mitochondria
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
what % of cell is composed of water ?
70
catabolic pathways
generate energy by break down of large molecules to smaller ones
anabolic
use energy to build large molecules from smaller ones
homeostasis
state of balance catabolism = anabolism
ATP is hydrolysed to…
ADP + inorganic phosphate
the hydrolysis of one ATP molecule generates how much free energy ?
7.3 kcal/mol
what does the chemiosmotic coupling theory state ?
ATP is generated by use of energy stored in form of protein gradients across biological membranes
draw the process of oxidative phosphorylation as per the chemiosmotic theory model
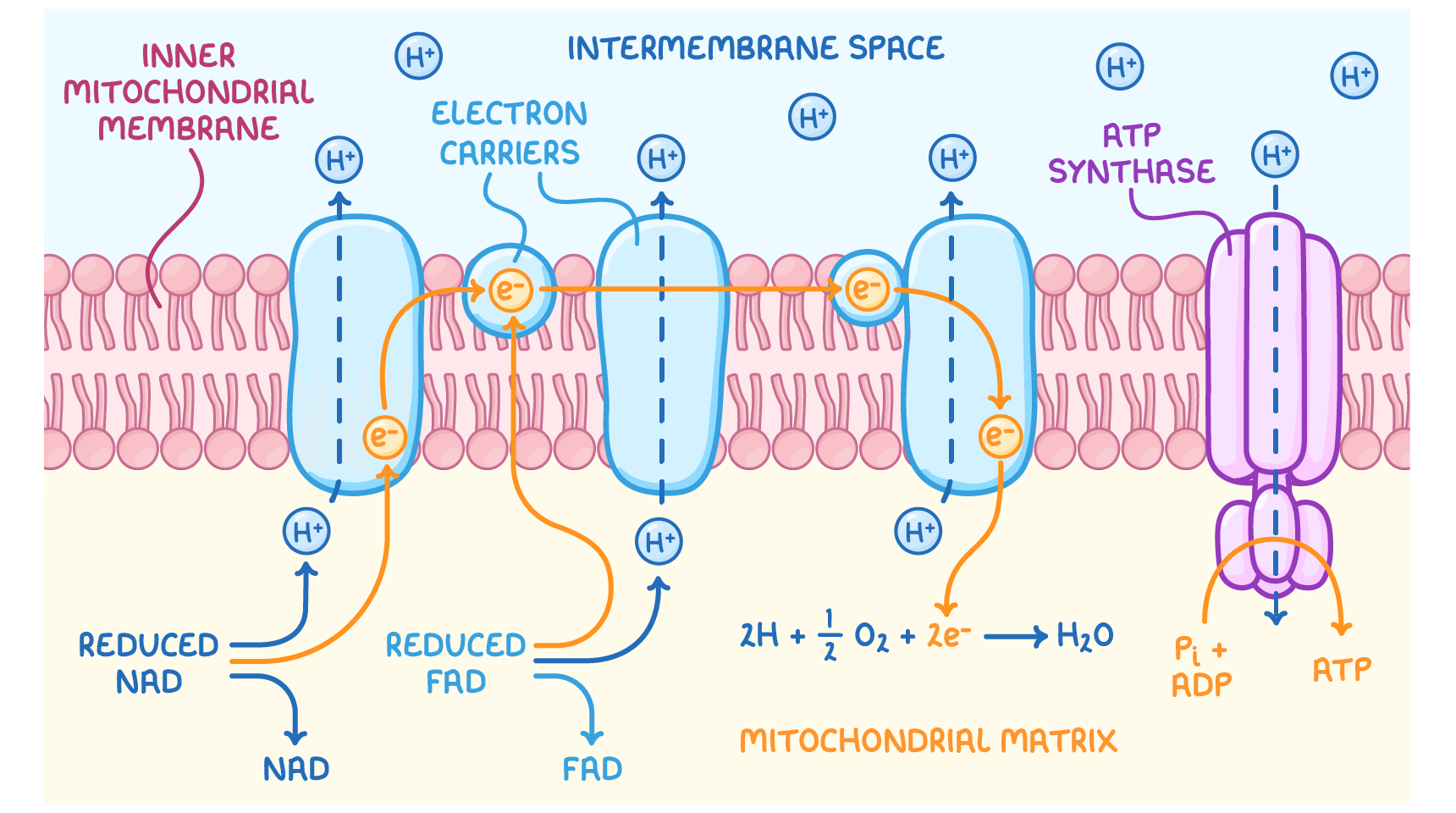
porins in the outer membrane of the mitochondria are permeable to what molecules ?
ions and molecules < 5 kDa
where are the ETC proteins located ?
cristae of inner mitochondrial mem
where do the TCA cycle and fatty acid oxidation occur ?
mitochondrial matrix
4 main functions of mitochondria
buffering redox potential in cytosol, urea production, biosynthesis of haem groups and ROS production
ROS
reactive oxygen species
what is a redox pair ?
oxidising and reducing eg. NAHD and NAD+
what are the 4 stages of respiration ?
glycolysis, link reaction, TCA cycle, ETC
aside from ATP and pyruvate what can glycolysis produce ?
biosynthetic intermediates like nucleotides and AA
anapleurosis
re-filling of catalytic intermediates
in what order are the protein complexes of the ETC found ?
NADH dehydrogenase, ubiquinone, cytochrome b-c, cytochrome c, cytochrome oxidase
where does pyruvate oxidation occur ?
in the mitochondrial matrix
list the intermediates between acetyl coA and oxaloacetate in the TCA cycle
citrate isocitrate a-ketoglutarate, succinyl, succinate, fumarate, malate
how many molecules of NADH FADH and ATP are produced by TCA cycle per glucose molecule (2 turns)
6 2 2
how does glutamine prevent reduced TCA function as a result of citrate loss to biosynthetic pathways ?
serves as alternative carbon source - converted to glutamate and a-KG which act as anapleurotic subs for the TCA cycle
lactic acidosis
accumulation of lactate in blood leading to acidic pH levels