complex circuit can be replaced by a current source with parallel resistance
1) Short the load and determine the current that would exist in the short
a. This will be the Norton current
2) Short all voltage sources, open all current sources, and determine the resistance that would be measured by the Ohmmeter placed across the output terminals
a. This will be the Norton resistance
Explain superposition with the steps required to solve a circuit.
A method for solving a circuit that has multiple sources
1) Solve for each source individually by shorting all other voltage sources and opening all other current sources
2) Sum the voltages and currents found by the previous step for each component
Explain the maximum power transfer theorem.
Maximum power is transferred to load when the load resistance is equal to the internal resistance of the source or the Thevenin equivalent resistance of the circuit.
Explain how maximum efficiency is achieved for a load.
When the load resistance is much larger than the internal resistance of the source or the Thevenin equivalent resistance.
Does wire have resistance? Explain.
Yes, the resistance of wire is small in relation to other components. However, long runs of wire can have significant resistance.
Resistance of wire is calculated by multiplying the resistivity of the material by its cross sectional area and its length.
What is the most important factor to consider when sizing wire for an application?
The heat that will be dissipated by the wire
This can be calculated by multiplying the resistance of the wire by the square of the current flowing through the wire
The current rating of all electrical equipment is based on this concept
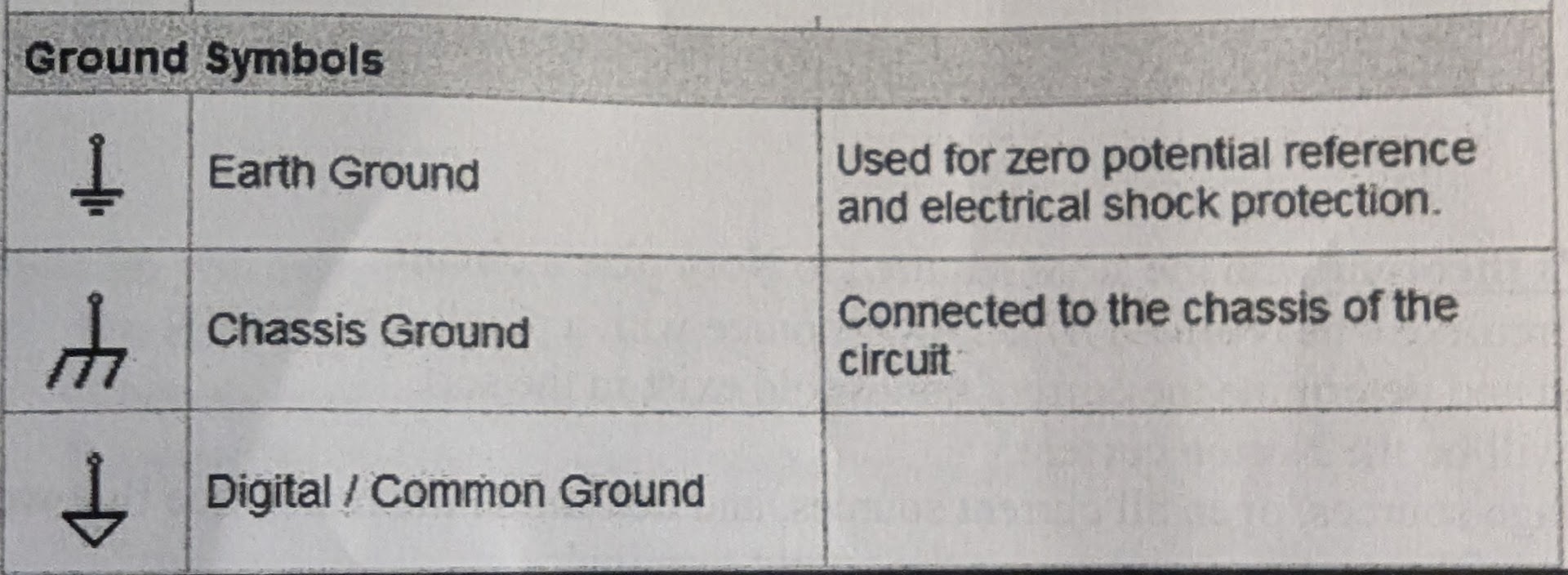
What is the difference between ground and common with symbols
Ground is a common reference point for circuit voltage measurements that is intentionally connected to earth ground.
Common is a common reference point for circuit voltage measurements that is not connected to earth ground
What is the name given to the black wire in a typical residential electrical system by the NEC?
Ungrounded conductor
What is the name given to the white wire in a typical residential electrical system by the NEC?
Intentionally Grounded conductor or Grounded Conductor
Why do we intentionally ground the white wire in electrical systems?
To keep the circuit common (neutral) voltage from floating with respect to ground. In the early days of electrical power distribution (pre-1970s) the white wire was attached to the shell of metal appliances. If that wire were allowed to float, then a potential difference could be developed between the shell of the appliance and the surrounding grounded objects like plumbing and concrete floors. This would create a dangerous shock hazard.
To provide a low resistance path to earth ground for lightning strikes.
What is the name given to the bare copper or green wire in a typical residential electrical system by the NEC?
Equipment Grounding Conductor, EGC, or Grounding Conductor
What is the general rule for the application of the EGC?
All noncurrent carrying metal parts of an electrical distribution system must be directly connected to or bonded to the EGC.
What is the role of the equipment grounding conductor (EGC) attached to metal parts of electrical devices?
For personnel safety to maintain all conductive parts of electrical systems at ground potential
To provide a low resistance return path so that the overcurrent protection device can operate in the event of a short-circuit between an ungrounded conductor and a non-current carrying conductive part of an electrical system
Is it possible to touch a high voltage circuit with your bare hand and not get shocked? Explain.
Yes, as long as you are 100% isolated from ground there will be no path for current flow.
This is how utility workers are able to work on energized electrical systems.
DO NOT ever try this because you will not have the proper equipment to 100% isolate you from ground
What are electricity’s two primary roles in society?
Most efficient way to transfer energy between to points
Communications