Rhytmn Test
1/69
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Remember: What is the Rate? Is it Regular? Is there a P wave before every QRS. Is the P wave upright and uniform? What is the PRI? Are all the QRS complexes the same? What is the QRS length?
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
70 Terms
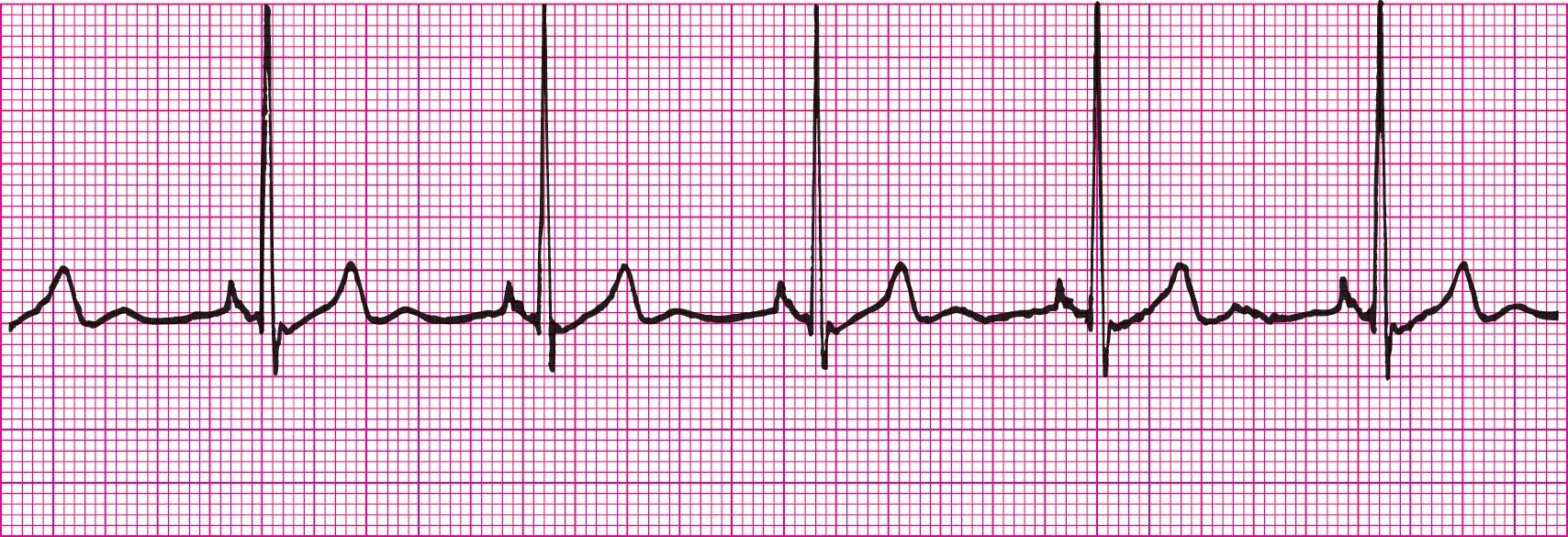
NSR
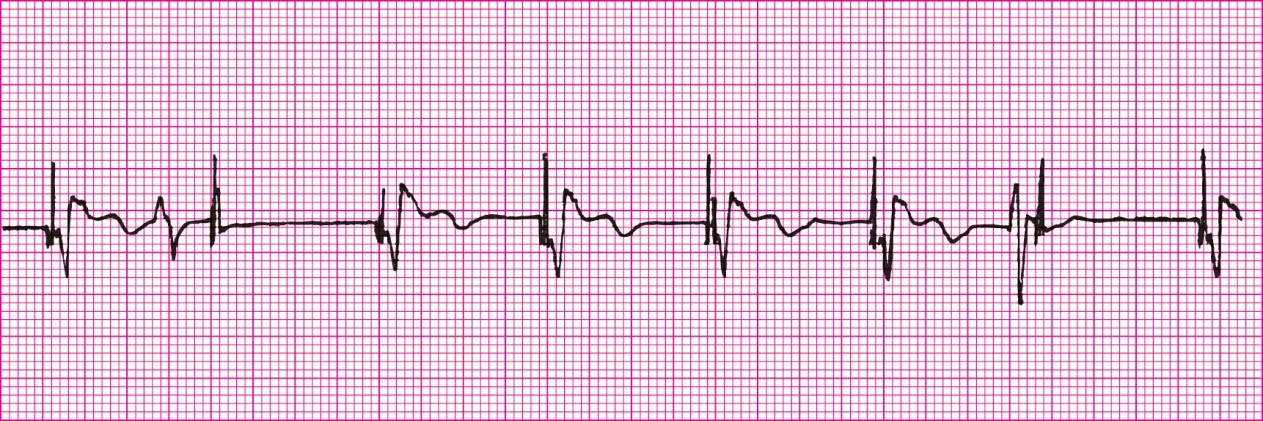
Sinus Tachycardia
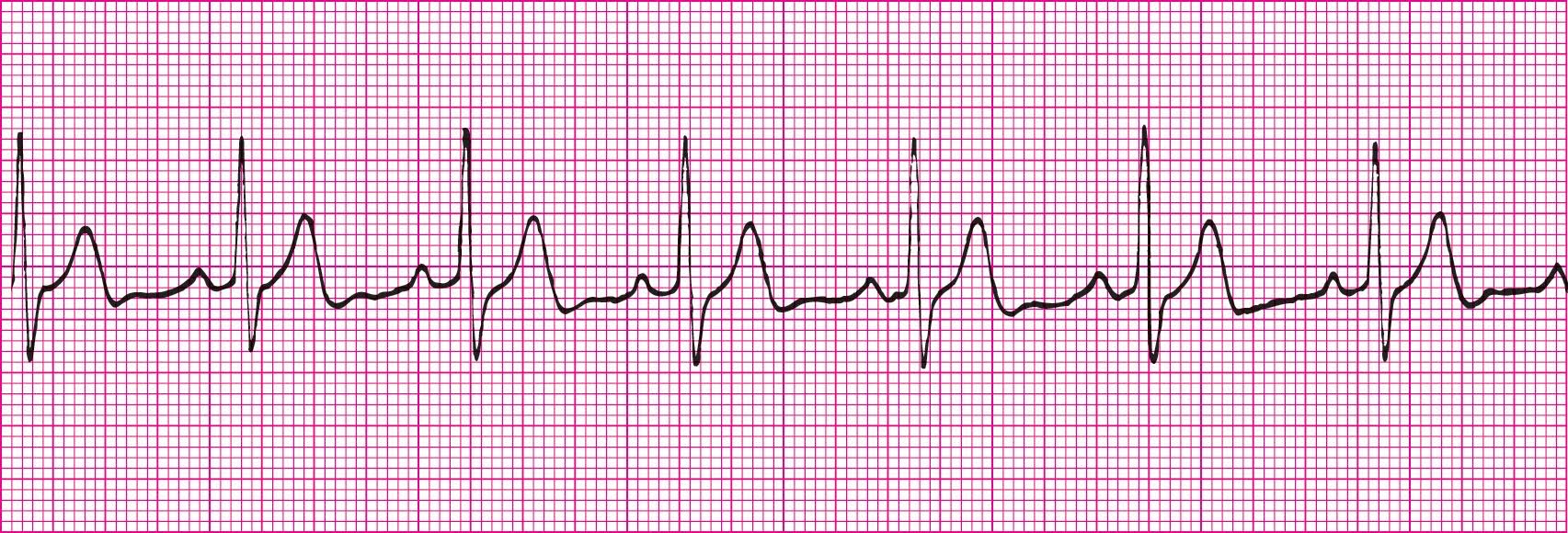
Sinus Brady
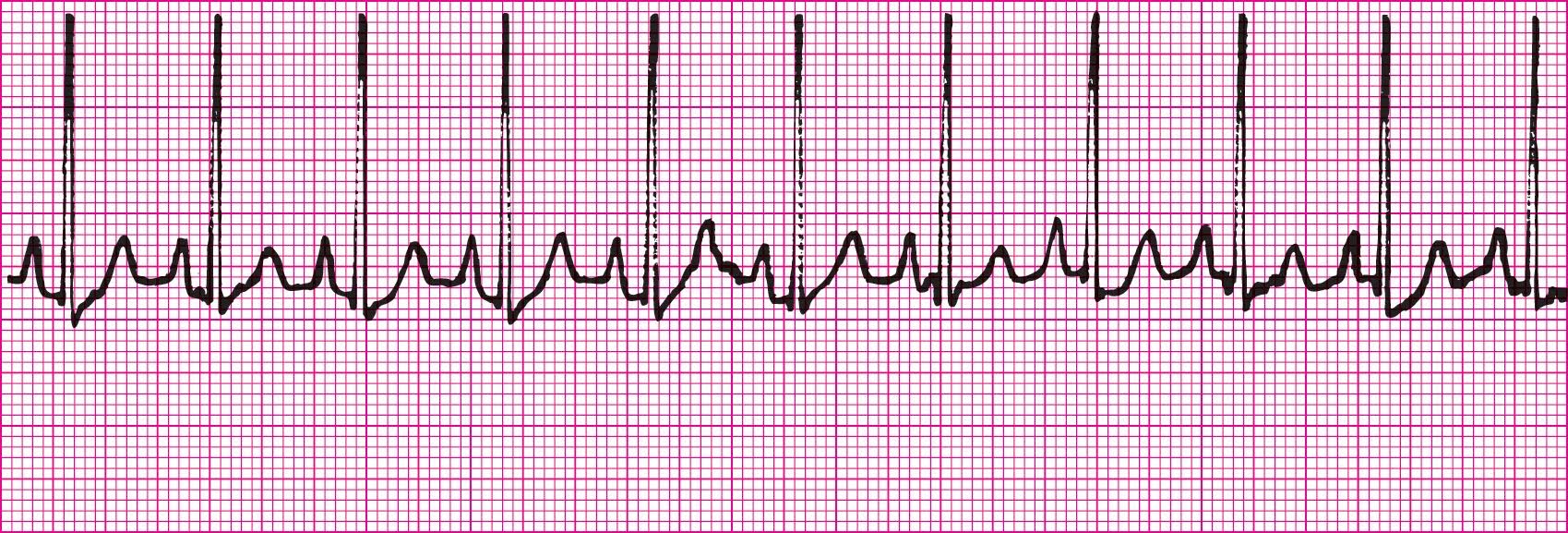
Sinus Dysrhythmia
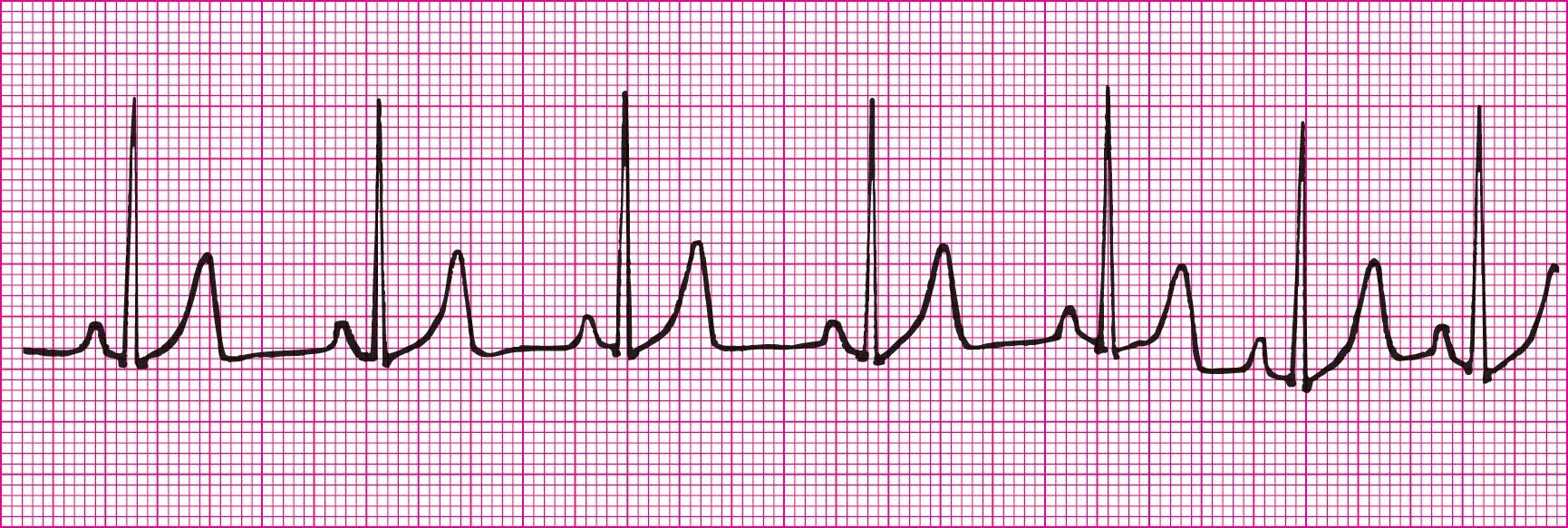
Sinus Brady with Sinus arrest
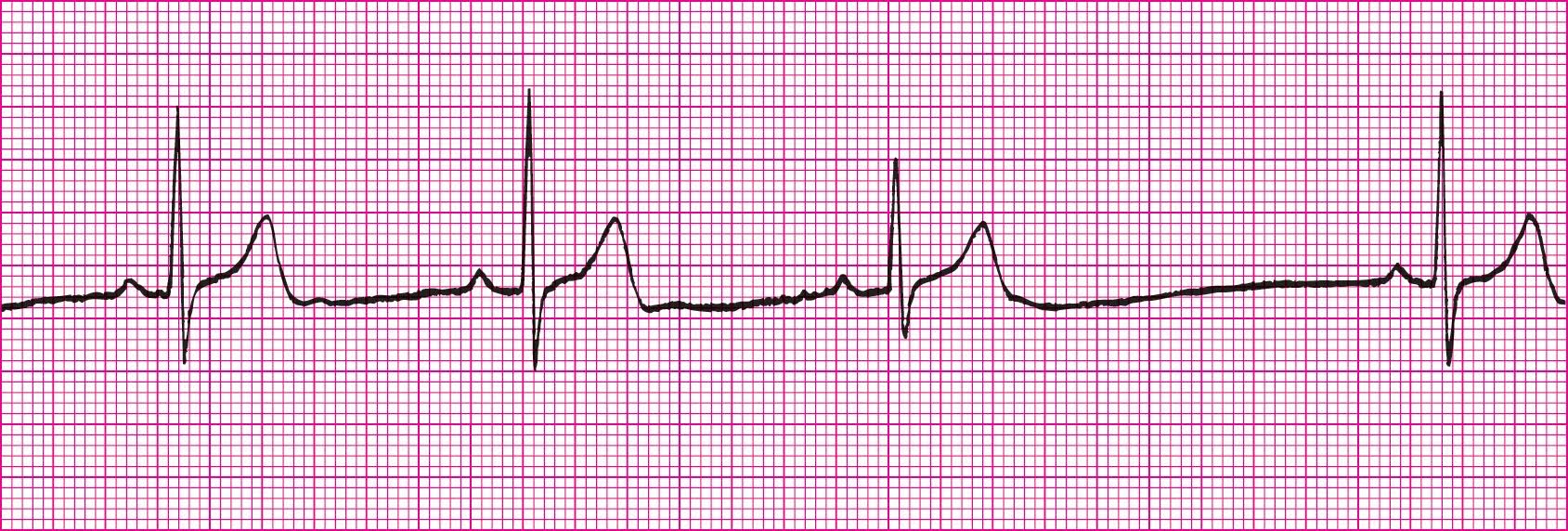
Sinus Dysrhythmia
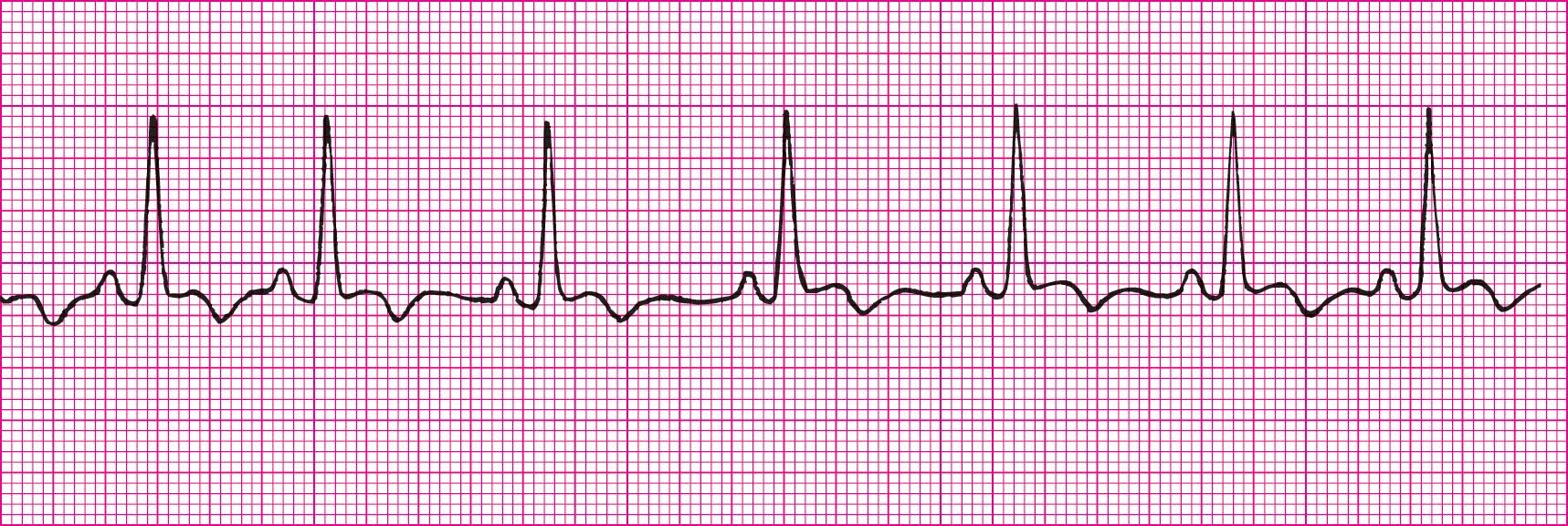
Sinus Tach
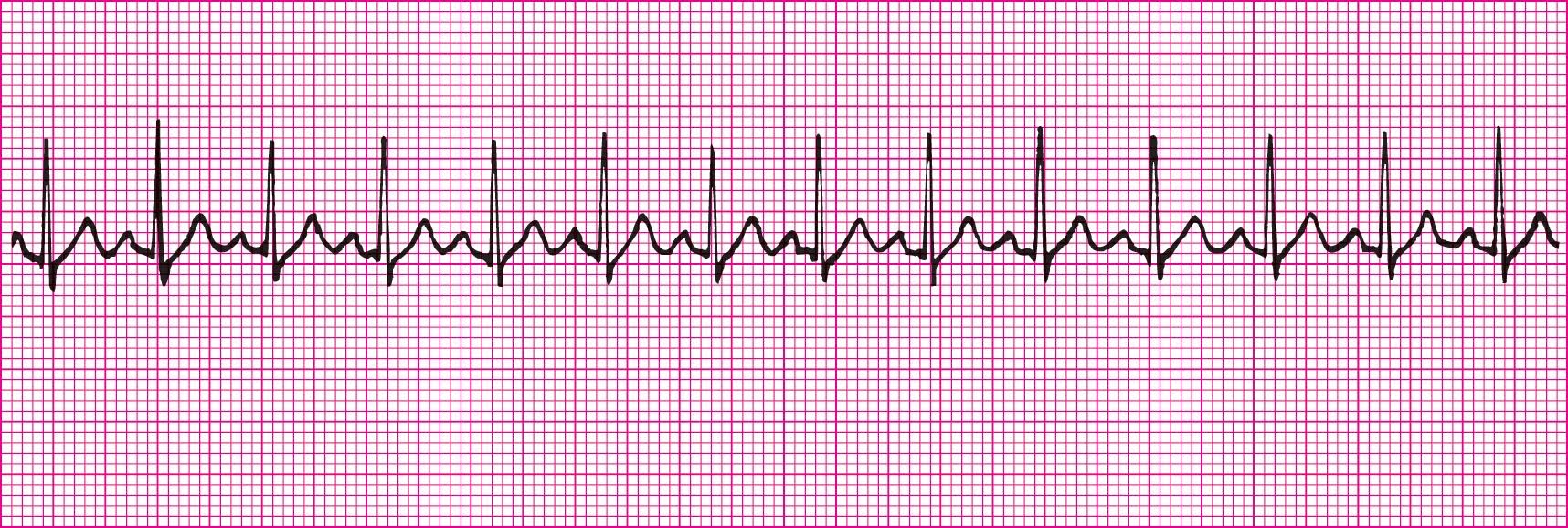
Sinus Dysrhythmia
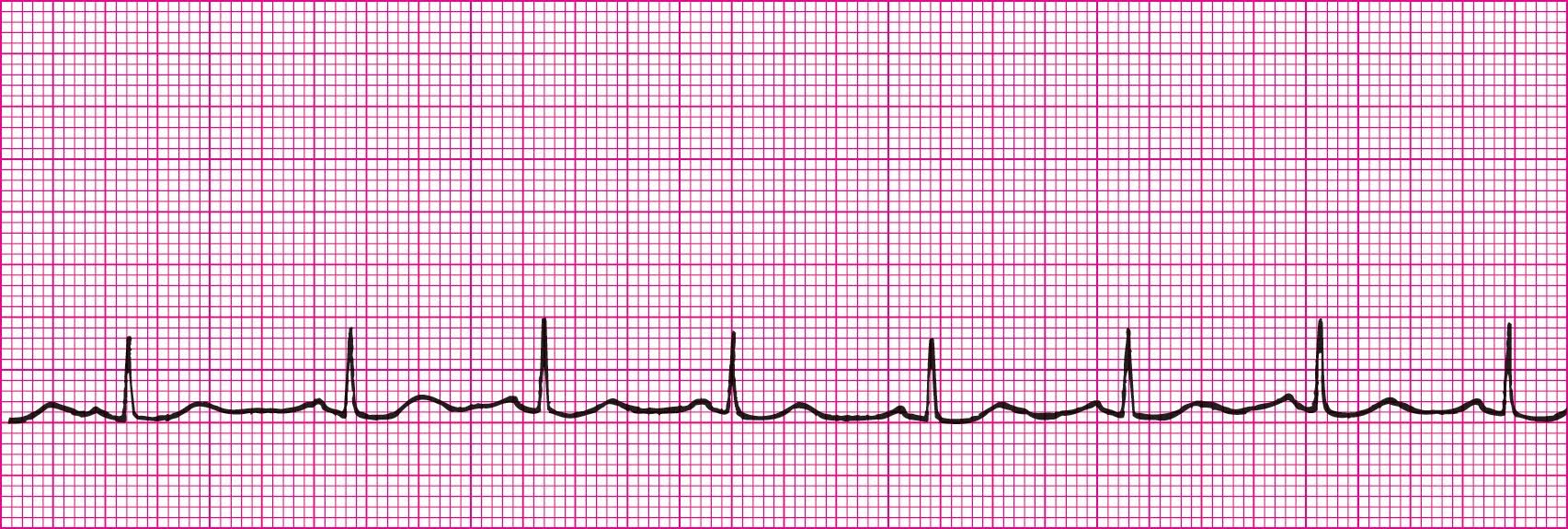
Sinus Brady
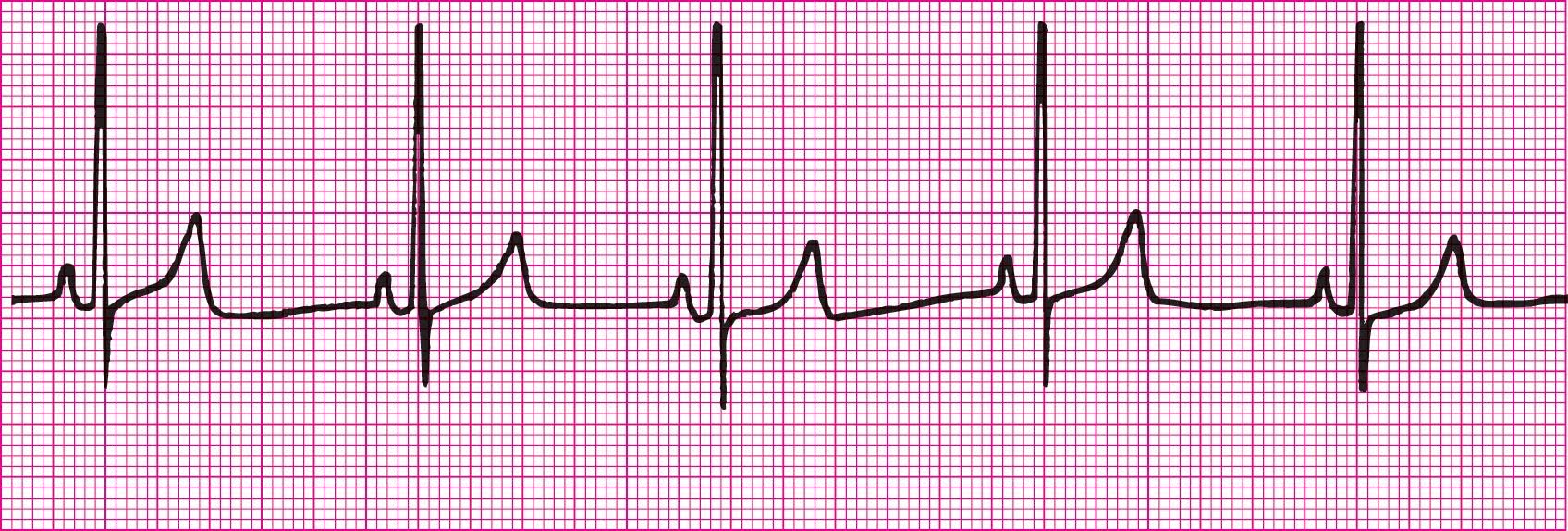
Sinus Rhythm with Sinus Arrest
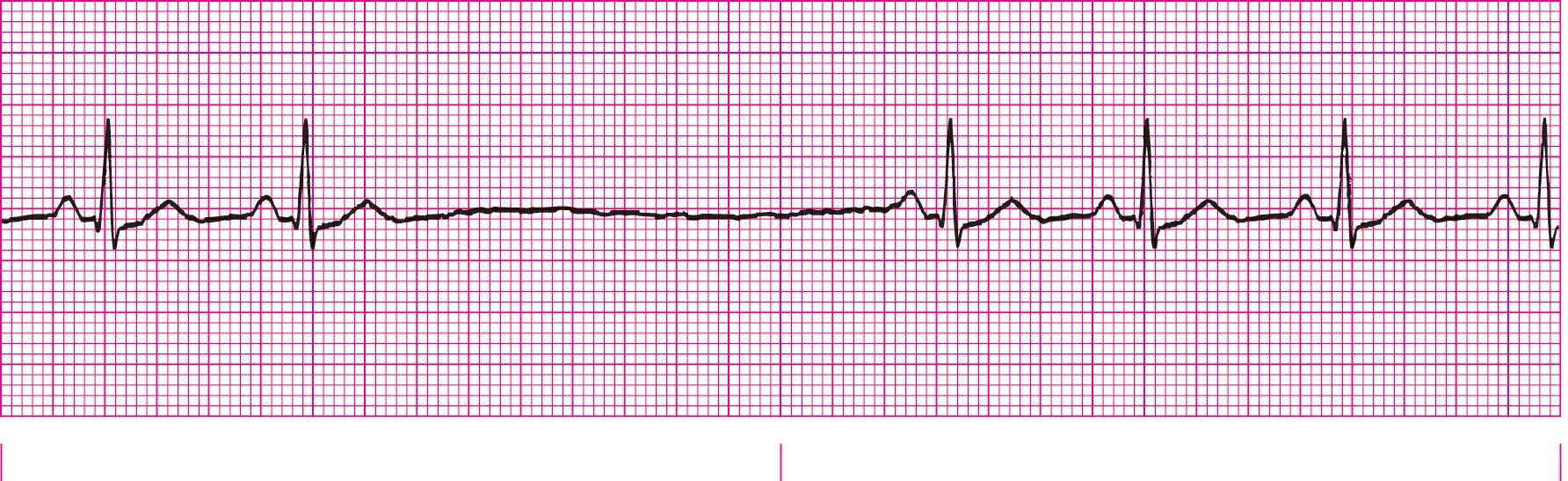
Wandering Atrial Pacemaker
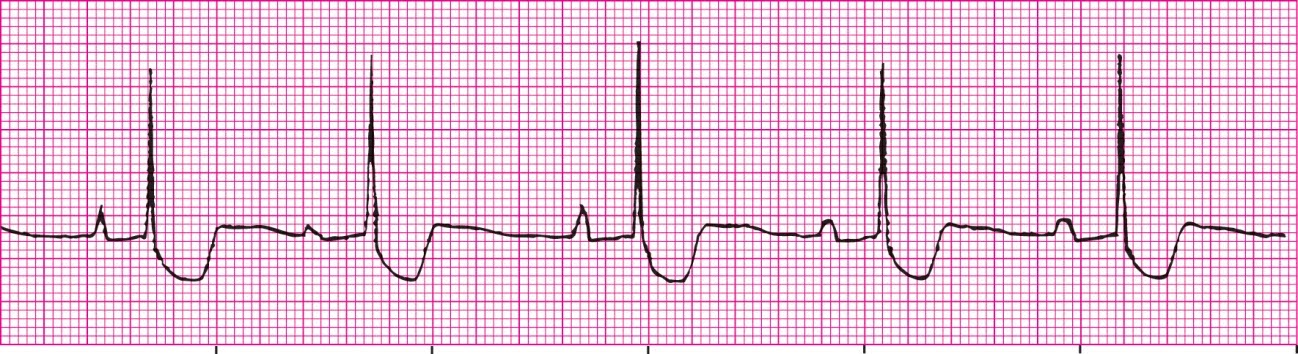
Atrial Flutter 4:1 Ratio
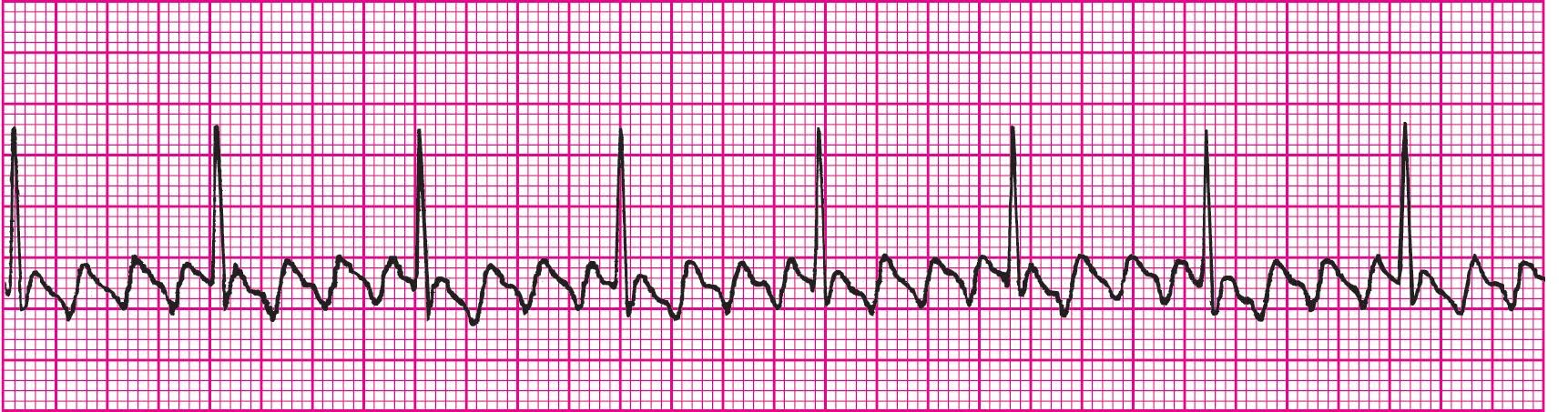
Atrial Fibrillation (Irregularly Irregular)
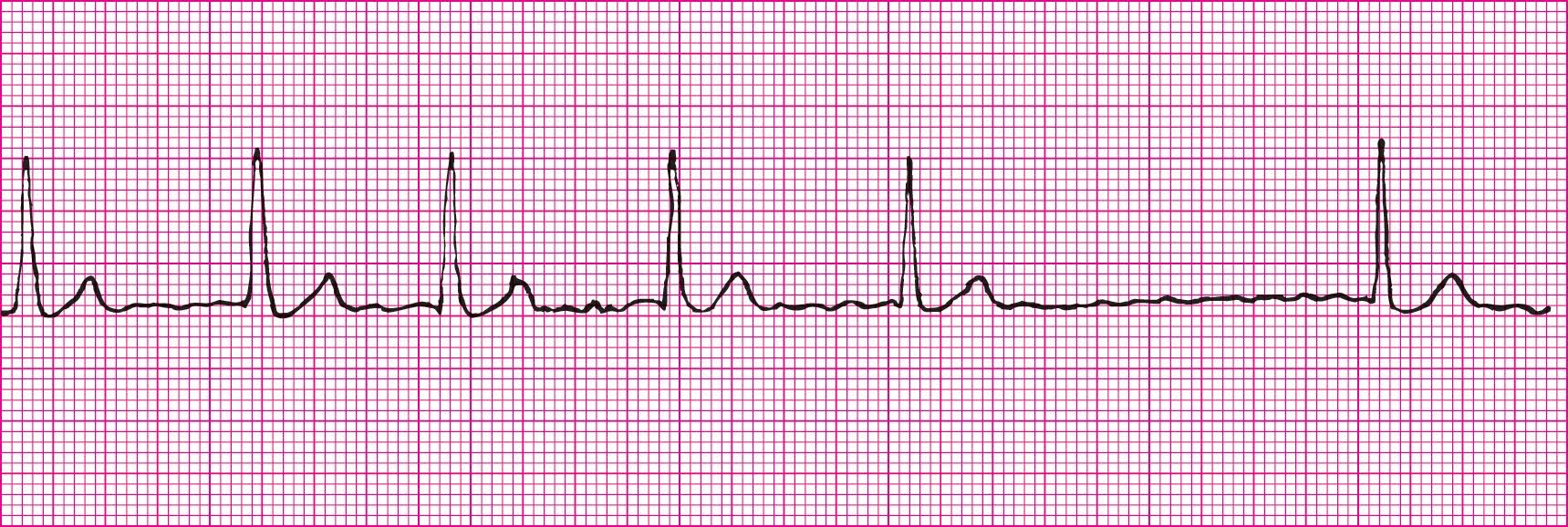
Sinus Rhythm with PACs
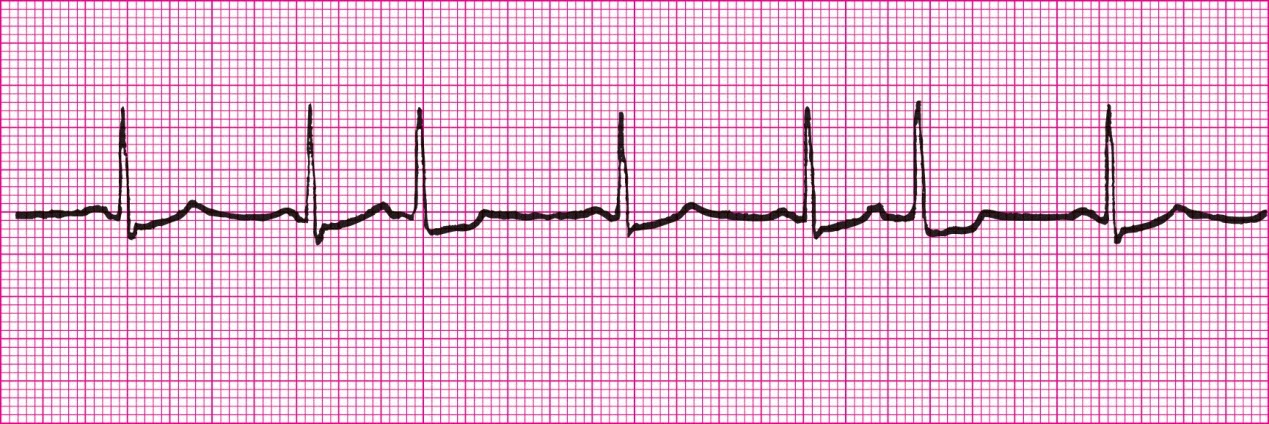
Supra ventricular Tachycardia
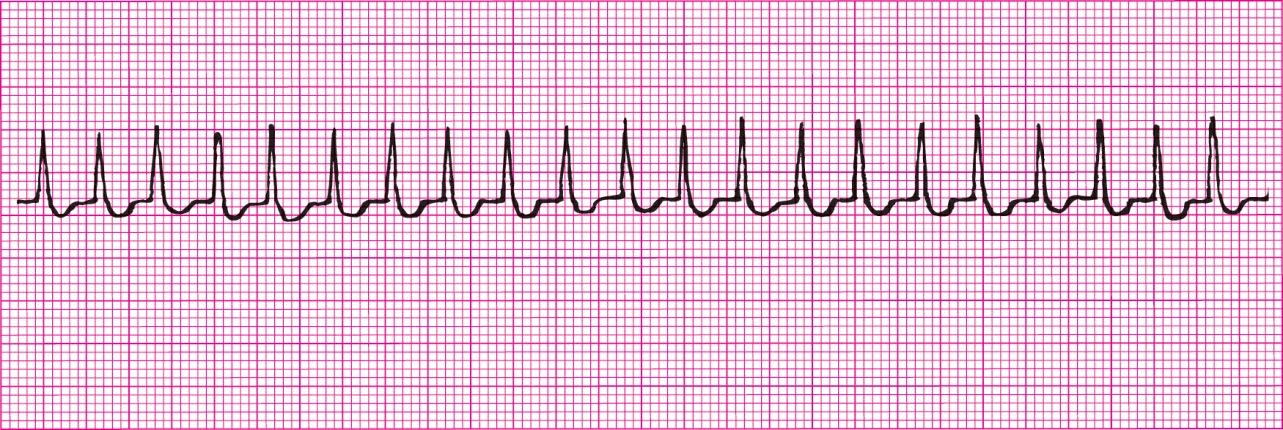
A-Fib (Irregularly Irregular, look at the F waves)
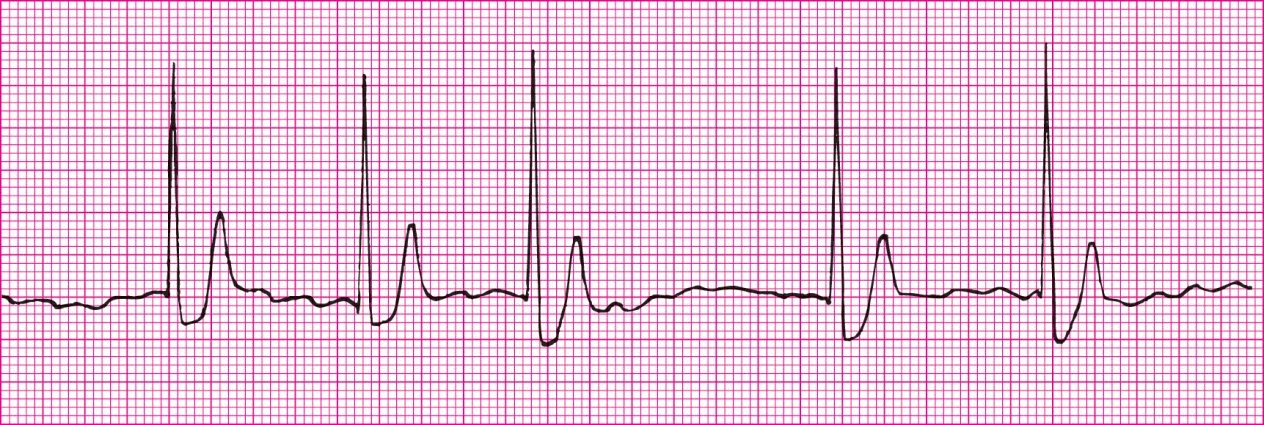
Sinus rhythm with a PAC
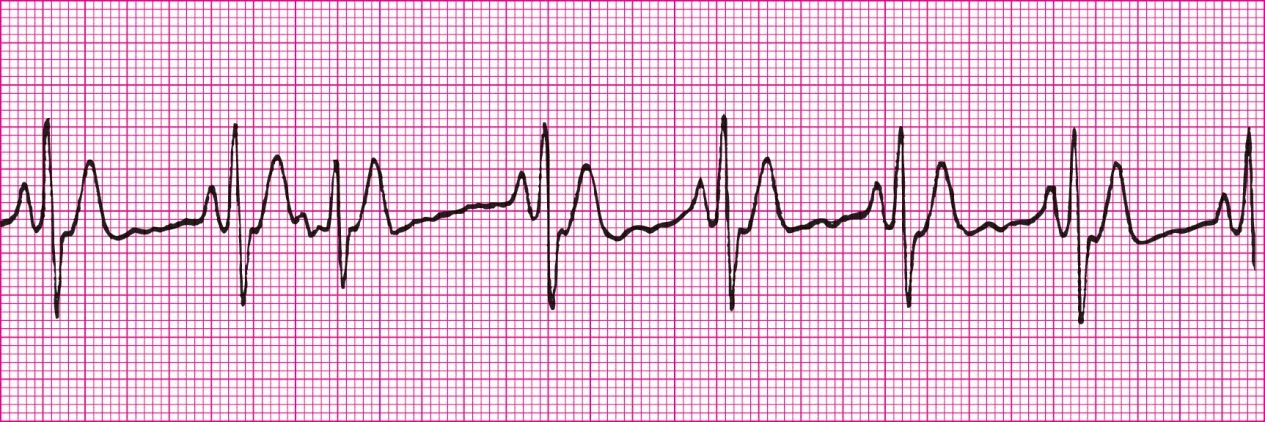
A-Fib with RVR. (Rapid Ventricular response, heart rate 100+)
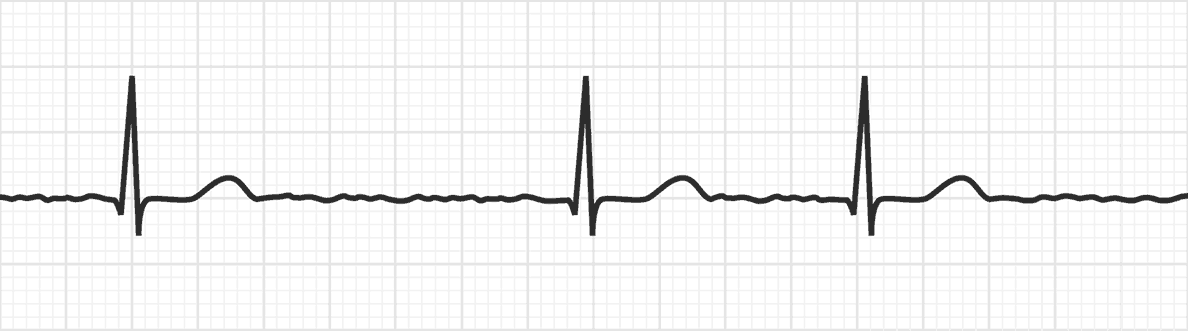
A-fib with SVR (Slow ventricular response, heart rate less than 60)
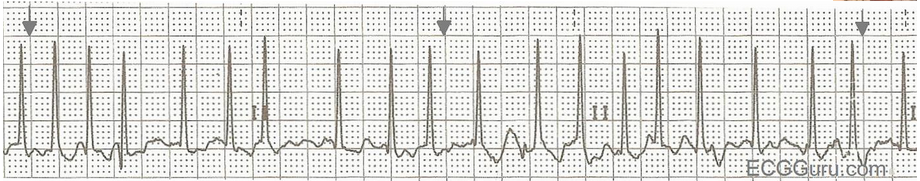
Atrial Flutter - variable ventricular response
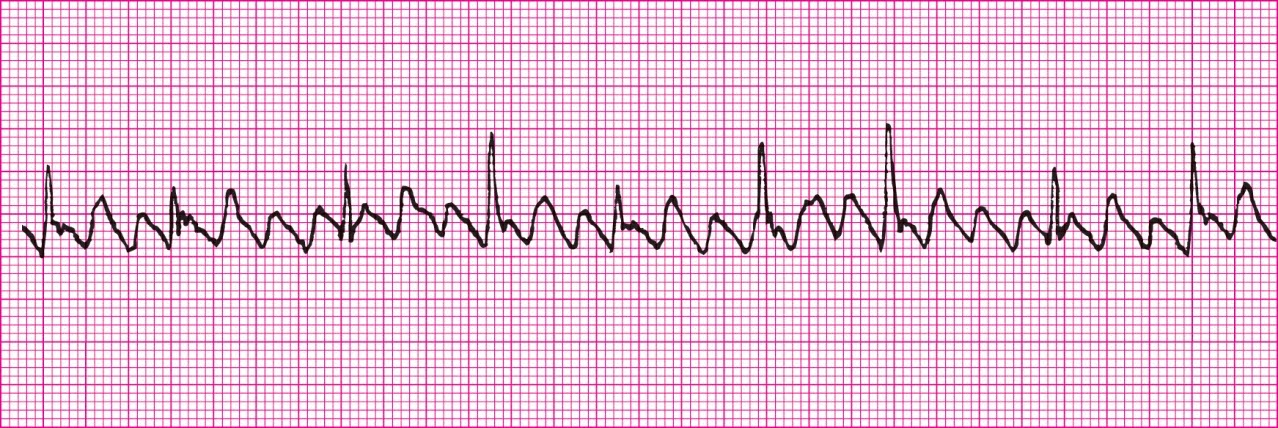
SVT
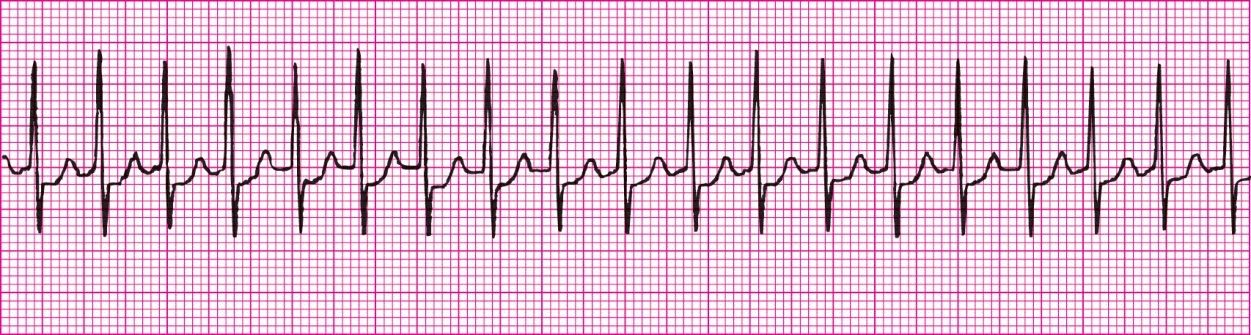
Wandering atrial pacemaker
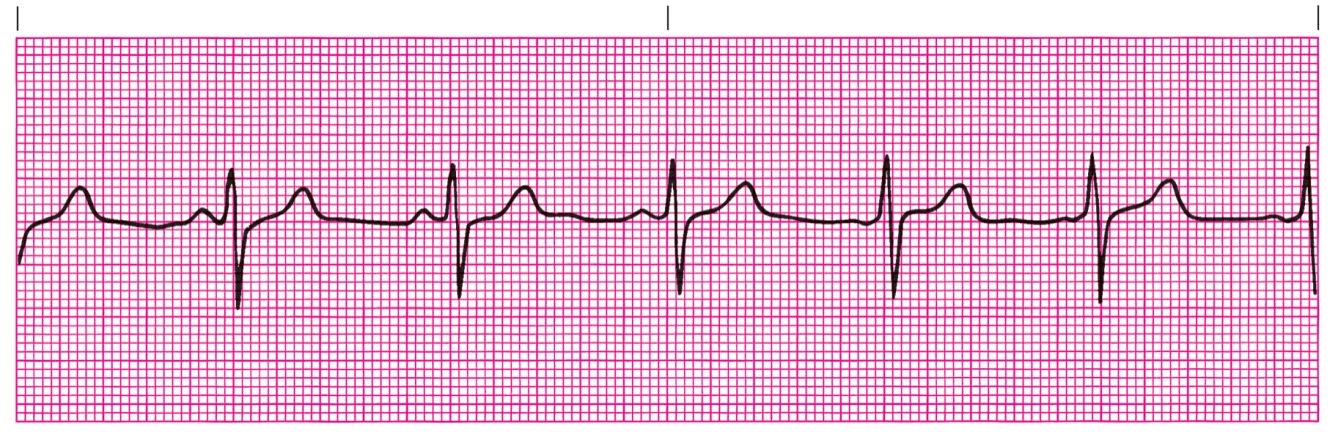
Accelerated Junctional Rhythm (HR over 60)
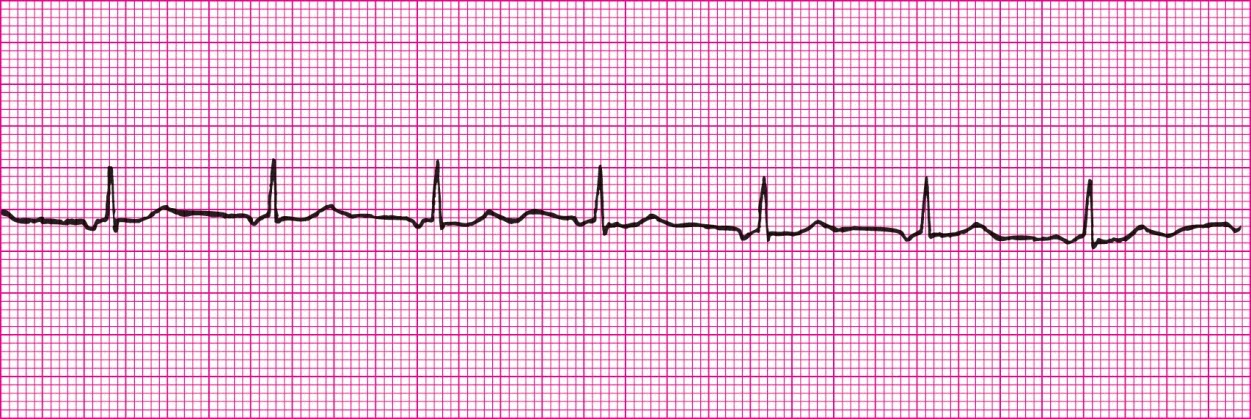
Junctional Rhythm (Inverted P wave after the QRS)
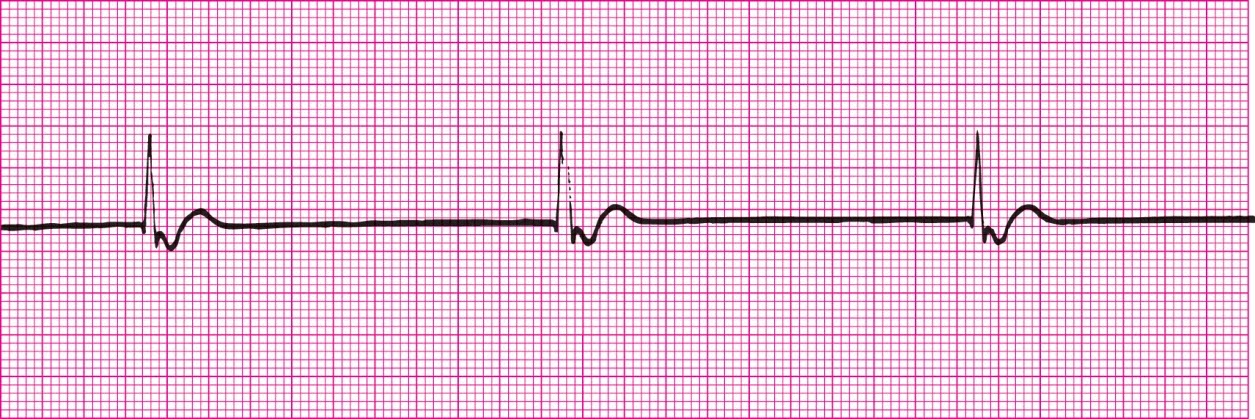
Sinus Rhythm with PJCs and 1 PVC (The two PJCs have inverted P waves)
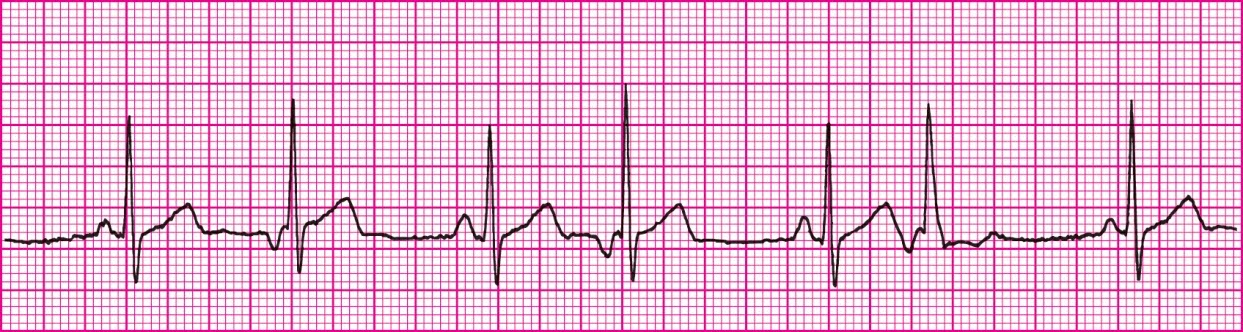
Junctional Tachycardia (Not Vtach, QRS complexes are inverted and narrow, absent P waves)
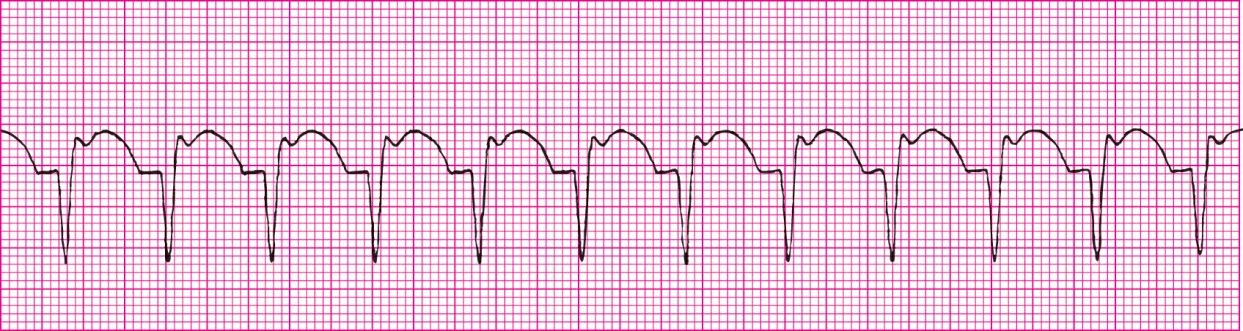
Sinus Rhythm with Bigeminal PJCs (after every normal beat)
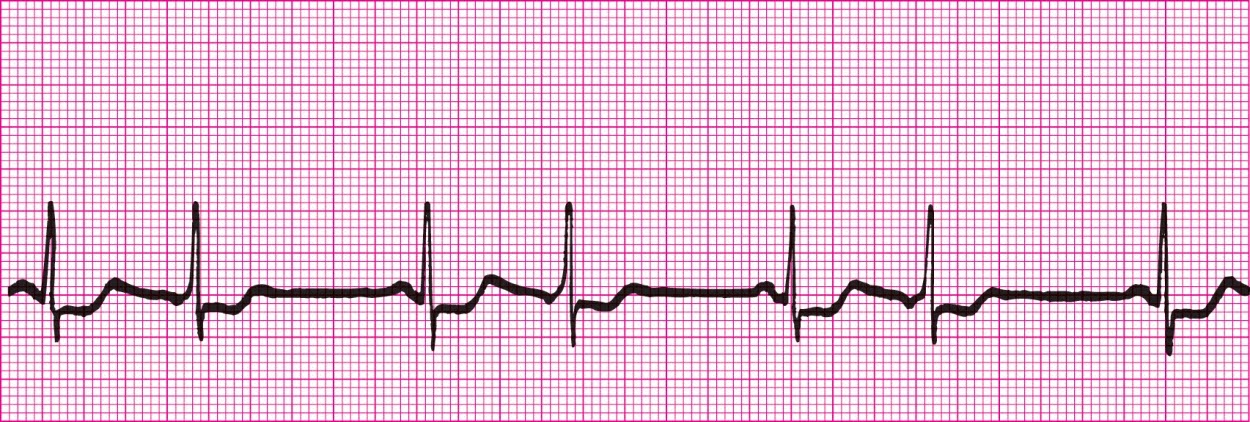
Accelerated Junctional Rhythm (HR over 60)
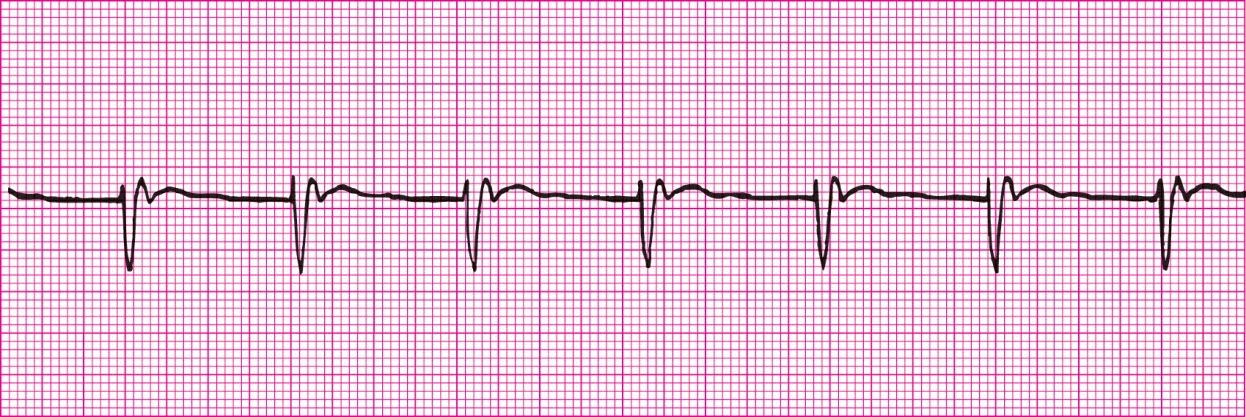
Junctional Rhythm
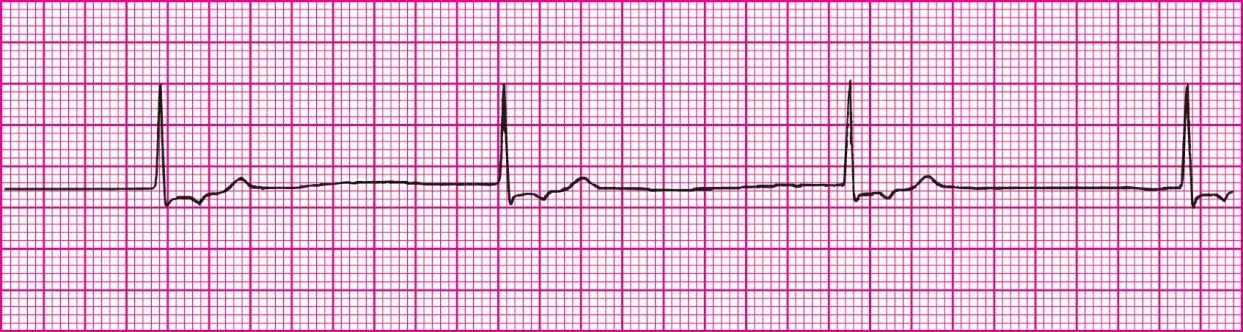
Junctional Tachycardia
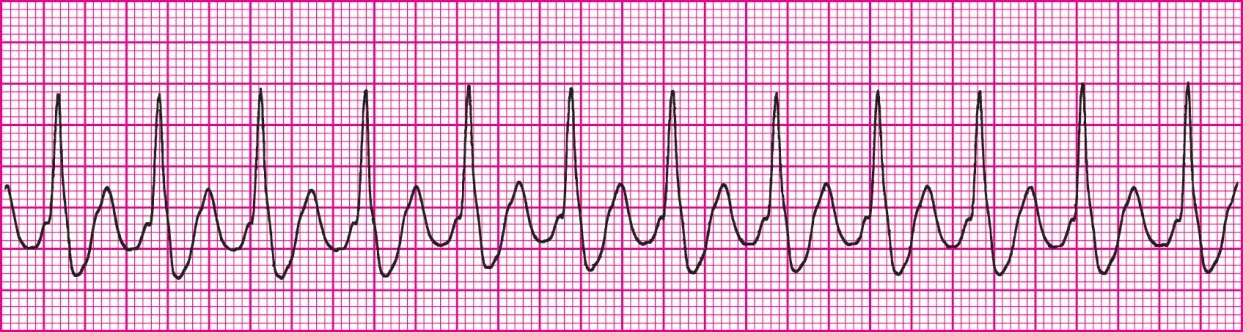
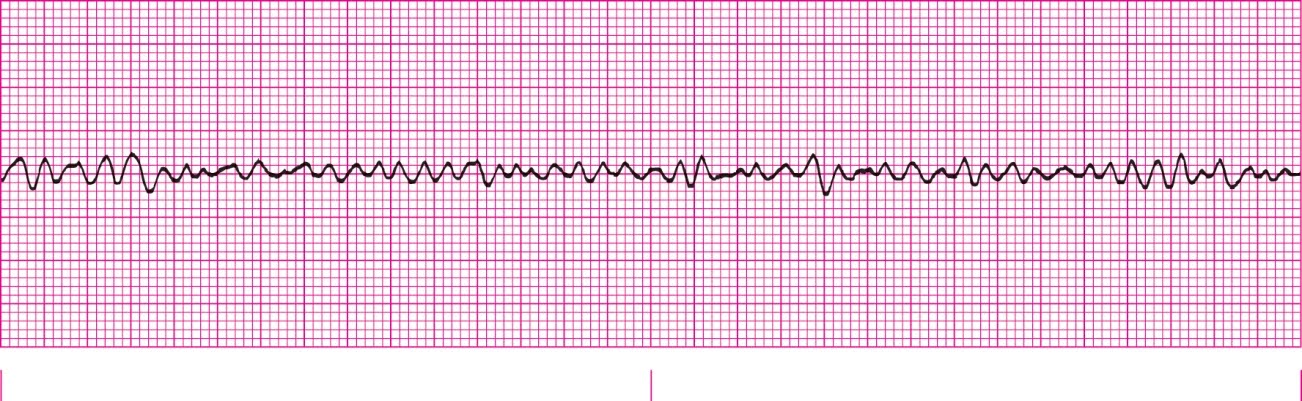
Coarse V-Fib (over 3mm)
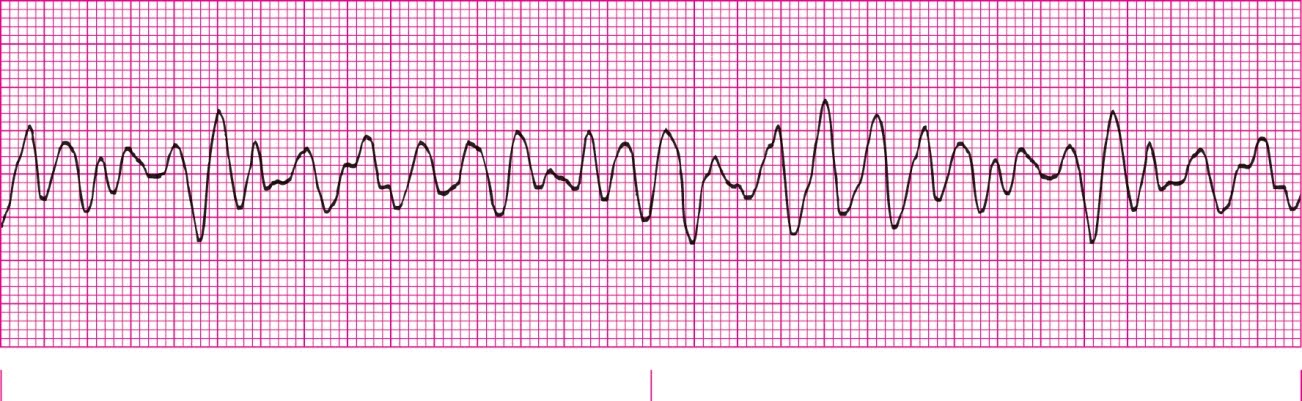
Fine V-fib (Less than 3mm)
Asystole
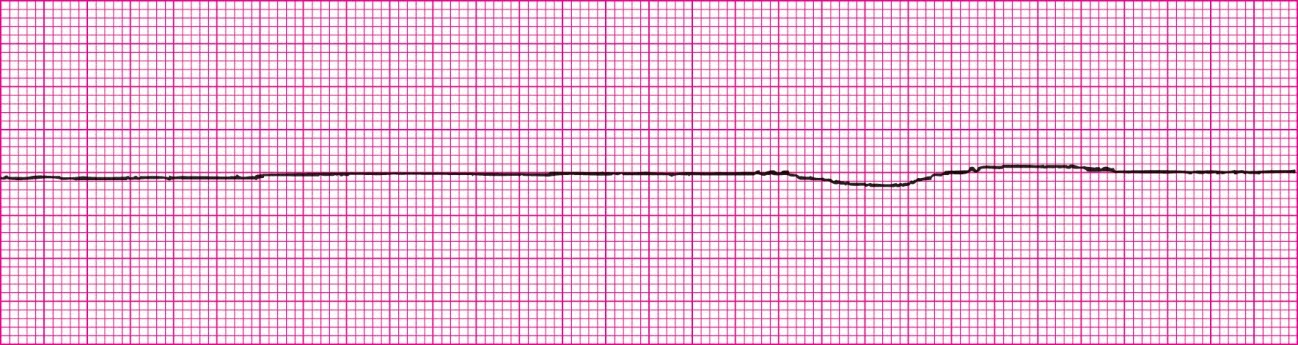
Ventricular Standstill
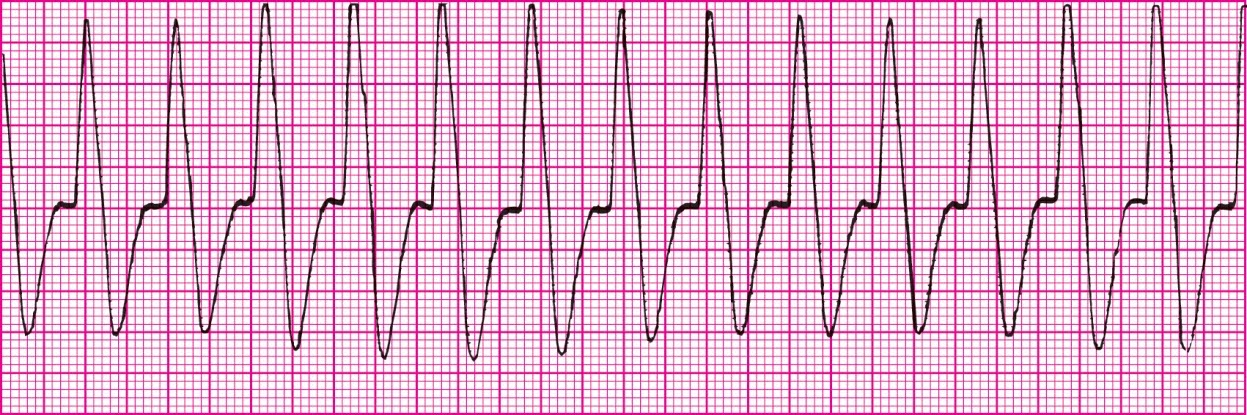
Ventricular Tachycardia
Sinus with quadreminal PVCs (every fourth beat)
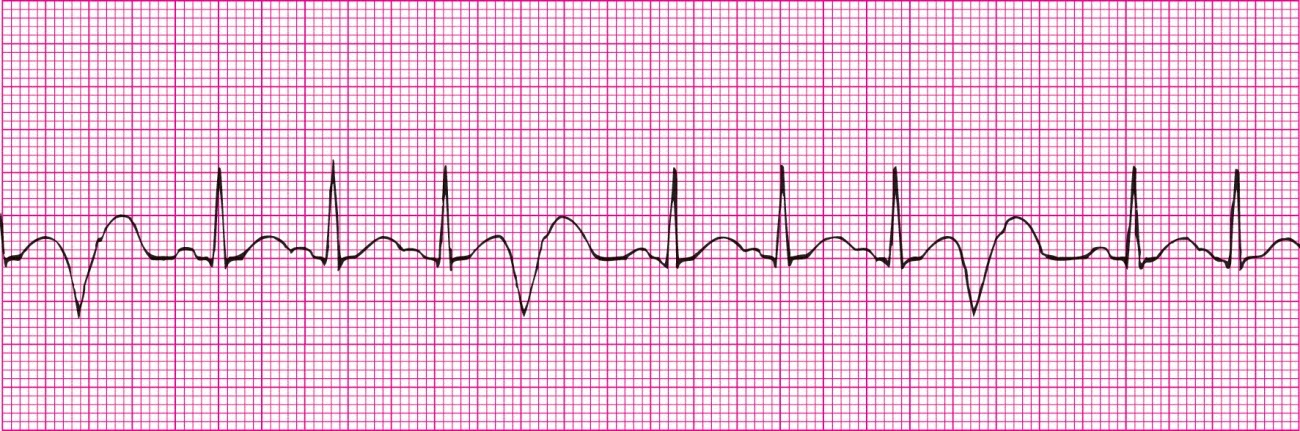
Sinus Rhytm with couplet PVCs (two PVCs together)
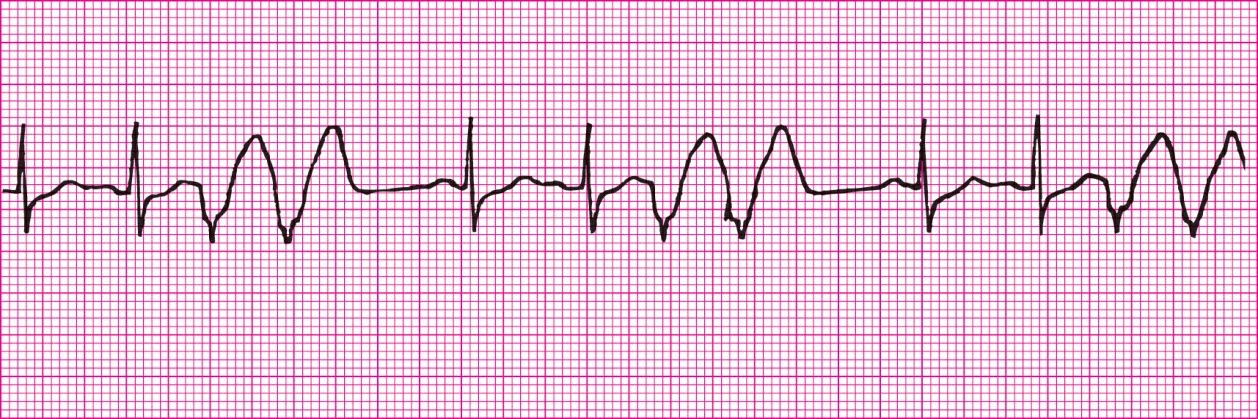
Sinus Rhytm with multifocal PVCs (PVCs from multiple sources)
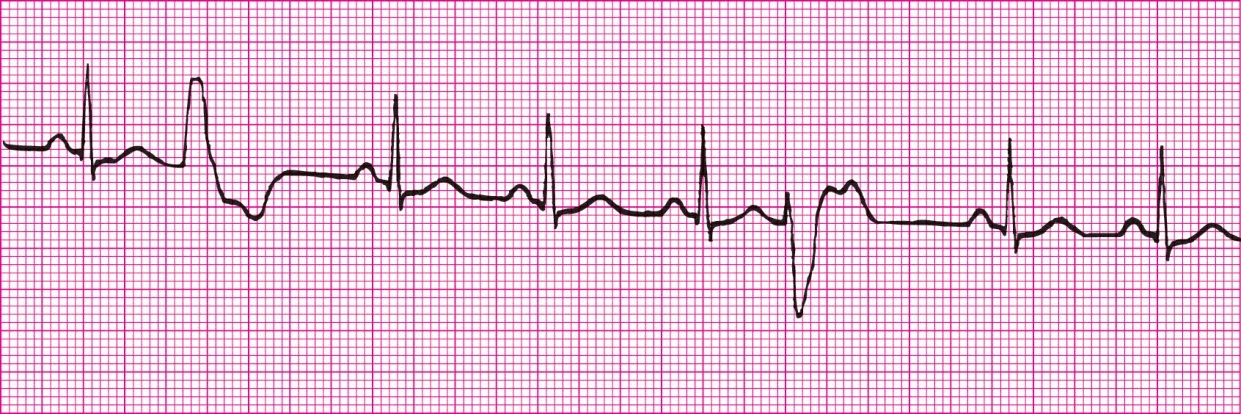
Sinus Rhytm with Trigeminal Unifocal PVCs (PVCs from one source, occuring every 3rd beat)
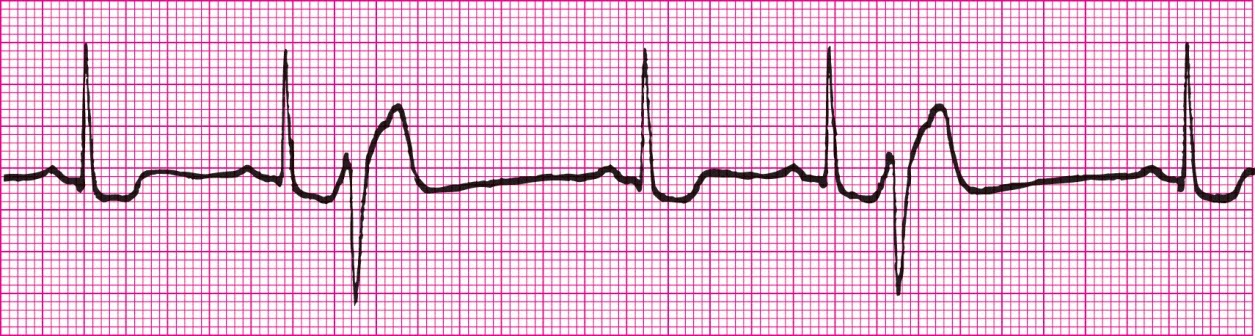
Torsades de pointes
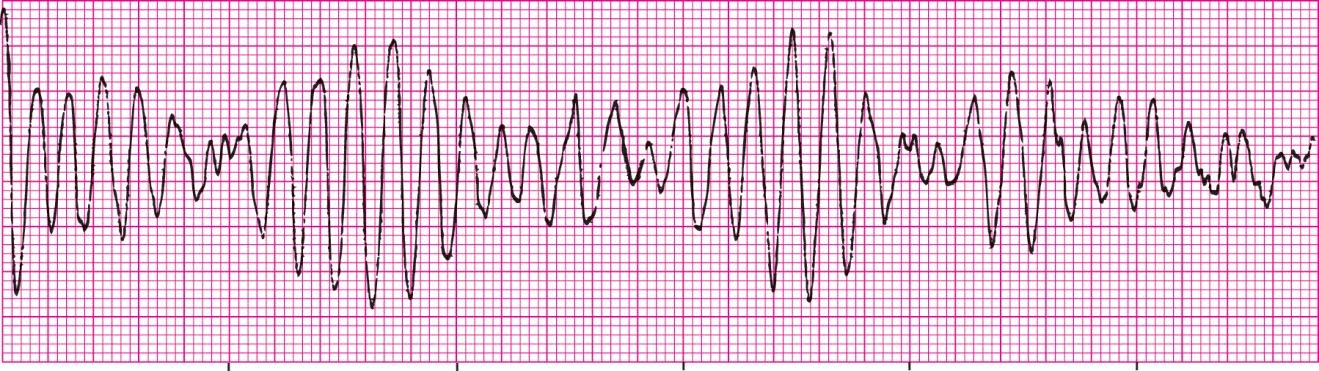
Ventricular Tachycardia
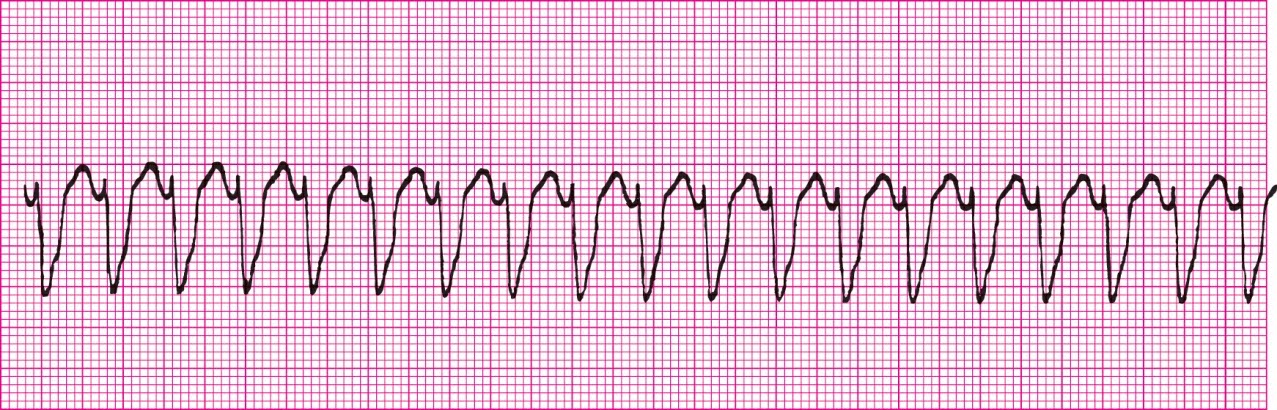
Sinus rhythm with unifocal PVCs (from same source, could be trigeminy, but the strip doesnt show enough)
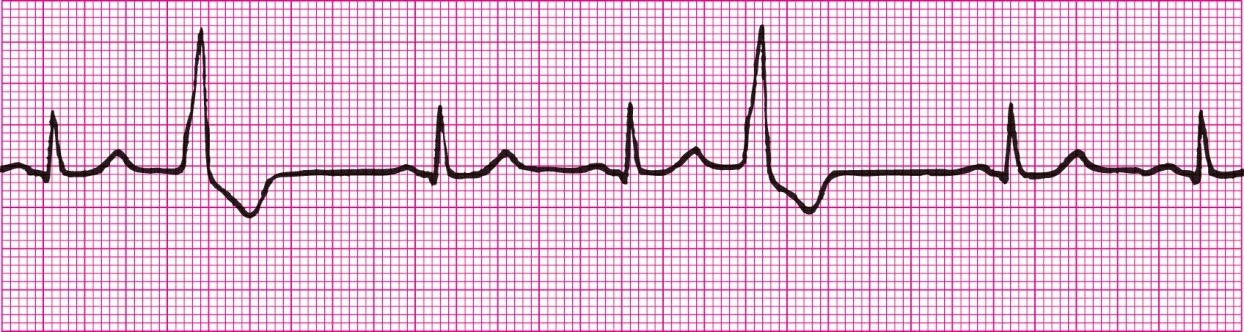
Sinus Rhythm with unifocal bigeminal PVCs (every other beat a PVC, all from same source)
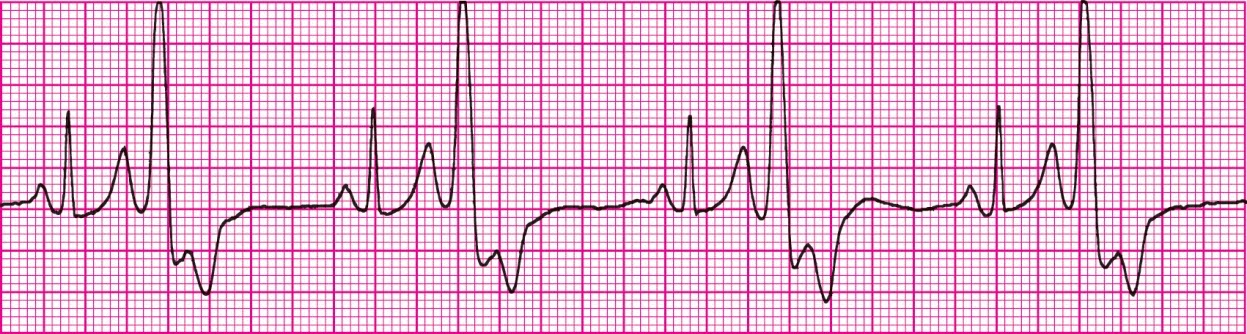
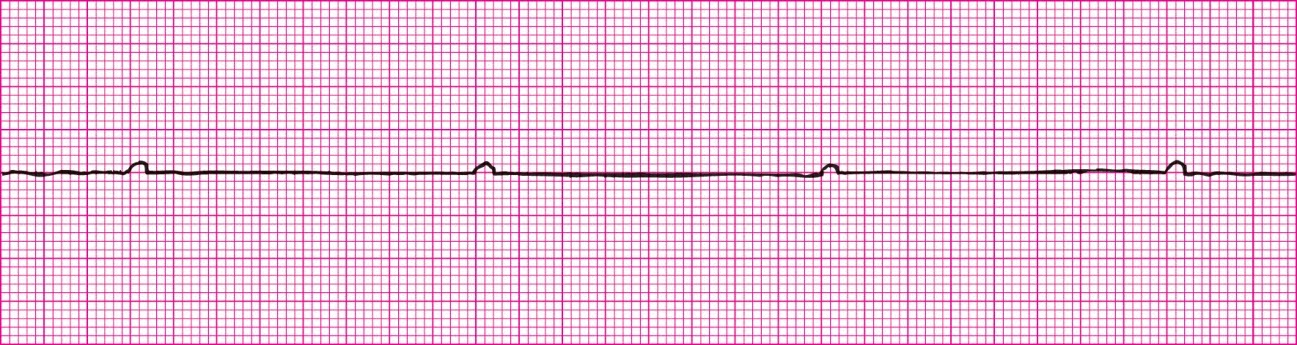
Idioventricular Rhythm
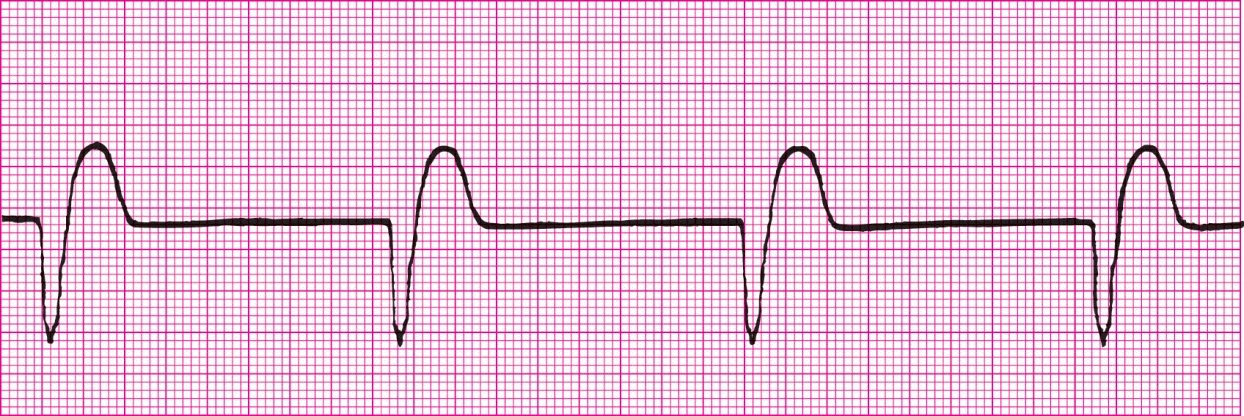
Accelerated Idioventricular Rhythm (Over 40 BPM)
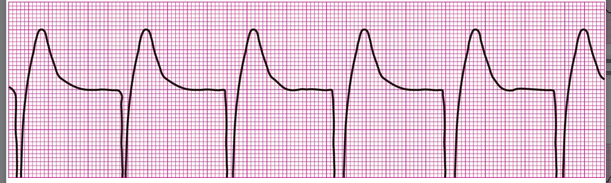
First Degree Heart Block (PRI greater than .20)
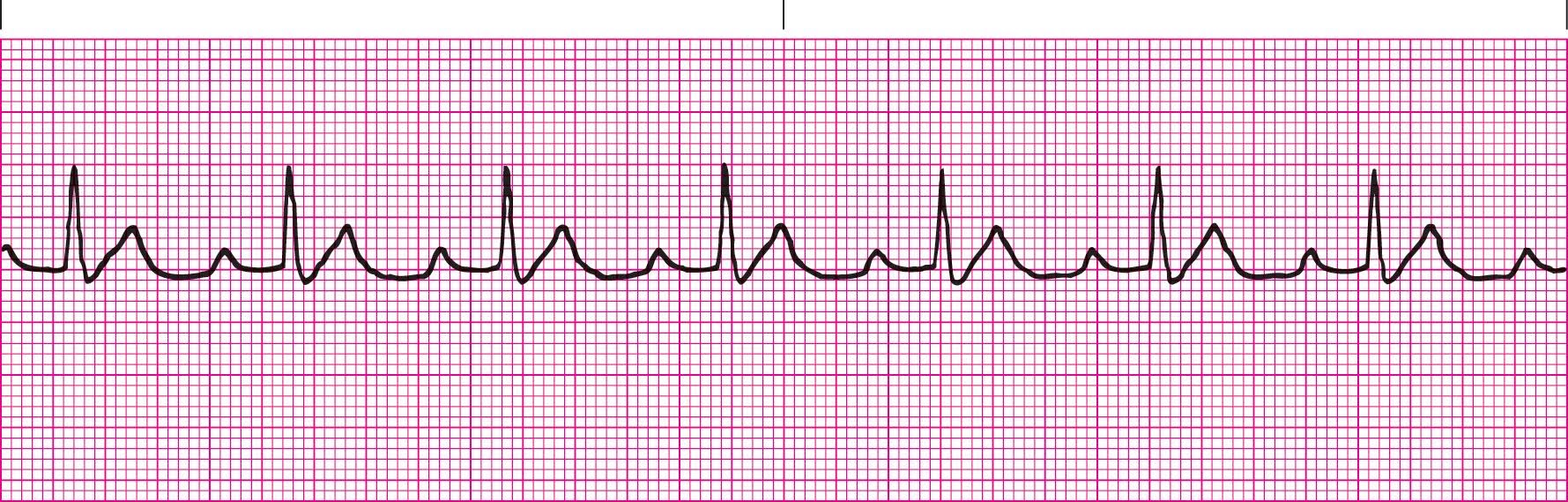
Second Degree Heart Block Type 1 (PRI gets longer each beat until beat is dropped)
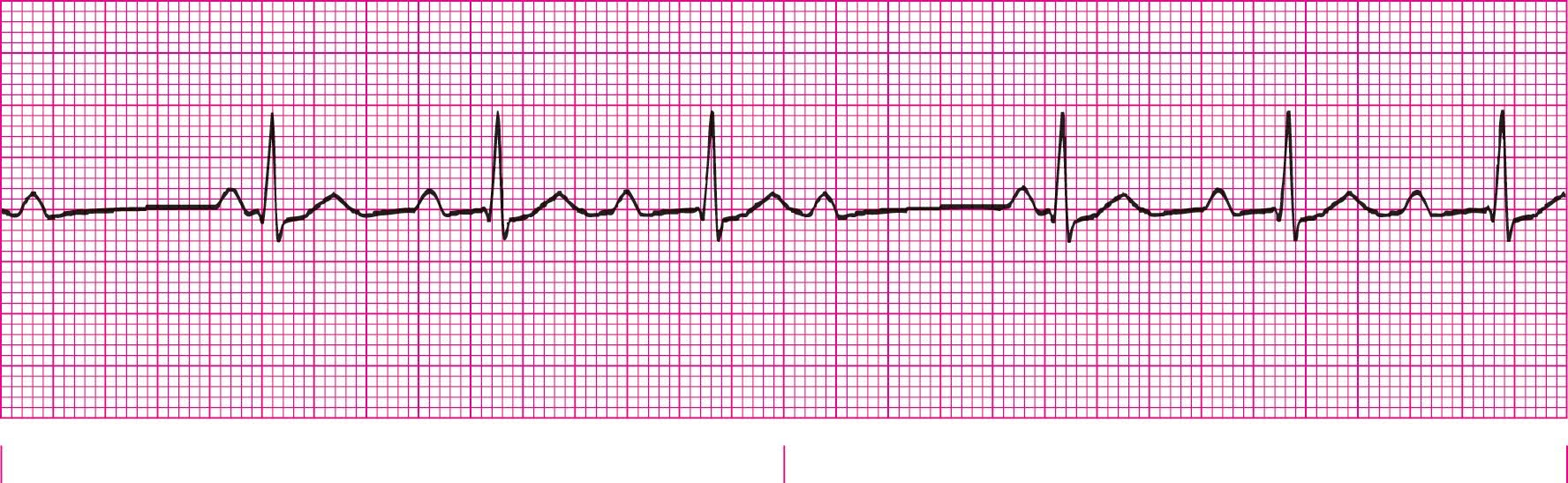
Second Degree Heart Block Type 1 (PRI gets longer each beat until beat is dropped)
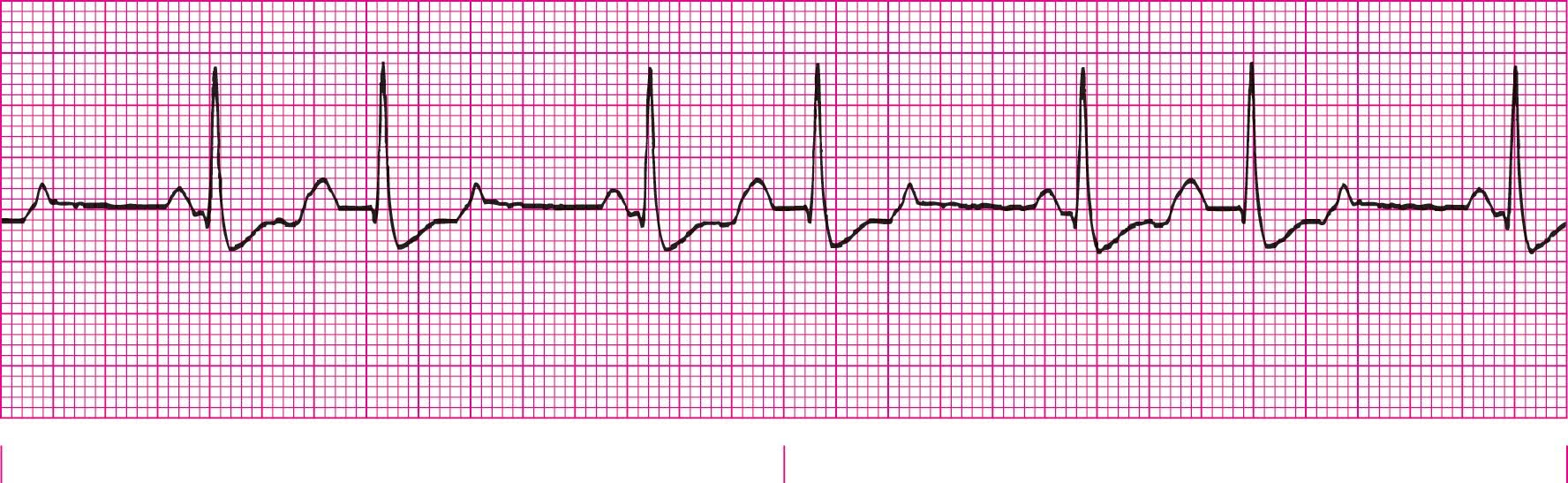
Second Degree Heart Block Type 1 (PRI gets longer each beat until beat is dropped)
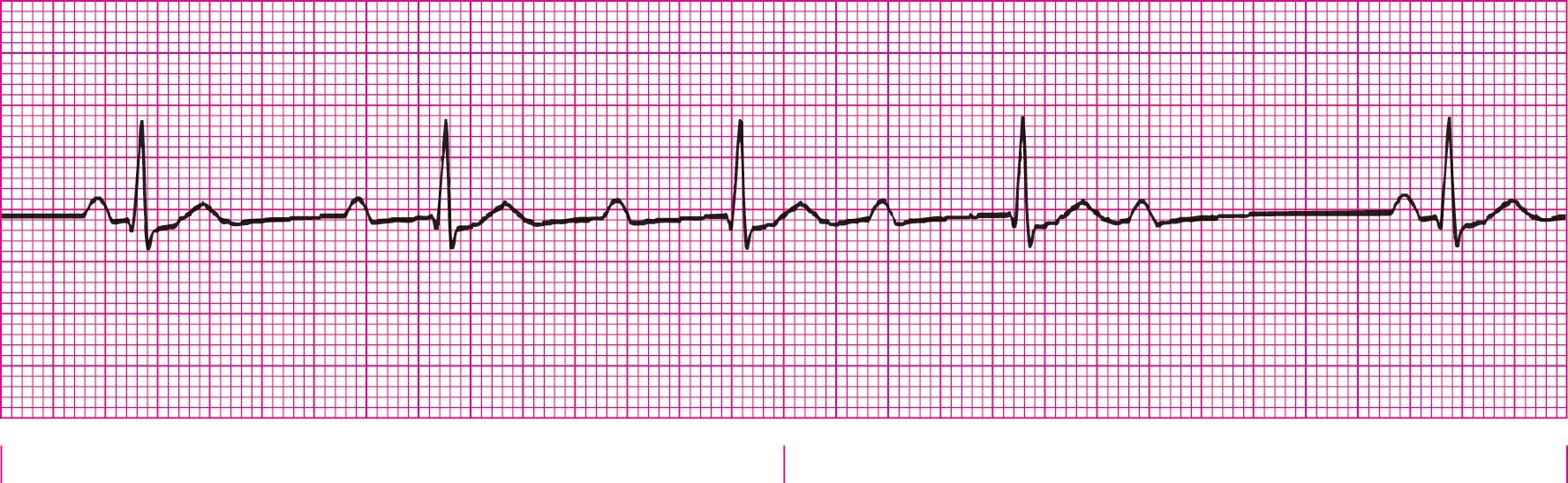
Second Degree Heart Block Type 2 (PRI is the same for every conducted beat)
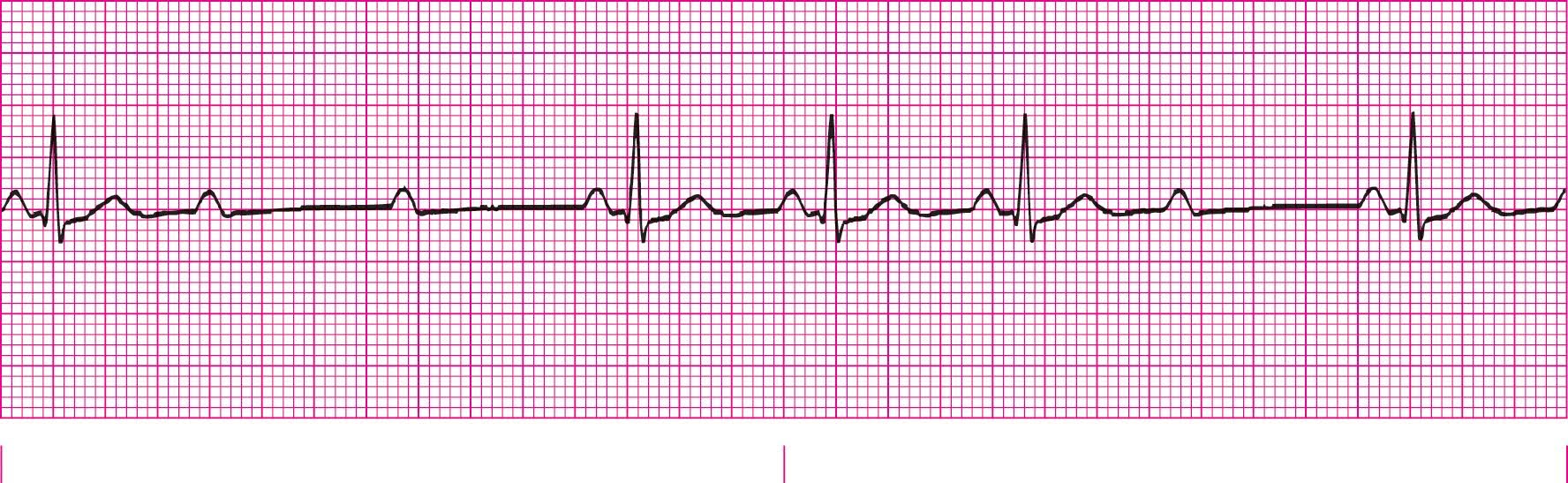
Second Degree Heart Block Type 2 (PRI is the same for every conducted beat)
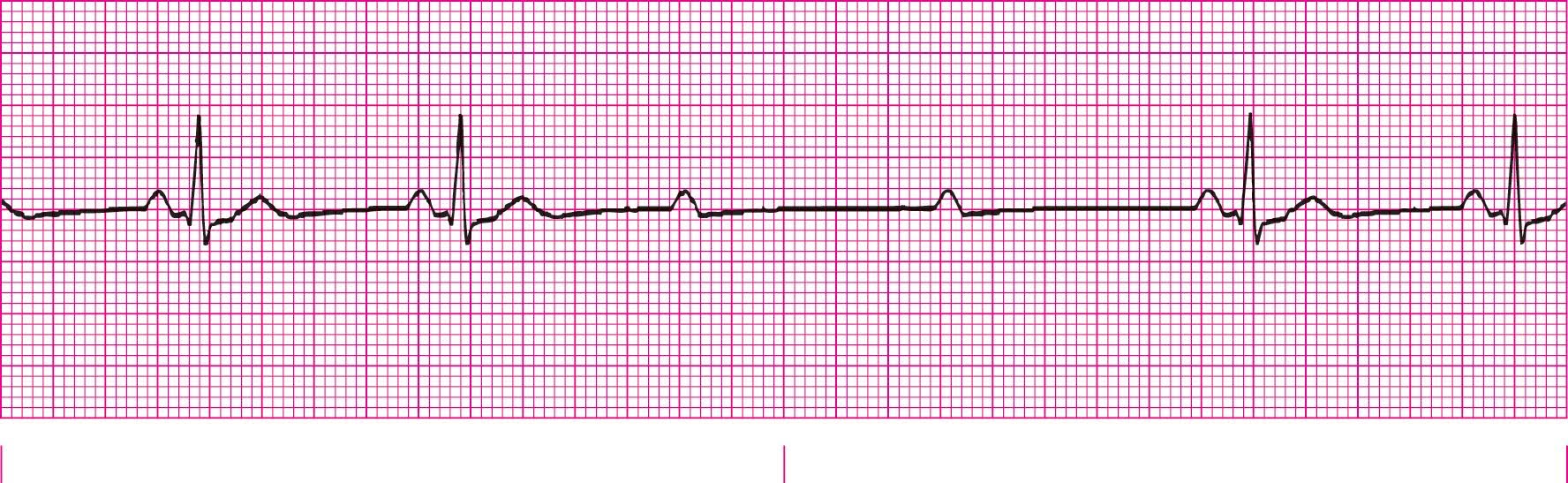
Second Degree Heart Block Type 2 (PRI is the same for every conducted beat)
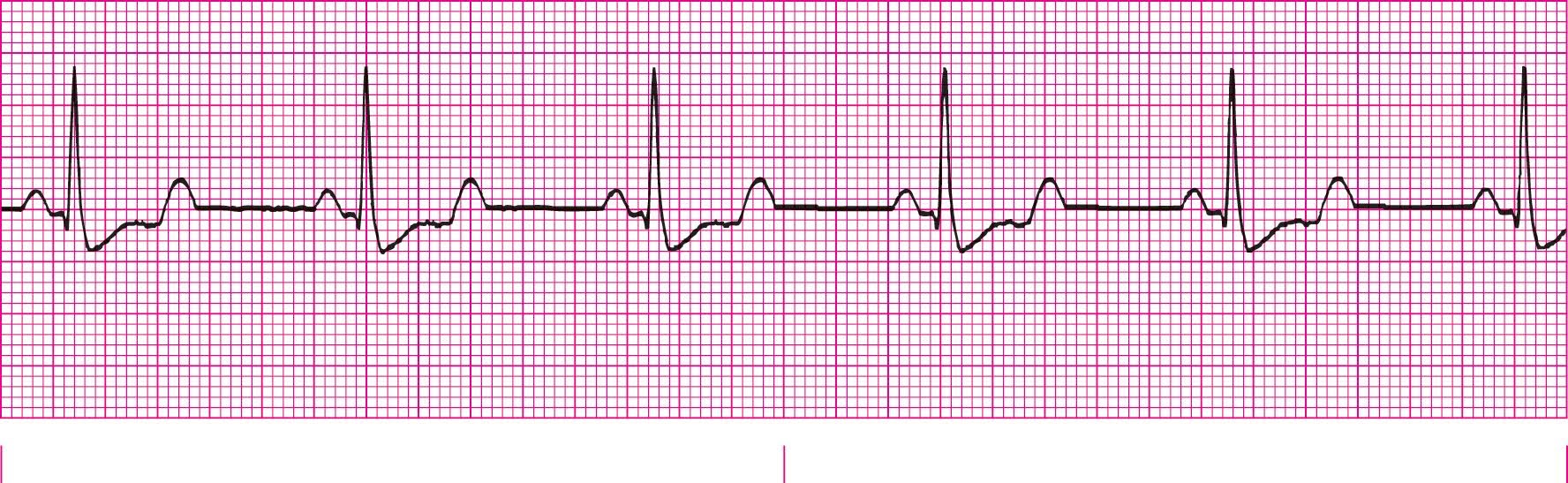
Third-Degree Heart Block (No correlation between P wave and QRS)
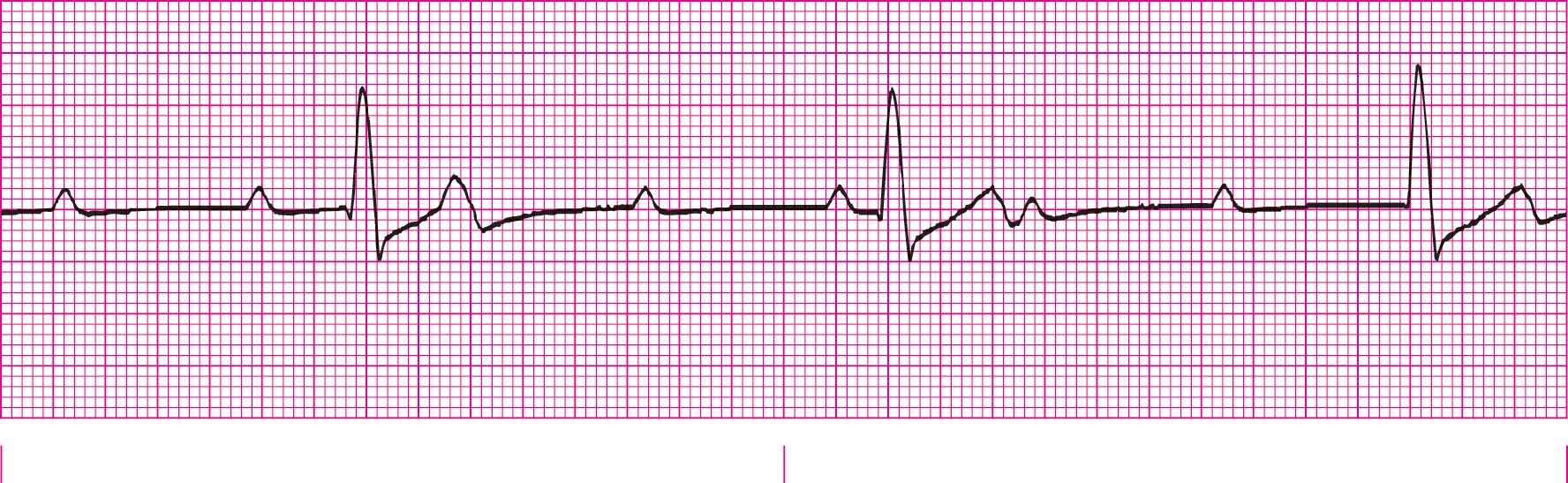
Third-Degree Heart Block (No correlation between P wave and QRS)
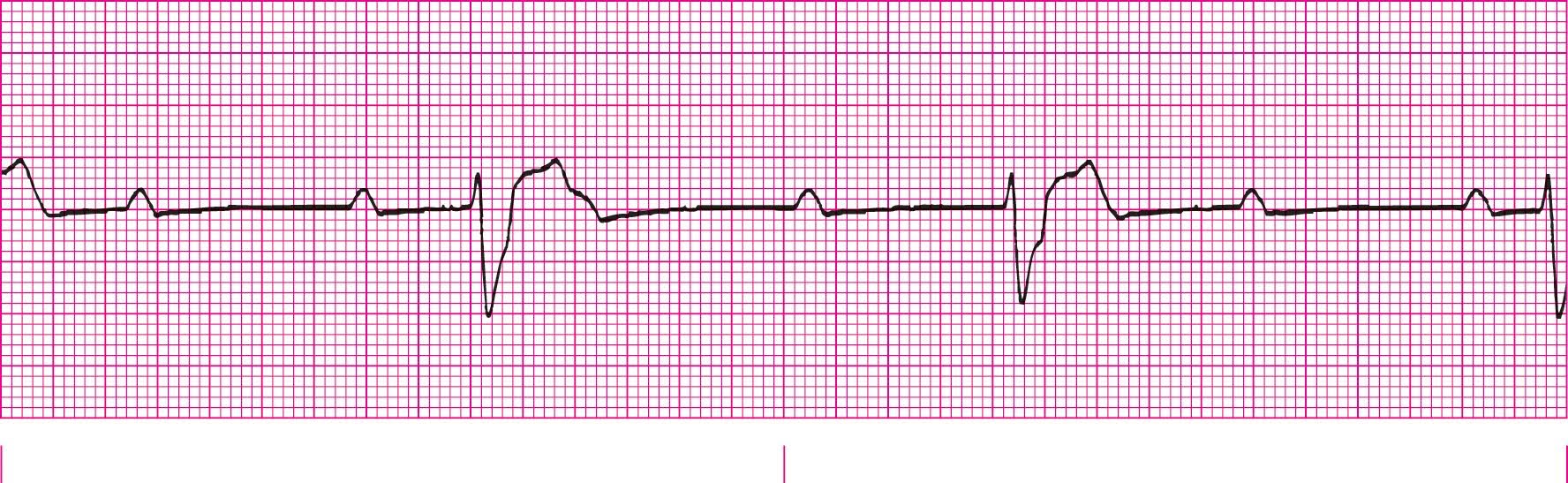
Third-Degree Heart Block (No correlation between P wave and QRS)
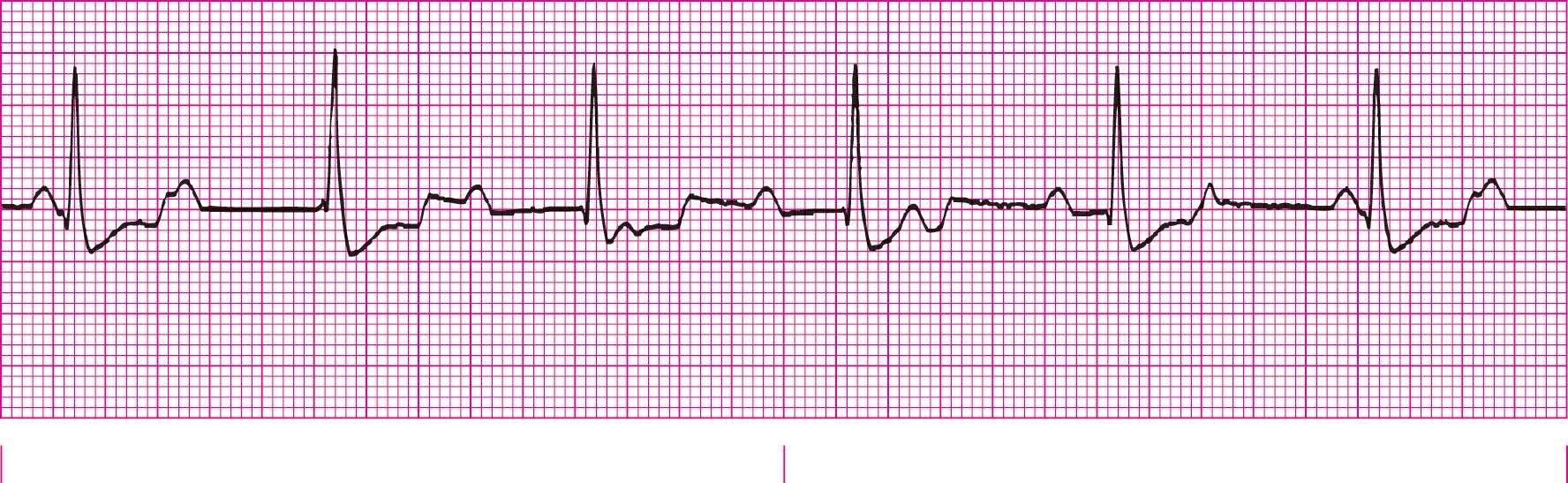
Third Degree Heart Block (with paced ventricular rhythm)
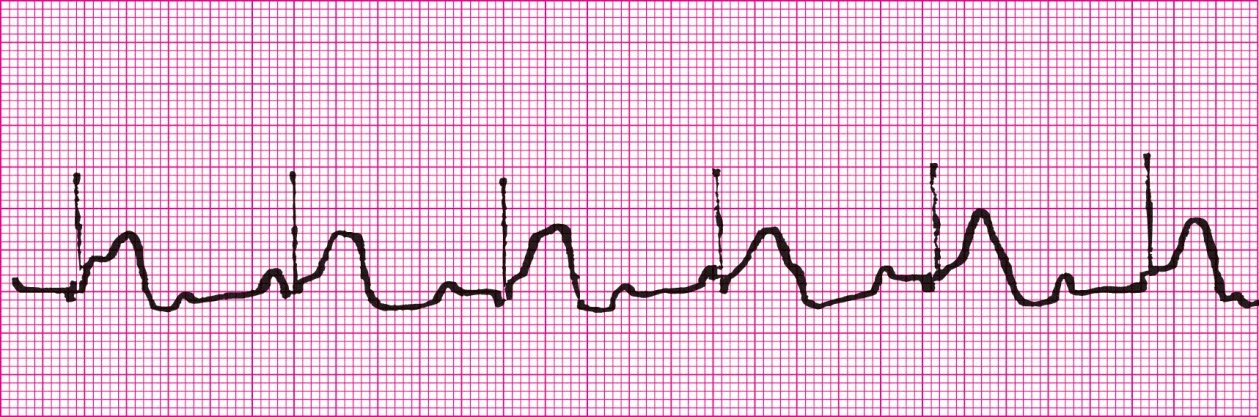
First Degree Heart Block (PRI greater than .20)
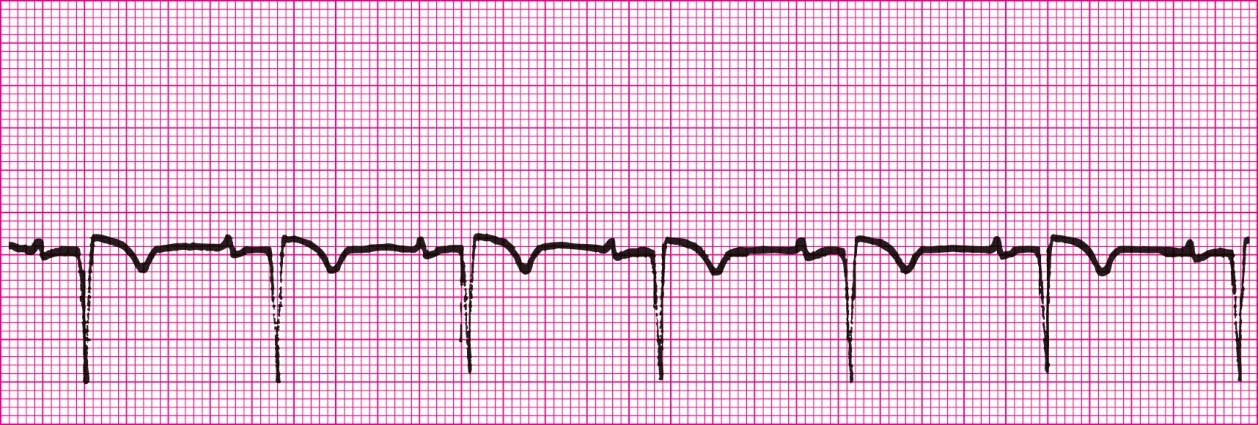
Second Degree Heart Block Type 1 (PRI gets longer each beat until beat is dropped)
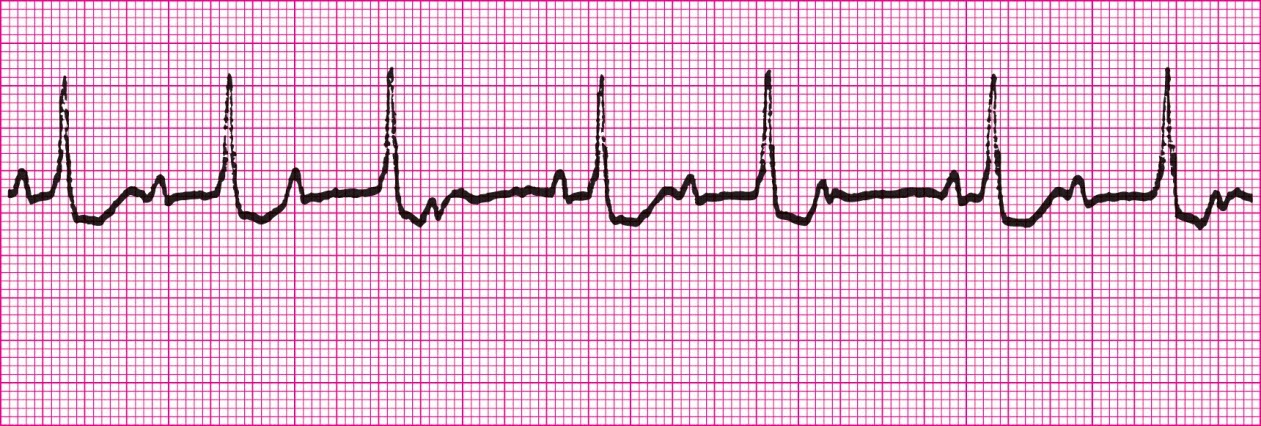
First Degree Heart Block (PRI greater than .20)
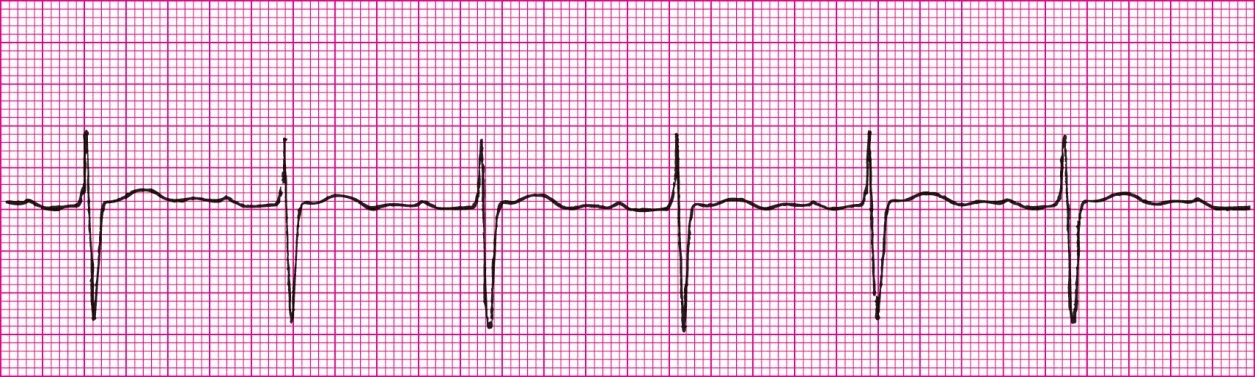
Third-Degree Heart Block (No correlation between P wave and QRS)
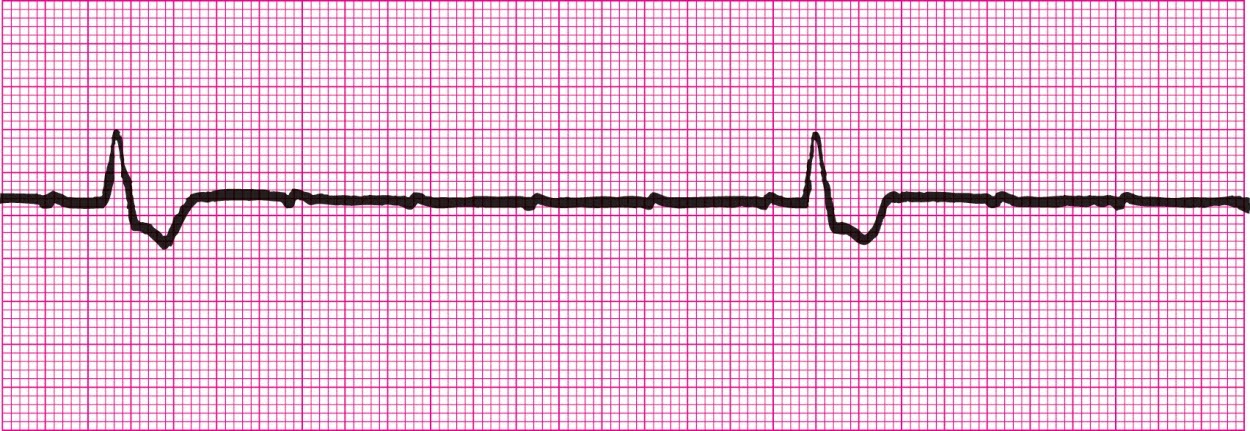
Second Degree Heart Block Type 2 (PRI is the same for every conducted beat)
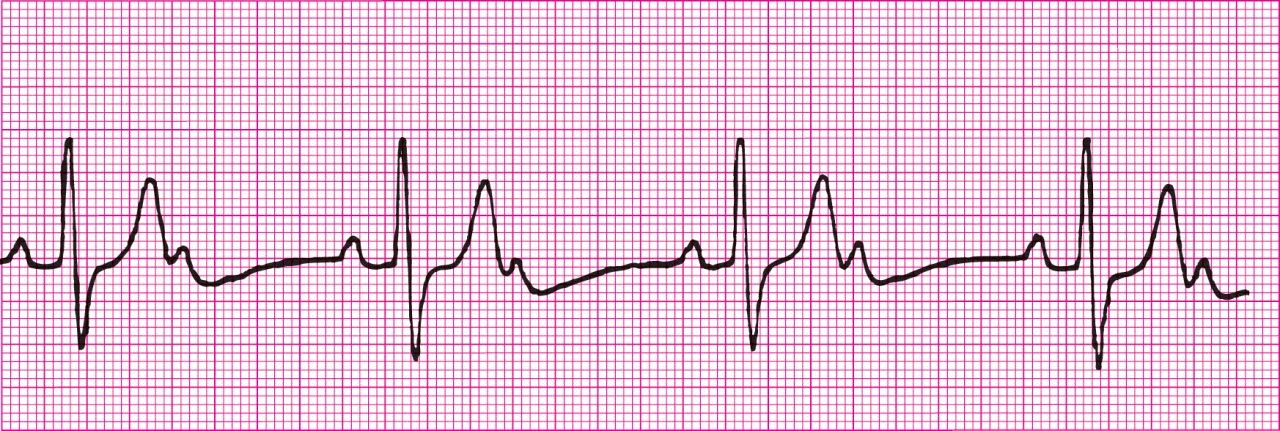
Second Degree Heart Block Type 1 (PRI gets longer each beat until beat is dropped)
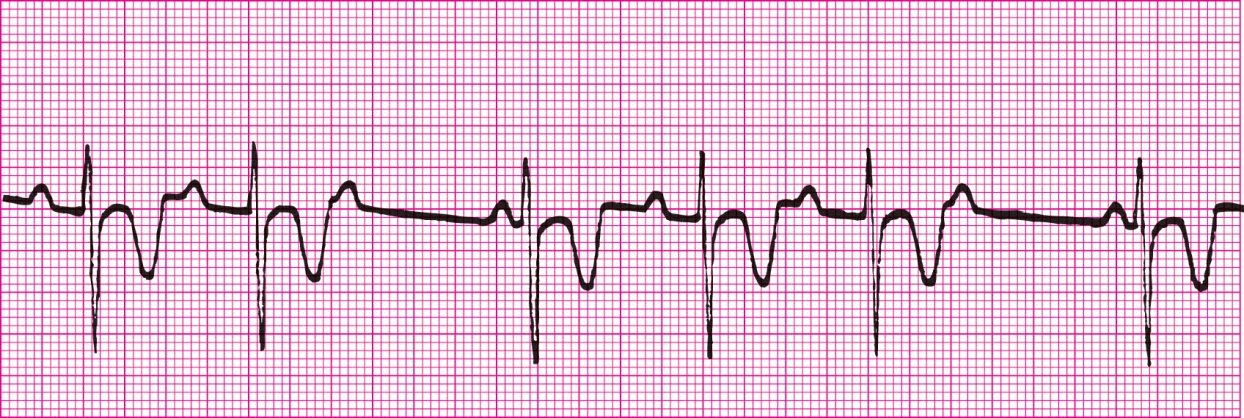
Malfunctioning pacemaker and 3rd degree heart block
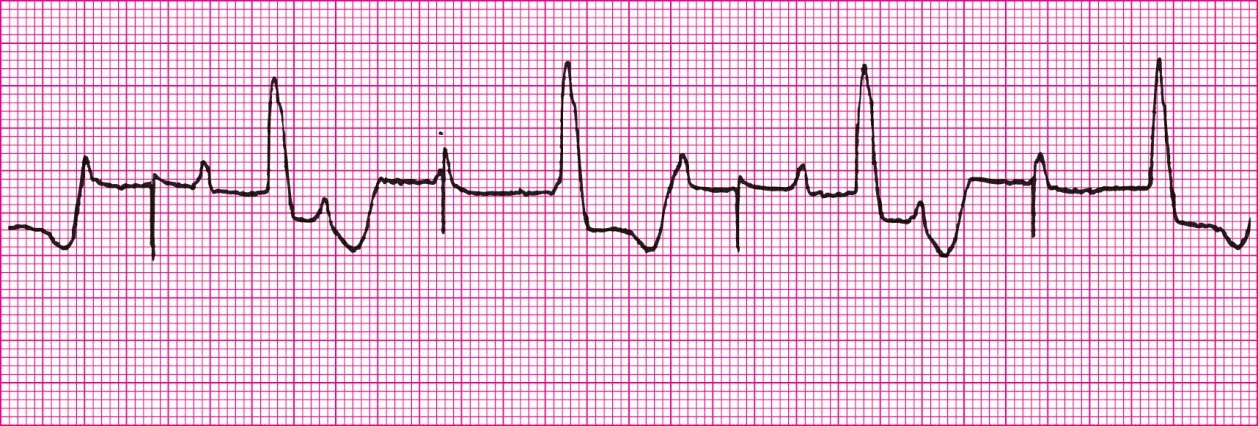
Sequential AV pacemaker rhythm
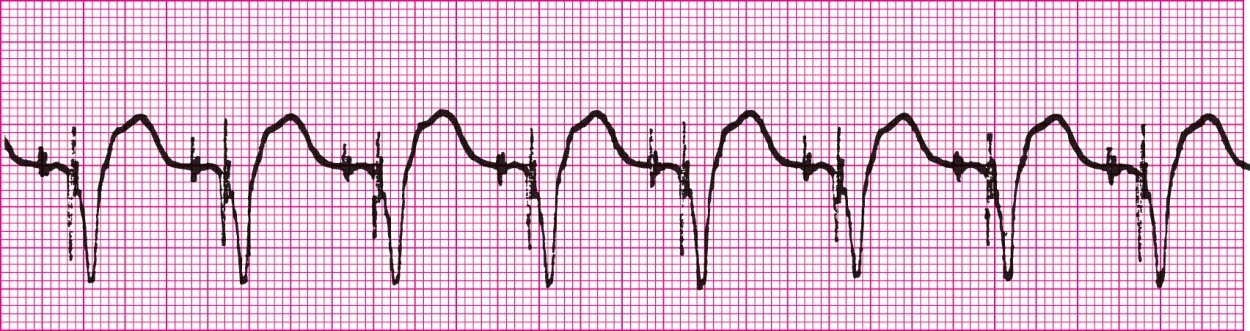
Sinus Rhythm with ventricular demand pacer
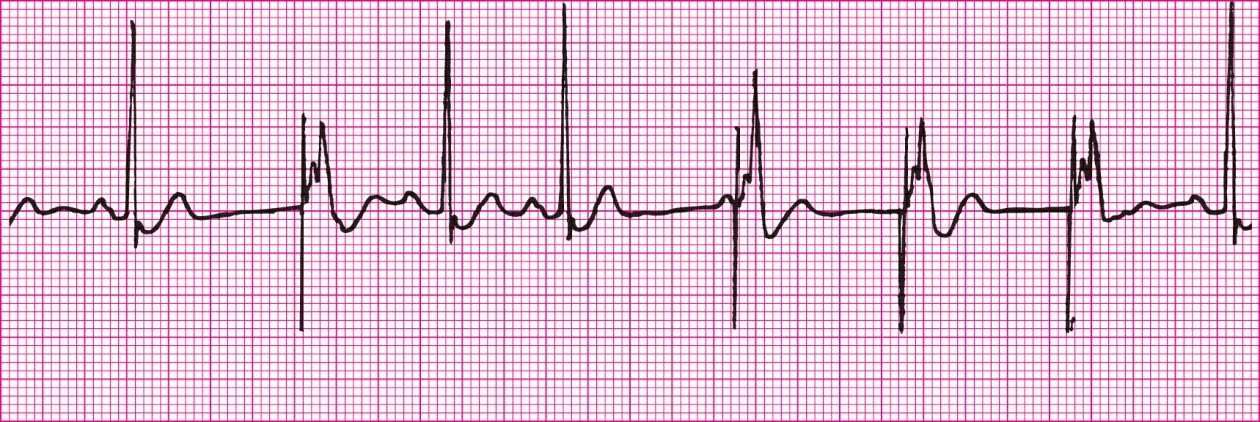
Ventricular pacemaker rhythm
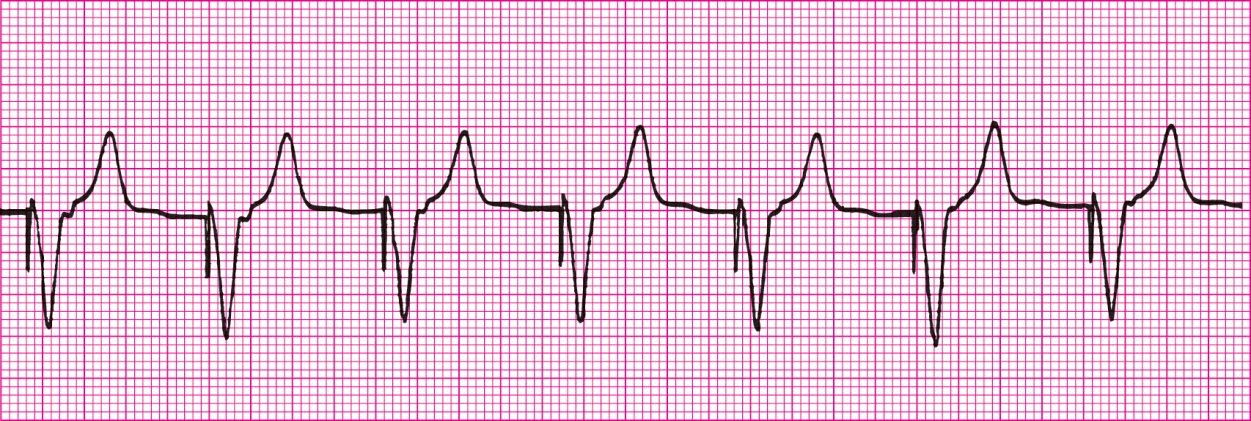
Ventricular pacemaker rhythm
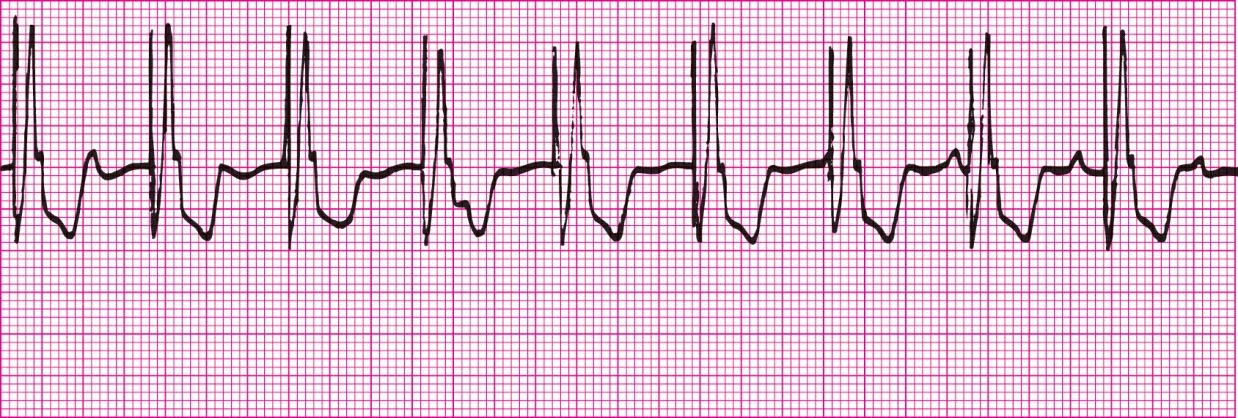
Malfunctioning pacemaker rhythm; first degree heart block

Ventricular Pacemaker rhythm
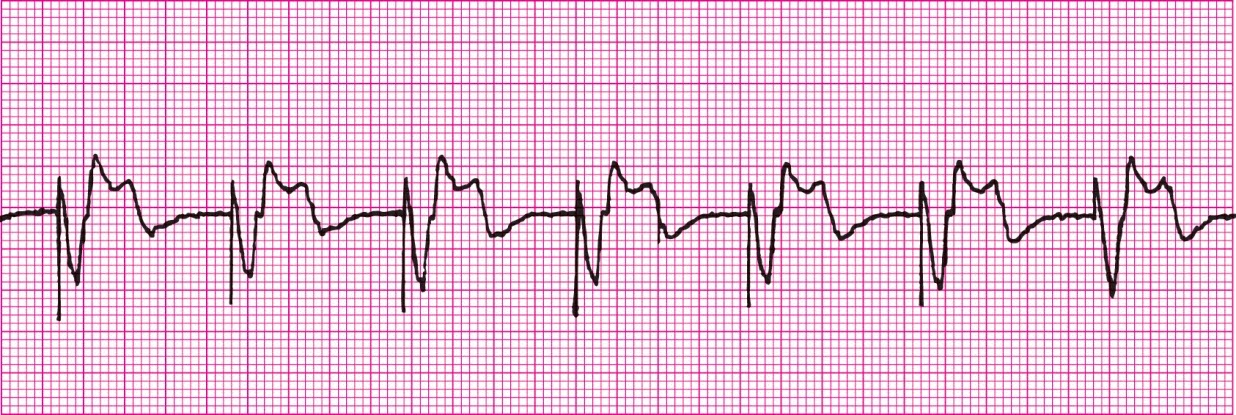
Malfunctioning pacemaker rhythm