Unit 6 - World War I (1914-1919)
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
Nationalism
A sense of unity binding the people of a state together; devotion to the interests of a particular country or nation, an identification with the state and an acceptance of national goals.

Prohibition
18th Amendment, established in 1919 and ratified in 1920 lasting until 1933; the manufacture, distribution and sale of alcoholic beverages was prohibited in the United States by a constitutional amendment. Largely passed as a measure to conserve resources for the WWI war effort.

Woodrow Wilson
Progressive President during World War I, ..., 28th president of the United States, known for World War I leadership, created Federal Reserve, Federal Trade Commission, Clayton Antitrust Act, progressive income tax, lower tariffs, women's suffrage (reluctantly), Treaty of Versailles, sought 14 points post-war plan, League of Nations (but failed to win U.S. ratification), won Nobel Peace Prize

Zimmerman Telegram/Note
1916 - A top secret telegram sent by German Foreign Secretary, addressed to German minister in Mexico City directing him to give it to Mexico if the US declared war on Germany due to unlimited submarine warfare. Stipulated that 1) make war with Germany who would assist Mexico in getting back Tex, NM, Arizona etc to Mexico. 2) Germany would give Mexico generous financial support 3) approach Japan to make and alliance with the. Telegram was intercepted by the Brits and given to U.S.. Printed in U.S. Papers - added to increasingly negative attitude toward the central powers.

Lusitania
A British passenger ship that was sunk by a German U-Boat on May 7, 1915. 128 Americans died. The sinking greatly turned American opinion against the Germans, helping the move towards entering the war.

Sussex Pledge
1916 - Germany promises to the U.S. to give warning to unarmed ships after the loss of Early in 1916, Germany had instituted a policy of unrestricted submarine warfare, allowing armed merchant ships - but not passenger ships - to be torpedoed without warning. Despite this avowed restriction, a French cross-channel passenger ferry, the Sussex, was torpedoed without warning on March 24, 1916; the ship was severely damaged and about 50 lives were lost.

Fourteen Points Plan
1917 - peace program presented to U.S. Congress by Pres. Woodrow Wilson to persuade Germany to agree to an armistice - if the Kaiser left the throne. Called for 1) evacuation of German-occupied lands; 2) re-drawing of borders & settling territorial disputes for populations seeking self-determination - nationhood; 3) creating an association of nations to preserve the peace / guarantee their territorial integrity; 4) freedom of navigation on the oceans.

Treaty of Versailles
Treaty signed in 1919 that ends WWI and is considered a major factor in the cause of WWII - 1) est. League of Nations; 2) Germany was responsible for starting war; required to pay reparations; German army and navy severely reduced; Rhineland a demilitarized buffer zone; 3) new nations in East, Southeast Europe, Middle East; German colonies become French, UK, or Japanese protectorates; BUT THE US NEVER SIGNED IT - WE SIGNED A SEPARATE PEACE TREATY!

Reparations
Compensation or repayment; compensation payable by a defeated nation for damages sustained by another nation as a result of hostilities., Cash payments for the damage of war. Germany was forced to pay $300 billion in damages for WWI which crippled them economically in the 20's leading to radical totalitarian regimes taking over

First Great Migration
In 1900 90% of African Americans lived in the South. From 1910-1930 blacks began moving north; PUSH FACTORS: agricultural changes (machines), violence and repression (KKK, Jim Crow laws), and economic repression (sharecropping system); PULL FACTORS: economic opportunities (industrial jobs - ESP WWI!), political opportunities (black enclaves), media campaigns (black newspapers)
18th Amendment
1919- Progressive amendment that made the production and sale of alcohol illegal in an attempt to improve morality and family life. Largely passed in an effort to conserve resources for WWI.

Victory Gardens
1917 - Americans grow their own foot - vegetables and fruit in order to help families who could no longer buy as much food as they were used to because of inflation and conserve for the war effort.

League of Nations (1919)
Part of Woodrow Wilson's plan for lasting peace, it was the first international organization founded in to promote world peace and cooperation but was weakened when the U.S. refused to join. The organization failed to stop aggression by Italy, Japan, and Germany in the 1930s, but laid the foundation for the creation of the UN after WWII.

war- guilt clause
in treaty of Versailles; declared Germany and Austria responsible for starting WWI; ordered Germany to pay reparation to Allied powers
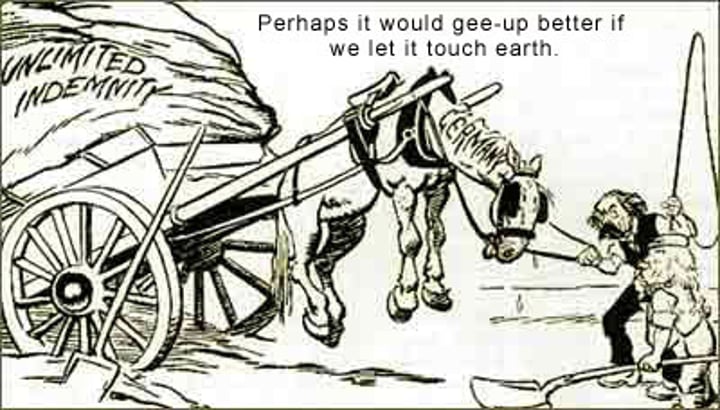
American Expeditionary Forces
lead by John J. Pershing, AEF, military forces fighting in Europe; soldiers were nicknamed "Doughboys".

World War One
militarism. alliances. nationalism. imperialism. assassination. competition for colonies - these are the causes of.......
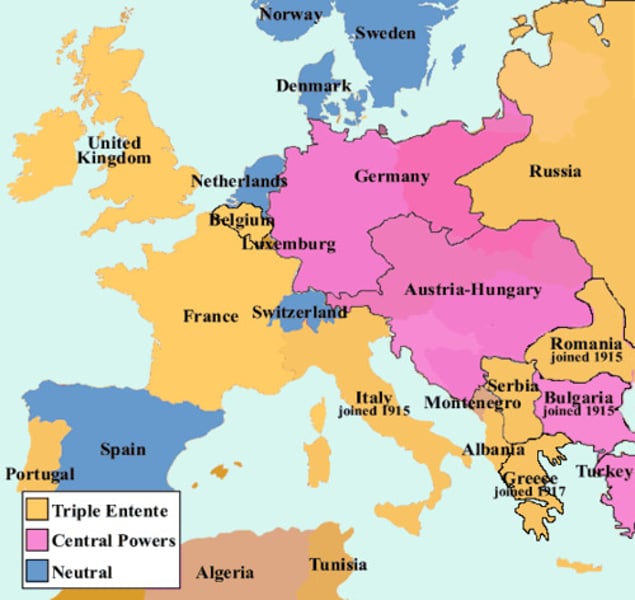
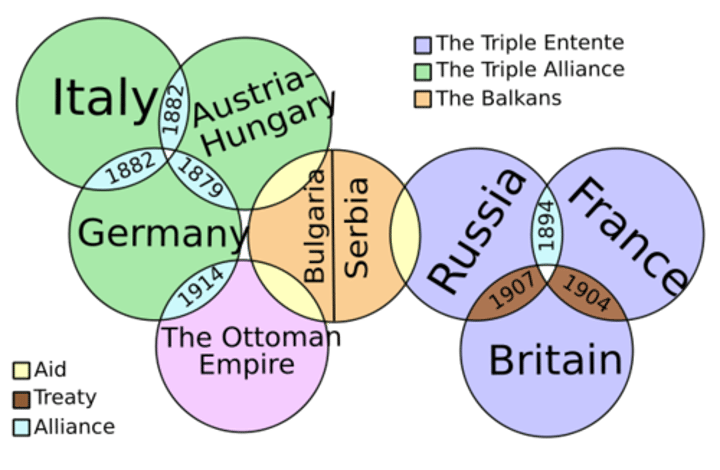
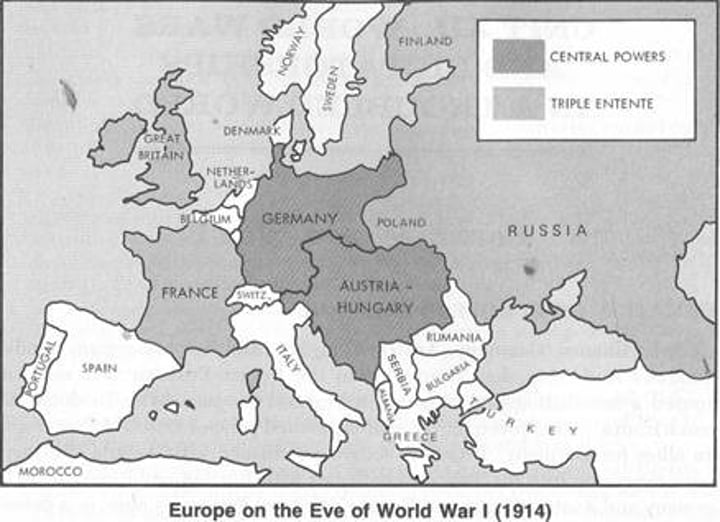
Triple Alliance - Central Powers
..., in World War I the alliance of Germany and Austria-Hungary and other nations allied with them in opposing the Allies
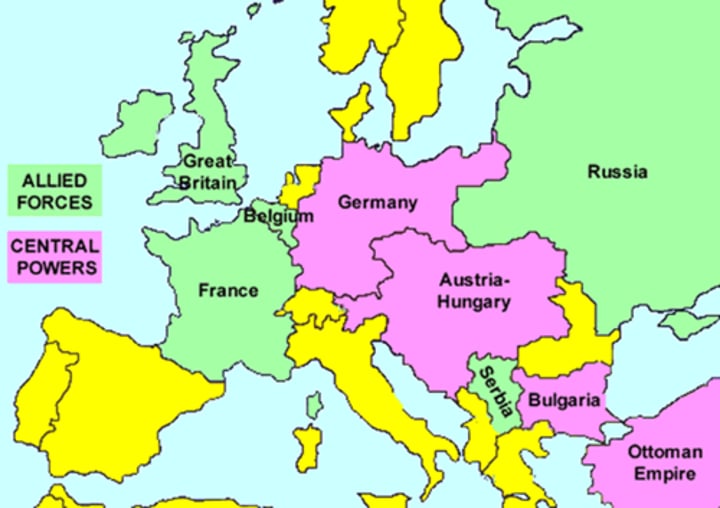
conscription
A forced enlistment of citizens of a country to fight for their country. A major reason why WWI was so huge in terms of deaths/wounded - massive armies

U-boats
Nickname for German submarines used to halt international trade with Britain and were a new piece of technology - a key factor in drawing the US into WWI.

sedition
Behavior that promotes rebellion, resistance or civil disorder against the state; inciting resistance to lawful authority and tending to cause the disruption or overthrow of the government.

Espionage Act
1917 This law, passed after the United States entered WWI, imposed sentences of up to twenty years on anyone found guilty of aiding the enemy, obstructing recruitment of soldiers, or encouraging disloyalty. It allowed the postmaster general to remove from the mail any materials that incited treason or insurrection.
espionage
N. The act of spying, especially a government spy obtaining secrets of another government
armistice
Agreement to stop fighting
unrestricted submarine warfare
A policy that the Germans announced on January 1917 which stated that their submarines would sink any ship in the British waters
new technology in World War I
Tanks, airplanes, machine guns, poison gas, flame throwers, grenade launchers
propaganda
Ideas spread to influence public opinion for or against a cause
war bonds
Short-term loans that individual citizens made to the government that financed two-thirds of the war's cost in both WWI and WWII.

The Triple Entente (Alliance)
Allies of World War I - Composed of France, Britain, and Russia, and later Japan and Italy, the Allies fought the Central Powers. The United States joined the them in 1917.
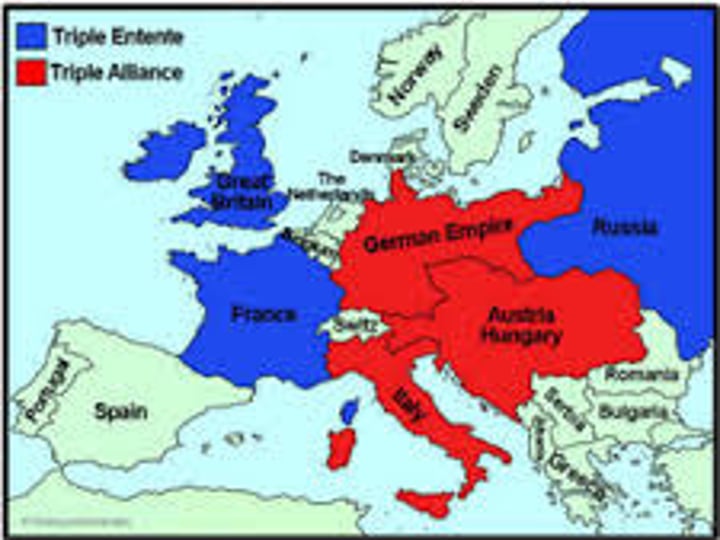
militarism
A policy of glorifying military power and keeping a standing army always prepared for war. A cause of WWI.

Selective Service Act 1917
This 1917 law provided for the registration of all American men between the ages of 21 and 30 for a military draft. By the end of WWI, 24.2 had registered; 2.8 had been inducted into the army. Age limit was later changed to 18 to 45.

alliances
Agreements between nations to aid and protect one another
convoy system
Protection of merchant ships from U-boat attacks by having ships travel in large groups escorted by warships.

self-determination
the right of people to choose their own form of government without outside interference.

sovereignty
Ability of a state to govern its territory free from control of its internal affairs by other states or nations

mobilization
Act of assembling and putting into readiness for war or other emergency: "mobilization of the troops".

conscientious objector
A person who is unwilling to participate in war and/or the military for reasons of personal belief about violence.
Sedition Act
..., 1918-Made it a crime to criticize the government or government officials. Opponents claimed that it violated citizens' rights to freedom of speech and freedom of the press, guaranteed by the First Amendment. About 2000 people jailed, half convicted (Eugene Debs)

Article 10 (Article X) of the Versailles Treaty
a portion of the Treaty of Versailles that REQUIRED members of the League of Nations to go to war if a member was attacked/invaded; this convinced the Republican-dominated (Henry Cabot Lodge) US Senate to not ratify the Treaty of Versailles - fear of Congress losing its power to declare war - given up to membership in the league and would lead to more foreign entanglements.
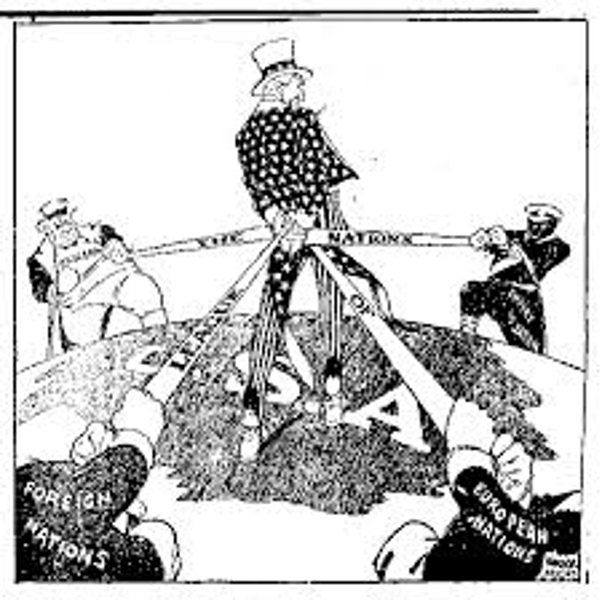

Committee on Public Information
It was headed by George Creel. The purpose of this committee was to mobilize people's minds for war, both in America and abroad. Tried to get the entire U.S. public to support U.S. involvement in WWI. Creel's organization, employed some 150,000 workers at home and oversees. He proved that words were indeed weapons. (propaganda spread through creating posters, employed actors in Hollywood and pushed slogans like - The War to End All Wars; War for Democracy)

Schenck v. US.
1919 man distributed leaflets saying conscription was unconstitutional; convicted because it threatened public order which means it did not pass the clear and present danger test; Supreme Court ruled that during wartime, words tolerable in peacetime can be punished if they present a clear and present danger to society

War Industries Board
Agency established during WWI to increase efficiency & discourage waste in war-related industries., Headed by Bernard Baruch, could order businesses to support war by building more plants, etc.

Food Administration
Created by Wilson during WWI - Led by Herbert Hoover - set up ration system to save food for soldiers; The slogan used to Conserve was "Hooverize" - also assisted in saving a starving Europe after WWI.

Fuel Administration
Like the Food Administration, the Fuel Administration encouraged Americans to save fuel with "heatless Mondays" and "gasless Sundays." The actions helped create a sum of $21 billion to pay for the war. Save coal and gas. Also promoted daylight savings time.

National War Labor Board
A federal agency founded in 1918 that established an eight-hour day for war workers (with time-and-a-half pay for overtime), endorsed equal pay for women, and supported workers' right to organize. Made agreements that Unions had worked for and been attacked for previous to the war - Unions signed no strike pledges.

Selective Service Act
This 1917 law provided for the registration of all American men between the ages of 21 and 30 for a military draft. By the end of WWI, 24.2 had registered; 2.8 had been inducted into the army. Age limit was later changed to 18 to 45.

Red Summer 1919
Used to describe the bloody race riots that occurred during the summer and autumn of 1919 (response to the Great Migration from the South due to competition for jobs and space) Race riots erupted in several cities in both the North and South of the United States. The three with the highest number of fatalities happened in Chicago, Washington, D.C. and Elaine, Arkansas.
Article #10 of the League of Nations
Key component to the the charter of the League of Nations which established "collective security" by mandating that all member nations would be required to protect the sovereignty and territorial status of other nations if attacked. Similar to the alliance systems of prior to WWI and would essentially require member nations to use military force to protect others as determined by the League of Nations. Opposed in the U.S. because it would take war making powers away from Congress and draw us out of isolation into unwanted wars.
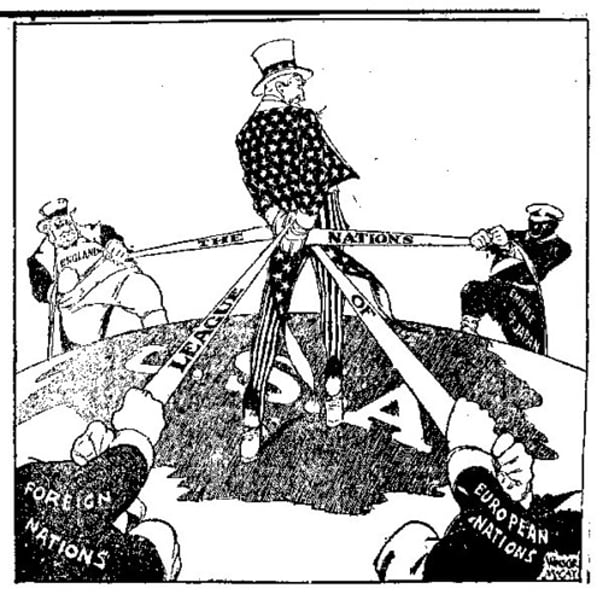

Balance of Power
A condition of roughly equal strength between opposing countries or alliances of countries. This was the goal of the alliance systems established before WWI - so that one side did not have a definite advantage over the other so that it had no incentive to go to war or feel that it had a strong chance of winning it. In this way peace was to be maintained.
managerial warfare
The practice of planning for war in peacetime; this includes strategies, training, preparing supplies for all scenarios. This meant that the nations of Europe were very prepared for war when the opportunity arrived.
isolationism
A policy of non-participation in international economic and political relations. This was the precedent set by George Washington in his farewell address in 1797, encouraging commerce but discouraging political alliances - especially Europe until World War I, when the U.S. joined on the side of the Allies - Britain and France. With the harsh conditions and concerns over the League of Nations drawing the U.s. into foreign entanglements, the Treaty of Versailles was rejected and the U.S. returned to isolationism in the 1920's and 1930's.
irreconsilables
After WWI, U.S. senators, mostly Republican were opposed to ratification of the Treaty of Versailles on any grounds; lead by isolationists William Borah, Hiram Johnson, and Robert La Follette were know as __________________ did not want League of Nations and feared its requirement to defend all member nations would esult in future 'entanglements and a loss of Congress's war making powers.
reservationists
After WWI, U.S. senators, mostly Republican were opposed the Treaty of Versailles, but might approv of it with some changes; lead by Henry Cabot Lodge they were know as __________________ did not want League of Nations and feared its requirement to defend all member nations would result in future 'entanglements and a loss of Congress's war making powers.

Americanism
After World War I, deep feelings of patriotism and anti-German (zenophobia - fear of foreigners) sentiment gave rise to the 100 Percent _______________ movement. The movement celebrated all things American while it attacked ideas (and people) it viewed as foreign and/or anti-American. (Extreme Nationalism)
Unlimited Submarine Warfare
(1917) The strategy used by Germany after Russia left WWI to launch a final effort to win the war on the Western front. The strategy was stated in the secret Zimmerman Note. Germany would sink all ships entering, without warning, the war zone off the coasts of Allied Nations. Germany realized that it might draw the U.S. into WWI. Germany believed cutting Allied supplies would allow Germany to win the war before the U.S. could make a difference. In response the U.S. broke diplomatic relations with Germany; ultimately led to the U.S. declaring war for attacks on neutral ships soon after.