2.1 - populations, species identification, interactions, carrying capacity
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
ecology
study of interactions between organisms and their biotic and abiotic environment
sphreres
biosphere
parts of Earth with life existing
atmosphere
air parts of Earth
hydroshpere
water parts of Earth
lithosphere
soil and earth parts
species
group of organisms that can interbreed and produce fertile offspring.
hybride
infertile offspring resulting from the crossbreeding of two different species or varieties.
keystone species
a species that has a disproportionately large effect on its environment relative to its abundance, playing a critical role in maintaining the structure of an ecological community.
impacts of keystone species
population control
threats of removal a keystone species
trophic cascade
habitat changes
biodiversity loss
population
the total number of individuals of a species living in a specific area or habitat, which are capable of inbreeding
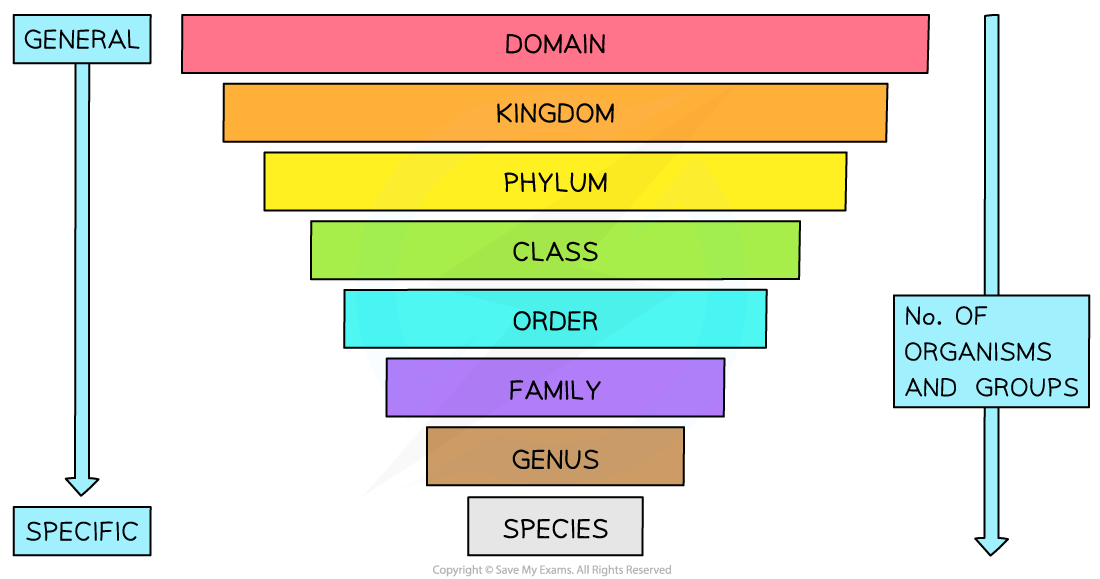
hierarchical classification system
ranks↓ = organism number ↓ = simmilarity between them ↑
Democratic → domain
King → kingdom
Philip → phylum
Came → class
Over → order
For → family
Good → genus
Sex → species
Binominal naming system
name of genus (capital letter)
name of species (small leter)
eg. Homo sapiens
tools for identifying species
dichotomous key → based on characteristics
comparison of specimens with reference to known samples and collections
DNA surveys → based on protein analysis
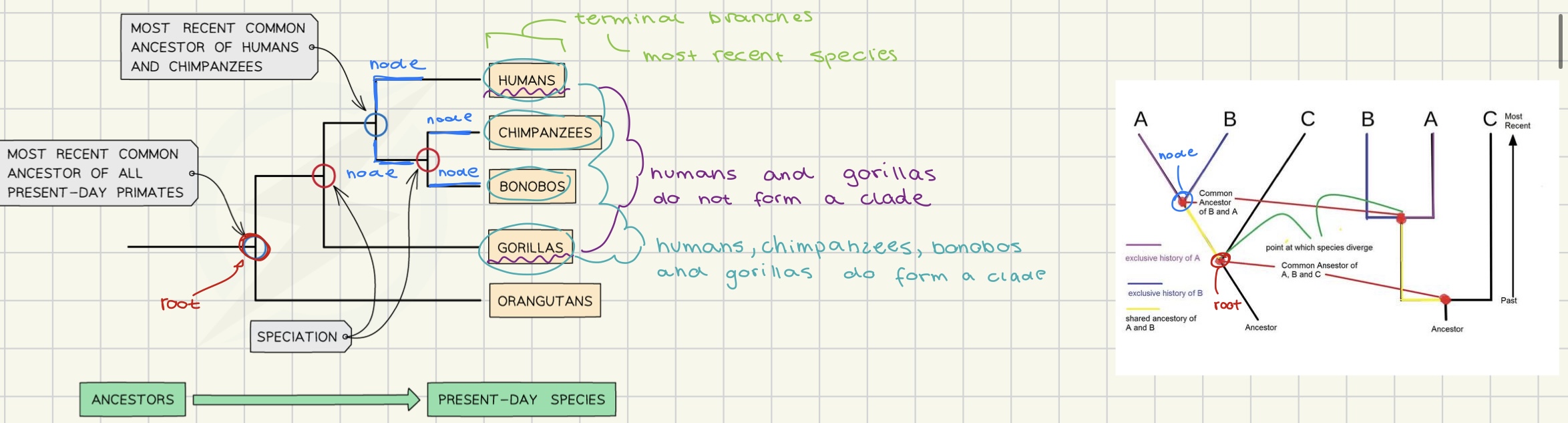
cladistics
taxonomy → classifying and naming organisms
cladistics
the process of classifying organisms into clades based on evolutionary relationships and common ancestry.
cladistics structure
clade → group of species evolved from common ancestor (all alive and dead)
terminal branches → most recent species
node → history line from common ancestor to new species
root → most recent common ancestor of all present primates
biotic factors
living components of an ecosystem that affect species interactions in a community
plants
fungi
animals
bacteria
etc
abiotic factors
non-living components of an ecosystem
water
temperature
pH
humidity
etc
ecological niche
the role and position a species has in its environment, including its
habitat
resources
interactions with other organisms.
fundamental niche
the broadest set of conditions under which a species can survive and reproduce, without the influence of competitors or predators.
realised niche
the actual conditions under which a species exists, influenced by competition and predation.
species interactions
predation
one by other eaten
herbivory
consumption of plants
decomposers
feed on dead and decaying
recycle nutrients
symbiosis
two species living in close relationship
mutualism
both benefit
commensalism
one benefit, other unaffected
parasitism
one benefit, host harmed
competition
struggle over limited resources
types of competition
intra specific
same species
inter specific
different species
competitive exclusive principle
two species competing for the same limited resource cannot coexist at constant population values.
one will decline
or both will narrow their niches
factors affecting population growth and decline
birth rate decline/ incline
limiting factors
density dependent
density independent
carrying capacity
the maximum number of individuals of a species that an area's resources can sustain indefinitely without significantly depleting or degrading those resources.
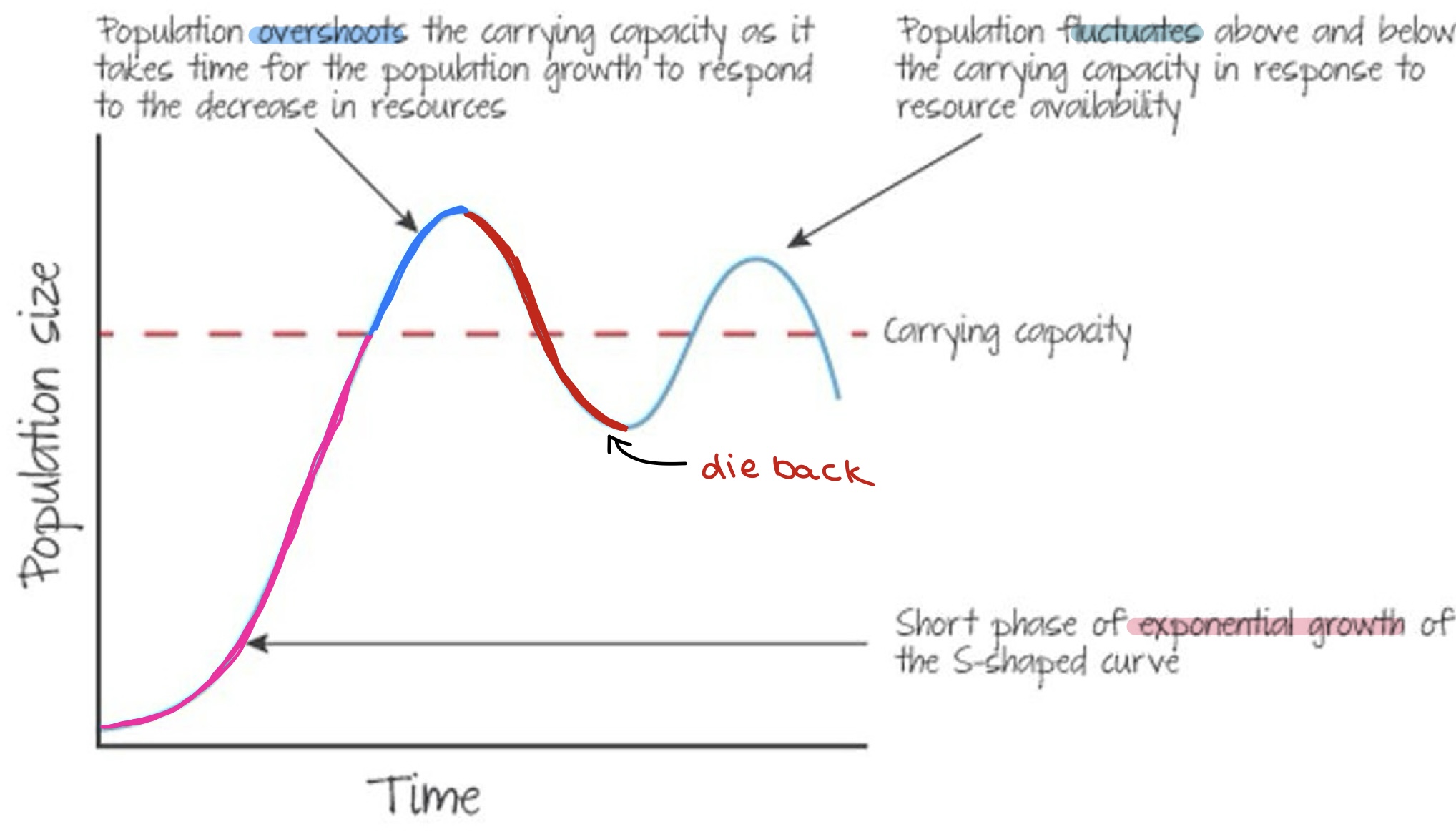
exponential growth
overshoot
die back
flutuations
*due to limiting factors
density dependent limiting factors
factors that affect a population only when it reaches certain density
*tend to be biotic
competition
disease
parasitism
predation
density independent limiting factors
control populations no matter what the density is
*tend to be abiotic
sunlight
temperature
water and natural disasters
human activities
J-shaped curve
exponential population growth
hasn’t yet reached carrying capacity
population at its biotic potential
no limiting factors
S-shaped curve
growth leveling off as it reaches carrying capacity
limiting factors slow the growth when it starts approaching