Bio/Biochem
1/219
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
220 Terms
spleen
stores blood and recycling old RBCs, lymph organ, filter
What element is required for muscles to contract?
Ca2+
Pyrimidines
Cytosine and Thymine
Purines
Adenine and Guanine
What amino acid is the only one that can form disulfide bonds?
Cysteine
Convergent evolution
process whereby distantly related organisms independently evolve similar traits to adapt to similar needs
What are gonadotropin hormones responsible for?
reproduction
helicase
separates the parent DNA strands at the origin of replication
ligase
binds two DNA fragments via phosphodiester bonds
primase
generates an RNA primer to match a fragment of DNA at the beginning of DNA replication
topoisomerase
relieves the overwinding of DNA strands ahead of the DNA replication fork by breaking, swiveling, and rejoining DNA strands.
If two genes are encoded by the same operon…
they share the same promoter and the same mRNA fragment.
digoxin effect caused by
increase in calcium
Na+K+ATPase is an example of what kind of transport?
Primary active transport because it uses ATP to move solutes against their concentration gradients
how are ketone bodies generated
from sustained oxidation of fatty acids
what branch of the peripheral nervous system does the adrenal medulla belong to?
the sympathetic nervous system of the autonomic nervous system
what supplies energy for the electron transport chain?
NADH
tubulin
a cytoskeletal protein whose expression is similar in different cells.
ETC complex 2
succinate dehydrogenase
ETC complex 1
ubiquinone oxioreductase
ETC complex 3
ubiquinol-cytochrome c oxioreductase
ETC complex 4
cytochrome c oxidase
gene imprinting
parent-specific transmission of traits
what do RNA viruses require to replicate themselves?
reverse transcriptase
what part of the nephron filters proteins?
the golermulus
what part of the nephron reabsorbs solutes and water from the filtrate?
the distal tubule
goblet cells
specialized epithelial cells that produce mucus in the respiratory tract
order in which filtrate passes thru the tubular regions of a nephron
Bowman’s capsule —> proximal tubule —> loop of Henle —> distale tubule —> collecting duct
liquid-liquid extraction
used to separate compound with disparate solubility characteristics; uses separatory funnel; take advantage of acid/base characteristics
thin-layer chromatography (TLC)
sample dabbed onto plate, then place in beaker with nonpolar solvent; capillary action draws the solvent up the plate, bringing the sample with it; nonpolar components move farther
size-exclusion column chromatography
used to separate components by physical size
cation-exchange column chromatography
trap positively charged molecules within the column; negatively charged stationary phase
anion-exchange column chromatography
positively charged stationary phase traps negative molecules
affinity chromatography
ligands designed to bind to a compound of interest are attached to the beads that make up the stationary phase
gas-liquid chromatography
time taken to move through the apparatus is measured and used to estimate its affinities for gaseous mobile and liquid/polymer stationary phases
High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC)
passing a liquid mobile phase through an absorbent-packed column; takes place under high pressure, allowing resolution to occur more rapidly
Normal HPLC
stationary is polar, mobile is nonpolar
Reverse phase HPLC
stationary is nonpolar, mobile is polar
recrystallization
solid product place in a liquid solvent and heated, dissolving. then cooled, which forms precipitate; repeated to increase purity
filtration
used to separate solid product from unwanted fluids; only liquid can pass through filter
Distillation
separates liquids based on boiling points
simple distillation
BP > 25° apart
fractional distillation
BP < 25° apart
vacuum distillation
very high boiling points; used to lower atmospheric pressure
Hydrophobic interactions in proteins
Keep proteins stable and biologically active by decreasing surface area and reducing undesirable interactions with water. During protein folding, the hydrophobic side chains become buried in the interior of the protein.
ATP synthase
Allows passive diffusion of protons down their concentration gradient into the matrix, which provides energy for the formation of ATP from ADP and inorganic phosphate.
Active Site Model
States that the enzyme’s active site binds to the substrate. A substrate matches the site like a puzzle piece, making the enzyme specific to its substrate.
Phagocytosis
Type of endocytosis. Process by which a cell uses its plasma membrane to engulf a particle.
Active site
A location on an enzyme where binding of one or more substrate (reactant) molecules occurs, followed by the formation of products.
Competitive inhibition
Involves an inhibitor binding to the enzyme’s active site. The inhibitor is structurally and chemically similar to the substrate. It blocks the active site and thus prevents substrate binding. Its effects can be reduced by increasing substrate concentration. Increases Km.
Citric acid cycle steps
Citrate -> Isocitrate -> α-ketoglutarate -> Succinyl CoA -> Succinate -> Fumarate -> Malate -> Oxaloacetate
Vesicle
Structure consisting of liquid or cytoplasm enclosed by a lipid bilayer. Forms during the processes of secretion, uptake and transport of materials within the plasma membrane.
Uncompetitive inhibition
Involves an inhibitor interacting with the ES complex at an allosteric site. Prevents an enzyme from letting go of a substrate that it has bound. Decreases Vmax and Km.
Lyase
An enzyme that cleaves bonds through non-hydrolysis mechanisms and often facilitates the formation of a double bond.
Net energy production per molecule of glucose for glycolysis, the PDH complex, and the TCA cycle
4 ATP, 10 NADH, and 2 FADH2 per glucose
Lipid raft
Cholesterol-rich microdomains of cell membranes. Influences membrane fluidity and membrane protein trafficking.
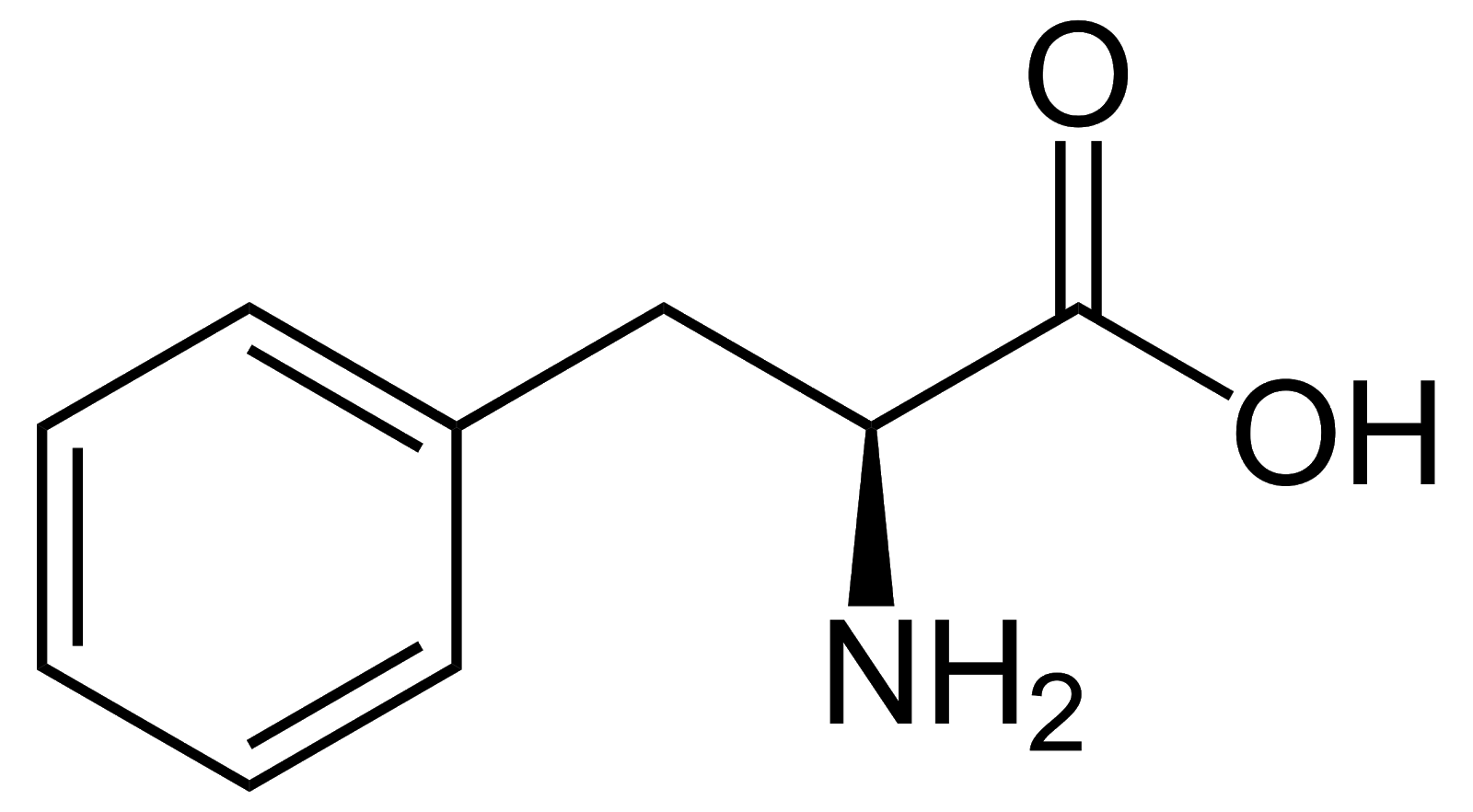
Phenylalanine, Phe, F, non-polar
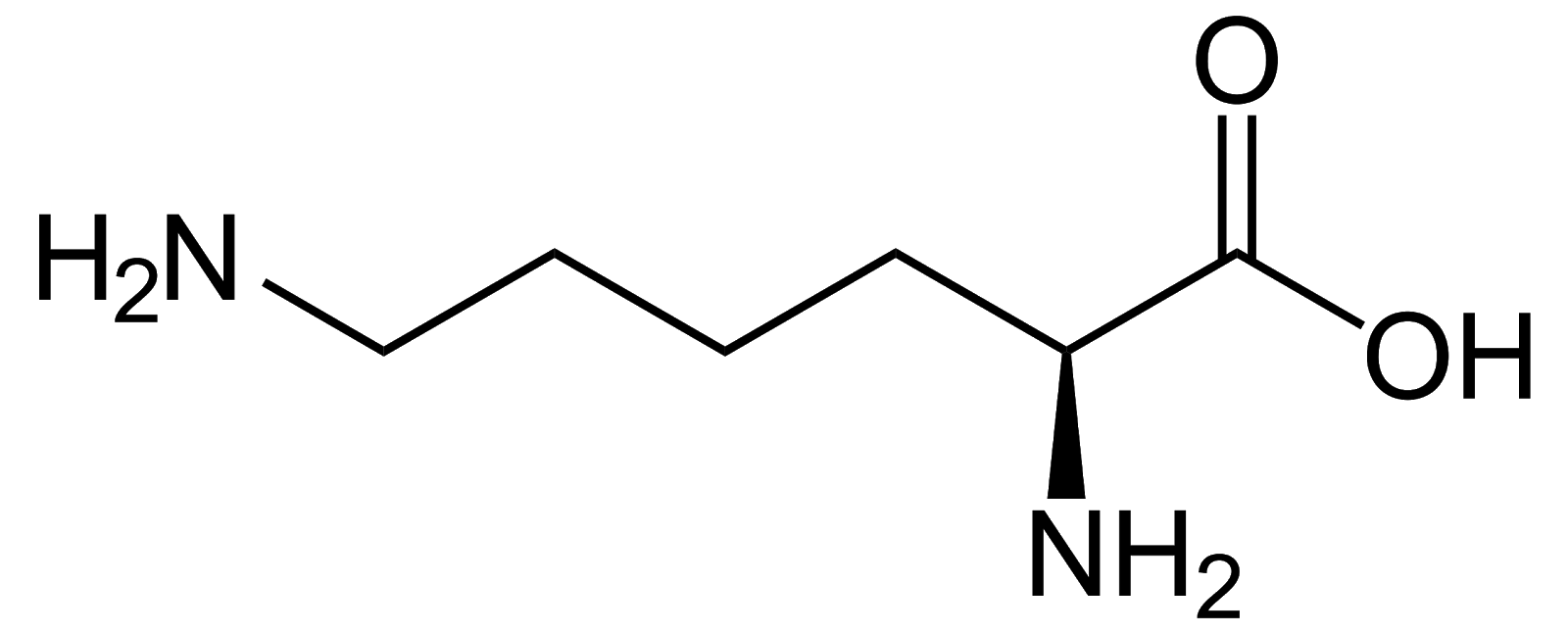
Lysine, Lys, K, basic/positively charged.
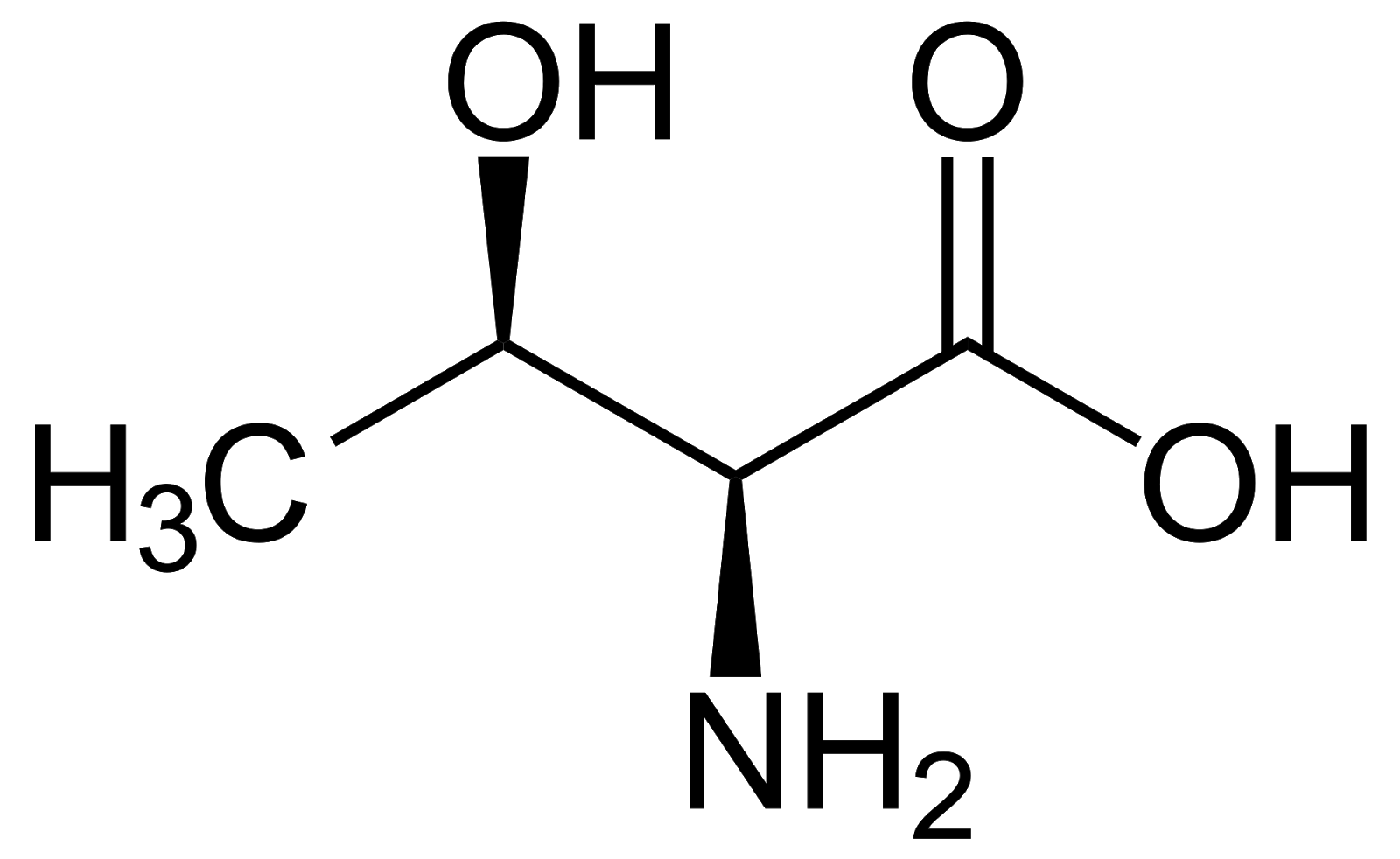
Threonine, Thr, T, polar, the alcohol group is the target for phosphorylation in post-transcriptional modification
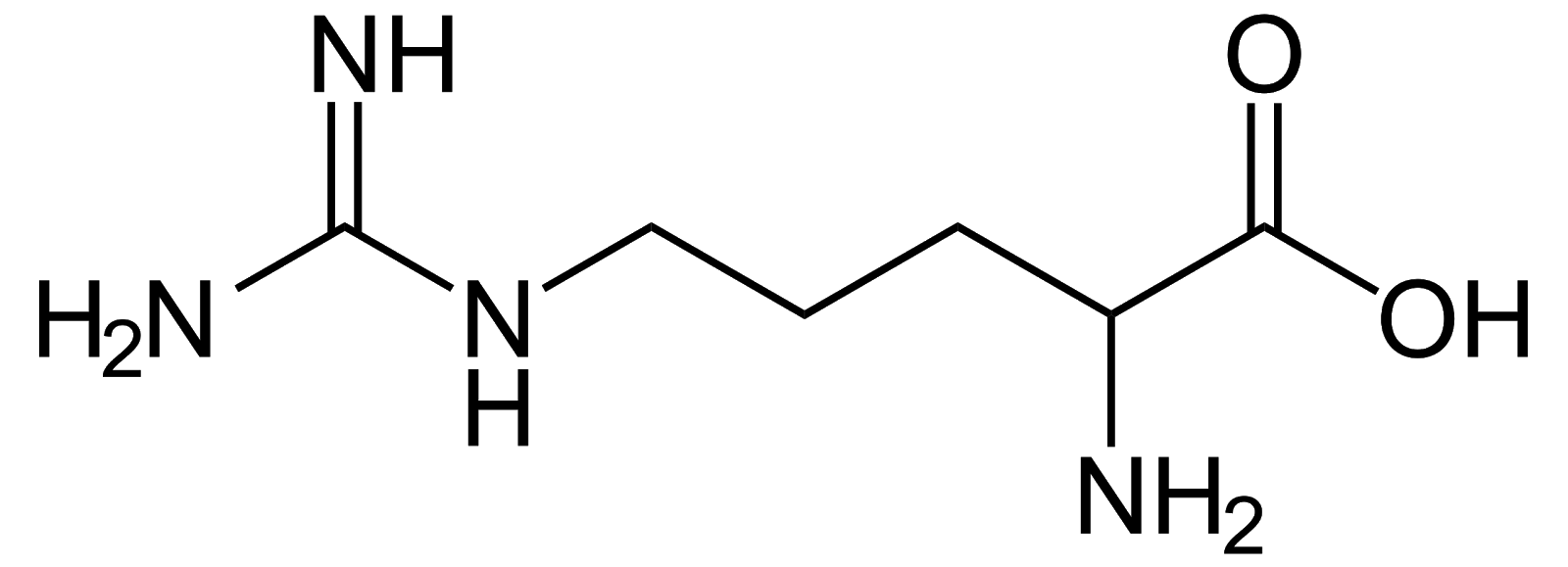
Arginine, Arg, R, basic/positively charged
Isomerase
An enzyme that catalyzes isomerization. It facilitates structural rearrangements.
Cofactor
A non-protein molecule that helps the enzyme carry out its biological functionality. Without these, enzymes remain within the inactive “apoenzyme” forms. Commonly in the form of a metal ion.
Gap junction
Intercellular channels that allow ions to diffuse between cells.
Beta oxidation
Process of breaking down a long-chain acyl-CoA molecule to acetyl-CoA molecules.
Triglyceride
Consists of 3 molecules of fatty acid combined with a molecule of glycerol. The major form of fat stored by the body.
Zymogen
Inactive forms of enzymes that must be cleaved to become active. e.g. trypsinongen to trypsin
Metabolism of proteins
Starts in the stomach, where enzymes break down proteins into amino acids. They are then transported into the bloodstream for circulation to the liver and cells throughout the body to create new proteins.
Tertiary protein structure
The 3D structures that result from interactions among the side chains of the amino acid residues of a protein. Many of these interactions are non-covalent charge-driven interactions.
Steroids
A category of lipid used for chemical signals and structurally supporting the cell membrane. Characterized by a 4 ring structure. Influence the membrane's fluidity.
Allosteric enzymes
Enzymes that have an additional site for an effector to bind to, as well as the active site. Binding of an effector changes the conformational ensemble.
Ketone bodies production and use
Produced from excess acetyl-CoA made during the oxidation of fatty acids. Serve as a fuel source if glucose levels are too low in the body.
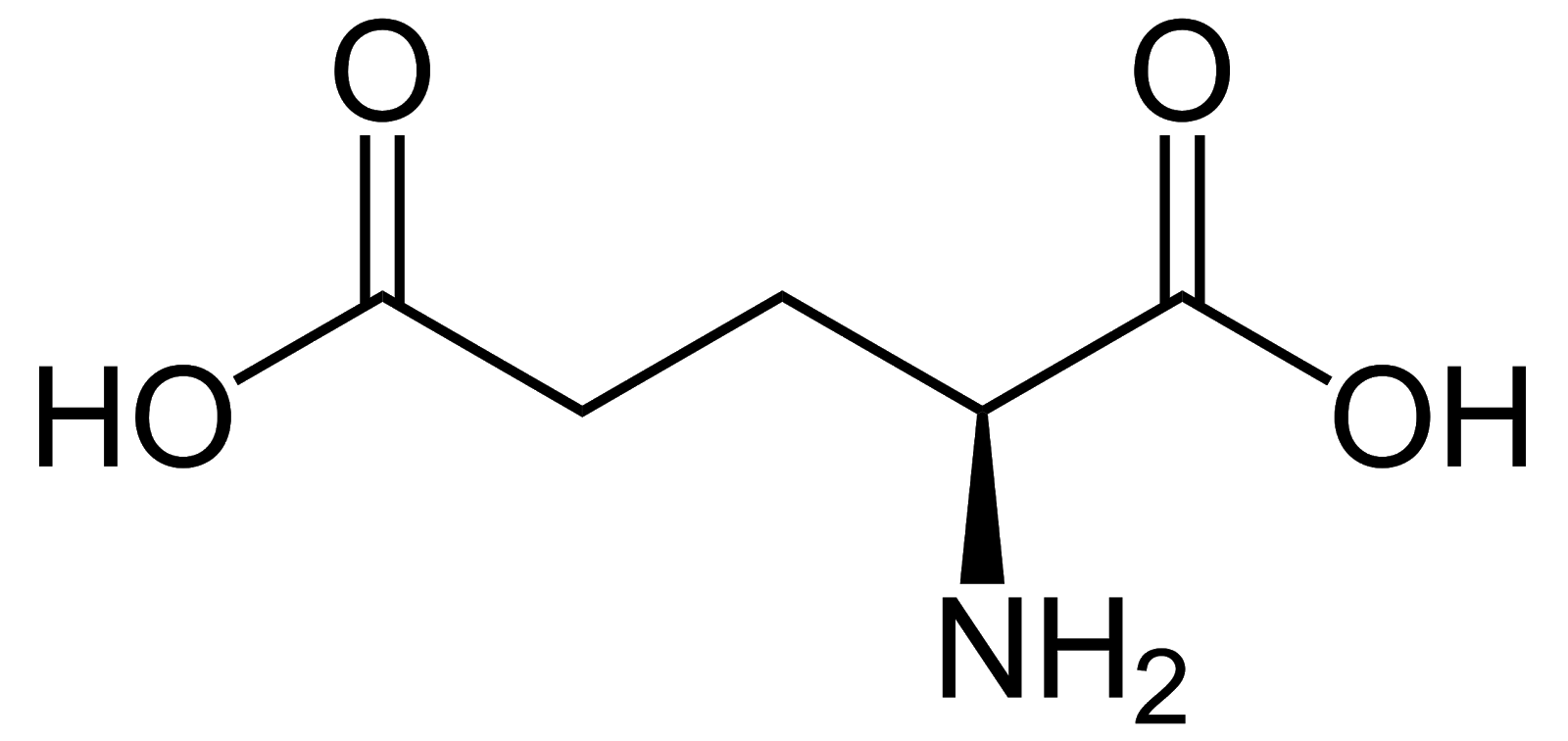
Glutamate, Glu, E, acidic/negatively charged, critical component of cellular metabolism
Tight junction
Closely associated areas (similar to Velcro) of two cells whose membranes join together to form a virtually impermeable barrier to fluid.
4 steps of beta oxidation
Dehydrogenation, hydration, oxidation, and thyolisis.
Water-soluble electron carriers
Refers to NAD+, FAD, NADPH, and NADP+. Play important roles during cellular respiration.
Pinocytosis
Type of endocytosis. Process by which liquid droplets are ingested by cells.
Adipocyte
Cells that primarily compose adipose tissue, specialized in storing energy as fat.
Effects of pH on enzyme activity
Increased or decreased pH from the optimal pH reduces enzyme activity.
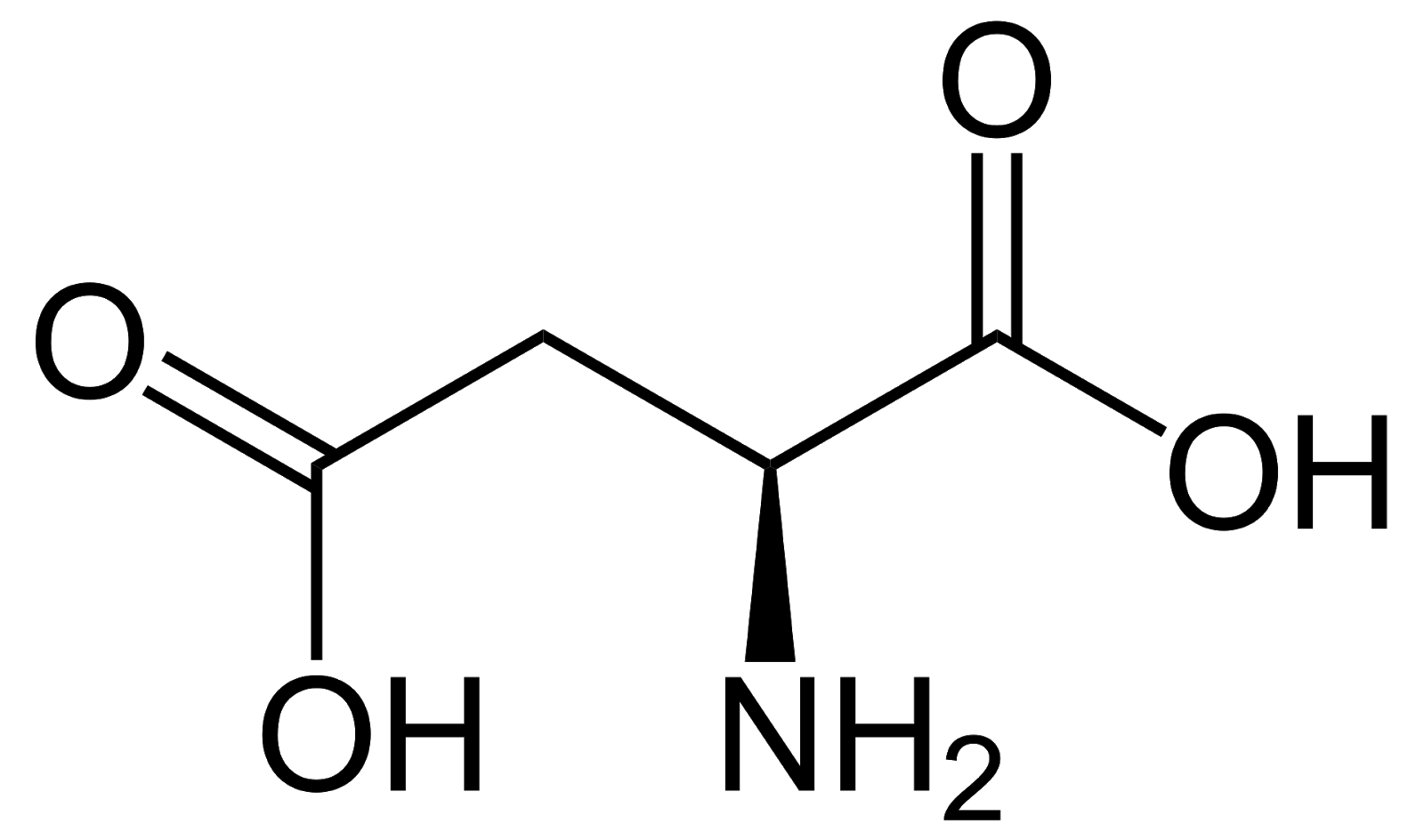
Aspartate, Asp, D, acidic/negatively charged
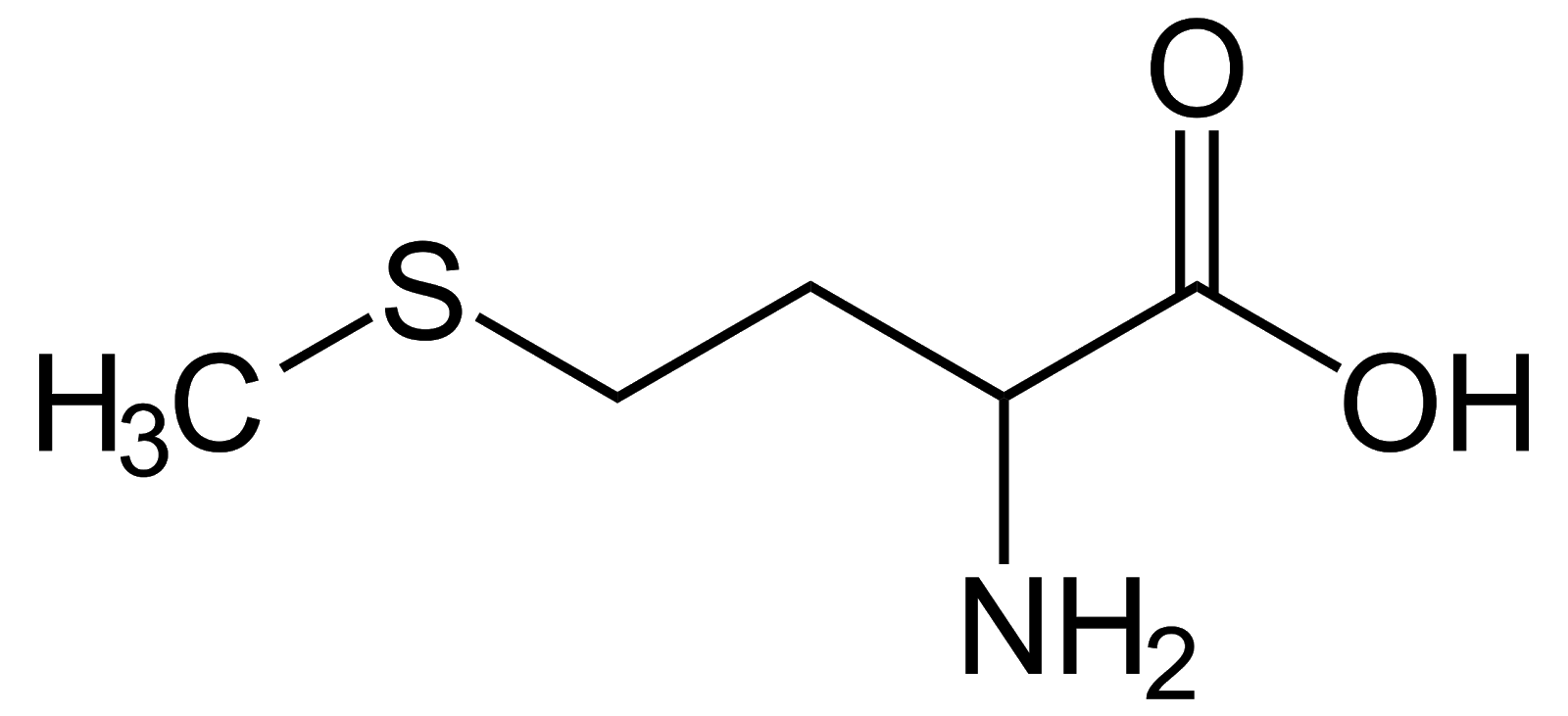
Methionine, Met, M, non-polar, one of two amino acids with sulfur
Fatty acid activation
Process in which a CoA molecule is added to the fatty acid to produce acyl-CoA, converting ATP to AMP in the process.
Motor proteins
Include kinesins, dyneins, and myosins. Structural proteins that generate mechanical force as a result of undergoing conformational changes.
Function of enzyme
Enzymes are biological catalysts that speed up the rate of a reaction by reducing the activation energy.
Induced-Fit Model
Suggests that an enzyme, when binding with its substrate, optimizes the interface through physical interactions to form the final complex structure. Explains the protein conformational changes in the binding process.
Citric acid cycle
A cycle of reactions involved in the oxidation of acetyl-CoA and the formation of reduced soluble electron carriers and high-energy molecules (GTP).
Products of one round of the citric acid cycle
2 carbon dioxide molecules, 1 GTP or ATP, 3 NADH, and 1 FADH2.
Exocytosis
Process in which intracellular vesicles in the cytoplasm fuse with the plasma membrane and release their contents into the extracellular space.
Protein solvation layer effect
Protein folding is largely dictated by the entropy of surrounding water.
Phospholipids
Has a hydrophillic head made of glycerol and a phosphate group, and a tail made of two fatty acids. Forms a bilayer in plasma membranes.
Electron transport chain steps
Redox of NADH at Complex I and Redox of FADH2 at Complex II -> Redox of Complex III -> Redox of Complex IV -> ATP synthase action
Oxidative phosphorylation
A transfer of electrons from soluble electron carriers (NADH and FADH2) to oxygen; the energy released in the process is used to form ATP.
Integral protein
Protein that is permanently attached to the biological membrane. Functions include channeling or transporting molecules across the membrane and acting as cell receptors.
Squalene
The precursor of steroids. A terpene that consists of 6 isoprene subunits.
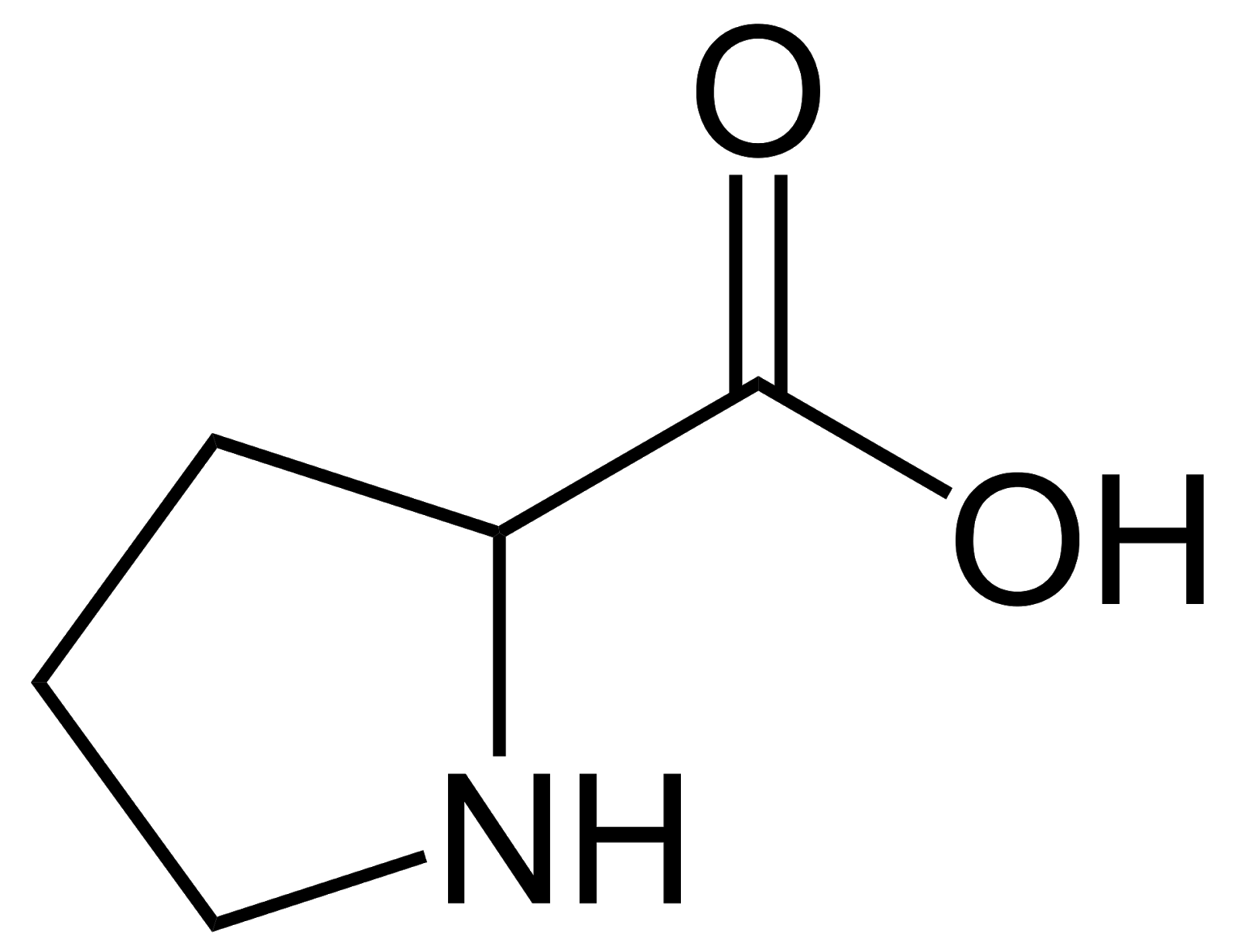
Proline, Pro, P, non-polar, has a cyclic structure in the side chain and a secondary amino group alpha to the carboxyl group.
Lipase
An enzyme that breaks down triglycerides into free fatty acids and glycerol.
Anabolism of fats
The synthesis of fatty acids from acetyl-CoA through elongation steps, increasing by two carbons each time.
Mixed inhibition
Involves an inhibitor binding the ES complex or a free enzyme at an allosteric site. Vmax is decreased. The effect on Km depends on the binding preference of a given inhibitor. If a mixed inhibitor prefers to bind the free enzyme, Km is increased. If a mixed inhibitor prefers to bind the ES complex, its overall effect can be thought of as similar to that of an uncompetitive inhibitor, and Km will be decreased.
Effect of temperature on enzyme activity
When the temperature is increased, the activity of an enzyme is increased. But an excessive rise in temperature can cause denaturation of the enzyme.
Desmosome
Adhesive protein complexes that localize to intercellular junctions and are responsible for maintaining the mechanical integrity of tissues.
Voltage gated ion channel
Channels that open or close in response to a change in membrane potential.