Ocular Anatomy
1/153
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
154 Terms
Orbit
eye socket
Globe
Eyeball
Adnexa
Everything except the globe: orbti, muscles, eyelids, conjuctiva, nictitating membrane, lacrimal system
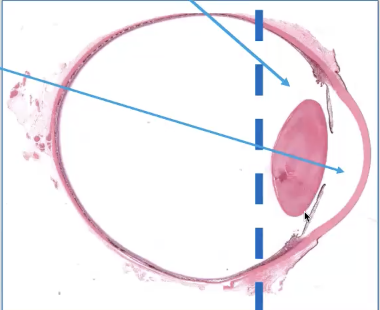
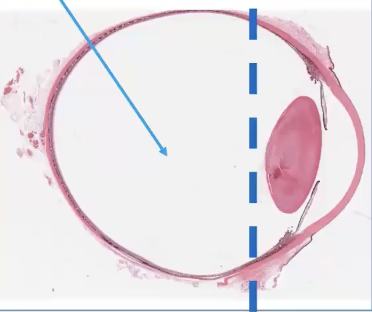
Anterior segment
cornea, anterior chamber, iris, irodocorneal angle, ciliary body, lens
Posterior Segment
vitreous humor
retina
choroid
optic nerve
posterior sclera
Orbit in carnivores
Eye socket has incomplete bony rim
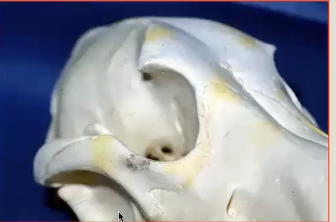
Orbit in herbivores
Complete bony rim eye socket
More trauma to break

Bony socket
lined with fascia,
wraped in conjunctiva, nictitans (third eyelid), fat, extraocular muscles, muscles of mastication, blood vessles, glands, cranial nerves 2-8, autonomic nerves
What does Ramus do?
Ramus of mandible contacts floor of orbit so can cause pain when opening mouth if infected.
Extraocular Muscles
move globe in orbit
Muscle cone anchored in back of orbit
Rectus uscles
oblique muscles (rotate globe)
retractor bulbi (pulls globe back in orbit
What do oblique muscles of extraocular muscles do?
Rotate globe
dorsal/superior
ventral/ interior
What do retractor bulbi do?
Pulls globe back in orbit; third eyelid comes up
What are eyelids made of?
skin, hair, mucocutaneous junction, conjucntiva, glands, musclesE
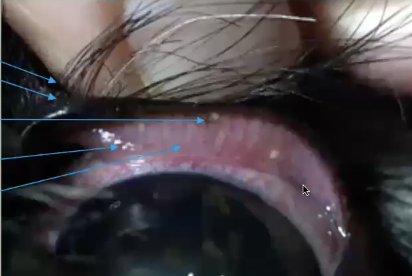
Eyelid skin is thin…
not much subcutaneous tissue near margin, elastic, but elasticity with vary with species and breed
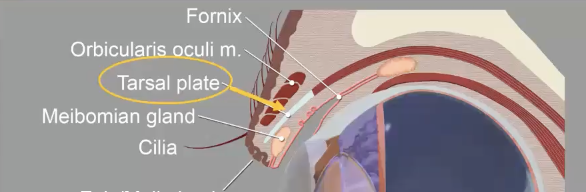
Cilia in eyes
eyelashes, varies among species, originate outside Meibomian gland opening
Meibomian glands
Row of sebacious glands are eyelid margin
What is gray line on eyelid?
Ducts open at mucocutaneous junction
Secrete lipid layer of tear film
Tarsus of eye
Tarsal plate gives toughness and support
extends 3-4 mm from eyelid margin
muscle attachment
Three types of eyelid muscles
Constrict palpebral fissure
depress lower lid
elevate upper lid
Leveator palpebrae
elevate upper eyelid
Orbicularis oculi
surrounds margins and closes upper and eyelids
Innervation of eyelid
5: sensory
3 + 7: motor
autonomic-0 sympathetic nerve
What is purpose of sphincter muscle setup?
Helps spread tears and clear debris
Mueller’s Muscle
Smooth muscle,
Sympathetic tone
Tone to the tarsus
Medial and lateral canthal ligaments
Ligament bands anchor medial and lateral
Muscle transect during enuclation
Vascular supply of eyelids
Well vascularized by longitudinal vessels
heal quickly and are rare to get infected
Palpebral
lines eyelids
Bulbar
lines exposed surfaces of globe
Fornix
cul-de-ac formed by reflections of conjunctiva at transition from lid to globe
Nictitans
covers palebral and bulbar surfaces of the nictitating membrane
What is conjunctiva?
Mobile, elastic membrane
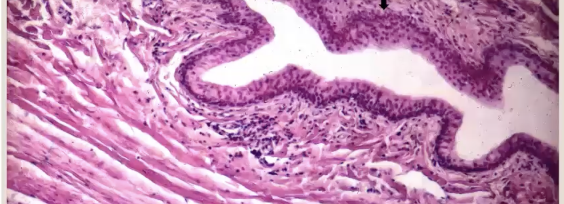
What does normal conjunctiva look like?
Pale, pink non-pigmented in most species, some pigment is normal
What is conjunctiva covered in?
Non-keratinized stratified squamous epithelium
Where are Goblet cells and why are they important?
Between epithelial cells that secrete mucous
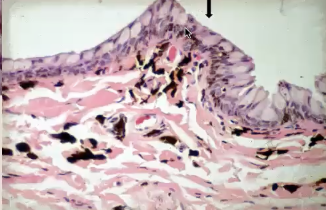
Substantia propria
loose CT, fenestrated (leaky) capillaires, lymphoid tissue
Subconjiunctival space
Between conjucntiva and space
Purpose of conjucntiva
Smooth gliding of nictitans and eyelid
muycus layer of tear film (goblet cells)
Immune protection
lymphoid tissue, immunoglobulins
corneal repair (graft)
Where does nictitans sit?
Medial fornix/canthus
leading edge is usually pigmented (but not always)
Function of nictitans
moves dorsolaterally as globe retracted
spread tear film
protect globe
removes particulate matter (squige)
How does nictitans function?
T shape cartialge squigee
gland of nictans produces water
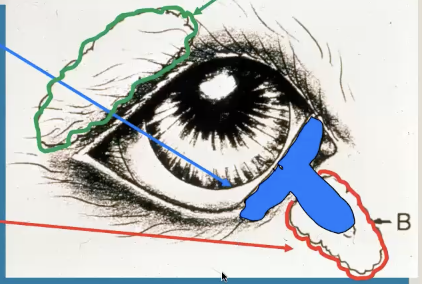
What is retropulsion?
retract third eyelid by gently pressing on the globe; check for cancer
Cherry eye
gland is prolapsed and not anchored
Tear layer films
Lipid layer: outer
Aqueous: middle
Mucin: inner
What are lipid layer produced by?
Meibomian
What is aqueous layer produced by?
lacrimal gland
What is mucin layer produce by?
Goblet cells
Lacrimal outflow apparatus
drains the tears from the eyelids to the nose
Steps for lacrimal outflow
Ocular puncta (in eyelids, conjunctiva)
canaliculi
lacrimal sac in medial canthus
nasolacrimal duct
nasal puncta
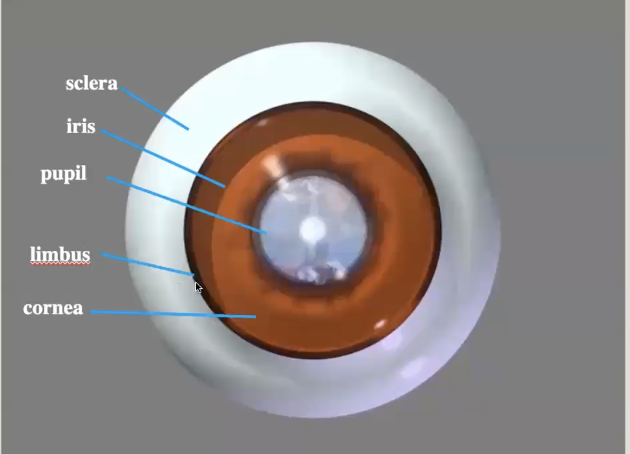
Anterior parts of eye
Sclera
Iris
Pupil
Limbus
Cornea
Inside anterior globe
3 concentric tunics of globe
fibrous (conrea, sclera)
vascular (iris, ciliary body, chorid)
nervous (retina, optic nerve)
What are fibrous tunics made of?
Cornea and sclera
Cornea function
avascular
.5-1mm thick
Transmit and refract light
protect internal contents
thin windshield
cornea innervation
Opthalmic branch of trigeminal nerve 5:
anterior 1/3 of cornea (superficial layer)
4 layers of cornea
epithelium
stroma
descemets membrane
endothelium
Corneal epithelium
non-keratnized, nonpigmented squmous cells
wing cells
basal cells
basement membrane
Cornea epithelium turnover rate
about 7 days
cornea stroma is made of
collagen (regularly arranged)
keratocytes
glycosaminoglycans
water (78%)
NO blood vessles
Corneal Stroma
hydrophillic; will swell if there is a break in epithelial or endothelial barriers
Needs to maintain deturgescence (deydration)
Deturgescence
relative dehydration to remain clear
ulceration
focal corneal edema
Diffuse corneal edema is likely damage to…
endothelium (innermost layer of cornea)
Descemets membrane
basement membrane of corneal endothelium
Endothelium
monolayer of hexagonal cell
activley pump fluid out of cornea to maintian deturgescence
mechanical barrier
Do endothelium undergo mitosis?
Only in young animals
What happens when there aren’t enough endothelial cells?
Corneal endothelial degeneration; does not have enough to maintain deturgence
What is gunderson flap?
Corneal endothelial degeneration with flap
Limbus
zone of transition from regularly arranged collagen and straight basement membrane
Sclera tissue
irregularly arranged, densley packed collage fibrils
Vascularized
opaque
Zone of transition in eyes
Point of weakness,
Blunt trauma can rupture
Sclera has opening for what?
posterior opening for optic nerve which is a point of weakenss
Lamina cribosa
Collage sieve supports axons of optic nerve (site of weakness)
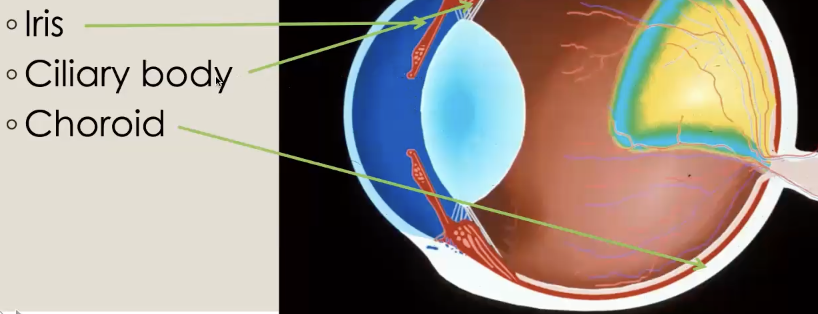
Uvea parts
Middle tunic of the eye
Iris
Ciliary body
Choroid
Iris
Most anterior portion
What does the iris/pupil do?
Regulate amount of light entering posterior portions fo the eye
Blood aqueous barrier
keeps cells protein, in blood vessels to keep fluid clear and protect eye from damage
Maintians clarity
Parts of Iris
sphinctor muscle (encircles pupil)
stroma
dilator muscle (backside fo iris longitudinally)
Posterior pigmenged epithelium
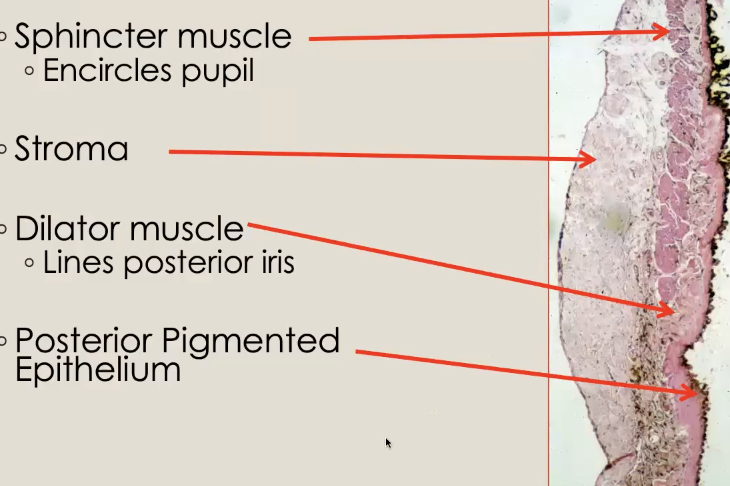
Iris stroma makeup
nerves, muscles, melanocytes, fibroblasts, vessels
What can inflamation do to pupil?
constrict them
Pupil shape is related to what?
Sphinctor muscle distribution
Iris color
related to melanin and other pigments
can be related to coat/skin color
Heterocrhomia
iris color variation
Dog vs cats iris color
dogs have dark brown round melanin
cats: golden brown pigment or linear shape
Iris color in albino rat
no melanin so iris will appear red because all you see is stromal tissue with lots of blood vessels
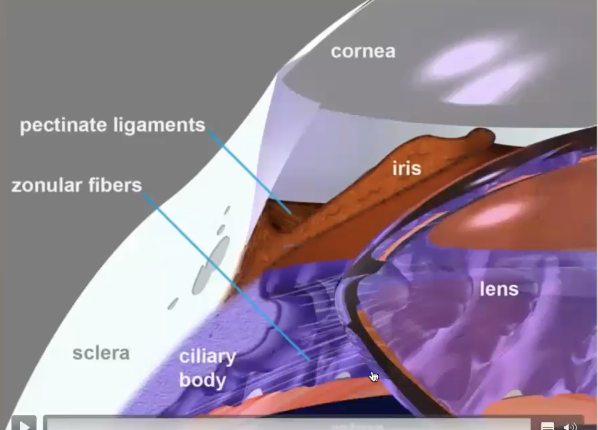
Iridocorneal angle
junction of iris at base via pectinate ligaments (collagen)
Site of drainage of aqueous humor through trabecular meshwork
Gonioscopy lens
looks right at iridocornela angle acros iris to drainage tissue
Ciliary body
posteior to iris
Oriented 3 directions
longitudenal
circumferential
radial
Pars plicata
ciliary process
Pars plana
flat protion where retina inserts
Accomodation
fine focusing with ciliary body smooth muscle
Dogs and horses accomodation
dont have developed accomodation because retina is not developed so cillary muscle is not developed
Ciliary body epithelium
pigmented epithelium
non-pigmented epithelium
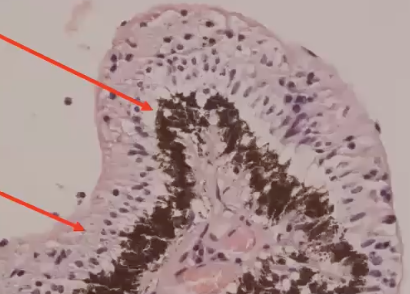
Aqueous humor produced by
non-pigmented epithelium in the posterior chamber and flows through Iridocorneal angle (ICA)
Aqueous prouduction outflow
ciliary epthelium
between iris and lens
pupil into anterior chamber
iridocorneal angle
trabecular meshwork
Sceleral Venous Pleus
Glaucoma
primary or secondary closure of iridocorneal angle (breed, inflammation)
Glaucoma
Obstruction of aqueous humor through the iridocorneal angle increase intraocular pressure. (overfilling water balloon)
Won’t burst but will create globe enlargement
How to address glaucoma:
laser surgery of endothelium?
Lens anatomy
non-vascularized
non-innervated
355 crystaline protein, 65% water
capsule of basement membrane
lens epithelium
lens fibers
zonules attachements
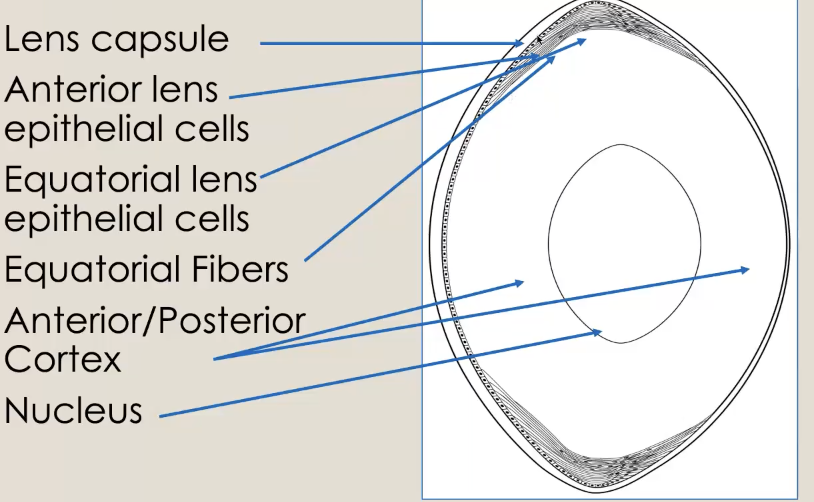
Lens capsule:
Anterior lens epithelial cells
equatorial lens
antiorr/posterior (choclate of mm)
nuclesu (nut in center of mm)
Lens fiber formation
lens fibers elongate and are move internally which is created by new fibers that push them
Central lens fibers compressed to form fetal and adult nuceleus