AP Macro Econ Study Guide
1/108
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
109 Terms
Economics is…
the study of scarcity
Economizing
The act of making decisions to fulfill needs first and wants second
Opportunity Cost
What one gives in order to gain.
ex. To gain extra sleep, one must give up scrolling on social media in the mornings
What are the 5 powers of economic thinking?
Resources
Rational Decisions
Decisions are make at the margin
Answers change depending on other factors
People are maximizers
Scarcity
Limited resources and unlimited wants
Resources
Land
Labor
Capital
Entrepreneurial Ability
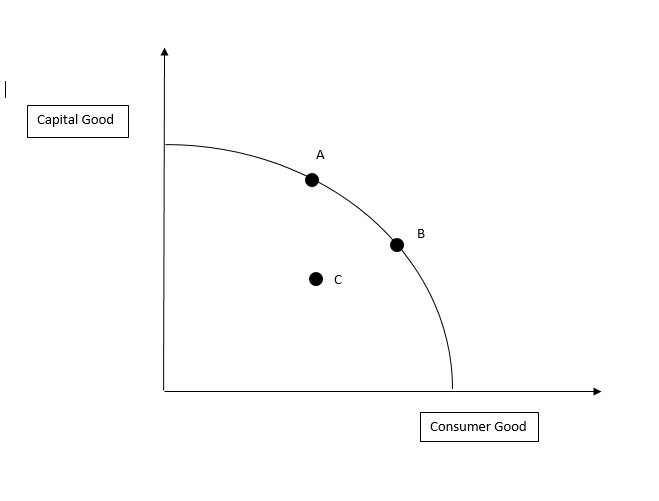
Productions Possibility Curve
A graph that shows the maximum feasible amount of two goods that can be produced with available resources and technology.
The Command System
Socialism / Communism
An economic system where the government makes all decisions regarding production and distribution.
2 major problems: coordination and lack of incentive
The Market System
Capitalism
An economic system where there is a private ownership of resources and the system uses the market to drive prices and direct the economy
9 characteristics: private property rights, freedom of enterprise and choice, self-interest, competition, markets driving prices, encouragement of capital goods and technology, specialization, use of money, and an active but limited government
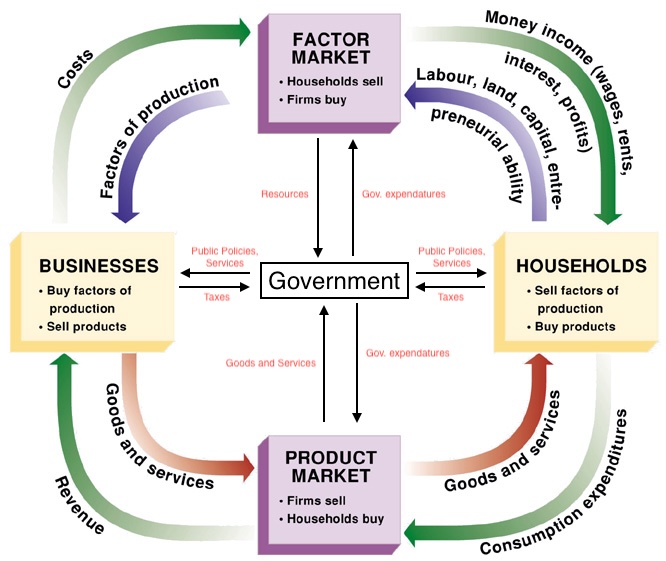
Circular Flow Model
Demand
Quantity of a product that will be purchased at a variety of possible prices
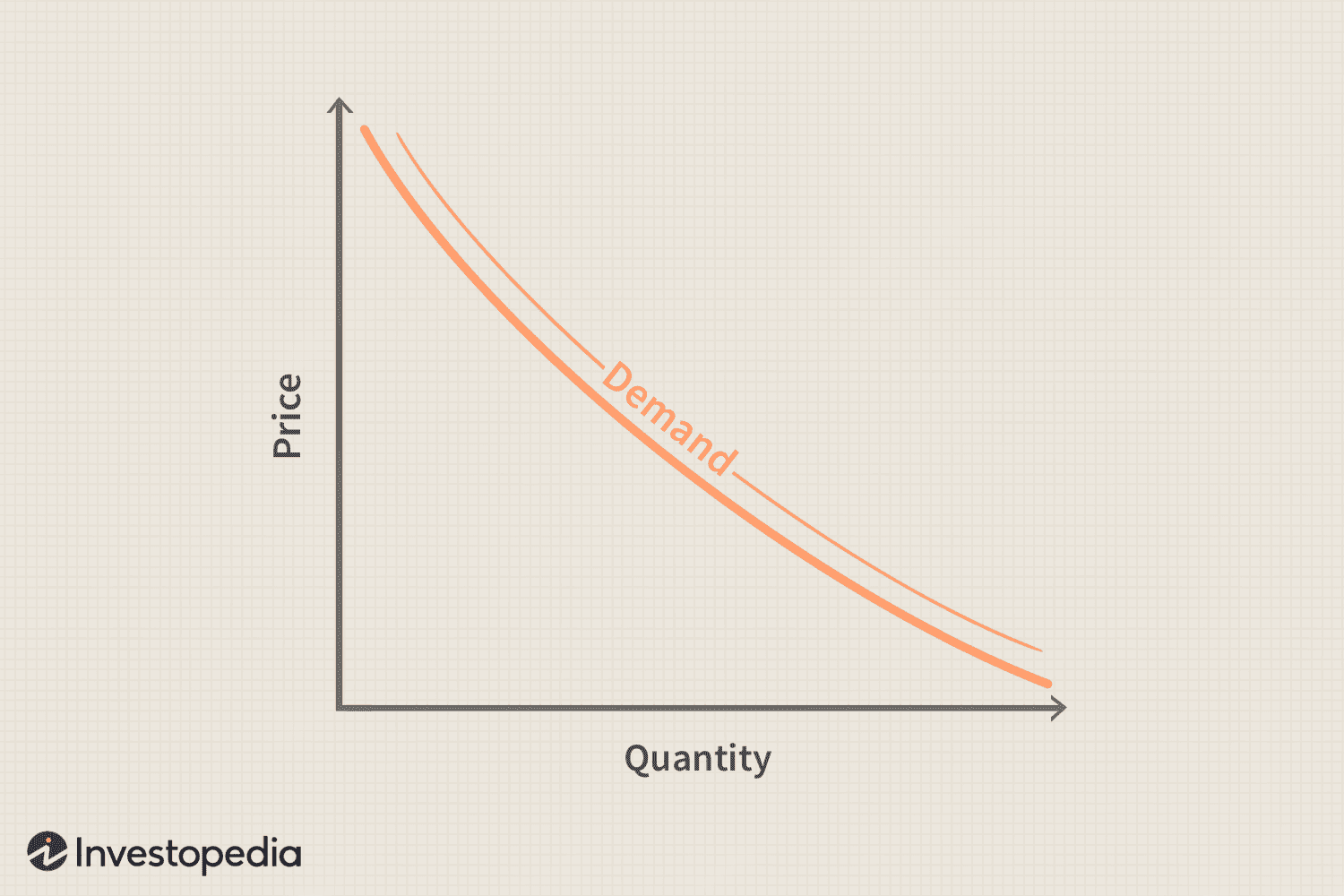
Law of Demand
As the price of a product increases the quantity of demand decreases, and as the price decreases, the quantity increases.
Determinants of Demand
Change in taste or preference
Change in number of customers
Change in consumer income
Change in the price of related goods
Change in consumer expectations
Supply
Various quantities of a product that producers are willing and able to make available at a series of possible prices
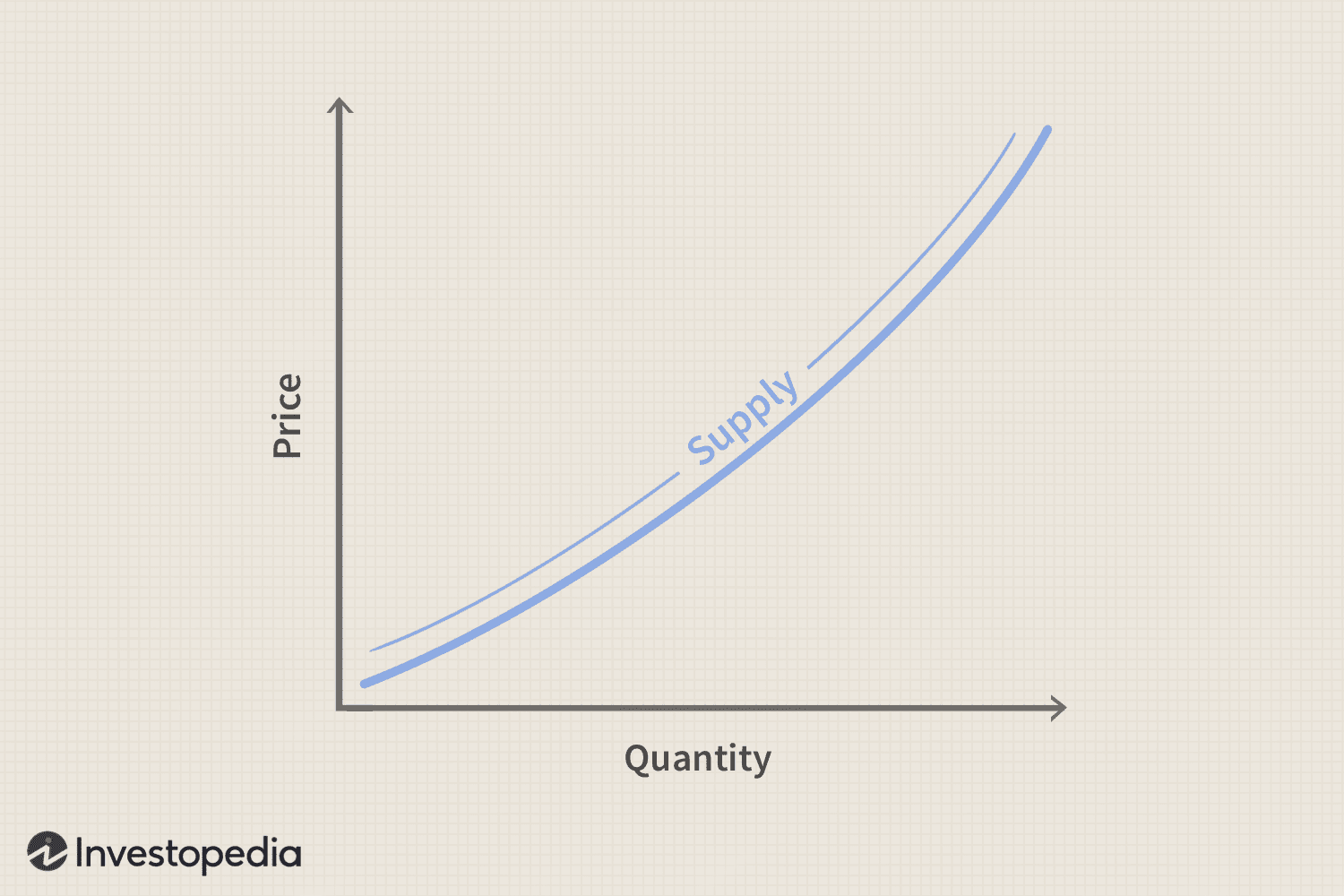
Law of Supply
As the price of a product increases the quantity of supply increases, and as the price decreases, the quantity decreases.
Determinants of Supply
Change in resource prices
Change in technology
Change in taxes and subsidies
Changes in prices and other goods produced
Change in the number of producers
Change in producer expectations
Equilibrium
What determines price and quantity a market where supply and demand meet. There is no shortage or surplus.
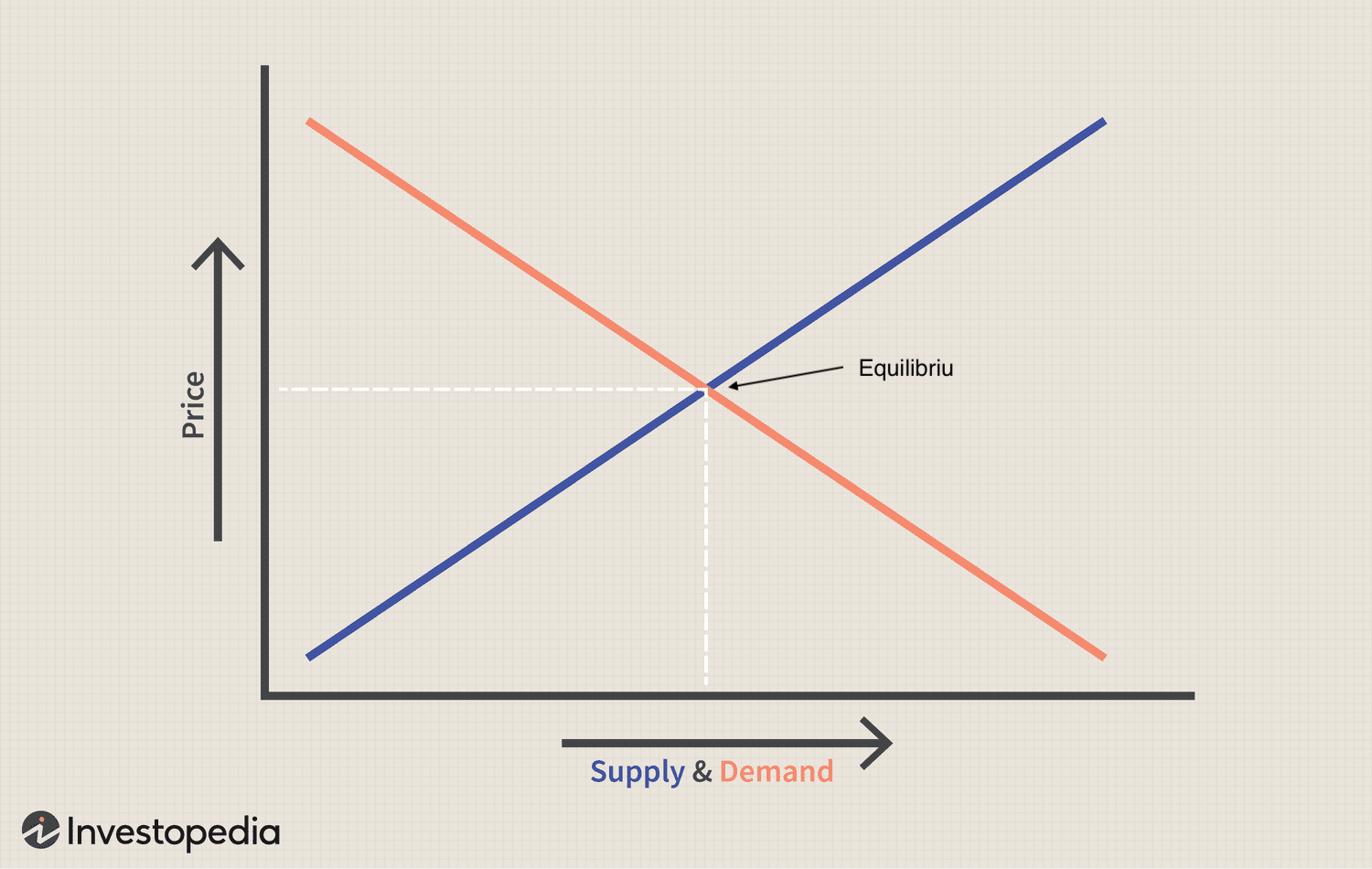
Shortage
When demand exceeds supply
Surplus
When supply exceeds demand
Price Ceiling
The maximum legal price a seller may charge for a good or service. It protects consumers but also causes shortages.
Price Floor
The minimum legal price set for a seller to charge for a food or service. It protects producers but causes surpluses.
GDP
Gross Domestic Product - The value of all goods and services produced INSIDE a country in a given year
Nominal GDP
GDP measured in current prices, without adjusting for inflation.
Real GDP
GDP that has been adjusted for inflation at a base years price.
Unemployment rate
The state someone is in if they don’t have a job but they are willing and able to and are actively seeking work.
Inflation
The increase in the general price level of goods and services in an economy over a period of time, affecting purchasing power.
Savings
When current consumption is less that current income
Economic Investing
The act of purchasing capital goods to produce more in the future
Shocks
Unexpected changes
What is counted in GDP?
final goods and services
items produced in the country
What is not counted in GDP?
used items (all ready counted)
stocks and bonds
transferred payments
underground economic activities
C
Personal consumption - what households spend on durable goods, non-durable goods, and services
I
Investment - what businesses spend on capital and other things
G
Government Purchases - what the government spends for the direct purchases of resources and goods and services
X-M
Net Exports - what foreign buyers spent on American goods/services (exports) MINUS what Americans spent on foreign goods and services (imports)
C + I + G + (X-M) = ?
GDP
The Income Approach
A method for calculating GDP that sums all incomes earned by factors of production, including wages, profits, rents, and taxes, minus subsidies.
GDP Per Capita
GDP divided by the population
Price Index
(Market Basket of year X / Market Basket of Base Year) x 100
Real GDP Calculation
Nominal GDP / Price Index in hundredths
Hours total of work x labor productivity
Growth Rate
(Change / Original) x 100
Rule of 70
To calculate doubling time, divide 70 by the annual growth rate percentage.
Institutional Structures the Promote Growth
Strong property rights
Patents and copy rights
Efficient financial institutions and systems
Education
Market System
Determinants of Growth
Supply factors
Increase in quality and quantity of natural resources, Human Resources, capital goods, and technology
Demand and efficiency factors
Increases in demand for goods and services, and full employment of resources
Factors Responsible for Productivity Growth
Technology advances (40%)
Quantity of capital (30%)
Education and training (15%)
Economies of scale and improved resource allocation (15%)
Antigrowth View
Growth causes environmental problems
Doesn’t solve sociological problems
Frantic job place
Unsustainable
Growth Positive View
Improved living standards
Reduces poverty
Improved working conditions
Allows more leisure time
Can deal with environmental concerns
Business Cycle
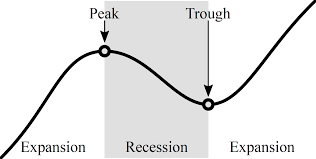
Business Cycle Phases
Peak - business activity is at a temporary maximum
Recession - a decline in output, income, and employment (lasting 6 months or longer)
Trough - temporary bottom or low for GDP, income, and employment
Recovery - expansion in GDP and employment
Labor Force Participation Rate
Labor force / Age Eligible to Work
Frictional Unemployment
Everyday unemployment - quitting, being fired, out of college and looking for a job
Structural Unemployment
Job skill is no longer needed - ex. machines taking over for humans or run out of iron, you don’t need steel workers
Cyclical Unemployment
Increases and the cycle goes down - due to changes in the business cycle and demand
Full Employment
When there is no cyclical unemployment and all available resources are being used efficiently.
Okun’s Law
For every 1% unemployment beyond the national rate a negative GDP gap of 2% occurs
Demand Pull Inflation
A rise in prices caused by increased consumer demand, often outpacing supply in the economy.
Cost Push Inflation
A rise in prices caused by increased production costs, such as wages and raw materials, leading to a decrease in the supply of goods.
Philips Curve
As unemployment decreases, inflation increases and vise versa
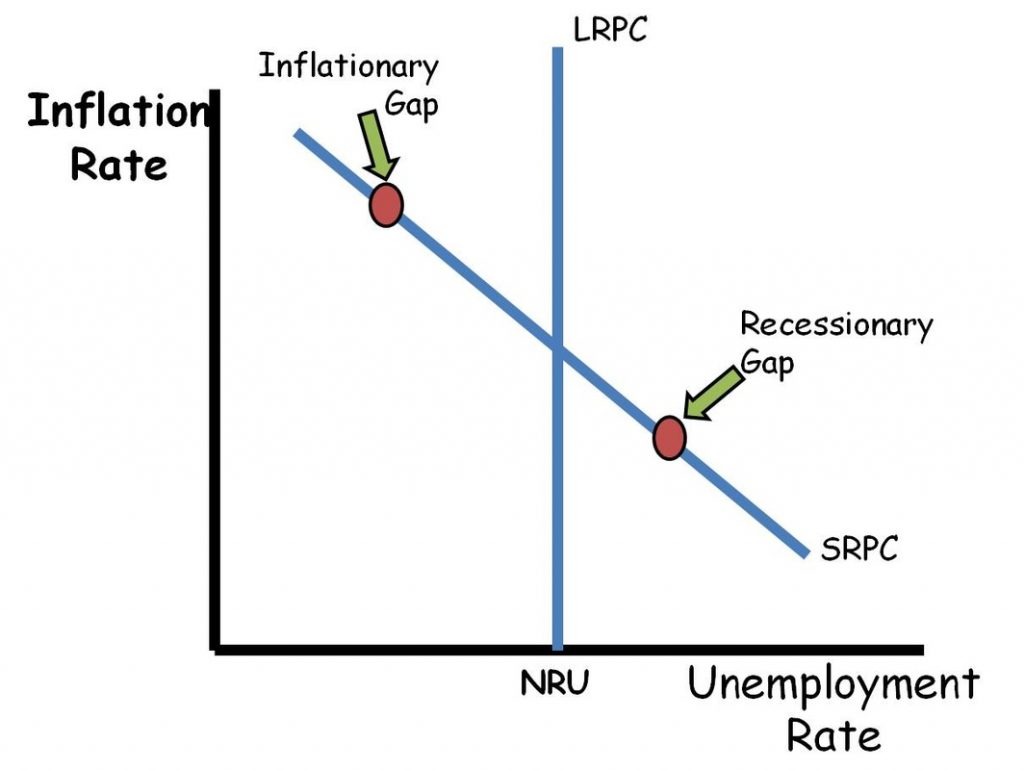
LRPC
Long Run Philips Curve - the natural rate of unemployment
Shifting the Philips Curve
Changes in…
labor market instructions
technological advancements
education and training
immigration policies
government regulations on employment
Disposable Income
Consumption (C) + Savings (S)
Average Propensity to Consume
1 - APS
Average Propensity to Save
1 - APS
Marginal Propensity to Consume
MPC = Change in C / Change in DI
Marginal Propensity to Save
MPS = Change in S / Change in DI
Investment
The purchase of capital goods or new construction. Decision based on marginal cost (i) and marginal benefits
Expected Rate of Return
(Profit / Cost) x 100
Real Interest Rate (i)
The interest rate that has been adjusted for inflation, reflecting the true cost of borrowing.
Determents of Investment
Change in..
Acquisition, maintenance, operating cost
Business taxes
Technology
Stock of capital and land
Planned inventory changes
Expectations
The Multiplier Effect
A change in a component of total spending leads to a larger change in GDP
Calculated by (1/MPS) or (1/1-MPC)
Multiplier x initial change in spending = change in GDP
Aggregate Demand
The total demand for all goods and services in an economy at a given overall price level and during a specified time period.
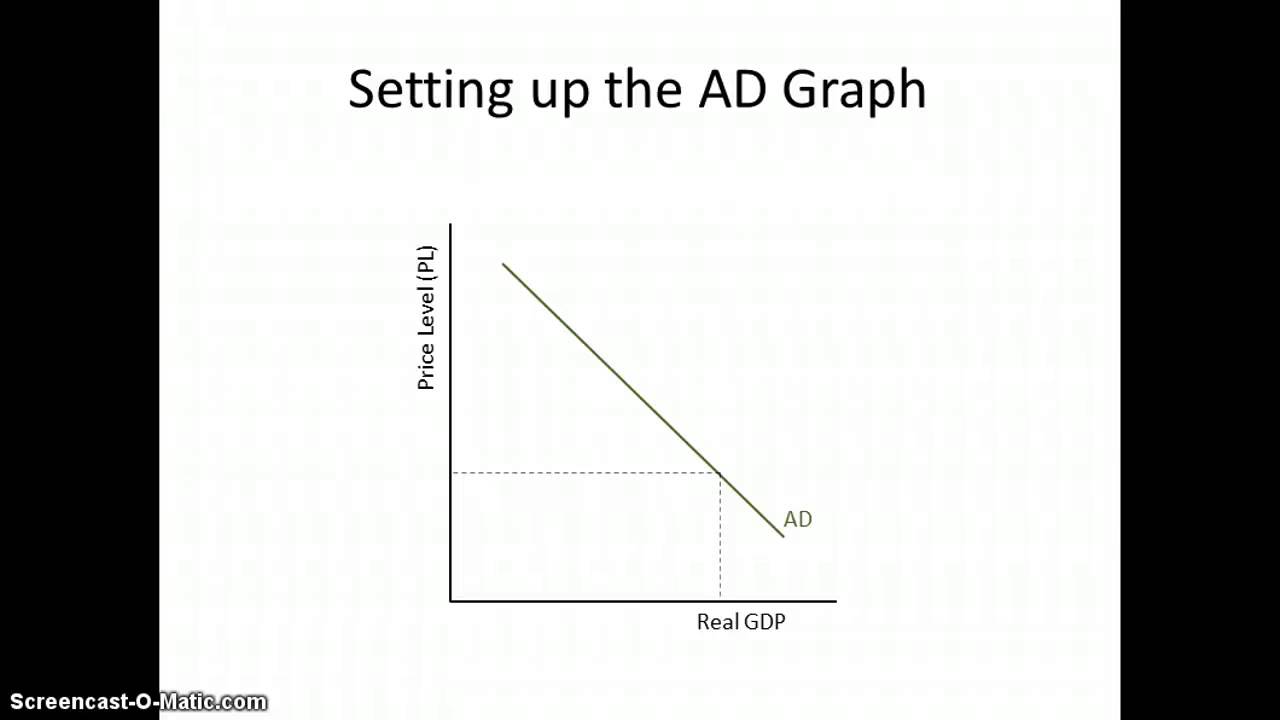
Determinate of AD
Changes in…
C - wealth, expectations, debt, taxes
I - interest rates and expected returns
G - government spendings
(X-M) - national income, exchange rates
Aggregate Supply
The total supply of goods and services that firms in an economy plan to sell during a specific time period at a given price level.
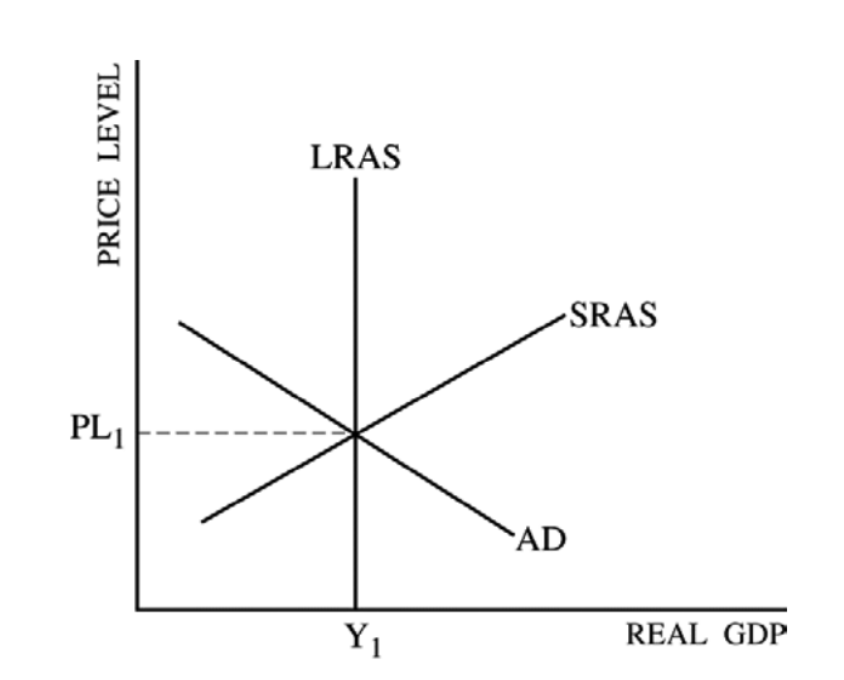
Determents of Aggregate Supply
Changes in…
input prices
productivity
legal/institutionalized environment
Fiscal Policy
A choice made by the government referring to the deliberate manipulation of taxes and government spending by Congress to alter RGDP and employment. control inflation and stimulate economic growth.
Expansionary Fiscal Policy
Used during a recession to increase G, decrease T, increase C, and boost overall demand in the economy. Shifts AD curve to the right.
Contractionary Fiscal Polity
Used when demand pull inflation is too high and to decrease G, increase T, and decrease C. Shifts AD curve to the left.
Tax Multiplier
T Multiplier = 1 / (1 - MPC) or 1 less than the multiplier
Change in GDP Calculation
Tax Multiplier x Change in T Multiplier
The Crowding Out Effect
Occurs when Government spending increases interest rates and reduces investment spending. Can be corrected with Monetary Policy and by manipulating the money supply.
Money is…
a medium of exchnage
M1 (Money Supply)
Currency: dollars/cents (physical money)
Checkable Deposits: amount of money in checking accounts easily spent
Savings Account Deposits: easily transferred to checking and spent
M2
Money market accounts
CDs
Mutual fund balances
The Federal Reserve
The central banking system of the United States responsible for regulating monetary policy and supervising financial institutions.
Assets
The things/money in a bank that the bank owns. Ex. cash, property, reserves, loan money, etc.
Liabilities and Net Worth
The things/money in a bank that the bank owes. Ex. shares, checkable deposits, etc.
Actual Resevrves
The total amount of cash that a bank has on hand, including the physical currency and reserves held at the Federal Reserve. This is used to meet withdrawal demands and required reserves.
Required Reserves
The amount of money the bank is required to keep on hand by the Fed. Calculated by multiplying the ratio by actual reserves.
Excess Reserves
The amount of money left over in reserves that the bank can loan out. Calculated by subtracting the required reserves from the actual reserves.
Monetary Multiplier
1/RR. Shows how an initial increase in the monetary base (central bank money) leads to a larger increase in the overall money supply
Money Market Graph
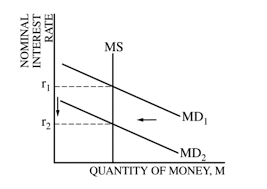
The Discount Rate
The interest rate charged on loand from the Fed to the Banks
Expansionary Monetary Policy
Used during a recession/unemployment to increase AD in order to increase RGDP. Put more money into M1 by buying securities, decreasing the reserve amount, decreasing the discount rate, and decreased interest on reserves
Restrictive Monetary Policy
Used during high inflation in order to decrease AD to decrease or control inflation. Take money out of M1 by selling securities, increasing the reserve requirement, increasing the discount rate, or increating interest rates.
Economic Investement
The purchasing of capital goods
Financial Investment
The buying or building of an asset in expectation of earning a financial gain.
Present Value
The measure of the current worth of an investment price of an asset.
Compounding Interest
Paying interest on the original amount and on any interest recieved
International Trade is…
a way for countries to specialize, increase productivity of their resurces, and realize a larger total output
Abosulte Advantage
Who can produce the most