Positron Emission Tomography (PET)
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
10 Terms
What is the general principle of PET? (3 things)
inject biologically-active molecule into the body, labelled with a positron emitter
positrons travel a short distance in tissue and annihilate with an electron, giving a pair of photons
they travel at 180 deg. to each other and are detected.
What are the isotopes like used for PET? (2 things)
have fewer neutrons
have short half lives
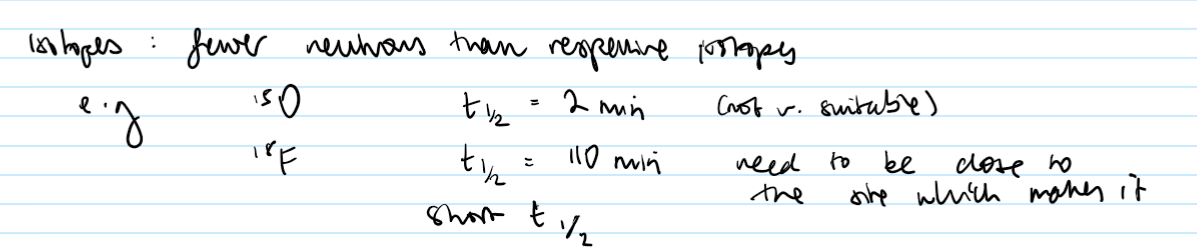
If the isotopes have short half-lives, is that good or bad?
Need a cyclotron on site. So despite the hazardous nature of a cyclotron, need to deliver ASAP for use in the patient.
Sketch graphs of counts per second as a function of time for PET and SPECT. Label where a scan time may take place, and compare their SNRs based on this.
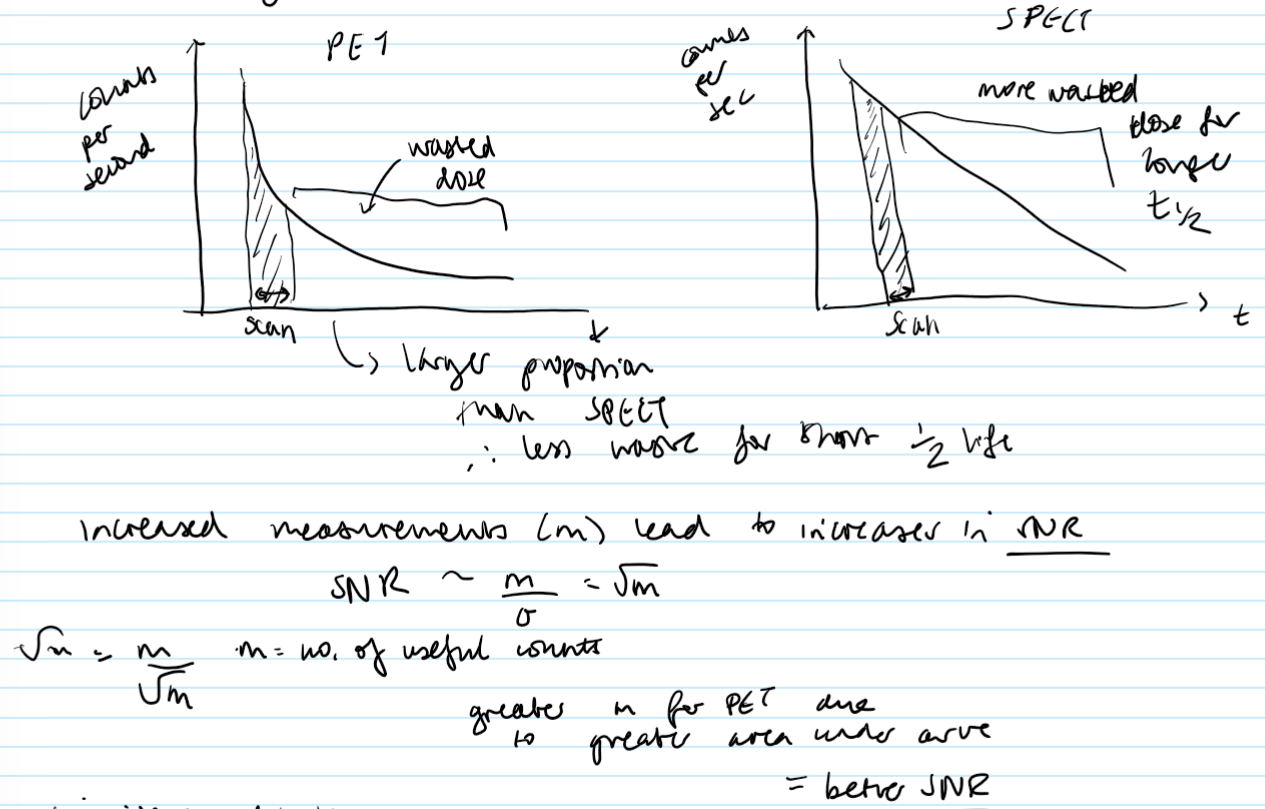
What is coincidence detection? (2 things)
photons that reach the detector at the same time are recorded
photons travel at the speed of light so there is drastic difference when measured/observed against noise on the same timescale.
What happens to the SNR during coincidence detection?
SNR is increased by having two photons recorded at the same time (± 5ns)
How does image reconstruction work?
if 2 coincident photons are detected, we know the source must lie on the path between 2 detectors.
same maths as CT
use similar back projection reconstruction technique like CT scanning for making functional images.
Note:
for SPECT, use collimators for getting straight lines
What is the spatial resolution affected by in PET?
the non-linearity of gamma rays (not totally opposite each other)
gamma rays at 180 deg ± 0.25 deg to each other

State disadvantages of PET
results in blurring of final images
positron has to find an electron to annihilate it
the distance travelled in the tissue by a positron limits resolution
2mm
Describe some applications of PET
cancer is most common
FDG is used (analog of glucose)
A marker of tissue uptake of glucose (linked to metabolism)
get high uptake in areas that require high energy e.g. cancers