BIO HL - UNIT 3
1/108
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
109 Terms
nucleic acids
polymers that are made up of monomers called nucleotides; DNA and RNA are different examples of these
DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid)
genetic instruction that codes for traits via proteins; more stable than RNA (less reactive); stored in chromosomes in the nucleus
has two strands; made of deoxyribose; bases are adenine, guanine, cytosine, and thymine
RNA (ribonucleic acid)
transfers and decodes the genetic info in DNA
has one strand; made of ribose; based are adenine, guanine, cytosine, and uracil
Nucleotide
consists of three parts:
1) 5-carbon pentose sugar (deoxyribose or ribose)
2) nitrogenous base; attached to 1' carbon
3) phosphate group; attached to 5' carbon
covalent bond
phosphate group of one nucleotide bonds to the sugar of another (at '3 -OH group)
forms a phosphodiester linkage via condensed reaction
Hydrogen Bond
hold two DNA stands together by binding complementary nitrogenous based
A-T
C-G
Purines
Bases with a double-ring structure.
Adenine and Guanine
Pyrimidines
Bases with a single-ring structure; cytosine, thymine, uracil
antiparallel
The two strands of DNA run in opposite directions; one runs 5' to 3' while the other runs 3' to 5'
Double Helix
two strands of nucleotides wound about each other; structure of DNA; looks like a twisted ladder; due to the strands being anti-parallel
Watson and Crick
Correctly proposed the structural model of DNA with guidance from earlier findings from Pauling, Chargaff, and Franklin
showed that DNA strands are anti-parallel (double helix), pair through complementary bases, outer edges of bases are exposed for transcription and replication)
Watson and Crick early model faults
triple helix; bases were outside and sugar-phosphates were inside; nitrogenous bases were not complementary
Linus Pauling
INSPIRED WATSON AND CRICK
discovered molecular distances and bond angles
Erwin Chargaff
INSPIRED WATSON AND CRICK
found that DNA consists of equal numbers of purines (A and G) and pyrimidines (C and T)
Rosalind Franklin
INSPIRED WATSON AND CRICK
discovered DNA is a helical structure; her X-ray crystallography confirmed DNA as a helix; her info was shared without her permission, but she is now recognized as a key contributor
volume
property of the cell that determines a cell's metabolism (sum of all the reactions that occur)
the bigger the cell, the more volume, the greater metabolism (more nutrients needed and waste produced)
surface area
property of the cell that determines its rate of diffusion (material exchange)
the bigger the cell, longer the membrane, greater the SA, faster the solutes can enter/exit
SA : V
as the cell grows, volume (cm3) grows faster than surface area (cm2); smaller SA:V ratio
cell diffusion cannot keep up with need to obtain and remove nutrients; need to divide so that it does not die
villi and alveoli
STRUCTURES USED TO INCREASE SURFACE AREA ON CELLS
1) Finger-like projections in intestinal cells
2) membranous extensions in lungs
Cell Cycle
set of events that produces two identical daughter cells after division
two main phases are interphase and M (mitotic) phase
Interphase
the resting phase between successive mitotic divisions of a cell; 90% of the cell's time; consists of three phases: G1, S, and G2
M (mitotic) phase
Period of active cell division; 10% of the cell's time; includes mitosis (nuclear division) and cytokinesis (cytoplasmic division)
G (gap) 1
first part of interphase:
-duplicates organelles
-ups cytoplasmic volume
-produced necessary proteins and enzymes
-obtains nutrients and cellular materials
-produces ATP
S (synthesis)
DNA replication
G (gap) 2
last part of interphase; completed unfinished steps from G2
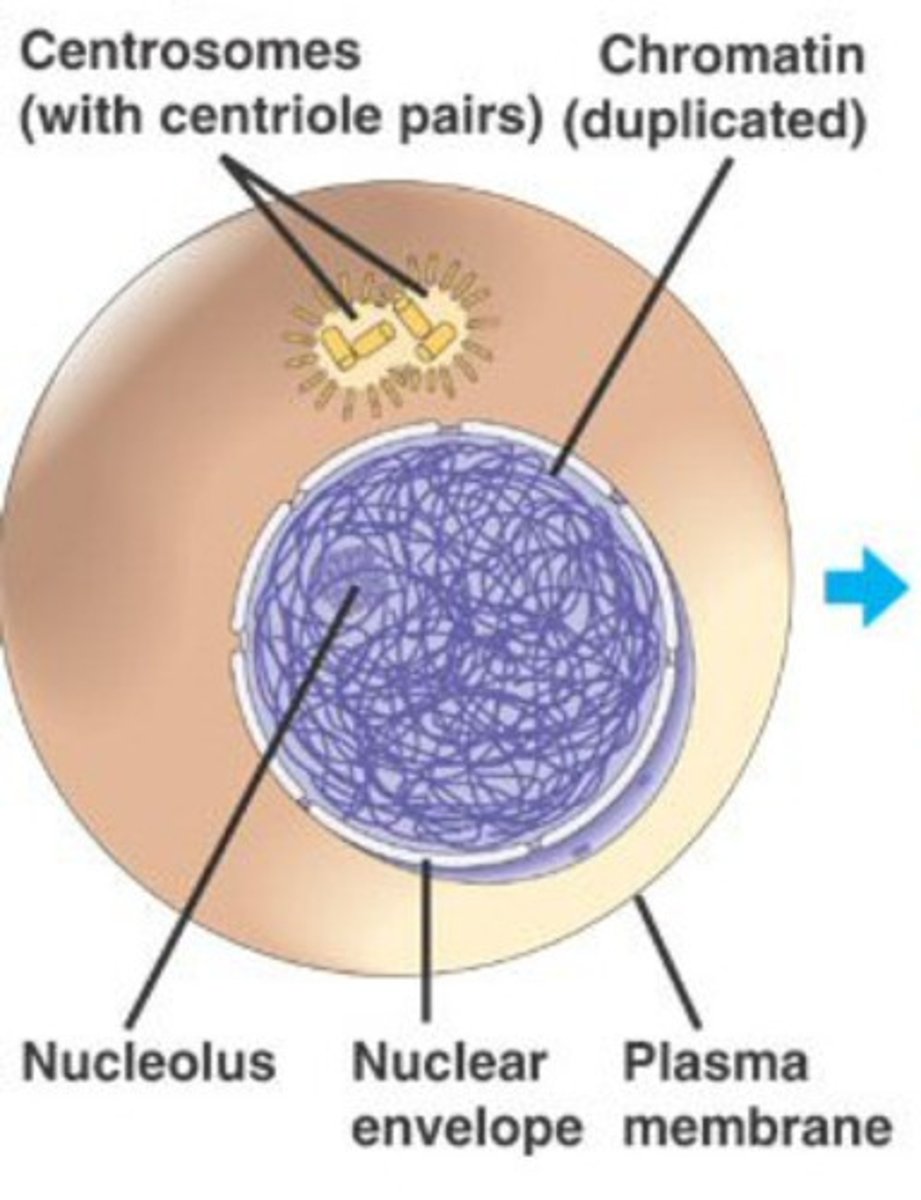
Chromatin
loose unraveled DNA; present in all non-dividing cells and those in interphase; allows room for transcription (turns genes on)
Chromosomes
DNA is supercoiled, tightly wound and condensed; occurs during prophase, reverses turning telophase; east to separate, difficult for transcription
sister chromatids
Identical copies of a chromosome; full sets of these are created during the S subphase of interphase; held together by the centromere; once they separate, they become chromosomes
Centromere
Area where the sister chromatids of a chromosome are attached
Interphase
What part of the cell cycle is this?
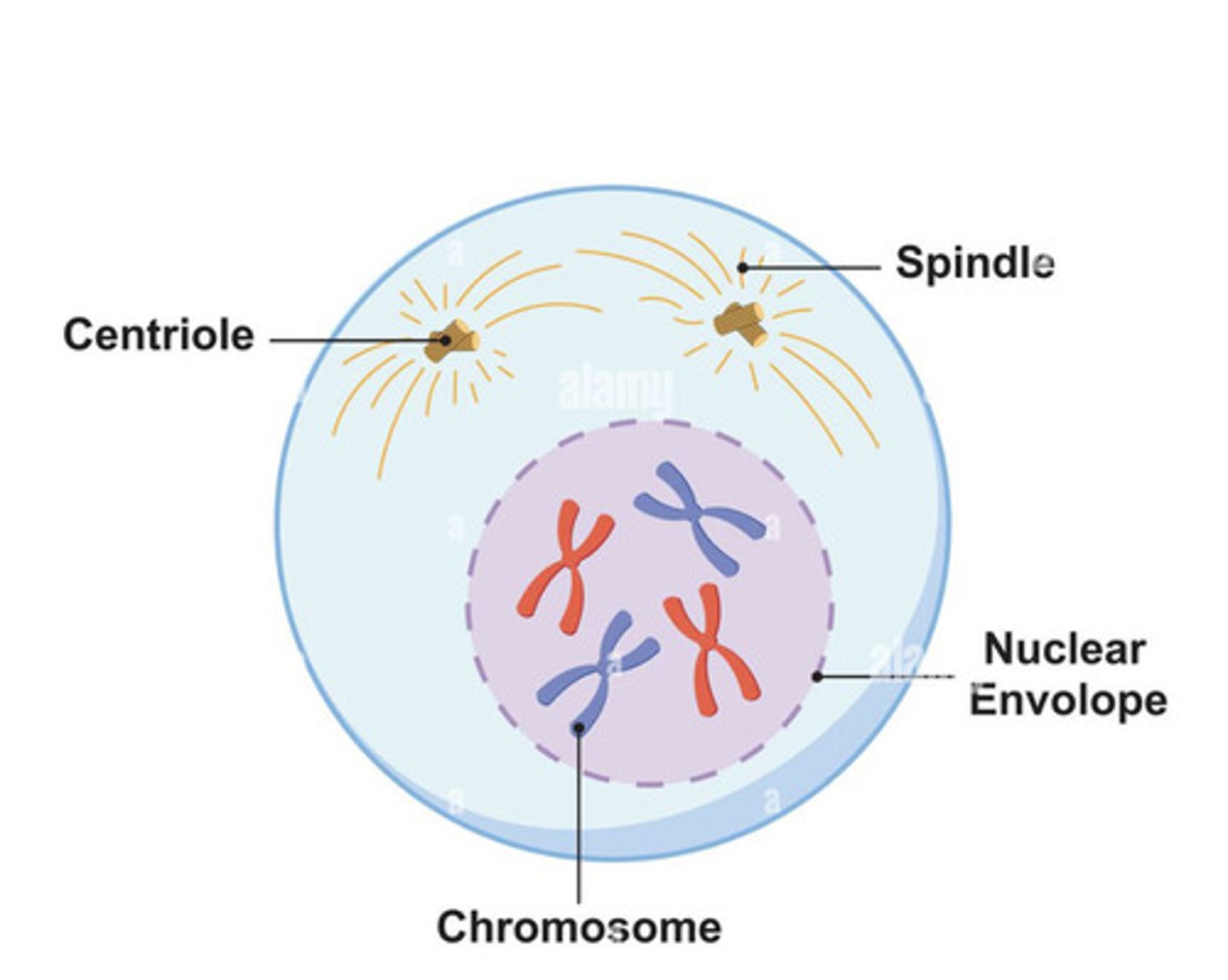
Prophase
What part of the cell cycle is this?
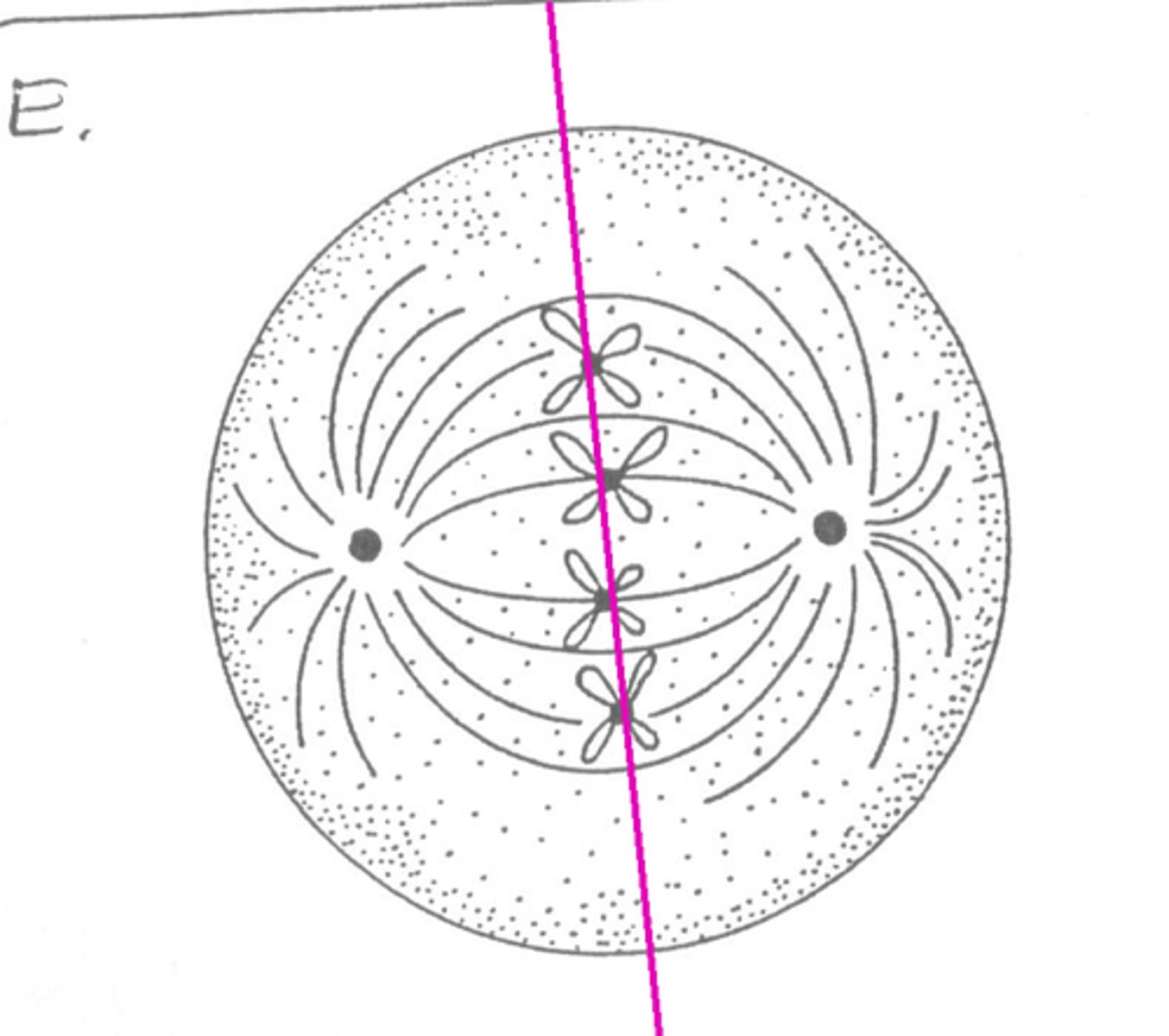
Metaphase
What part of the cell cycle is this?
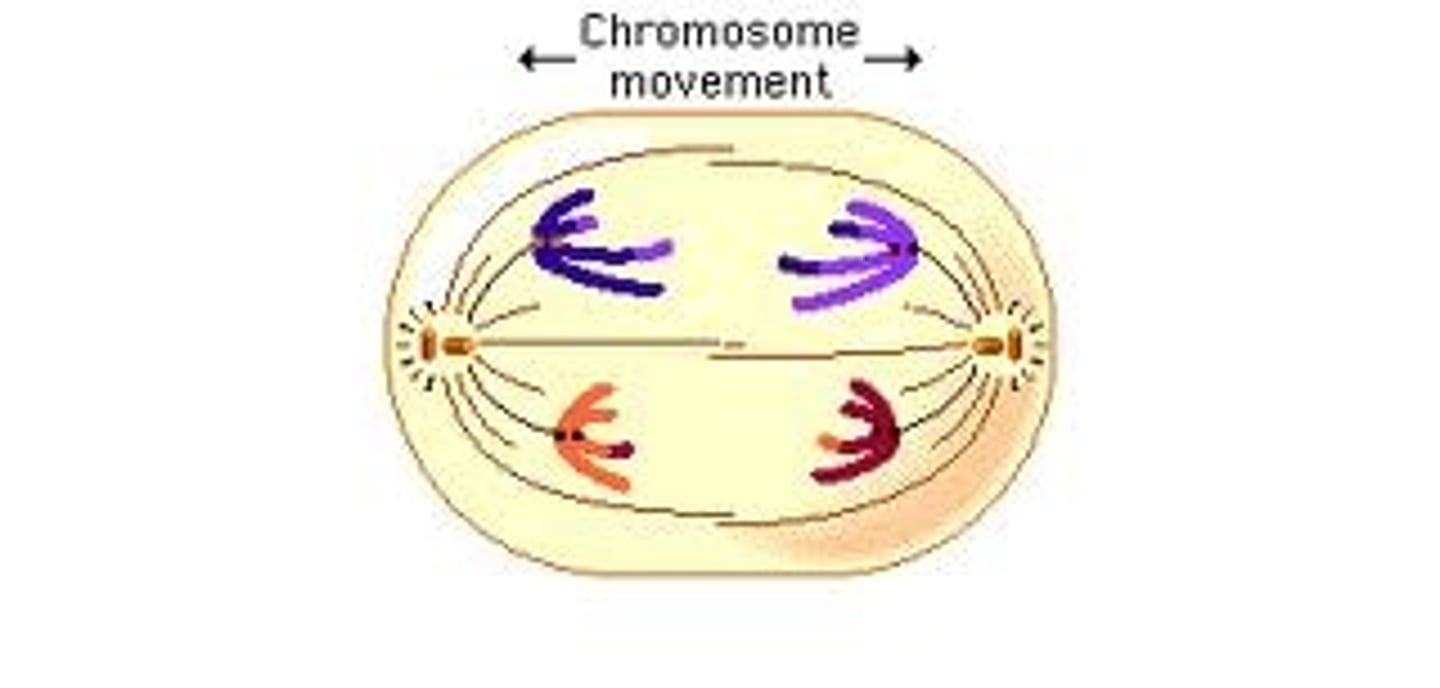
Anaphase
What part of the cell cycle is this?
Telophase
What part of the cell cycle is this?
Prophase
DNA supercoils (X shape); chromosomes exist as sister chromatids joined at the centromere; centrosomes move to opposite poles and produce microtubule spindle fibers; nuclear membrane breaks down
Metaphase
microtubule spindle fibers connect to centromeres (kinetochores); depolymerization causes spindles to shorten and contract; orientation of each pair is random; CHR align on the center of the cell (equator or metaphase plate)
Depolymerization
causes spindle fibers in metaphase to shorten and contract
Anaphase
continued shortening of spindles cause sister chromatids to separate; once separated, they are considered to be individual CHRs; genetically identical CHRs move to opposite poles of the cell
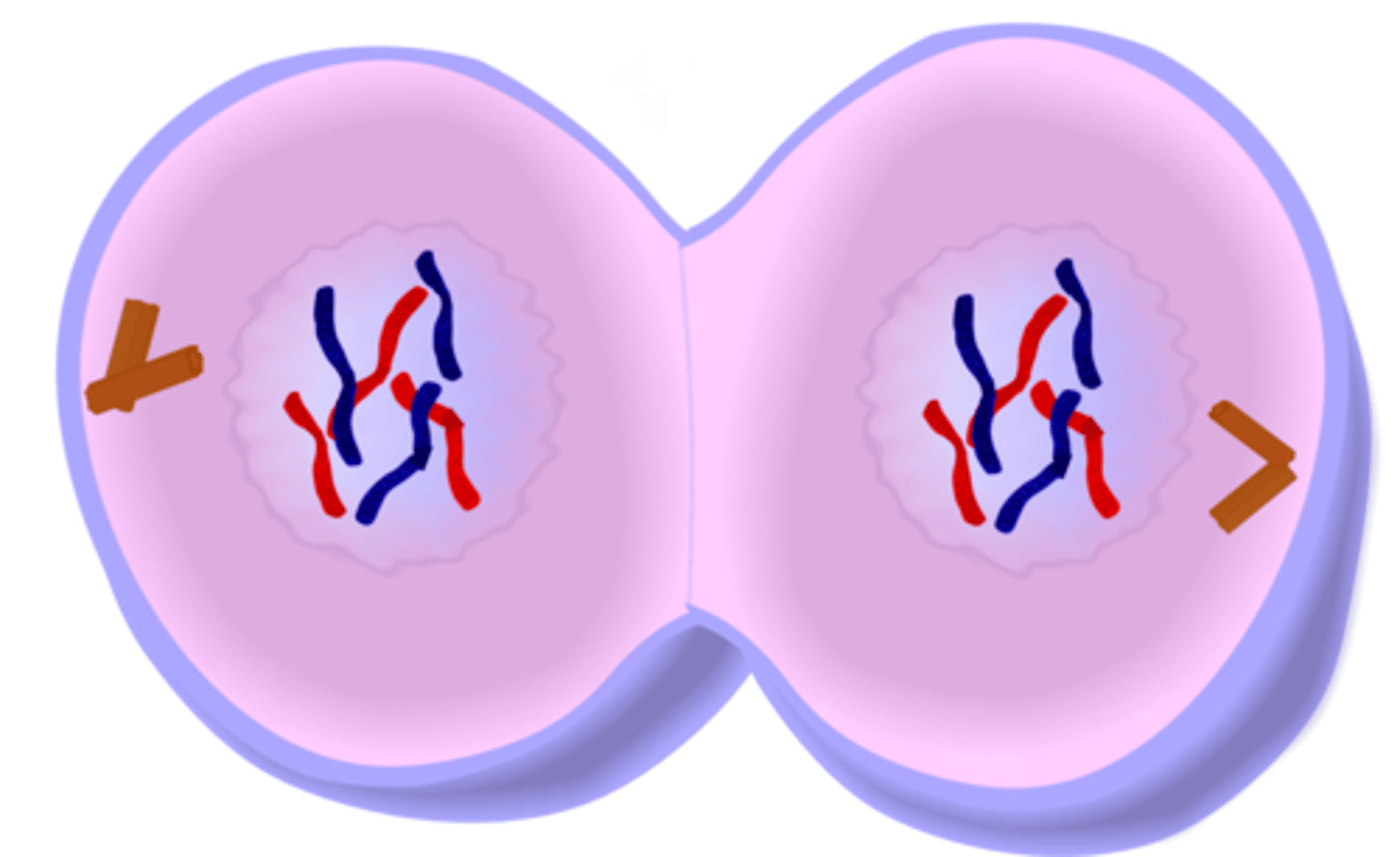
Telophase
spindle fibers disappear; CHRs deco dense into chromatin (invisible under microscope again); nuclear membrane reforms; cytokinesis (cytoplasmic division begins concurrently)
Mitotic index
measure of the proportion of dividing cells (proliferation status); higher during growth and repair (division); important prognostic tool for predicting cancer cells' response to chemotherapy
Cells in mitosis/total number of cells
equation for calculating the mitotic index
Animal Cell Cytokinesis
after anaphase, microfilaments form a ring around the center and construct to form cleavage furrow; centripetal (forms on the out, moves inward); when furrow meets, cell completely pinched off, forming two cells
cleavage furrow
The first sign of cleavage in an animal cell; a shallow groove in the cell surface near the old metaphase plate; when it meets, the parent cell is pinched off into two daughter cells
centripetal
forms from a periphery, moves toward the center (animal cytokinesis)
Plant Cell Cytokinesis
after anaphase, vesicles filled with cellulose form a line around the center; vesicles fuse together and form the early cell plate; plasma membrane forms on either sides of the cell; centrifugal (in to out); eventually extends and fuses with the cell wall, forming two cells
vesicles filled with cellulose
what forms the early cell plate in plant cell cytokinesis?
centrifugal
forms in the center, moves toward the periphery (plant cytokinesis)
cell cycle checkpoints
points at which the cell cycle automatically stops until overridden; must verify that there are enough materials for the next phase
G1 checkpoint
most important cell cycle checkpoint; checks for cell size; cells that pass usually complete the cell cycle; cells that do not enter the G0 phase
G0 phase
A nondividing state occupied by cells that have left the cell cycle, sometimes reversibly (ex. nerve cells)
G2 checkpoint
cell cycle checkpoint after S phase; checks for DNA replication, completion, and mutations
M-spindle (metaphase) checkpoint
checks for microtubule attachment to kinetochores (on centromeres)
kinetochore
A specialized region on the centromere that links each sister chromatid to the mitotic spindle.
Maturation Promoting Factor (MPF)
cyclin + cyclin-dependent kinases; made when the fluctuating amounts of cyclin bind with and activate the CDKs through phosphorylation; activates target proteins needed for an event in the cell cycle (ex. chromosome duplication); breaks apart after passing the checkpoint
cyclin
regulatory protein that controls the cell cycle (helps pass checkpoints) by binding with and activating CDK; rise in [ ] leads to the formation of MPF; degrades after passing the checkpoint
cyclin-dependent kinases (Cdks)
always present in the cell (inactive; doesn't fluctuate); after cyclin bonds to it, it becomes active, and activates target proteins through phosphorylation; the proteins trigger events needed in the cell cycle; after passing the checkpoint, cyclin dissolves and it becomes inactive again
Phosphorylation
The transfer of a phosphate group, usually from ATP, to a molecule. Activates the target molecule.
Cyclin Expression
different cycling specifically bind to and activate different CDKs
MPF levels will peak to pass checkpoints and remain lower at all other times
tumors
abnormal cell growths resulting from uncontrolled cell division; occurs in the absence of signals or ligands; ignore density-dependent inhibition & anchorage dependence; causes the disease cancer
density-dependent inhibition
The phenomenon observed in normal animal cells that causes them to stop dividing when they come into contact with one another (prevents overcrowding)
anchorage dependence
The requirement that to divide, a cell must be attached to a solid surface (prevents free-floating division)
mutagens
agents that change the expression of genes, either by changing the DNA or proteins used in replication; can be caused physically, chemically, or biologically
physical mutagens
radiation including X-rays, ultraviolet light (UV), and radioactive decay that changes the expression of genes
chemical mutagens
DNA interacting substances including reactive oxygen species (ROS) and metals (ex. arsenic) that change the expression of genes
Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS)
highly reactive molecules that contain oxygen (like H20) that act as chemical mutagens
biological mutagens
Viruses, certain bacteria and mobile genetic elements (transposons) that change the expression of genes
Carsinogens
all mutagens that lead to cancer
Oncogenes
genes that have the potential to cause cancer (proto-oncogenes and tumor suppressor genes); cancer occurs when one or both genes mutate or over/under express
proto-oncogene
a gene that codes for proteins that promote the cell cycle and therefore cell growth and proliferation; if mutated, can cause cancer
tumor suppressor gene
a gene that codes for proteins that repress the cell cycle and promote apoptosis (programmed cell death); if mutated, can cause cancer
metastasis
the spread of cancer from its original location (primary tumor) to another (secondary tumor); made of the same type of cells; can be benign or malignant
primary tumor and secondary tumor
1 - the original location of a cancer
2 - the area to which the cancer spreads; made up of the same type of cells as the first location, and treated with the drugs for that location
Benign vs. Malignant
1 - tumors that stay at their original location
2 - tumors that spread and invade neighboring tissue
cancer
according to studies, what does smoking lead to?
carsinogenic
cigarette smoke contains more than 4000 chemicals, and over 60 are ___________.
90%
the percent of lung cancer caused by smoking; smoking also increases risk of other cancers like mouth, throat, stomach, liver, pancreas, and large intestines
Central Dogma
(DNA -> RNA -> Protein)
flow of genetic info from genes to proteins; DNA must be replicated (S phase) to be passed on to offspring
semi-conservative
DNA replication is _______ because DNA consists of one original (parent) strand and one new (daughter) strand
the original strand serves as a template for the new; allows every new strand to be identical to the old
complementary base pairing
In DNA, T pairs with A; G pairs with C;
RNA, U pairs with A and G pairs with C
conservative model
in DNA replication, the model that two entirely new strands were being synthesized from the old; disproved by generation one in Meselson and Stahl's experiment
dispersive model
in DNA replication, model in which each daughter DNA is made of old and new segments patched together; disproved by generation two in Meselson and Stahl's experiment
Meselson and Stahl (1958)
used radioactive isotopes of nitrogen; replicated DNA in a heavy medium (15N) during the first round, then a lighter medium (14N) in a second round; DNA separated by density through centrifugation
generation one: one mixed band of 15N & 14N found; disproved conservative model
generation two: one band of 14.5N & one of 14N; disproved dispersive
DNA helicase
An enzyme that unwinds and separates the DNA double helix during DNA replication; breaks the hydrogen bonds between nitrogenous bases
two separate strands act as templates
DNA polymerase III
during DNA replication, enzyme that synthesizes new strands using the old as templates; cleaves two phosphates off deoxynucleoside triphosphates, using the energy to phosphodiester bond the nucleotide to the 3' end of the new strand
5' to 3'
in DNA replication and transcription, the direction that the new strand grows
deoxynucleoside triphosphates
Free nucleotides with three phosphate groups that align with complementary bases in DNA replication
DNA polymerase III breaks covalent bond to release two phosphates, providing energy to connect nucleotides
polymerase chain reaction (PCR)
replication procedure used to generate large amounts of copied DNA in a short period of time; each cycles doubles the amount of DNA (grows exponentially)
money standard procedure of 30 cycles makes 1 billion copies
1. DNA of Interest
2. DNA primers
3. free nucleosides
4. taq polymerase
Materials needed for PCR
Taq polymerase
material for PCR; derived from a hot spring bacteria and can function without denaturing
DNA primers in PCR
short strands of DNA used to isolate the gene of interest in PCR; synthesized to be complementary to either end of the gene
denature (90C), anneal (55C), elongate (75C)
temperature controlled procedures of PCR
1) separate DNA strands by raising temperature to (~___)
2) attach primers by lowering temperature to (~___)
3) allow taq polymerase to grow DNA at optimal temperature (~___)
protection and speed
Why we use RNA in transcription:
1) DNA can be kept safely inside the nucleus (lysosome-free area)
2) one gene = many mRNAs
one mRNA = many polypeptides
Transcription process
RNA polymerase II separates DNA, ribonucleoside triphosphates align opposite of exposed DNA; RNA polymerase II removes additional phosphates, uses energy to join nucleosides; polymerase detaches, double helix reforms
nucleus and nuclear pores
1) where transcription occurs
2) where the resulting mRNA leaves through
RNA polymerase II and ribonucleoside triphosphates
in transcription, _______ separates DNA and produces a complementary mRNA strand of one DNA
removes phosphates from ________ and uses energy to join nucleotides with phosphodiester bonds
Gene
DNA sequence transcribed into a polypeptide or RNA; comprised of the antisense strand and the sense strand
antisense strand and sense strand
1) transcribed strand; complementary DNA that serves as the template (strand RNA polymerase II sits on)
2) strand NOT transcribed; identical to RNA, but with T not U
Genetic code
set of rules by which mRNA is converted to polypeptides
codons
non-overlapping, triplet bases in mRNA that code for one amino acid; 64 possibilities; four possibilities for each of the three bases (4^3 = 64)
AUG (methionine)
the start codon; coding always begins with this codon