wound management
1/131
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
132 Terms
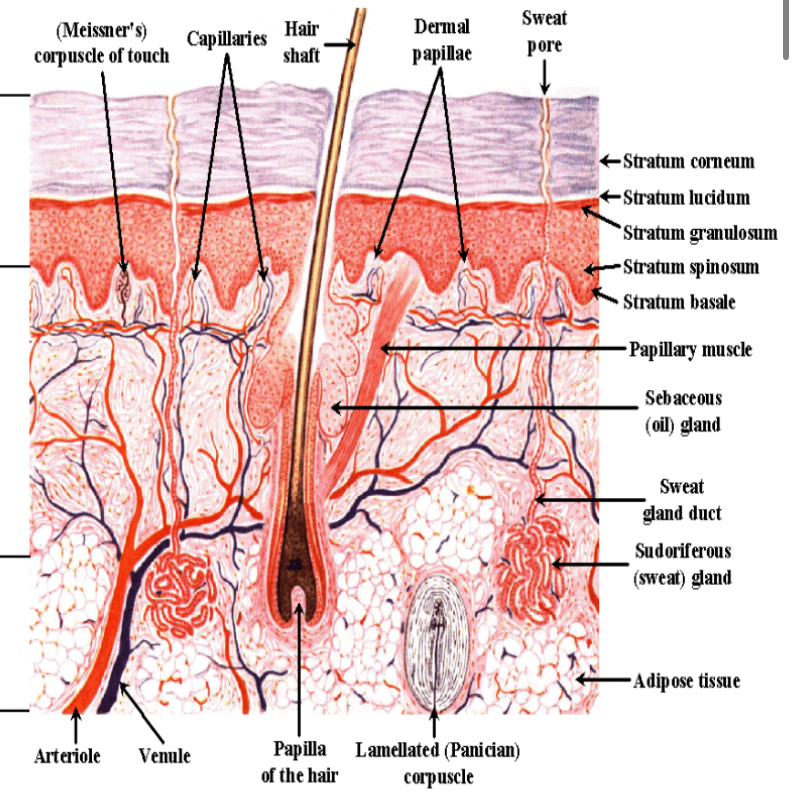
epidermis layers superficial→deep
stratum corneum
stratum lucidum
stratum granulosum
stratum spinosum
stratum basale
specialized epidermal cells
melanocytes—pigmentation
langerhans cells—infection barrier
merkel cells—infection barrier
dermis layers superficial→deep
papillary—thin layer of collagen
reticular—collagen, elastic tissue, reticular fibers; provides skin elasticity, more scarring when injured
epidermis
very thin
avascular
thickest on palmar hand & plantar foot
specialized dermal cells
sweat glands, sebaceous glands
subcutaneous tissue
provides thermal regulation
basement membrane
junction btwn dermis and epidermis
cancer metastasizes when it crosses this
more corrugated when younger, makes it firmer
more smooth/parallel when older, makes skin easier to tear (shearing)
acid mantle
provides protective coating
pH 4-5.5
low pH better (low pH lotion helps!)
CT injury
interruption in continuity
each phase has distinct characteristics
inflammation: immediate-2 weeks
proliferation: 48 hrs to 2-4 weeks
maturation: 2-4 weeks to 1-2 years
time frames of CT injury repair depend on
shape of wound, type of wound (acute v chronic), depth of wound (partial vs. full thickness), type of closure (pry vs. sec)
shapes of wounds & what they result from
round/elliptical—pressure
jagged edges—shear/friction
irregular—venous
linear—trauma/friction
acute wounds
heal by themselves uneventfully
surgical, trauma/burn, skin tear
complex non healing/chronic wounds
pressure injury
neuropathic (diabetic)
vascular—venous ulcer, arterial/ischemic ulcer
mixed—diabetic/arterial, venous/arterial
two mechanism of CT repair determined by depth
regeneration & repair
regeneration
partial thickness: epidermis & superficial dermis
heal by epithelialization
repair
heal by granulation, contraction, epithelialization
start by filling wound in with granulated tissue, then epithelialize and contract from outside in
wounds surgically repaired
full thickness: all layers
deeper wound=
more involved repair process
primary intention
closure by direct approximation without tension due to little loss
clean or clean-contaminated wounds— ex. surgical incisions, lacerations
within 4-8 hrs of injury
palpable healing ridge under suture during proliferation phase
ex. sutures, steri strips, dermabond, stitches
linear shaped wound cleaning techniques
gently wipe from top to bottom in one motion from wound outward starting directly over wound and moving outward
open circular wound cleaning techniques
gently wipe in concentric circles, starting directly over wound and moving outward
secondary intention
contaminated or dirty wounds
enough tissue loss cannot close w/o tension
delay in clinical consultation
wound is left open to heal spontaneously
delayed primary/tertiary intention
delayed closure after several days to weeks of healing
combo btwn pry and sec intention
surgical closure after granulation tissue present in wound bed—skin graft, skin flap, skin substitute
hemostasis
blood flows into wound
immediate vasoconstriction
vasocongestion
blood coagulation, platelet aggregation
fibrin-rich clot
seals disrupted vessels and fills tissue
vascular spasm→platelet plug formation→blood clotting
inflammation phase
mast cells release histamines: incr vasodilation
migration of leukocytes: polymorphic neutrophils (PMNs), monocytes (macrophages) for phagocytosis, release of GFs, matrix for cell migration
stim nociceptive receptors
phagocytosis
remove foreign debris
release of growth factors
initiates repair process
classic signs of inflammation
erythema, swelling, incr tissue temp, pain, los sof function
proliferation (collagen phase)
deposition of collagen (cross linking): fibroplasia
vascular integrity restored: neoangiogenesis
fibroplasia
fibroblast proliferation
collagen synthesis (Type III)
neoangiogenesis
formation of capillary sprouts
new capillary and arteriole production
results in development of granulation tissue
wound healing contraction
during proliferation
wound edges contract
fibroblasts and myofibroblasts create closure
shrinks defect
limited by tension in surrounding tissues
wound healing epithelialization
proliferation of keratinocytes
differentiation
clinical considerations of healing phases
maintain proper moisture of wound surface
granulation tissue is fragile
monitor for infection
consider underlying pathology
type III collagen doesn’t provide tensile strength
maturation
lasts up to 1 yr in normal healthy adult, 2 in child, elderly or immunocompromised pts
tensile strength incr to 80% ish
matrix remodeling—collagen synthesis/degradation, bond conversion (type III to I or II)
scar tissue compaction/contraction
normal scar
white or pink, indented below skin surface
hypertrophic scar
white, pink, or red, slightly raised; firm; follow wound borders
keloid scar
deep red or purple; very raised; firm; extend beyond wound borders
keloid scar treatment
surgical excision
laser
anti-histamines/corticosteroid therapy
cryotherapy w/ liquid nitrogen
radiation
responds poorly to reconstructive surgery
vancouver scar scale: vascularity
0=normal
1=pink (incr in blood supply)
2=red (greater incr in blood supply)
3=purple (significant vascularity)
vancouver scar scale: pliability
0=normal
1=supple
2=yielding
3=firm
4=banding
5=contracture
vancouver scar scale: pigmentation
0=normal
1=hypopigmentation
2=mixed pigmentation
3=hyperpigmentation
vancouver scar scale: height
0=flat
1=<2mm
2=2-5mm
3=>5mm
visual analog scale with scar ranking
scoring system: 0-100; excellent to poor
attributes: vascularity, pigmentation, acceptability, observer comfort + contour and summing individual scores
deficiencies: photo based, does not include patient
advantages: simpler than VSS; interrater and intrarater reliability easier to conduct
patient and observer scar assessment scale
scoring system: 5-50
attributes: VSS+surface area; pt assessments or pain, itching, color, stiffness, thickness, relief
deficiencies: may not adequately express pt perceptions and concerns
advantages: focuses on scar severity from clinician and pt perspective
adheremeter
measures adherence of post surgical scar (restriction or scar mobility)
good validity when compared to VSS at initial exam; less after rehab
good to excellent interrater reliability
excellent intrarater reliability
scar management: pain
extracorporeal shockwave therapy of 100 impulses per cm² on affected location (ESWT)
pulsed high-intensity laser therapy (HILT)
PT
massage 30 min at least 3x/week
scar management: pruritus
rehabilitation massage therapy, containing effleurage, friction, petrissage techniques
CO_2 laser
silicone gel sheets
scar management: pigmentation
silicone gel applied 2x/day on hypertrophic burn scars
silicone gel sheets
5 minute massage treatment
scar management: pliability
pulsed dye laser (PDL) therapy postsurgical scars (wavelength 585 nm w/ pulse duration of 450 ms)
massage
silicone gel and sheets (hypertrophic)
scar management: surface area
PDL (wavelength 585 nm, pulse duration 450 ms, mean fluence per pulse 7.0 J/cm²)—need more evidence on parameters
scar management: thickness
PDL (wavelength 585 nm, pulse duration 450 ms, mean fluence per pulse of 7.0 J/cm²)
joint mobilization and silicone and massage
takeaways of scar management
laser, silicone, massage
hx of wounds
how did the wound occur? (mechanism of injury)
when? (Timeline)—acute vs complex nonhealing/chronic
previous treatments
allergies—iodine, latex, bovine
last tetanus shot?
diagnostic tests
arterial: capillary refill (>5 seconds), ABI, tcPO2, doppler ultrasound (mono or biphasic waveforms)
venous: duplex ultrasonography
radiologic exams
lab values to consider
HbA1C
glucose
serum albumin
pre-albumin
CBC
total lymphocyte count
lipids and triglycerides
creatinine
HbA1C
long-term index of average blood glucose level
glucose
increased blood sugar levels associated with/ incr risk of ulceration and impaired wound healing
serum albumin
levels fall rapidly with protein deficiency and malnutrition
levels <3.5 mg/dL associated with longer length of stay and increased complications
there is a positive correlation btwn low serum albumin and pressure injury severity
pre-albumin
mortality risk increases as prealbumin levels drop; good indicator of effect of nutritional intervention
CBC
used to determine anemia, infection, oxygen-carrying capacity
SED rate will determine infection/inflammatory process
total lymphocyte count
indirect measure of nutritional status and immune function
decreased=associated w/ delayed wound healing, incr mortality
less than 1,500 cells/mm³ =immunocompromised
less than 1,200 cells/mm³=protein deficiency
lipids and triglycerides
level of risk for CV disease
creatinine
malnutrition decr creatinine levels
factors affecting wound healing
age >65
obesity
pressure/friction/shear
infection
nonadherence
lifestyle
health
medications
pain level
mobility
smoking
nutrition
comorbidities: stroke, HTN, PVD, diabetes, CV
effects of aging on wound healing
delayed wound contraction
decr tensile strength
decr epithelialization
decr inflammatory response
decr pain perception
decr mast cells
decr capillary growth
incr in wound dehiscence
pediatric considerations
poor wound care protocols
difficulty in rating pain
integumentary maturity at 33 weeks
decr dermal thickness
incr risk of medical device psi injury
epidermal stripping
epidermal injuries
decr epidermal to dermal cohesion
avoid adhesives, use silicone dressings
pediatric wounds
extravasation injuries
diaper dermatitis
congenital conditions—aplasia cutis, epidermolysis bullosa (NO tape, no gait belt, could cause sloughing)
factors affecting healing
current/PMH: diabetes, vascular insufficiency, previous wounds, sickle cell anemia, chemo, lymphedema, HIV/AIDS
radiation: injury to fibroblasts, decr collagen production, destruction of cells in mitosis, vascular damage, decr tolerance to bacterial burden
factors affecting healing: meds
NSAIDs: decr inflammation
immunosuppressive therapy: prostaglandins and WBC decr
steroids: inhibit collagen synthesis; topical affect epidermal resurfacing
factors affecting healing: pain
pt centered concern: incorporate words pt uses; neonates to 6mo—CRIES; 2mo-7yr—FLACC; children >7–VAS
cause of pain: infection vs inflammation; tissue debridement and trauma
moisture balance (too little=adherent dressing, bleeding; too much=exudate, odor, periwound maceration)
pain meds, modalities, distraction
factors affecting healing: obesity
impaired skin barrier repair: higher skin surface pH, incr sweat glands activity
impeded lymph flow
insulin resistance syndrome
decr vascularity of adipose tissue
excess tension on wound edges, incr likelihood of dehiscence
dehiscence
complication of wound healing including separation of skin and tissue layers that commonly occurs 3-11 days after injury
skin disease aggravated by obesity
skin infections—candida, cellulitis, necrotizing fasciitis (group A streptococci, staphylococcus aureus, fournier’s gangrene affects perineum)
increase in hospitalizations
necrotizing fasciitis
rapidly progressing anaerobic bacterial infection
appears red, swollen, hot, painful
skin becomes blue-gray, fluid filled blisters
full thickness skin loss
extensive gangrene
high mortality
factors affecting healing: social hx
smoking, alcohol, dietary intake, weight loss
activity level
financial resources
family support
home environment
international travel
pt motivation
factors affecting healing: nutrition
nutrients to meet energy demands or cellular proliferation and repair
poor nutritional status can delay wound healing
malnutrition is diagnosed if:
serum albumin levels below 3.5mg/dL
total lymphocyte count <1,800 cells/mm³
BW decr by 15%
systems review
CVP system
integumentary: shoes and orthotics, W/C fit
MSK: gross screen
NMSC:transfers, gait, use of ADs
communication ability, affect, cognition, language and learning style
instruments used to monitor healing
sussman wound healing tool (SWHT)
wound healing scale
pressure sore status tool
wound healing scale
national pressure ulcer advisory panel pressure ulcer scale for healing (PUSH)
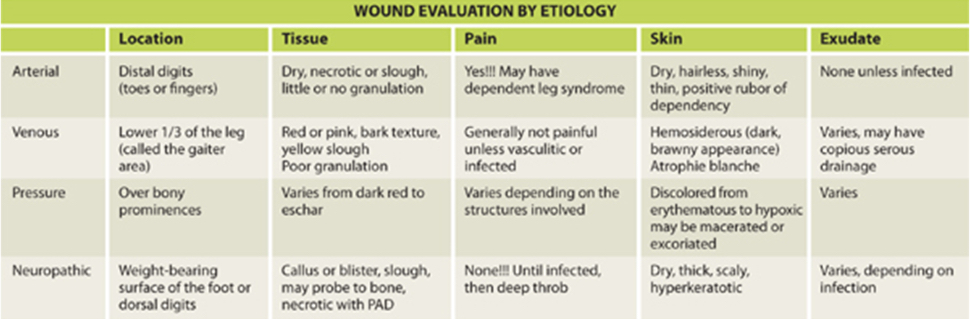
identify wound etiology
acute: heal by themselves uneventfully—surgery, trauma/burn, skin tear
complex nonhealing (chronic) wounds
wound assessment: size
linear measurement: length x width x depth
greatest length x greatest width method
wound edge to wound edge in a straight line
measure in cm
clock method, wound as face of the clock
12 is head, 6 toward feet, 3 to 9 side to side
on feet, heel=12 toes=6
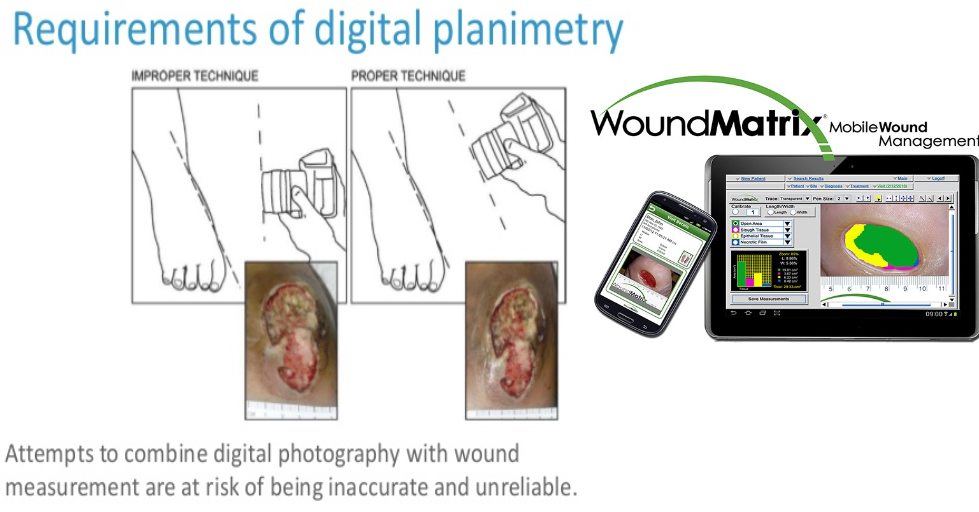
wound photography
need informed consent
confidential, accurate pt ID
control timing of photographs
criteria for validating competency
camera equipment/techniques
guidelines on cell phones
information on maintaining photographs safely
effective method of releasing copies to pt
wound planimetry/digital imaging
wound assessment: depth
staging: psi injuries only
partial thickness: involves epidermis and portion of dermis
full thickness: entire epidermis and dermis, extends in subq tissue, potentially beyond fascial plane; slough and/or eschar
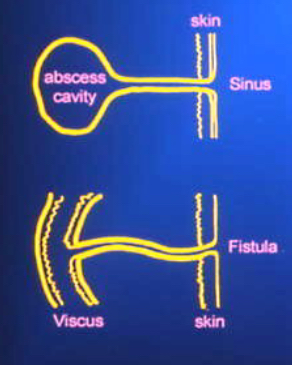
tunneling
channel or pathway extends in any direction from the wound through subq tissue or muscle, resulting in dead space w/ potential for abscess formation
=sinus tract

undermining
tissue destruction underlying intact skin along wound margins/edges
caused by shearing
measured at 12, 3, 6, 9 position
=fistula

sinus tract
blind ended tract from surface of skin to underlying area or abscess cavity
caused by degradation of subq tissue in a linear manner
pack
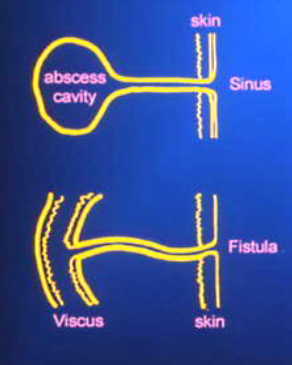
fistula
abnormal communication btwn 2 or more structures or spaces
“sinus tract that forms between two organs)
caused by a dehisced wound or surgical incision
tx by surgery, NPWT
drain

red wound base
clean; healing; granulation

yellow wound base
possible infection; needs cleaning; necrotic (slough)

black wound base
needs cleaning; necrotic (eschar)
granulation tissue
growth of small blood vessels and connective tissue into the wound cavity (capillary buds)
bright, beefy, red, shiny, granular
may bleed easily (angiogenesis)
exposed structures: tendon, bone
documentation of granulation
% of tissue type & location (rule of 5s)
skin intact/partial thickness wound
bright, beefy red; 75% to 100% of wound filled and/or tissue overgrowth
bright, beefy red; <75% & >25% of wound filled
pink and/or dull, dusky red and/or fills <25% of wound (anemia or poor blood flow)
no granulation tissue present (agranular)
hypergranulation

agranular/friable

necrosis
eschar, slough, pseudoeschar
adherence?
adherent slough

loosely adherent slough

wound edge: contraction

wound edge: adherence
