AP Psychology Unit 3 - Development and Learning
1/164
Earn XP
Description and Tags
AP Psychology Unit 3 (2025)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
165 Terms
Developmental Psychologists
Psychologists who study how our thoughts and behaviors change over the course of our entire lives
Nature
Refers to genetic factors
Nurture
Refers to environmental factors
Cross-Sectional Research
A method of research that uses participants of different ages to compare how certain variables may change over the lifespan
Longitudinal Research
A research method that examines one group of participants over time
Teratogens
Certain chemicals or agents that can cause harm to an unborn child if ingested or contacted by the mother
E.g. alcohol, psychoactive drugs, and certain viruses
Fetal Alcohol Syndrome (FAS)
A serious condition resulting from the mother's alcohol consumption during pregnancy, leading to physical, behavioral, and cognitive defects in the child (Such as malformed skull and intellectual disability)
Reflexes
Specific, inborn, automatic responses to certain specific stimuli
Rooting Reflex
When touched on the cheek, a baby will turn their head towards the side where they felt the touch and seek to put the object in their moutn
Sucking Reflex
When an object is placed into a infant’s mouth, they will suck
Grasping Reflex
If an object is placed into a baby’s palm or foot pad, the baby will try to grasp the object with his or her fingers or toes
Moro Reflex
When startled, a baby will fling their limbs out and then quickly retract them, making themselves as small as possible
Babinski Reflex
When a baby’s foot is stroked, they will spread their toes
Motor Skills
The abilities that enable movement and coordination of the body, including both gross motor skills (large movements) and fine motor skills (small, precise movements)
Gross Motor Skills
The abilities that involve the use of large muscle groups for movements such as running, jumping, and climbing
Gender Roles
The societal expectations and behaviors considered appropriate for individuals based on their gender. These roles can influence personality, interests, and overall development
Continuous vs. Discontinuous
A debate in developmental psychology concerning whether development occurs in a gradual, steady rate, or through distinct stages that include rapid development and relatively no change
Gender Schema
The cognitive framework that children develop to understand and organize information about gender
Growth Spurt
A rapid increase in physical growth and development that often occurs during puberty, affecting height and weight
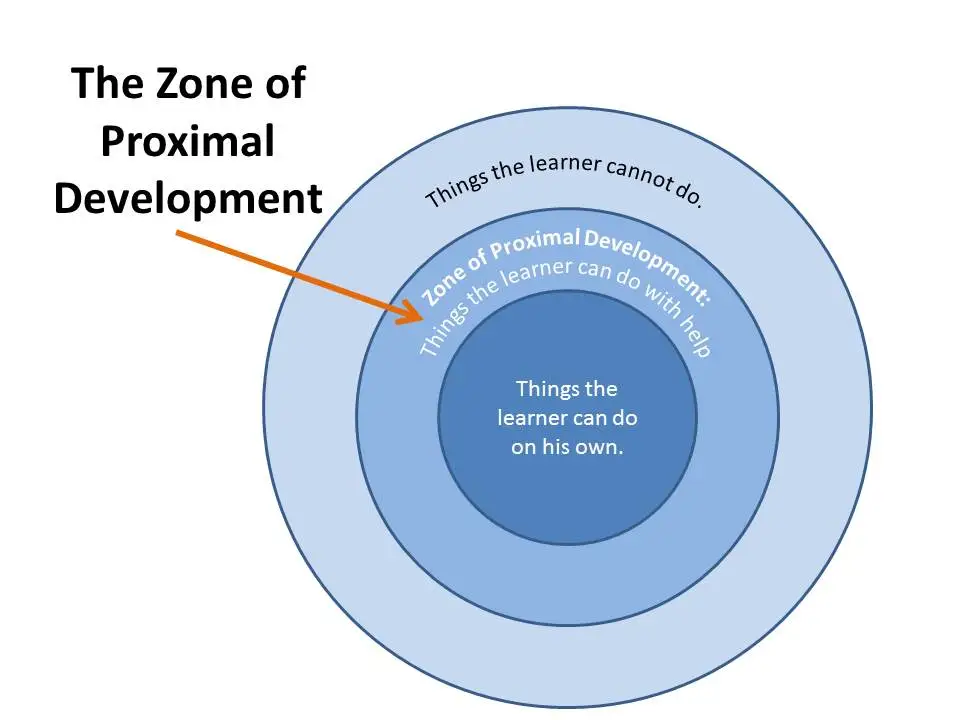
Zone of Proximal Development
A concept created by Lev Vygotsly, it encompasses the range of tasks a child can perform independently and tasks the child needs assistance with
Scaffolding
When a more knowledgeable person provides support to a learner to help them achieve a new skill
Psychosocial Stage Theory
A developmental theory created by Erik Erikson, it is one of the first to propose changes throughout the whole life. It involves eight stages, each involving a specific social conflict
Trust vs. Mistrust
The first stage in Erikson’s Psychosocial Theory. It spans from ages 0 to 1.5 years, and the crisis involves learning to trust the caregiver
E.g. a crying baby learns whether their parent will come feed them when they’re hungry
Autonomy vs. Doubt
The second stage in Erikson’s Psychosocial Theory. It spans from ages 1.5 to 3 years, and the crisis involves a child making their own decisions and gaining independence
E.g. a toddler putting on their shoes, will the parent let them or try to help?
Initiative vs. Guilt
The third stage in Erikson’s Psychosocial Theory. It spans from ages 3 to 6 years, and the crisis involves children asserting themselves and taking control
E.g. children often make friends who will back them up and take their side
Industry vs. Inferiority
The fourth stage in Erikson’s Psychosocial Theory. It spans from ages 6 to 12 years, and the crisis involves children comparing themselves to other children
E.g. children who are always picked last in class will start to develop a sense of inferiority
Identity vs. Role Confusion
The fifth stage in Erikson’s Psychosocial Theory. It spans from ages 12 to 18, and the crisis becomes internal as the person tries to figure out who they are and what they want to become
E.g. people change how they look, their friend groups, their music
Intimacy vs. Isolation
The sixth stage in Erikson’s Psychosocial Theory. It spans ages 19 to 40 years, and the crisis involves finding people to share yourself with
E.g. many people form friendships and romantic relationships with people from college, work, etc
Generativity vs. Stagnation
The seventh stage in Erikson’s Psychosocial Theory. It spans ages 40 to 65 years, and the crisis involves feeling satisfied and productive with your life/life choices
E.g. someone with an unfulfilling job will find other ways to feel good about their place
Integrity vs. Despair
The eighth stage in Erikson’s Psychosocial Theory. It spans ages 65 to death, and the crisis involves looking back and wondering if you’ve lived a meaningful life
E.g. someone who is older and feels their time running out may be extra worried about if they’ve made their mark
Imaginary Audience
A psychological phenomenon often experienced by adolescents, where they believe they are the center of attention and everyone is watching and evaluating their behavior. This perception can lead to feelings of self-consciousness and heightened concern about public image
Assimilation
A process where we incorporate new information into existing schemata
Accommodation
A process where we modify existing schemas to fit new experiences
Piaget’s Theory of Cognitive Development
A comprehensive framework created by Jean Piaget that outlines how children's cognitive abilities develop through distinct stages: sensorimotor, preoperational, concrete operational, and formal operational
Sensorimotor Stage
The first stage in Piaget’s Theory of Development, it ranges from ages birth to 2. In this stage, children explore the world through their senses, develop object permanence, and develop separation anxiety
Object Permanence
The understanding that items still exist in the world even when not being sensed
Separation Anxiety
When children become distressed when they are removed from the caregiver they are used to/attached to
Preoperational Stage
The second stage in Piaget’s Theory of Development, it ranges from ages 2 to 7. Children develop language, symbolic thinking, and engage in pretend play. Children still struggle with logic and exhibit characteristic errors in thinking (Like animism and egocentrism)
Animism
When children assign human traits to inanimate objects
Egocentrism
When children assume everybody shares their perspective/are very selfish in their actions and thinking
Mental Symbols
Mental representations used by children to visualize concepts or communicate ideas (Usually develops in the preoperational stage)
Pretend Play
Also known as imaginative play or make-believe, it is a type of play where children use their imagination to create scenarios and act out different roles and events
Theory of Mind
The ability to think about and consider the mental states (beliefs, desires, intentions, etc) of others
Concrete Operational Stage
The third stage in Piaget’s Theory of Development, it ranges from ages 7 to 12. Children develop enhanced logical thinking abilities, problem solving, conservation, and reversibility
Concepts of Conservation
The realization that properties of objects (volume, area, number) remain the same even when their shapes change
Reversibility
The ability to undo a sequence of events back to its original starting point
Formal Operational Stage
The fourth stage in Piaget’s Theory of Development, it ranges from ages 12 to adulthood. People develop abstract reasoning, hypothetical reasoning, and metacognition
Abstract Reasoning
The ability to manipulate objects and contrast ideas in our mind without physically seeing them or having real-world correlates
Hypothetical Thinking
Being able to reason from a hypothesis
Metacognition
The ability to think about the way we think
Personal Fable
A person’s belief that they are unique or different from everyone else. It is a type of egocentrism that develops in the formal operational stage
Phonemes
The smallest units of sound used in a language
E.g. s-i-t, th-a-t
Morphemes
The smallest unit of meaningful sound in a language
E.g. unforgettable = un-forget-able
Syntax
The rules for combining words into grammatically sensible sentences
E.g. In English the adjective comes before the noun —> “White house” not “House white”
Semantics
A set of rules that tell us the meaning of morphemes, words, and sentences
E.g. in English, s at the end of a word means its plural, and ed at the end of a word means its past tense
Cooing
An early stage of language development (typically occurs between 2-4 months) where children produce vowel-like sounds and start to explore language
Babbling
An early stage of language acquisition (starts around 4 months) in which infants produce repetitive consonant-vowel combinations, often characterized by repetitive syllables like "bababa" or "dadada" - They start to explore phonemes
One-Word Stage/Holophrasitc Stage
The stage in language development where children use single words to speak and convey complex ideas. Usually occurs in 10-18 month olds
Two-Word Stage/Telegraphic Speech
The stage in language development where children first start using multi-word speech, usually 2 or 3 word expressions. Usually occurs in 18-30 month olds
Overgeneralization/Overregularization
The misapplication of grammar rules- very common in children when developing language or people learning a new language
E.g. A child knows that the suffix “-ed” signifies past tense, so they say things like “hitted” and “throwed”
The Nativist Theory of Language Acquisition
A theory created by researcher Noam Chomsky, it states children have an inherent ability to learn language, which is evident in their ability to acquire complex grammatical structures without explicit instruction
Critical Periods
Windows of opportunity during which we must learn a skill or our development will permanently suffer (Common term associated with language acquisition)
Sensitive Periods
Specific time frames in development when an individual is particularly receptive to certain environmental stimuli and experiences that can shape their growth
Imprinting
A rapid learning process occurring during a critical period in an organism's early life, where it forms strong attachments or recognizes specific stimuli, typically involving caregivers or important figures
Attachment Parenting
The reciprocal relationship between caregiver and chi;d
Temperment
Our emotional style or typical way we react to stressful situations
Secure Attachment
An attachment style that involves healthy communication styles, being able to ask for help when needed, and the ability to self-regulate emotions
Avoidant Attachment
An attachment style that involves difficulty expressing emotions, being emotionally withdrawn from others, and an unwillingness to ask for help
Anxious Attachment
An attachment style that involves being clingy, afraid of abandonment, and a constant need for reassurance
Disorganized Attachment
An attachment style that involves aspects of both anxious and avoidant attachment styles, a fear of rejection but difficulty with intimacy, and low self-worth
Ecological Systems Theory (Also Developmental Systems Theory or Biological Model)
Proposed by Urie Brofenbrenner, the theory gives us a system to identify and explain the different environments we operate in as individuals
Microsystem
A system in the EST that includes the immediate people/places around an individual. This system involves reciprocal relationships and personal interactions that are important for development
E.g. family, friends, school
Mesosystem
A system in the EST that includes the interactions of people in an individual’s microsystem. If influences the individual less, but the influence is still there
E.g. your parents and teachers interacting at a conference
Exosystem
A system in the EST that includes people/things that indirectly impact an individual, but still have influence
E.g. a parent who always works- their absence will directly affect the child, but the money they make will indirectly affect the child later in life by giving them more opportunities
Macrosystem
A system in the EST that includes social/cultural values, geography, socioeconomic status, ideology, race, etc. (Essentially, the culture an individual is immersed in)
E.g. someone raised in a community that believes men and women can have any job may have more doors open for themselves than someone raised the opposite
Chronosystem
A system in the EST that includes development over time, life changes, historical events, etc
E.g. people who were alive during 9/11 may have been impacted in a way that those who weren’t can’t understand
Stability vs. Change
A debate in developmental psychology over whether personality traits remain the same or evolve over time
Authoritarian Parenting
A parenting style that involves setting strict standards, applying harsh punishments for violation of those standards, and valuing obedience in children.
Permissive Parenting
A parenting style that involves having very few rules for children, very few demands, and little to no punishment
Authoritative Parenting
A parenting style that involves setting consistent standards, encouraging children’s independence, and following through on consequences when rules are broken
Negligent Parenting
A parenting style that involves parents being uninvolved with their children, being neither responsive nor demanding, and no close relationship between the parent and child
Adolescence
The transitional period between childhood and adulthood, typically marked by physical growth, cognitive development, and social changes
Puberty
The period of sexual maturation during which a person becomes capable of reproducing
Sex
Refers to the biological characteristics that differentiate males (XY chromosomes) from females (XX chromosomes)
Gender
The sociocultural roles, behaviors, activities, expectations, and attributes typically associated with being male or female in a given society
Primary Sex Characteristics
The biological and physiological features that differentiate males from females, such as reproductive organs. They are present from birth and play a direct role in reproduction
E.g. testes, ovaries, uterus
Secondary Sex Characteristics
The physical traits that emerge during puberty, which differentiate males from females but are not directly involved in reproduction
E.g. breasts, facial hair
Menarche
The first menstrual cycle or first menstrual bleeding in female humans. It signals the beginning of fertility potential
Spermarche
The onset of sperm production in males, marking a key milestone in male puberty
Menopause
A natural biological process that marks the end of menstrual cycles in women, typically occurring between ages 45-55
Jean Piaget
A Swiss psychologist known for his work on child development. He proposed the theory of cognitive development (the four stages), which explains how a child constructs a mental model of the world
Lev Vygotsky
A Russian psychologist who emphasized the role of social interaction in cognitive development. He believed that children learn and develop through their interactions with more knowledgeable individuals in their social environment (He’s the Zone of Proximal Development, Scaffolding, etc. guy)
Dementia
A gradual, progressive decline in cognitive function that affects speech, memory, judgment, and mood
Language
A complex system of communication that involves the use of words, symbols, or signs to express thoughts, ideas, and emotions
Adverse Childhood Experiences (ACEs)
A range of negative and traumatic experiences that occur during childhood, such as abuse, neglect, and household dysfunction. These experiences can significantly impact brain development, emotional regulation, and overall health throughout a person's life
Attachment
The deep emotional bond that forms between individuals, typically between a child and caregiver
Insecure Attachment
A type of emotional bond where children do not trust their caregivers consistently and may show various degrees of resistance or avoidance towards them. Includes anxious, avoidant, and disorganized attachment styles
Stranger Anxiety
The fear or distress that infants experience when interacting with unfamiliar people
Parallel Play
A type of play where children play alongside each other without actively engaging or interacting with one another (Common in the preoperational stage of development)
Psychosocial Conflicts
Synonymous with internal conflict. It describes the mental or emotional struggle that characters experience within themselves