Clinical Chemistry -- Exam 1
1/109
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
110 Terms
Wavelengths of light are measured in _____ units.
Nanometer (nm)
Match the following approximate wavelength ranges to the correct region name:
180-380 nm
Ultraviolet
Match the following approximate wavelength ranges to the correct region name:
380-750 nm
Visible
Match the following approximate wavelength ranges to the correct region name:
750-1200 nm
Infrared
Match the common light source used for the following regions of wavelengths:
Deuterium
Ultraviolet
Match the common light source used for the following regions of wavelengths:
Tungsten
Visible
Match the common light source used for the following regions of wavelengths:
Hydrogen
Ultraviolet
Match the common light source used for the following regions of wavelengths:
Mercury arc
Ultraviolet
Which of the following curves can be used to determine the optimal wavelength to use for a
given spectrophotometric procedure:
Spectral absorbance curve, spectral transmission curve
The optimal wavelength of light of a test solution may be defined as the wavelength of light
that produces the ________ peak on a spectral absorbance curve.
Maximum absorbance
The optimal wavelength of light of a test solution may be defined as the wavelength of light
that produces the ________ peak on a spectral transmission curve.
Minimum %Transmission
The optimal wavelength of light is the wavelength of light producing the maximum absorbance peak
which is the same as the wavelength of light producing the minimum %Transmission peak.
True
If the %T value is 62.0%, the absorbance value may be calculated as ____.
0.208
When measuring the response of a test solution, the instrument detects the amount of incident light
that is absorbed by the compound of interest in the test solution.
False
The intensity of light being transmitted through a test solution (Is) is expected to be less than the
original incident light (Io) due to incident light being:
Absorbed by the compound of interest, absorbed by reagent or solvent molecules, reflected off the surface of the sample cell
Setting the baseline of the spectrophotometer to 100%T is the same as setting the baseline to
0.000ABS
True
Choose the correct relationship statement (choose all correct answers):
Absorbance and concentration are directly related, transmission and concentration are inversely and logarithmically related
By using a lightpath length of 2cm as compared to a standard 1cm lightpath, it is expected
the absorbance value will _______.
Double because there will be twice as many absorbing molecules for the light to pass
through
The maximum absorbance wavelength will be the same as the minimum %T wavelength.
True
A curvy line will result when plotting absorbance and concentration on linear graph paper.
False
Upper limit of linearity
Concentration of substance is at the highest
level where concentration and absorbance are still
directly related
Exceeds upper limit of linearity
Concentration of substance is too high and absorbance and concentration are no longer directly related
Lower limit of sensitivity
Concentration of substance is at the lowest level where concentration and absorbance are still directly related
Less than lower limit of sensitivity
Concentration of substance is too low and absorbance and concentration are no longer directly related
Beer’s Law states that:
Absorbance is directly related to concentration of substance in solution only to the upper
limit of linearity and above the lower limit of sensitivity.
Calculate the concentration of substance using the Beer’s Law equation and the following
data:
absorbance = 1.650
millimolar absorptivity constant = 0.235
light path length = 2cm
3.5
Evaluate the following data:
Limit of linearity: 1250 mg/dL
Limit of Sensitivity: 1.0 mg/dL
Specimen test result: 1500 mg/dL
The action that best correlates with this data is to:
Do not report; dilute specimen, repeat analysis, and correct for dilution.
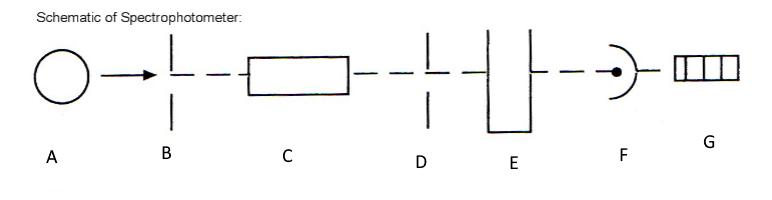
Which component corresponds with A?
Light source
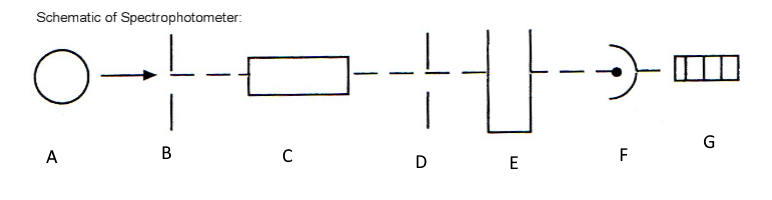
Which component corresponds with B?
Entrance slit
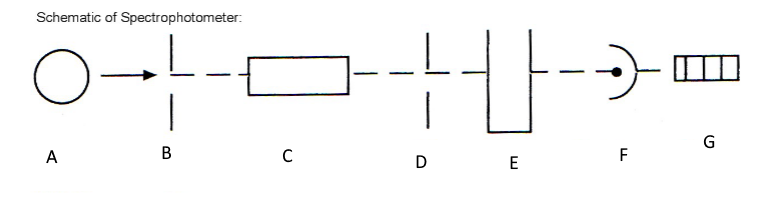
Which component corresponds with C?
Monochromator
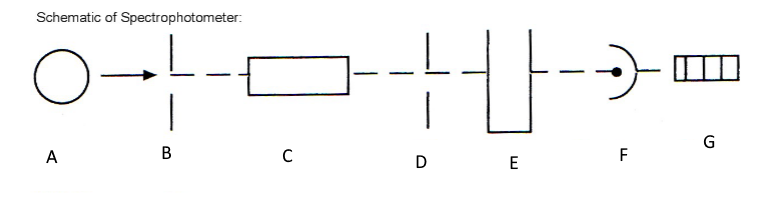
Which component corresponds with D?
Exit slit
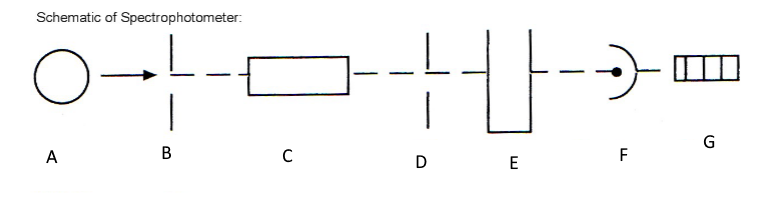
Which component corresponds with E?
Cuvet
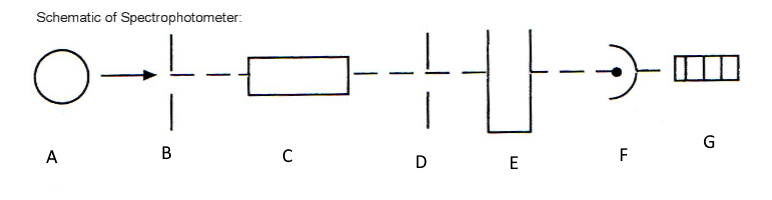
Which component corresponds with F?
Detector
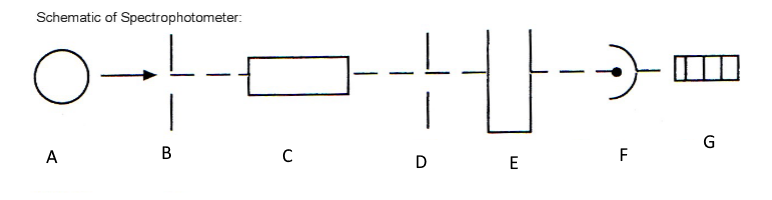
Which component corresponds with G?
Meter
Light source
provides polychromatic incident radiation (light)
Monochromator
separates or disperses polychromatic light into the individual wavelengths
Exit slit
isolates the desired wavelength to pass through the test solution
Cuvette
holds the test sample for light to beam through
Detector
measures the amount of light passing through the test cuvette (PMT)
Meter
readout device (Abs, %T, units)
What are the advantages of using a narrow bandpass instrument as compared to a wide bandpass instrument?
Increases sensitivity of the instrument (can detect lower concentration of substance), increases linearity of the instrument (can detect higher concentration of substance), increases resolution of substances in test solution (able to differentiate absorbance peaks from similar compounds; this means the specificity is improved.)
Explain how lipemic test samples will falsely affect spectrophotometric test results including how lipemia affects %T and absorbance values and if you expect the test result to be falsely increased or falsely decreased (or have no affect at all).
Lipemic test samples will cause the %T of light going through the test sample to be decreased. This equates to the ABS value being falsely increased.
The purpose of performing preventive maintenance on instruments is to:
All of the above are correct
After performing preventive maintenance, quality control specimens are analyzed to verify instrument performance has not been jeopardized by doing the maintenance.
True
Checks for changes in bandpass and the amount of light energy falling on the photocell ensuring a constant and stable ABS value is obtained
Photometric Accuracy
Checks for presence of extraneous light striking the detector
Stray Light Detection
Ensures light energy being emitted from the monochromator’s exit slit is the same wavelength as that set on the wavelength dial
Wavelength Accuracy
Ensures reaction temperature is accurate and stable
Temperature Calibration
Ensure the response (ABS) from various dilutions of a check solution are linear and proportional
Photometric Linearity
Ensures the blank reading when set at 100%T/0.000 ABS is stable over time
Baseline Stability
Colorimetry is best defined as the measurement of
Colored compounds in solution
A spectral absorbance curve is used to determine the
Optimal wavelength of a specific test solution
A reagent blank is used in spectrophotometric measurements to
Negate the effects of reagent absorption
Choose the correct relationship statement:
Maximum absorbance correlates to minimum %T
Plotting ______ and concentration on ____ graph paper will result in a ______ line.
Absorbance; linear; straight
The upper limit of linearity on a standard curve is defined as the:
Highest concentration of substance that follows Beer’s Law
Evaluate the following data:
Limit of linearity: 500.0 mg/dL
Limit of Sensitivity: 1.0 mg/dL
Specimen test result: 0.5 mg/dL
The action that best correlates with this data is to report the specimen test result as:
Report the specimen test result as <1.0 mg/dL
The purpose of the ‘Wavelength Accuracy’ Performance Check on a spectrophotometer
is to:
Confirm exit slit is set at the specified wavelength
Potential
Expression of energy
Current
Flow of a charge
Measuring electrode
Where sample activity is measured
Reference electrode
Device that can maintain a constant potential under a variety of conditions
Salt bridge
Device that allows ionic movement between compartments of an electrochemical cell to maintain an electrical current
Most common reference electrode
Silver/Silver Chloride Electrode
Amperometry
Measurement of the current flowing between two electrodes and generally involves an oxidation/reduction type of reaction
Potentiometry
Measurement of electrical (potential) difference between the measuring and reference electrodes
When calibrating electrodes, a “two point” calibration is performed to correct for:
Changes in the slope of the calibration line
What type of membrane does the pH electrode have?
Glass
This amperometric electrode measures an analyte that passes through a membrane that has an enzyme immobilized its middle layer:
Glucose
The principle of measurement of the pCO2 and pH electrodes is:
Potentiometry
The sodium ion-selective electrode has ____________ as its membrane.
Specially formulated glass
The co-oximeter is a spectrophotometer which requires samples to be?
Well-mixed whole blood
Which of the following should be performed daily on the blood gas analyzers for preventative maintenance?
Injecting a cleaning solution through the system
Which of the following statements does NOT apply to enzymes:
Enzymes are resistant to denaturation
Choose the FALSE statement about isoenzymes:
Are not helpful in diagnosis of disease
An advantage of the kinetic method for measuring enzyme activity versus an end-point method is that it:
It is easier to demonstrate linearity of the reaction sequence
Substrate depletion is observable
Is the most accurate method of measurement
Which of the following phases of an enzyme reaction is the most accurate phase to measure enzyme activity?
Linear phase
The linear phase of an enzyme reaction is defined as when
The amount of product formed is consistent per unit of time
The change in absorbance per unit of time is consistent
Activation energy is:
decreased by enzymes
Enzyme reaction rates are increased by increasing temperatures until they reach the point of denaturation at:
40° - 60°C
Competitive inhibition
Inhibitor binds to active site of enzyme (E-I); this complex competes with free enzyme for substrate binding sites and prevents product formation. Generally reversible by diluting patient sample (ie increasing substrate concentration and changing the substrate to sample ratio)
Noncompetitive inhibition
Inhibitor binds to regulatory or allosteric site of enzyme (E-I); this complex prevents product formation
Uncompetitive inhibition
Inhibitor binds to enzyme-substrate complex that has formed (ES-I), preventing product formation
The first step of the reaction is called the ___________ and the final step of the reaction is generally called the ___________ step.
rate-limiting / measuring
Which of the following co-enzymes shows an absorbance peak at 340 nm?
NADH
When a reaction is performed in zero-order kinetics the:
Rate of the reaction is independent of the substrate concentration
low substrate concentration
The velocity of the reaction is approximately proportional to the substrate concentration
first-order kinetics
The velocity of the reaction is approximately proportional to the substrate concentration
zero-order kinetics
The velocity of the reaction is independent of the substrate concentration
high substrate concentration
The velocity of the reaction is independent of the substrate concentration
Certain factors affect the rate of enzyme-catalyzed reactions and must be controlled during the analysis to ensure accurate test results. Factors that are controlled during analysis include all the following EXCEPT:
Enzyme concentration in patient sample
An enzyme may be defined as a:
Protein catalyst of biological origin
The general relationship among the principle ‘players’ in an enzyme catalyzed reaction may be represented as follows: S + E → ES → P + E, The ‘ES’ stands for which of the following:
Enzyme-substrate complex
The site at which an enzyme binds to its substrate is called the:
Active site
To obtain valid measurements, enzyme activity measurements must be made in:
Zero-order kinetics
The Michaelis-Menten constant (Km), can be defined as the:
Substrate concentrate required to achieve ½Vmax
Which of the following terms is best described by the statement:
The velocity of a kinetic enzyme reaction (i.e. the amount of product formed) is dependent upon the concentration of enzyme in the test sample
Zero order
The rate of an enzyme reaction approximately doubles for every ____°C rise in temperature.
10
Which of the following best describes a kinetic monitoring system for enzyme analysis:
The rate of product formation is monitored throughout the reaction period