Immunology Chapter 4
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/104
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 6:25 PM on 10/4/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
105 Terms
1
New cards
An antibody is a _____ BCR
Secreted
2
New cards
Name the 3 components of an amino acid
N group, central Carbon, Carboxy
3
New cards
What are the 5 classes of antibodies
IgG, IgA, IgM, IgD, IgE
4
New cards
What is the antibody repertoire?
Total number of antigen specificities
5
New cards
What can an antigen be?
Anything a BCR or TCR can bind to
6
New cards
Immature B cells have _____ on their surface
IgM
7
New cards
What do mature B cells have on their surface?
IgM and IgD
8
New cards
What protease cleaves the antibody into Fab and Fc fragments?
Papain
9
New cards
What does Fab stand for?
Fragment Antigen Binding
10
New cards
What does an Fc fragment do?
Binds to Fc receptors
11
New cards
What is Agammaglobulinema?
An inability to make an Ab response
12
New cards
What is the yellow component? What is the green?
Yellow: Light chain; Green: Heavy chain
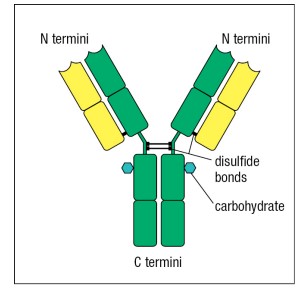
13
New cards
What kind of bonds do peritopes make with epitopes?
Noncovalent
14
New cards
What kind of bond links the light chain with the heavy chain?
Covalent disulfide
15
New cards
The stem of an antibody is referred to as the ______ domain
Constant
16
New cards
What color is the variable region? The constant region?
Red; Blue
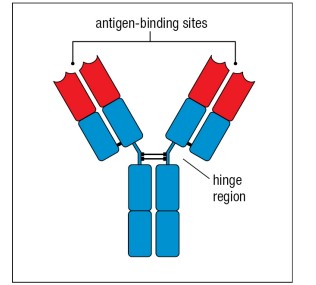
17
New cards
What is affinity?
The tightness of binding of an antibody site to an antigen
18
New cards
What is avidity?
The firmness of associated between a multideterminant antigen and the antibodies produced against it
19
New cards
How many isotypes are there of the light chain? What are they called?
2; κ & λ
20
New cards
What defines the immunoglobulin isotypes? (i.e., IgE, IgD, etc.)
Heavy chain constant region
21
New cards
What is the V region at the N terminal of the H or L chains composed of?
V domain, VH or VL
22
New cards
___ and ___ form the antigen binding site
VH and VL
23
New cards
What is the constant region of the light chain composed of?
CL domain
24
New cards
What is the constant region of the heavy chain composed of?
3-4 C domains (CH1-4)
25
New cards
___ and ___ have 4 domains with no hinge regions
IgM and IgE
26
New cards
How many CDR or HV regions in one binding site of an Ig?
6
27
New cards
What is another name for epitope?
Antigenic determinant
28
New cards
What is a multivalent antigen?
An antigen with two or more different epitopes
29
New cards
What is the difference between a discontinuous and linear epitope?
Linear is formed with contiguous amino acids; discontinuous uses different parts of the polypeptide
30
New cards
What is somatic recombination?
Bringing together V, D, and J segments to make a functional gene
31
New cards
What kind of cells can go through somatic recombination?
B cells
32
New cards
What is a monoclonal antibody?
Antibodies with identical antigen binding sites made from a single clone of a B cell
33
New cards
What does a flow cytometer do?
Allows individual cells to be identified by monoclonal Abs (CD markers)
34
New cards
____ codes for light chain CDR1&2
V segment
35
New cards
____ codes for light chain CDR3
V/J junction
36
New cards
____ codes for heavy chain CDR3
D segments; V/D & D/J segments
37
New cards
Can T cells use RAG1&2 to rearrange genes in the bone marrow? (T/F)
False; only B cells
38
New cards
Where does BCR somatic recombination occur?
Bone marrow
39
New cards
What does RSS stand for?
Recombination Signal Sequences
40
New cards
Can a B cell express RAG-1&2 in a secondary lymphoid tissue after activation?
No
41
New cards
What is VDJ recombinase?
Set of enzymes needed to recombine V, D, and J gene segments
42
New cards
What is the function of enzyme TdT?
Adds nucleotides randomly
43
New cards
What is the germline configuration?
DNA that has not been recombined/changed by somatic recombination (original DNA)
44
New cards
Define junctional diversity
Variation present in immunoglobulin and T-cell receptor
polypeptides that is created during the process of gene
rearrangement
polypeptides that is created during the process of gene
rearrangement
45
New cards
What are P nucleotides?
Palindromic nucleotides; Additional nucleotides created after RAG opens hairpin in DNA
46
New cards
What are N nucleotides?
Non-templated nucleotides; Random nucleotides added by TdT
47
New cards
Recombination does not occur at every junction (T/F)
False
48
New cards
What is allelic exclusion?
Ensures only one heavy chain and one light chain is created
49
New cards
Are B cells diploid or haploid?
Diploid
50
New cards
When does somatic hypermutation take place?
After activation
51
New cards
Is μ always expressed on a immature B cell? (T/F)
True
52
New cards
When IgM and IgD are on a mature B cell, do they have the exact same binding site?
Yes
53
New cards
Are Igα and Igβ found on every Ig isotype?
Yes
54
New cards
Igβ is a BCR isotype (T/F)
False
55
New cards
IgG, IgD, and IgE change their isotype in the ___, IgM and IgD change their isotype in the ___
DNA; RNA
56
New cards
Immature B cells express both IgM and IgD on their surface (T/F)
False
57
New cards
What allows for the antibody to be soluble/secreted?
Hydrophilic sequence
58
New cards
What does somatic hypermutation do?
Introduces point mutations (single nucleotide substitutions) throughout V regions at a very high rate
59
New cards
What is activation-induced cytidine deaminase (AID)?
Enzyme that converts cytosine to uracil, which is then excised and replaced with normal DNA bases
60
New cards
What enzyme is somatic hypermutation dependent on?
Activation-induced cytidine deaminase (AID)
61
New cards
What is the benefit of somatic hypermutation?
Enables selection of B cells
making higher-affinity antibodies
making higher-affinity antibodies
62
New cards
____ has the highest avidity out of all of antibody isotypes
IgM
63
New cards
Define affinity maturation
The increase in affinity of the binding sites of antibodies
64
New cards
What is the first antibody produced during an immune response?
IgM
65
New cards
IgM has a (low/high) affinity but a (low/high) avidity
Low affinity; high avidity
66
New cards
IgM is secreted as a _____ with ___ binding sites
Circular pentamer; 10
67
New cards
Define isotype/class switching
The process by which a B cell changes the class of immunoglobulin
it makes
it makes
68
New cards
What enzyme is used during isotype/class switching?
AID
69
New cards
What occurs during isotype switching?
A somatic recombination process that attaches a different heavy-chain C-region gene to the existing V-region exon
70
New cards
What is the result of isotype switching?
Production of Igs with different C regions but identical antigen specificities
71
New cards
Switch regions are in front of every C gene except for ___ gene
δ
72
New cards
Why is there no switch region in front of the δ gene?
It is already being made in the RNA
73
New cards
Transcription begins at the ___ switch region
μ
74
New cards
What does AID do in isotype switching?
Changes cytosine to uracil in the Sμ and Sγ regions
75
New cards
What happens after the Sμ and Sγ regions are targeted by AID?
DNA in both regions is nicked on both strands and are looped/cut out
76
New cards
When does isotype switching occur?
After activation
77
New cards
Where does isotype switching occur?
Secondary lymphoid tissue; in germinal center of follicle
78
New cards
Isotype switching is a recombination event (T/F)
True
79
New cards
Does isotype switching take place in the DNA or the RNA?
DNA
80
New cards
Antibodies with different constant regions do not have different effector functions (T/F)
False
81
New cards
How many subclasses of IgG are there?
4
82
New cards
There are ___ subclasses of IgA
2
83
New cards
Do antibodies kill anything directly?
No
84
New cards
What is the main function of IgM?
Activates classical complement pathway
85
New cards
IgM is principally made by ____ cells in ____ organs
Plasma; lymphoid
86
New cards
IgM is composed of __ four-chain units with ___ combining sites
5; 10
87
New cards
What is the most abundant antibody in the internal fluids?
IgG
88
New cards
What can IgG do?
Can be bound to by Fc receptors, activate complement, cross the placenta
89
New cards
What differentiates the 4 IgG subclasses?
Slightly different H chains
90
New cards
How do we gain effector function?
Isotype switching
91
New cards
Monomeric IgA is found in the ____, while dimeric IgA is found in the ____
Circulation; lymphoid tissue
92
New cards
What is the principle antibody in bodily secretions?
IgA
93
New cards
______ is made the most out of any Ig isotype
Dimeric IgA
94
New cards
What Ig isotype is most abundant in the blood?
IgG
95
New cards
Dimeric IgA is synthesized locally by _____ cells in ____ and ____ glands
Plasma; Mammary and salivary
96
New cards
How does dimeric IgA get out into the lumen of the gut?
Poly-Ig receptor binds to the J chain which leads it into an endocytic vesicle, and then releases dimeric IgA into the lumen of the gut
97
New cards
What is the secretory component (SC)?
A portion of the Poly-Ig receptor that stays on the dimeric IgA
98
New cards
What kind of infections is IgE involved in?
Allergies, parasitic worm infections
99
New cards
IgE has a high affinity receptor on what kind of cells?
Mast cells
100
New cards
What does IgD do?
Aids IgM in recognition of pathogens and activation of B cells