AP Human Geo - Unit 3 (Cultural Patterns & Processes)
1/79
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
80 Terms
Culture
the collective experience of people who live together in a particular place.

Cultural trait
a single element of culture (like a tradition, belief, food, language, or style of clothing) that is shared by a group of people.
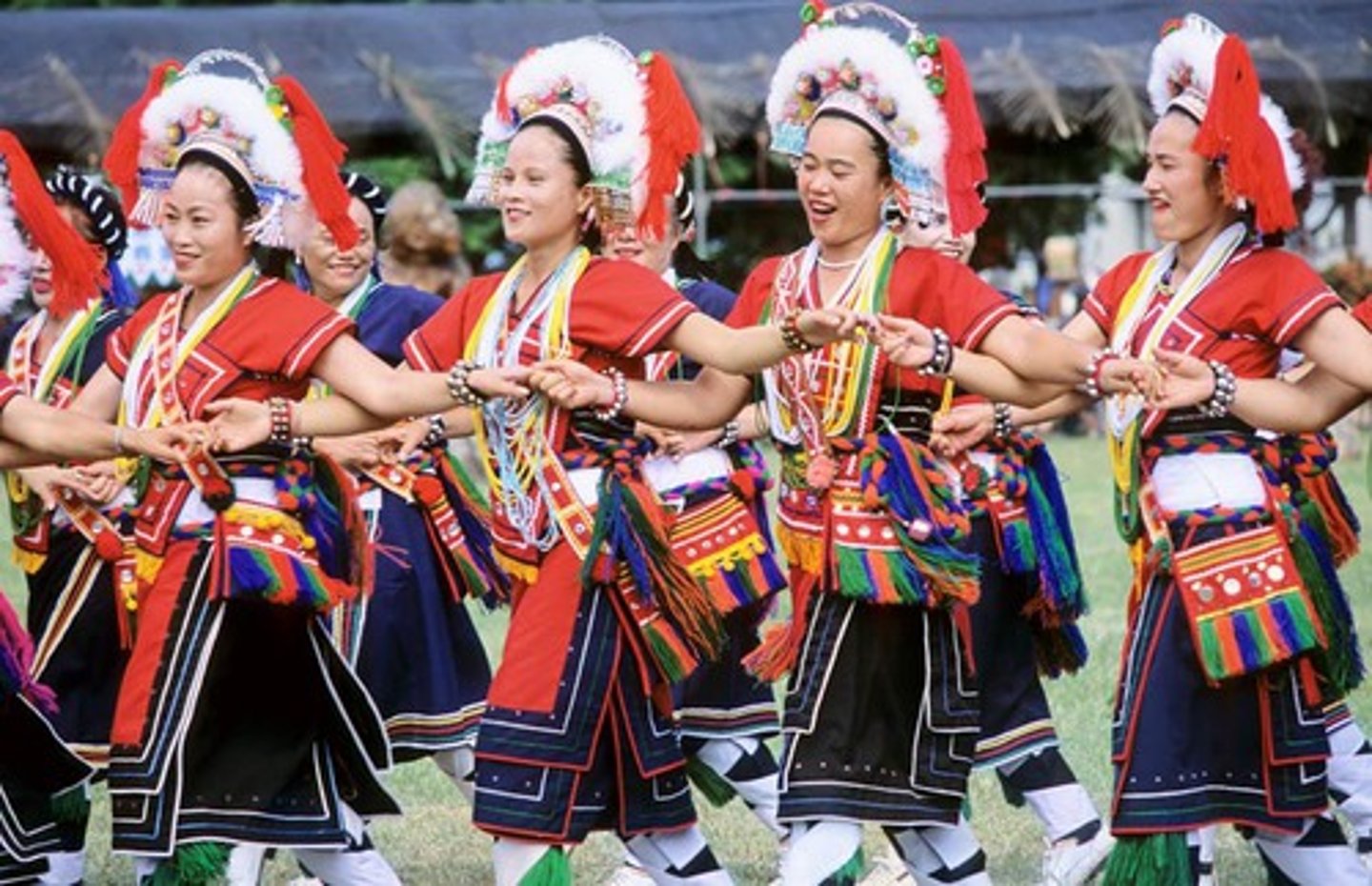

Material/surface culture
traits that are easily seen when observing a culture.
eg: food, clothing.
Nonmaterial/deep culture
traits that aren't as noticeable because they exist under the surface of a culture.
eg: belief systems, gender roles.

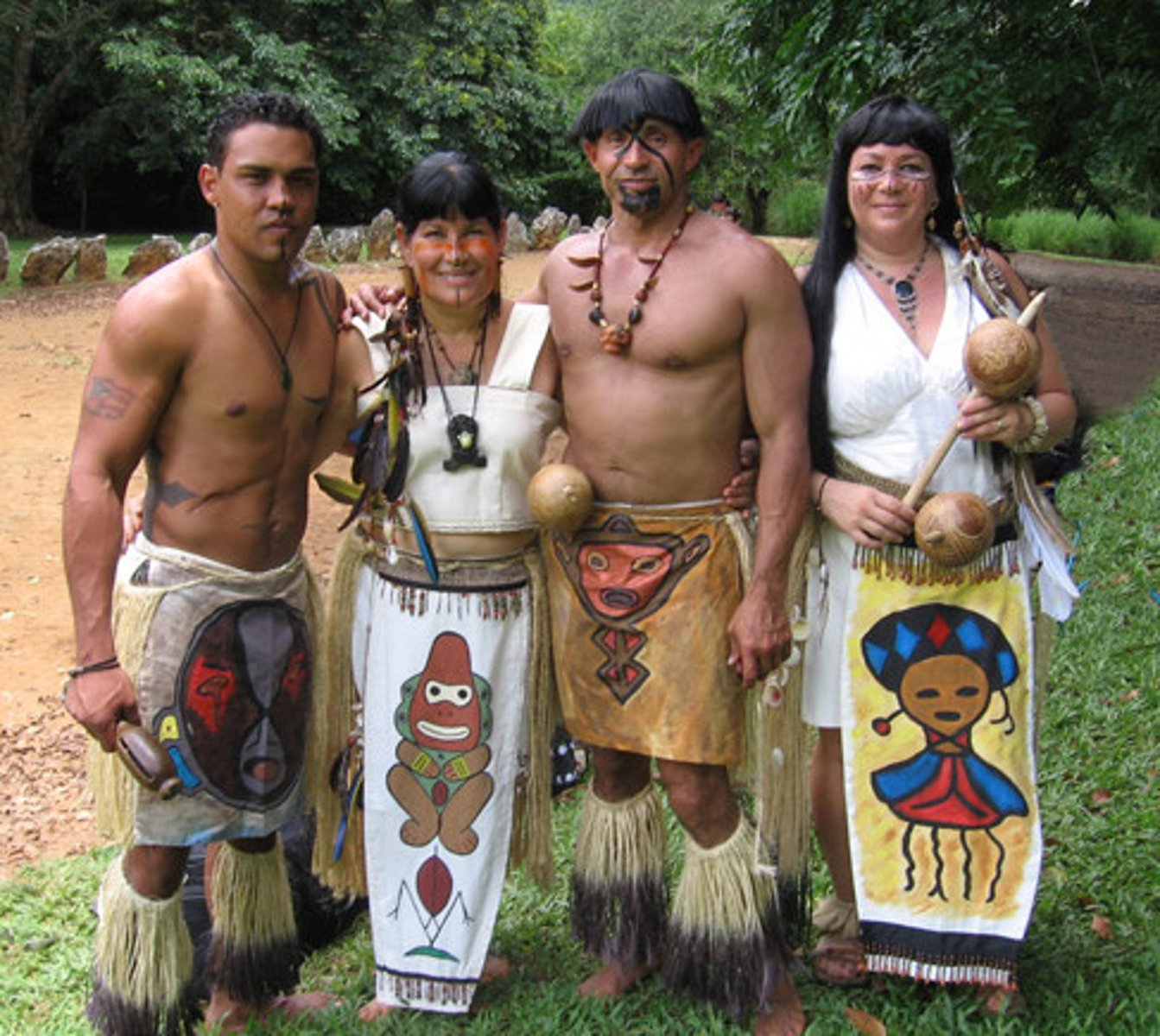
Indigenous culture
the original inhabitants of a region that are no longer dominant because of immigration, colonization, etc.
eg: native americans

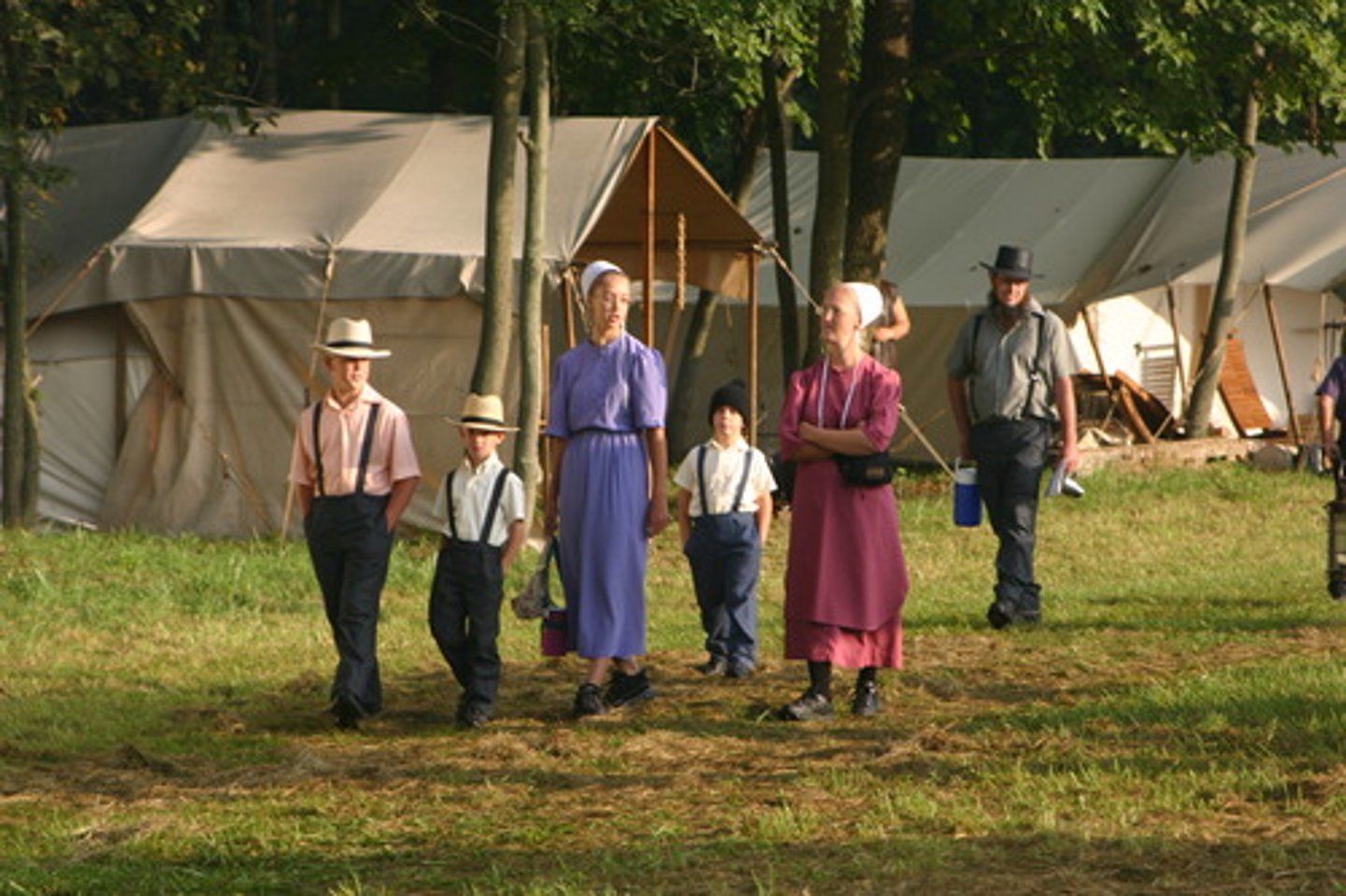
Local culture
a small, homogeneous group of people who share similar customs and live close together.
eg: amish
Popular culture (global)
the ideas, trends, music, movies, fashion, slang, and entertainment that are liked by many people in society (especially young people) at a certain time.
eg: k-pop

Cultural diffusion
the spread of a cultural trait to another area in the world.
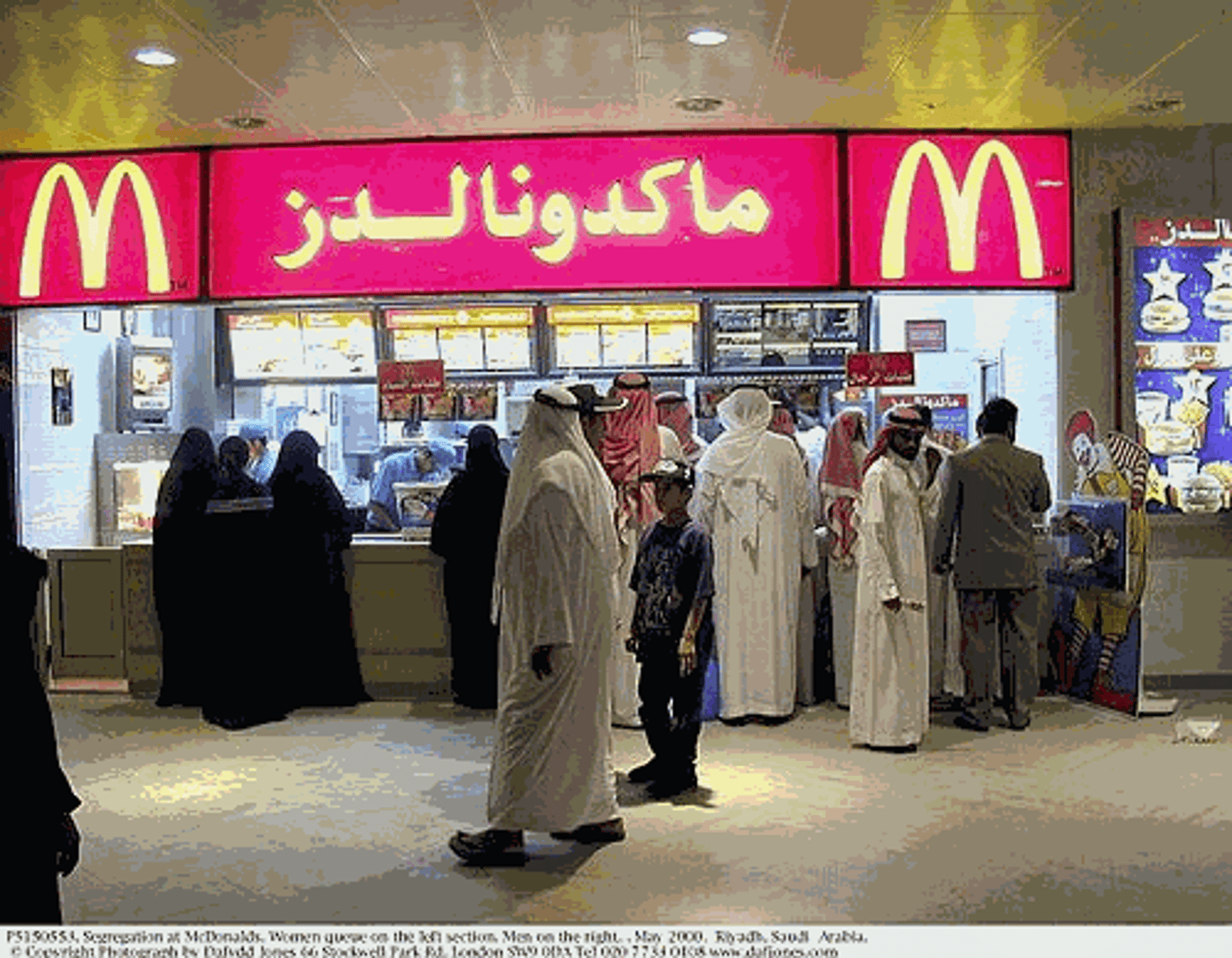

Acculturation
learning/adopting parts of a new or different culture.
eg: an egyptian moving to france and speaking french/eating french food.

Enculturation
learning your own culture.
Assimilation
abandoning your original culture for a new one.
Integration
learning a new culture while still maintaining your original culture.
Separation/isolation
maintaining your own culture and staying in your own little bubble. not bothering to learn about a new culture.
Marginalization
not being part of any culture. the new culture doesn't welcome you when you try to fit in.
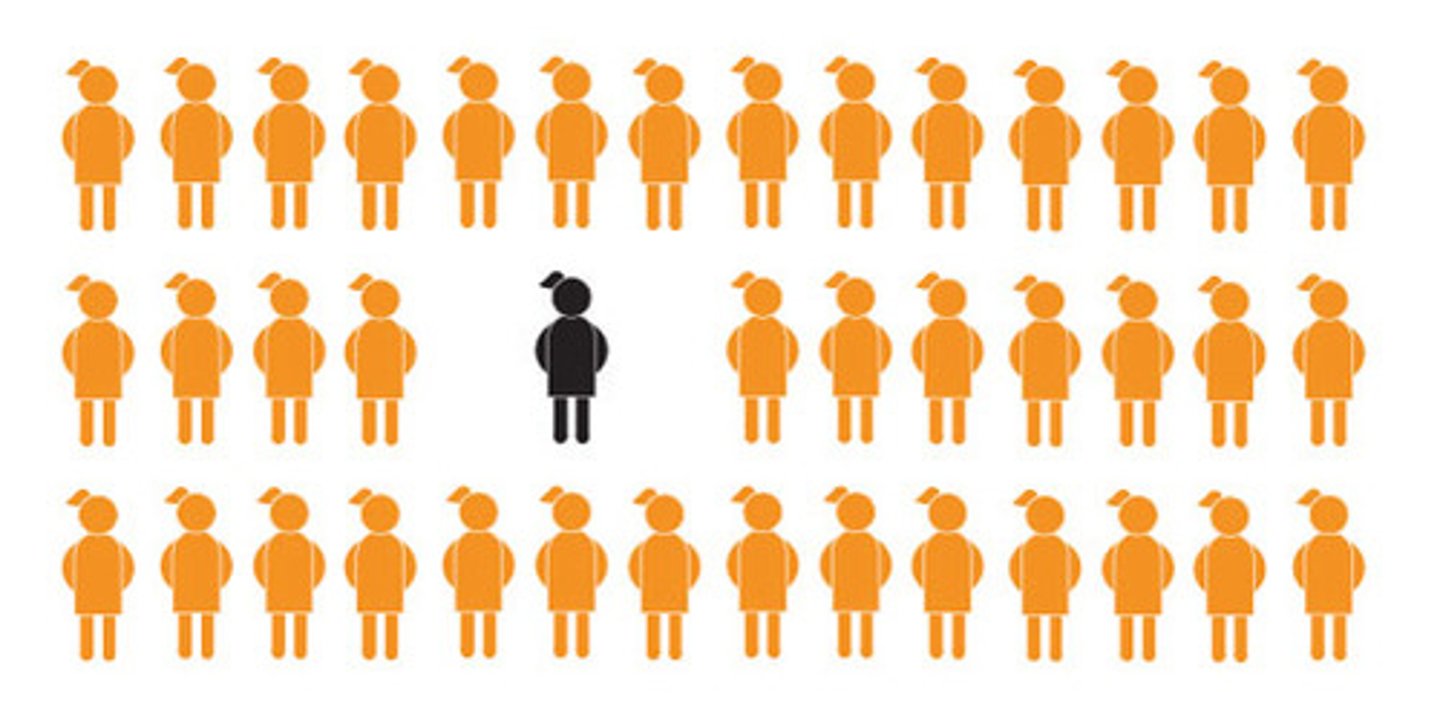

Transculturation
when two cultures exchange traits equally and both change as a result — a two-way blending.
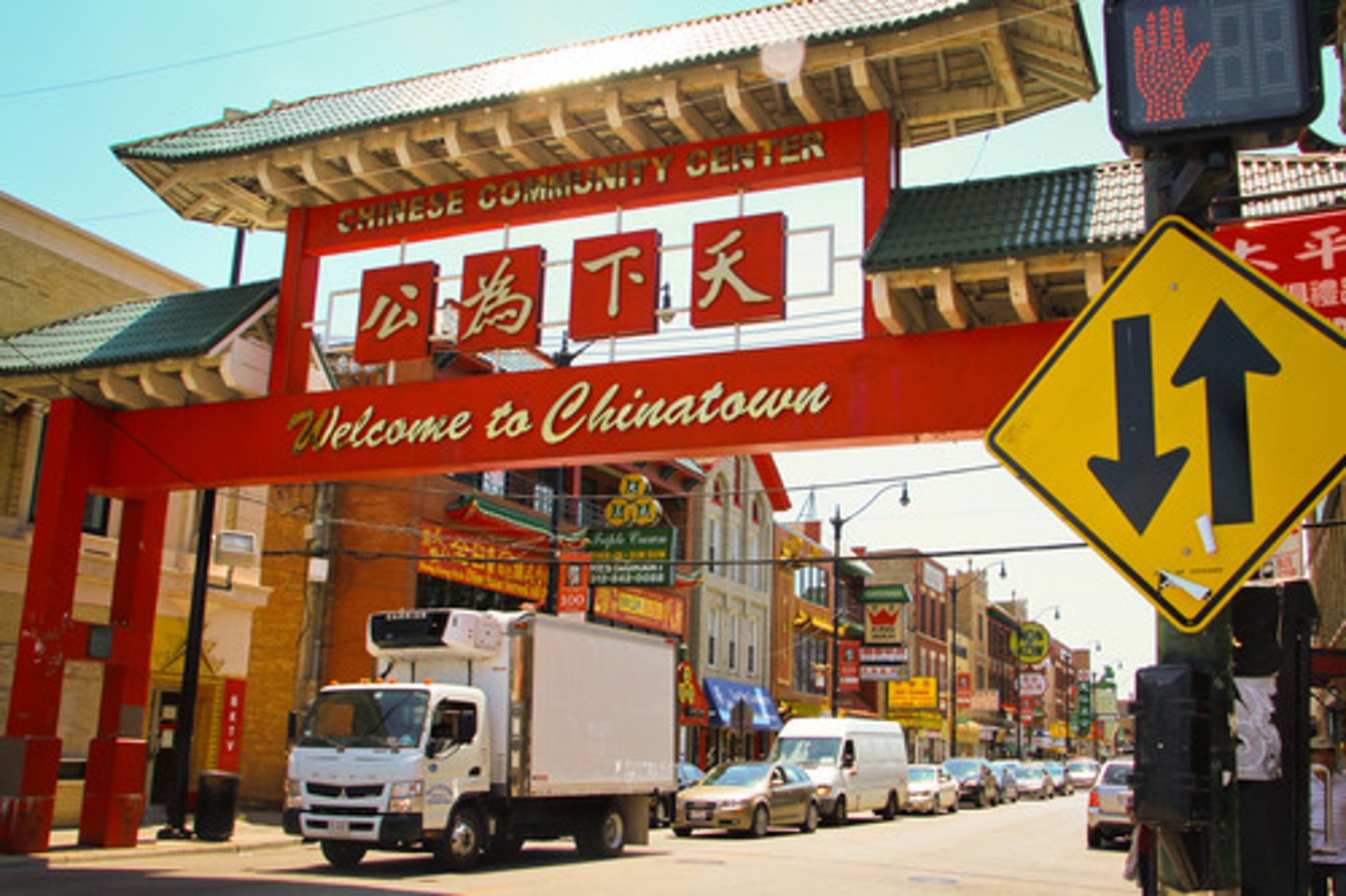
Ethnic enclave
communities of people of the same ethnicity so they can live comfortably in their cultural bubble.

Acultural stress
cultural shock.
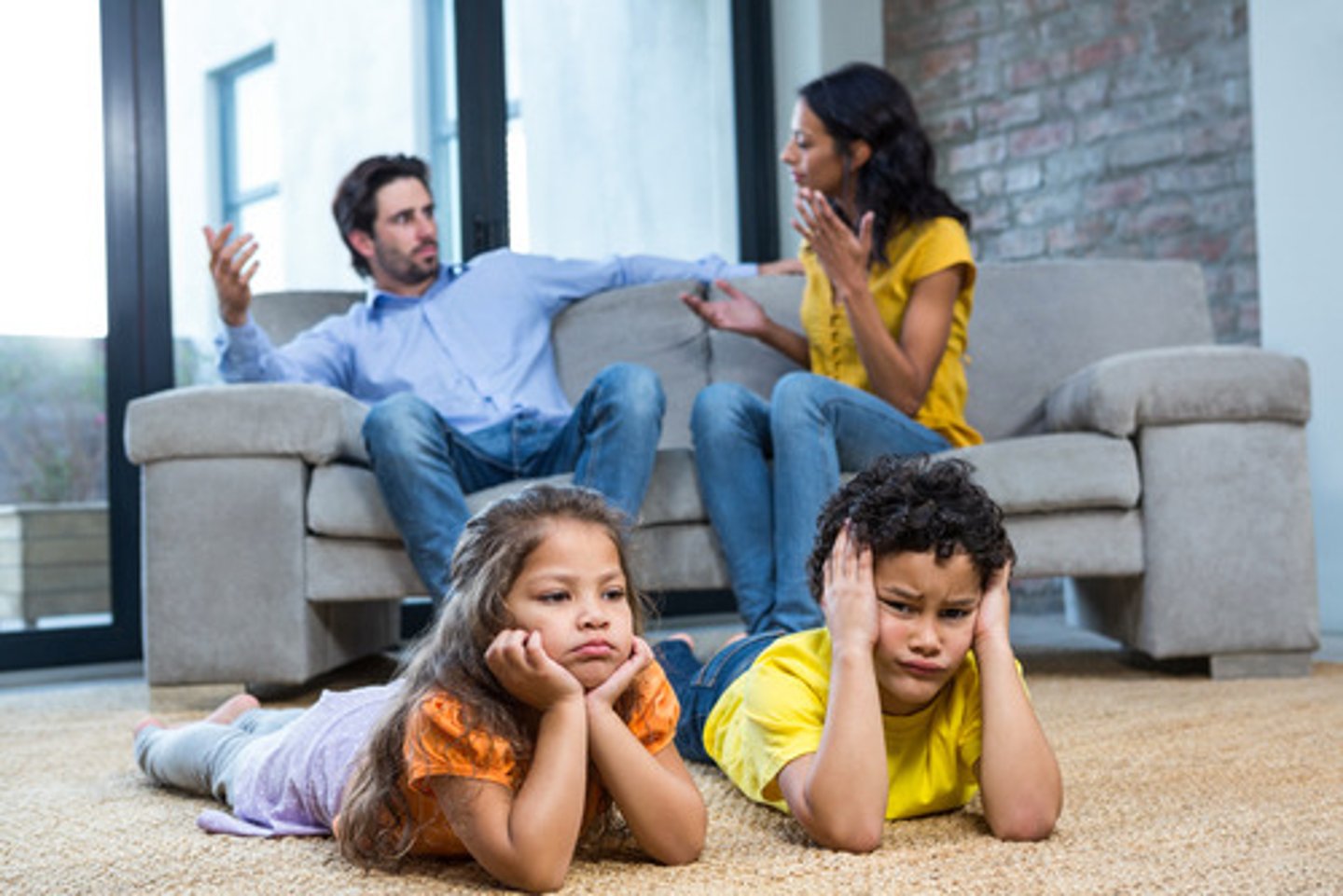
Acculturation gaps
generational differences in acculturation and how it leads to conflict within the family.
eg: immigrant kids are way more familiar with the new culture than their parents.

Homogenous culture
everyone speaks the same language, shares beliefs, celebrates the same holidays, etc.
eg: egypt
Heterogenous culture
people from all over the world live side by side.
eg: new york city
Customs
common ways of doing things in a society; norms.
Traditions
beliefs/activities passed down from generation to generation.
Multiculturalism
appreciation of cultural diversity.

Preadaption
when a culture already has traits that help it adjust easily to a new environment/situation.
Imperialism
controlling or influencing another country/region from afar, often for power or money; doesn't always involve settling there.

Colonialism
when a country takes over land and settles it with its own people to control it directly.
Cultural clash
brief often unintentional misunderstandings between cultures.

Cultural conflict
longer, deeper struggle between groups because of different beliefs, traditions, or lifestyles.
Genocide
deliberate killing of a large group of people, especially because of their race, religion, or ethnicity.

Race
physical characteristics like skin color, facial features, or hair type that societies use to categorize people.

Ethnicity
cultural identity, including shared language, ancestry, traditions, religion, and history.

Ethnocentrism (etic)
believing ur own culture is better than others and judging other cultures by ur own standards.
Cultural relativism (emic)
understanding and judging a culture based on its own values and beliefs, not your own.
Cultural landscape
the visible imprint of human activity and culture on the landscape.

Symbolic landscape
places with visual info ab the language, religion, gender roles, and deeper cultural practices of the ppl that live there.
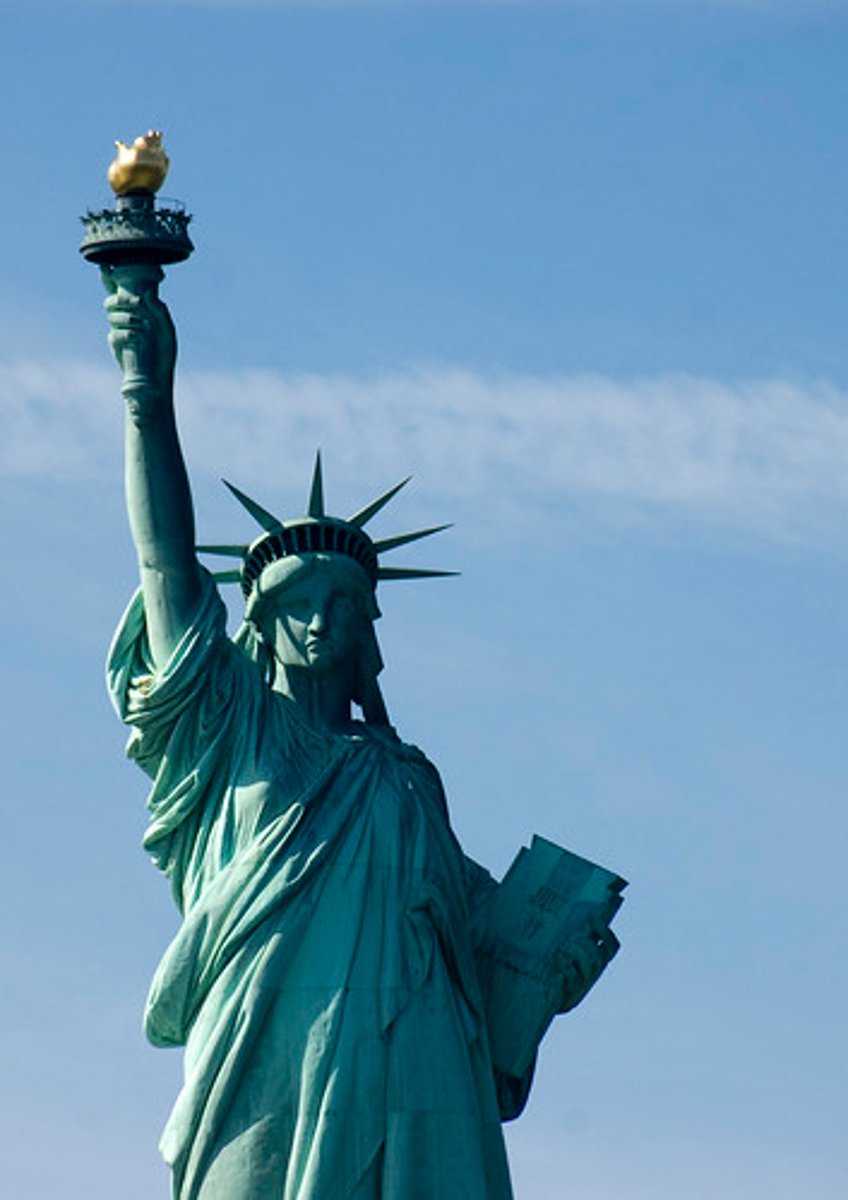

Sequent occupency
evidence of other cultures having been in a place before.
Placelessness
many places looking similar to each other rather than uniquely culturally distant from one another.
Placemaking
all the efforts to make an area better so that people connect a positive sense of place with it.
Sense of place
how we perceive a place based on past experiences, how it's depicted in the media, and what we've heard about it from others.
Modern architecture
very simple. includes straight lines, big windows, and are highly functional.
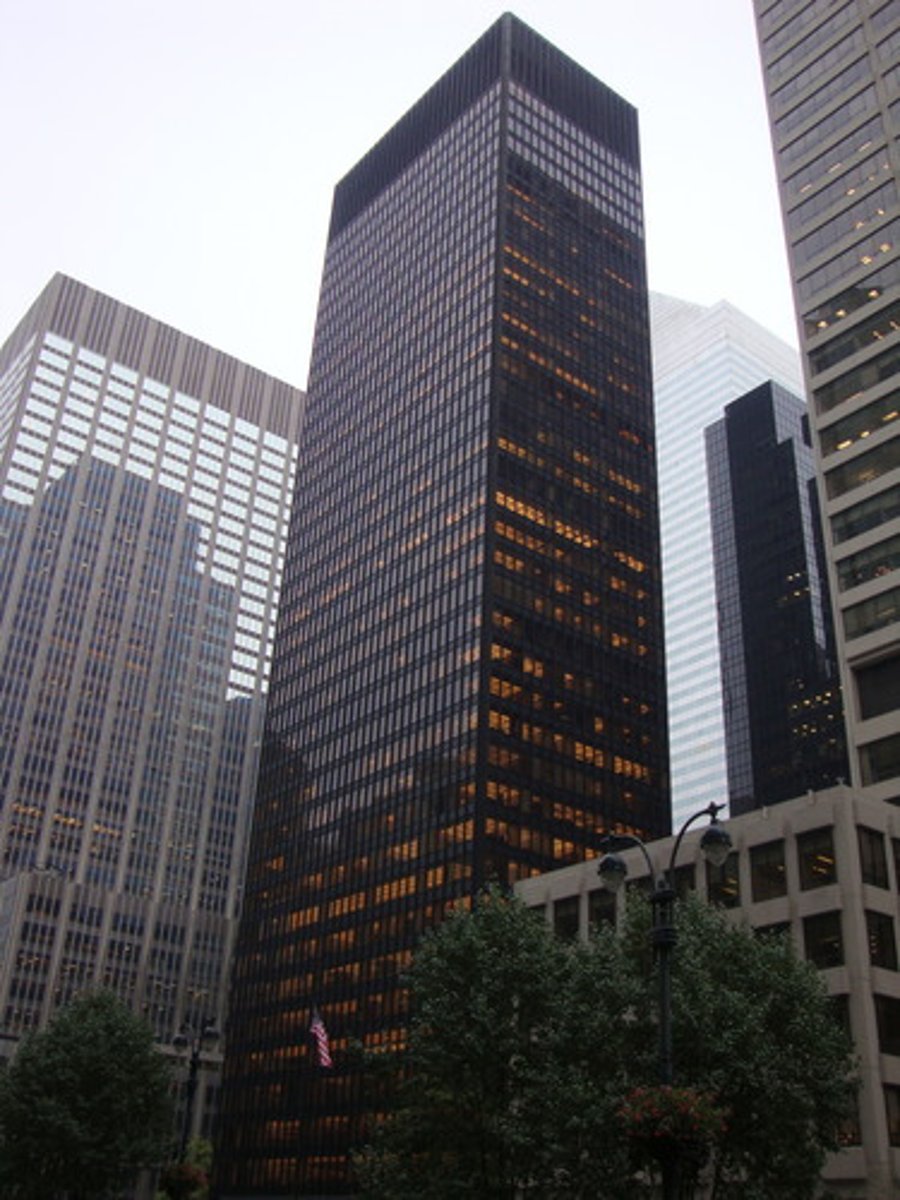

Postmodern architecture
blends historical foundations with modern touches.
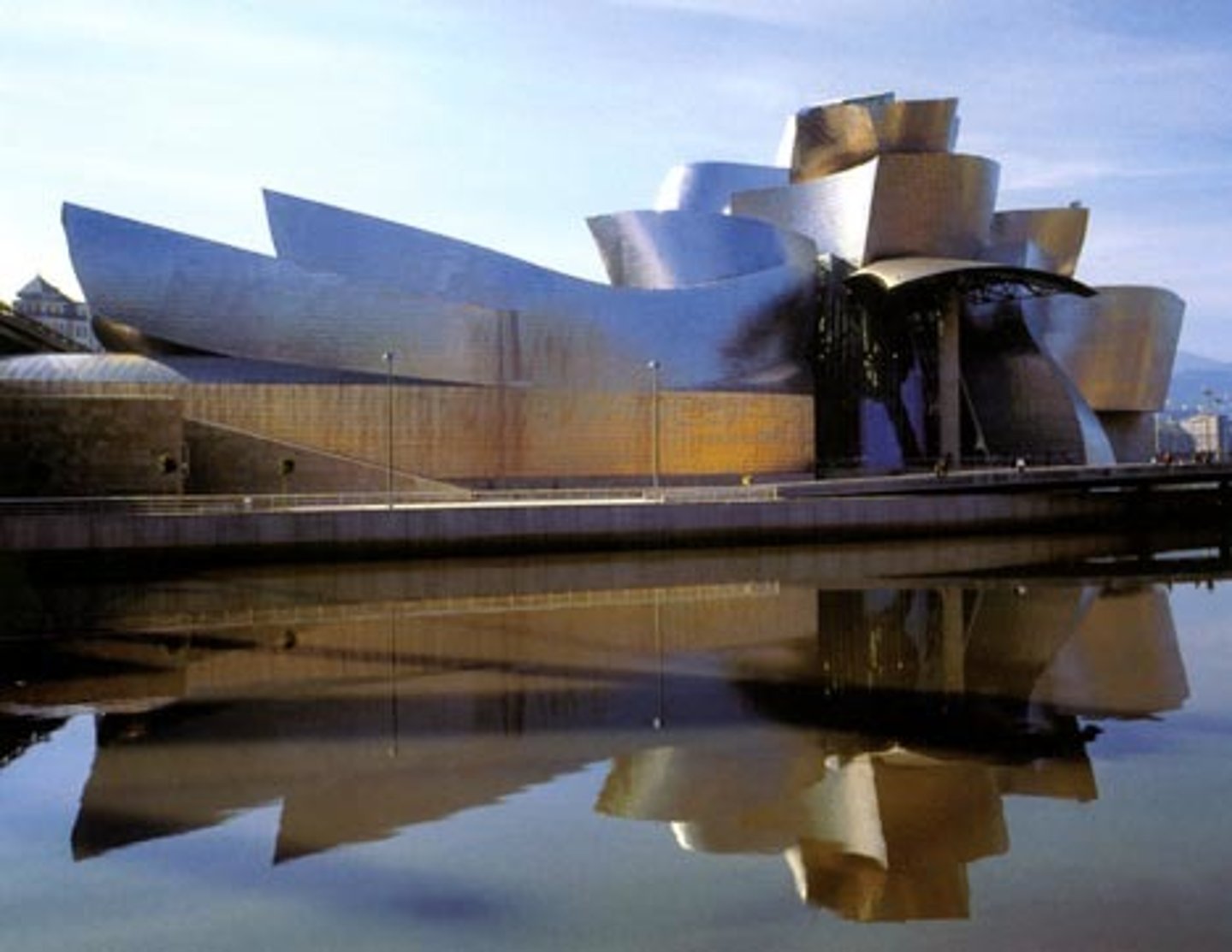

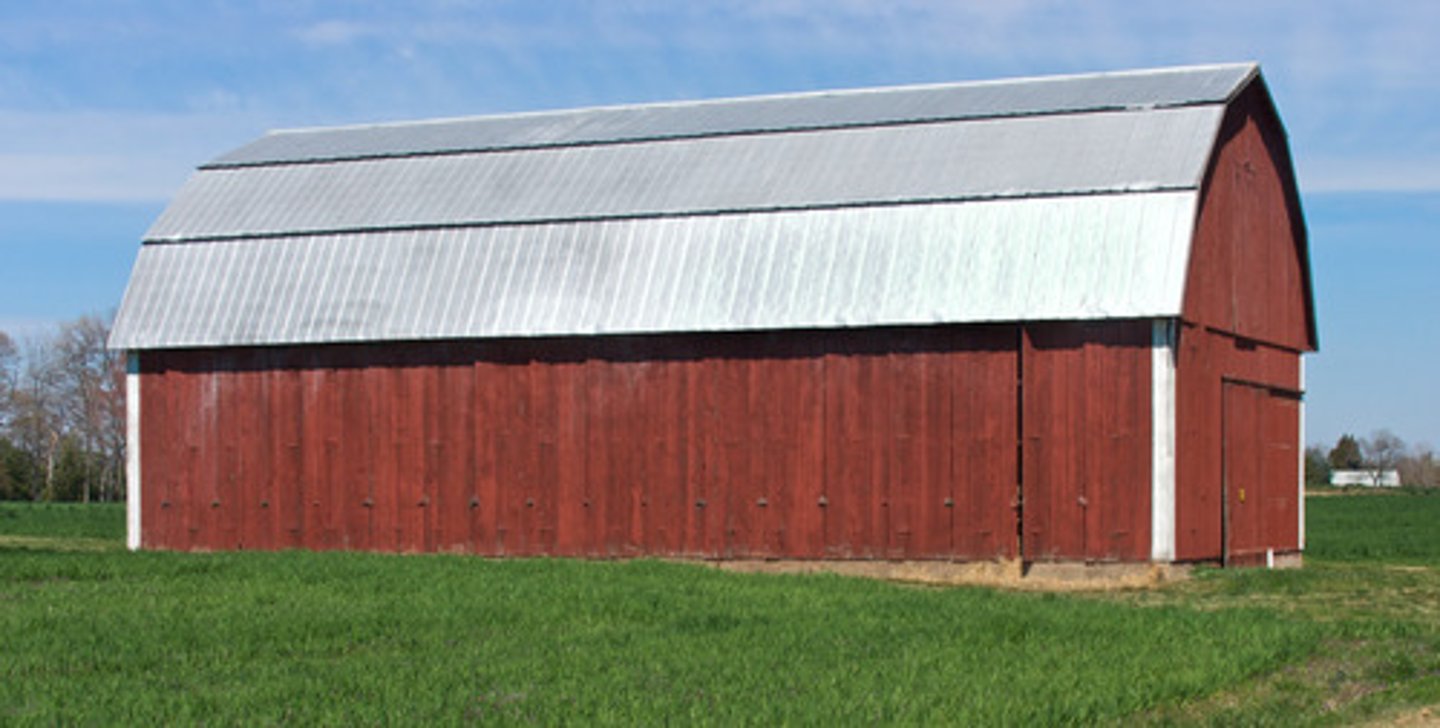
Local architecture
architecture that's specific to a certain area/culture.

Centripetal force
things that bring people together in a place.

Centrifugal force
things that tear a community apart.
Secularization
a society becoming less religious.

Relocation diffusion
moving to a new place and bringing ur cultural traits with you.

Hierarchical diffusion
the spread of a feature or trend from one key person or node of authority or power to other persons or places.

Contagious diffusion
the rapid, widespread diffusion of a feature or trend throughout a population.
Stimulus diffusion
trait that spreads to a new area but is slightly changed by the culture of a new area.

Absorbing barriers
completely stop a cultural trait from being spread.
Permeable barriers
allow a trait in but will change it in a more acceptable way.
eg: egypt and the gay scene in the barbie movie
Cultural hearth
where a religion originated.
Monotheistic
belief in one god.

Polytheistic
belief in multiple gods.

Universalizing religions
try to get more people to convert.

Missionary
a person sent on a religious mission, especially one sent to promote Christianity in a foreign country.

Christianity
most common religion. monotheistic and follows Jesus Christ.

Buddhism
believe in a Buddha: a man, not a god.

Islam
monotheistic. believe in Allah and prophet Mohammed.

Ethnic religions
focus on one ethnic group and generally have not spread into other cultures.
Shintoism
religion; located in japan and related to Buddhism; focuses particularly on nature and ancestor worship.

Hinduism
indian religion. believe in brahman as the essence and the gods brahma, vishnu, and shiva.

Judaism
the monotheistic religion of the Jews.

Syncretic
mix of 2 or more religions or cultural beliefs blended together.

Proselytic
describing a religion that spreads its message to others through missionary work.

Animism
belief that natural objects like trees, rivers, or animals have spirits or souls.

Language
system of communications used for speech between a group of people.

Language family
group of languages that come from the same ancient language.
Lingua franca
common language used by people who don't share the same native language — it helps them communicate.
eg: english.
Official language
the language adopted for use by the government for the conduct of business and publication of documents.

Endangered languages
language at risk of disappearing because very few people speak it.
Pidgin
a simplified form of speech developed from two or more languages.

Creole
pidgins that become a full language.
Esperanto
a made-up (constructed) language created in the 1800s to be an easy international language so everyone could communicate.
Extinct languages
languages no one speaks anymore.
eg: latin.

Dialects
regional variety of a language within its own vocab, grammar, or pronounciation.
Accents
the way words are pronounced in a language.
Isogloss
boundary line on a map that shows where certain words, pronunciations, or grammar features change between regions.
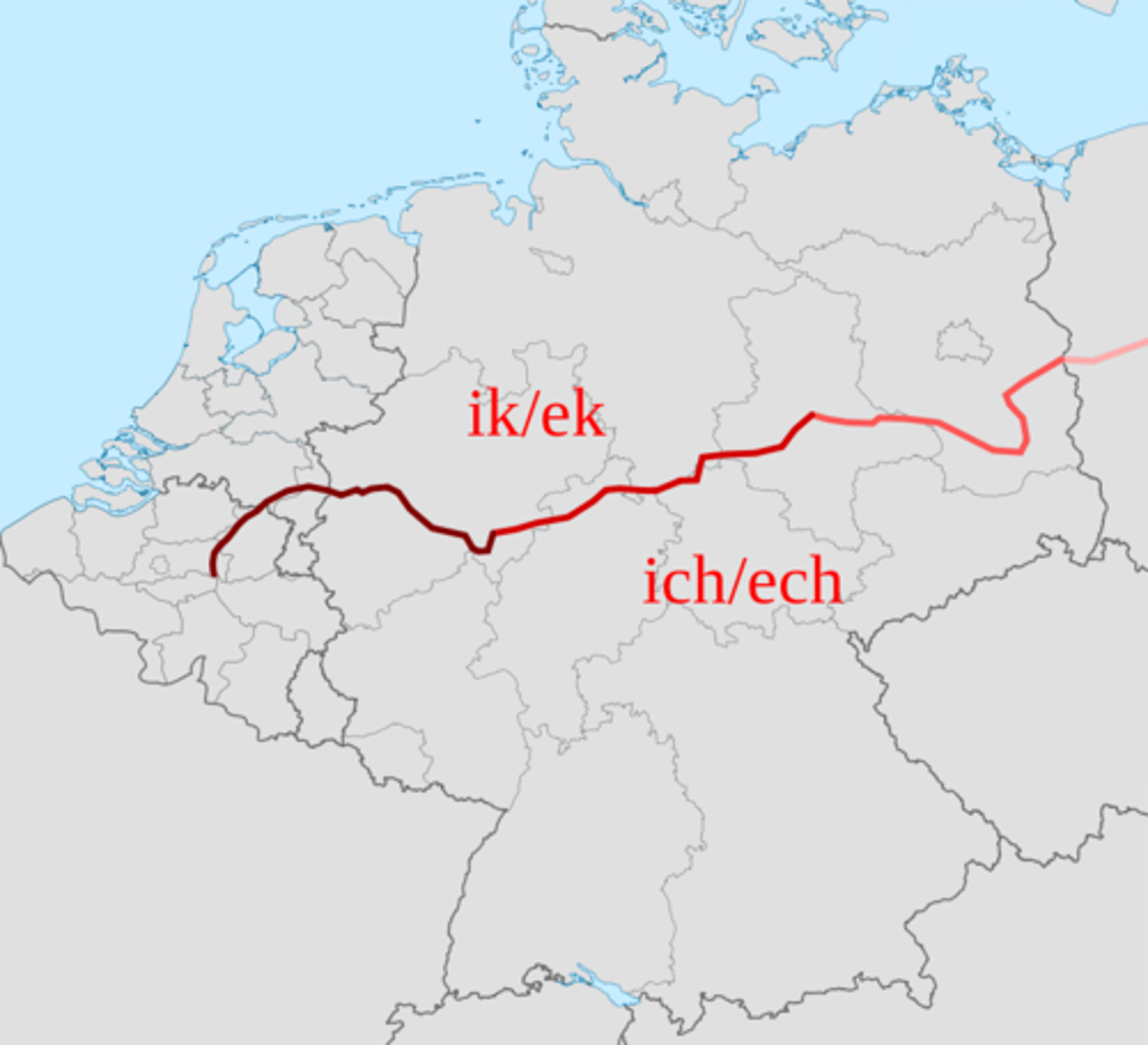
Polyglot
someone who speaks multiple languages.

Toponyms
the names that we give places.