1. transporting O2
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
HAEMOGLOBIN
made of 4 globular polypeptide chains (globin)
each w/ an iron ion (haem prosthetic group)
the molecule that allows erythrocytes to carry respiratory gases (esp O2)
has an affinity for O2 (can carry up to 4 O2 molecules)
Hb + 4O2 —> Hb(O2)4
when haemoglobin becomes oxygenated, known as oxyhaemoglobin
OXYGEN TRANSPORT- LUNGS
in lungs, O2 diffuses into blood plasma
then passes down conc gradient and into erythrocytes
O2 binds to haemoglobin to maintain this conc gradient
O2 binds to haem Fe²+ group of haemoglobin
OXYGEN TRANSPORT- RESPIRING TISSUE
in respiring tissues, O2 disassociates (releases) from oxyhaemoglobin
O2 can then diffuse out of erythrocytes and to respiring cells
OXYGEN TRANSPORT- LUNGS (pO2)
amount of O2 in tissue is referred to as its partial pressure for O2 (pO2) or O2 tension
measured in kPa
ventilation allows lung tissue to have high pO2
where pO2 is high, more O2 can associate w/ haemoglobin molecules to be transported
% of haemoglobin saturation highest here
OXYGEN TRANSPORT- RESPIRING TISSUES (pO2)
in respiring tissue, pO2 is low
at low pO2, O2 dissociates from oxyhaemoglobin and can diffuse to respiring cells
OXYGEN ASSOCIATION
after first O2 molecule associates, the conformation of haemoglobin changes
conformational change makes it easier for 2nd and 3rd O2 molecules to associate
difficult to associate a 4th O2 molecule
bc haemoglobin molecule becomes full
why curve plateaus below 100%
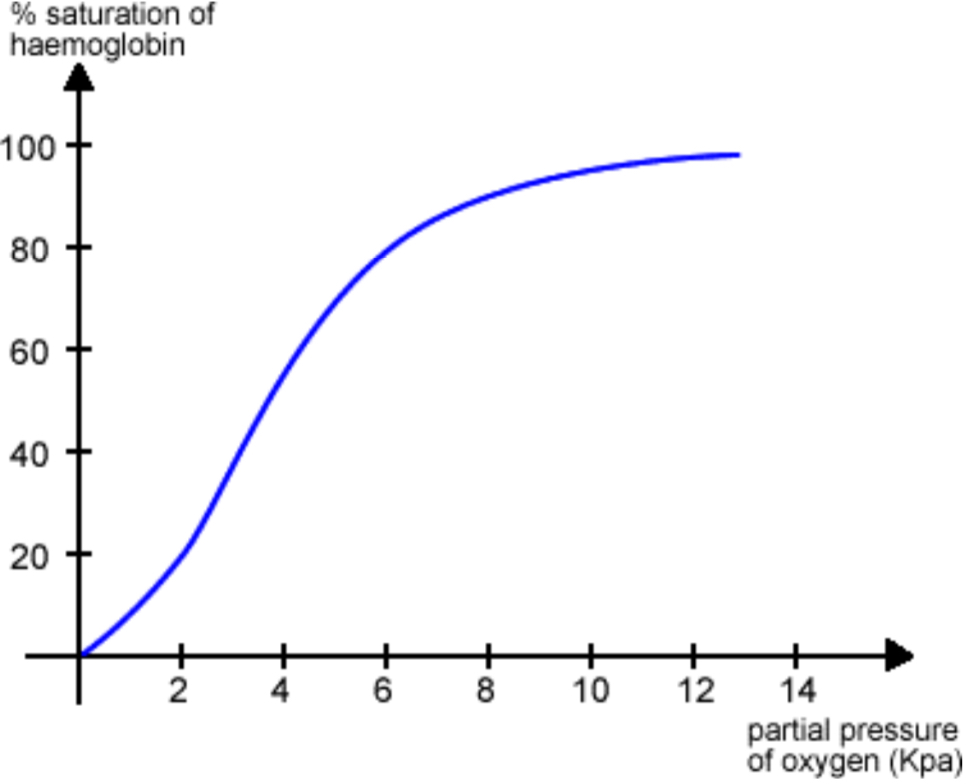
OXYGEN DISSOCIATION CURVE
s-shape
% Hb saturation w/ oxygen not directly proportional to pO2
difficult to achieve 100% saturation
conformation of haemoglobin molecule changes as O2 molecules become associated with/ it
changes haemoglobin ability to associate w/ further O2 molecules
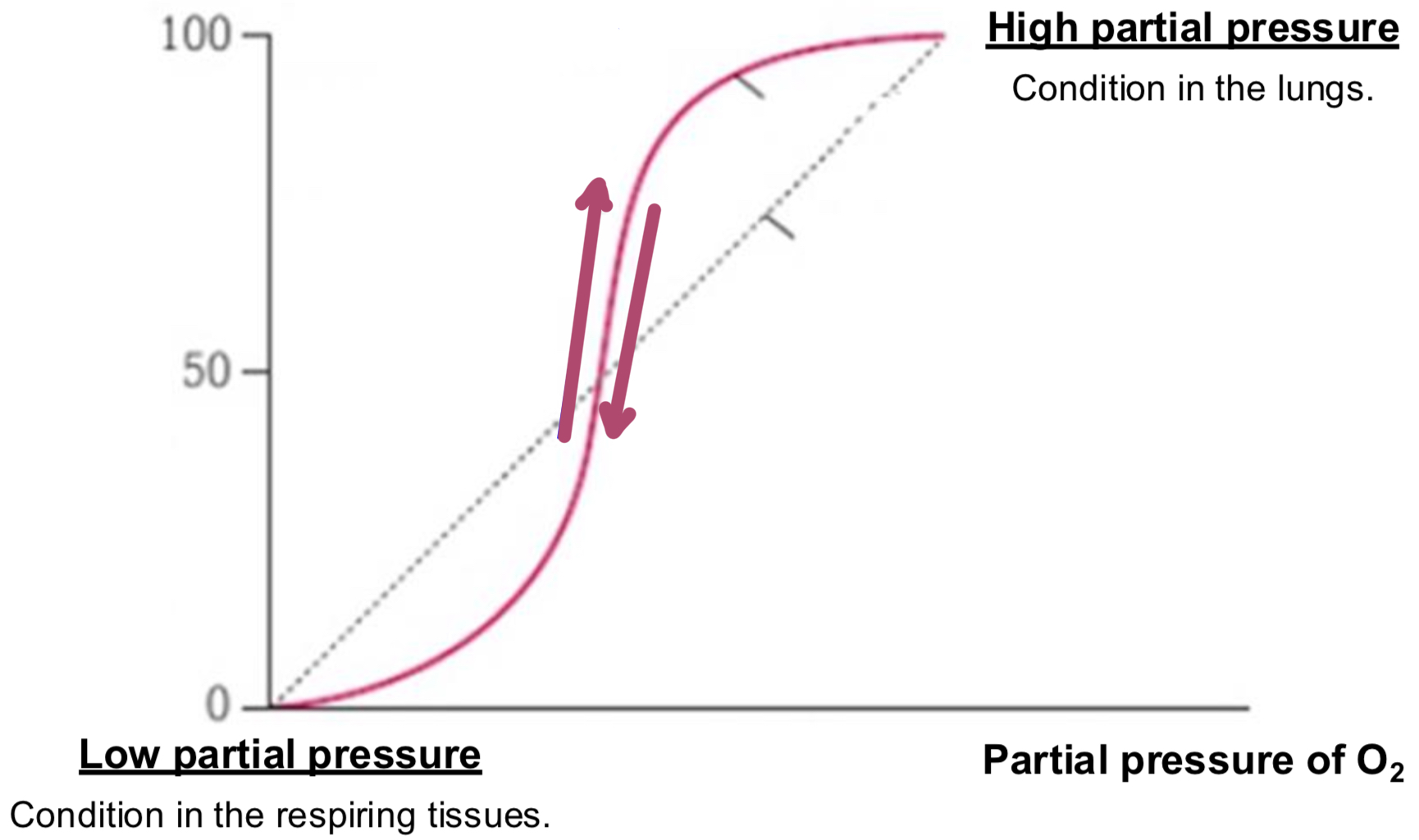
OXYGEN DISSOCIATION CURVE- SECTIONS
curve going up
as deoxygenated blood approaches lungs, the steep part of curve means that small increase in partial pressure cause large increase in % saturation
curve going down
as oxygenated blood approaches tissues, steel part of curve means small decrease in partial pressure causes large decrease in % saturation
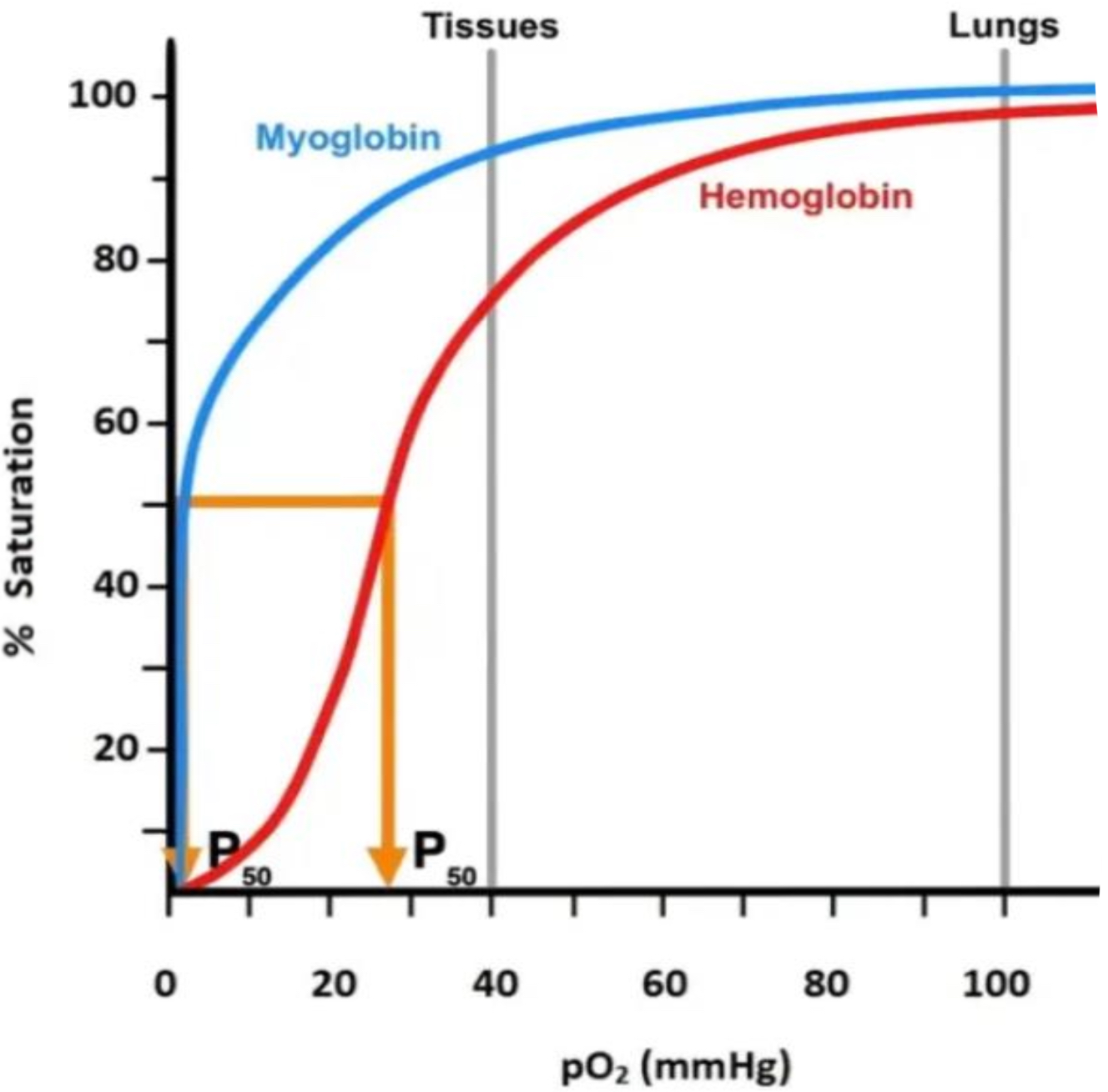
MYOGLOBIN
made of single globular polypeptide chain w/ 1 iron ion (haem prosthetic group)
stores O2 in muscle cells and has higher affinity for O2 than haemoglobin in same partial pressure
means that as blood passes through muscles, O2 more readily binds to myoglobin so is transferred to muscle cells
supplies the O2 working muscles need for aerobic respiration, providing energy required for them to contract
OXYGEN DISSOCIATION CURVE 2
O2 dissociation curve compares % saturation of haemoglobin and myoglobin at diff partial pressures
at partial pressure similar to that at the tissues (muscles) myoglobin is significantly more saturated than haemoglobin
must have a higher affinity for O2 for this to be true
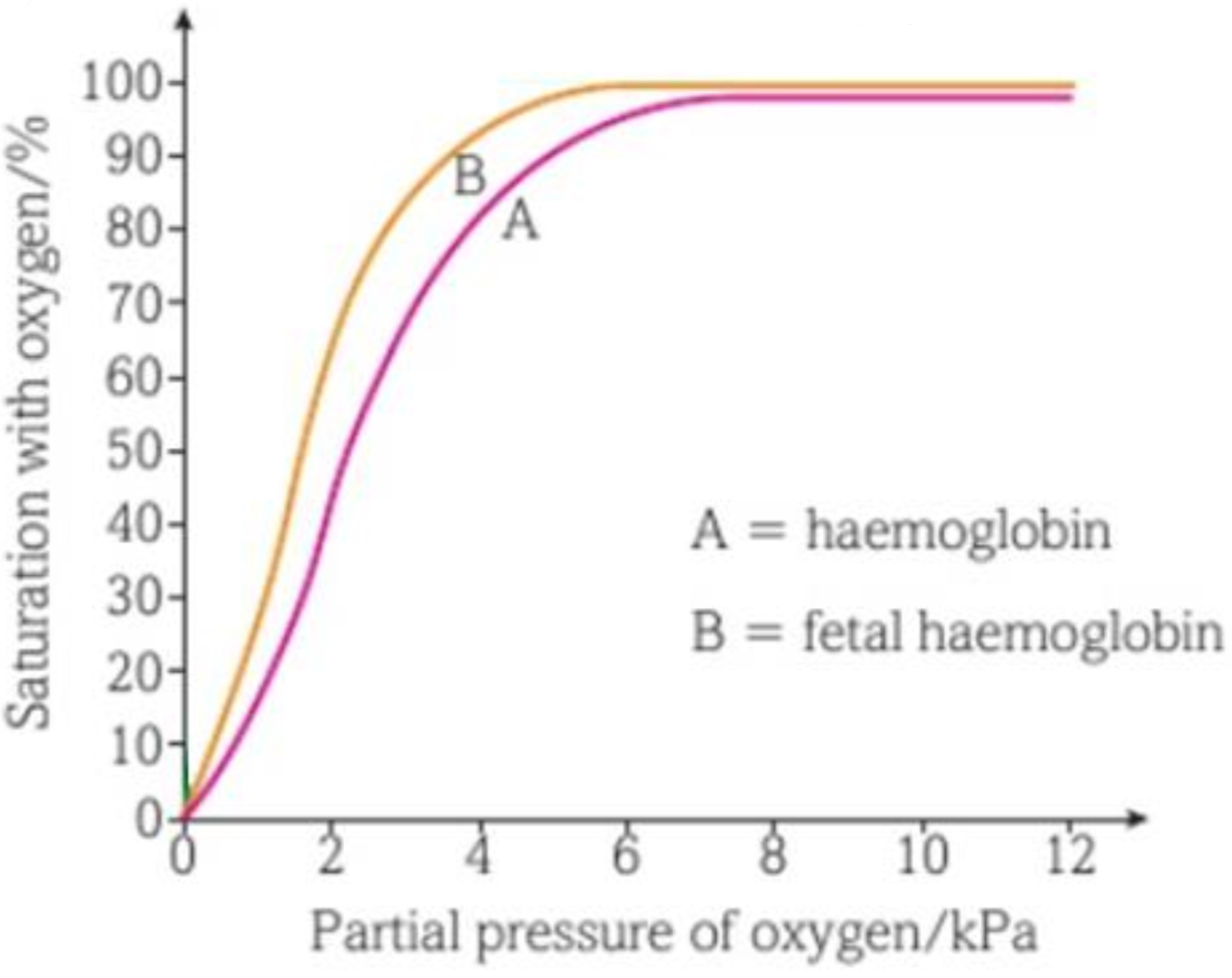
FOETAL HAEMOGLOBIN
foetal and maternal blood is kept separate in placenta
to get O2 from maternal to foetal blood, foetal haemoglobin needs a higher affinity for O2 than maternal haemoglobin
foetal haemoglobin O2 dissociation curve are left of adult curves- their stronger affinity means they can become saturated at lower pO2