Unit 2 Matter and Energy
1/211
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
212 Terms
All things around us (both visible and invisible) are classified as…
matter, energy, or both
matter
anything that takes up space and has form/shape
energy
ability to do work
there are many different forms of…
matter and energy
matter has
mass
mass
quantity of matter contained in an object
SI unit of mass is the…
kilogram (kg)
1 kilogram equals…
1000 grams
mass is a term associated with _____, but they are not strictly the same
weight
weight
force that an object exerts under gravity
gravity
force of attraction that exists between any two masses, bodies, or particles
weight is dependent on _____
gravity
as mass increases, so does the….
attraction (gravity)
acceleration of gravity (g)
objects that fall to earth do so at a constant rate
acceleration of gravity on Earth
9.8 m/s2 (approx. 32 feet per second)
acceleration of gravity on the moon
1.6 m/s²
acceleration of gravity on Jupiter
24.8 m/s²
the weight of an object changes due to its surroundings, which is…
influence of gravity
T/F: mass changes due to its surroundings
false, weight does
which four elements did the ancient greeks believe made up all matter?
fire, air, water, earth
who believed that regardless of the number of times you cut a form of matter in half, you would always have a smaller piece of that matter?
aristotle
who put forth the idea that all matter was formed from different types of tiny particles he called “atomos” (Greek for indivisible or unable to be cut)?
democritus
the atomic idea of matter espoused by democritus fell out of favor because…
aristotle did not agree with it
It was not until the early 1800s that scientists began to discover that ______ were the building blocks of all matter
atoms
matter is usually a mixture of ____ or _____ substances
two, more
substances
any material that has a definite and constant composition
simple substances are…
elements
simple substances cannot….
be broken down into simpler substances by ordinary means
atoms
smallest particle of an element that still possesses its chemical property (ex: silver AG is made up of only silver atoms)
complex substances are…
compounds
complex substances
2 or more different elements chemically united (H2O)
what are the basic states of matter?
solid, liquid, gas
solid
substances with a fixed volume and shape
in a solid, their particles are ____ _____ and ___ ____ compressed
tightly packed, not easily
solids are mostly made up of which type of energy?
vibrational
liquids
substances with a defined volume, but undefined shape
in liquids, particles are ____ ____, _____ ____ compressed, but can ___ ____ one another
slightly packed, not easily, move past
in a liquid, atoms and molecules are in
motion
liquids can take the shape of their
container
gasses
substances with indefinite volume and shape
in a gas, particles are ___ ___ apart, _____ compressible, and ___ ___ move past one another
very far, easily, can easily
in a gas, atoms and molecules move in ____ direction and _____ bump into one another
any, occasionally
gasses can be easily _____ and _____ ___ ____ of their container
compressed, take the shape
john dalton
elements differentiate from each other based on mass (different strokes for different folks)
atoms of a particular element react the same way chemically (if u get slapped in the face regardless of who its by, youre gonna get pissed either way)
dmitri mendeleev (developed periodic table of elements)
arranged the known elements in order of increasing atomic mass and on the basis of similar chemical properties
ernest rutherford
developed nuclear model of the atom
the atom has a _____ charged dense center called the _____, and is surrounded by a _____ charged cloud of electrons
positively, nucleus, negatively
niels bohr
proposed a model for the atom that is still widely used in explaining composition of atoms
atom is a mini “solar system” where electrons revolve around nucleus in fixed orbits
erwin scrodinger
abandoned the idea of precise electron orbits and replaced them with a description of the regions of space around the nucleus called “orbitals”
orbitals are _____ for location of where electrons were most likely to exist within an atom at any given moment in time
probabilities
the greatest probabilities are associated with ______ model
bohr’s
nucleus
small, dense center that contains nucleons (protons, neutrons)
orbitals (electron shells) contain…
electrons
different atoms vary in the number of ____ present
nucleons
atoms differ in the number of _____ present and the number of ____ available for the electrons
electrons, shells
protons
positively charged sub-atomic particles
the mass of protons
1.673 × 10-27 kg
what distinguishes one element from another?
number of protons in an atom’s nucleus
neutrons
sub-atomic particles that have no charge
what is a neutron’s mass?
1.675 × 10-27 kg (largest)
electrons
negatively charged sub-atomic particles
mass of an electron
9.109 × 10-31 kg (smallest)
electrons are in _____ motion found in space around the nucleus
continuous
the energy level of an electron determines…
the orbital it occupies and the relative distance from the nucleus
each orbital and the electrons therein have a certain…
electron binding energy
Eb
what is the SI unit for binding energy?
electron volt (eV)
eV
energy of one electron when accelerated by one volt
1 keV amounts to how many electron volts?
1000
atoms vary in total number of electrons and orbitals present, but individual electrons in every atom have the same….
mass
quarks
sub-nuclear structures that exist in groups of 3 inside a proton/neutron
(quarks do NOT exist in an electron)
string theory
physicists believe that quarks/electrons are not particles but small loops of rapidly vibrating string-like matter
M theory
attempts to link quantum physics and relativity
nucleons (protons, neutrons) make up most of the mass of an atom since they are larger than…
electrons
neutrons are how many times larger than electrons?
1838
protons are how many times larger than electrons?
1836
the mass of the orbital electrons is disregarded when determining…
overall mass of an atom
atoms vary in mass (size) based on…
the number of nucleons present
when precision is not needed, how may sub-atomic particles be expressed rather than the kilogram?
carbon 12 atoms by using the atomic mass number (A)
since protons and neutrons are almost the same mass, what do they have a mass of? (its a number)
1
electrons are so small in relation to nucleons and contribute little to the mass of an atom. what is their atomic mass number?
0
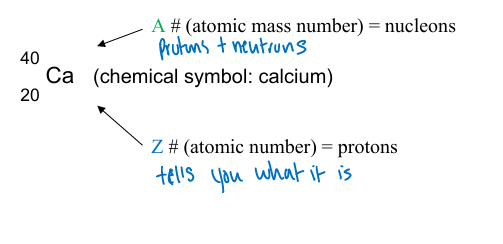
atomic mass number (A)
mass of an atom can be expressed using this
what is the A number for an atom?
the total number of nucleons present
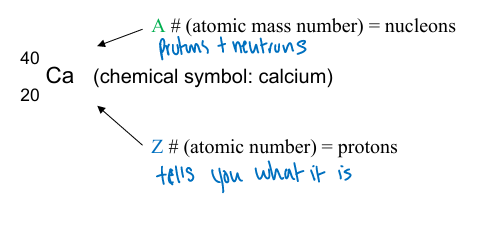
atomic number
number of protons in an atom that determines what element it belongs to
isotope
an atom of a particular element that differs in the number of neutrons present
isotopes would have the same ____ _____, but a different _____ _____
atomic number, atomic mass
isotopes can be man-made by ____ or _____ _____ (neutrons) to an atom’s nucleus
removing, adding particles
what is needed when removing/adding atoms to an atom’s nucleus?
particle accelerator/nuclear reactor
radioisotopes
isotopes that have unstable nuclei (either natural or man-made) and emit radiation (gamma rays/particles) from the nucleus
what is the most abundant element in the universe?
hydrogen
hydrogen has how many naturally occurring isotopes?
3
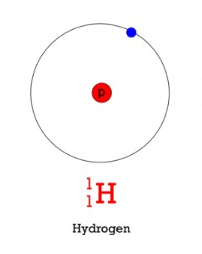
protrium (hydrogen 1)
stable isotope that is the most common form of hydrogen on earth
it makes up 99.985% of all hydrogen
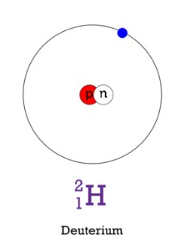
deuterium (hydrogen 2)
stable isotope that is much less abundant
makes up .015% of all hydrogen
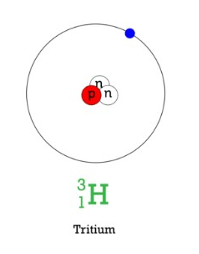
tritium (hydrogen 3)
unstable isotope that is radioactive
extremely small amounts of it exists as a result of the interaction of cosmic rays with atmospheric gasses & from being released during nuclear weapons testing
atoms must contain at least 1 energy shell (orbital) to…
exist
maximum number of shells any atom can possess is…
7
principal quantum numbers
letters or numbers to label shells
which forces maintain electrons positions and motion in orbit?
centrifugal force and electrostatic force
centrifugal force
electron tends to fly out into space
electrostatic force
positively charged nucleus and negatively charged electrons
the number of electrons present in each energy shell varies according to what?
the atoms of a particular chemical element