IBS/IBD- Jones
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
What is GALT?
“Gut associated lymphoid tissue”
basically our immune system in the GI tract
What cell in the GALT produces mucus for protection, which allows for normal bacteria to function???
Goblet cells
What cell in the GALT job produces IgA?
Plasma cells
What is IgA’s role in the immune system?
identifying bacteria and triggering the immune response
What cell in the GALT produces antibacterial factors that helps to defend/identify bad bacteria? This cell is also located in the crypts.
Paneth cells
What cell in the GALT captures antigens and presents them to Treg cells to mediate lymphoid cell expression??
Dendritic cells
What cell in the GALT has no cytoskeleton and functions as a “doorway”? This cell is critical and allows dendrites and other immune cells to function right.
M-cells
What are localized areas of lymphoid tissue and where lymphoid cells aggregate (B and T cells) in the GALT called?
Peyer’s Patches
What is the gut microbiota?
normal bacteria found in the gut
What are the 3 functions of the microbiota?
ferment non-digestible substrates (like fiber and mucous)
synthesis of Vit K and B
antimicrobial protection/ stimulate the immune system
When the microbiota ferments non-digestible substrates, what is produced?
produces SCFA’s
butyrate- energy source in the colon
propionate- regulates gluconeogenesis/metabolism
acetate- bacterial growth
What term describes the “loss of beneficial microbiota” and triggers the immune system to lead to inflammation and irritation? What are common causes?
dysbiosis- common causes are antibiotics, sulfur foods, stress
What are some common good bacteria in our gut?
Bifidobacteria
Escherichia coli
Lactobacilli

What are the 3 forms of IBS?
IBS-C: constipation predominant IBS
IBS-D: diarrhea predominant IBS
Mixed—> cycles of constipation and diarrhea
What are some of the causes of IBS? (general overview- ex: gut-brain axis)
gut-brain axis
genetic (SCN5A)
Microbiota
Immune
Bile acid metabolism
visceral/enteric nervous system (serotonin role)
How can stress cause IBS?
stress releases CRF and that is known to inhibit gastric motility, increase propulsion in colon and alter the epi barrier (leaky gut)
(FYI: CRF deals with cortisol)
What is the proposed genetic link to IBS?
mutation in the SCN5A channel which is voltage-gated sodium channel associated with abdominal pain
Immune responses to food allergies is an Ig__ mediated link to IBS.
IgG
How is serotonin related to normal GI function?
NORMALLY good bacteria stimulate 5-HT release of serotonin. When 5-HT activates afferent fibers in the myenteric plexus this increases motility and secretions.
(Think: serotonin—> increase gut motility and secretions)
What happens to serotonin in IBS-D and IBS-C?
IBS-D: higher serotonin= increase motility= diarrhea
IBS-C: low serotonin= decrease motility= constipation
What are the name of 2 IBDs?
ulcerative colitis
Crohn’s Disease
What are some causes of IBD?
epithelial changes
genetic
environmental (lifestyle, diet, sleep)
microbial
immune factors
IBD can be caused by decreased _______ due to reduced __________ cells.
mucous, goblet
In dysbiosis, dendritic cells stay in Peyer’s Patches and release what 2 inflammatory mediators using JAK?
IL-12
IL-23
In dysbiosis, macrophages become more active and release what inflammatory mediators?
TNF
IL-12
IL-6
IL-23
In dysbiosis, what defense cells don’t work?
paneth cells
How does pattern of inflammation look in Crohn’s versus UC?
Crohn’s- skip lesions
UC- continuous
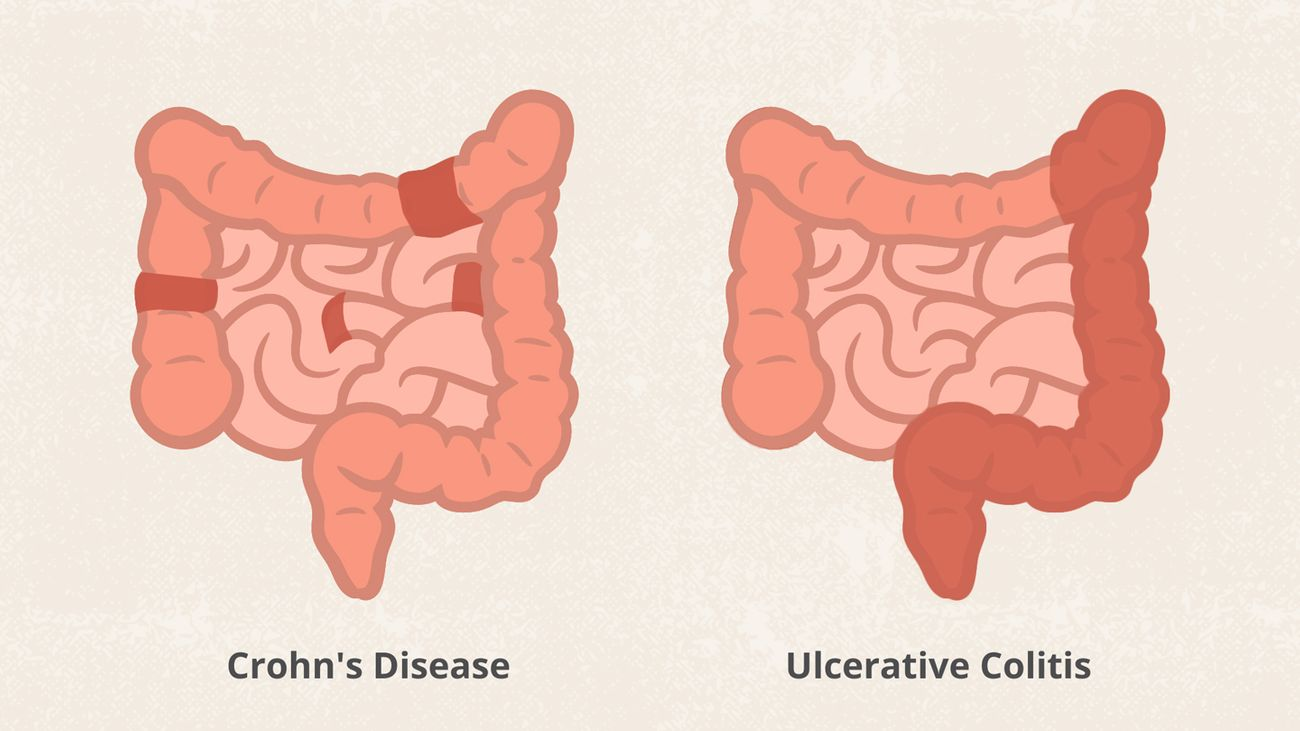
Where is Crohn’s and UC found?
Crohn’s- anywhere from mouth to anus ('“from gum to bum”)
UC- LARGE INTESTINE and rectum
How thick is the wall inflammation in Crohn’s versus UC?
Crohn’s- transmural (entire wall)
UC- mucosa (surface)
What are complications of Crohn’s and UC?
Crohn’s- FISTULA, abscess, obstruction
UC-TOXIC MEGACOLON, hemorrhage
(pic is what toxic megacolon looks like)
What are the symptoms of Crohn’s and UC?
Crohn’s- abdominal pain
UC- bloody diarrhea
Does UC or Crohn’s extremely increase the risk of colon cancer?
UC
PRACTICE:
Inflammation is localized to the colon in what kind of IBD?
UC
PRACTICE:
Which of the following is not a function of the normal microbiome/ GALT?
a. produce SCFA
b. primes immune system
c. Synthesis of Vitamin B and E
d. Ferment non-digestible substrates
c
PRACTICE:
Which of the following descriptions matches the closest to dendritic cells?
a. capture bad bacteria and degrade it
b. protect from bad bacteria
c. produce IgG
d. capture antigens and present them to Treg cells
d
PRACTICE:
Which of the following is a possible etiology of IBS?
a. changes to the mouth-brain axis
b. increase/decrease in serotonin
c. increase/decrease in dopamine
d. bile acid synthesis
b