TestOut LabSim ITF+ Unit 3 "Computer Hardware"
1/126
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
127 Terms
Bus
The communication system that allows data to be transferred between the components inside a computer. The term bus comes from the Latin word omnibus that means for all.
For example, a motherboard has many small wires spanning the motherboard. These tiny wires, or circuitry, make up the bus which has been imprinted on the circuit board, or PCB. The computer bus is responsible for transferring the following:
• Power - Each component requires electricity; the bus provides this power.
• Data - The data is the information that is transferred between the components in the computer.
• Memory Location - Memory is a major component in a computer system, as it temporarily stores the data while its needed for processing. The bus keeps track of the address or location where the data is stored in the memory.
• Clock Timing - A computer has a clock mechanism, often performed by the CPU, which synchronizes how all the components work together over the bus.
(For even more information, go to 3.3.7)

Central Processing Unit (CPU)
The most important part of any modern computer system; it controls the other parts of the computer.

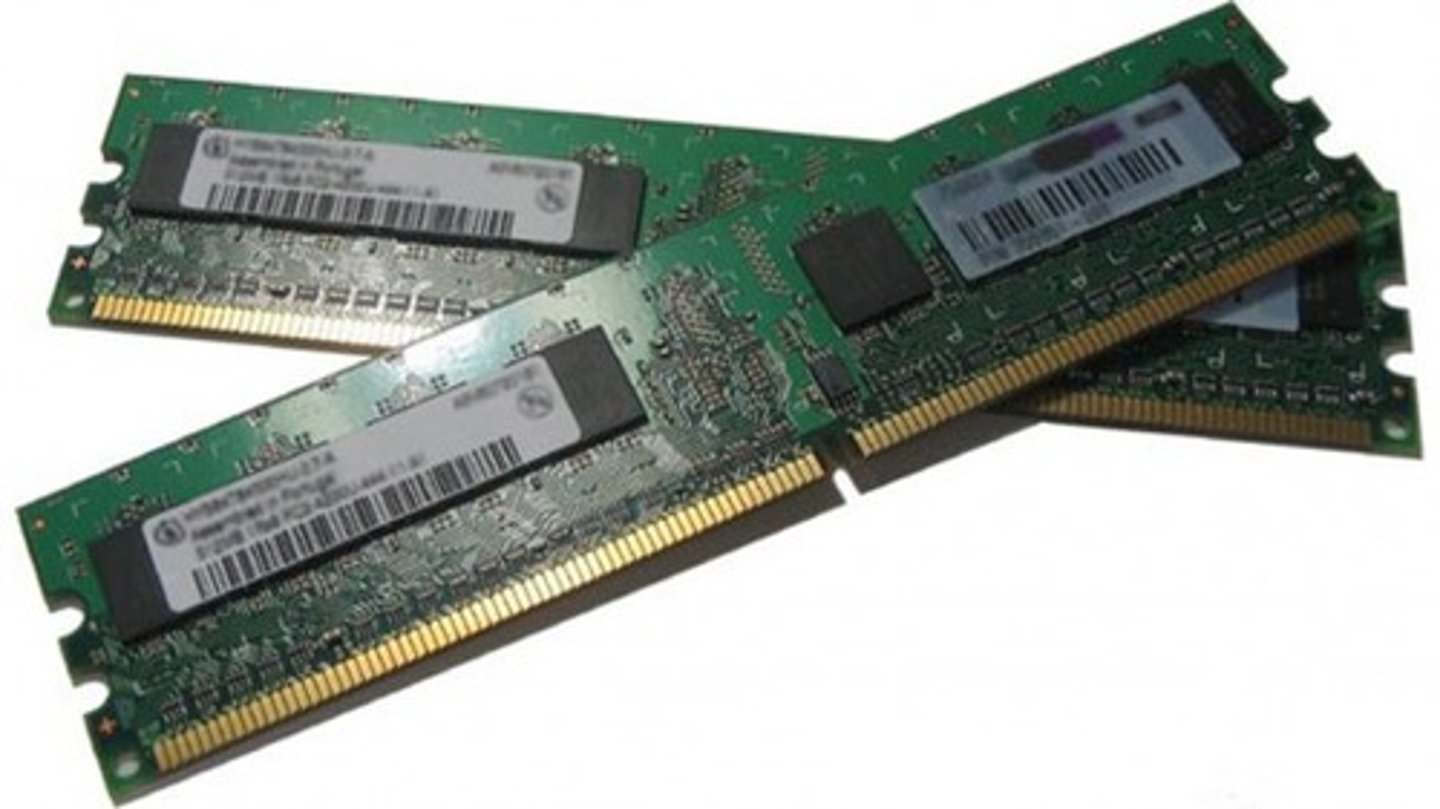
Random Access Memory (RAM)
The main memory of a computer that can be quickly accessed by the CPU. It is where the computer stores data and instructions that it is actively using.

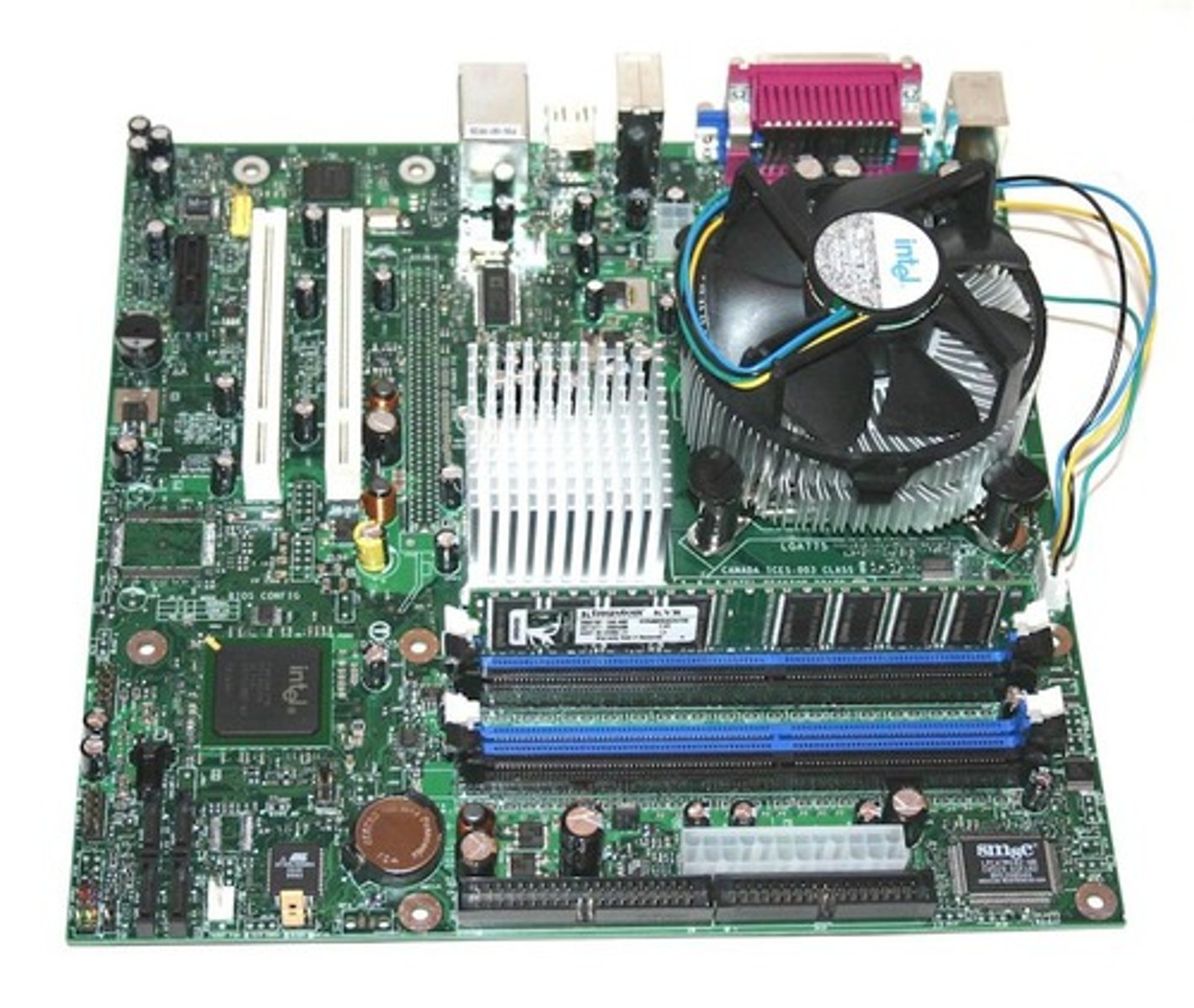
Motherboard
A large, flat computer component that connects the important components of the computer, such as the CPU, RAM, and the BIOS chip. It also has power and other communications connections.

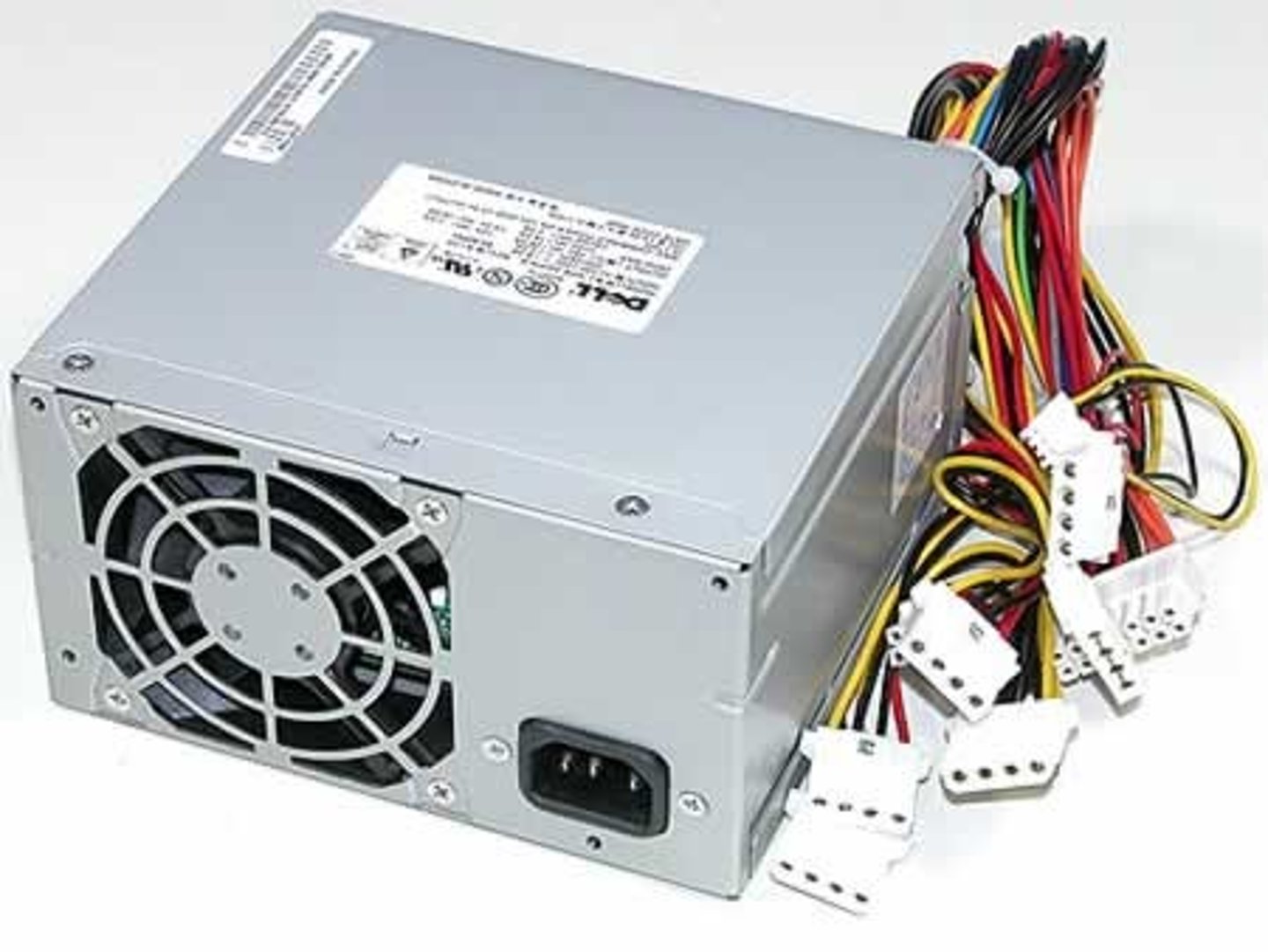
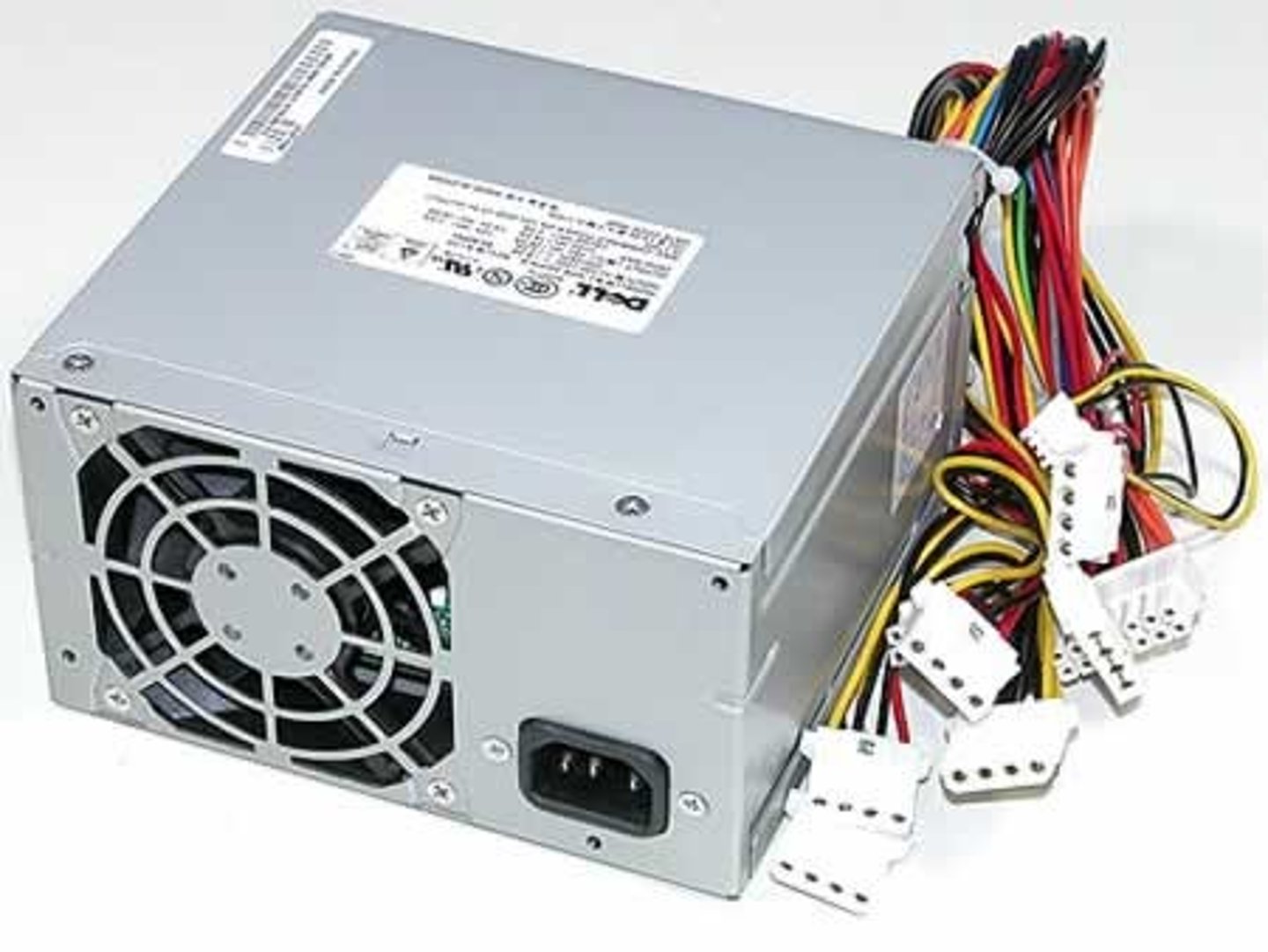
Power Supply Unit (PSU)
A unit that supplies electricity to the motherboard and other computer components.

Graphics Processing Unit (GPU)
An additional computer processor that provides graphics processing. It improves performance by relieving the CPU of this duty.

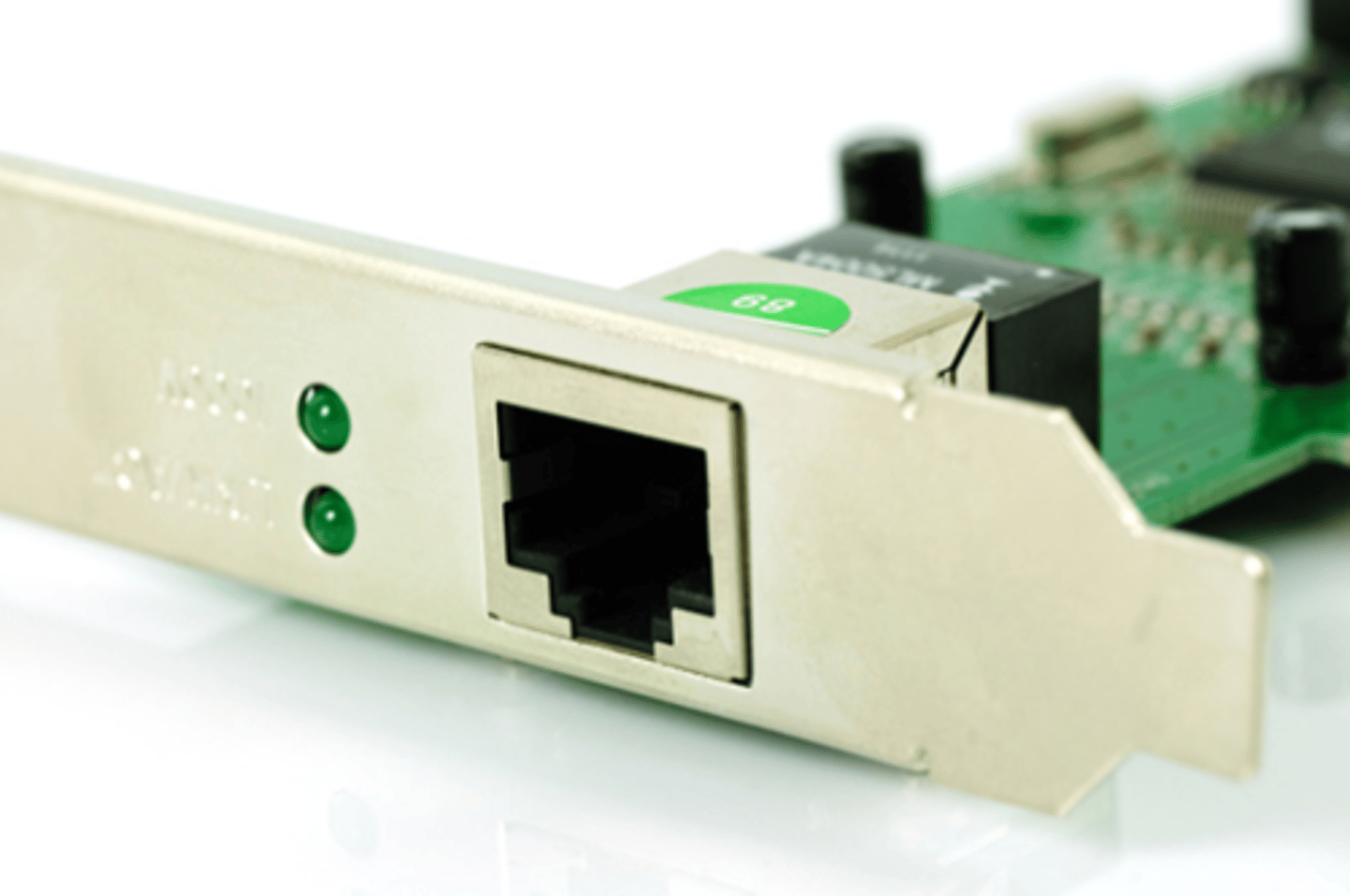
Network Interface Card (NIC)
A component, sometimes built into and sometimes plugged into the motherboard, that provides network connectivity.

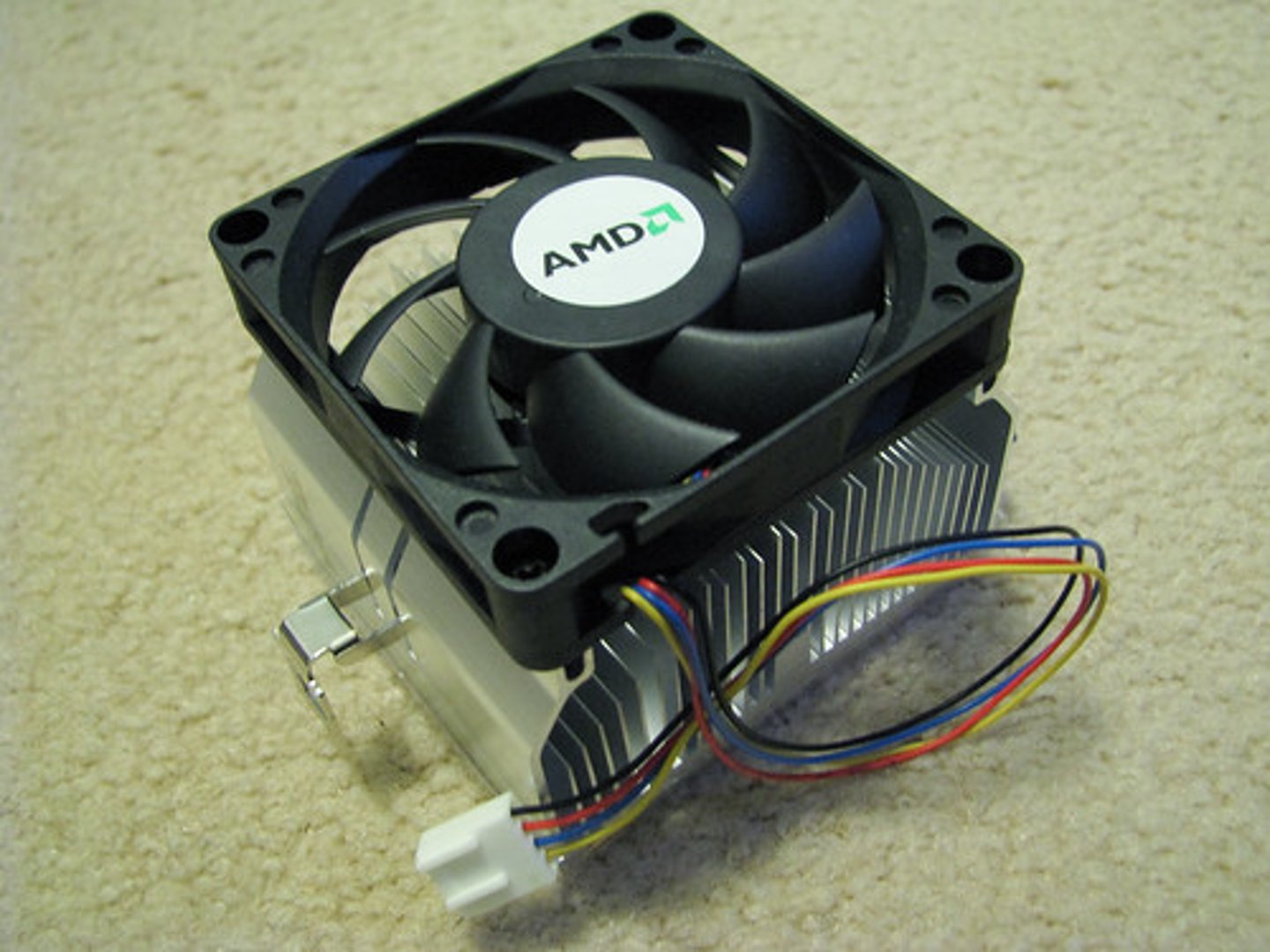
Cooling System
Components, including heat sinks and fans, that keep computer components from overheating.

Electrostatic Discharge (ESD)
An event in which two objects with different charge levels come together resulting in an electrostatic shock.

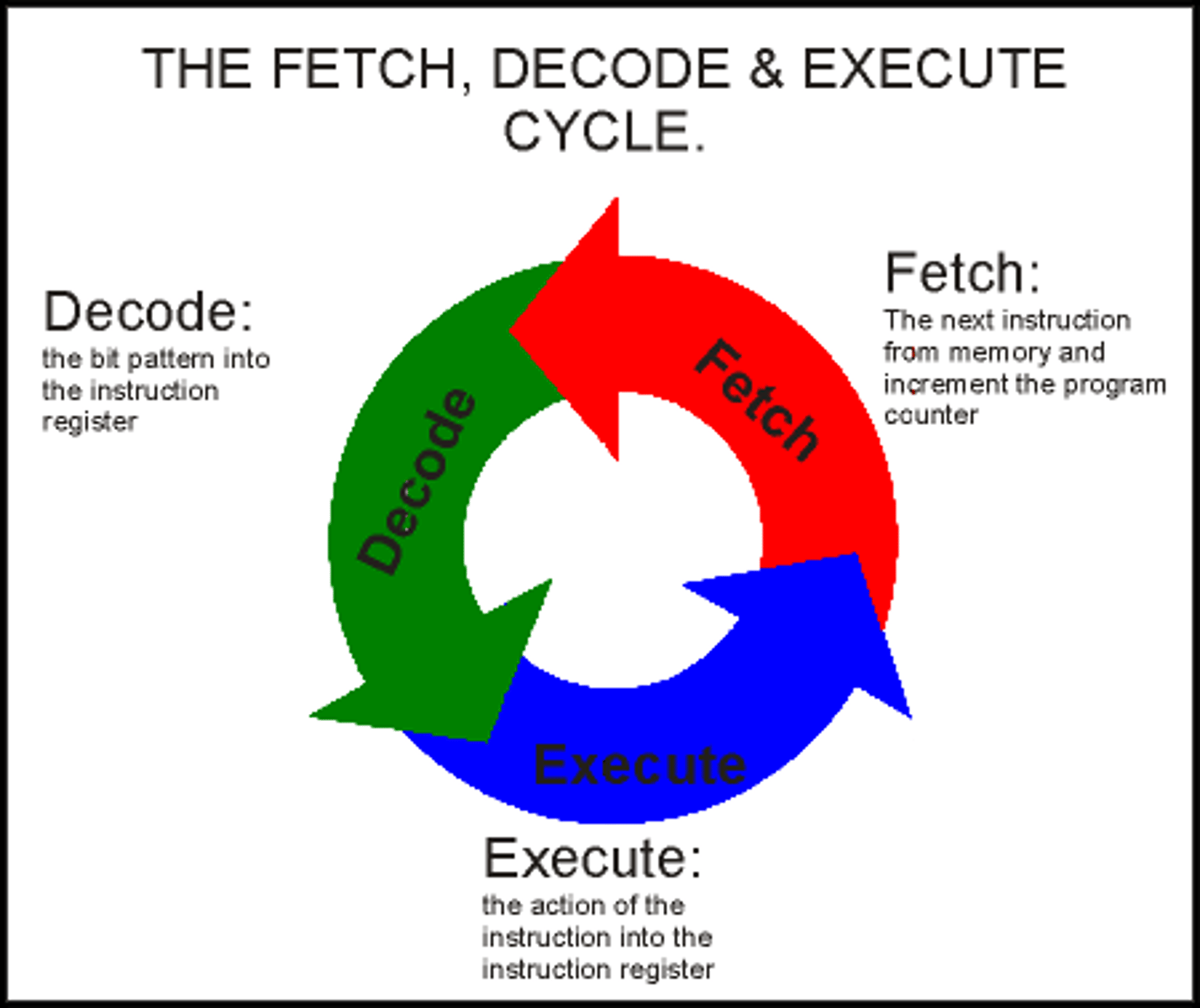
The Fetch-Execute Cycle
A three-step cycle (fetch, decode, and execute) that processors use to execute instructions.
x86 Processors
A family of processors manufactured by Intel and AMD that use a common instruction set (list of commands that the processor can execute).
Most large computers, such as desktops, laptops, and servers, use x86 processors. x86 refers to the processor's instruction set which is the list of commands that a processor can execute. Today, most x86 CPUs are designed to process 64 bits of information at once. Older x86 processors could only process 32 bits at a time. The original x86 processors were designed for 16-bit instructions. The two biggest manufacturers of x86 processors are Intel and AMD.
(i) 64-bit x86 processors were originally referred to as x86-64 to distinguish them from the 32-bit x86 processors. This is now typically shortened to x64 for 64-bit and x86 for 32-bit processors. 64-bit computers are backwards compatible; they can run both 32-bit and 64-bit programs.

Advanced RISC Machines (ARM) Processors
A family of processors most often used in smartphones due to its lower power requirements. This is accomplished by reducing the processors' instruction set.
The x86 processors are extremely powerful, but they consume a lot of power and generate immense heat. That's a problem for mobile devices, which depend on battery power and are often carried in their owners' pockets. Most tablets and smartphones use Advanced RISC Machine (ARM) processors. ARM processors use a reduced instruction set. This means they can't do as many types of things as x86 processors. The tradeoff is that they are smaller, consume less power, and generate less heat. These processors are used in many mobile devices and phones made by Apple, HTC, Nokia, Xiaomi, Sony Ericsson, Samsung, nVIDIA Tegra, and others.

Expansion card
A circuit board that connects to a computer's motherboard, giving it additional power or functionality.
Expansion slots on a motherboard:
• Video cards
• Network cards
• Audio cards
• Other card types
Typically, expansion cards connect to a slot in the motherboard called a Peripheral Component Interconnect (PCI). Another common type of slot is the PCI Express (PCIe).

Heat Sink
A computer component that attaches to a chip (such as a CPU) that disperses heat and prevents overheating.

Air Cooling
A common method of cooling that uses fans to move hot air out of a system.

Water Cooling
A liquid-cooled system that places a water-cooled heat exchanger near a heat source. The exchanger removes the heat, reducing the air temperature.
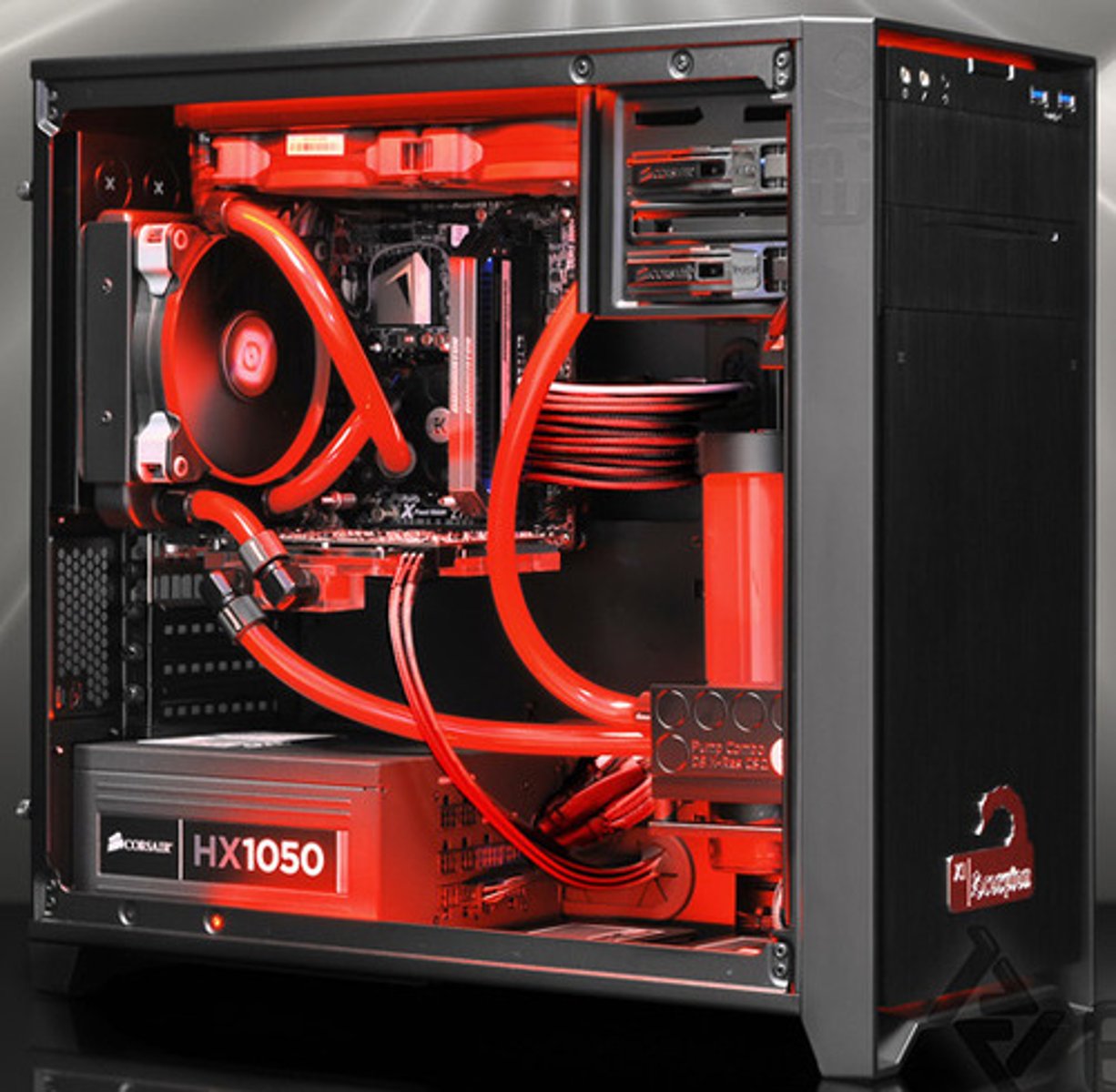

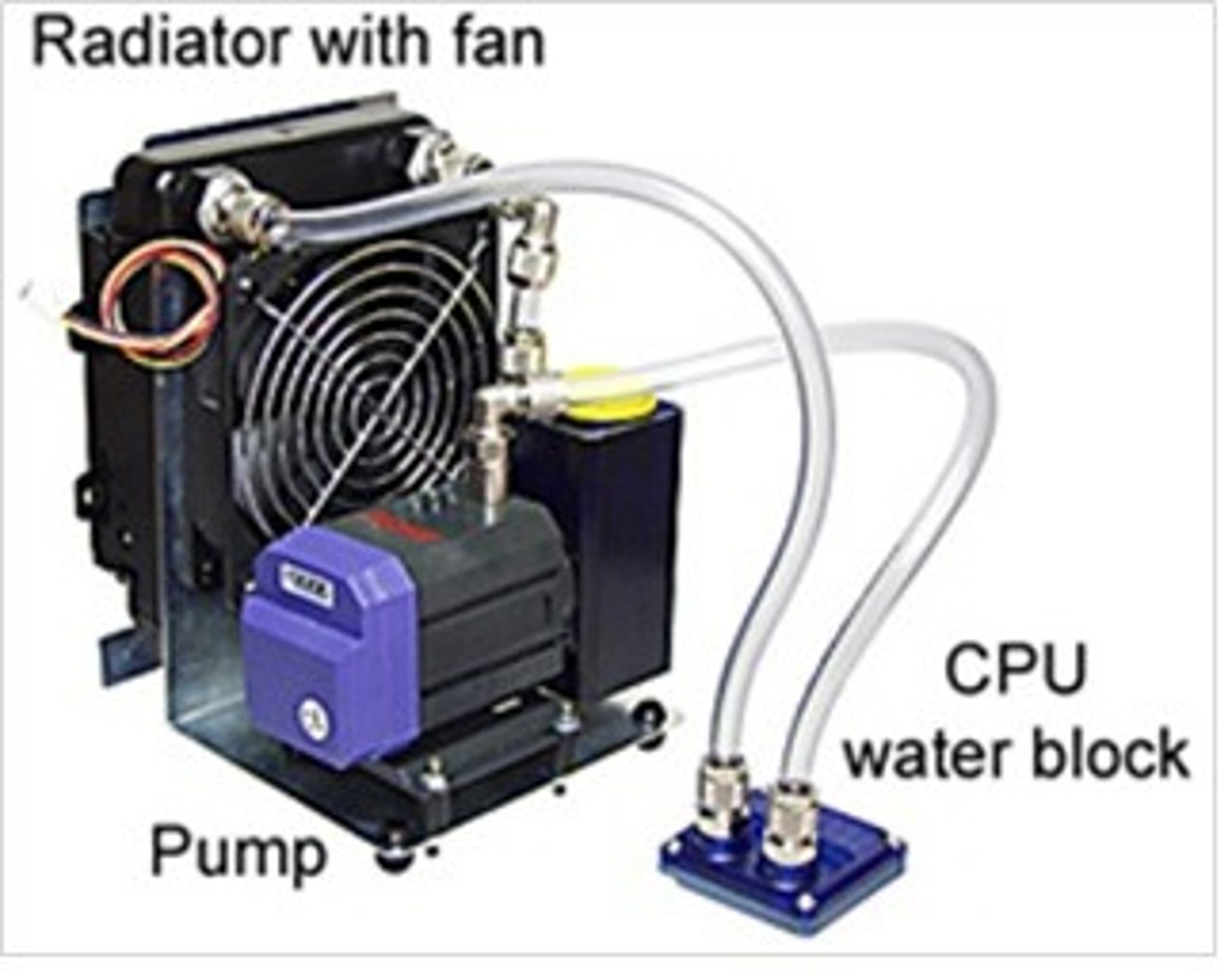
Active-Liquid Heat Sink
A cooling system composed of a liquid heat sink, internal liquid pump, a fan, and a radiator that all actively pump liquid in and out with no help from an outside pumping system.
Immersion Cooling
An advanced system of cooling in which liquid coolant is in direct contact with the CPU. It offers a high level of heat transfer that quickly reduces the temperature of the CPU's surface.
Desktops
Also known as workstations or PCs, desktops are computer systems that are small enough to on, under, or near a desk. They are widely used, especially for business, industry, and home use. Desktops have been around for many years.
Desktop systems are equipped with peripheral devices, such as a monitor, keyboard, mouse, and speakers. Desktop systems typically have the following advantages:
• Modularity allows them to be customized to perform specific functions.
• Ease of repair and upgrade.
• Power to run CPU-intensive tasks.
• Storage capacity to handle larger amounts of data than other types of computing devices.
Desktop systems also have some disadvantages:
• They are not mobile.
• They require continuous access to an A/C power outlet.
*Desktop computers are often used to connect to a network and therefore can be considered a network client.
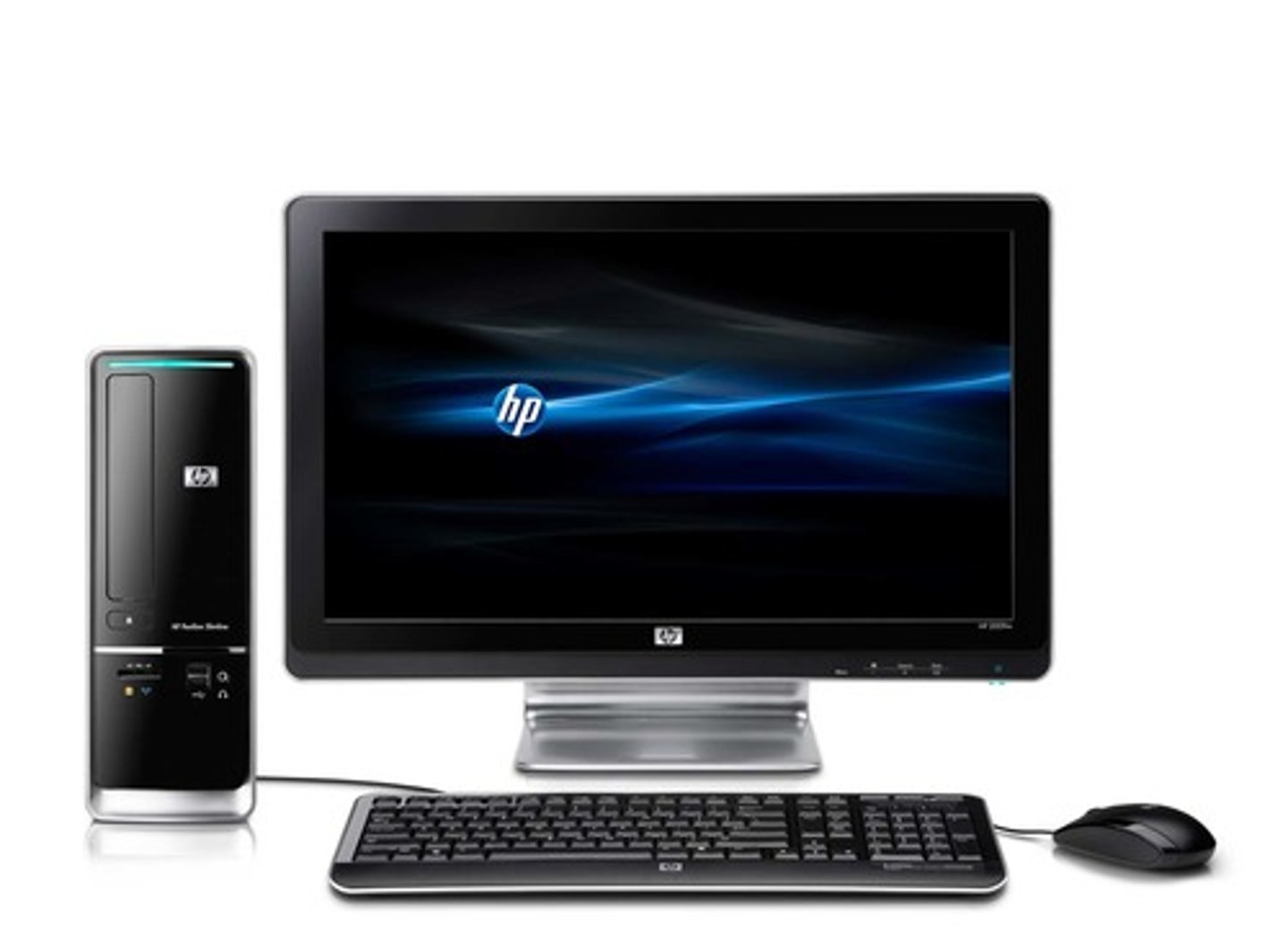

All-In-One Device (AIO)
A desktop computer that contains every component except the keyboard and mouse in the same case as the monitor. All-in-one systems have several advantages:
• They require less space than a desktop.
• They are easy to move to a new location.
All-in-one systems also have some disadvantages:
• They are harder and more expensive to repair. If any component (other than the keyboard or mouse) goes bad, you will probably have to take it into a shop to get repaired.
• In most cases, you are not able to expand the memory or disk space. However, external drives can still be added using USB ports.

Notebooks and Laptops
Also known as subnotebooks, notebooks and laptops are computers with all components built into one case. These systems have several advantages, they:
• Can run the same productivity applications as desktop systems.
• Are much smaller, weigh less, and use less power than desktop systems.
• Include batteries that allow them to run without external power for a period of time.
• Use flat-panel screens, that makes them easy to transport.
• Are mobile.
• Usually include built-in wireless networking.
Notebook and laptop systems also have several disadvantages. They:
• Are more difficult to upgrade or repair.
• Are usually more expensive than comparable desktop systems.
• Typically have less computing power than comparable desktops.

Hybrid Laptop Devices(2-in-1)
A computer that caters to the needs of both tablet and laptop users. Hybrid laptops provide a touchscreen and other tablet-style conveniences, but also provide an operating system and keyboard.
Hybrid laptops are often referred to as "2-in-1" devices. These systems have several advantages. They:
• Can run standard laptop operating systems.
• Have laptop type processors.
• Have a touch screen that provides a dimension not available on a standard laptop.

Gaming Consoles
A computer system specifically built to be operated by a gaming pad instead of a keyboard and mouse. Gaming consoles are also referred to as gaming box or video game console. A gaming console includes the major computer components, such as CPU, GPU, RAM, an operating system, disk storage, etc. These components, however, are designed to work best with games and the high graphics capabilities required by these games. Another difference is that gaming consoles often use a high-definition TV for its screen or display. Example of gaming consoles include Xbox, PlayStation, Nintendo Switch, and Wii.

Network Client
A device that can connect to a network.
Mobile Devices
Small computing devices, such as tablets and smart phones. Advantages are that mobile devices:
• Are much more mobile than any other type of computing device.
• Include a variety of integrated devices, such as cameras, microphones, and wireless networking.
• Can be less expensive than notebooks or desktops.
• Use a touch-screen interface.
Disadvantages are that mobile devices:
• Are difficult to repair and nearly impossible to upgrade.
• Don't typically let you replace the battery.
• Don't typically support the same productivity applications as notebook and desktop systems.
• Provide much less computing power than a desktop or notebook system.

Servers
A computer whose purpose is to provide shared disk storage or to perform a special service for a large number of people, such as web processing, email, or database services. As such, this is not something you would typically have in your home or would use for personal use. Servers are widely used in business. Although each server is different, most servers use many of the same components that a desktop or client computer uses. However, servers typically have more memory, disk space, and processing power than a desktop computer.

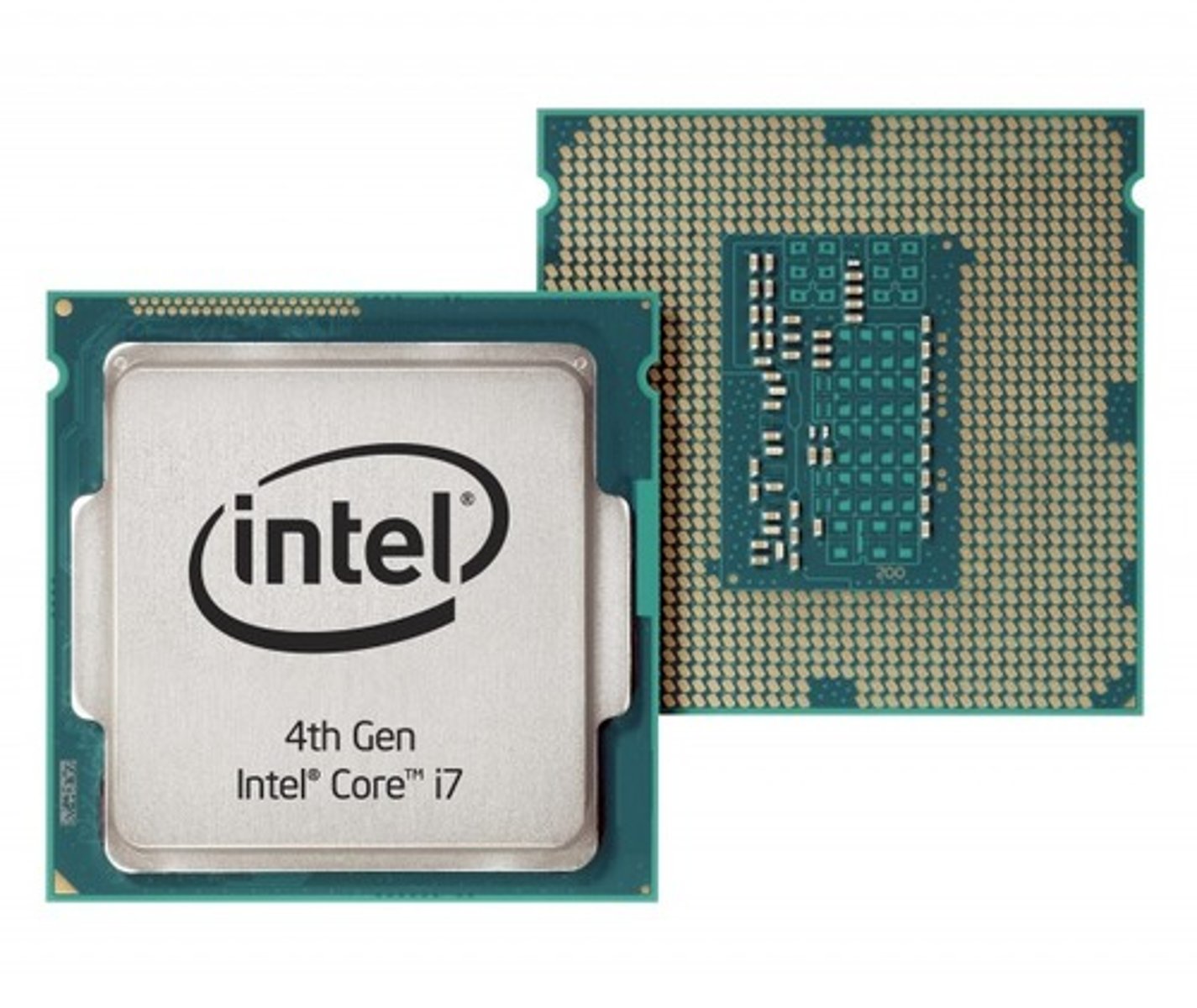
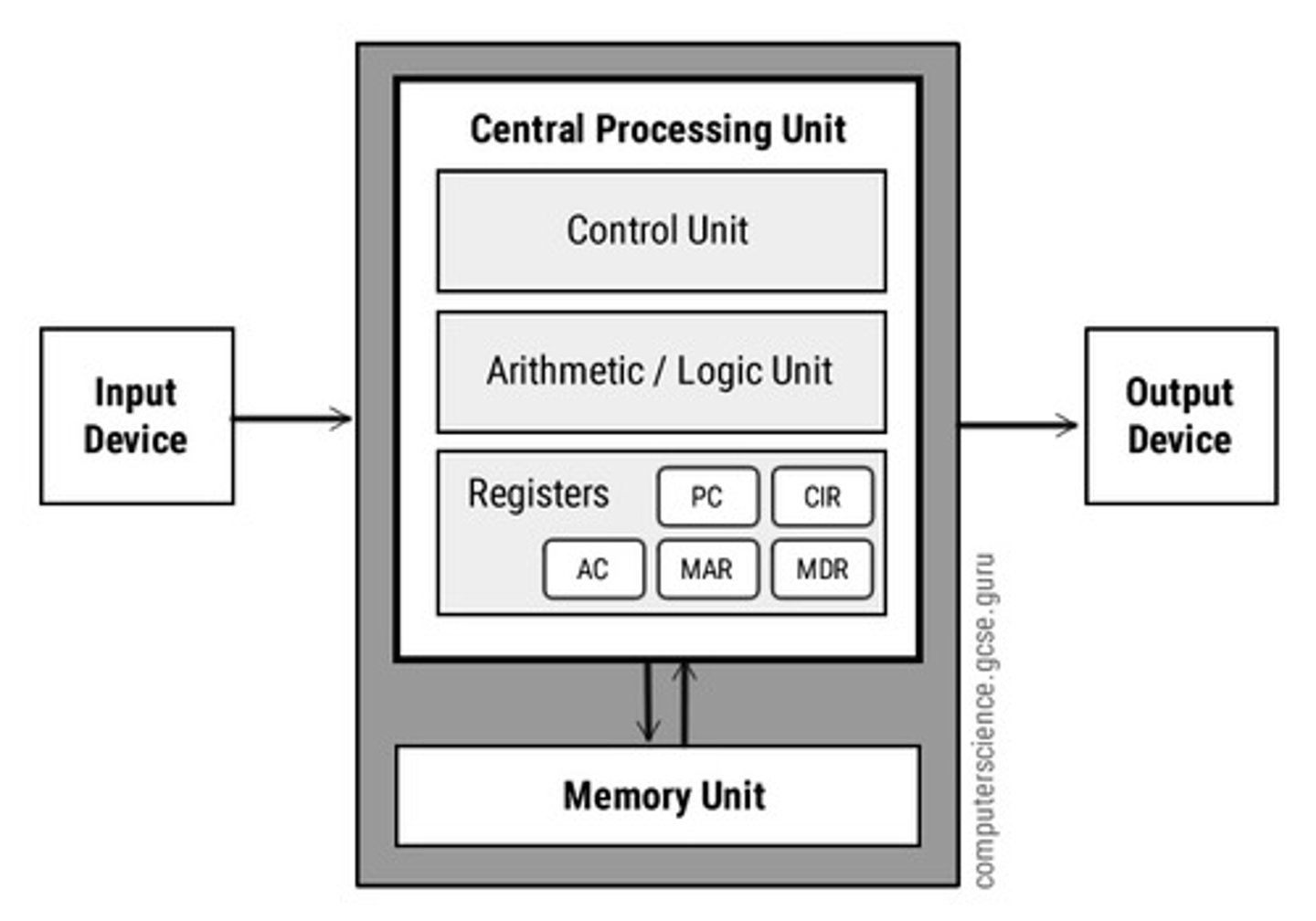
CPU
The most important part of any modern computer system is the central processing unit, or CPU. Just like the brain controls the body, the CPU controls the other parts of the computer by getting information from them, then telling them what to do. After receiving raw input data from the user, the CPU applies the data to a list of instructions, called a computer program. Then, the CPU follows, or executes, each line of the computer program in order, turning the data from the user into information. This is called processing.

RAM
The CPU is great at performing calculations, but it can only deal with one line of instructions at a time - it can't keep track of the whole program all at once. Instead, the computer stores this information in RAM, or random-access memory. When you run a program, the computer loads the instructions into its RAM. Then, the processor gets the first line of instructions from the RAM, executes it, and writes the result back into RAM to use later. RAM is extremely fast, but it's also volatile. If you turn off the computer system, RAM will forget everything. For this reason, RAM is sometimes called short-term memory - it's only concerned with whatever the computer is working on right now.

Motherboard (2)
The CPU and RAM are connected by a large flat component called a Motherboard. The Motherboard is like the spine in your body - it connects all the other parts to each other and sends electrical signals between them. An important part of the motherboard is a chip that contains the BIOS, or Basic Input Output System. The BIOS is like your brainstem, which controls basic functions like heart rate and respiration. When you restart a computer, the BIOS makes sure all the necessary parts are plugged in and working properly, then tells the operating system to start loading.

Power Supply (2)
Another responsibility of the motherboard is to make sure all the components get the right amount of electricity. This electricity comes to the computer through a power supply unit. Power supplies take AC power from the wall outlet and convert it into DC power. They typically have a variety of cables and plugs that attach to the motherboard near each powered component.
PSUs are generally designed with around 40% greater capacity than the required power consumption of the system. A PSU that doesn't provide the right amount of power can result a variety of issues whose cause can be difficult to identify, such as random restarts and freezes.
Power requirements for a personal computer without high-performing CPUs or graphics cards is usually 300W to 500W. High-performance computers can use up to 1000W. Most modern desktop computer PSUs conform to the ATX specification that provides 5-Volt Standby (5VSB) voltage.

GPU
The CPU is the main processor in a computer, but computers require additional processing power for creating images and graphics. This is supplied by a graphics processing unit, or GPU. Most computers today handle graphics processing through the CPU and RAM on the motherboard. This is called integrated graphics (or on-board graphics). But computers that are used primarily for gaming, video editing, and 3D modeling and animation need a second GPU that's dedicated to graphics processing. The best dedicated graphics cards (sometimes called video cards) are expensive because they also include their own specialized RAM and cooling fan.

NIC
Today, most computers need to connect to the Internet. That's the job of the Network Interface Card, or NIC. Some motherboards have a NIC built in, while others need one to be added on. Some NICs are for a wired connection, some are for wireless, and some can do both.

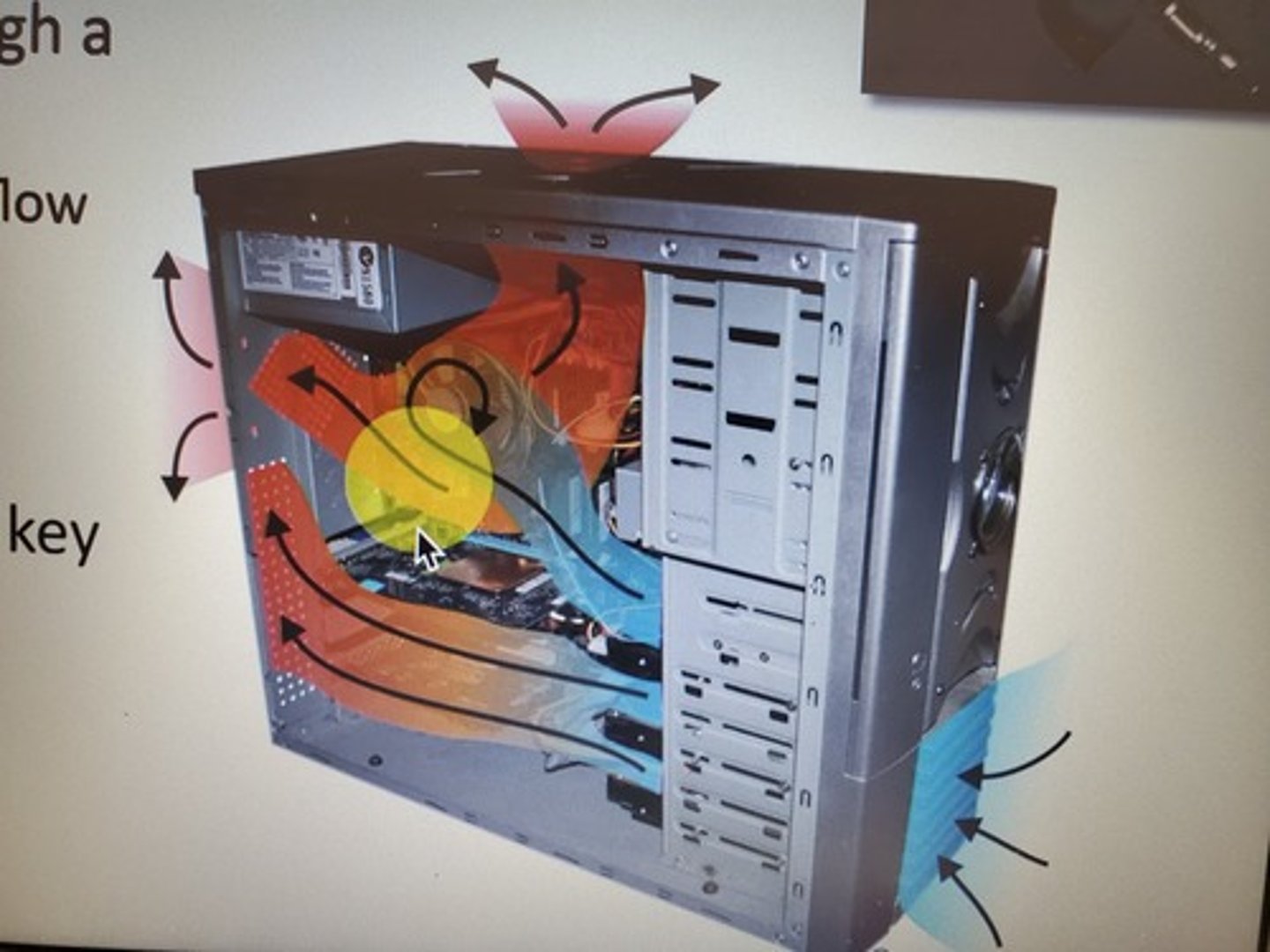
Cooling
One of the problems of high-speed computing is that it can produce a lot of heat. A typical desktop CPU can get hot enough to boil water. This much heat can damage delicate components if it isn't appropriately dealt with. In a typical desktop system, this is done with heat sinks and fans. A heat sink is a piece of metal that absorbs heat in a way that makes it easy to dissipate. Heat travels up the heat sink into thin branches, which maximize its contact with the air. Then, fans throughout the system replace the hot air inside the machine with cool air from the outside.
CPU Brands
Many companies, including, Intel, AMD, NVIDIA, Qualcomm, and Hewlett-Packard, manufacture CPUs.
AMD
AMD has the following brands:
• AMD Athlon is the Intel Pentium equivalent. It is still found in lower-end desktops and laptops.
• AMD Ryzen is the current platform with various models that are used in laptops, desktops, and workstations.
*Currently, the models include the Ryzen 3, Ryzen 5, Ryzen 7, and Ryzen 9. Ryzen 3 is primarily for home computers and low-end gaming.
They increase from mid-range computers (Ryzen 5) to high-end workstations and gaming systems running Ryzen 7 or 9.
There are mobile versions of the Ryzen series optimized for laptops. There is one extremely high-end processor in the Ryzen family called the Threadripper. It is geared toward the most intense and demanding tasks. Uses include 3-D modeling or computer-aided design (CAD) for engineers.
• The Ryzen and Athlon series also have a "Pro" designation for configurations geared toward enterprise customers.
• AMD Epyc is the high-performance server line of processors.

Intel
Intel has the following brands:
• Pentium 4 - Is Intel's brand for an entire series of single-core CPUs for desktops, laptops and entry-level servers. Pentium 4 CPUs were used from 2000 through 2008.
• Core - Intel's original 32-bit mobile dual-core x86 CPUs derived from the Intel P6 microarchitecture.
*Later the Core 2, 64-pit processor was released. It had multi-core support. Still later, Intel released three variants named Core i3, Core i5 and Core i7, but the names do not correspond to specific technical features like the number of cores. Intel divided the processors by their performance level, with i3 being low-level, i5 is mid-range, and i7 and i9 providing high-end performance.
• Celeron - Intel's brand for a number of low-end IA32 and x86-64 CPUs. Intel used the Celeron for many low-cost personal computers.
• Atom - Intel's IA-32 and x86-64 ultra-low-voltage microprocessors were designed to reduce electric consumption and power dissipation in comparison with other processors of the Intel Core series. The Atom CPU was used for devices, such as netbooks, nettops, smartphones, and tablets.
• Xeon - Intel's CPU was introduced in 1998 and is used primarily for non-consumer workstation, servers, and embedded system markets.

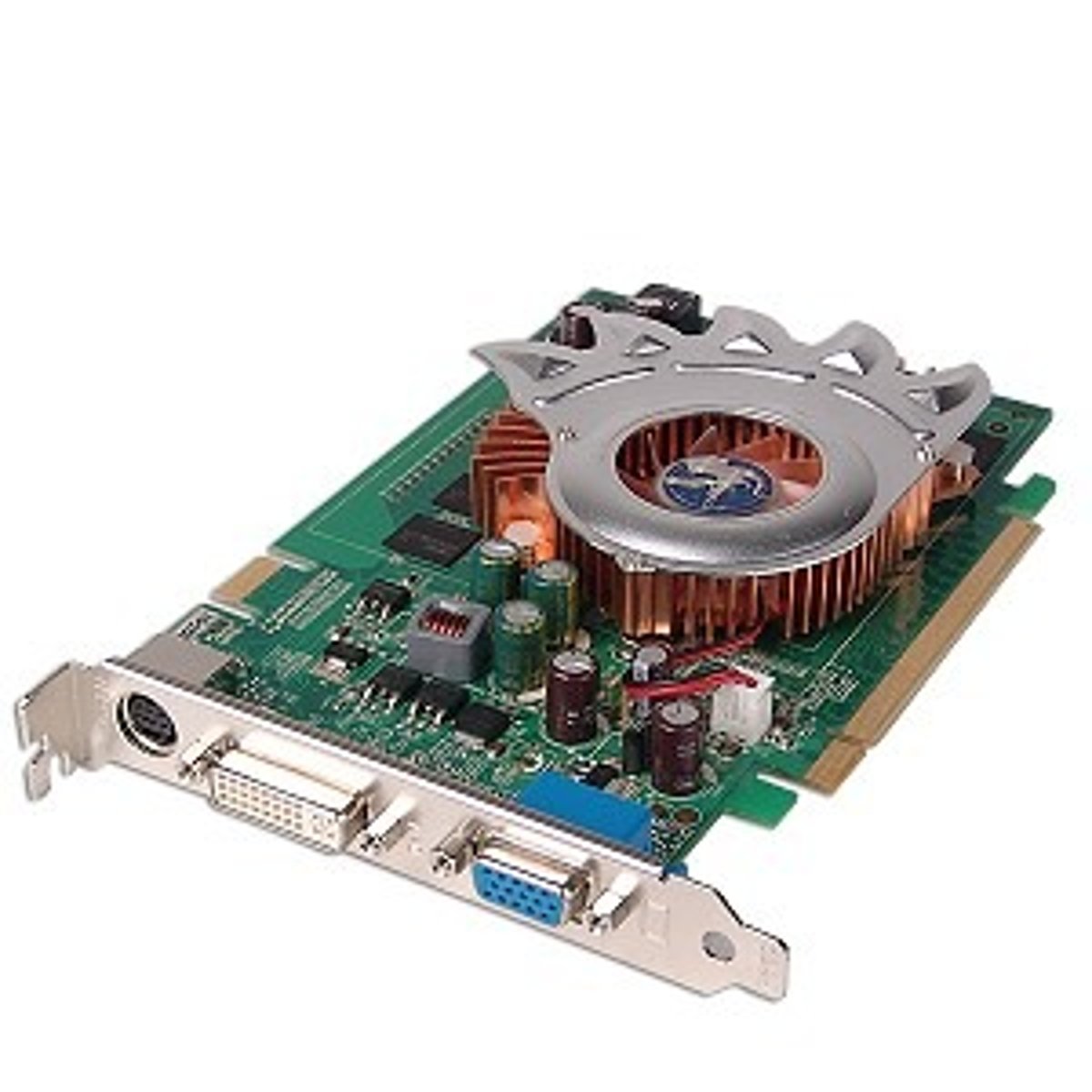
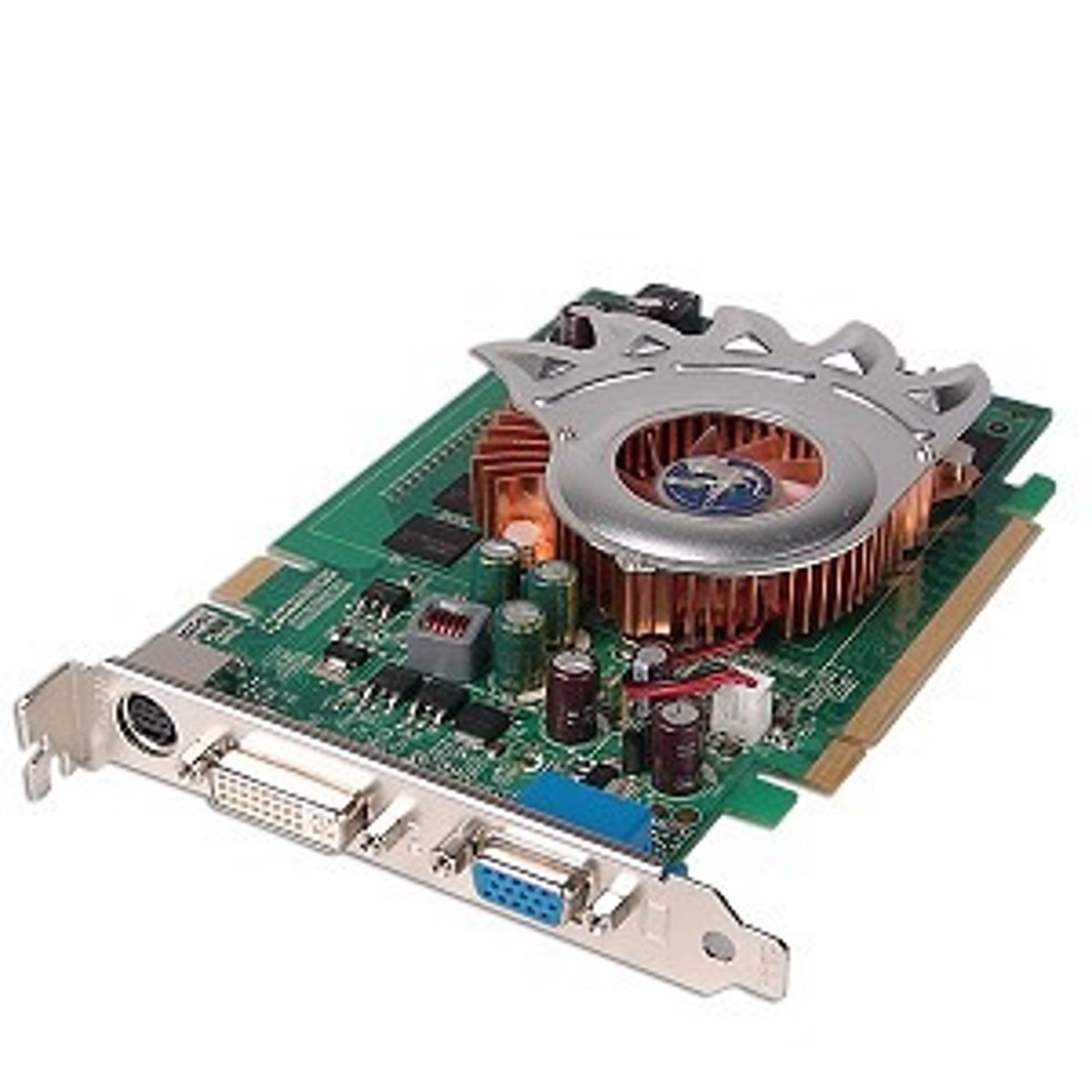
Video Cards
A video card, also called a display or graphics card, is used to enhance the quality of images shown on a display. Rendering images requires a lot of processing power.
A video card acts like an extra CPU that works exclusively on graphics. This frees up the computer's main processor for other tasks. A typical video card includes a graphics processing unit (GPU); a cooling mechanism (such as a fan); and memory and monitor ports such as HDMI.

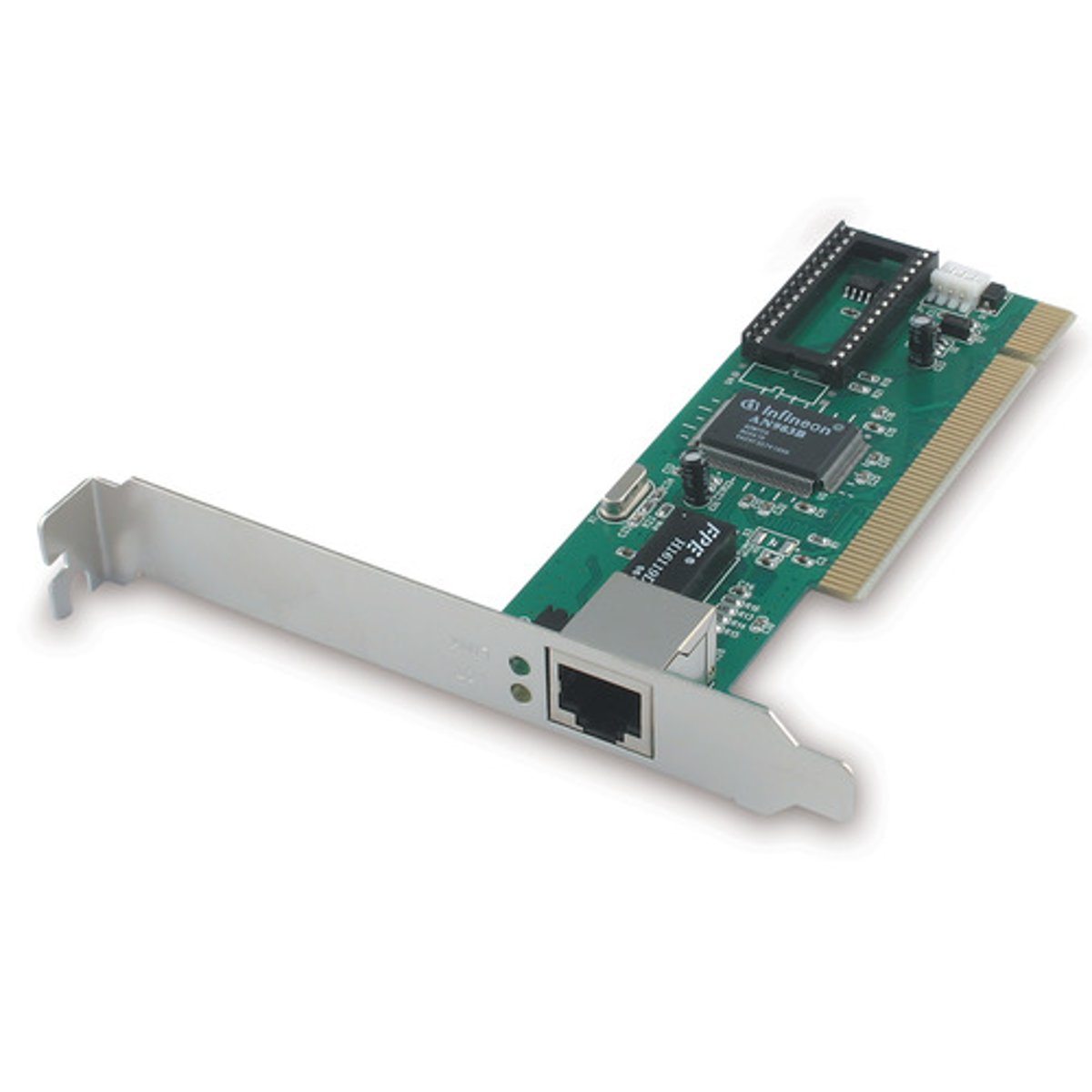
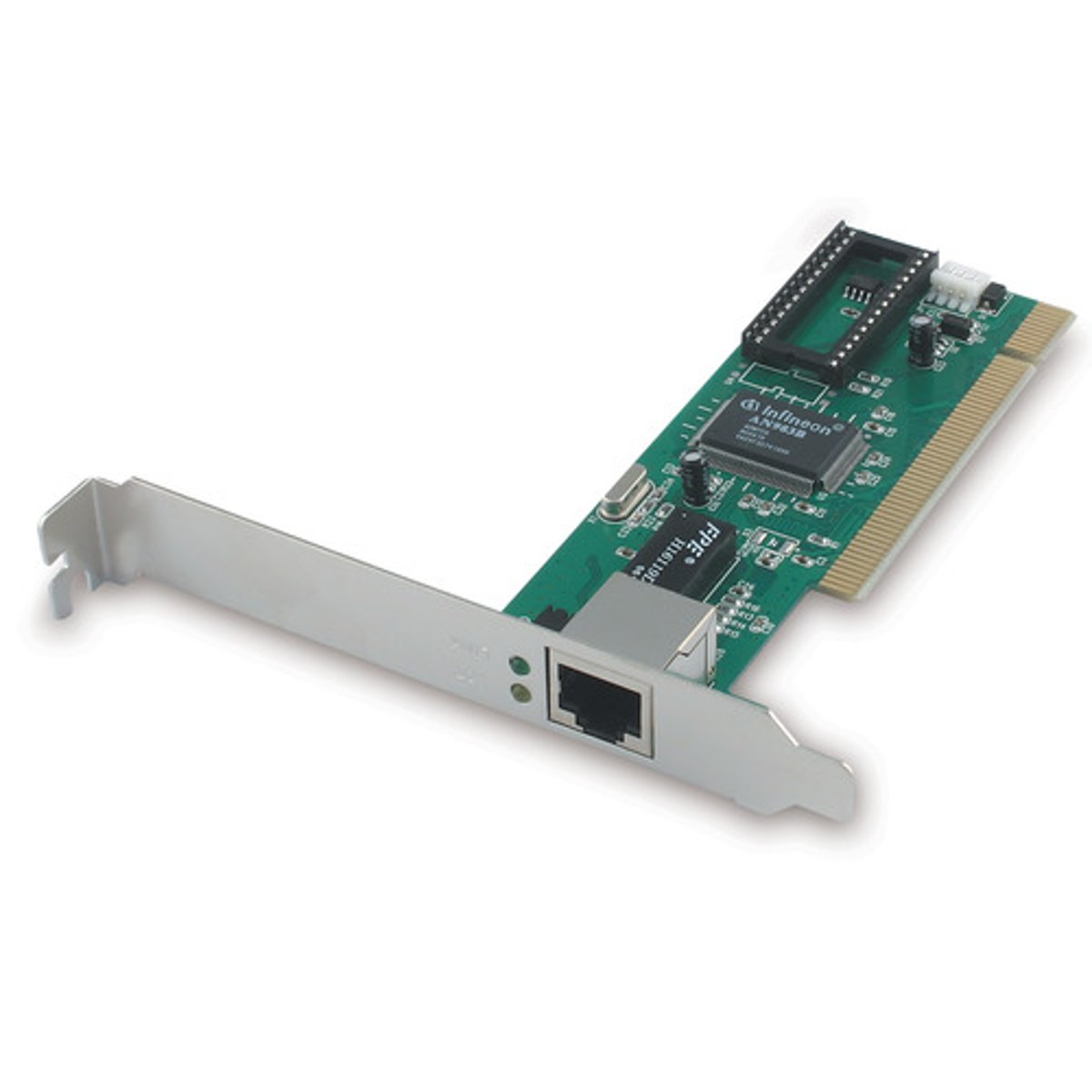
Network Cards
A network interface card (NIC) enables a device to connect to a network. Many modern computers have a built-in NIC, but also have the option to add additional NICs to expand the functionality of the system.
A NIC connects the device to the network through a RJ-45 port that connects to an unshielded twisted pair cable, as shown in the following graphic.

Audio Cards
An audio card (sound card) converts electrical signals to audio signals. This is done using a digital signal processor (DSP) chip.
• This specialized chip has been optimized for the operational needs of converting electrical signals to audio signals.
• The conversion recreates the sound we hear through computer speakers or earphones.
• Sound cards are also used for voice over IP (VoIP), teleconferencing, and other audio functions.
Most audio cards use different kinds of input/output jacks and ports for connecting such things as headphones, microphones, or speakers. Audio cards have many uses, but are often used in configuring surround sound systems, such as a digital theater system used in a home theater.
• Surround systems are often referred to as 5.1 or 5.7 systems.
• The number (such as 5.1) refers to the number of speaker placements found in the system.
Other Card Types
Desktop computers typically have built-in USB ports. But in some cases, they may require more depending on the number of USB devices needed for a task. You can install a multi-port USB expansion card to increase the number of USB ports. It allows for faster connection than a USB splitter.
CPU Register
The CPU register stores values the computer is working with at a particular moment in time.
CPU Clock
The CPU clock controls the speed that a processor executes instructions.

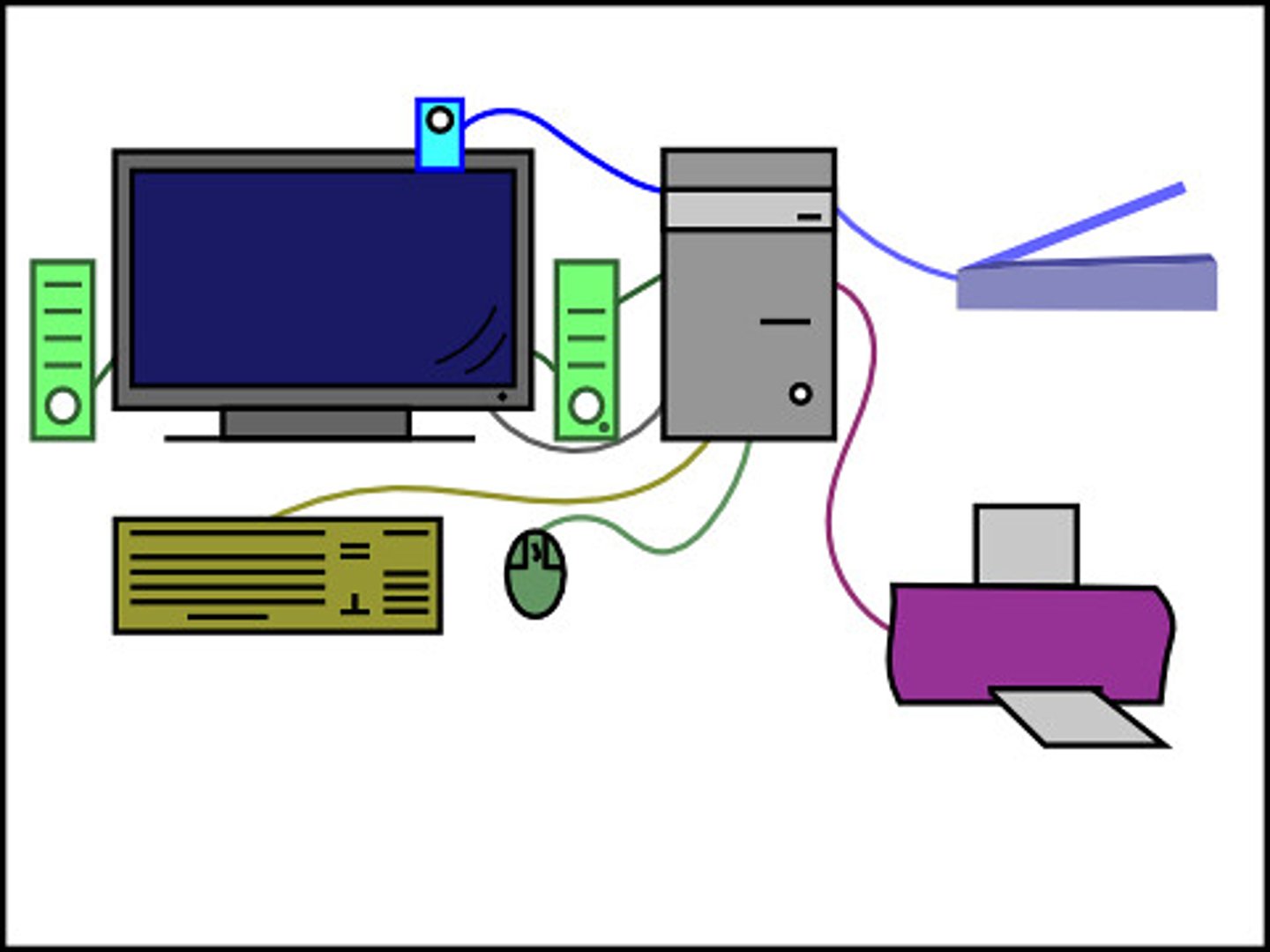
Peripheral
A device, usually external to a computer, that is plugged into a computer's communication port or is connected wirelessly. Common peripherals are keyboards, mice, monitors, speakers, and printers.
Touch Screen
A display device that allows a user to interact with a computer by touching, tapping, and swiping areas on the screen.

Inkjet Printer
A printer that sprays small dots of ink from an ink reservoir onto a sheet of paper.

Laser Printer
A printer that uses electrical charges and heat to fuse tiny plastic particles (called toner) to the paper.

Scanner
A device that scans paper documents and converts them into digital files.

Universal Serial Bus (USB)
A common interface used to connect peripherals, such as mice, keyboards, printers, and digital cameras to a computer.

FireWire (1)
An interface used to connect peripherals such as digital cameras and external hard drives to a computer. It is no longer commonly used.

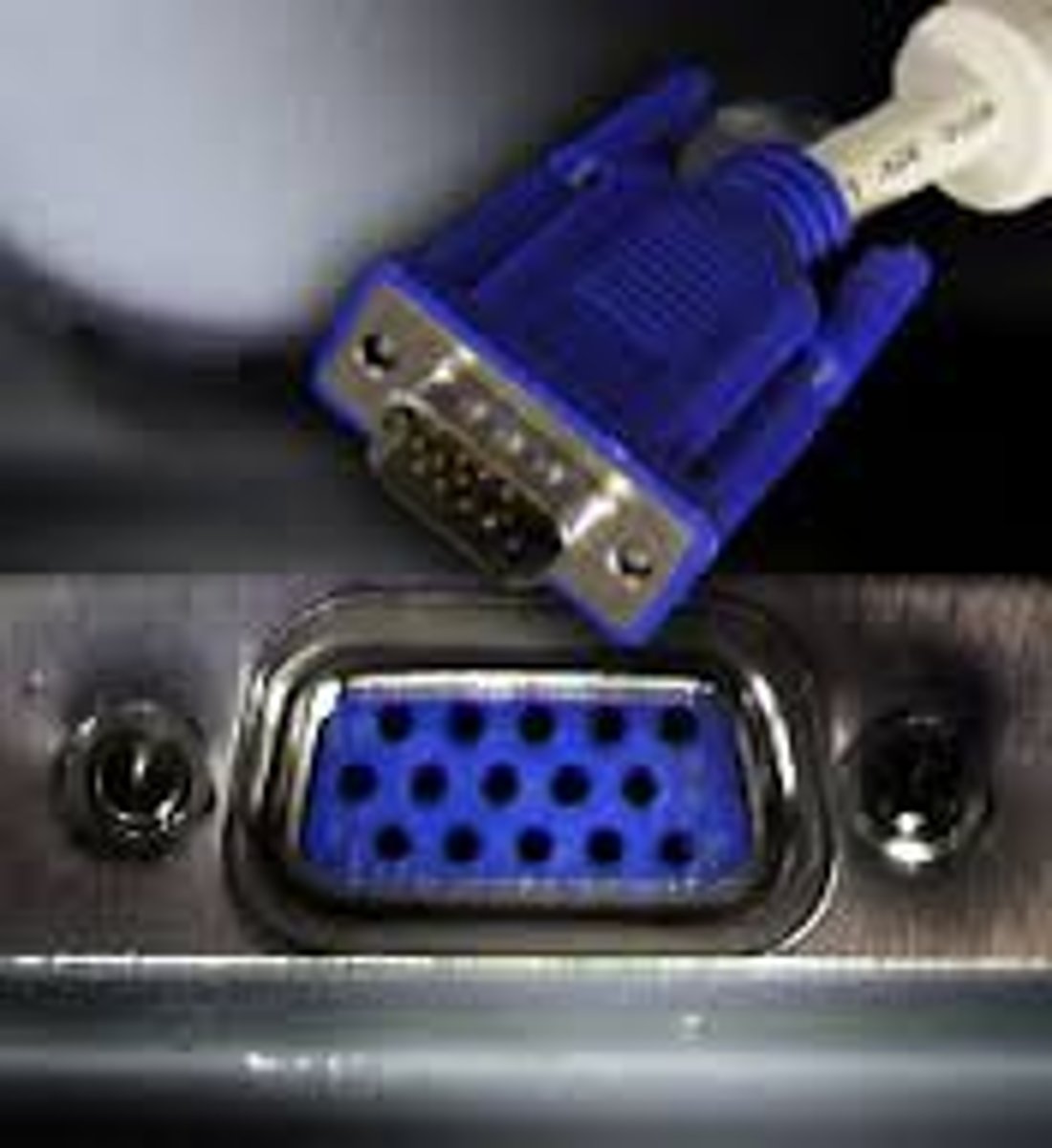
Video Graphics Array (VGA) Connector
A connector, identified by its blue color and three rows of pins, that is used to connect older monitors to a computer.

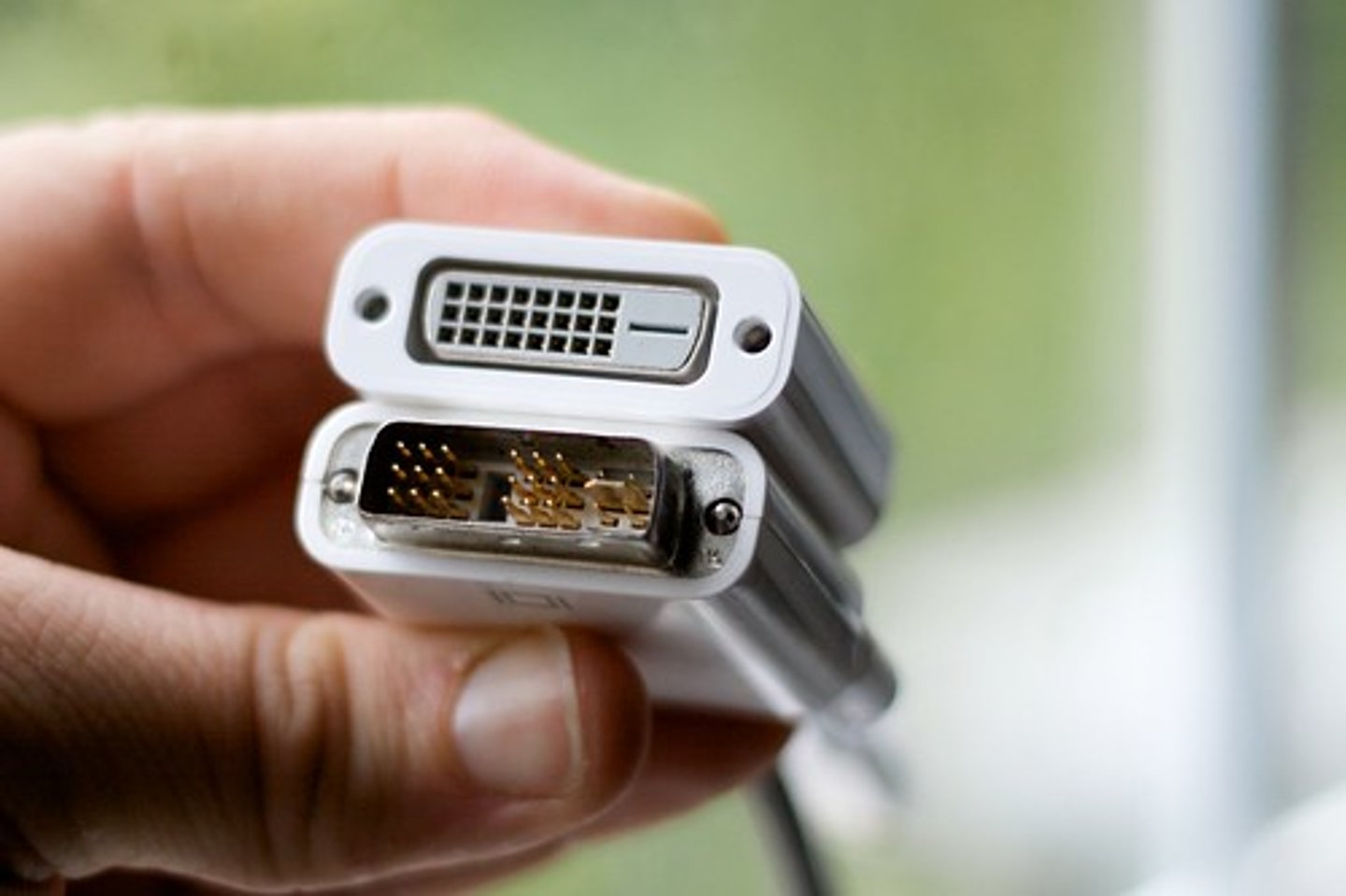
Digital Visual Interface (DVI) Connector
A connector, typically white with three rows of eight pins, designed to connect digital monitors to a computer.

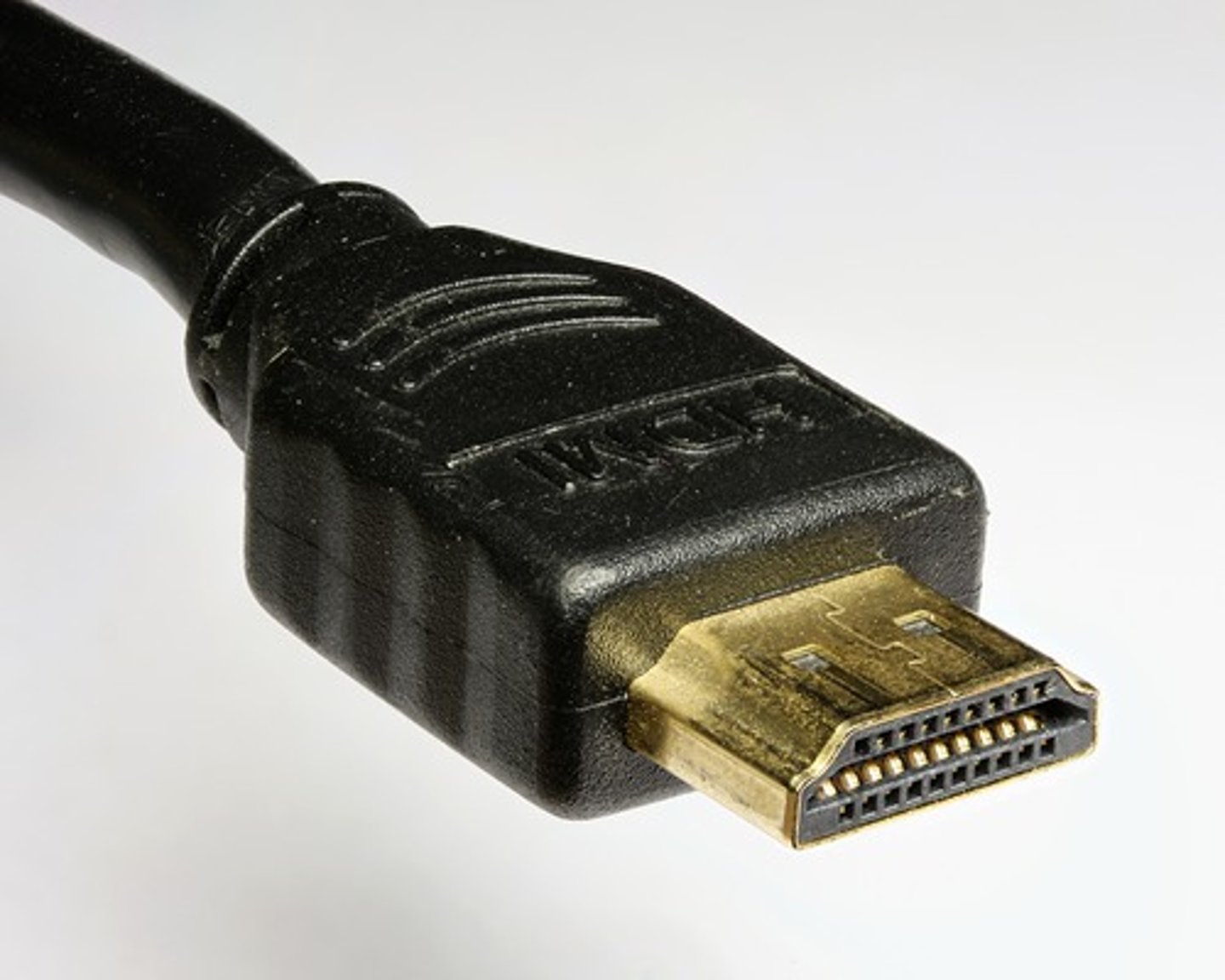
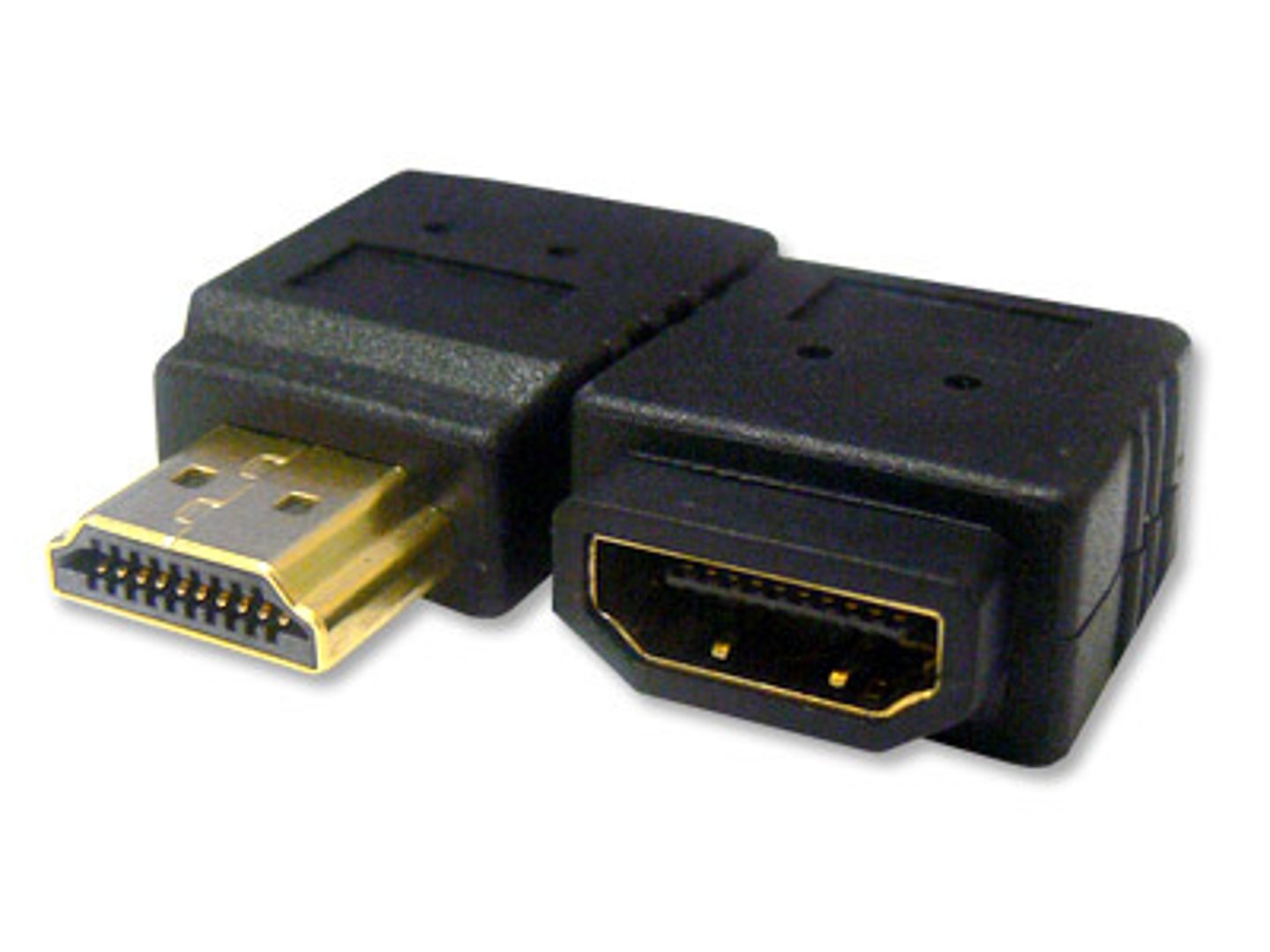
High-Definition Multimedia Interface (HDMI) Connector
A connector now available on a wide variety of devices such as computers, monitors, TVs, Blu-Ray players, and more. HDMI is used to transfer high-definition signals. It supports both audio and video data.

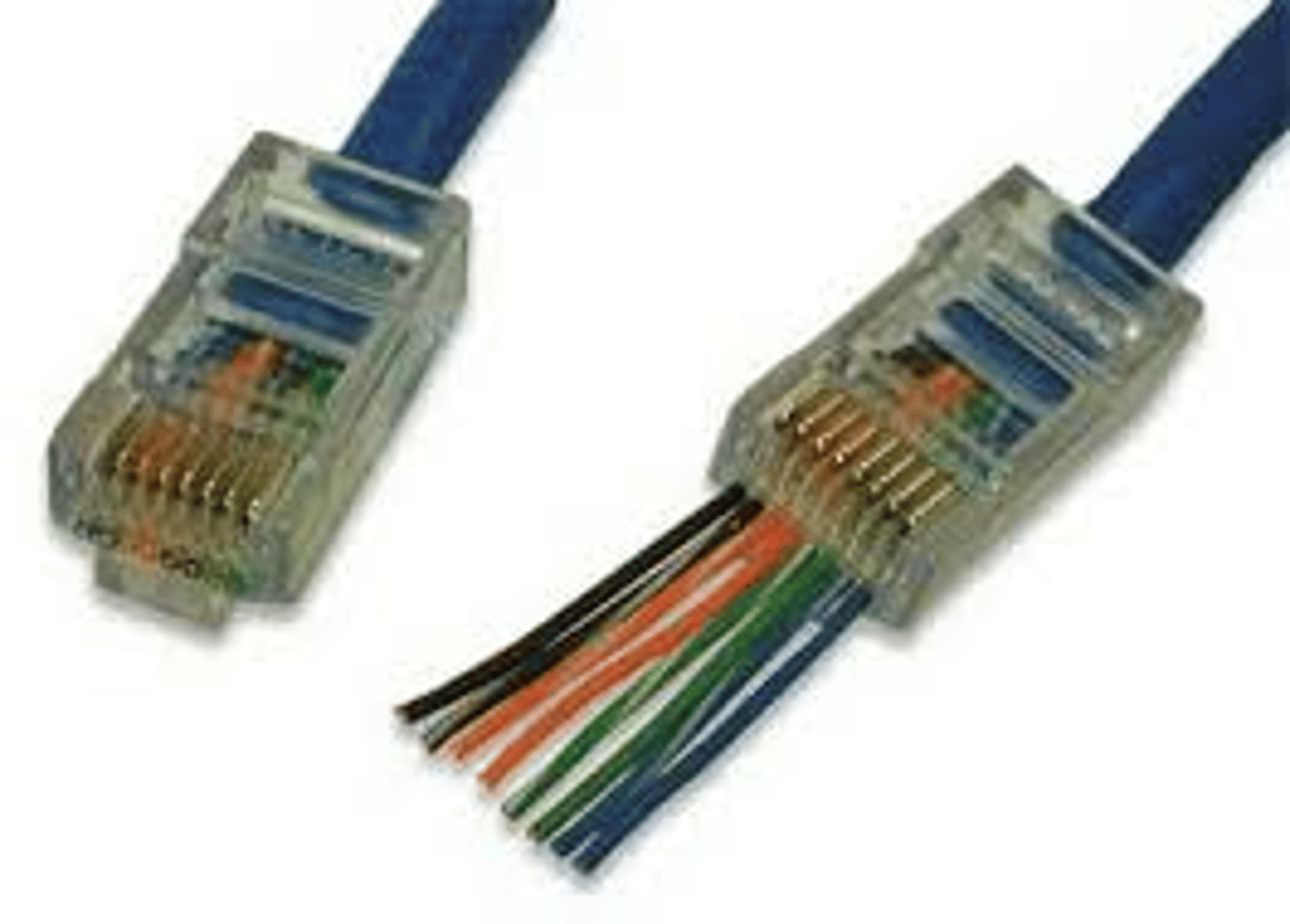
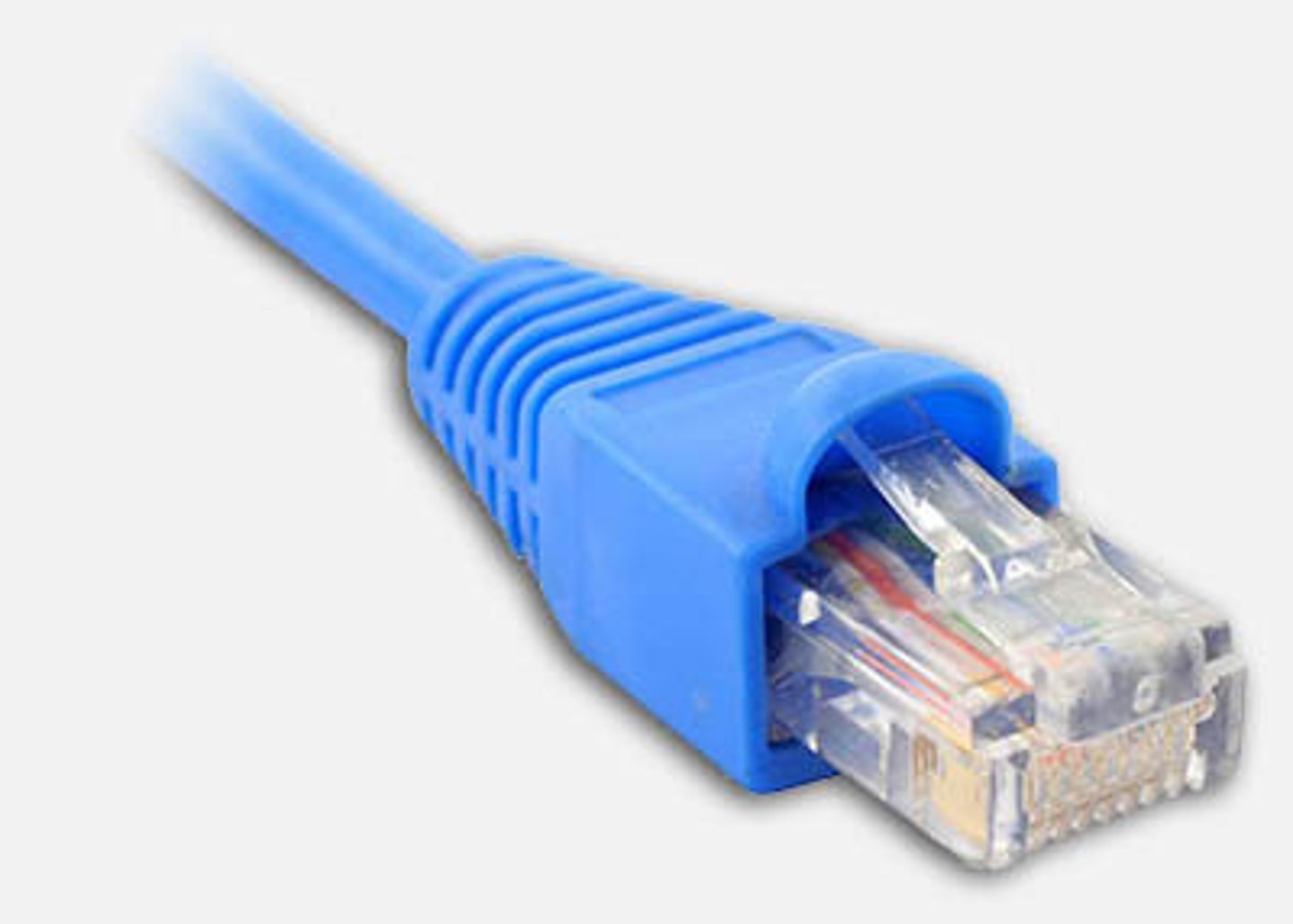
Registered Jack 45 (RJ-45) Connector
A connector used to connect a computer to a wired network.

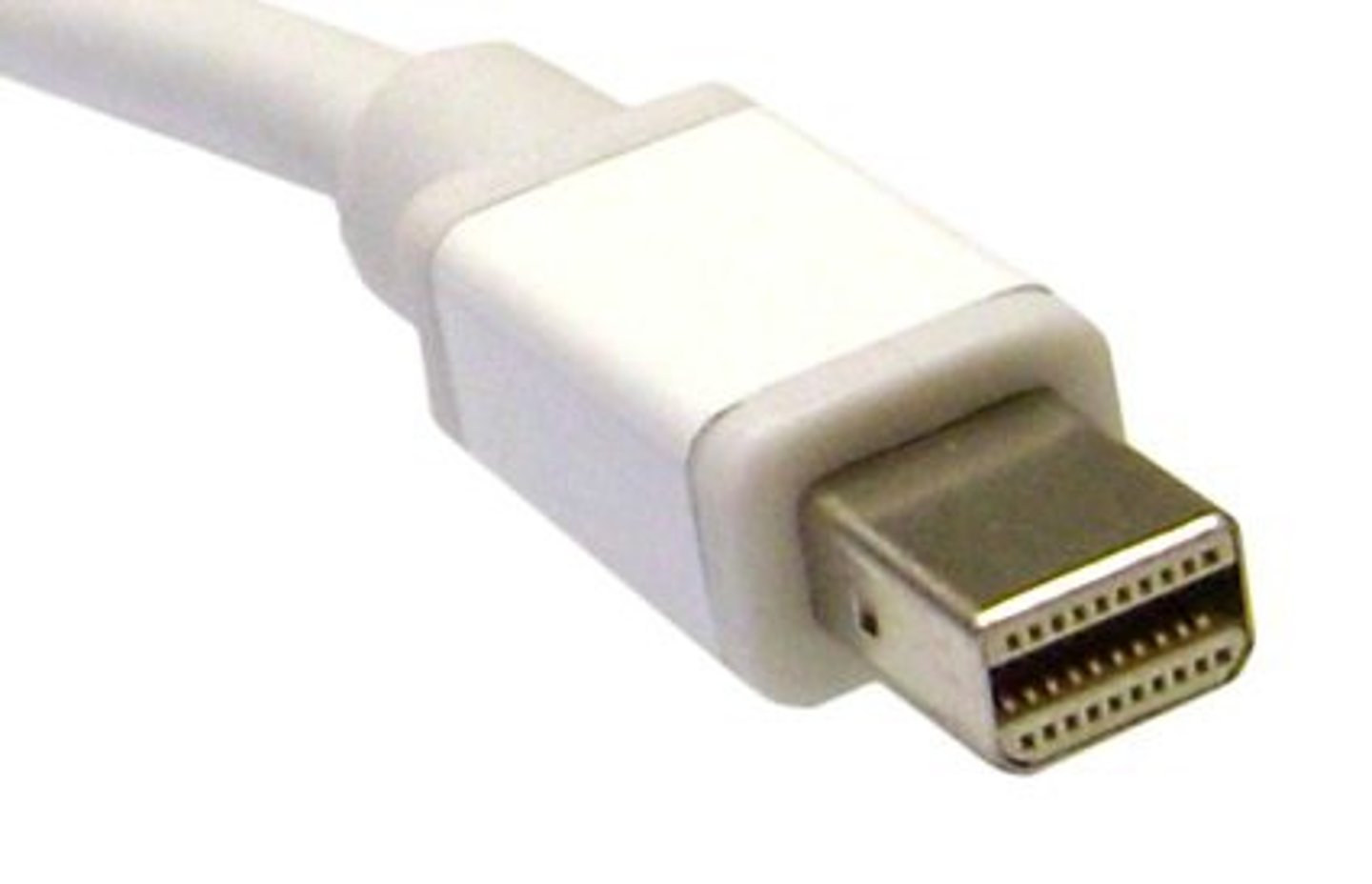
Thunderbolt (1)
An interface primarily used on Apple computers that connects a monitor to a computer and can also provide DC power.

Infrared
A communication technology that uses light waves to transmit information through the air. The light used by IR devices is just beyond the visible red-light spectrum, so it's invisible to us.
Bluetooth
A short-range wireless communication technology used to connect peripherals such as wireless headphones, speakers, keyboards, mice, smart watches, printers, and game controllers to a computer, including smartphones.

Camera Lens
A camera component that focuses the light that enters it into a point. Behind the point, the light spreads out again, eventually creating an upside-down image of the light that entered.
Photosensitive Material
A light sensitive surface used to capture the image focused by the lens.
Camera Shutter
A camera component that sits between the lens and the sensor, allowing light to enter for a short time.

Digital Projectors
In today's world there is often a need to project images from a computer to a larger output, such as a wall or screen.
These are often used a team meeting or for training purposes. The devices used to do this are called digital projectors or video projectors.
Depending on the need, these can be purchased as small portable devices or more expensive, larger ones are often mounted permanently on the ceiling or wall.
These projectors can use LCD or CRT, but the better projectors use the digital light processing, which is a set of chipsets based on optical micro-electro-mechanical technology that uses a digital micromirror device.
When used in conjunction with a computer, projectors can be connected to the computer using many of the same interfaces used by other devices, such as Thunderbolt, HDMI, VGA, and DVI.

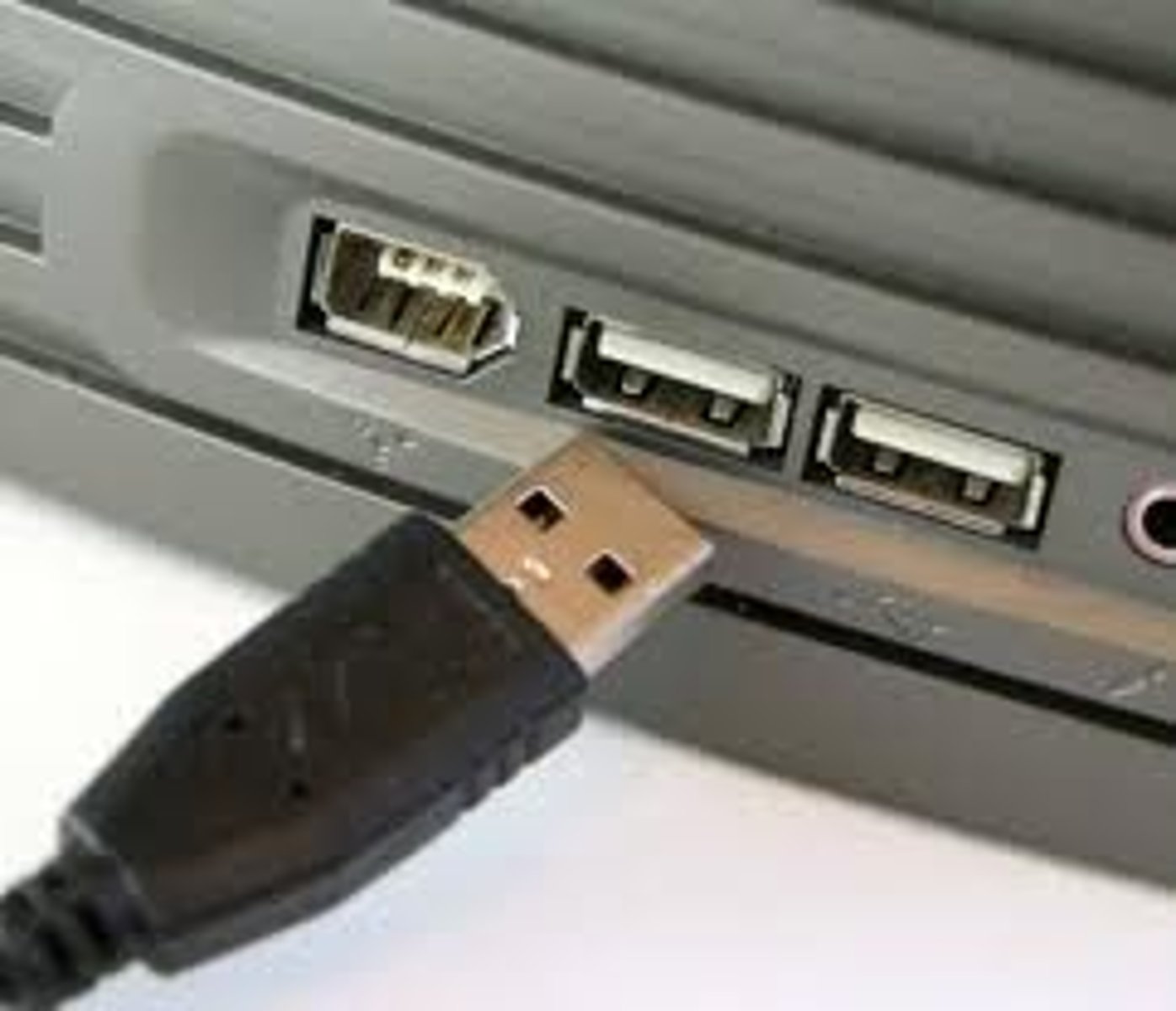
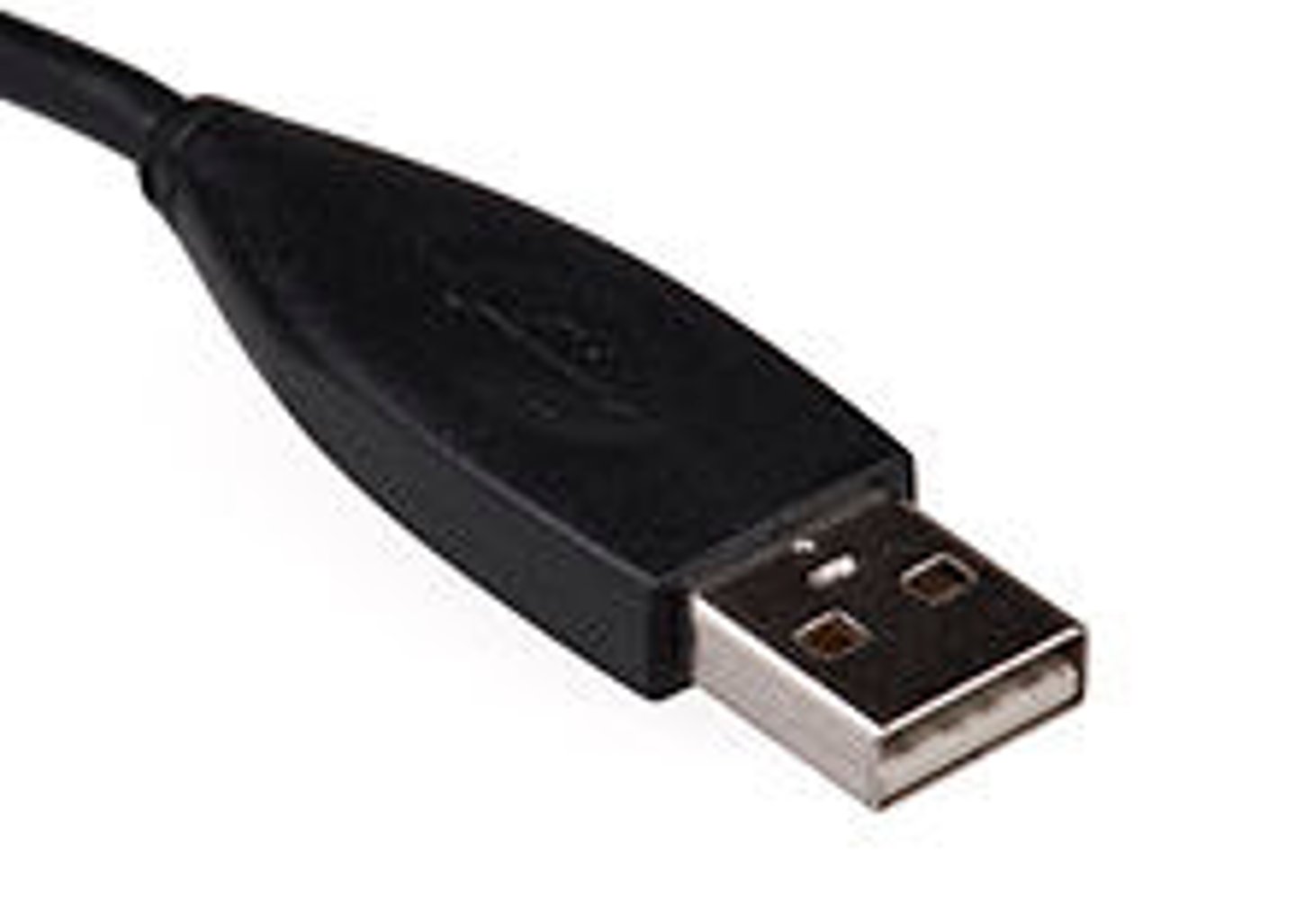
USB Type A
Universal Serial Bus (USB) Type A connectors are rectangular in shape. One end is typically plugged directly into the computer. The other is plugged into a peripheral device. They are designed for devices that may be plugged in and out frequently, such as:
• Keyboards.
• Mice.
• Cameras.
• Flash Drives.
• External Hard Drives.

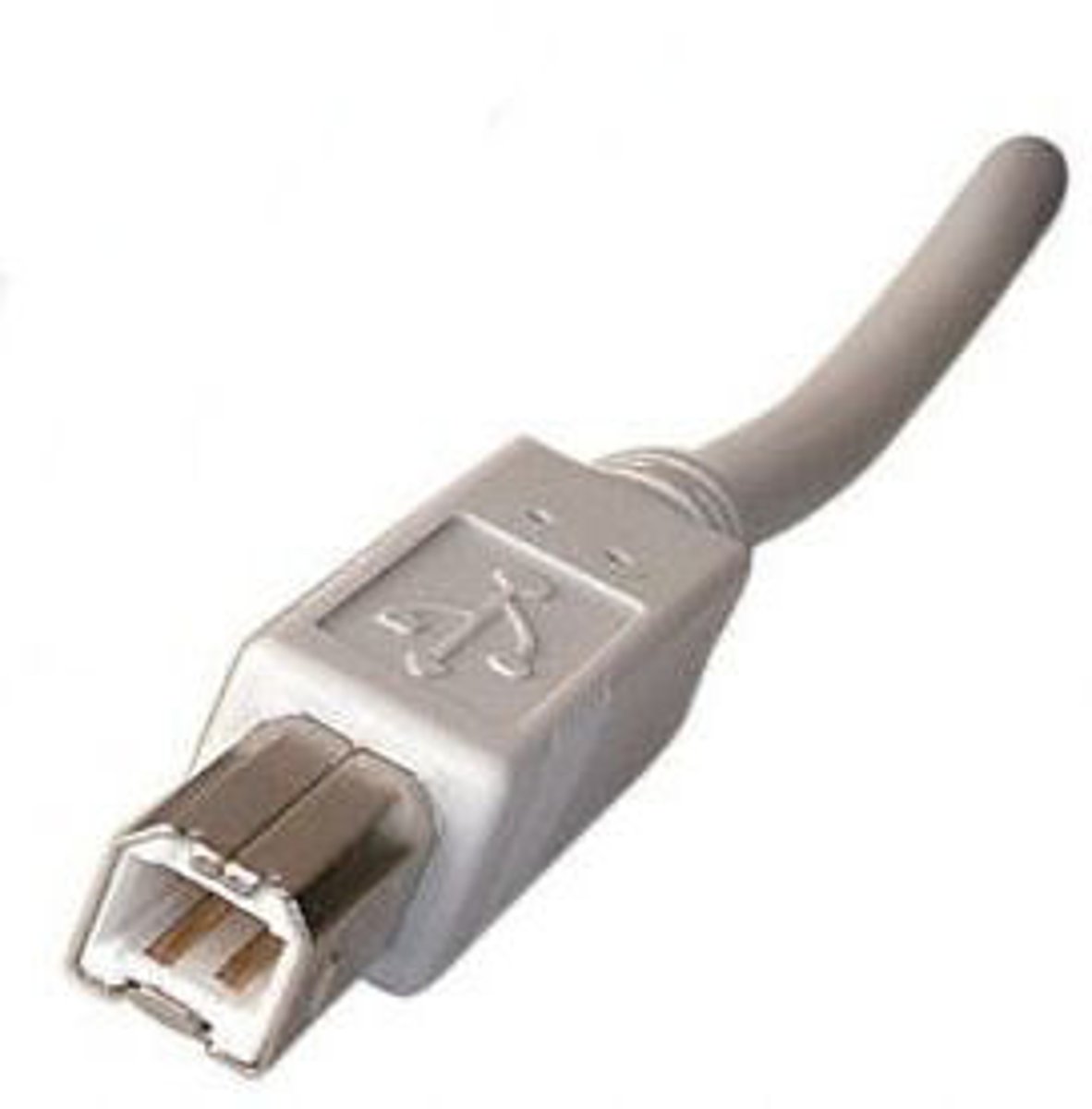
USB Type B
USB Type B connectors have a square shape with a bevel on one edge to keep them from being plugged in the wrong way. They are designed for devices that are usually left plugged in for long periods of time, such as:
• Printers.
• Scanners.
• USB Hubs.
*Cables with a USB Type B connector typically use a Type A connector on the other end of the cable to connect to the computer.

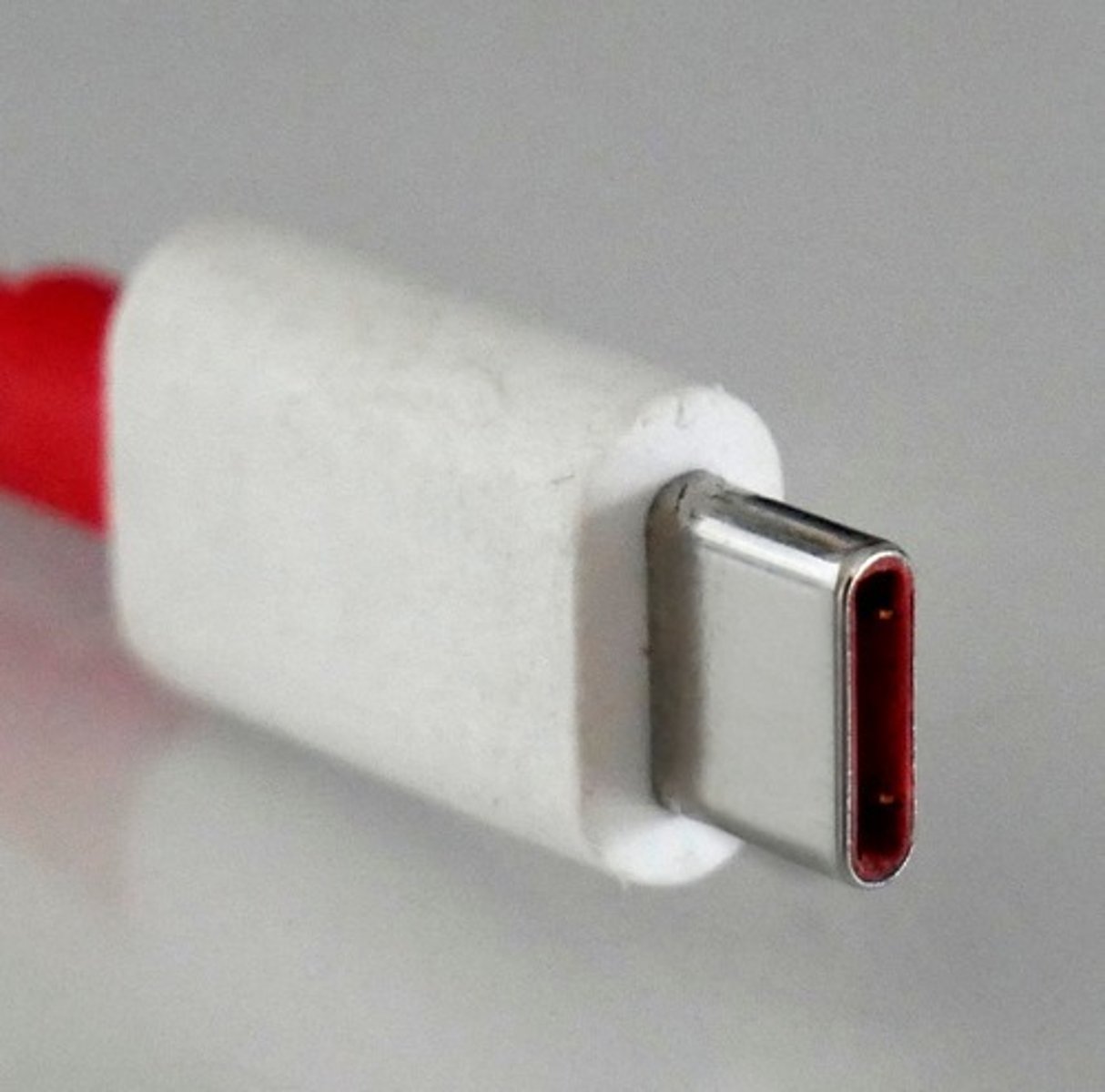
USB Type C
The USB Type C specification was introduced in 2014. It is simpler than the previous types. Both ends of a Type C connector are the same and the cord allows bi-directional power flow, so a host device can charge a peripheral and a peripheral device can charge a host.

Mini USB
Mini USB connectors are a smaller type of USB connector. They are commonly used for digital cameras and sometimes external hard drives. Cables with a Mini USB connector usually use a Type A connector on the other end of the cable to connect to the computer.
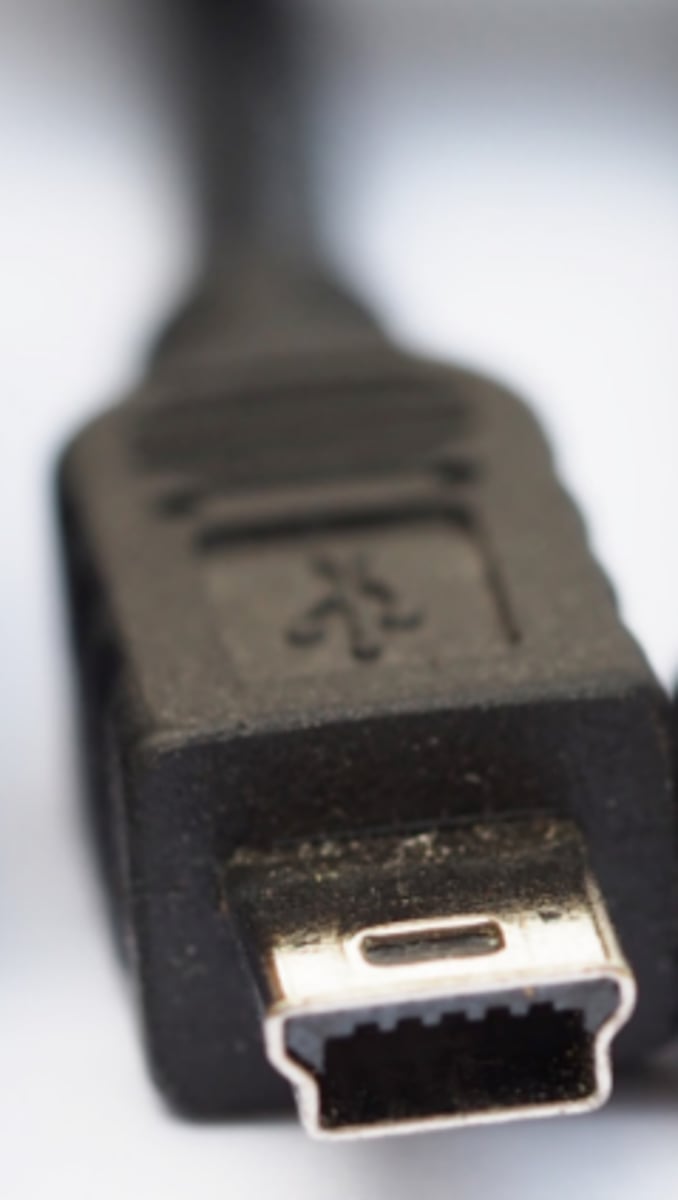

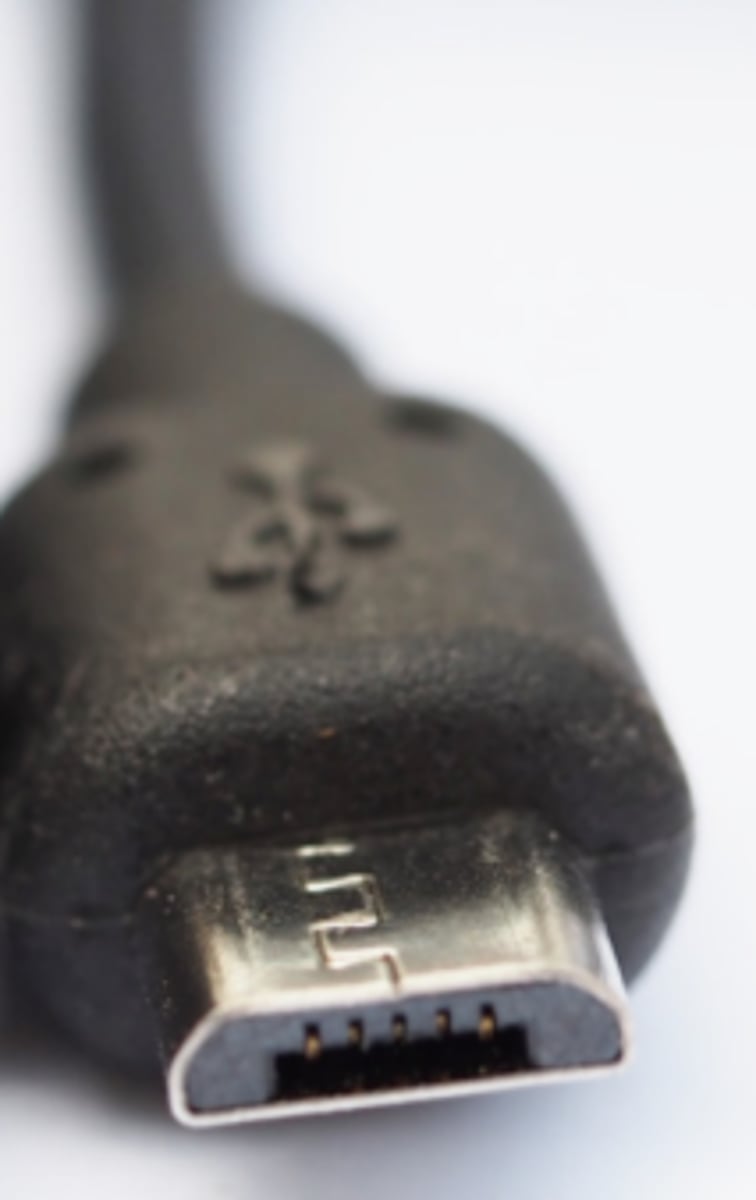
Micro USB
Micro USB connectors are the smallest type of USB connector. They are commonly used for connections to mobile devices, such as tablets and phones. Cables with a Micro USB connector generally use a Type A connector on the other end of the cable to connect to the computer.

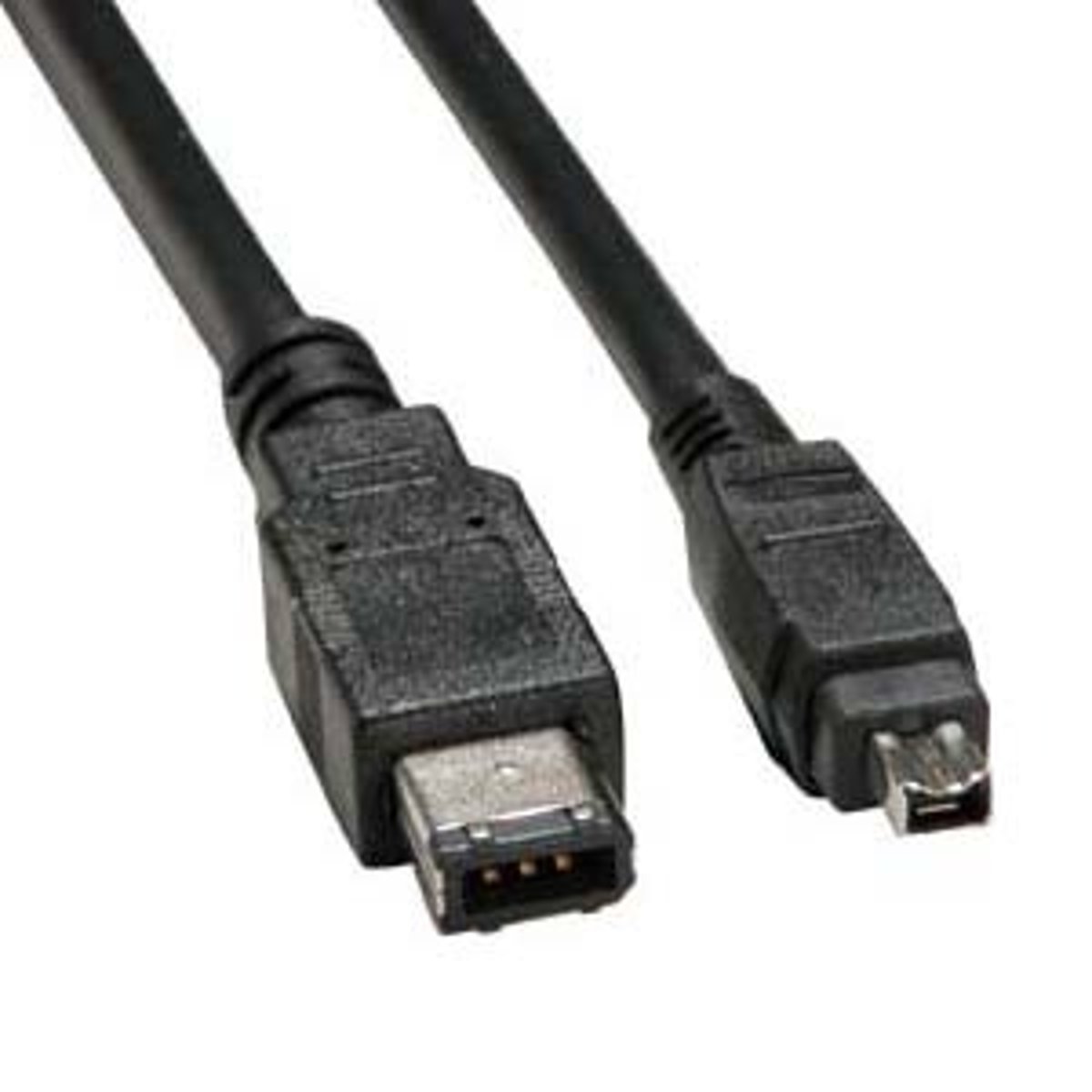
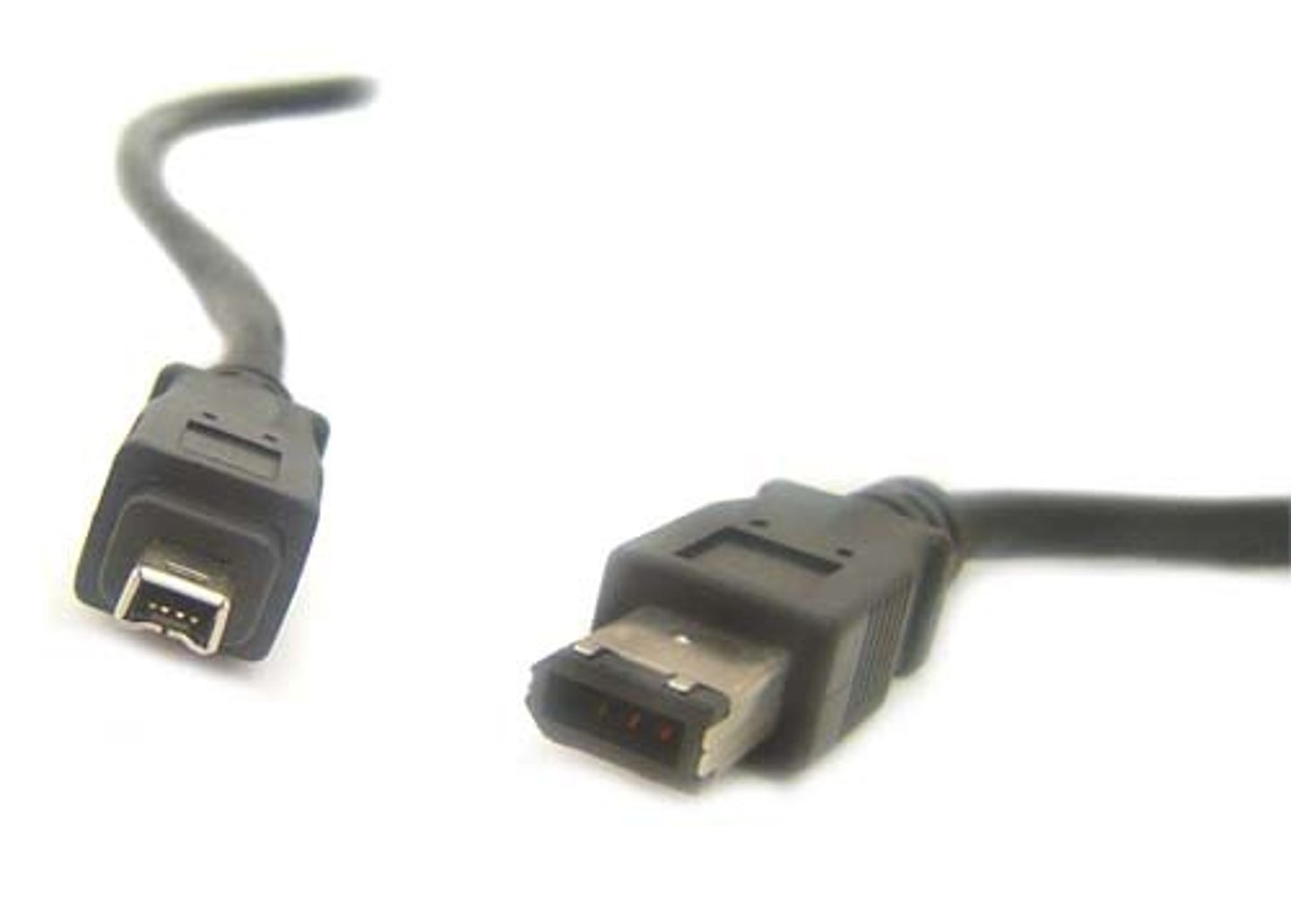
FireWire (2)
Some computers provide a FireWire connector. FireWire is an IEEE 1394 interface standard for a serial bus for high-speed communications and isochronous real-time data transfer. It's connectors are rectangular in shape with a bevel on one end to keep you from inserting them the wrong way.
FireWire allows you to connect external devices, such as digital cameras, external hard drives, and scanners to the computer. A powered FireWire connector has 6 pins (FireWire 400 standard) and an unpowered one has 4 pins.
The 400 standard has a transfer speed of up to 400 Mbps. FireWire can handle up to 63 units on the same bus, supports PnP, and is hot swappable. It was first developed by Apple.
FireWire also has an IEEE 1394 interface standard; it is known as FireWire 800 and has 9 pins. It provides increased data transfer rates of up to 3200 Mbps using an optical cable or beta mode. Other FireWire standards include: FireWire S800T (IEEE-1394c) and FireWire S1600 and S3200.

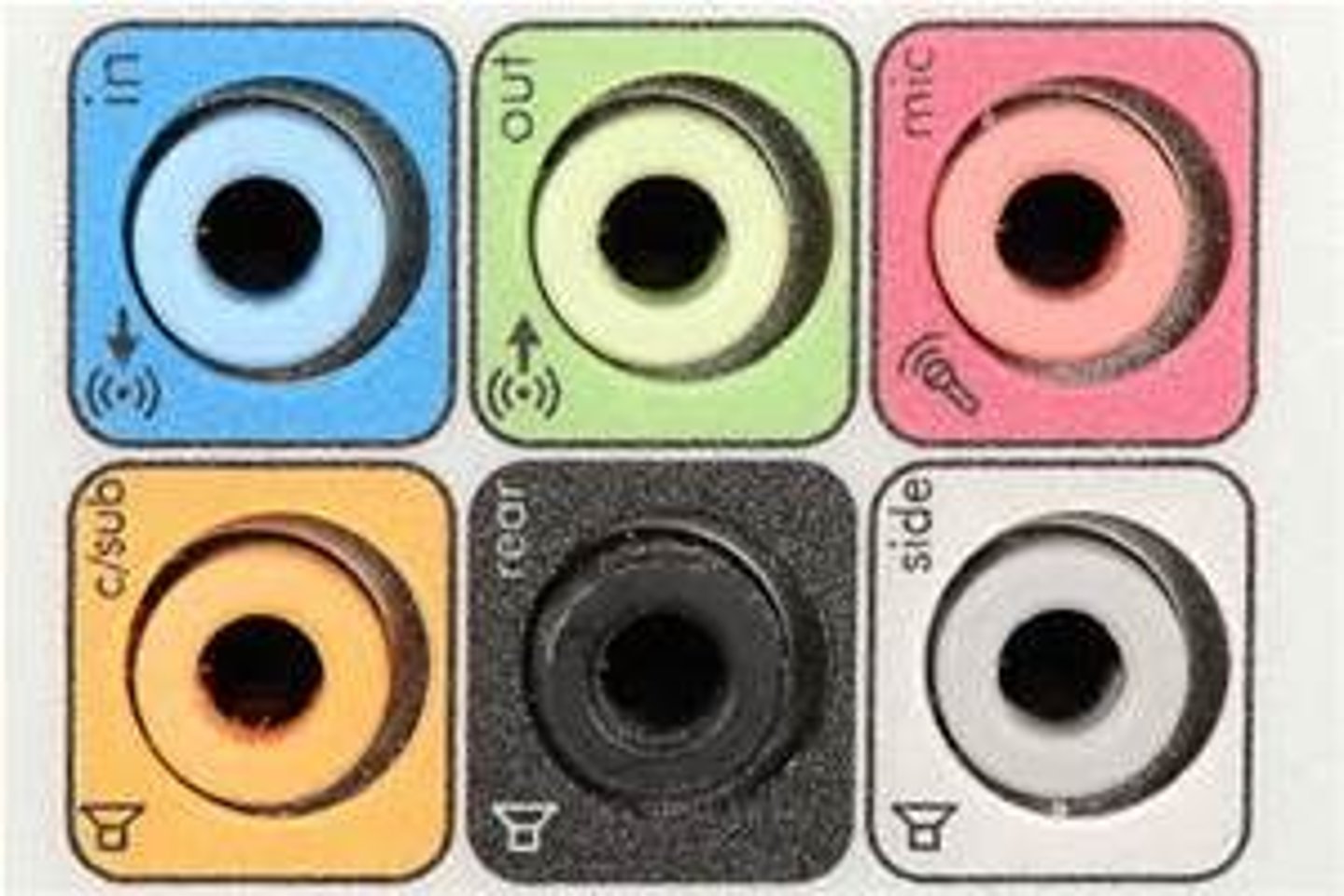
Audio
Most computers provide audio connectors. The pink connector is the microphone jack. It is used to connect a microphone to the system. The blue connector is the line-in connector. You can use it to connect an external audio source to the computer. The green connector is the line-out connector. It is used to connect speakers to the system.

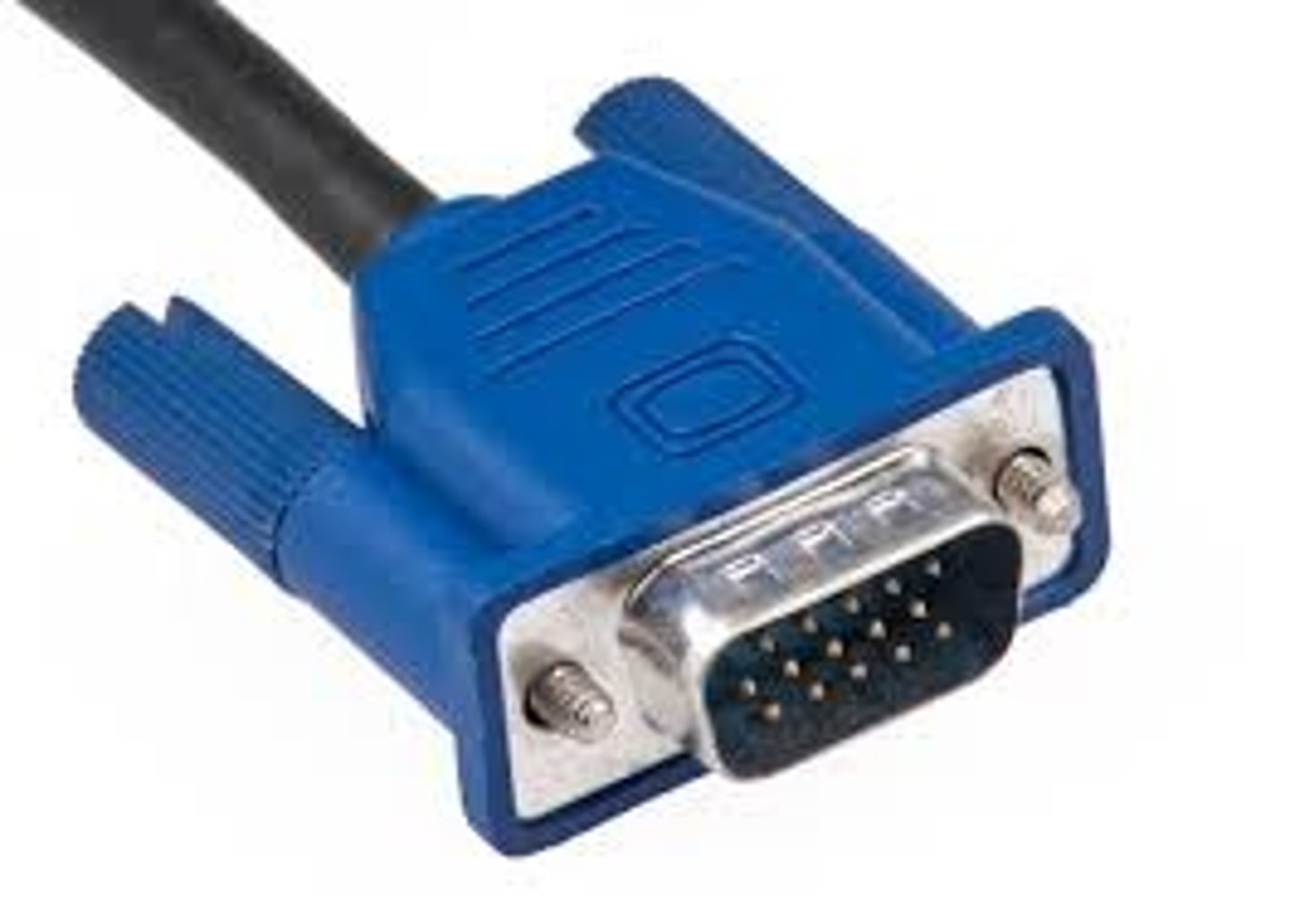
VGA Video
The Video Graphics Array (VGA) connector is designed for analog signals and has 15 pins. It is used to connect older or legacy monitors to a computer. You can identify this connector by its blue color and three rows of pins. VGA is not efficient at supporting high resolutions.
There have been several versions of VGA standards over time, but all have used the same port and are generally backwards compatible. Most modern displays use the XGA standard described below:
VGA:640 x 480 resolution16 colors
SVGA:800 x 600 resolution4- or 8-bit colors
XGA:1024 x 768 resolution32- bit colors

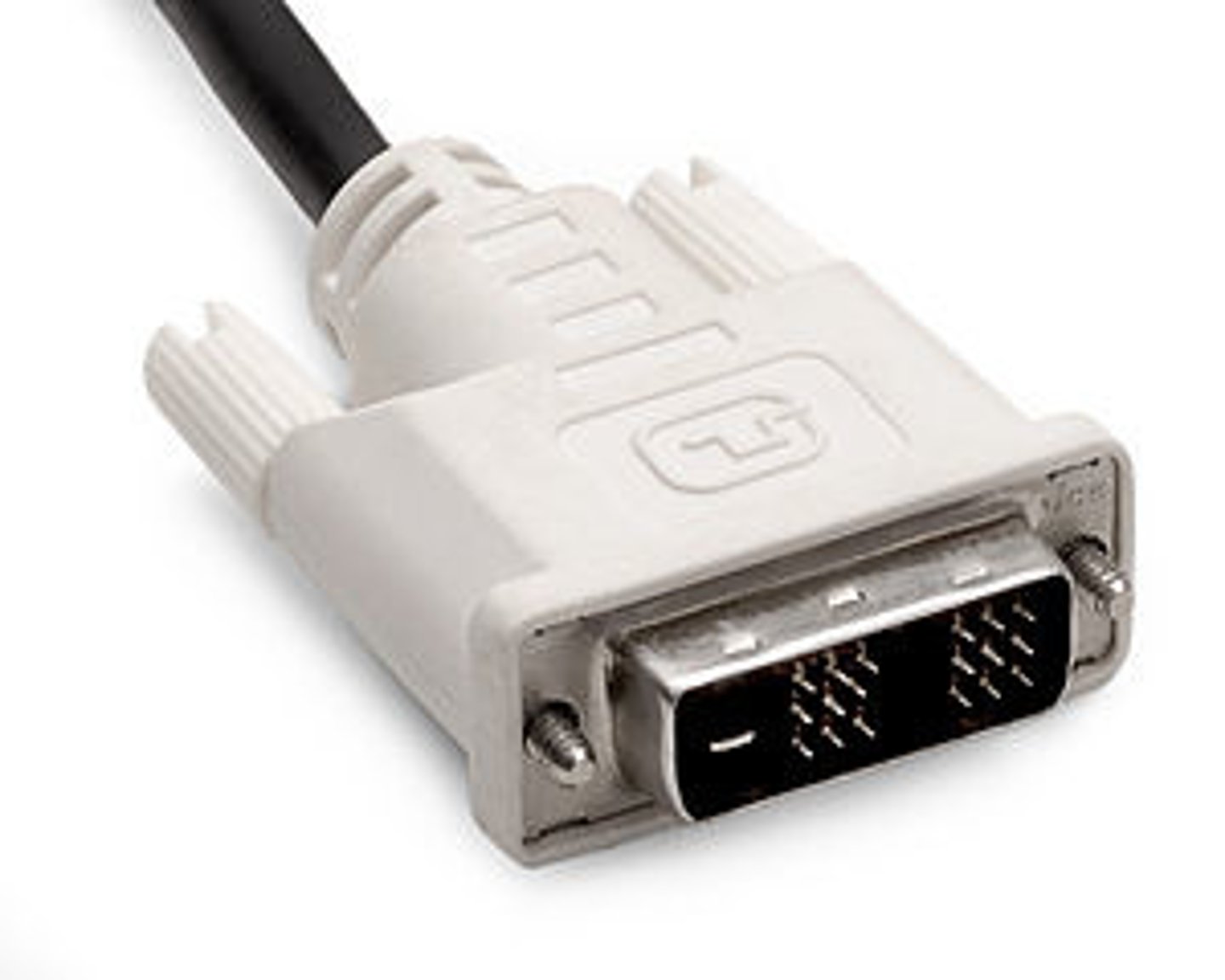
DVI Video
The Digital Visual Interface (DVI) connector is designed to connect digital monitors to a computer, typically flat panel. It is typically white with three rows of eight pins. There are multiple versions of DVI connectors, such as DVI-I (it integrates both digital and analog connections), DVI-D (digital connections only), and DVI-A (analog connections only).
DVI-D and DVI-I come in either Single Link or Dual Link. Dual link supports higher resolutions. Single link cables can be identified as having 8 pins missing, while dual link cables use all 24 pins. Most computers now use HDMI, DisplayPort, or Thunderbolt instead of DVI.

HDMI
The High-Definition Multimedia Interface (HDMI) connector uses digital signals and is now available on a wide variety of devices such as computers, monitors, TVs, Blu-Ray players, etc. It requires a royalty to use. As the name implies, cables using an HDMI connector are used to transfer high-definition signals and supports both audio and video data.
There have been several versions of HDMI; v2.1 is the latest. It offers faster bandwidth than previous versions.
HDMI uses a 19 pin configuration for types A, C, and D. Type C is the Mini HDMI connector (often used for portable devices, such as DSLR cameras). Type D is smaller and is known as the Micro HDMI (often used on smaller portable devices such as smartphones).

RJ-45
Most computers provide a Registered Jack 45 (RJ-45) connector that allows you to connect the system to a network.

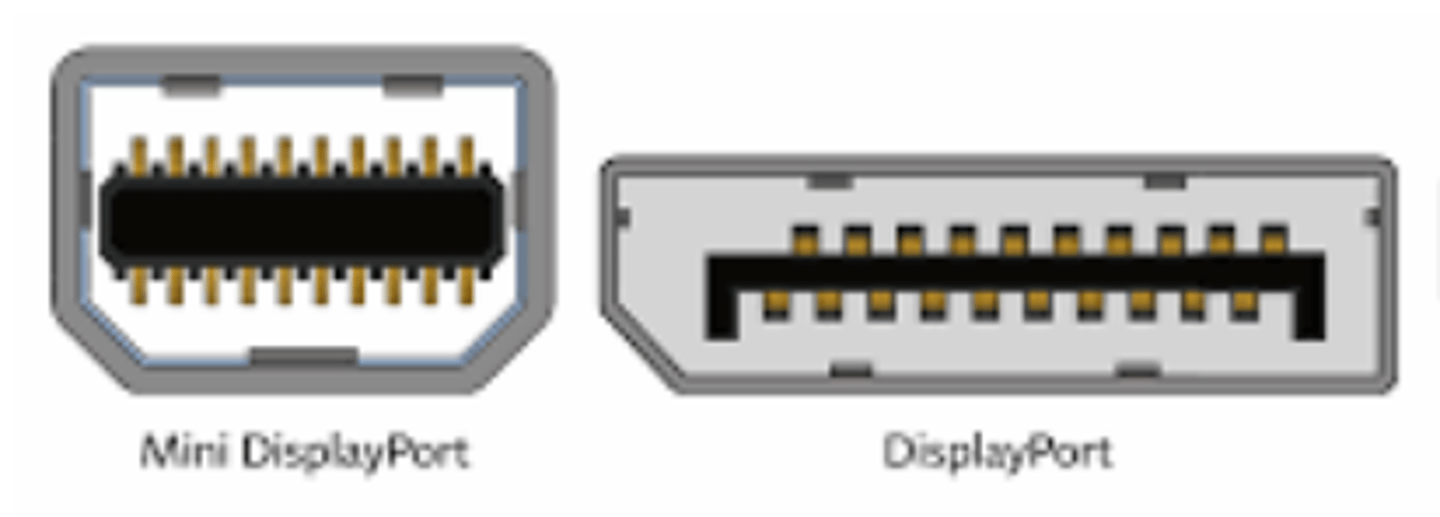
DisplayPort / Mini DisplayPort
DisplayPort connectors have 20 pins and come in two sizes: the standard DisplayPort and a smaller Mini DisplayPort. These interfaces are used to send high-quality, digital video and audio signals.
DisplayPort and Mini DisplayPort function similarly to the HDMI. The main difference in appearance is that HDMI is beveled on two corners and DisplayPort is beveled on only one. DisplayPort has a greater bandwidth than HDMI. While HDMI supports a maximum bandwidth of 18 Gbps, DisplayPort 1.4 has a maximum bandwidth of 32.4 Gbps which supports a much greater resolution.
Unlike HDMI, DisplayPort is royalty free (manufacturers do not have to pay a fee to use the interface). Because of this, DisplayPort has the potential to replace HDMI. DisplayPort uses a 20-pin connector. There is also a DisplayPort Dual-Mode (DP++). It allows DisplayPort sources to use simple passive adapters to connect to HDMI or DVI displays.
Thunderbolt (2)
The Thunderbolt (TB) interface is compatible with DisplayPort and is primarily used on Apple computers. Thunderbolt ports can also provide DC power. They are mainly used for external displays, but they can also be used to connect other peripheral devices. There have been many versions of this connector:
Thunderbolt 1 - Developed around 2011
Thunderbolt 2 - Developed 2013 and supports up to 20 Gbps.
Thunderbolt 3 - Developed by Intel and doubles the bandwidth to 40 Gbps. Maximum performance is for cable lengths over 0.5 meters (1.6 feet).
Thunderbolt 4 - Key differences between 3 & 4 are: support for USB4, minimum bandwidth of 32 Gbps, and support for dual 4K displays.

USB
USB devices are hot-swappable. This means you can plug and unplug USB peripherals while the system is running. The system will automatically detect the addition or removal of a device and make the necessary configuration changes.
To prevent data corruption when disconnecting external storage devices, you must stop them properly in the operating system before removing them. USB devices can be plugged in directly to a USB port on the computer or to an external USB hub that's connected to the computer.
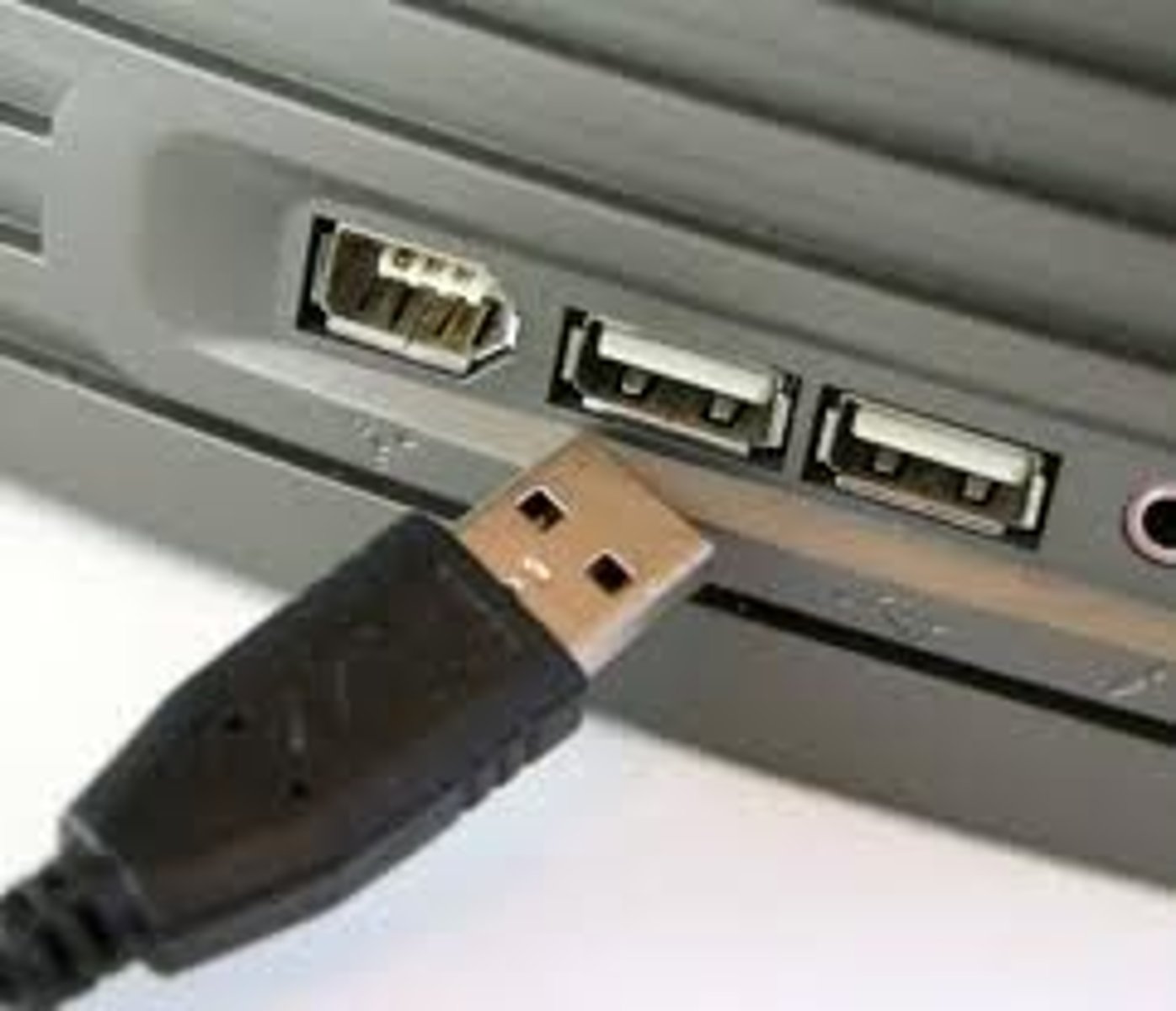

Self Powered USB Devices
USB ports can provide power over the connection. USB devices can receive up to 500 milliamps of power from a USB 2.0 port and up to 900 milliamps of power from a USB 3.0 port. If a device can operate on this much power, it's considered a bus-powered device. This means the USB port provides 100 percent of its power.
If a device needs more power than this, it's considered a self-powered device and will typically have an external power adapter that plugs into a wall outlet.
USB 2.0 ports can provide 2.5W of power. A standard USB 3.0 port can provide 4.5W of power and allows data transfer. A USB 3.0 dedicated charging port can provide 7.5W of power for a single device but does not allow data transfer.

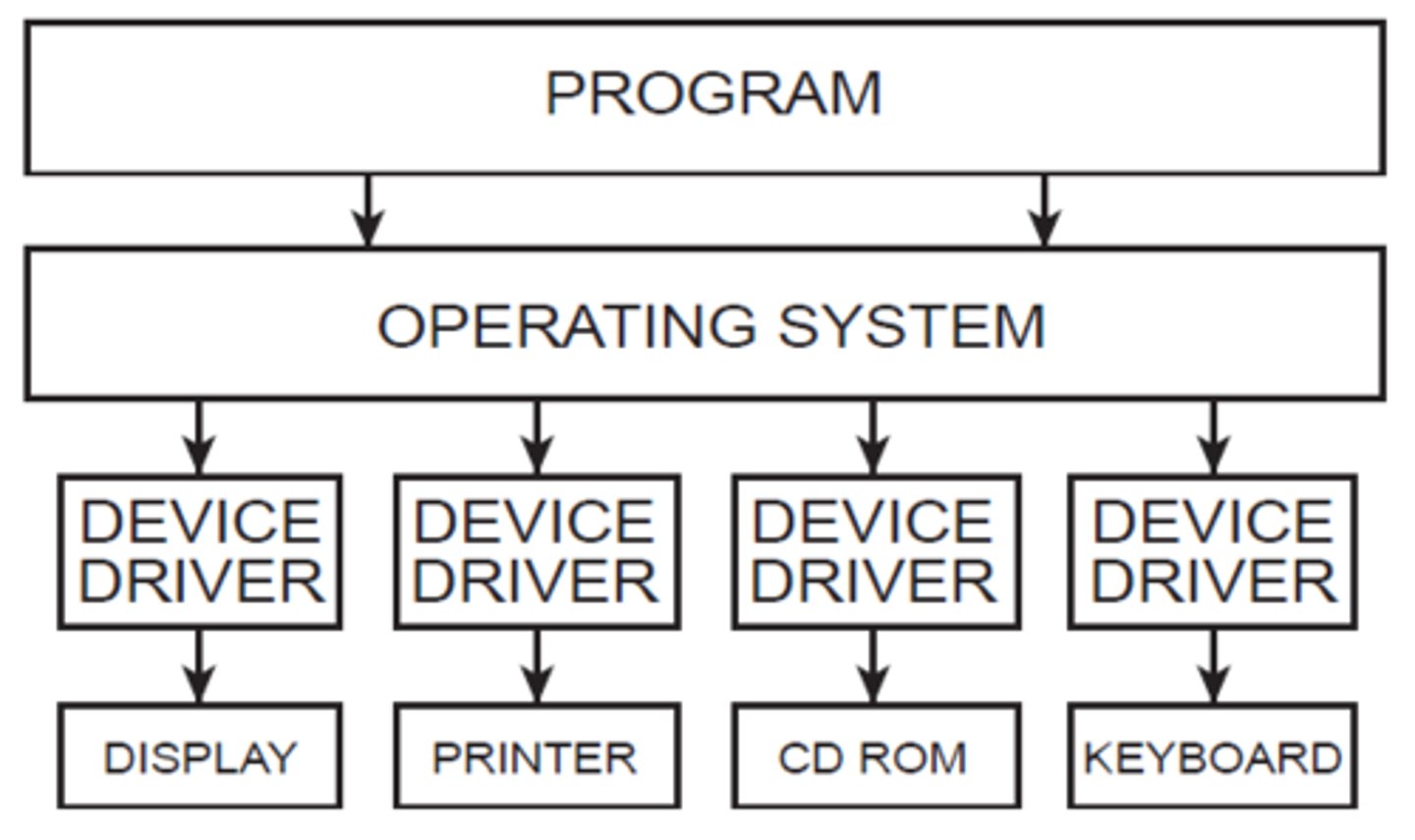
Drivers
For some peripheral devices, you may need to load drivers before connecting the device for the first time. Drivers contain software instructions that the computer needs in order to communicate with the device.
For many devices, the necessary drivers are included with the operating system. Other devices may require you to manually install the drivers on the system prior to the first connection.
Device drivers may also need to be updated when manufacturers fix bugs and vulnerabilities. If you need to uninstall a driver, the easiest and most effective method is to uninstall the original software package that was installed with the device.
Sometimes, driver updates can cause new problems with your software. In this case, a very easy solution is to choose the Roll Back Driver option. This will revert the computer back to its state before installing the update.
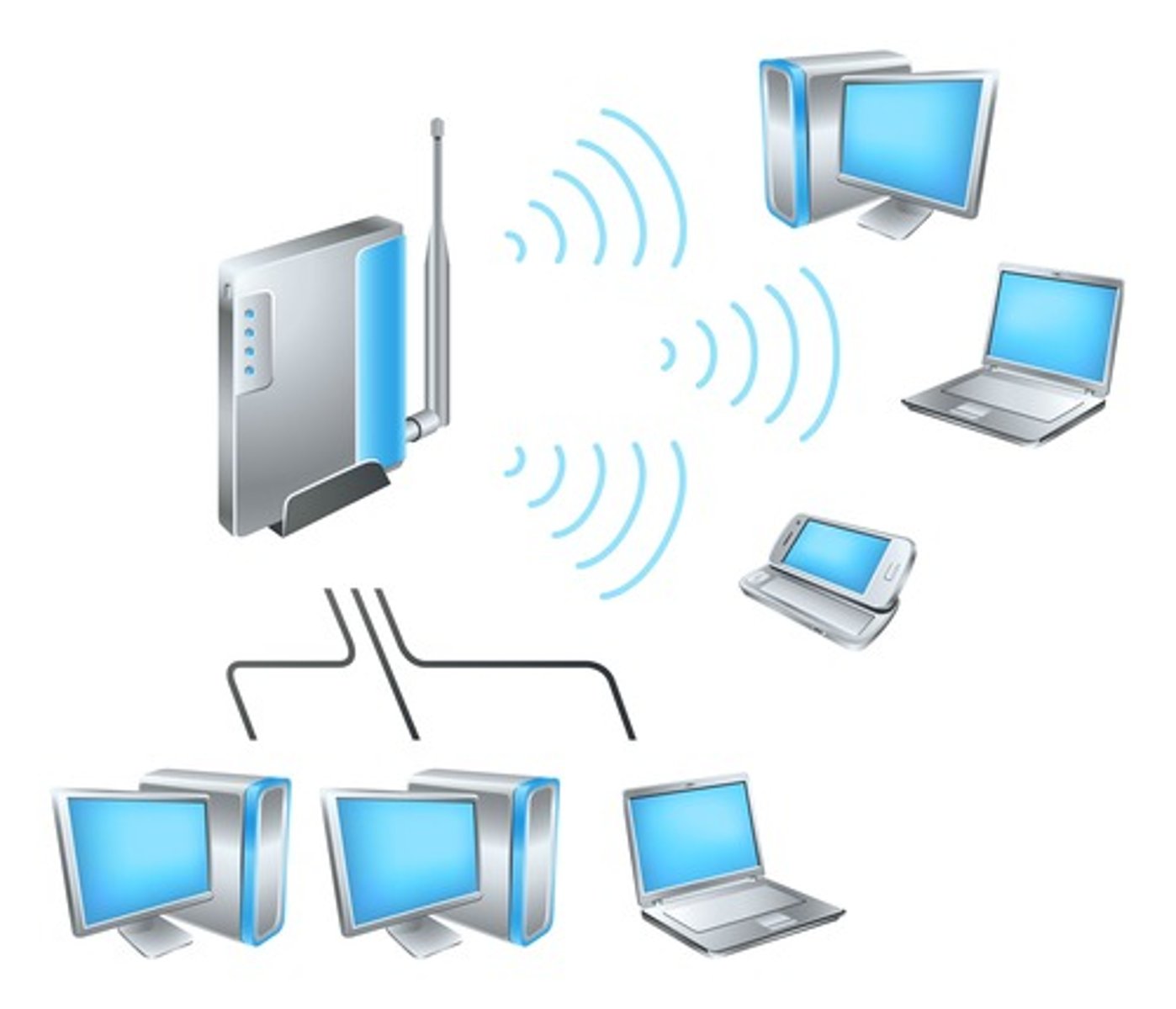
Network
If a computer has access to a local network, either wired or wireless, you might install and configure peripherals to be accessed over the network. For example, you might install an Internet Protocol or IP-based printer and then configure it using a web page in a browser. Another example would be a Wi-Fi access point.
USB 1.0
12 Mbit/s
USB 2.0
480 Mbit/s

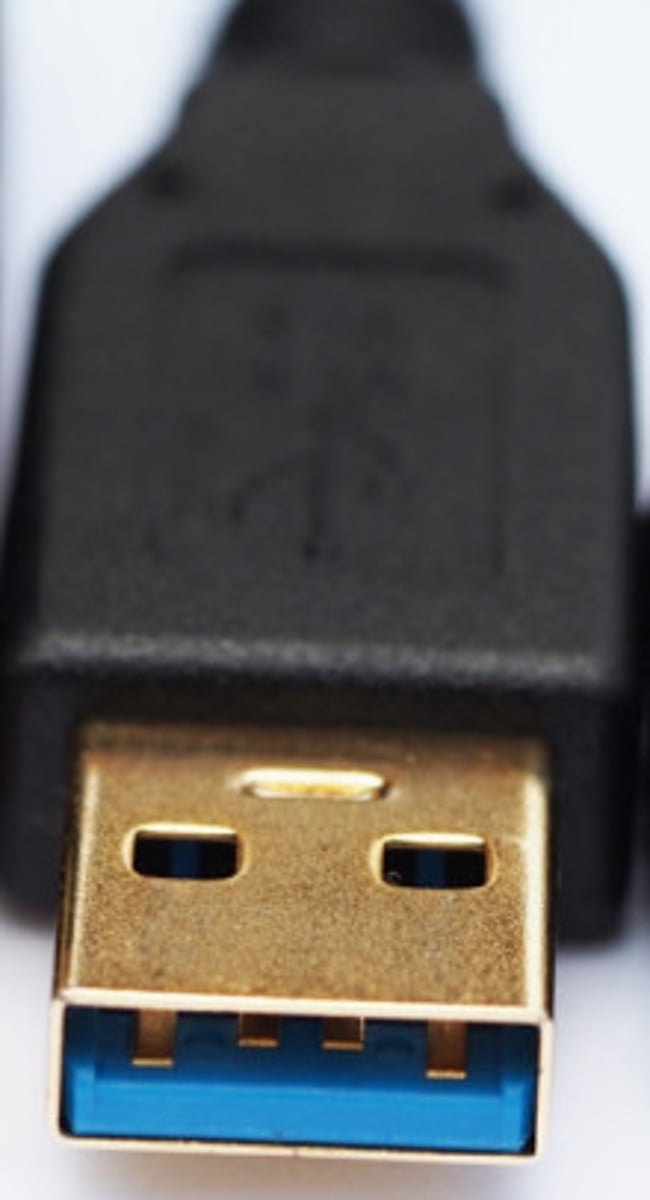
USB 3.0
5 Gbit/s or 5000Mbps Called SuperSpeed and provides full duplex.

USB 3.1
10 Gbit/s called SuperSpeed+
USB 3.2
20 Gbit/s
USB 4
40 Gbit/s
FireWire 400 (IEEE 1394)
400 Mbit/s 6 Connectors; called alpha connector.
FireWire 800 (IEEE 1394b)
800 Mbit/s 9 connectors; called a beta connector
FireWire S1600 (IEEE 1394c):
1.6 Gbit/s 9 connectors
Resistive Touchscreen Advantages
• Cheaper to manufacture
• Fewer accidental touches
• Can sense any object touching the screen
• Better survival against heat and water
Capacitive Touchscreen Advantages
• Sharper images
• Sensitive to light touch
• Better multi-touch sensing
• Better survival against rough handling
Resistive Touchscreen
As their name implies, resistive touchscreens rely on the resistance, or pressure, that's applied to the screen itself. They consist of two thin layers of transparent material. The top layer is made of flexible plastic film, and the bottom layer is typically made of glass. Each of these layers is coated in indium tin oxide, which is a transparent material that conducts electricity. The layers are kept apart by tiny bumps called spacer dots, which prevent the top layer from sagging and creating false touches.
Capacitive Touchscreen
Capacitive touchscreens take advantage of the fact that the human body naturally conducts electricity. They consist of a piece of glass coated with a thin layer of indium tin oxide. Electrodes at the corners of the screen maintain a constant voltage over the conductive layer whenever the device is powered on. When a conductive finger touches the screen, it creates a change in voltage. Sensors under the screen detect the location of the change, which the computer translates into instructions. Smartphones typically use capacitive touchscreens.
Hard Disk Drive (HDD)
The most common type of long-term storage that uses thick magnetic disks encased in a protective housing to store data.
• Relatively inexpensive
• Fast
• Can hold a lot of information.
• Most desktop computers usually use a form factor of 3.5 inches.
• Most laptops use a 2.5-inch form factor.
• This measurement represents the approximated diameter of the platter encoded in the driver.
• The 3.5 HDD are usually faster, but due to their size won't fit in a laptop computer.
The capacity of an HDD is ever increasing, from 100 GB up to 18TB. As technology continues to improve, these numbers are likely to increase. The performance of an HDD is determined by:
• How fast it can read and write data, measured in revolutions per minute (RPM).
• Latency (access time).

Optical Drive
A storage device that uses light instead of magnetism to store information. This includes CD-ROM, DVD, and Blu-ray devices.

Flash Storage
A compact, portable storage device that uses special memory chips to store data.

Solid State Devices (SSD)
A device with similar capacity to an HDD that uses flash storage instead of magnetic disks to store data. SSDs are much faster and more durable than hard disk drives but usually are more expensive.

External Hard Disk Drives
An HDD that can be connected as a peripheral to a computer.

Heat-Assisted Magnetic Recording
Type of drive that allows bits of data to become smaller and more tightly packed together while still retaining data. It uses a tiny laser to briefly heat the recording surface of the hard drive to write the data making it more receptive to the effects of magnetism, which allow writing on much smaller areas than were possible before.
3D Flash Memory
Type of memory that implements tiers of solid-state flash memory stacked on top of each other allowing for much greater storage capacity at a lower cost than 2D flash memory.
Synthesized DNA Strands
Synthetically produced artificial DNA that is capable of storing vast amounts of information and may be a solution to long-term massive storage.
File
The smallest container within a computer's storage system that is used to store information such as data, settings, and commands used in a computer program. A file is the smallest container that can be copied, deleted, or moved within a file system.
File Format
The way a file is organized. File formats are indicated by an extension such as .jpg, .gif, .png., .mp3, .wav, .wma, .mp4, .avi, and .wmv.
