ECHO-Ventricular Dysrhythmias
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
What dysrythmia has an ectopic impulse that occurs early in the cycle and originates from the ventricles?
premature ventricular complexes (PVCs)
What are PVCs caused by?
ischemic region in the ventricles; ischemia increases irritability of ventricular myocardium
What is it called when a patient has less than 6 PVCs in a minute?
occasional PVC
What is it called when a patient has more than 6 PVCs in a minute?
frequent PVC
What are the criteria for PVCs?
P-P and R-R intervals are regular with early QRS complexes, ventricular rhythm faster than normal rhythm, PVC QRS shape is wide (0.12 sec or greater) and bizarre, T wave occurs in opposite direction of ventricular depolarization
How is ventricular tachycardia defined?
when more than 3 PVCs occur in a row
What can ventricular tachycardia lead to?
sudden cardiac death
How is the heart rate affected by ventricular tachycardia?
exceeds 100 bpm and eventually exceeds 250 bpm
How are the ventricles in ventricular tachycardia?
continuous state of contraction-relaxation
What does Torsade de Pointes mean?
the twisting of points
How are the QRS complexes in torsades de pointes?
twisted around the isoelectric line
What causes torsades de pointes?
depolarization impulses move to different locations in one ventricle, then the other; occurs due to electrolyte deficiencies or from medications that prolong the QT interval or can be congenital
What is the criteria for ventricular tachycardia?
P-P interval usually not identifiable, R-R interval usually regular, can be slightly irregular, Ventricular Rate: 100-200 BPM, Atrial rate: cannot be determined, P wave usually absent, QRS duration greater than 0.12, wide appearance, T wave in apposite direction from QRS (usually down)
How is ventricular fibrillation defined?
chaotic, asynchronous electrical activity within ventricualr tissue; ventricle walls quiver, preventing ejection of blood; no cardiac output
What is the criteria of ventricular fibrillation?
P-P and R-R intervals cannot be determined, Rate: no rates determined, no P waves present, QRS cannot be determined
How is the patient in true ventricular fibrillation?
unconscious, apneic, and pulseless; true emergency situation
What do you do when a patient has ventricular fibrillation?
initiate Code Blue and begin CPR/ACLS procedures immediately
How is ischemia different from infarction?
ischemia: blood flow decreased→ hypoxia (insufficient oxygen)
infarction: blood flow cut off → necrosis (cell death)
A zone of _______ typically produces ST segment depression.
ischemia
A zone of _______ produces ST segment elevation.
injury
A zone of ________ produces a large Q wave in the QRS complex.
infarction
T/F: in ischemia, injury and infarction you view the leads separately
false; view in groups
What has an ST segment depression of 1 mm or more?
myocardial ischemia
What has an ST segment elevation of 1 mm or more and occurs when blood flow to the myocardium is decreased for a longer time?
myocardial injury
What has a pathological Q wave?
myocardial infarction
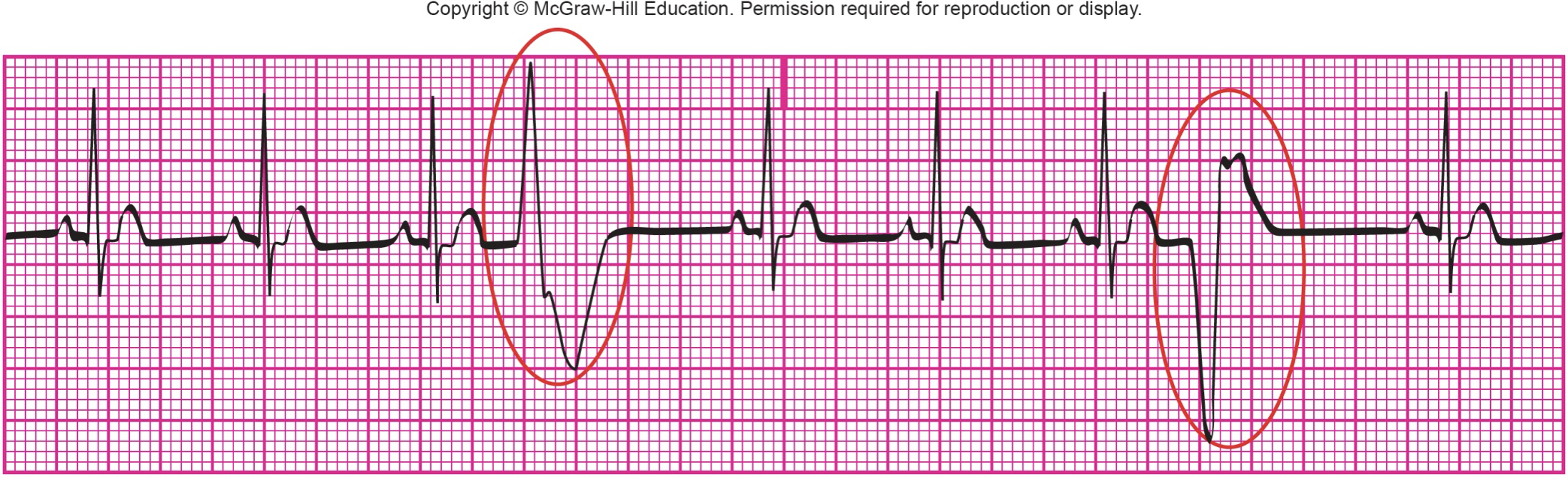
What is shown?
PVCs
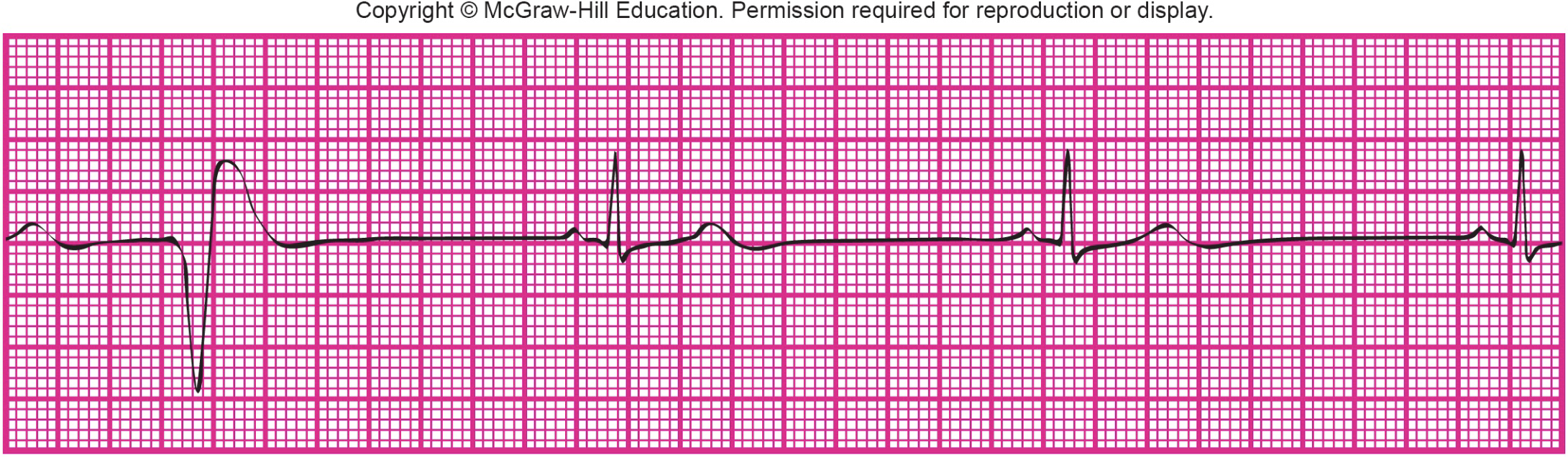
What is shown?
occasional PVC
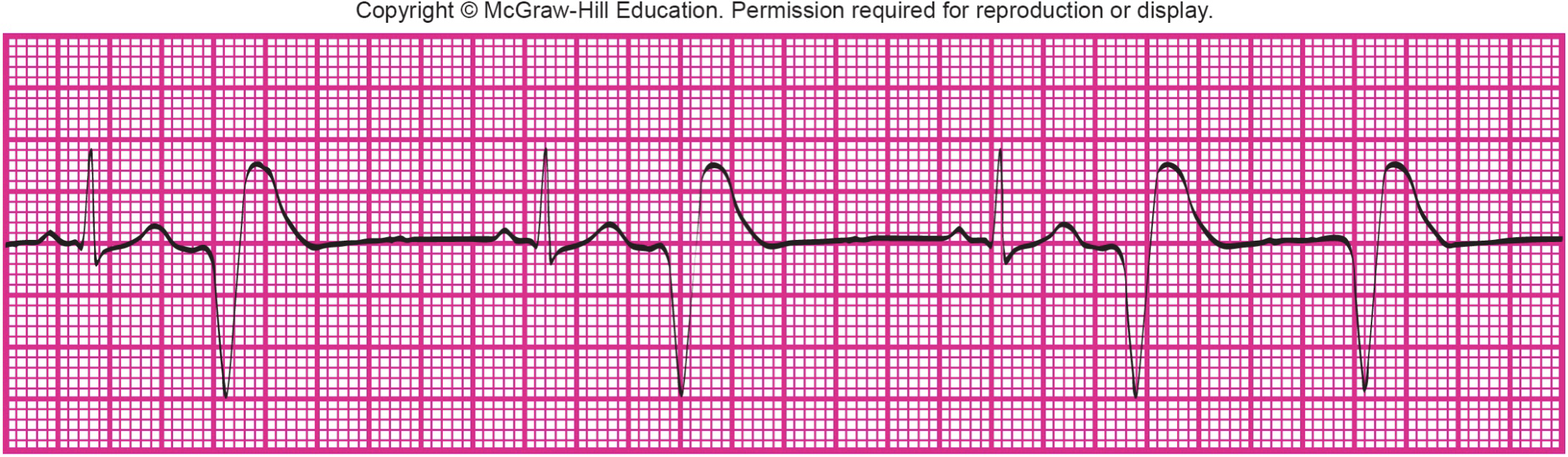
What is shown?
frequent PVCs
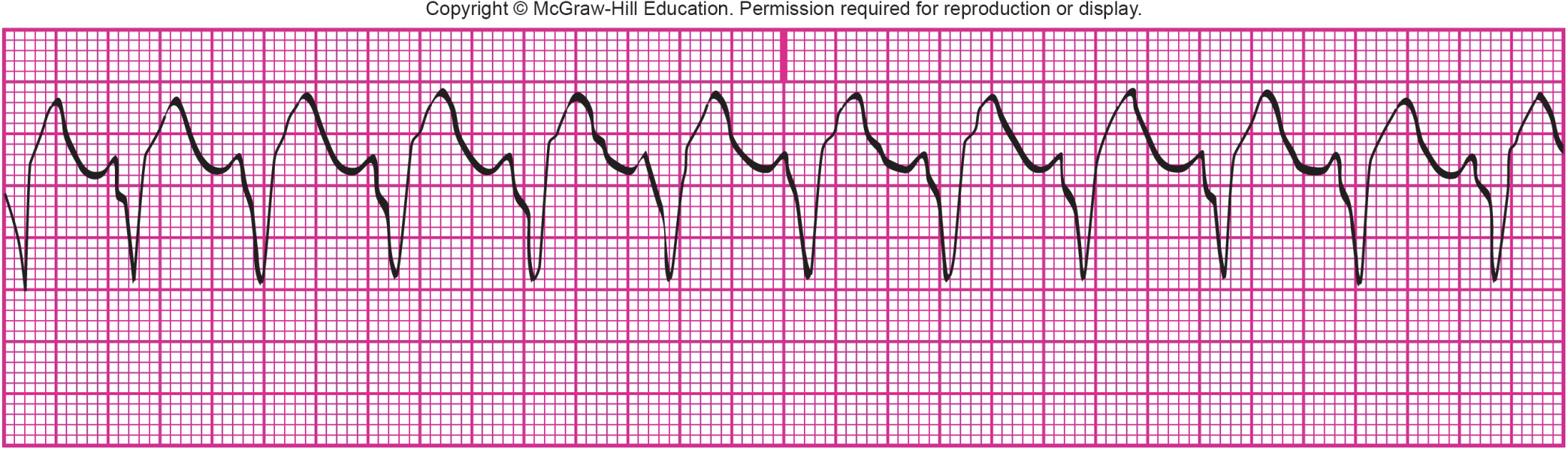
What is shown?
ventricular tachycardia
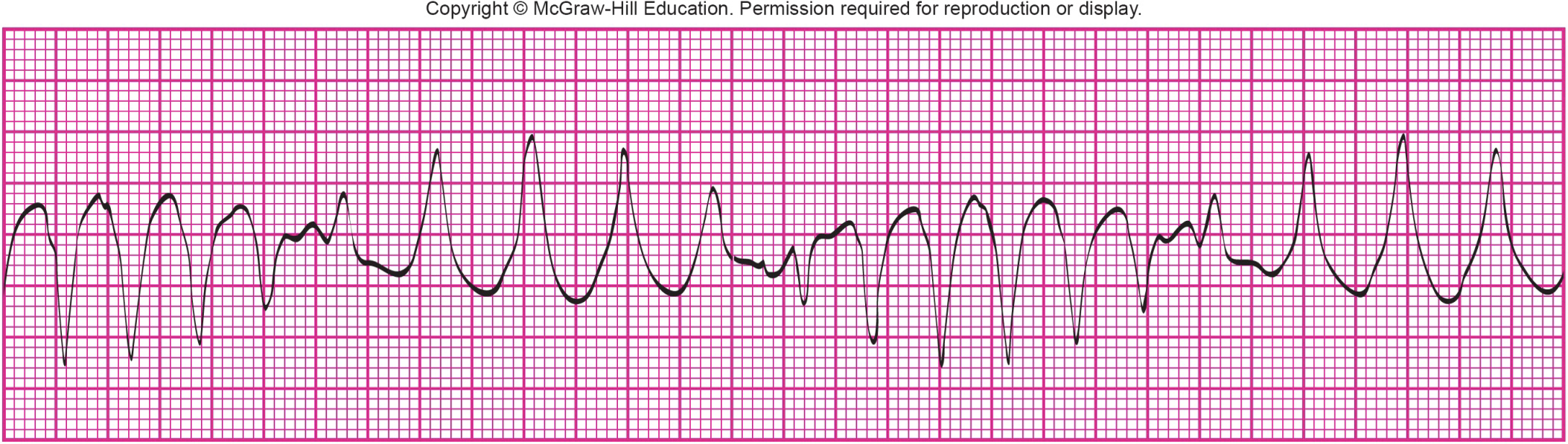
What is shown?
Torsades de Pointes
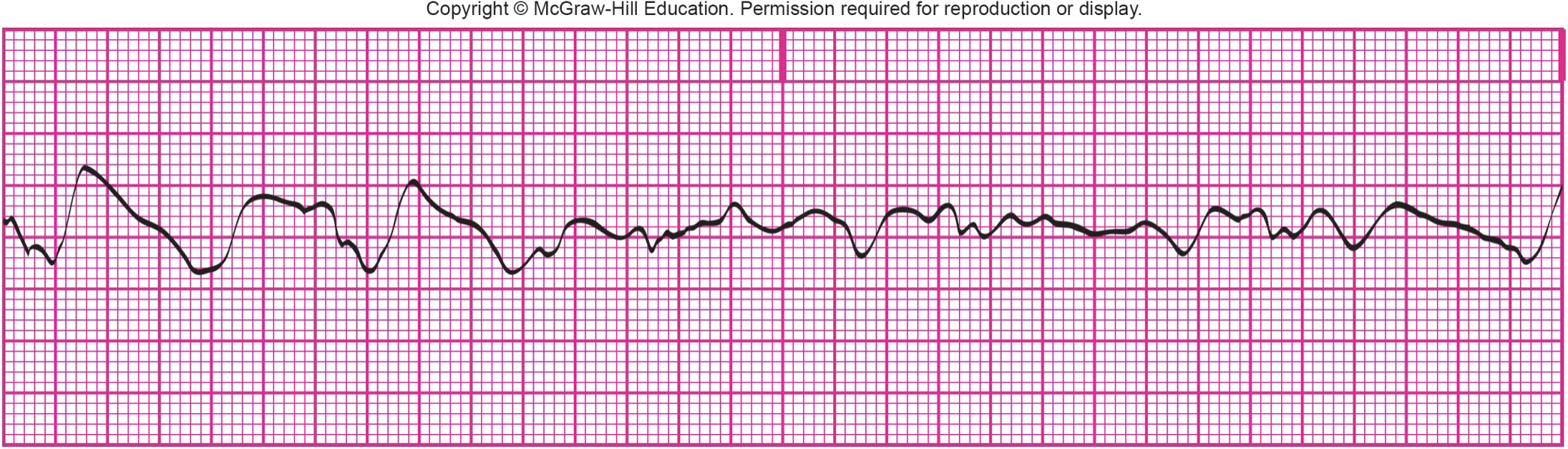
What is shown?
ventricular fibrillation
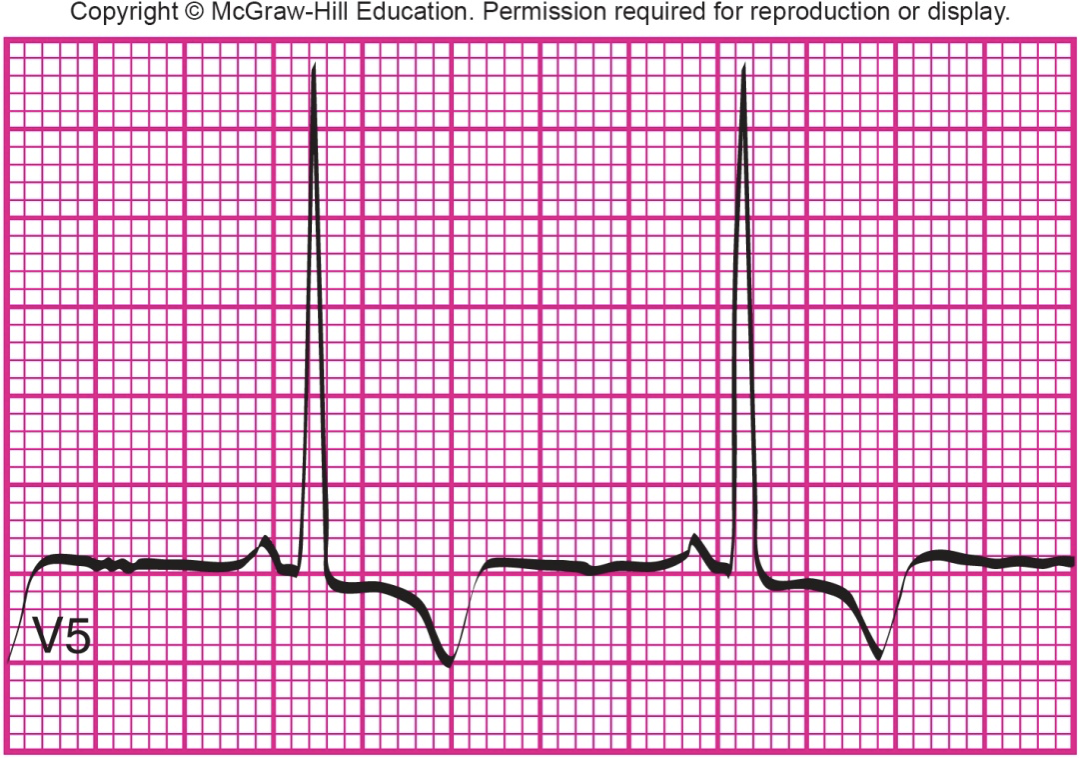
What is shown?
myocardial ischemia
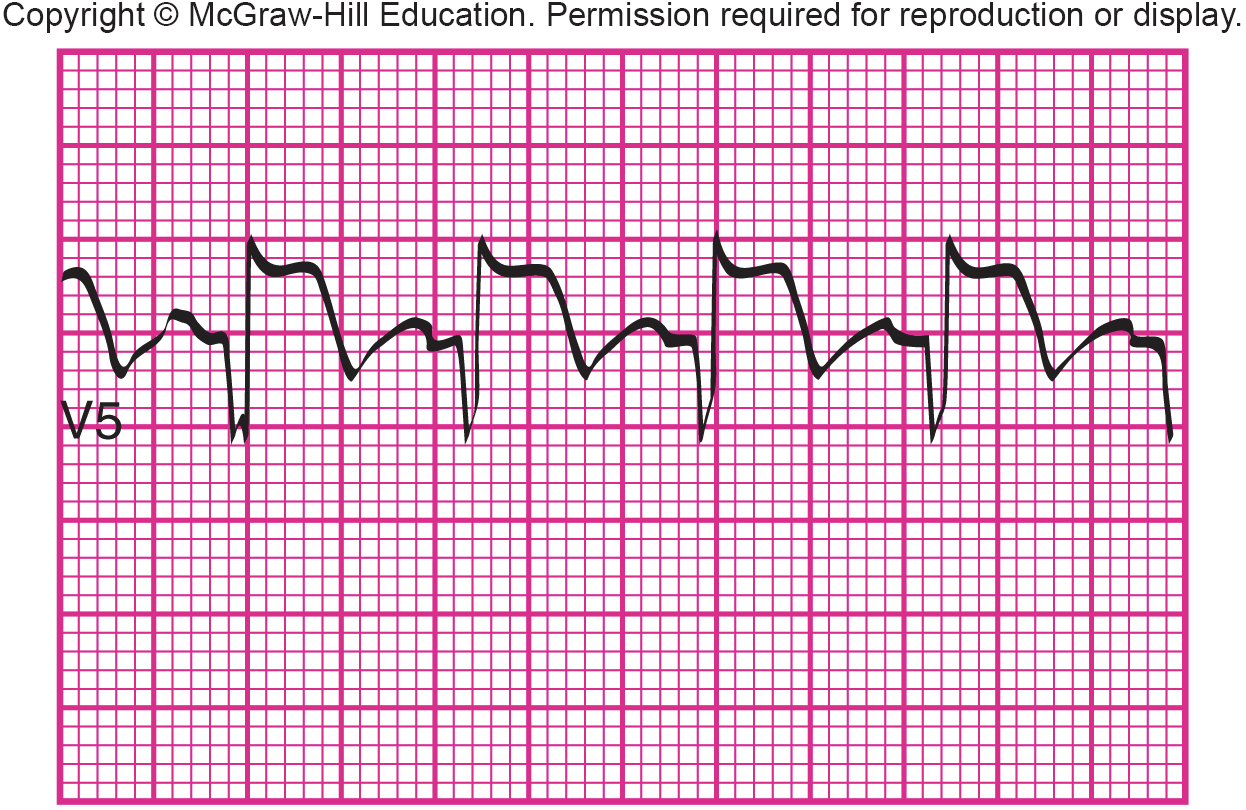
What is shown?
myocardial injury
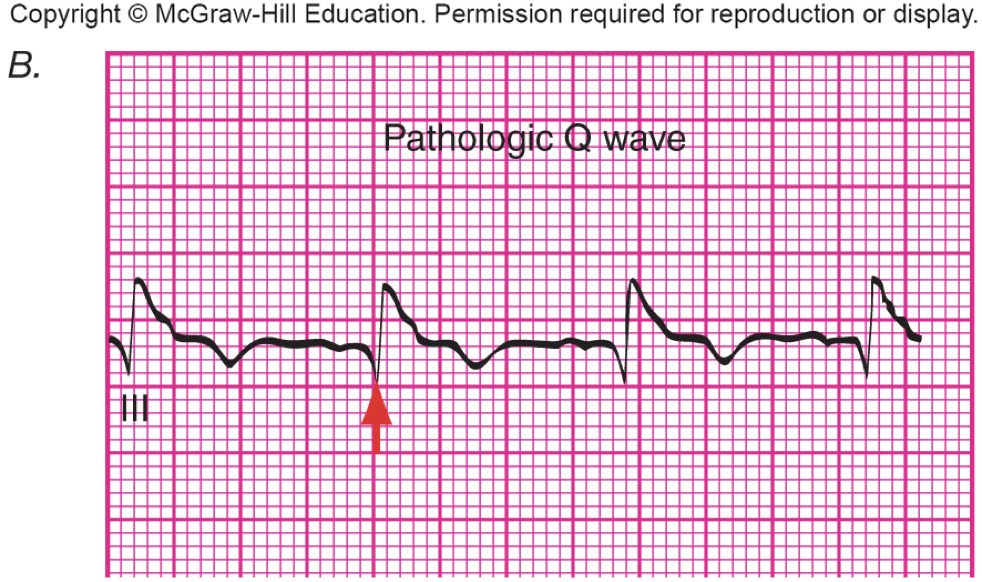
What is shown?
myocardial infarction