moles and molar calculations
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
what is Avogadro’s constant ?
1 mole = 6.022 × 10(23) atoms
molar mass =
atomic masses x subscript no.
what is the molar mass of 1mol of glucose ?
180g
moles =
mass/molar mass
the molarity of a substance refers to…
the no. of moles of a compound dissolved in 1L of liquid
molarity is measured in
Molar (M)
a 1M solution has
1mol of compound dissolved in 1L of solvent
what does Beer’s Law state ?
higher the conc. higher the absorbance (AU)
absorbance
quantity of light absorbed by solution
transmittance
quantity of light that passes through a solution
our eyes see light
that is NOT absorbed
Lamberts Law
greater the thickness greater the absorption
in a cuvette the path of light is standardised
to 1cm
what equation represents the Beer-Lambert law
A = Ecl
the pH scale measures
the acidity of a substance
acid
any sub that releases protons - donor
base
proton acceptor
strong acids
completely dissociate
weak acids
incompletely dissociate
equation for pH
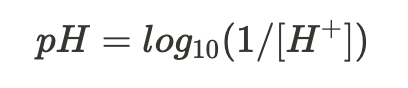
equation for pKa
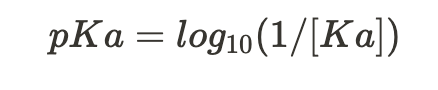
Ka
acid dissociation constant
pKa
pH at which half of acid is dissociated
Henderson-Hasselbalch equation
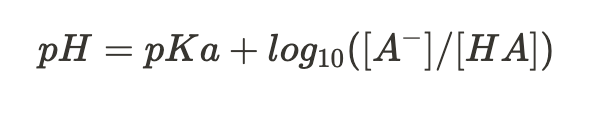
in water sodium hydroxide…
completely dissociates
pOH =
-log (OH-)
pH + pOH =
14
what is a lower pKa indicative of ?
stronger acid