lab exam1
1/174
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
175 Terms
sympathetic nervous system
"fight or flight"
controls many organs all over the body
has sole control over arrector pili muscles, adrenal glands
parasympathetic nervous system
"rest and digest"
controls many organs all over the body
has sole control of lacrimal glands
sympathetic trunk/chain ganglia
Runs along vertebrae, part of the sympathetic nervous system, keeps whole body in sync
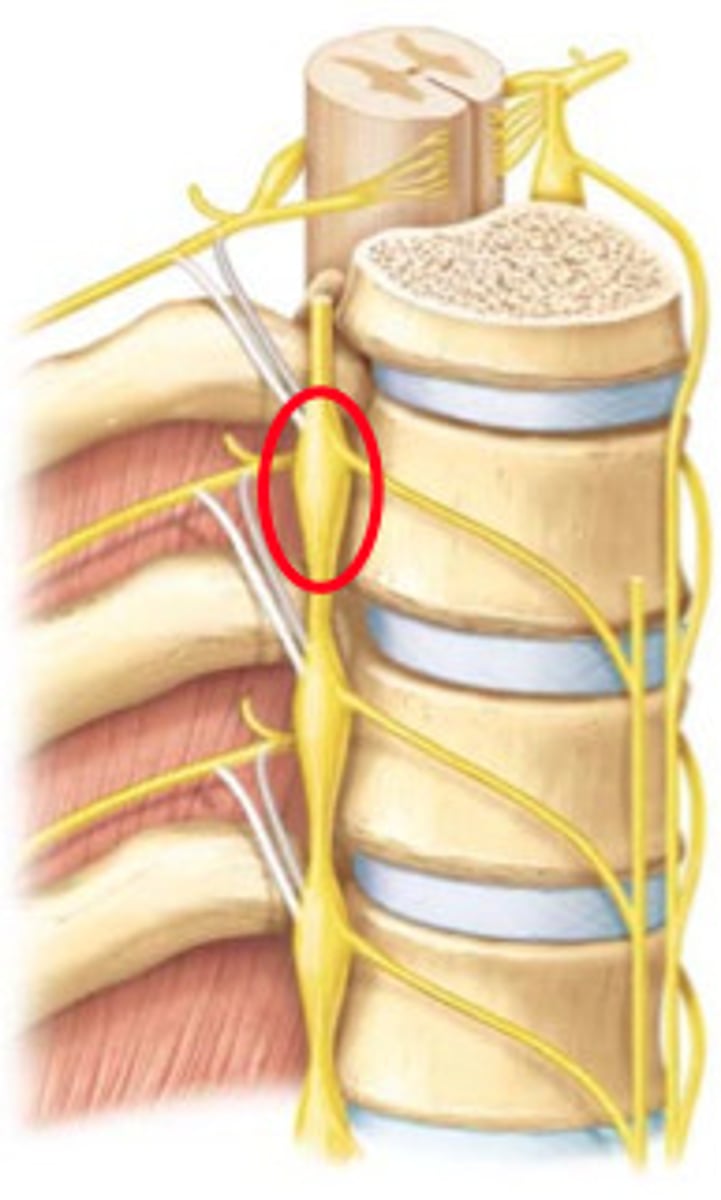
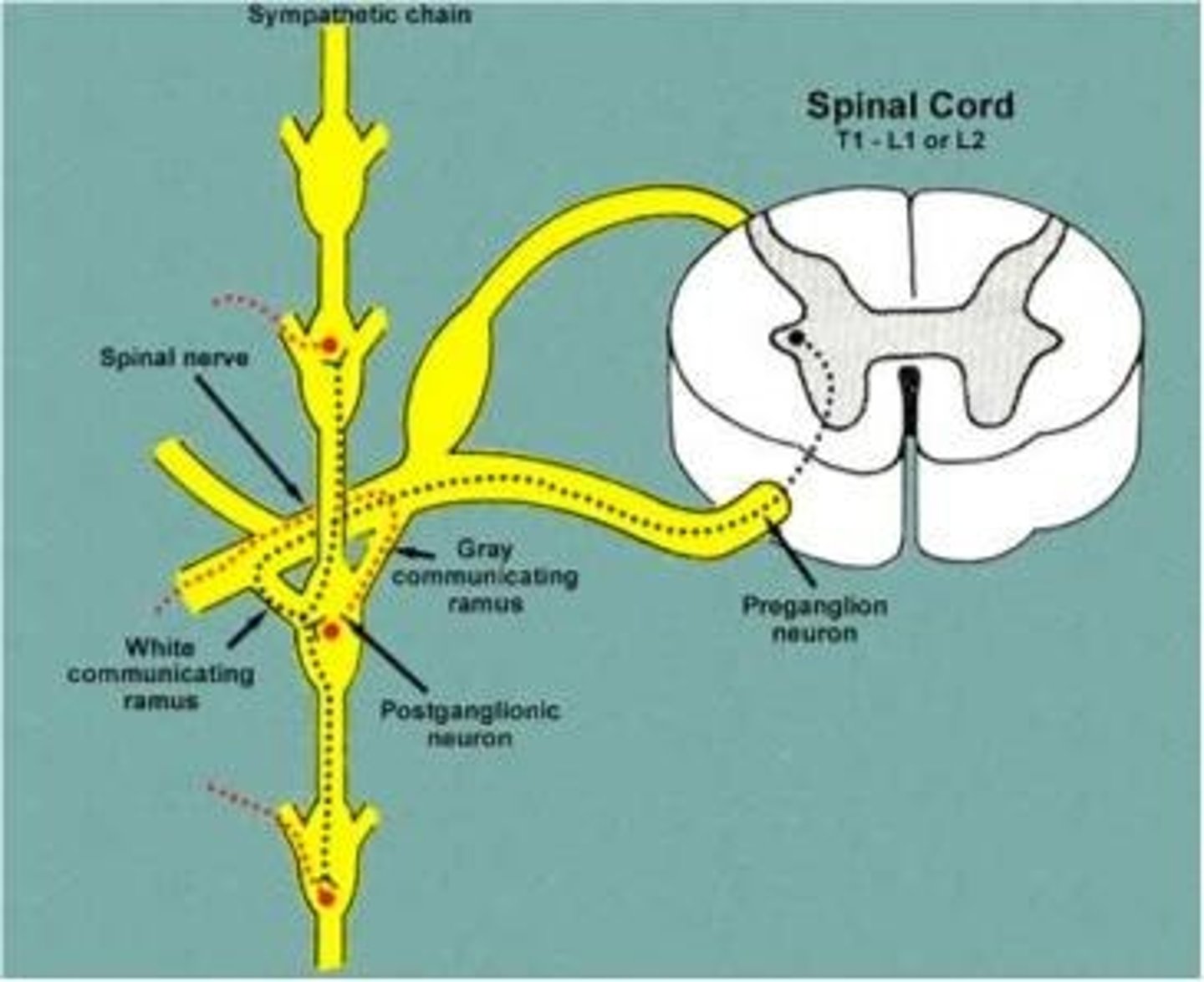
White rami communicans
contain myelinated preganglionic fibers traveling to sympathetic trunk ganglia
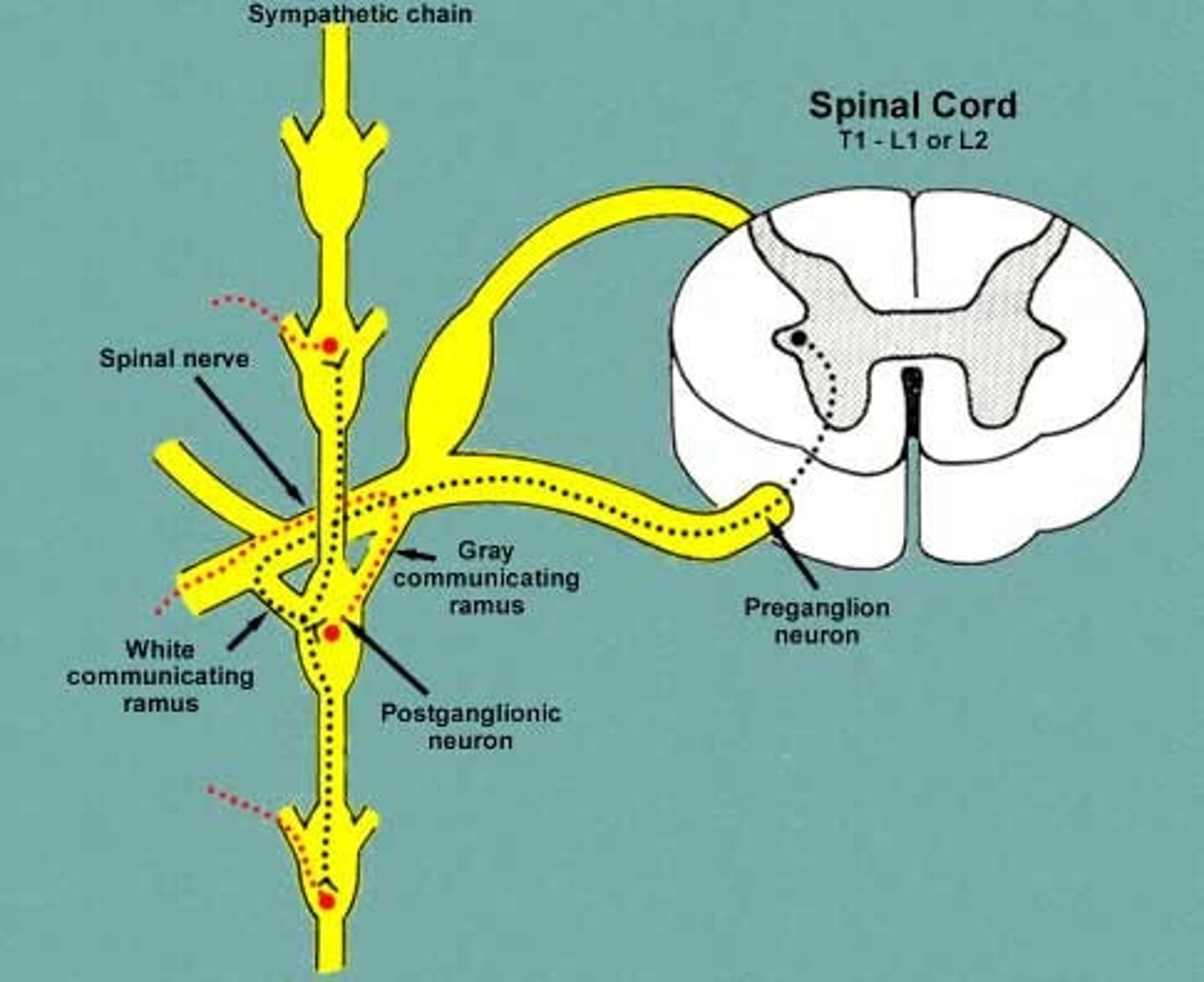
gray rami communicans
contain unmyelinated postganglionic fibers traveling from ganglia to peripheral structures
general senses
somatic and visceral senses - temperature, pain, touch, pressure, vibration, proprioception
special senses
sight, hearing, smell, taste, balance
nociceptor
pain receptor (free dendritic ending) - tonic
thermoreceptor
detects heat, changes in temperature, rates of conduction (free dendritic endings)
mechanoreceptors
detect mechanical deformation of cell membranes - pressure, vibration, deep touch
tactile receptors
mechanoreceptors, associated with touch
baroreceptor
a sensory receptor that responds to changes in pressure, monitors blood pressure
proprioceptor
stretch receptor - are joints bent or straight
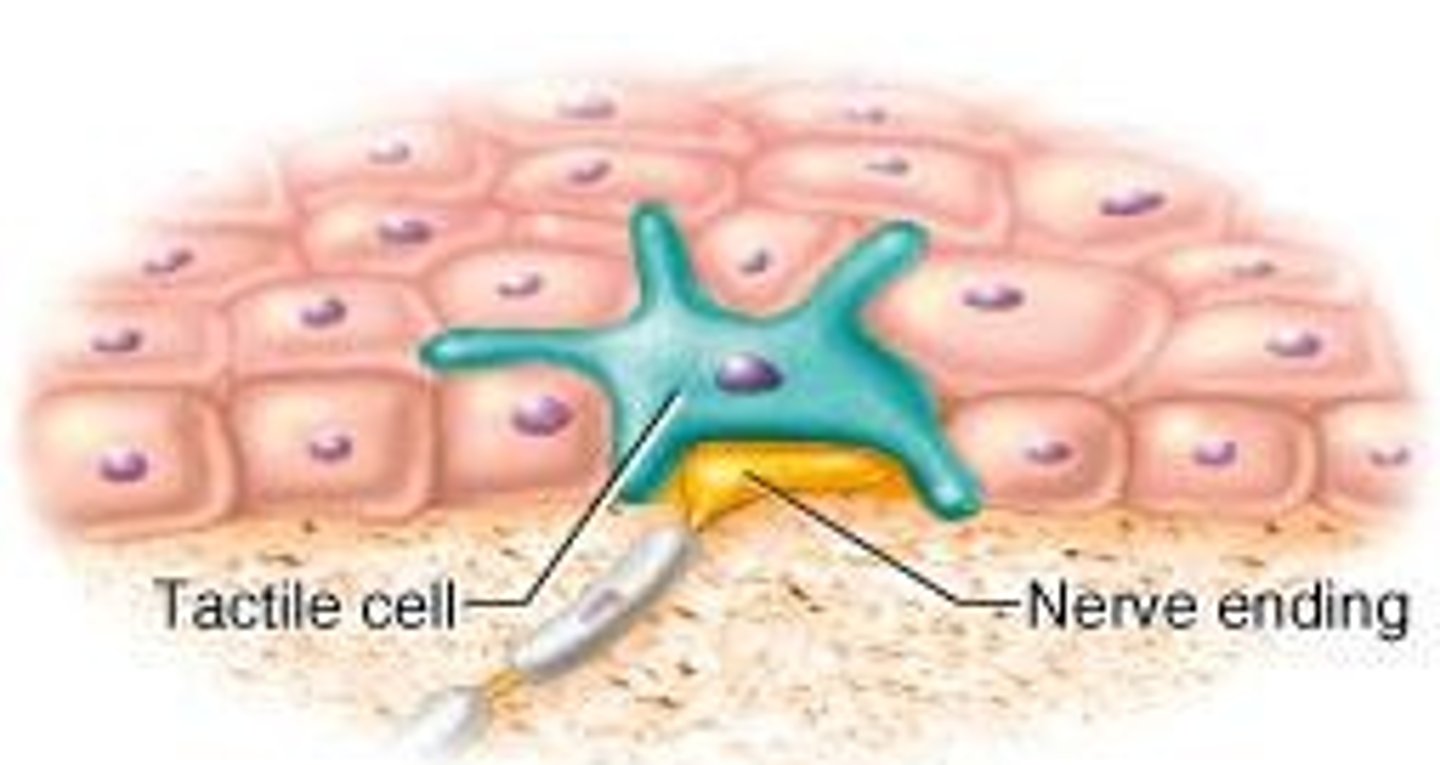
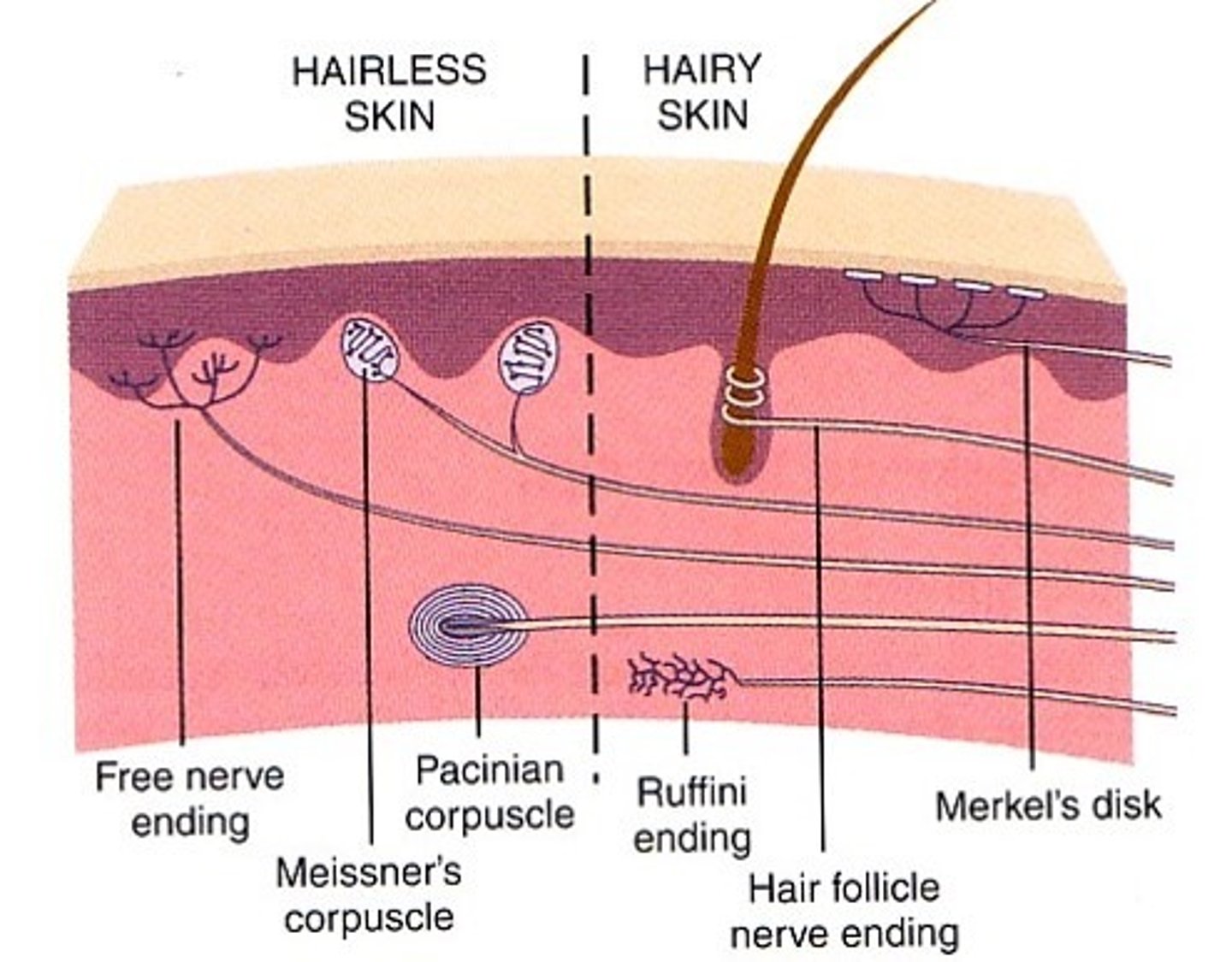
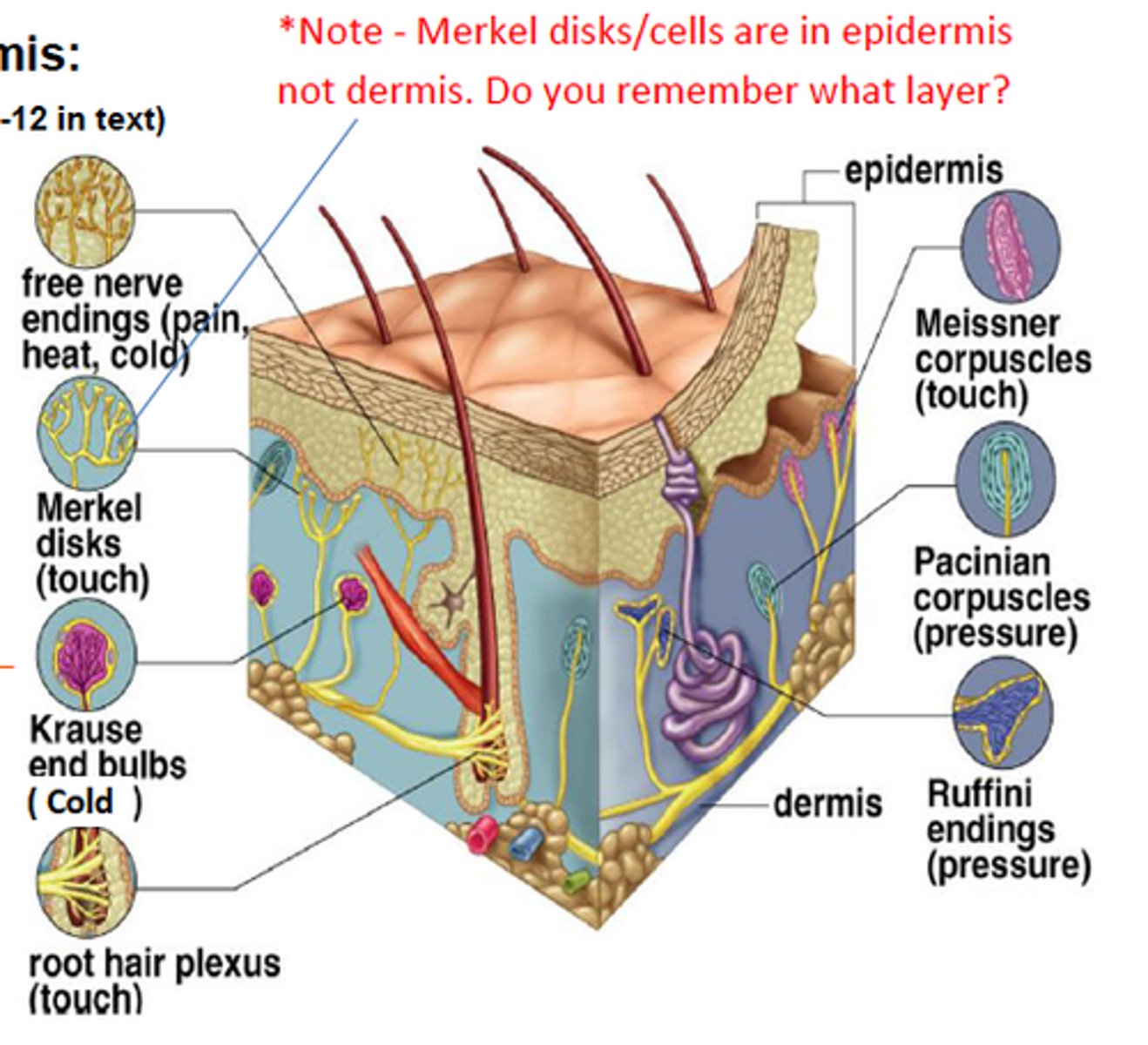
tactile (merkel) discs
located at the border of dermis/epidermis - detect light touch, free dendritic endings, phasic/fast adapting, concentrated in hands and face
free nerve endings
bare dendrites - pain, temp, tickle, light touch
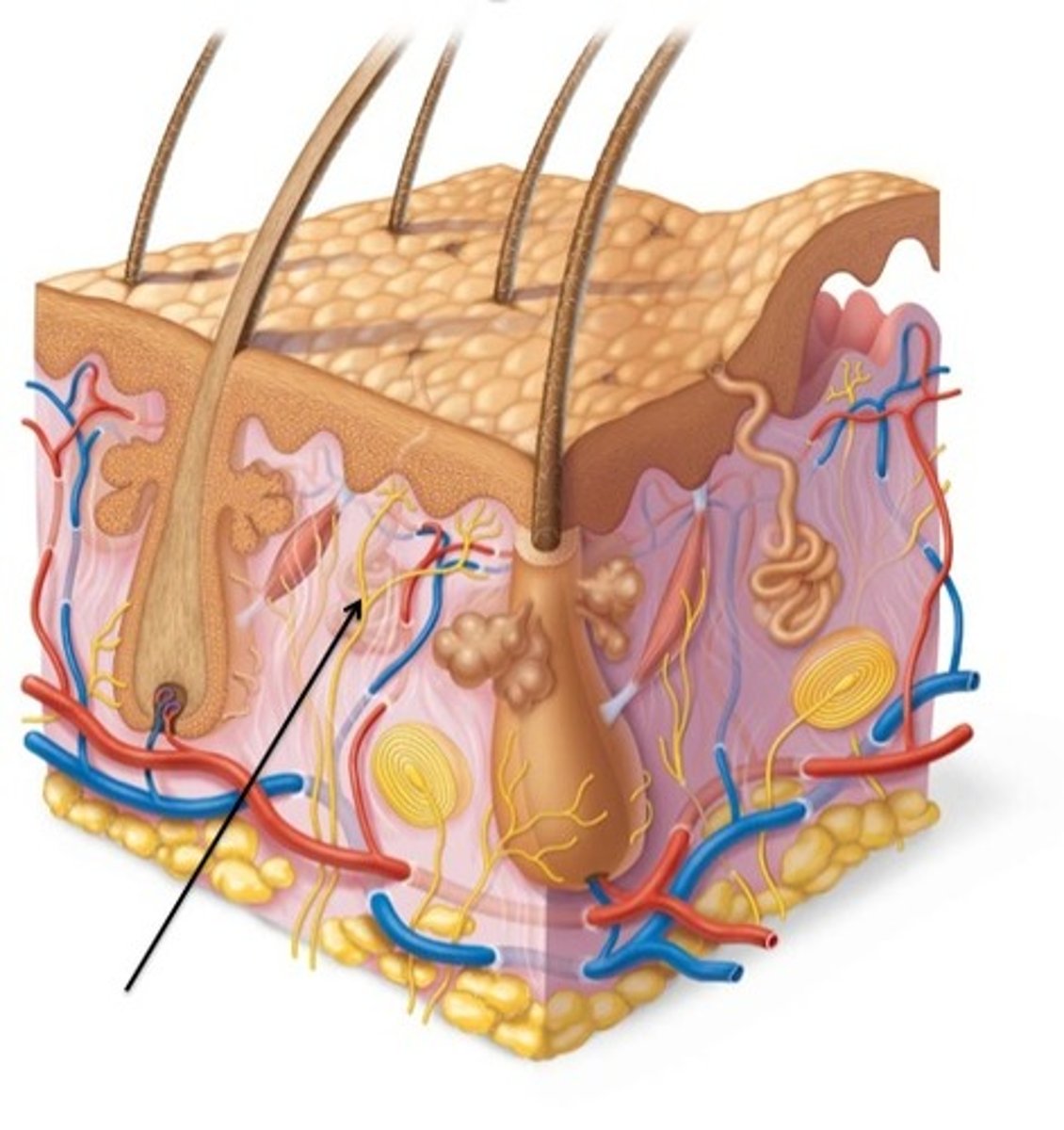
hair root plexus
track/sense hair movement
Free dendritic endings, phasic/fast-adapting, only absent in palms and soles, exteroreceptor
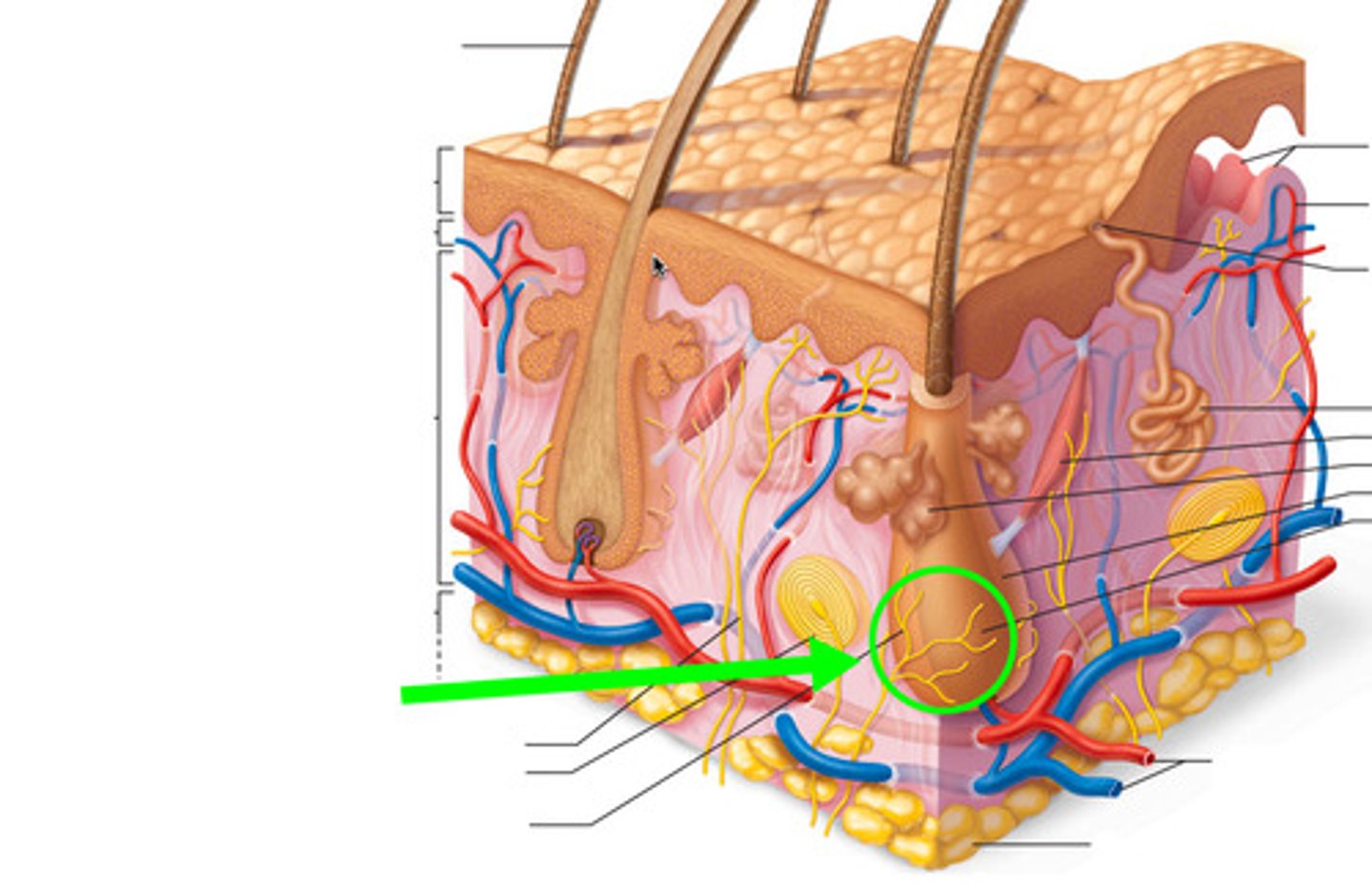
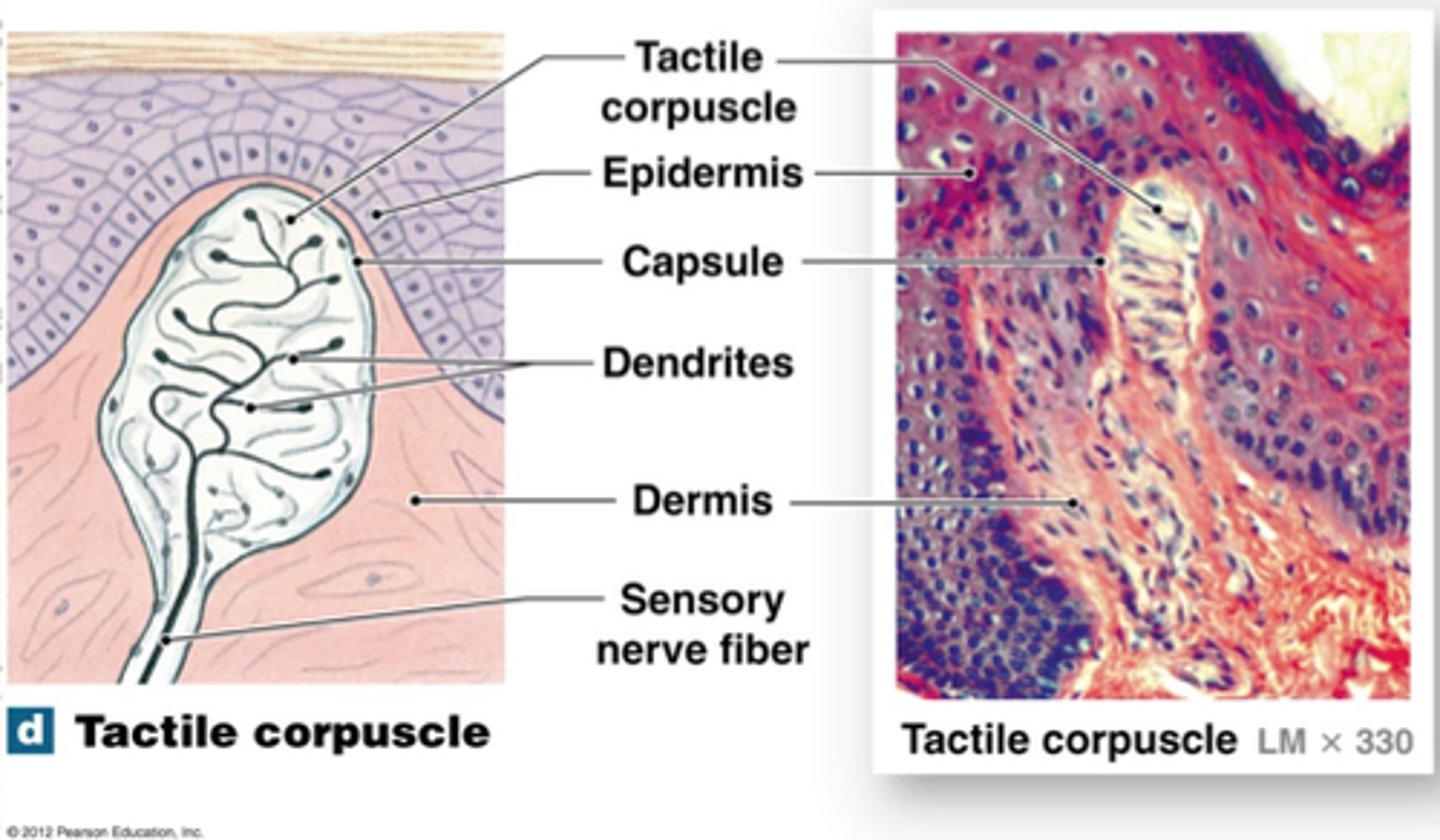
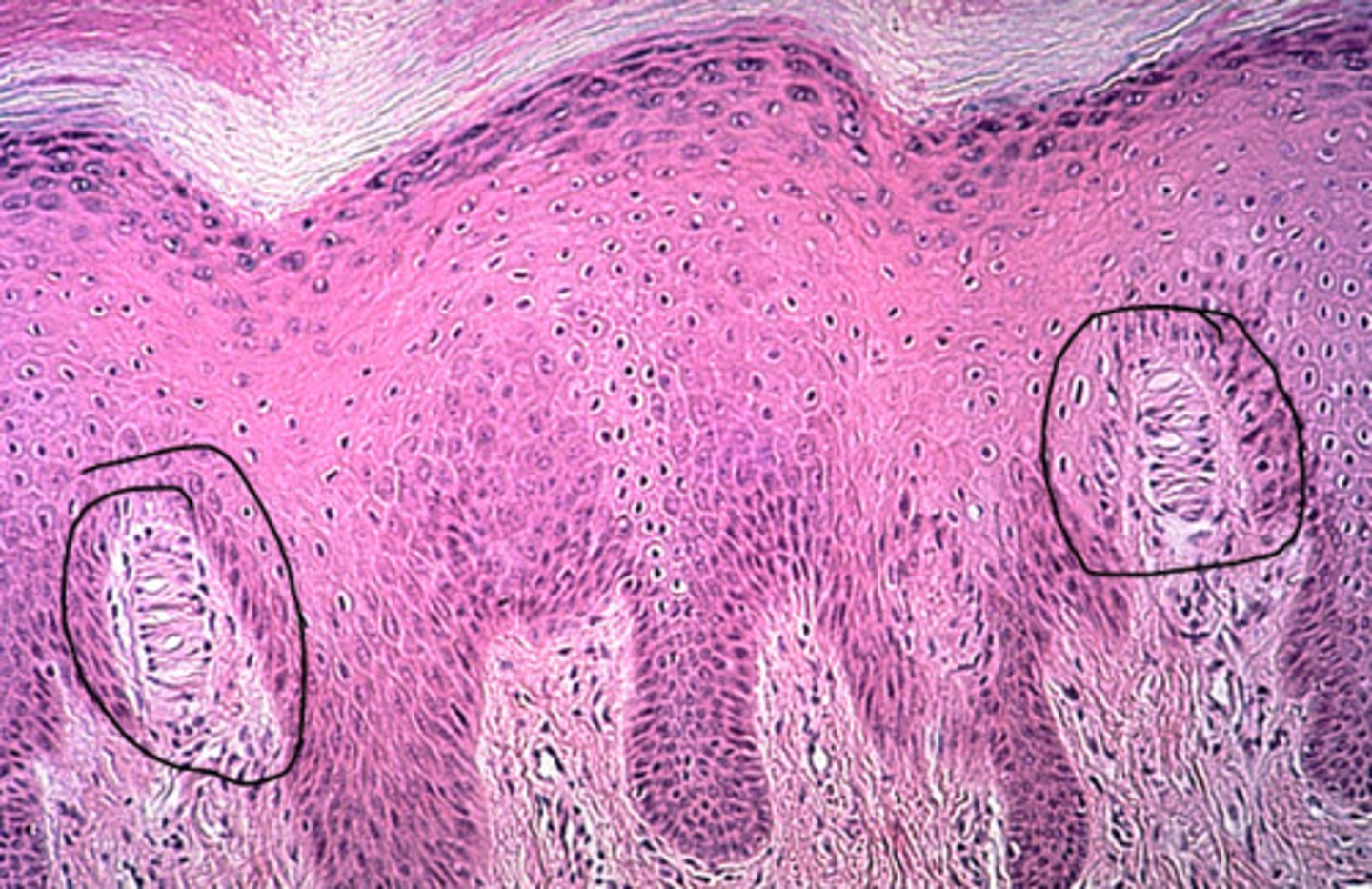
Tactile (Meissner's) corpuscles
in the dermal papillae, detect fine touch, fast adapting/phasic, concentrated in face, fingers, and genitals, exteroreceptor
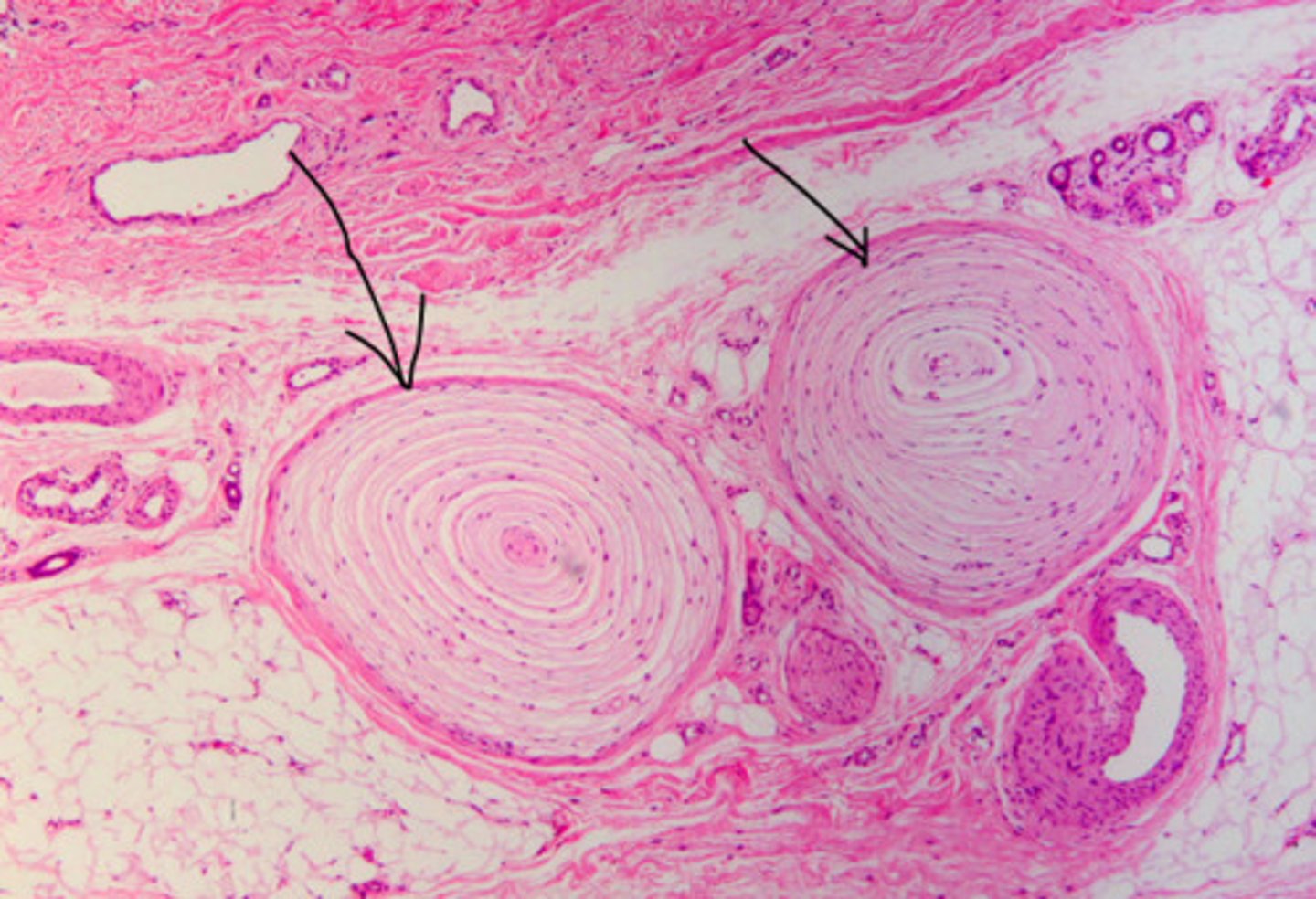
lamellated (pacinian) corpuscles
in dermis, detect deep touch
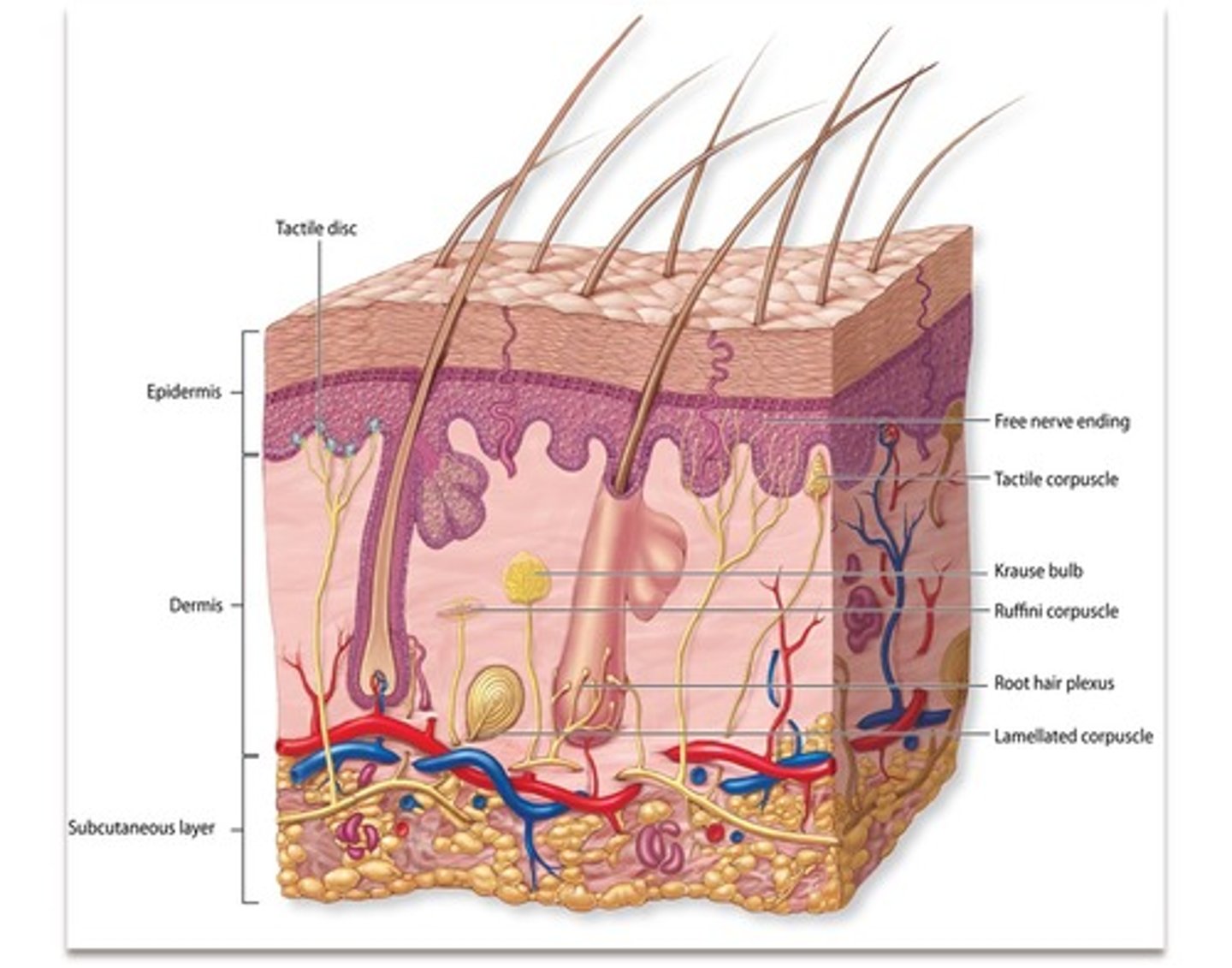
Ruffini's (Bulbous) corpuscles
detect position of joints, heavy/continuous touch, pressure, tonic. Located in deep dermis, all over body.
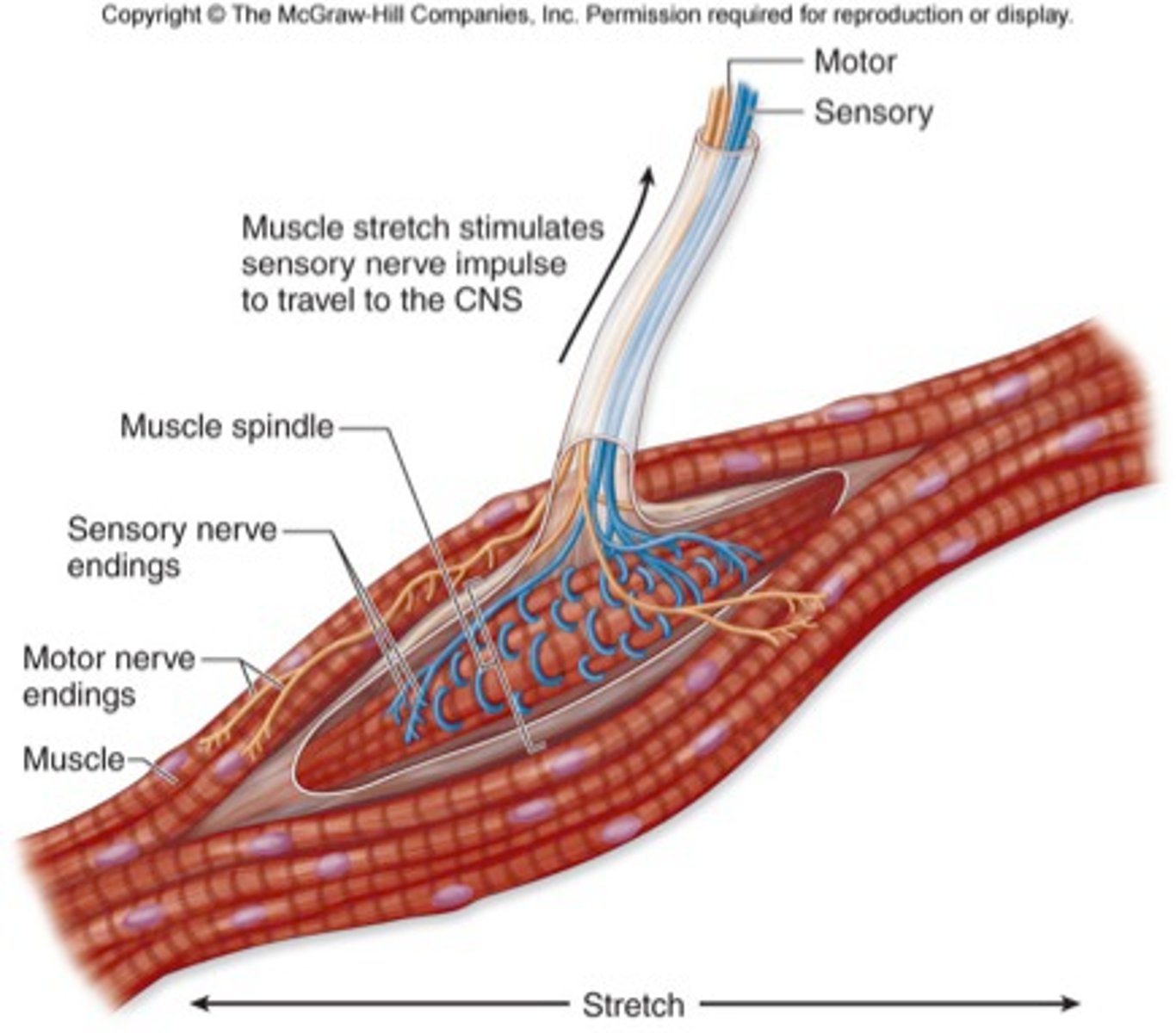
Muscle spindles
Proprioceptors that detect the rate and degree of muscle stretch
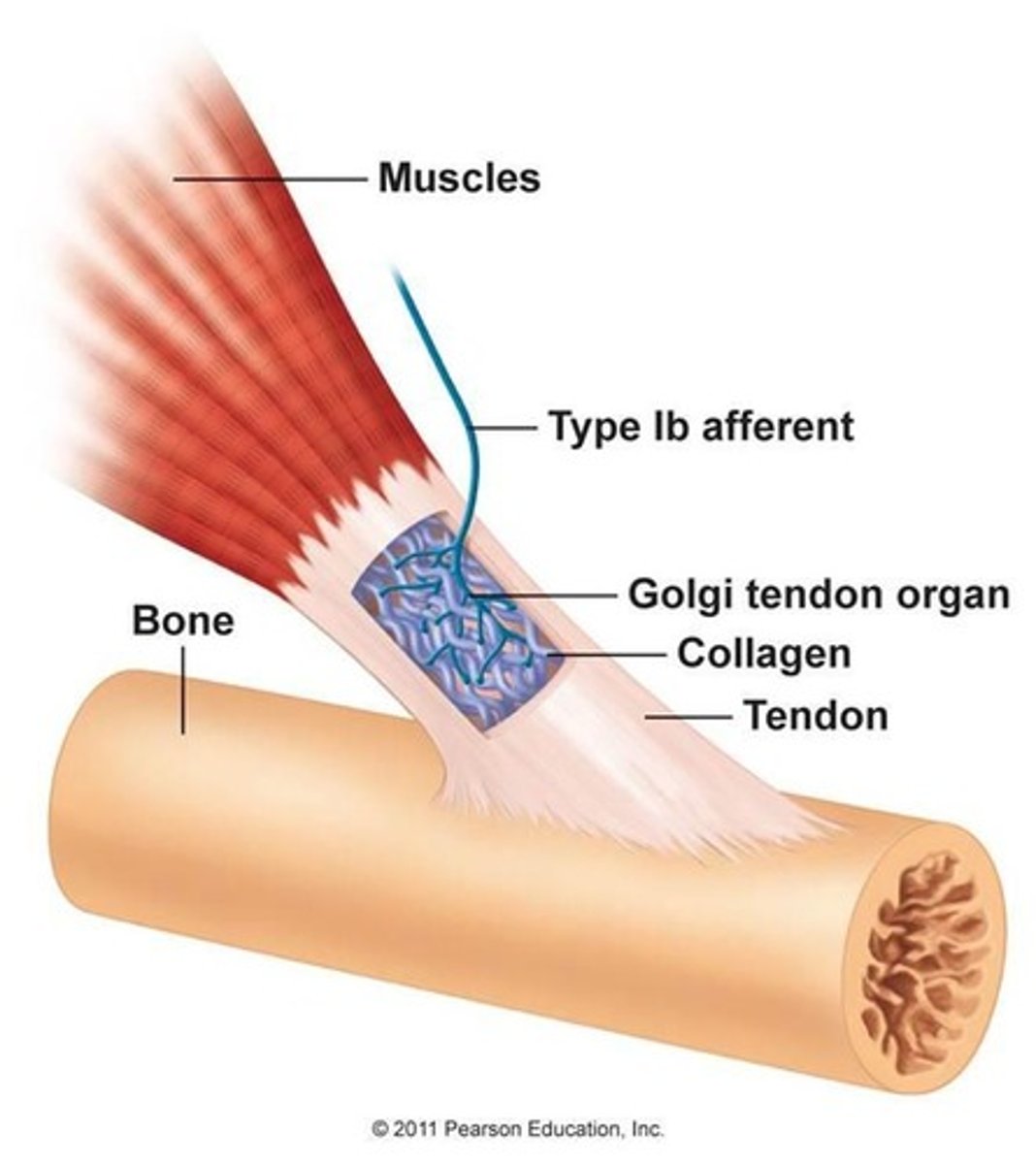
Golgi tendon organ
monitors tension in tendons, found at junction of tendon and muscle, prevents over-stretching/ripping by forcing action of antagonist/forcibly relaxing muscles
End Bulbs of Krause
encapsulated mechanoreceptor, tonic, found all over the body but highly concentrated in upper lip, responsible for mammalian dive reflex
lamellated/pacinian corpuscle
tactile/meissner's corpuscle
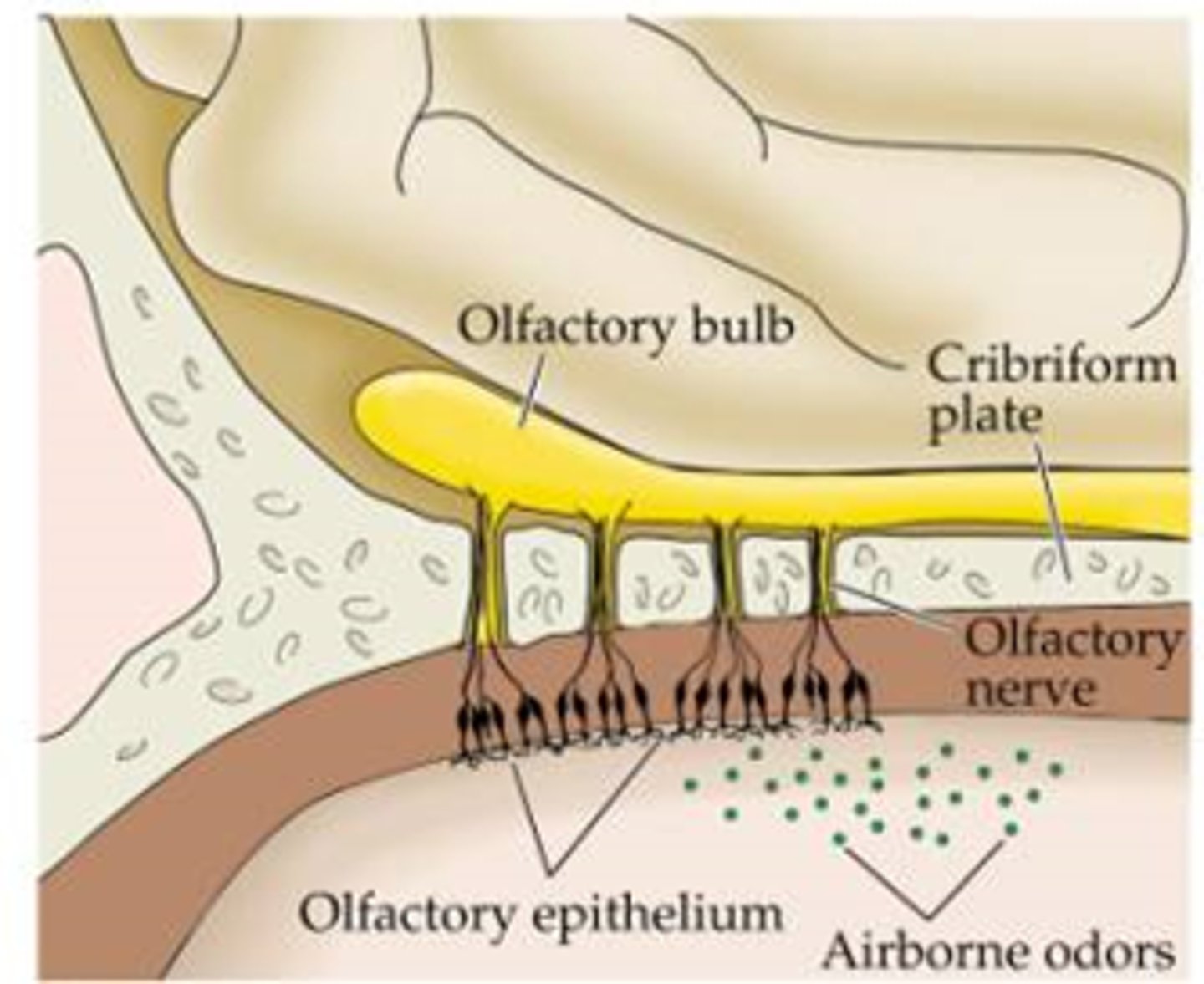
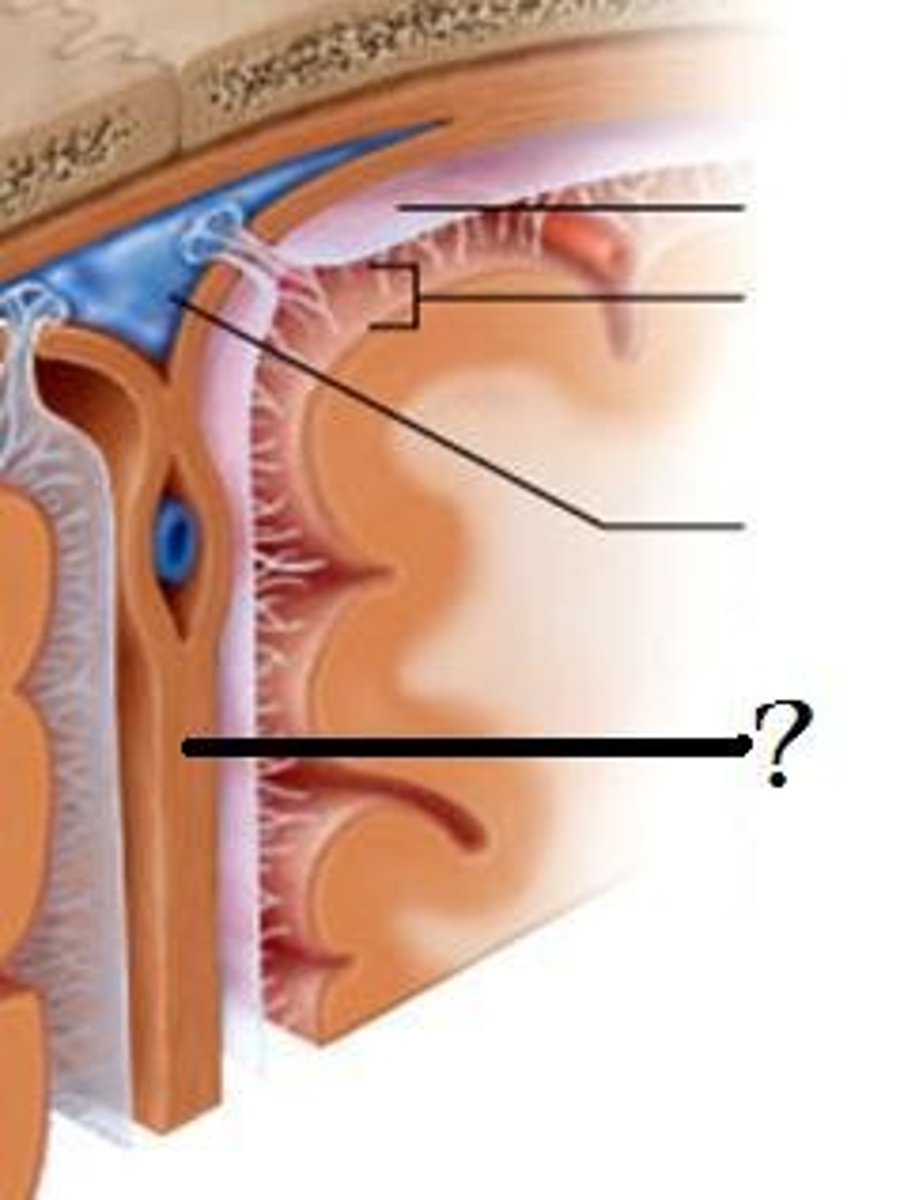
Olfactory (Bowman's) gland
produce the mucous that dissolves odorants to help you smell
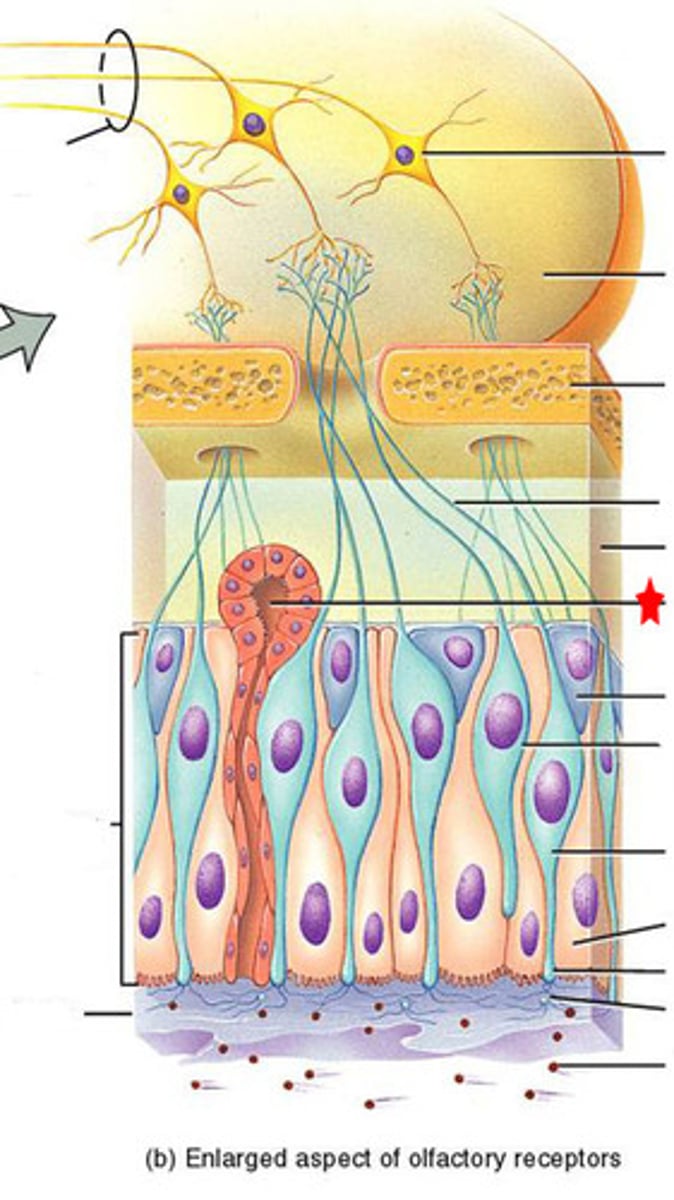
Olfactory neuron (receptor cell)
bipolar, ciliated neurons, contain binding sites for odor molecules, axons pass through cribriform plate, get replaced every 60 days
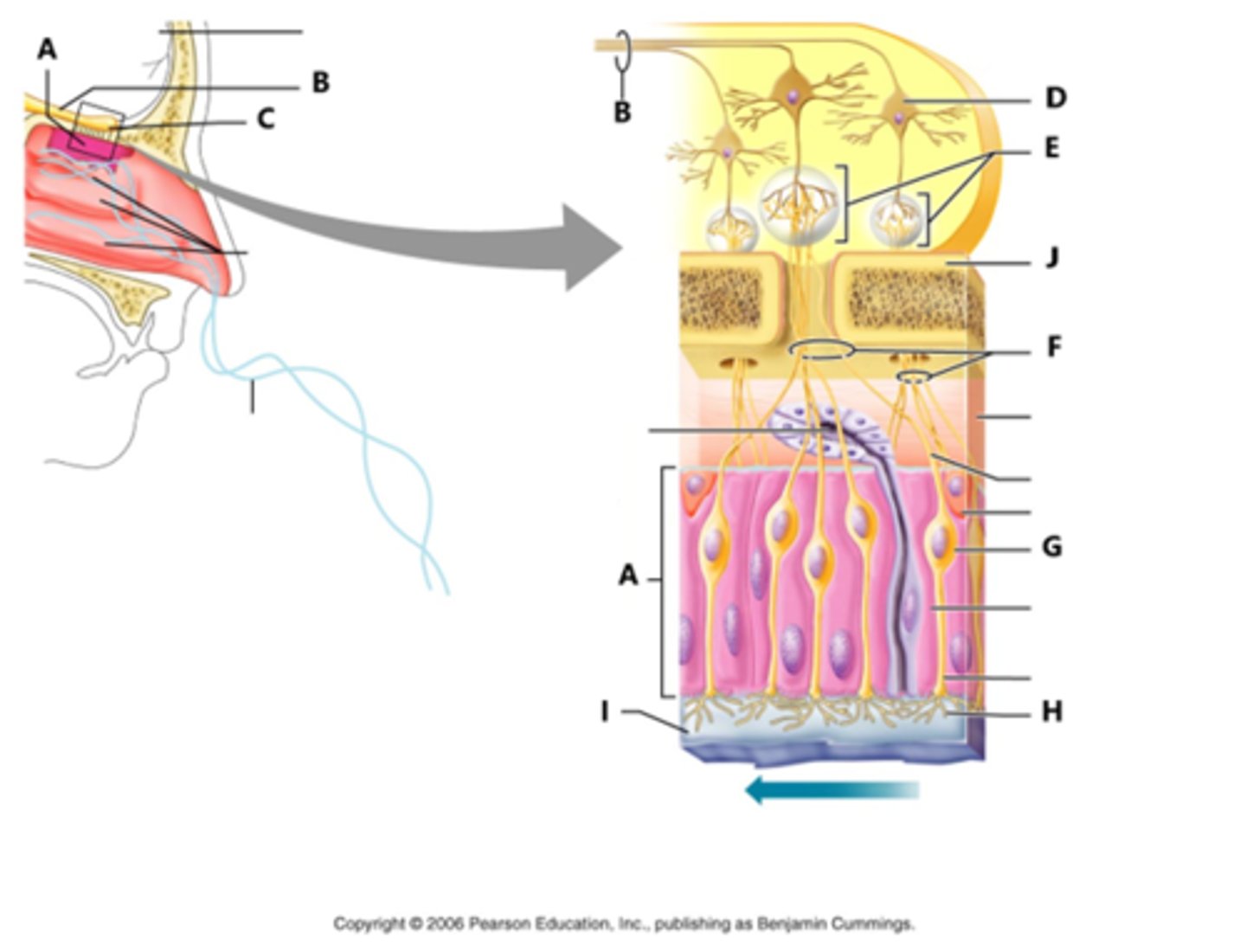
supporting cells (olfaction)
protect olfactory neurons
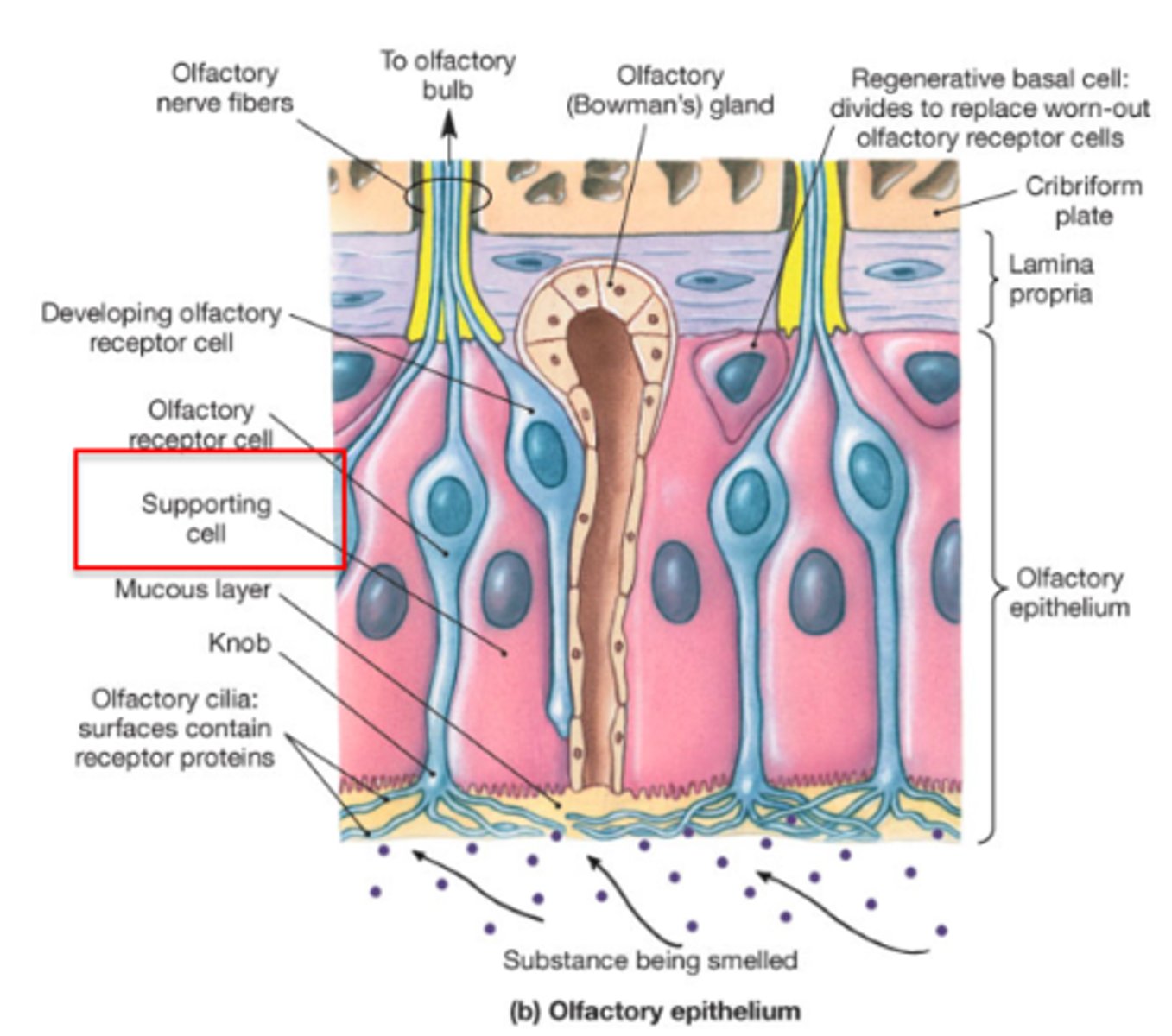
Olfactory nerves
olfactory axons in PNS
olfactory tract
olfactory axons in the CNS
olfactory bulb
the end of the olfactory tract
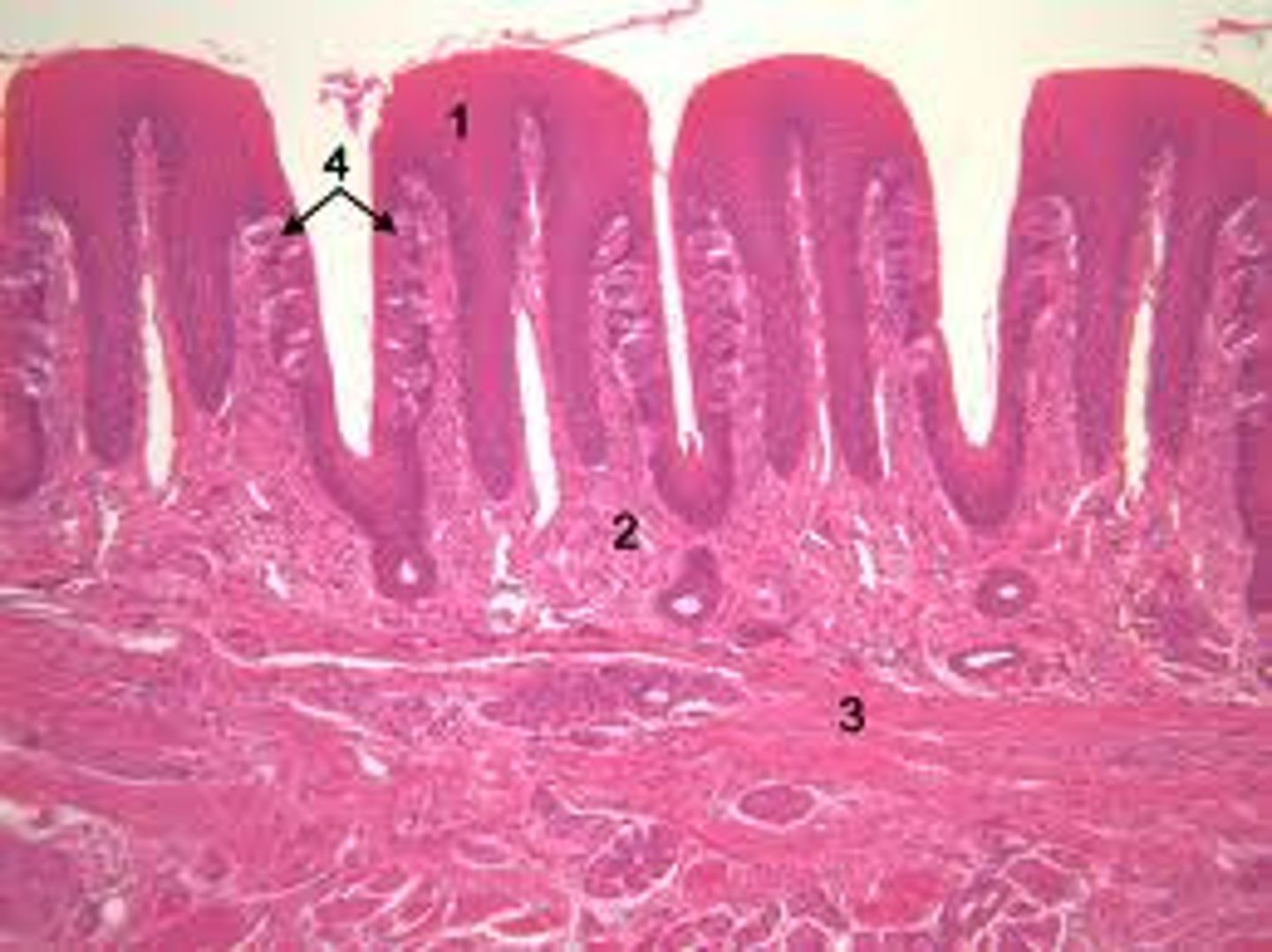
circumvallate papillae
large papillae at the rear of tongue, associated with taste buds
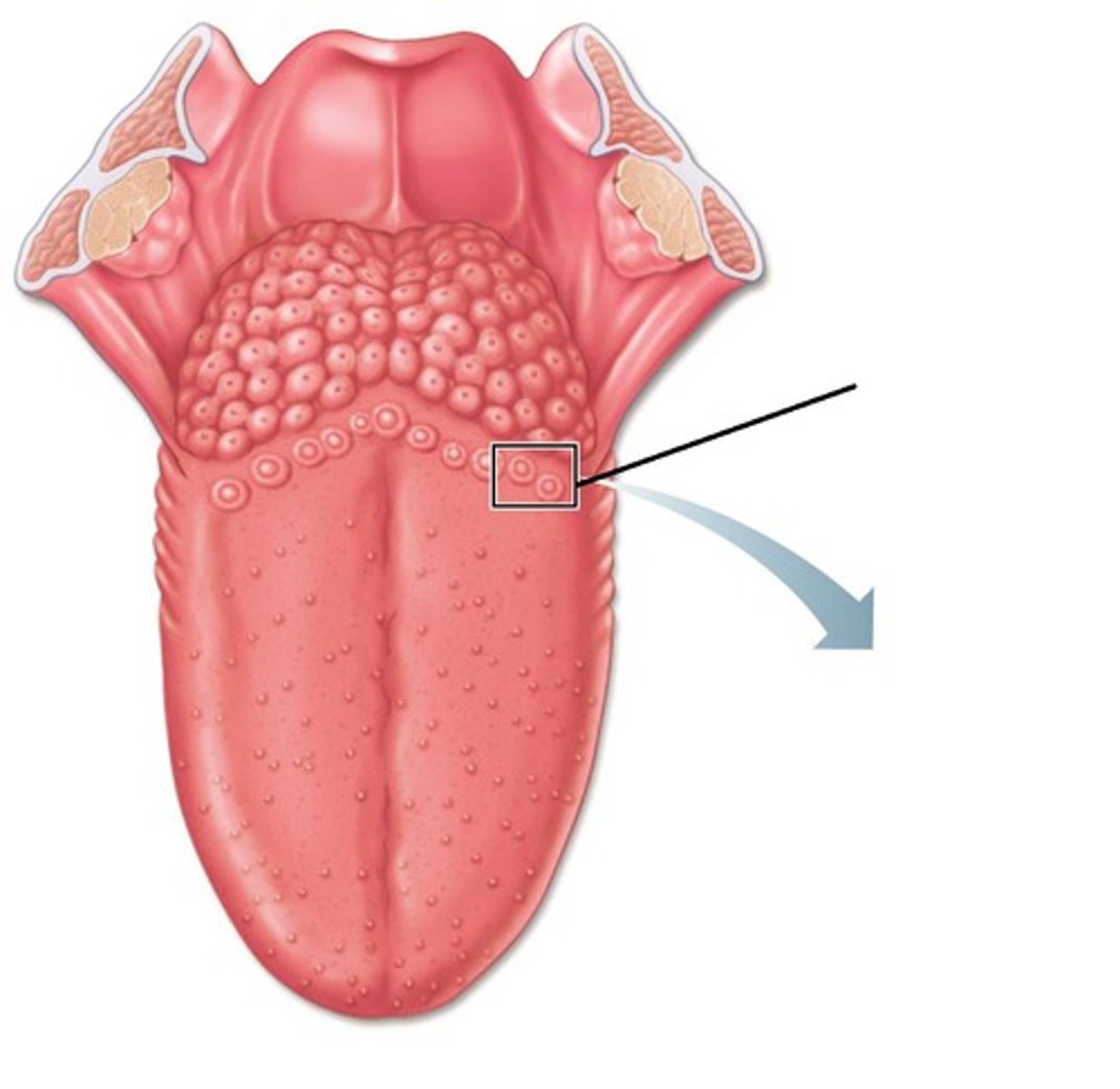
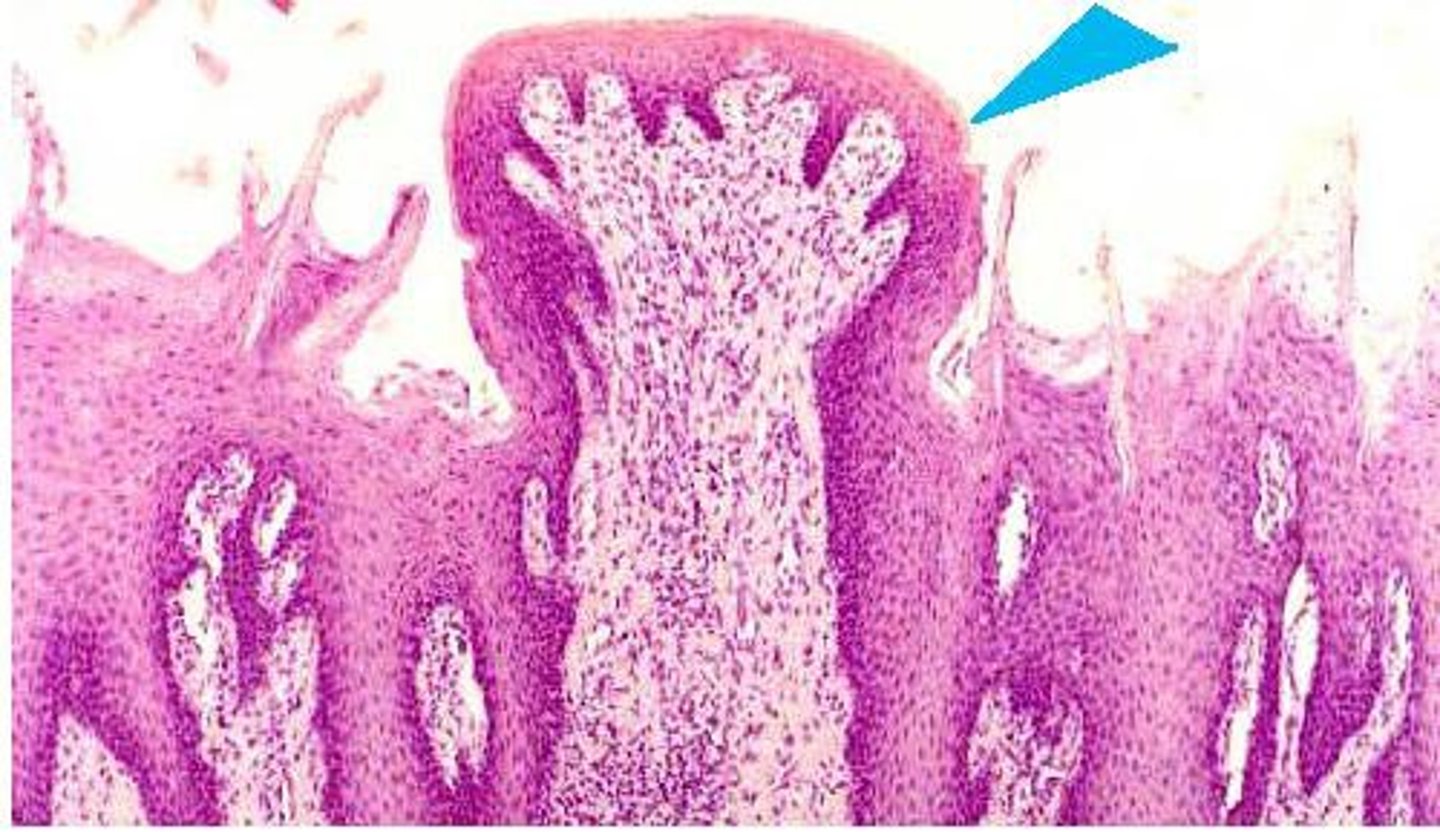
fungiform papillae
scattered over tongue, concentrated at tips and lateral sides, look like a mushroom
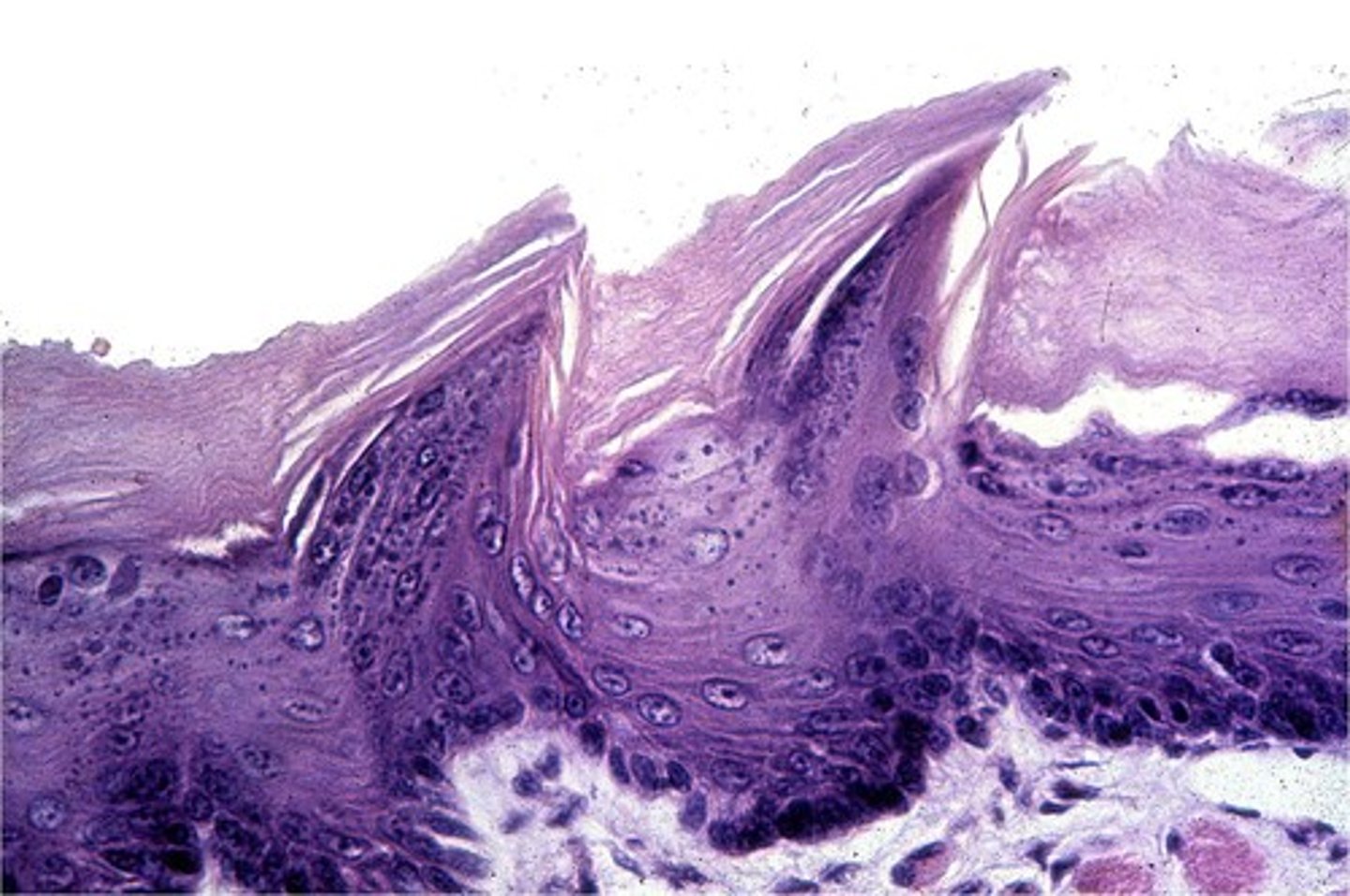
filiform papillae
no taste buds, detect texture
foliate papillae
all over tongue, concentrated on the lateral sides
what are the five primary tastants?
salty, sweet, bitter, sour, umami, water
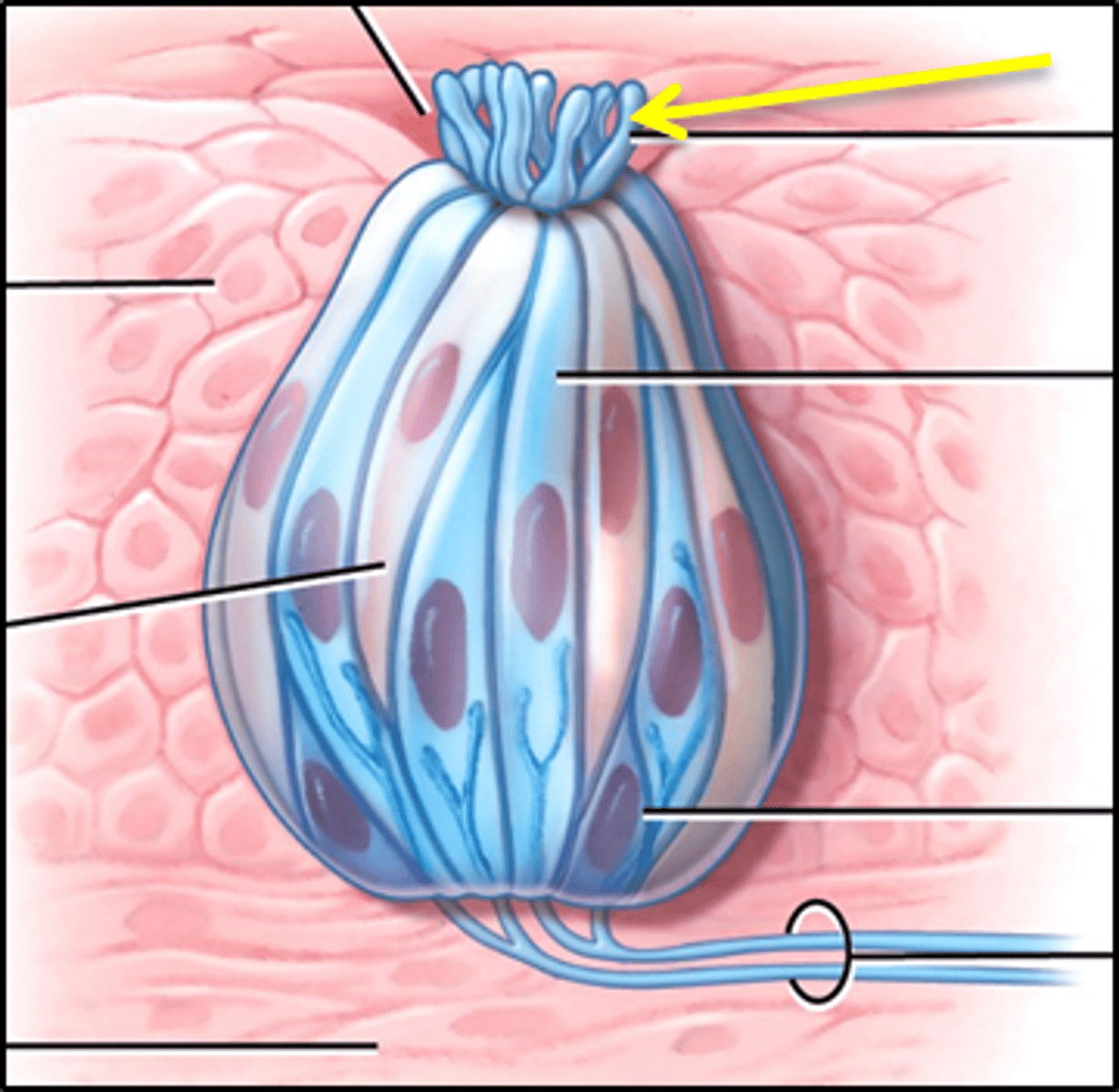
taste pore
opening in taste bud
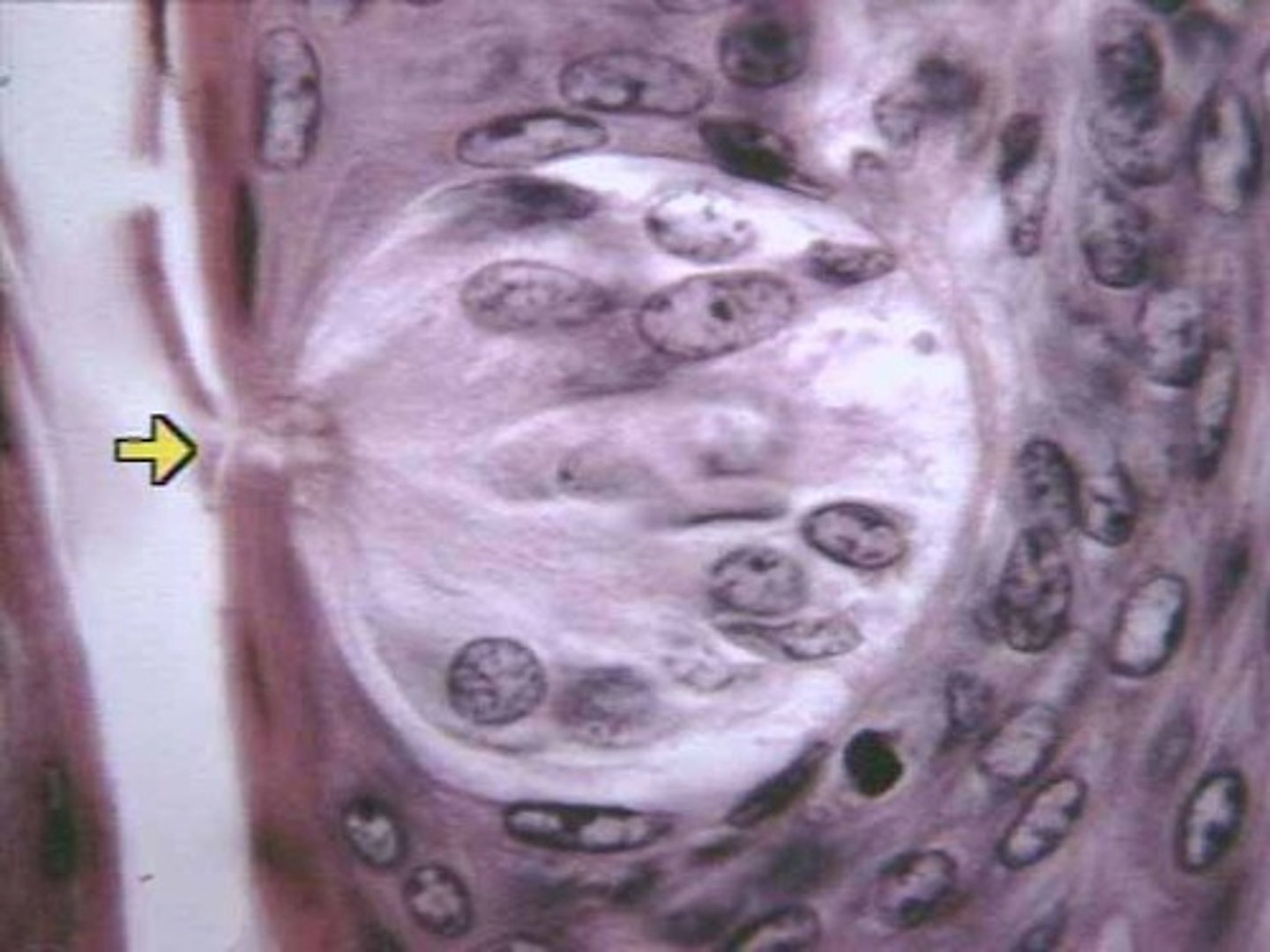
gustatory receptor cells
sensory cells in the taste bud that transduce the chemical stimuli of gustation
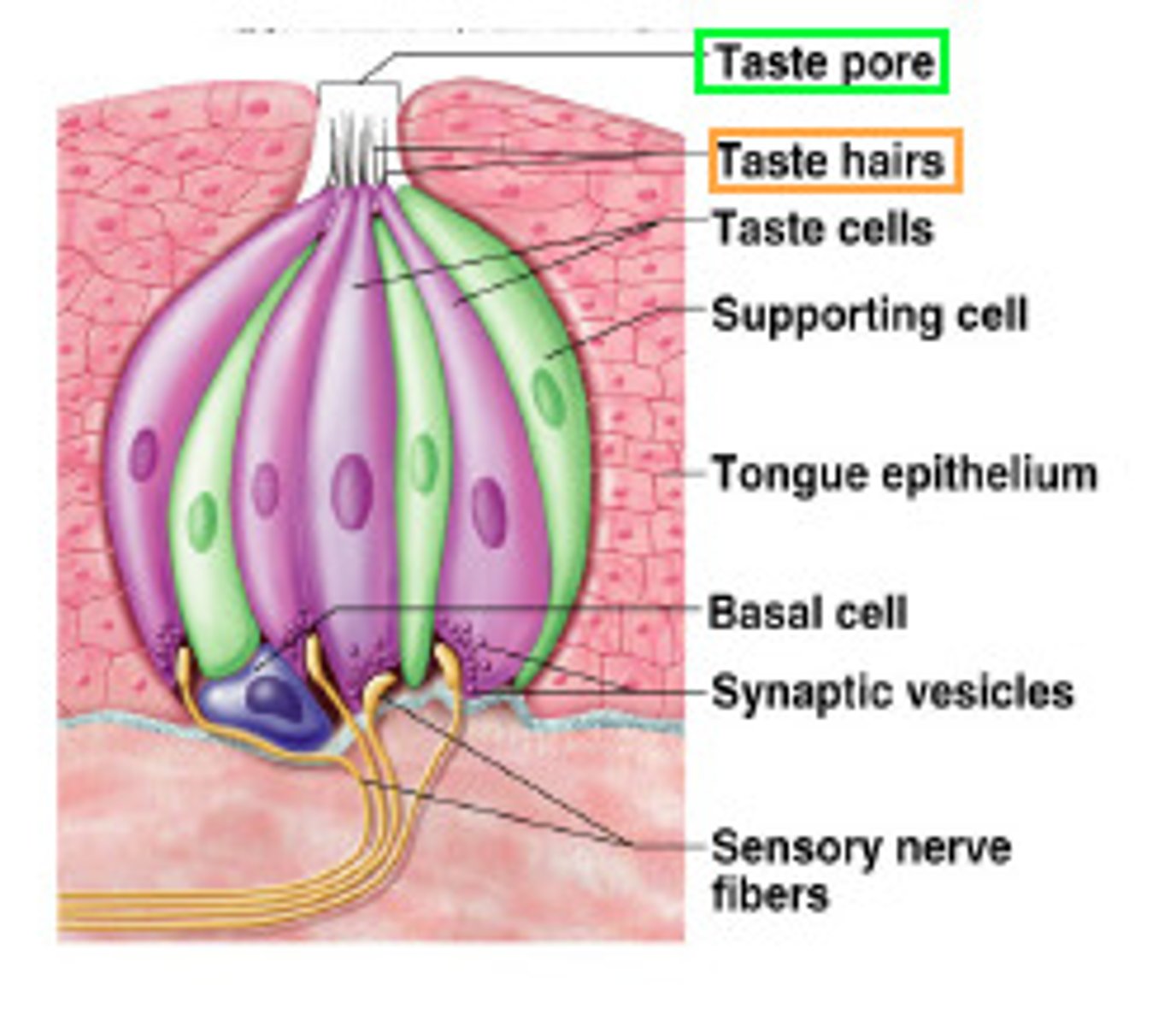
gustatory hairs
increase surface area of taste pore
bitter
concentrated at the rear of tongue, alkaloids, hydroxyls
sour
concentrated on lateral sides of tongues, respond to acids
salty
monovalent metallic cations - lateral sides of tongue
sweet
organic molecules, concentrated at tip
umami
glutamate, savory
olfactory epithelium
a thin layer of tissue, within the nasal cavity, that contains the receptors for smell
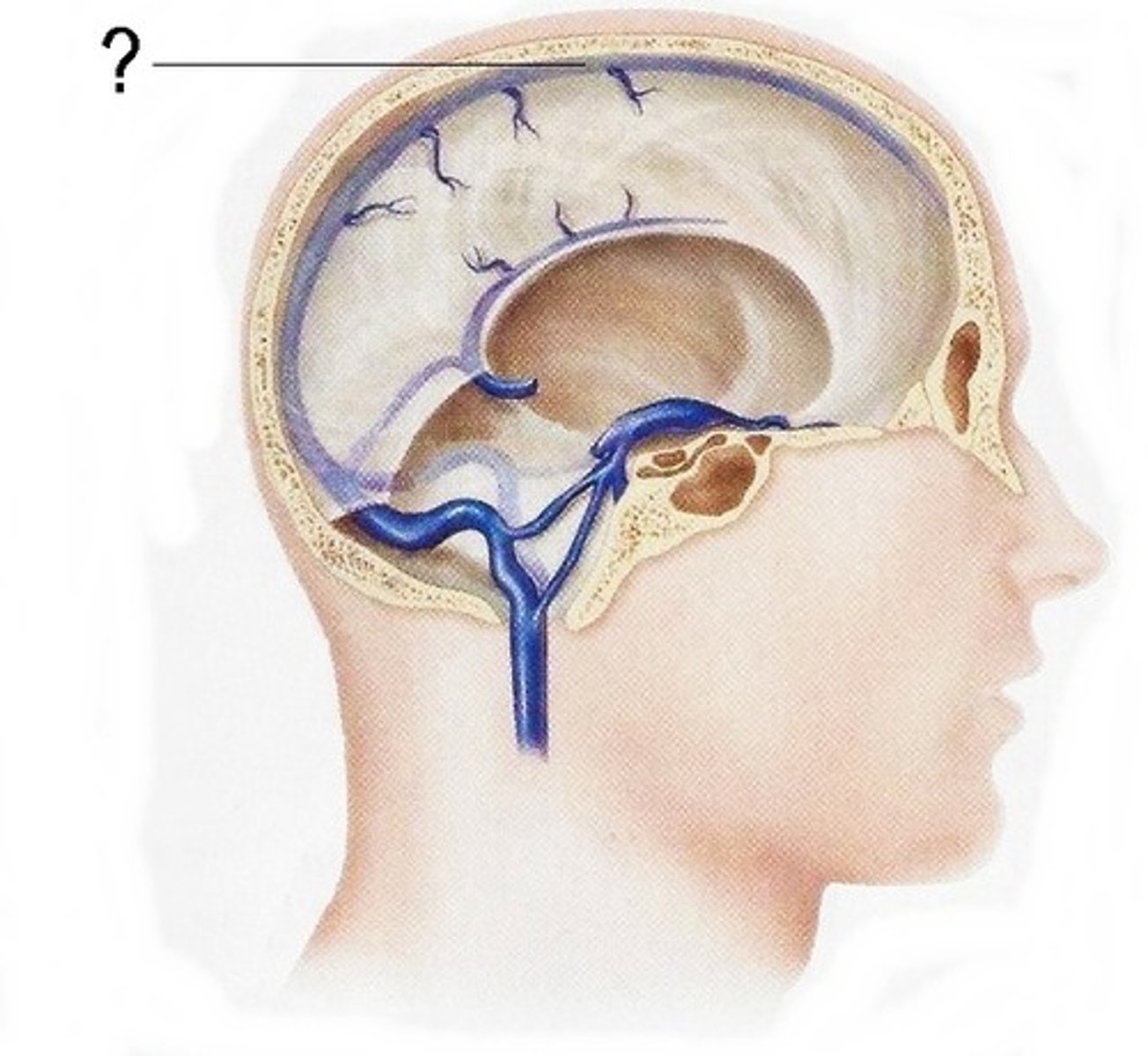
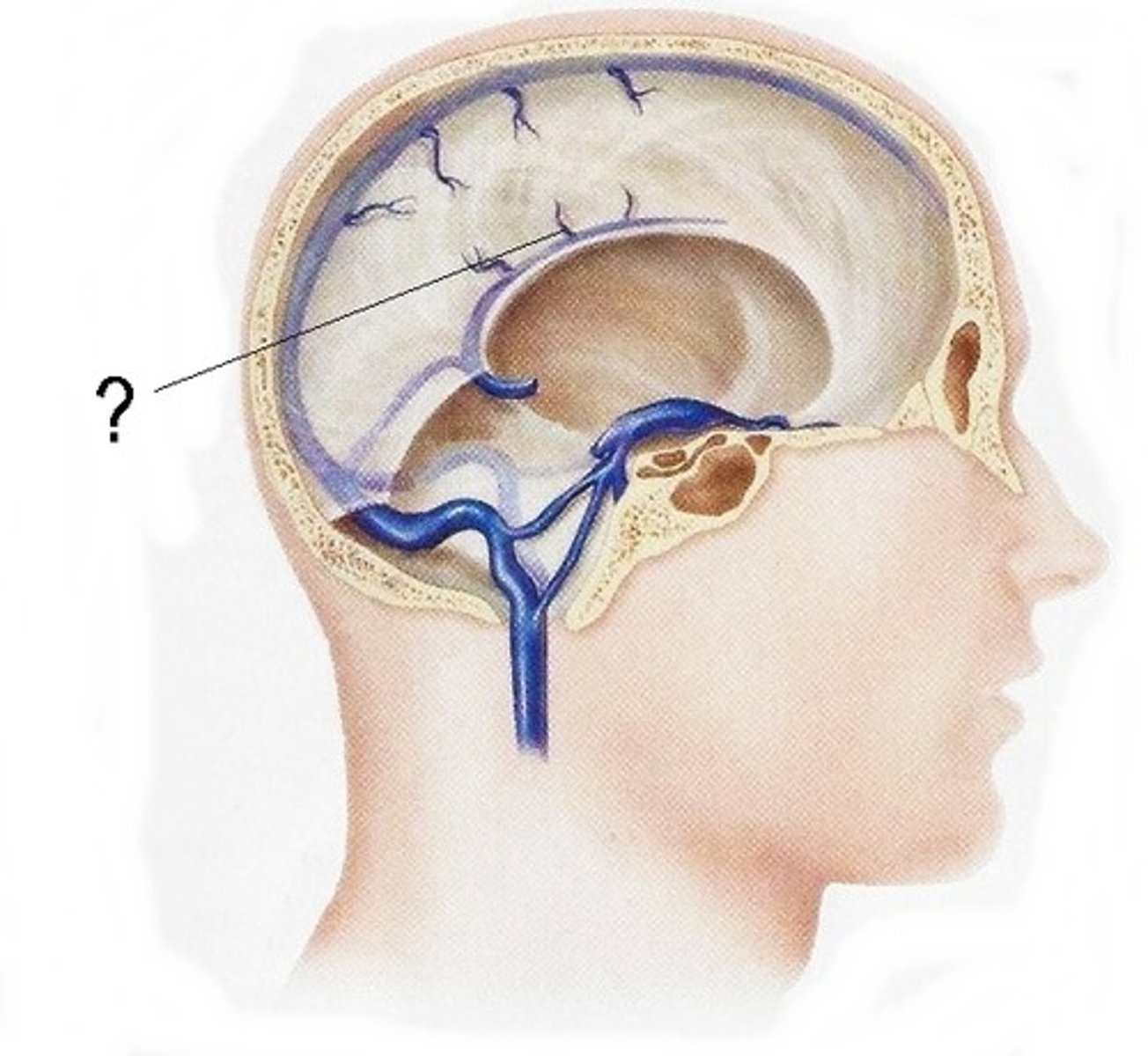
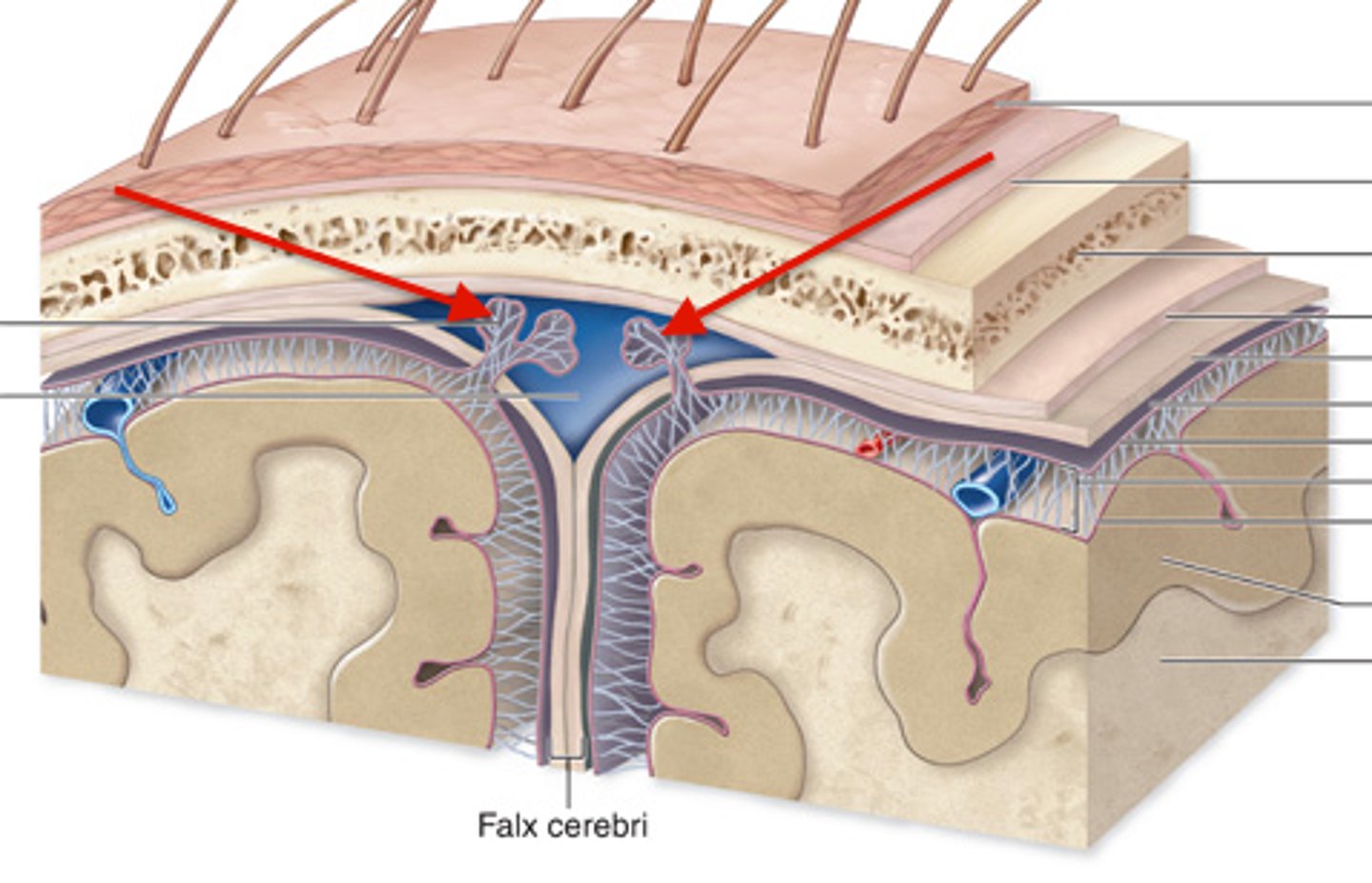
Dura mater
outermost layer of meninges - 2 layers, periosteal and meningeal
What is contained between the inner and outer layers of dura?
venous sinuses
what are the venous sinuses? where do they drain?
cerebrospinal fluid, they drain out of the internal jugular
superior sagittal sinus
inferior sagittal sinus
what are dural folds?
folded layers of dura where there is no sinus
falx cerebri
separates the two cerebral hemispheres
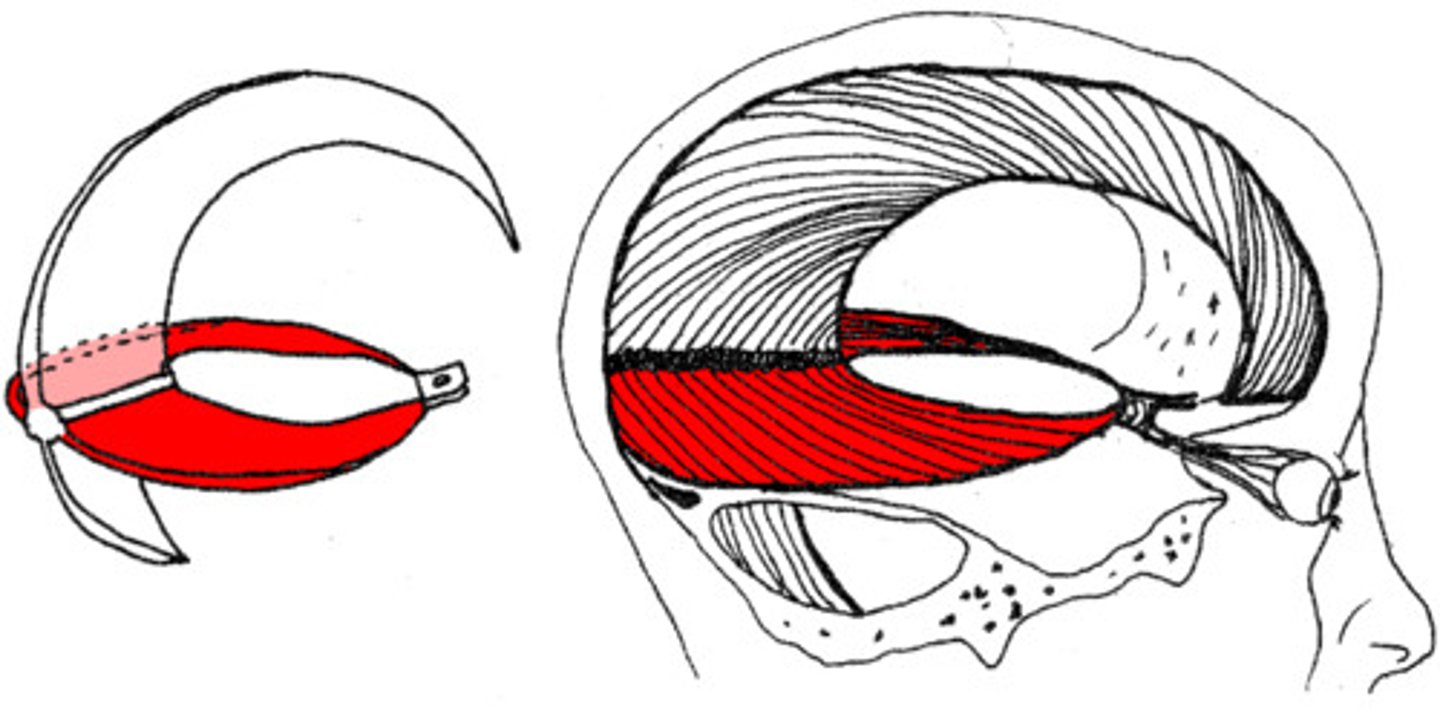
tentorium cerebelli
separates cerebrum from cerebellum
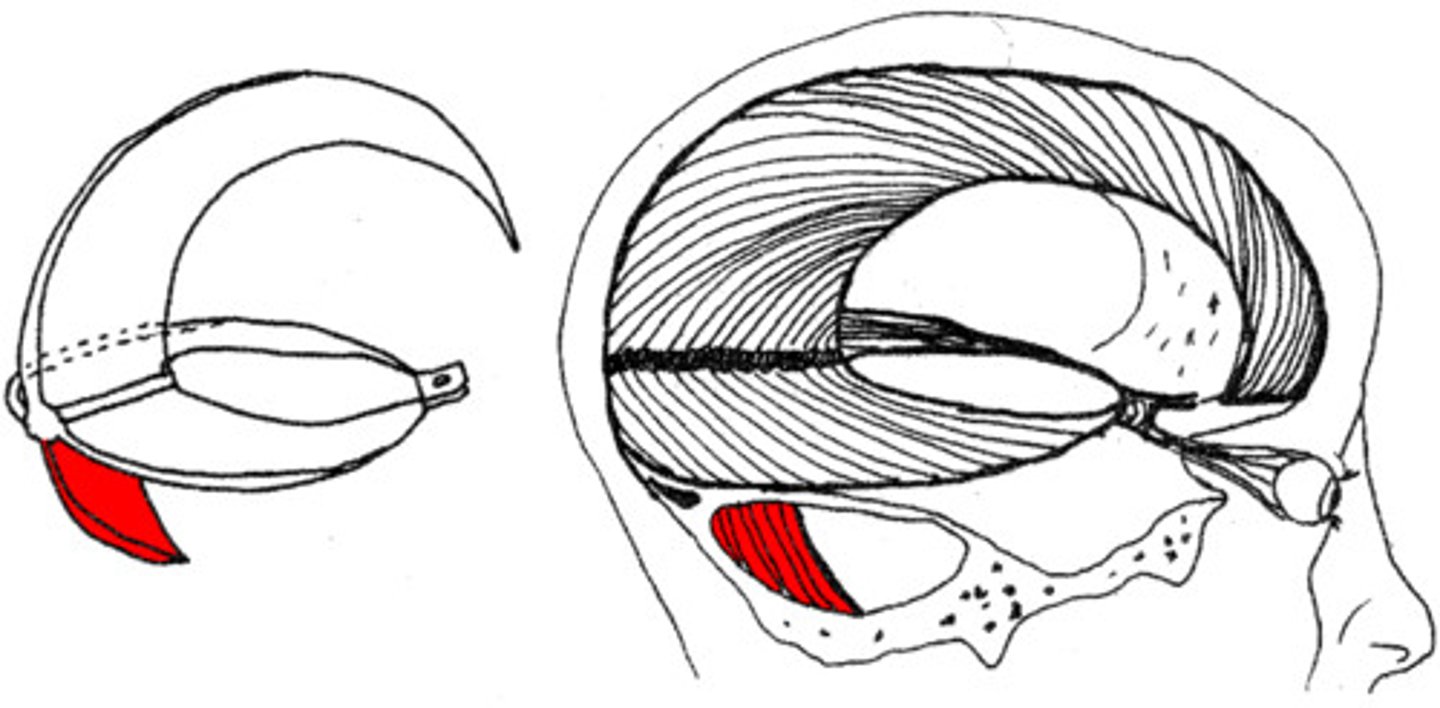
falx cerebelli
separates the two hemispheres of the cerebellum
arachnoid mater
middle layer of meninges, weblike
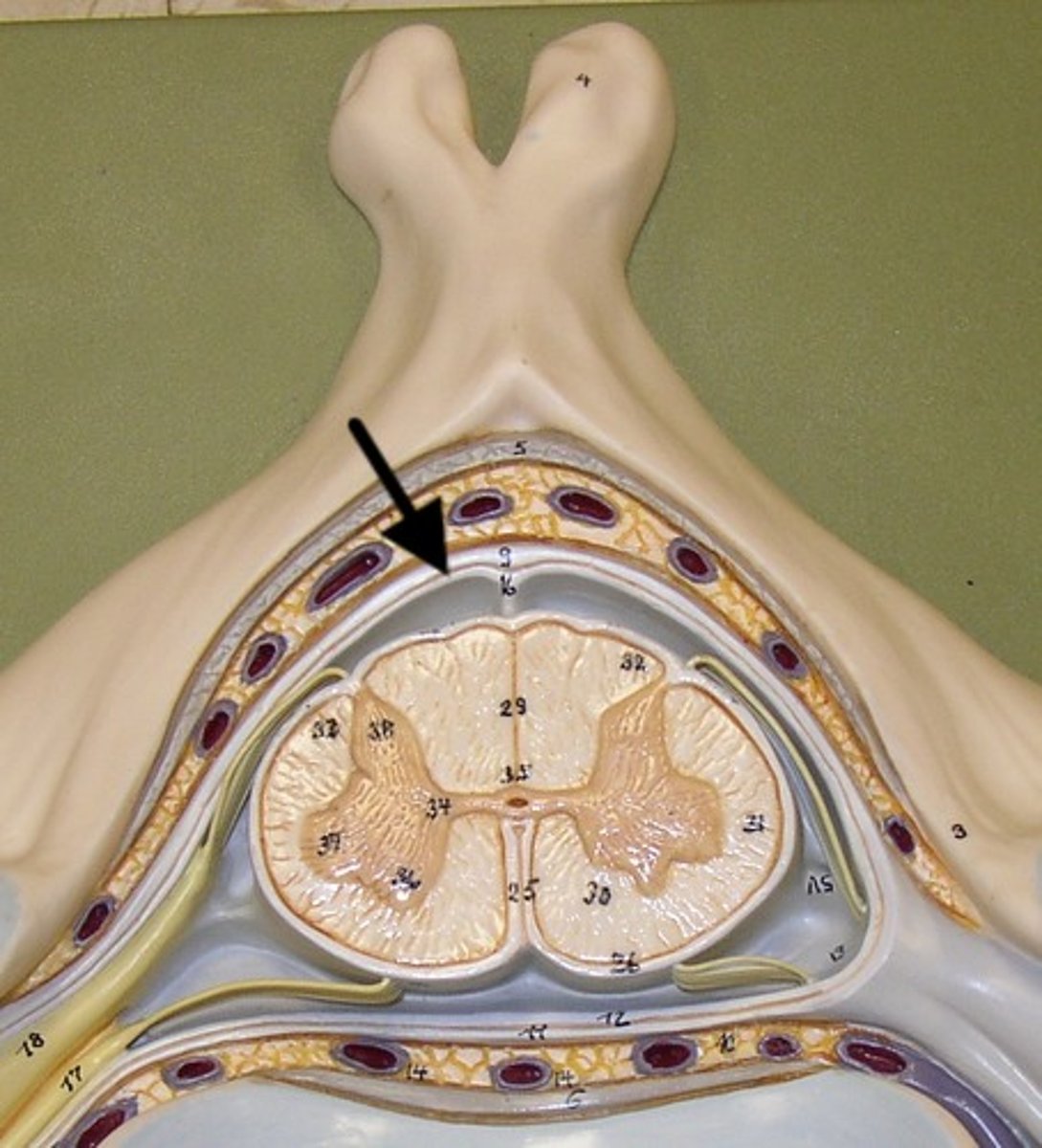
what is in the subarachnoid space?
cerebrospinal fluid
pia mater
"delicate mother," innermost layer of meninges
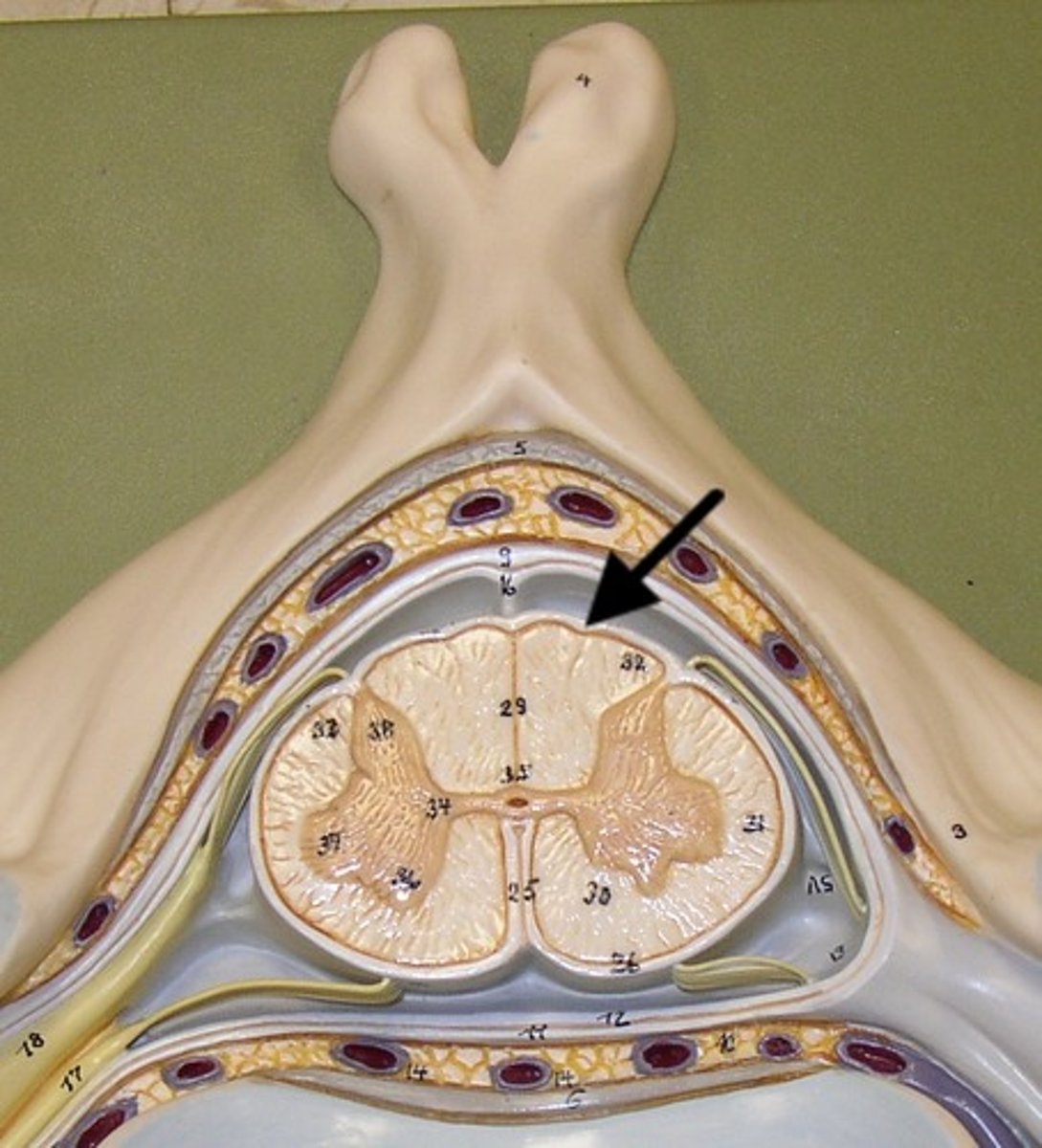
what attaches the pia mater to the surface of the brain?
collagen fibers
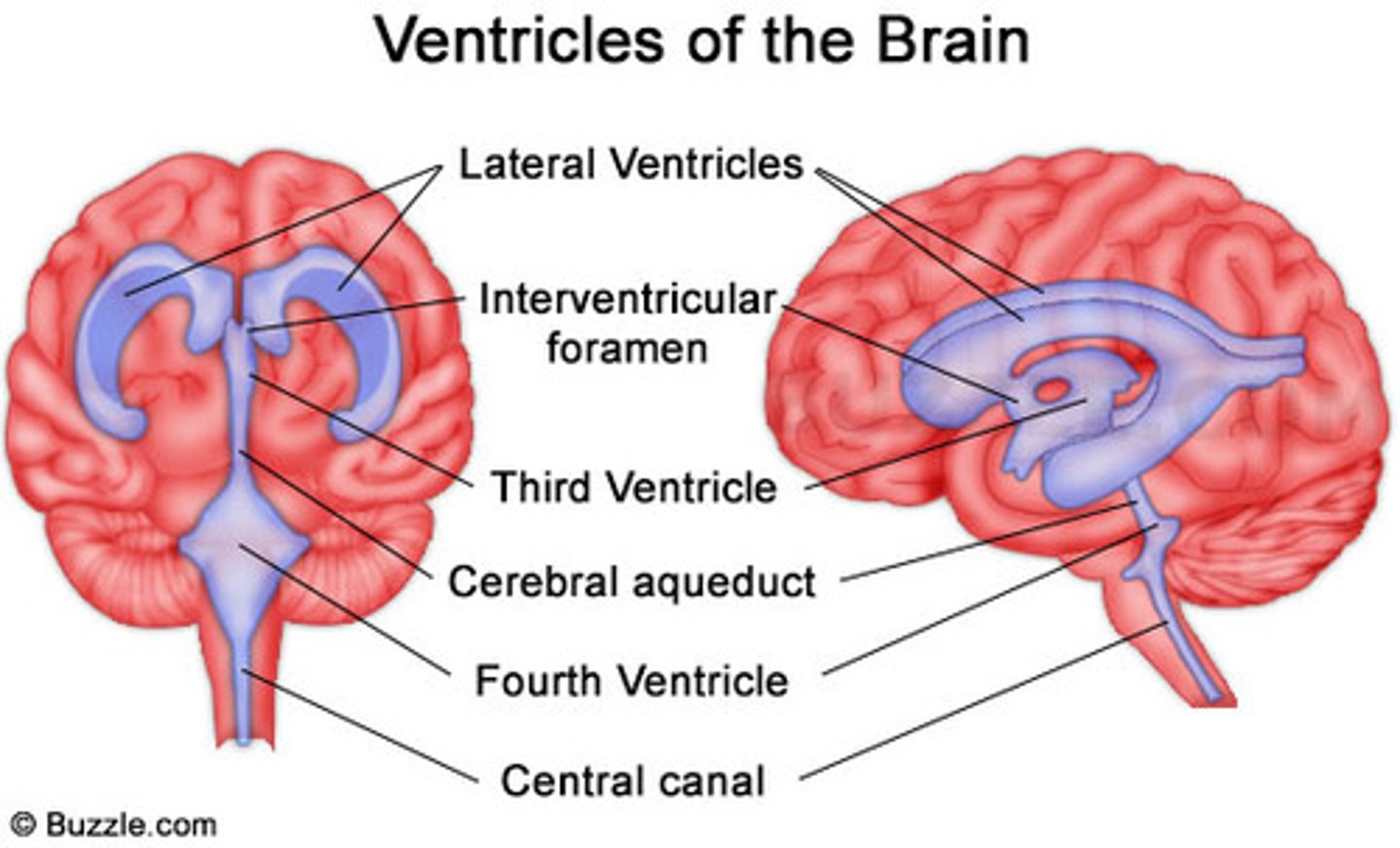
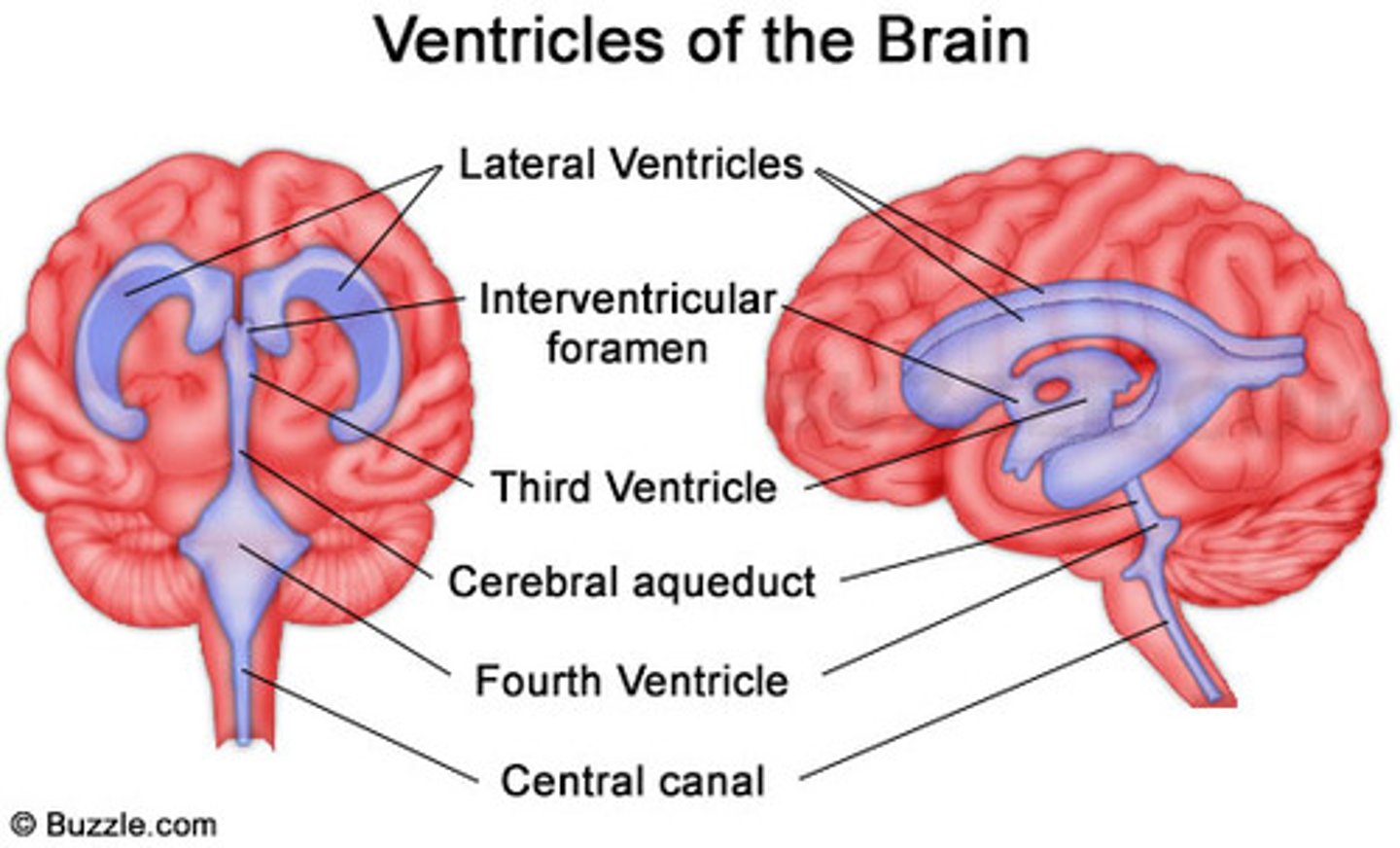
lateral ventricles
third ventricle
fourth ventricle
interventricular foramen
connects lateral ventricles to third ventricle
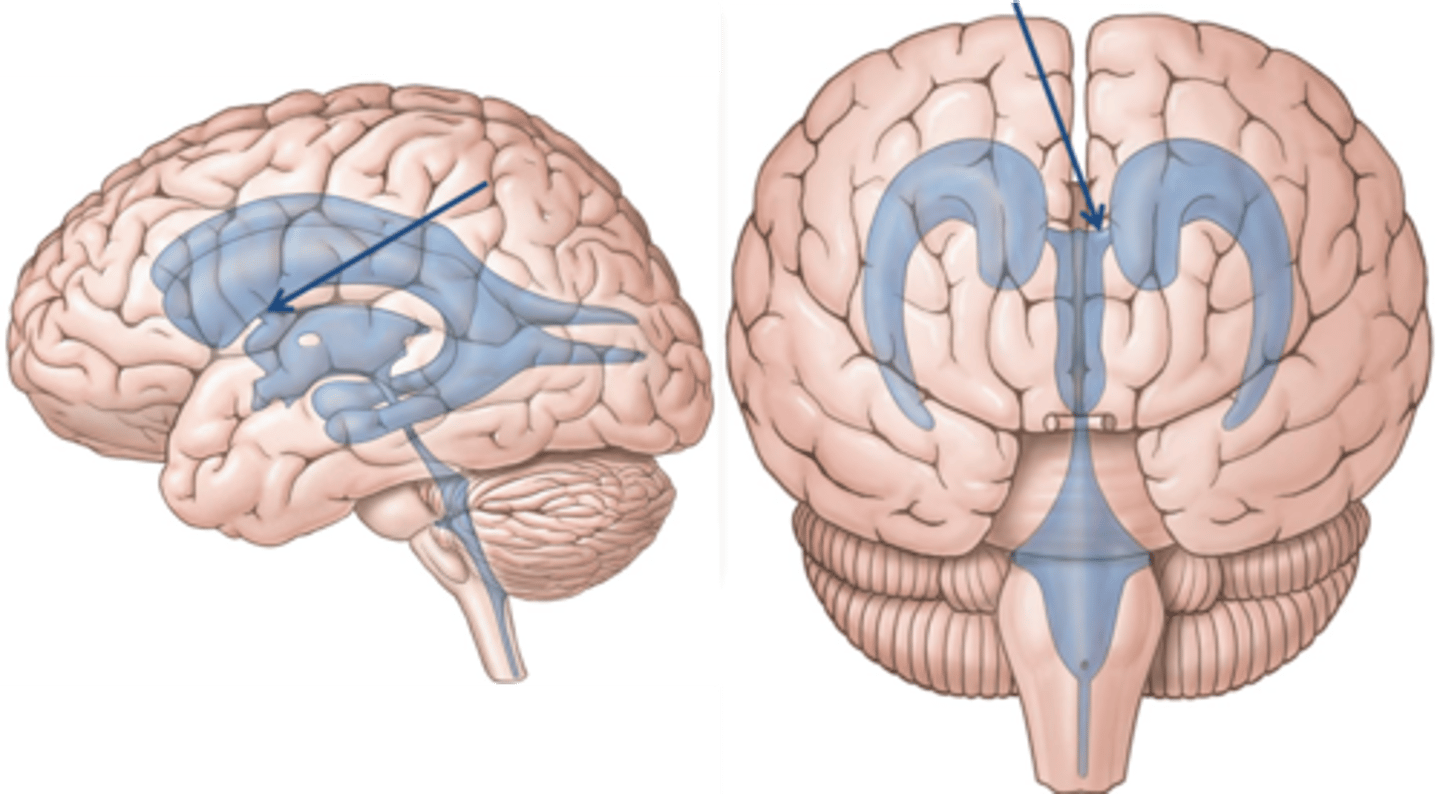
cerebral aqueduct
connects the third and fourth ventricles
choroid plexus
on the floor of all the ventricles, produces CSF
arachnoid villi
reabsorb/drain CSF into venous blood
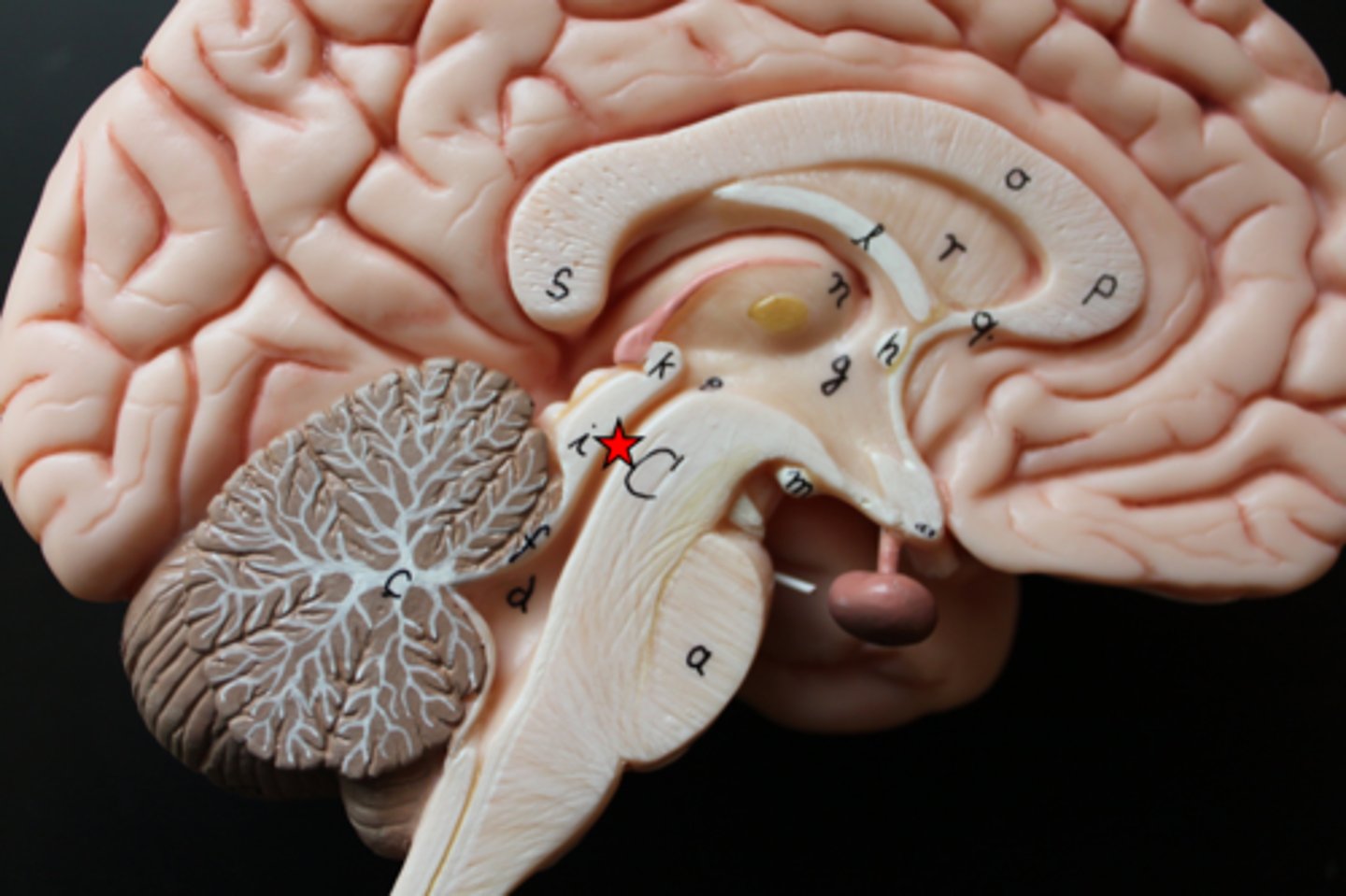
medulla oblongata
basic life support, heart beating, etc.
decussation of pyramids
where the cleavage furrow becomes almost flat - the reason for contralateral control
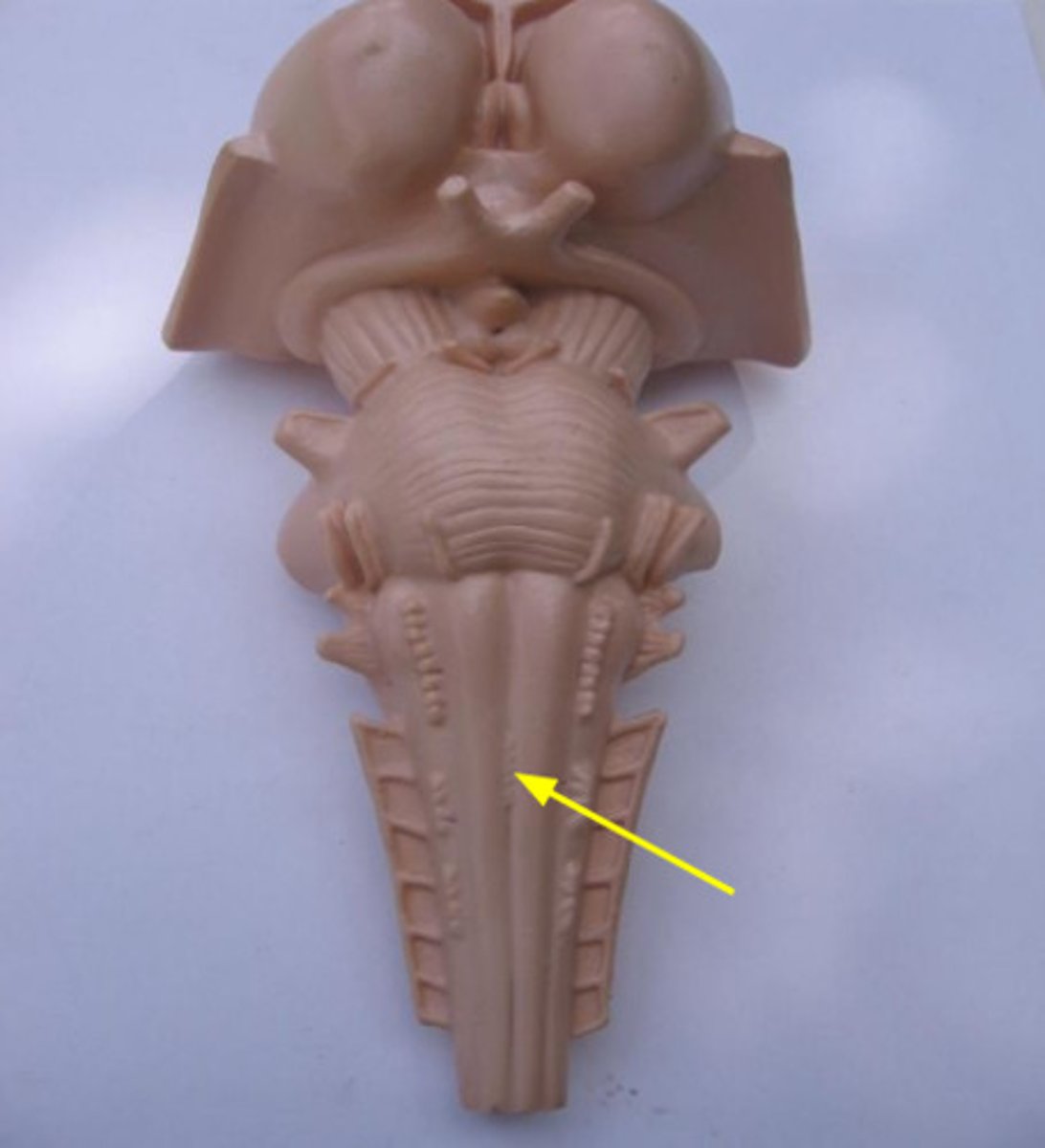
pons
control of breathing
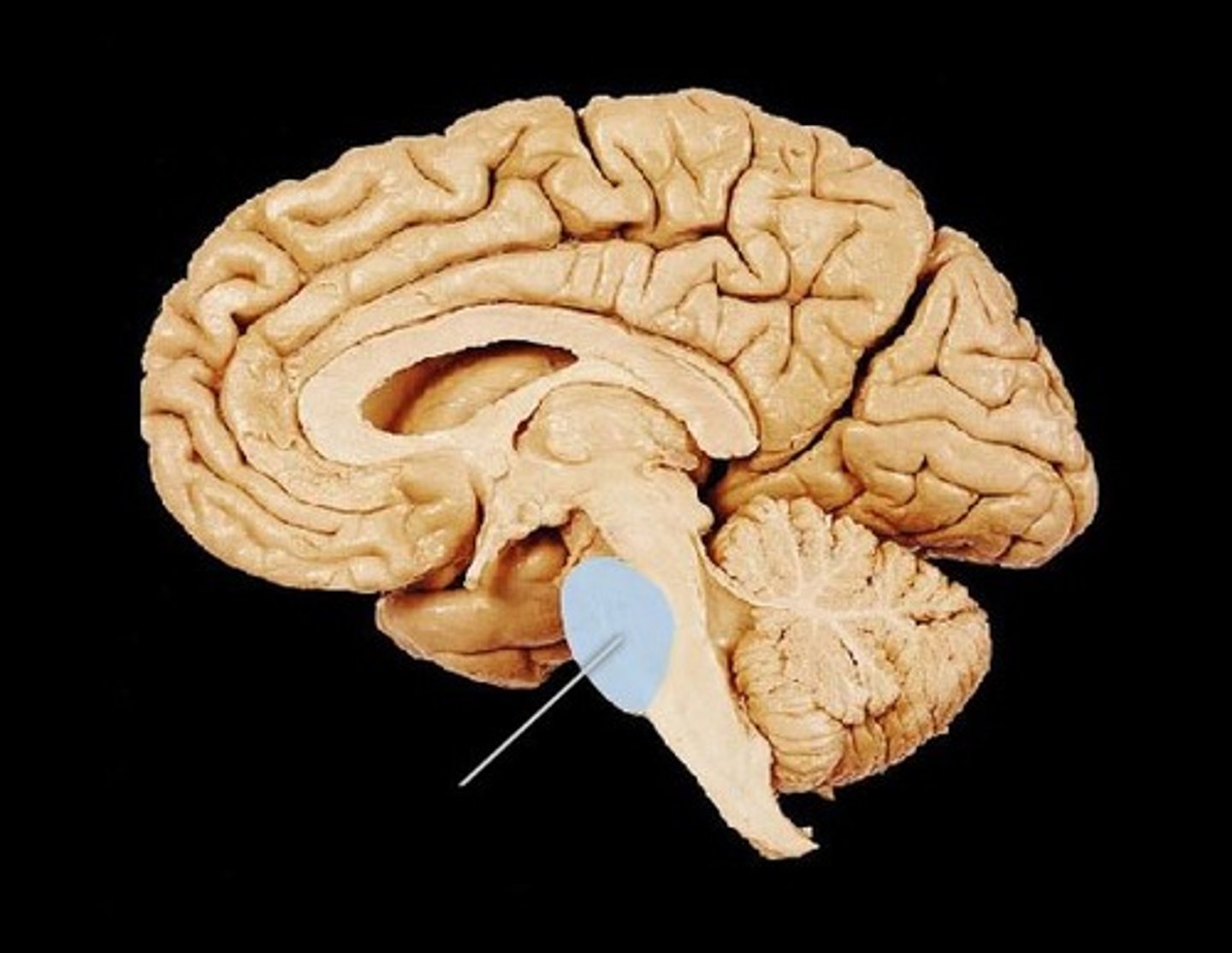
midbrain
immediate reflexes
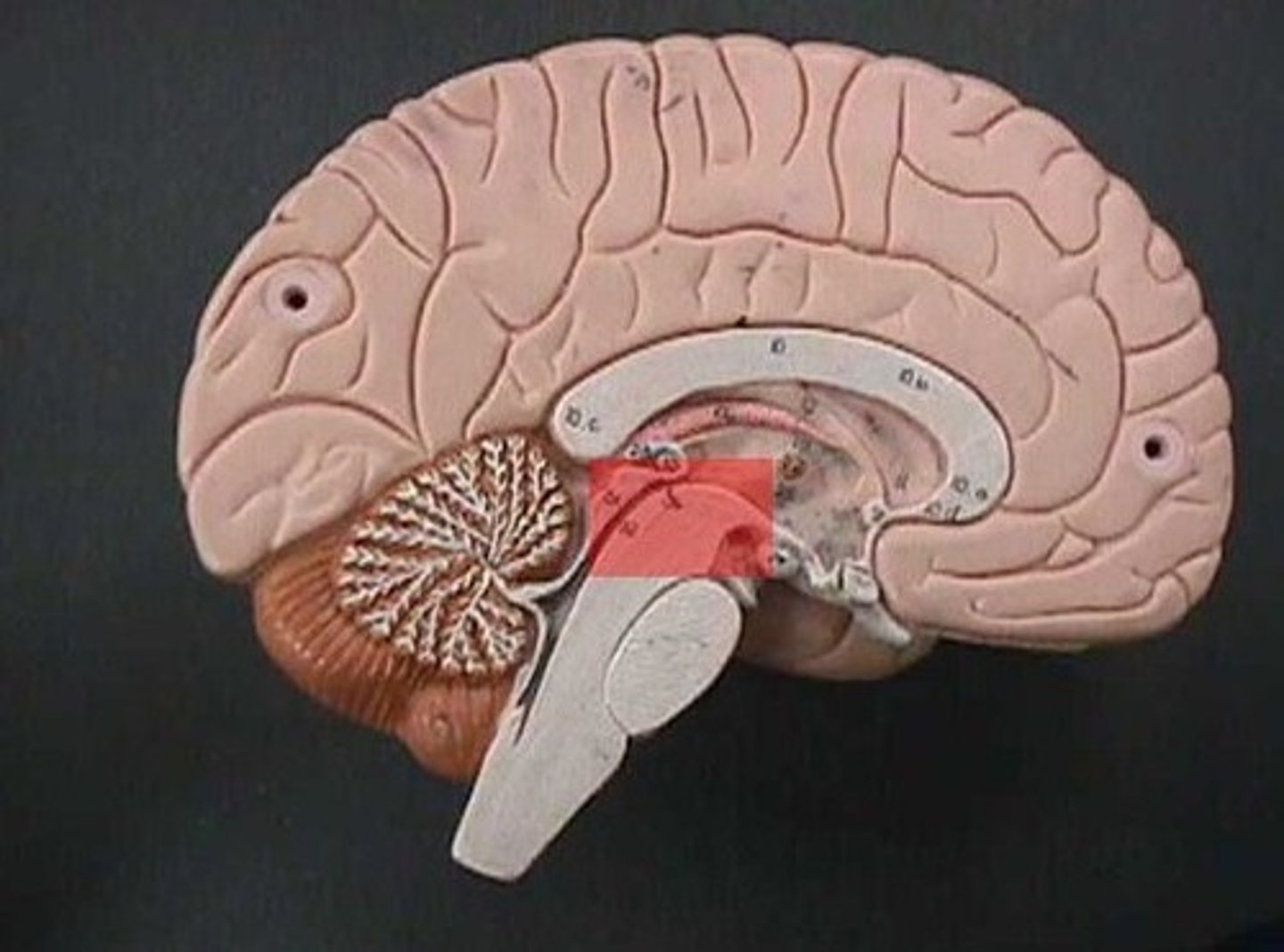
cerebral peduncles
connect lower and upper brain, cerebrum to brainstem
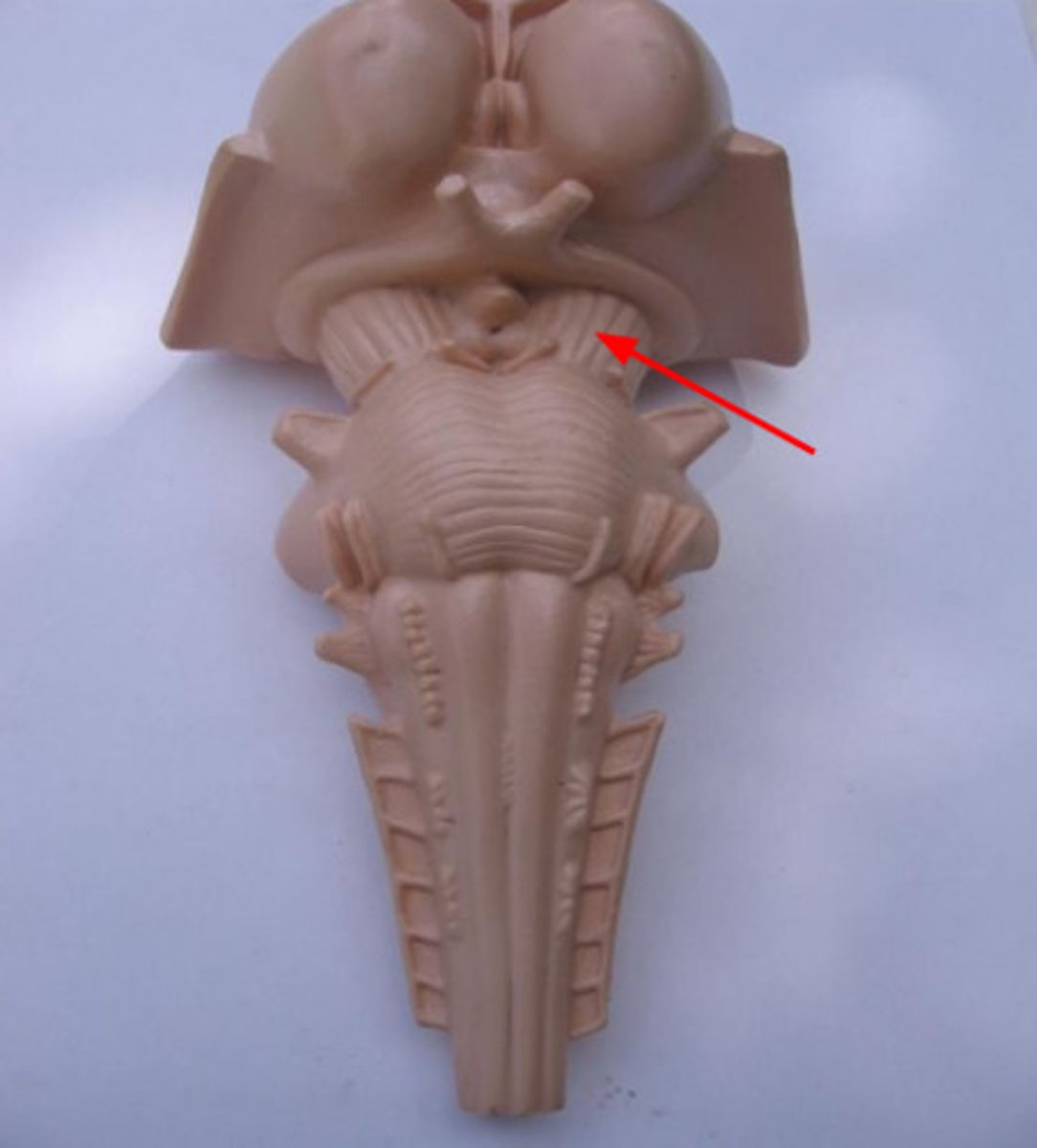
corpora quadrigemina
located in the midbrain; contains reflex centers for vision and auditory reflexes.
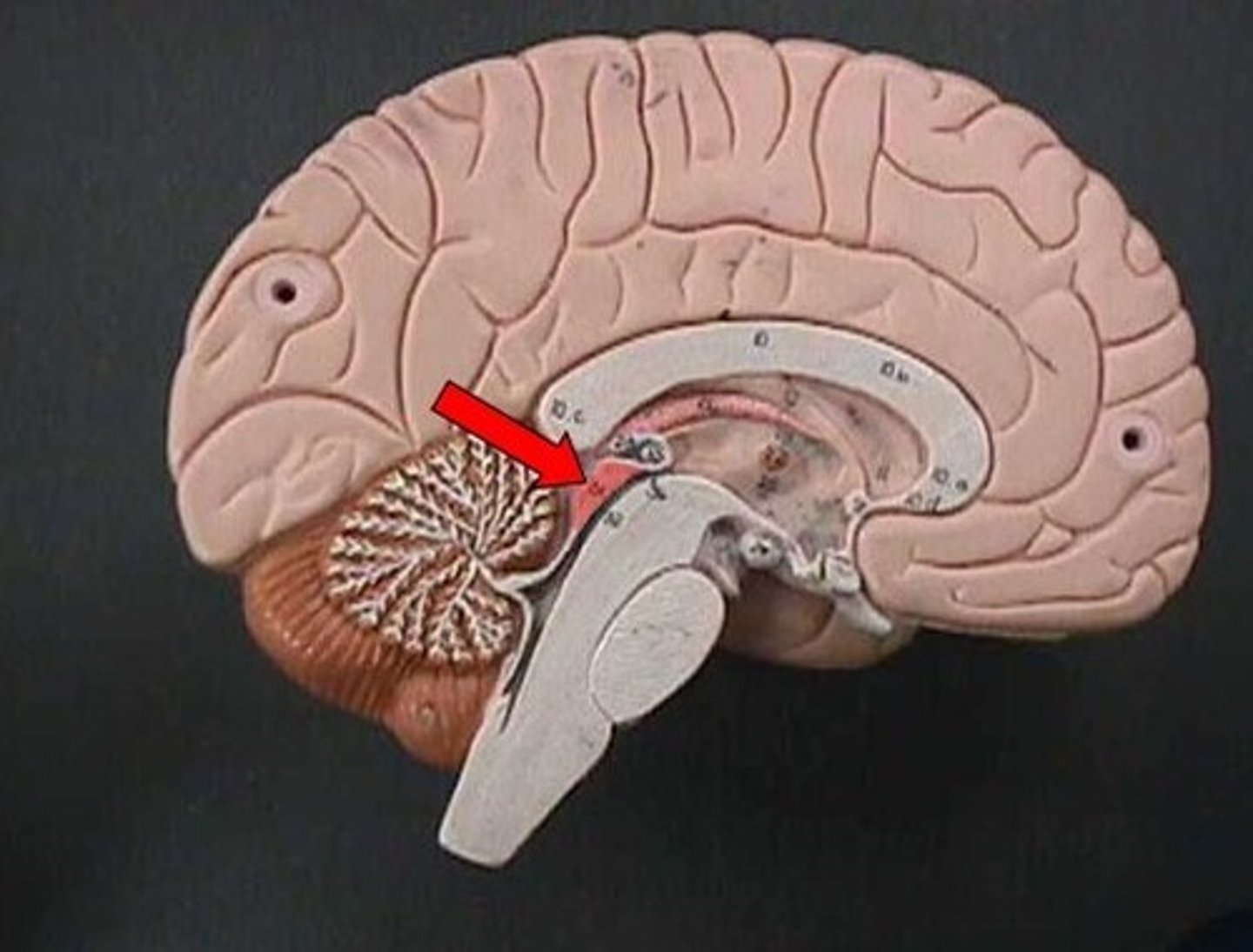
superior colliculi
part of corpora quadrigemina, visual reflexes
inferior colliculi
part of corpora quadrigemina, auditory reflexes
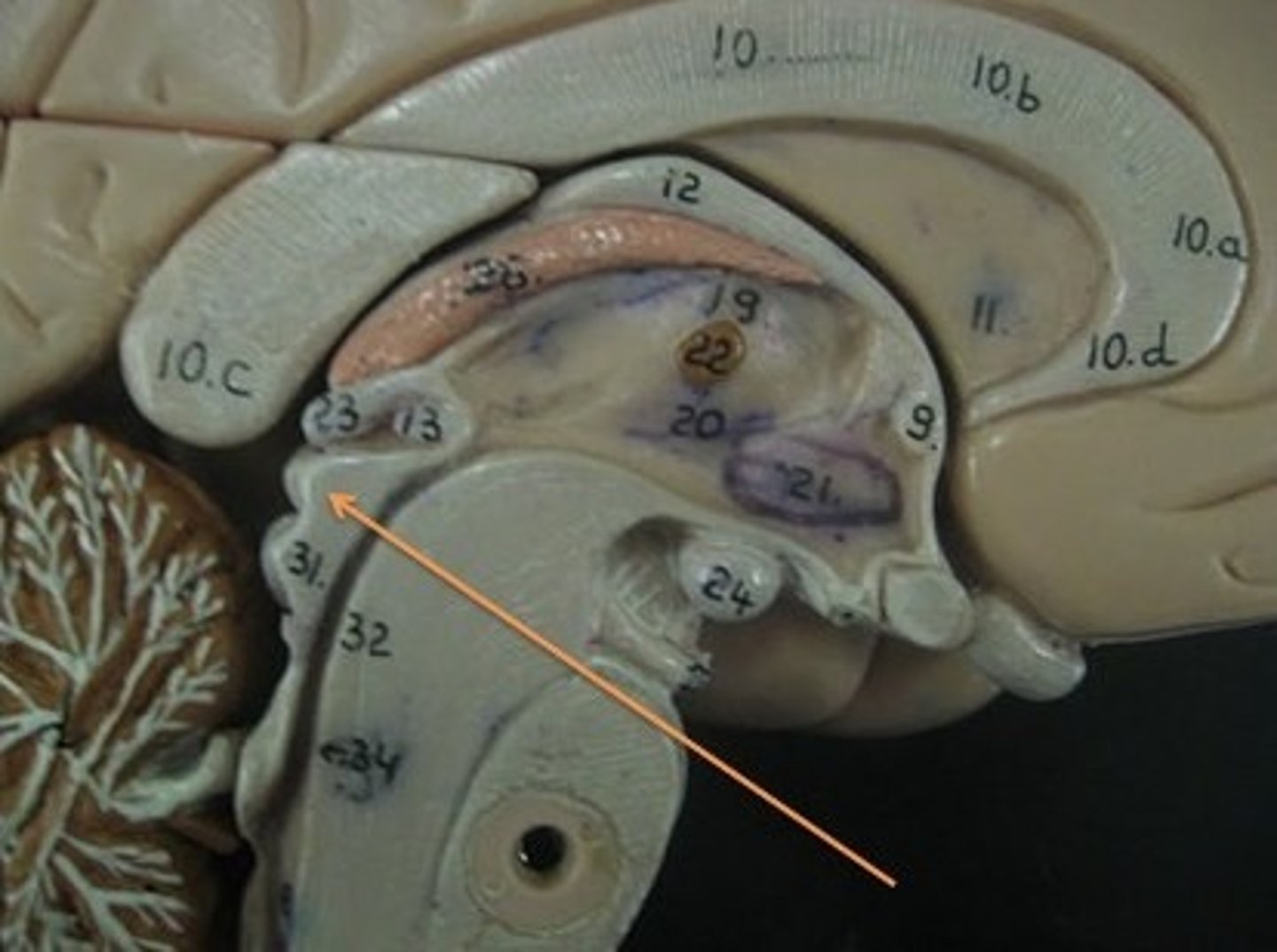
diencephalon
thalamus and hypothalamus
thalamus
relay station for all somatosensory information
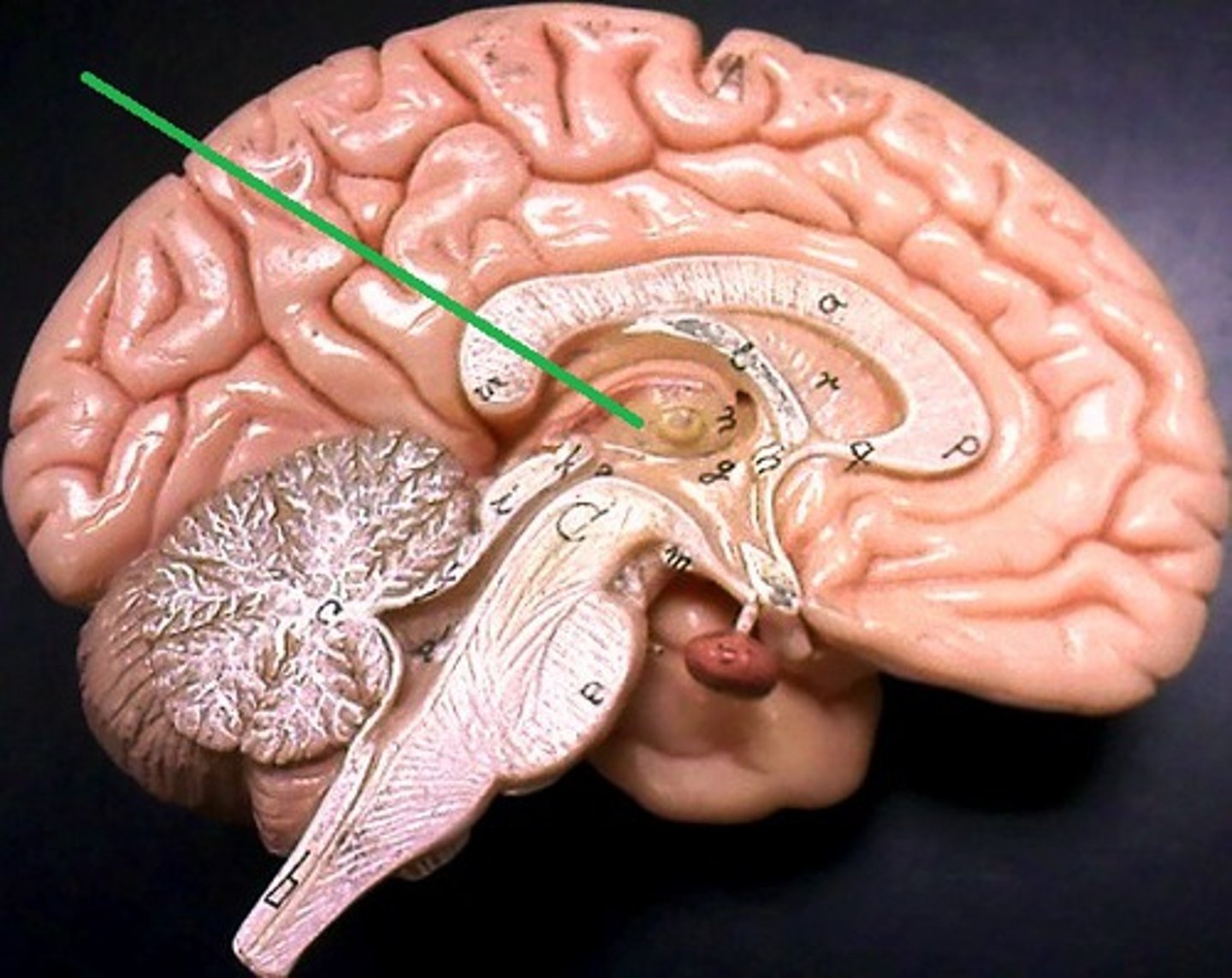
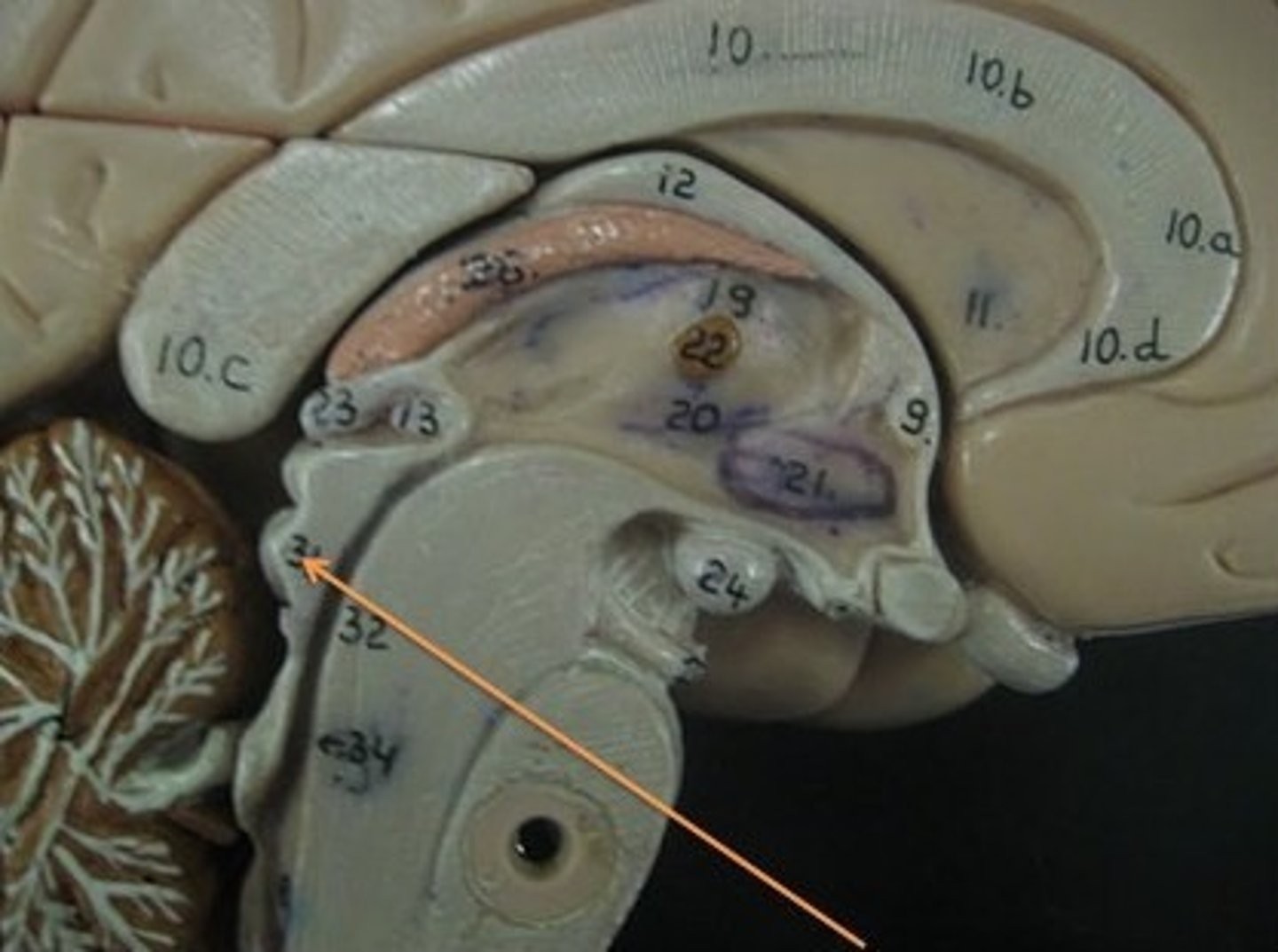
intermediate mass
connection between the two thalami across the third ventricle, dumbbell shape
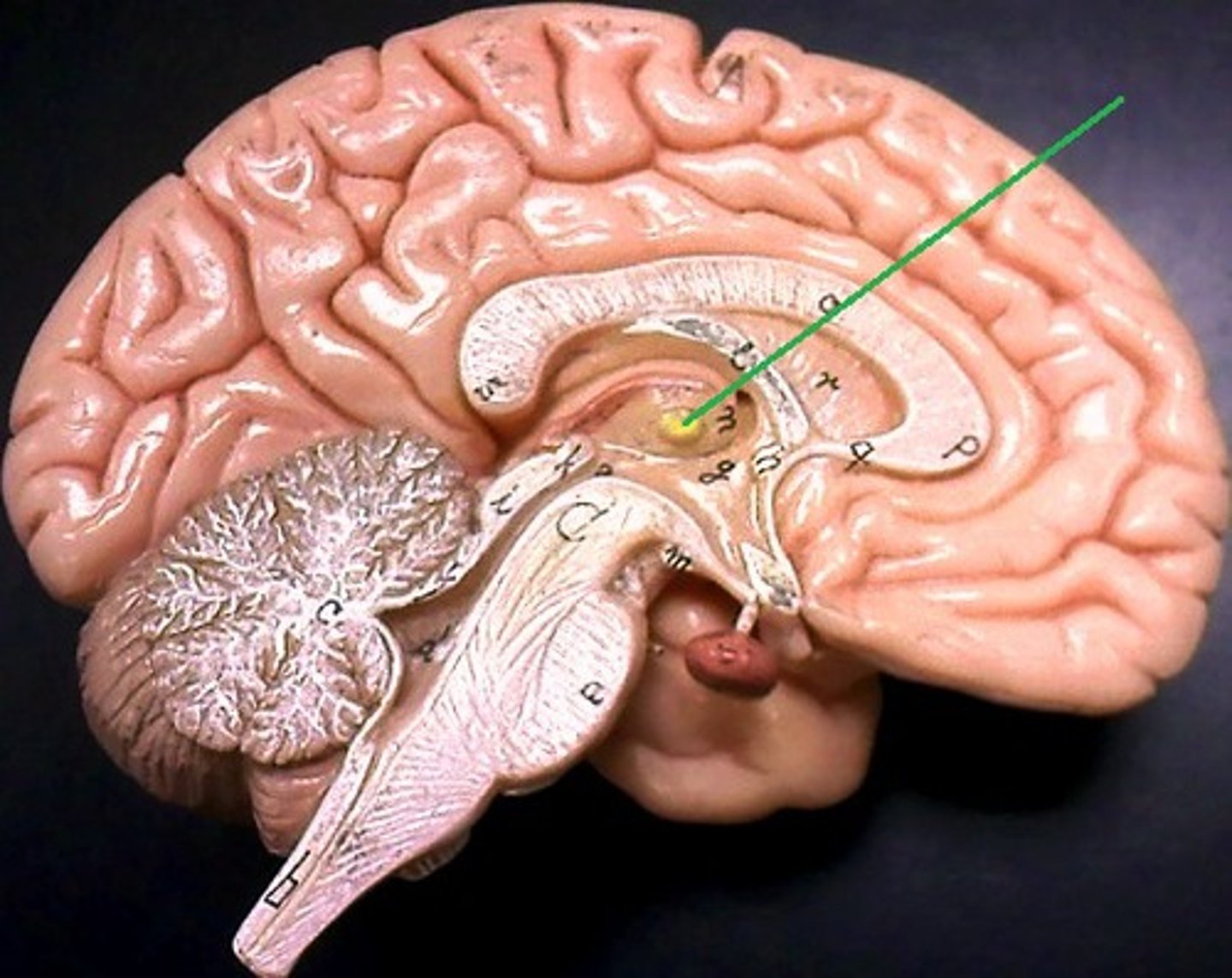
hypothalamus
brain region (many nuclei) in charge of maintaining homeostasis
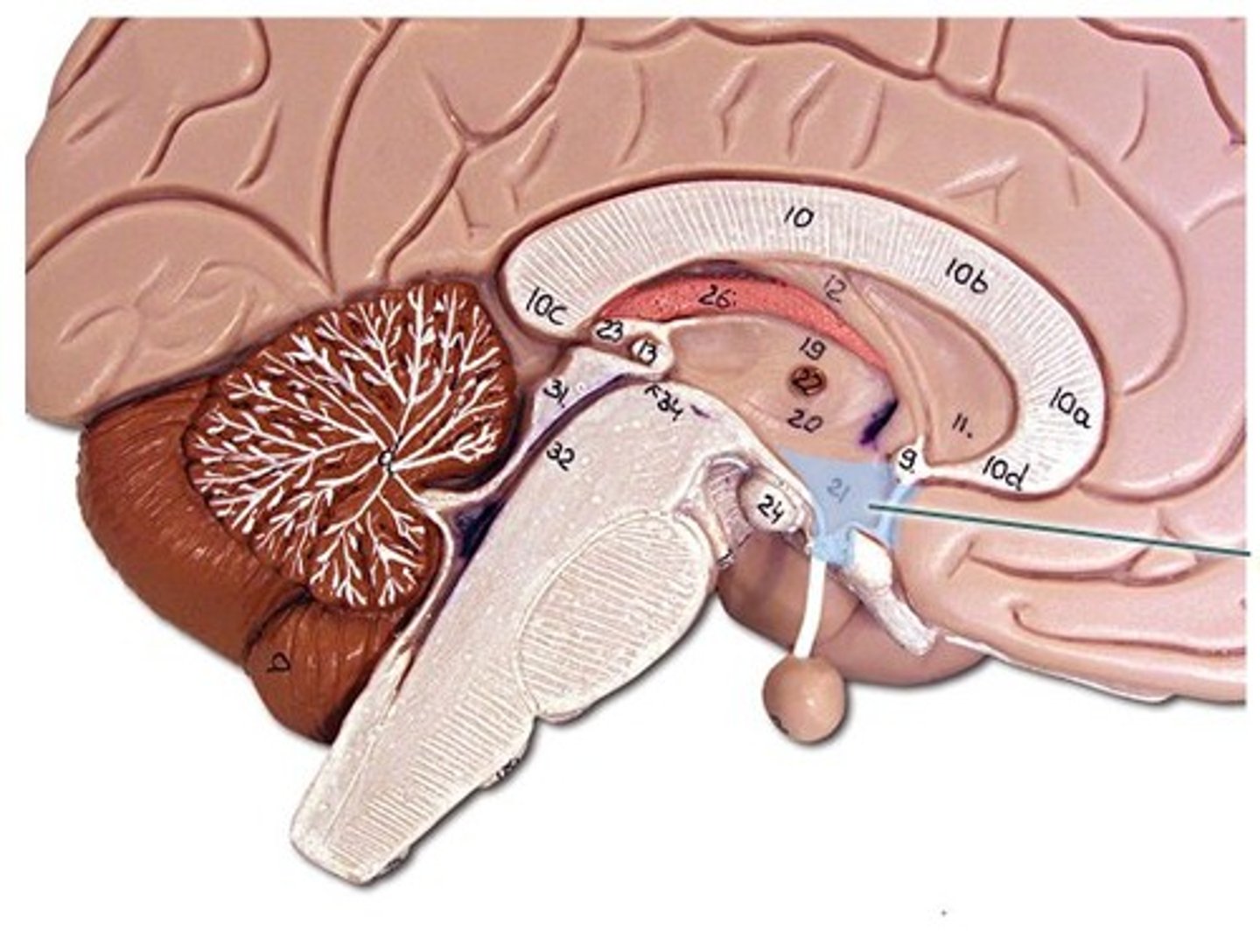
pituitary gland
produces hormones
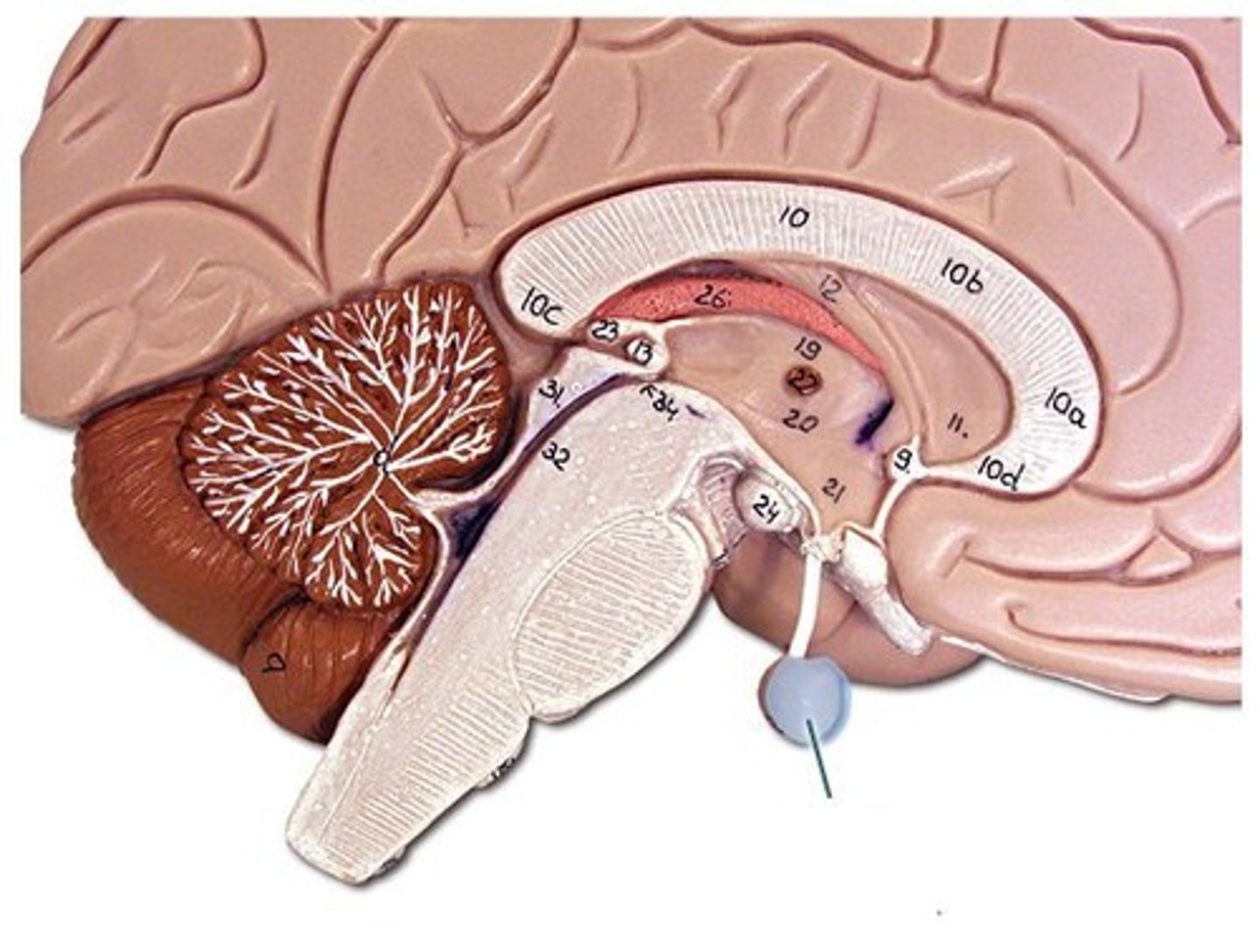
mammillary bodies
olfactory relay stations
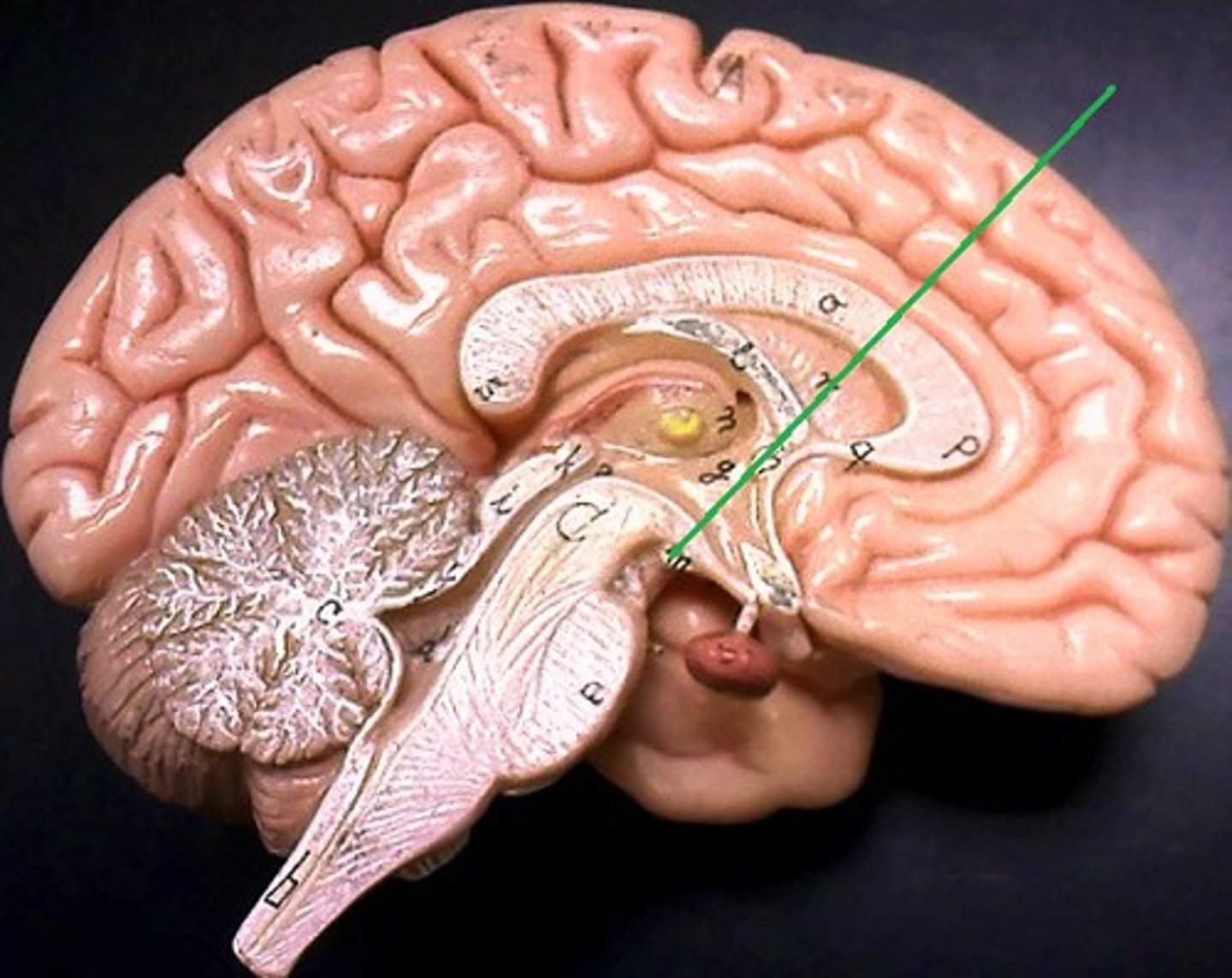
epithalamus
region above midbrain that contains pineal gland
pineal gland
regulates sleep-wake cycles, secretes melatonin
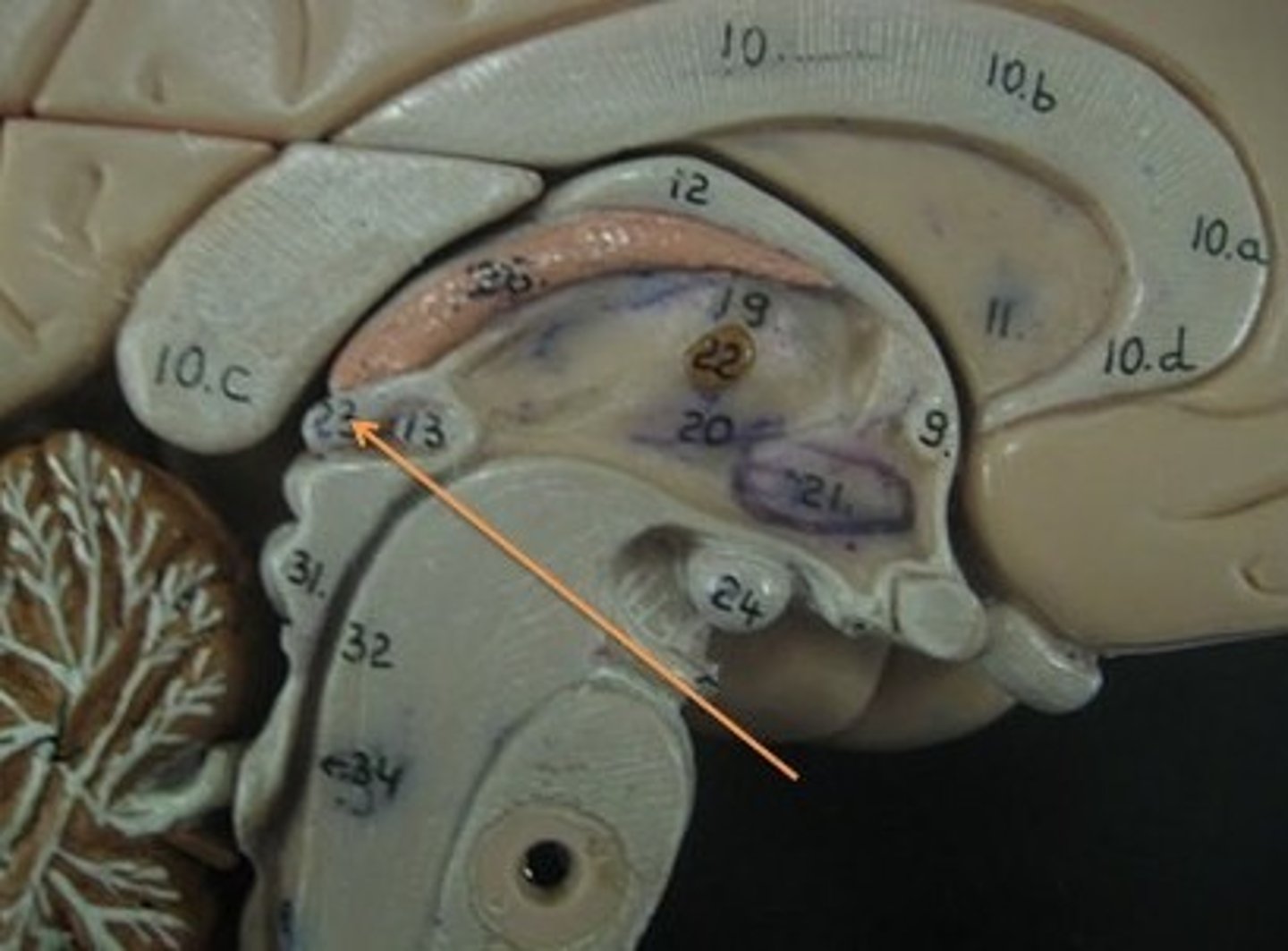
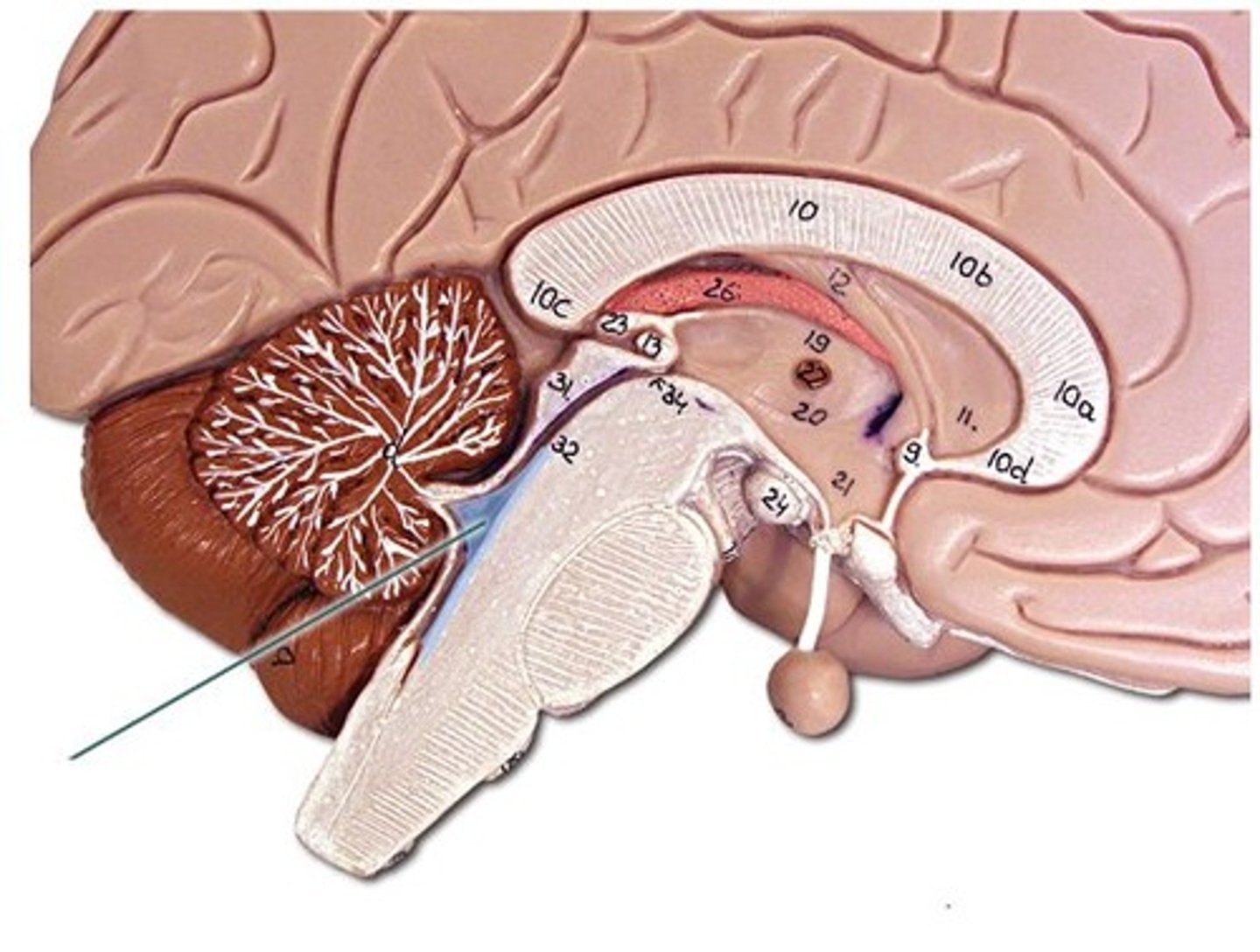
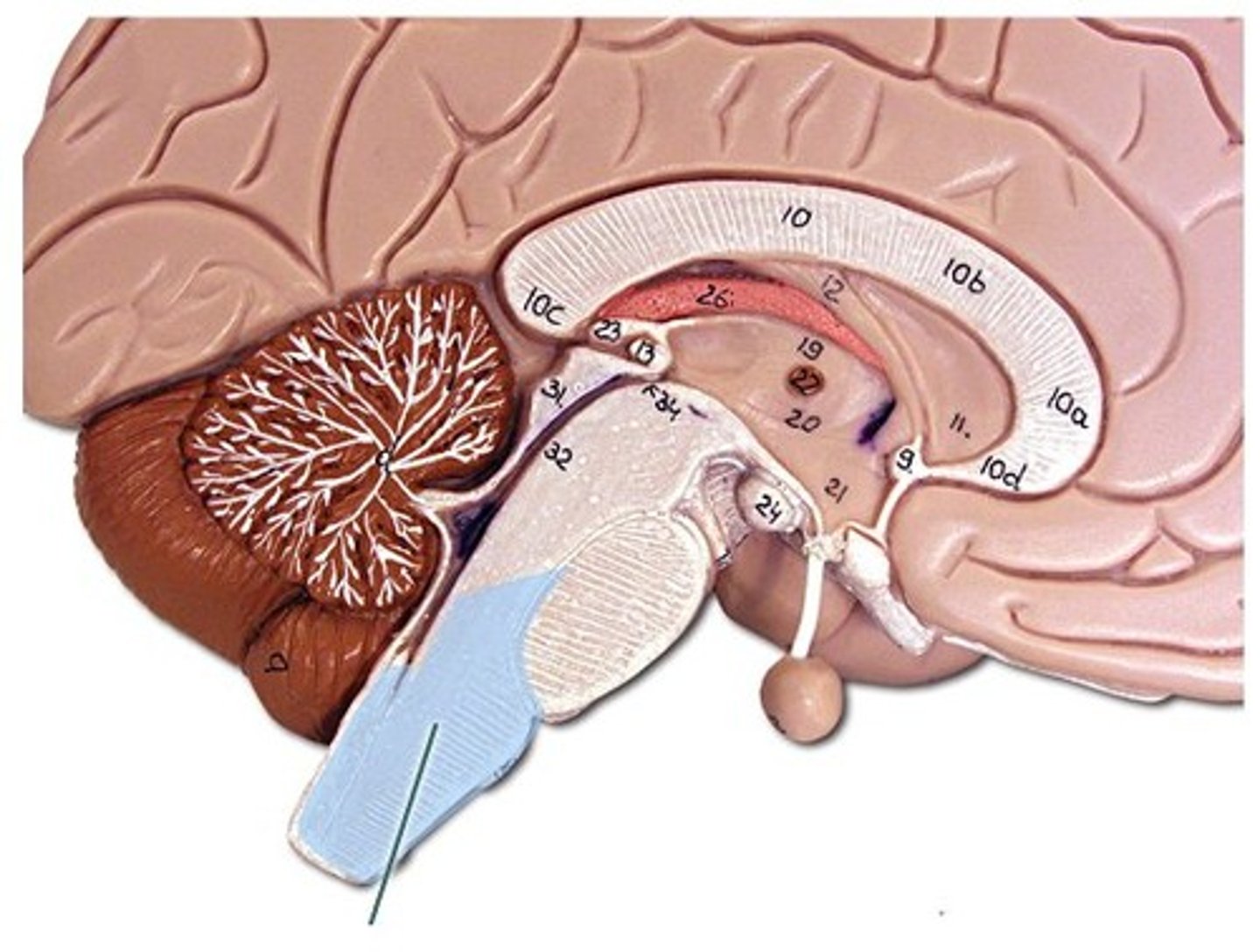
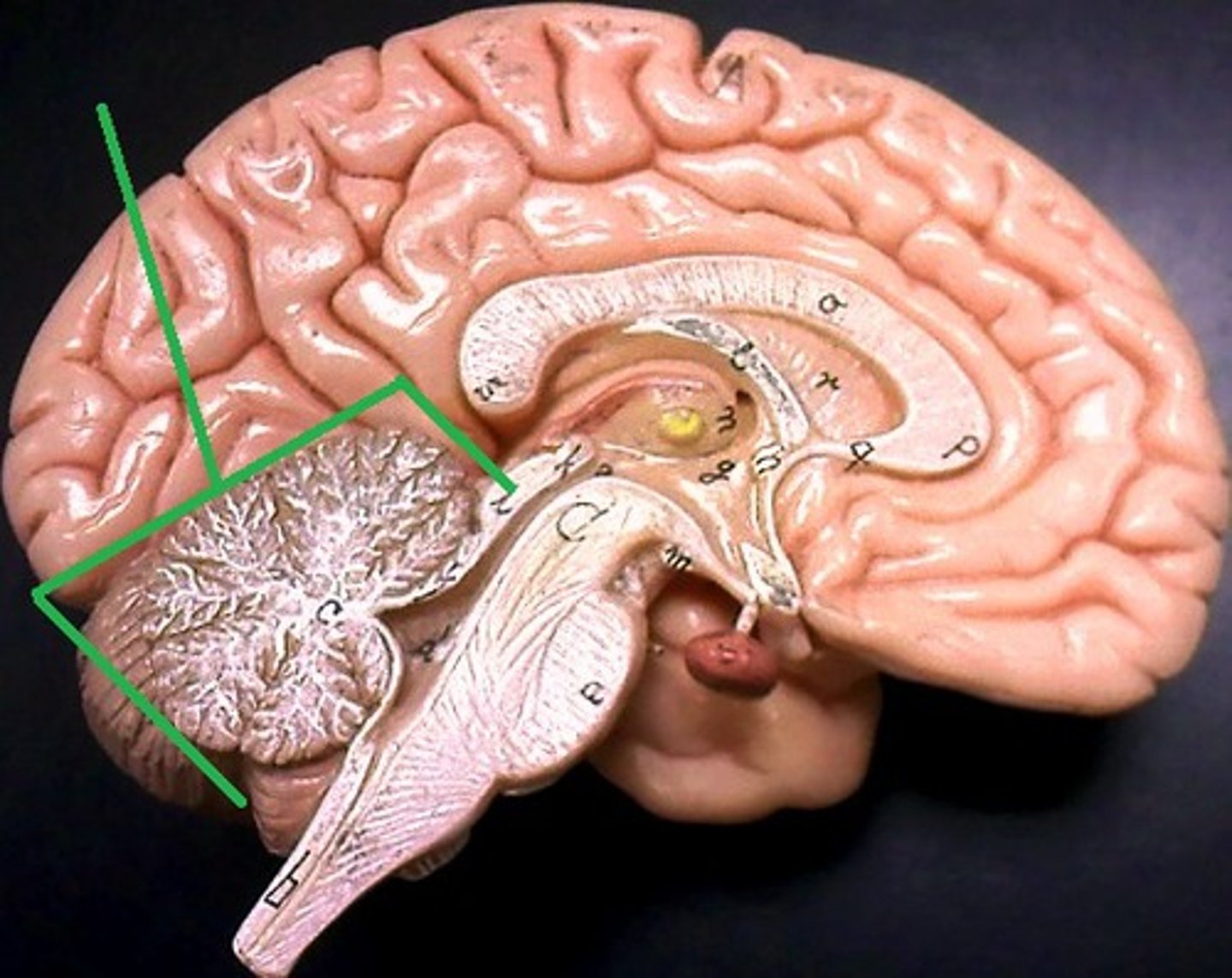
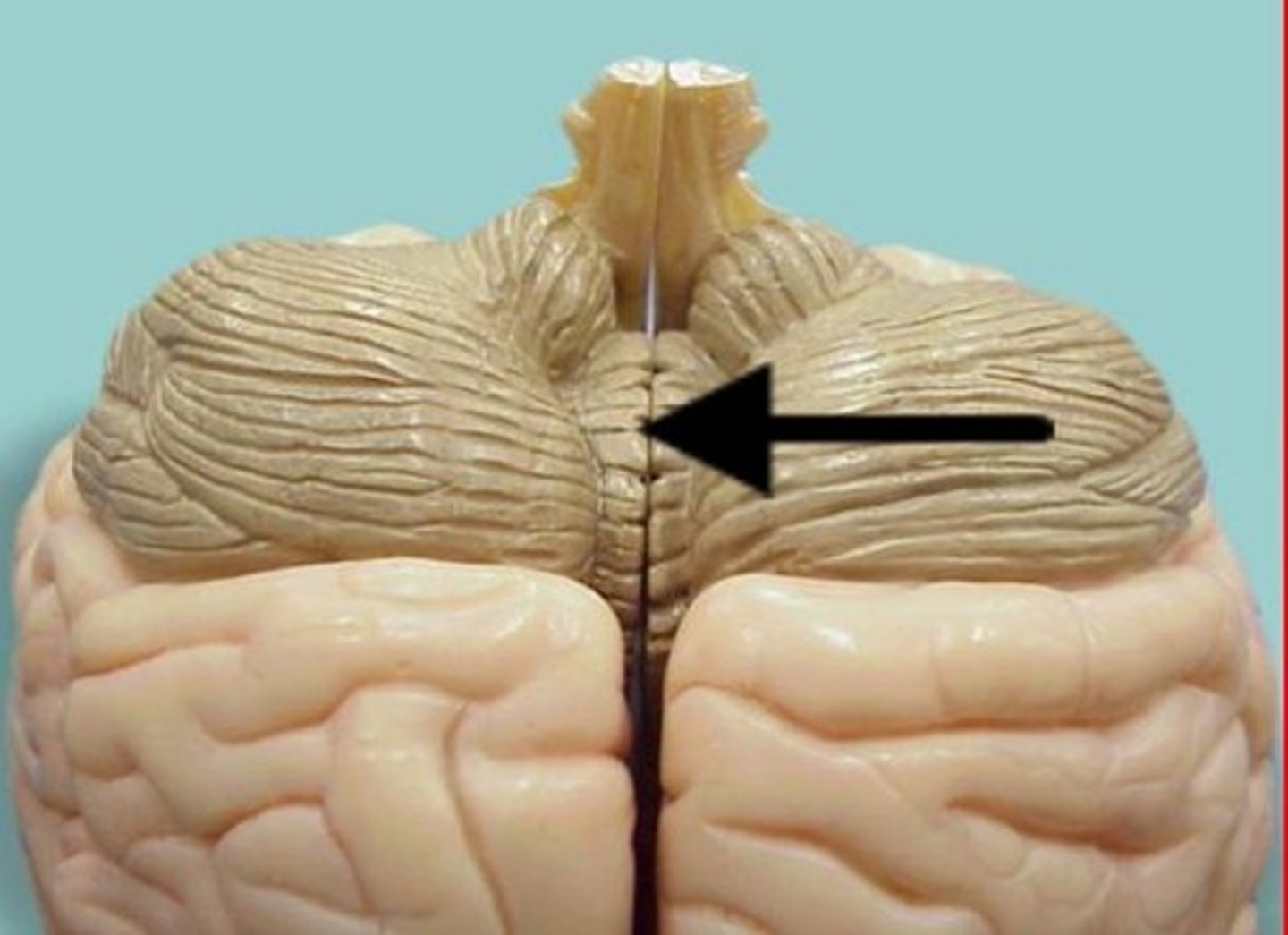
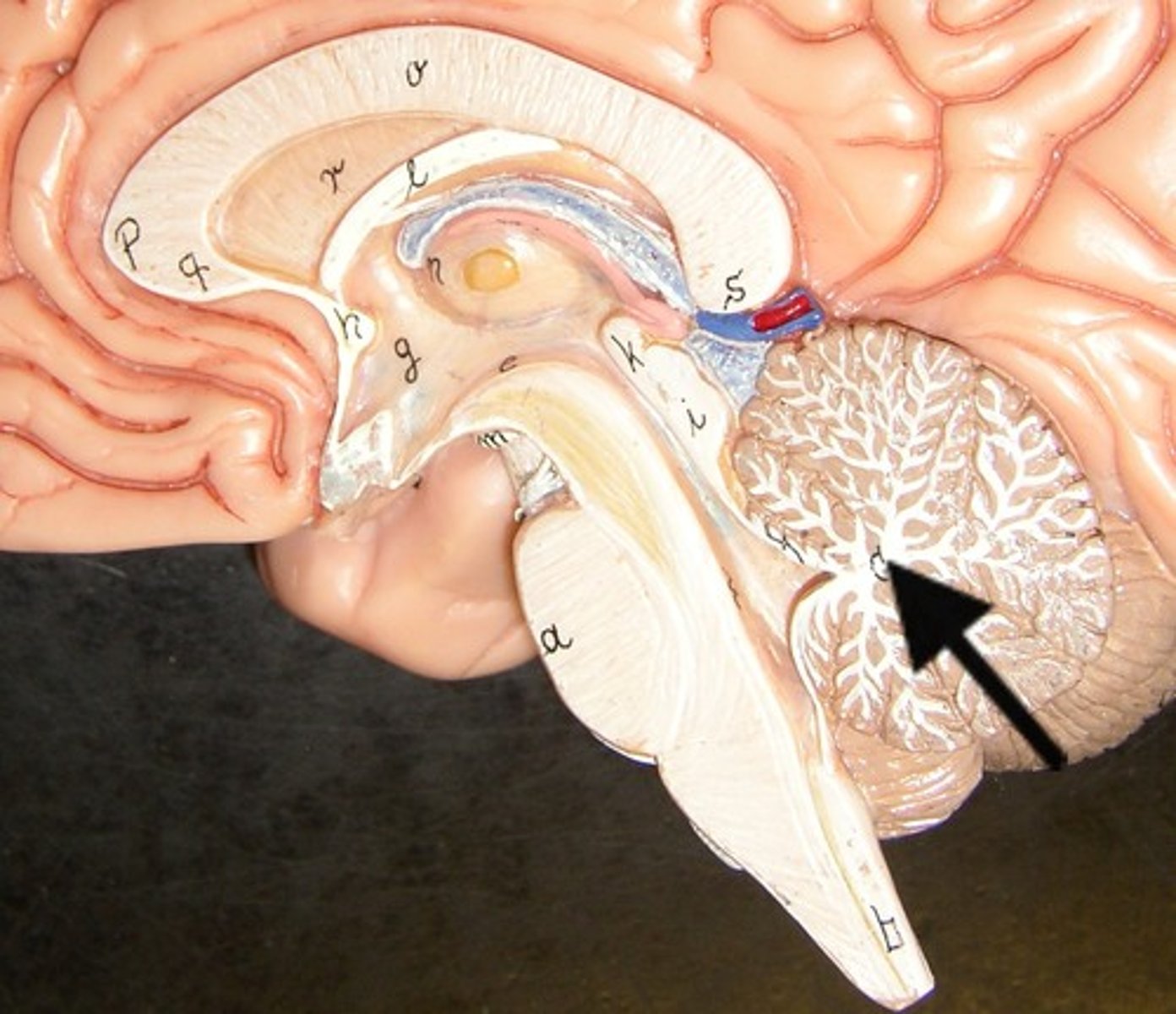
cerebellum
balance, equilibrium, gross motor movement
vermis (cerebellum)
The tissue between the two cerebellar hemispheres
arbor vitae
"tree of life," white matter of cerebellum
cerebrum
cerebral cortex
outer region of the cerebrum, containing sheets of nerve cells; gray matter of the brain

corpus callosum
the large band of neural fibers connecting the two brain hemispheres and carrying messages between them
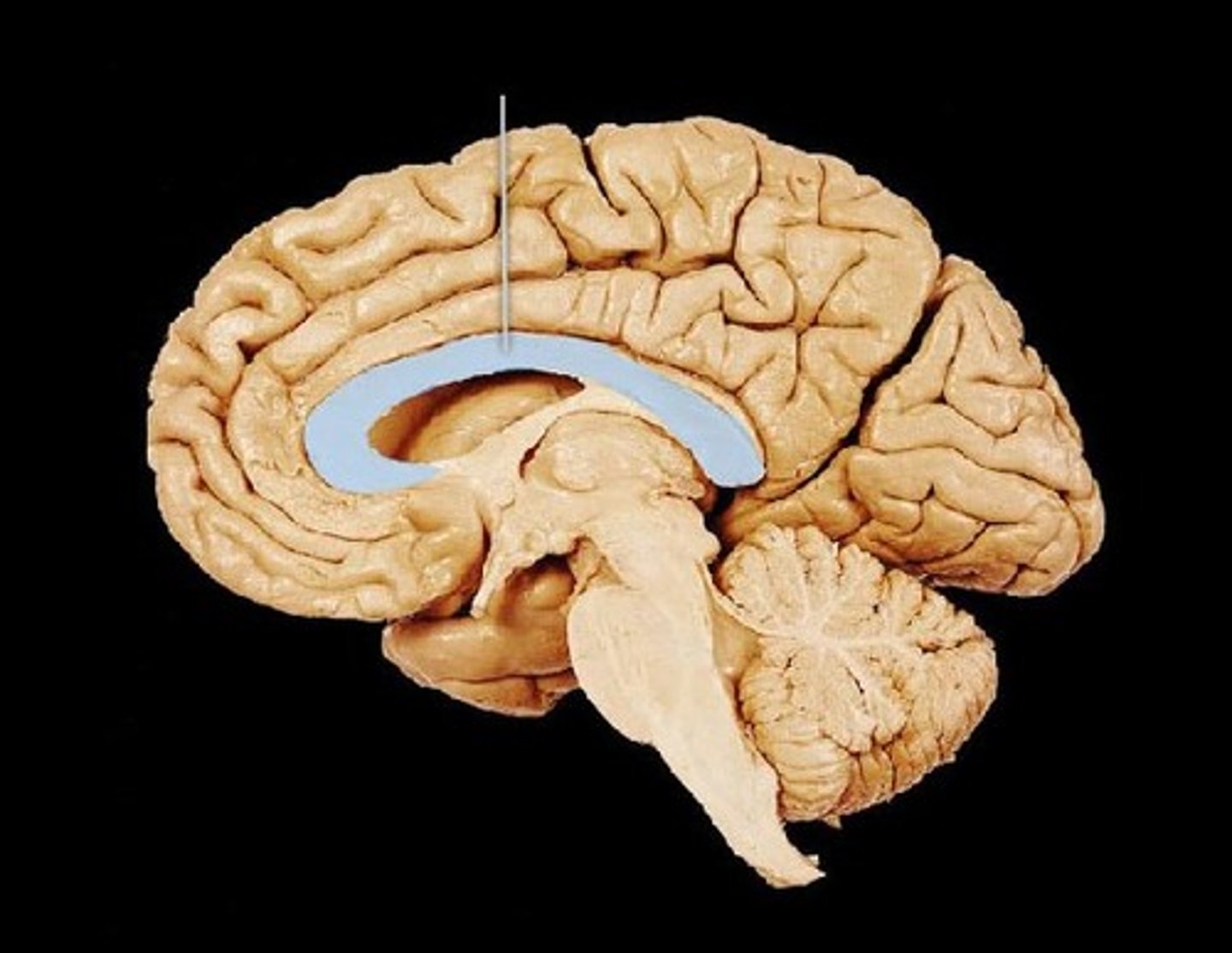
septum pellucidum
membrane that separates lateral ventricles
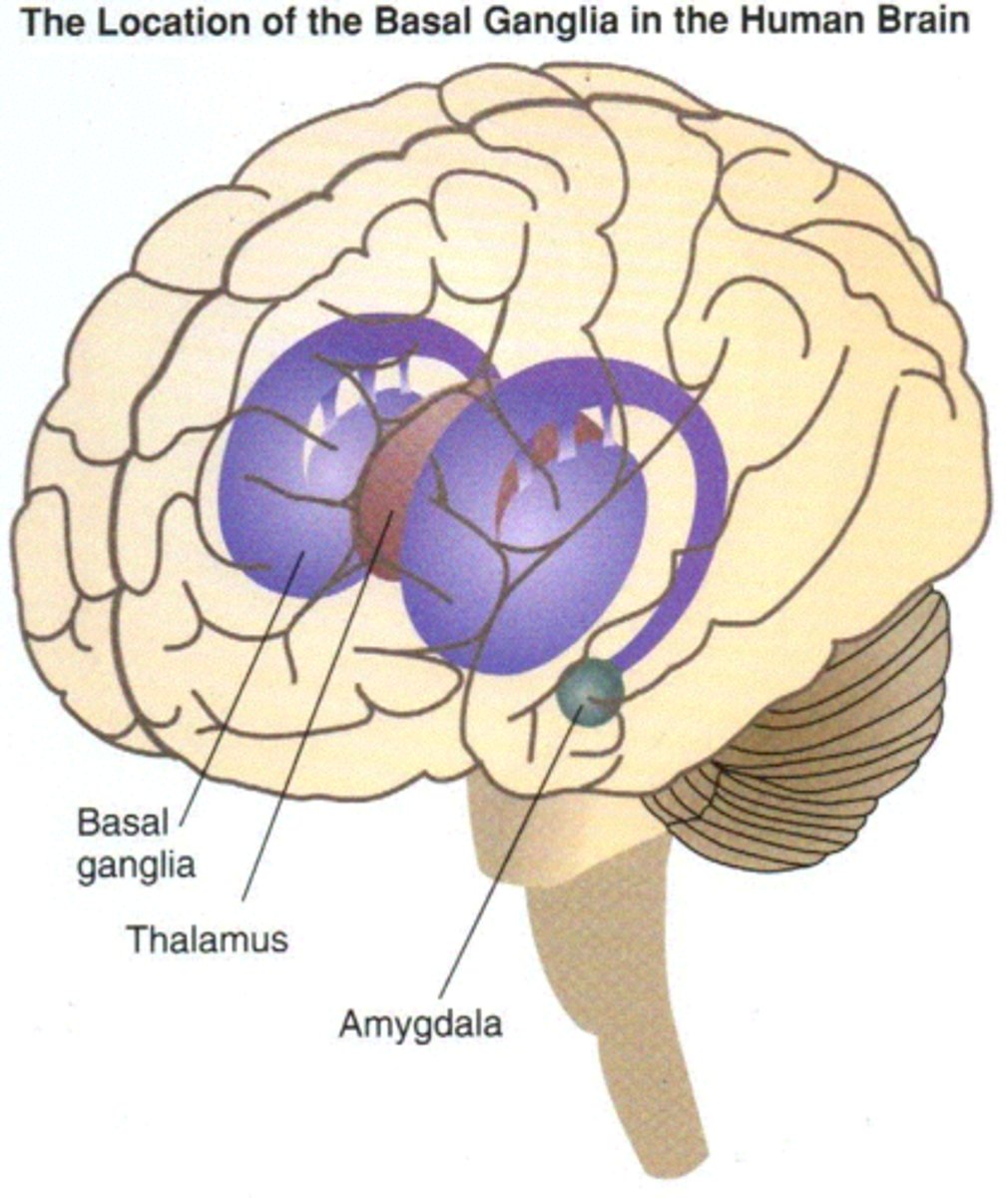
basal nuclei
internal masses of gray matter, smooth out motor movement
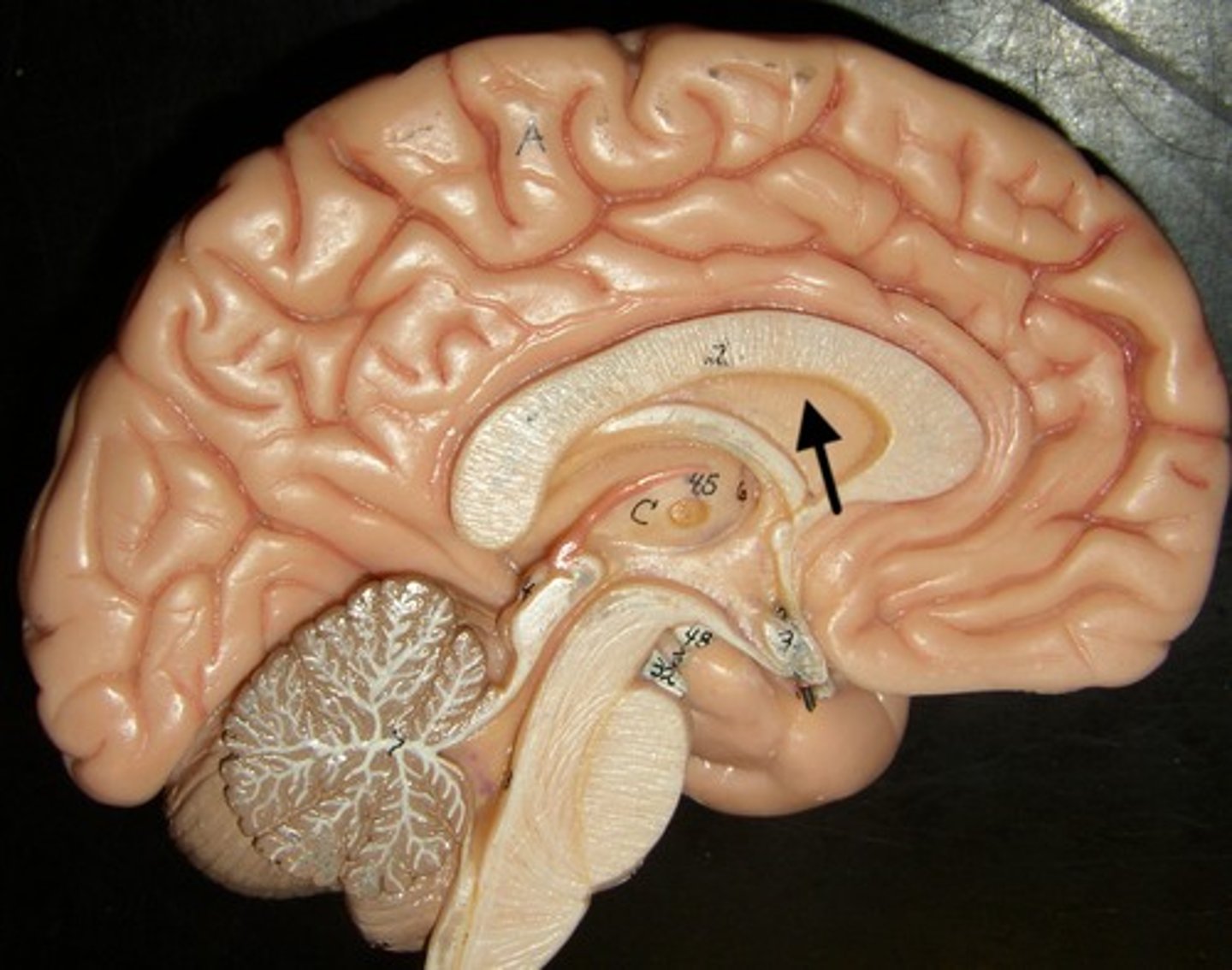
fornix
band under septum pellucidum
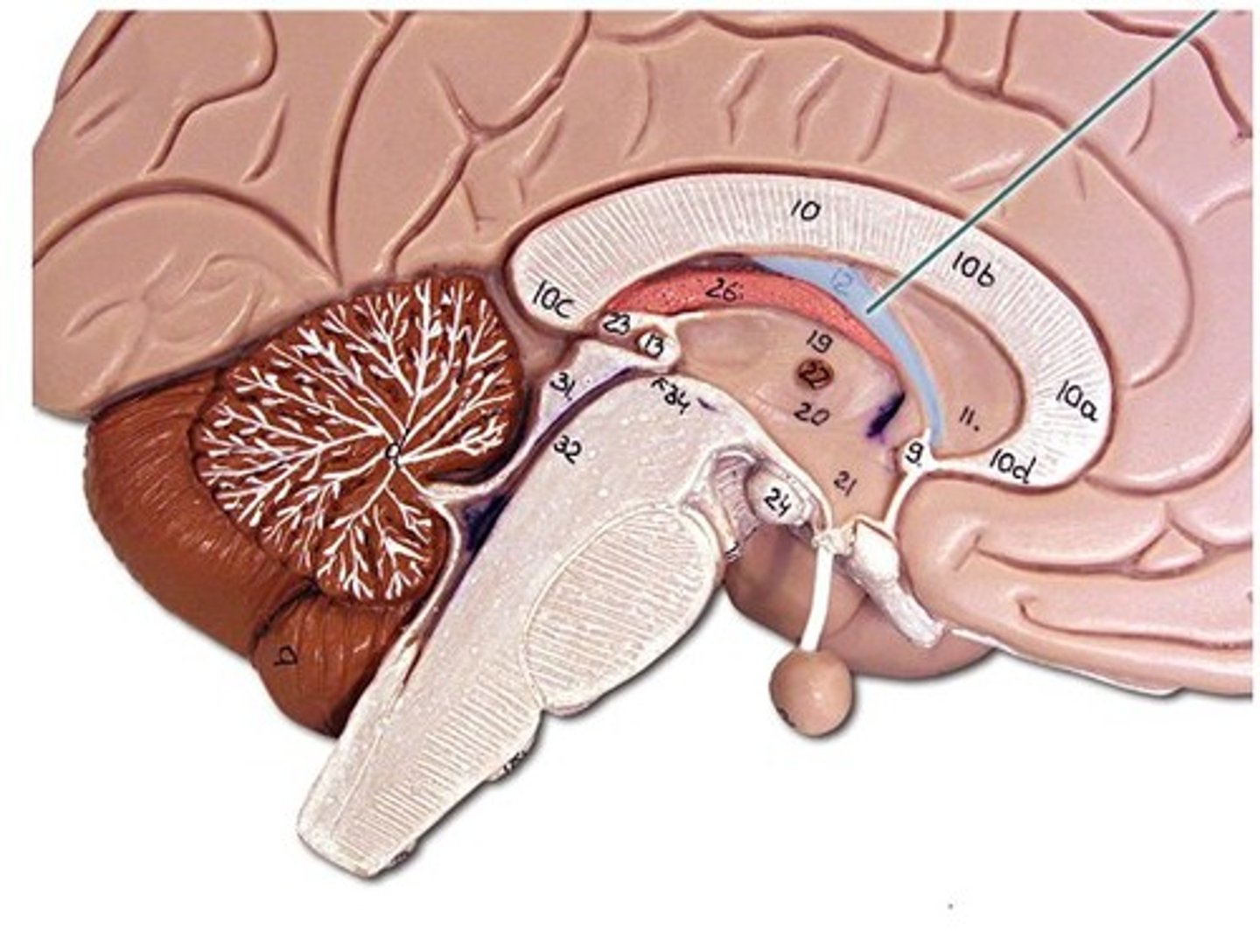
how is the arrangement of white and gray matter of the cerebrum different than in the spinal cord?
in the cerebrum, the gray matter is on the outside, in the spinal cord it's on the inside
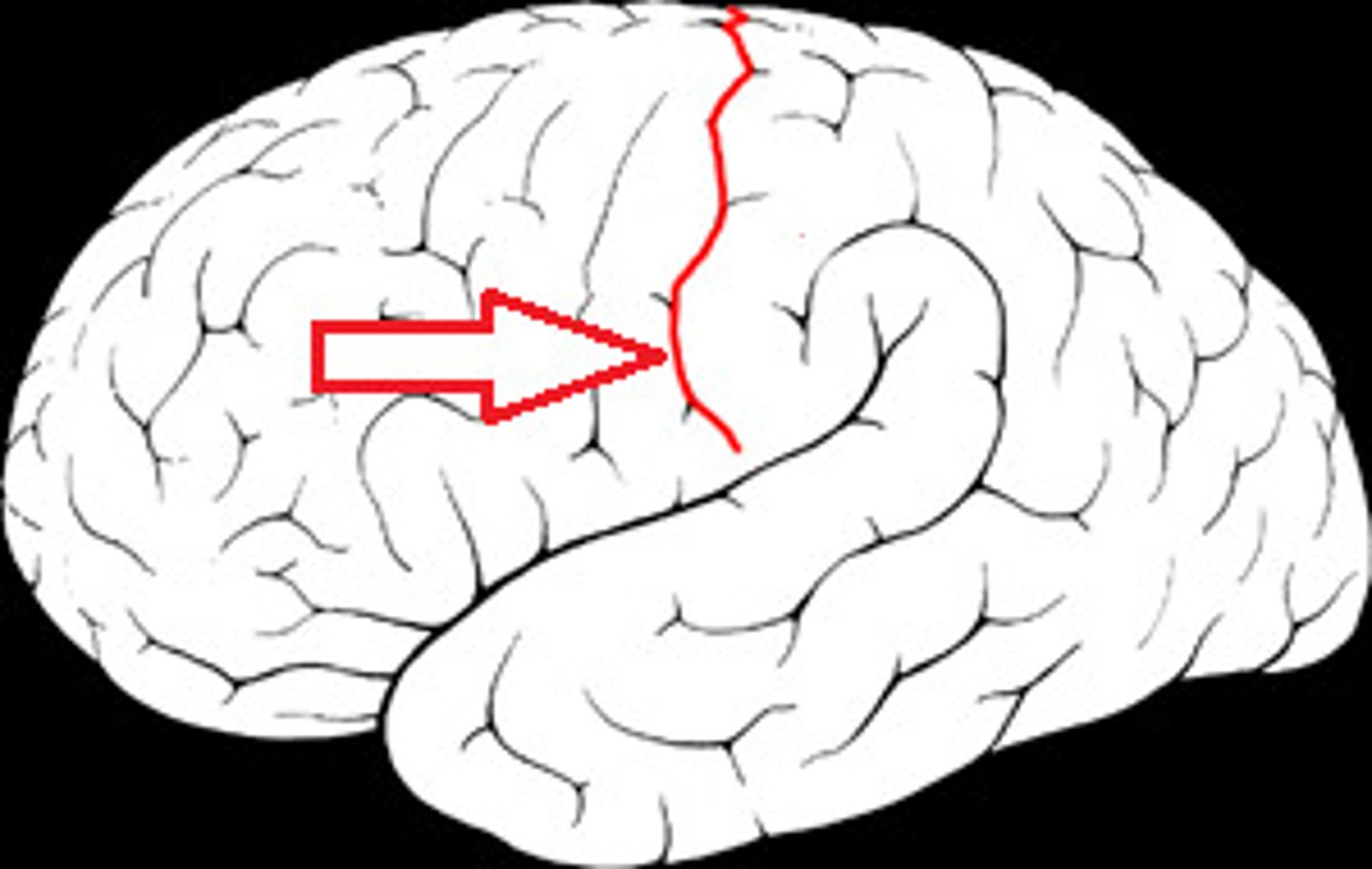
central sulcus
between postcentral and precentral gyri
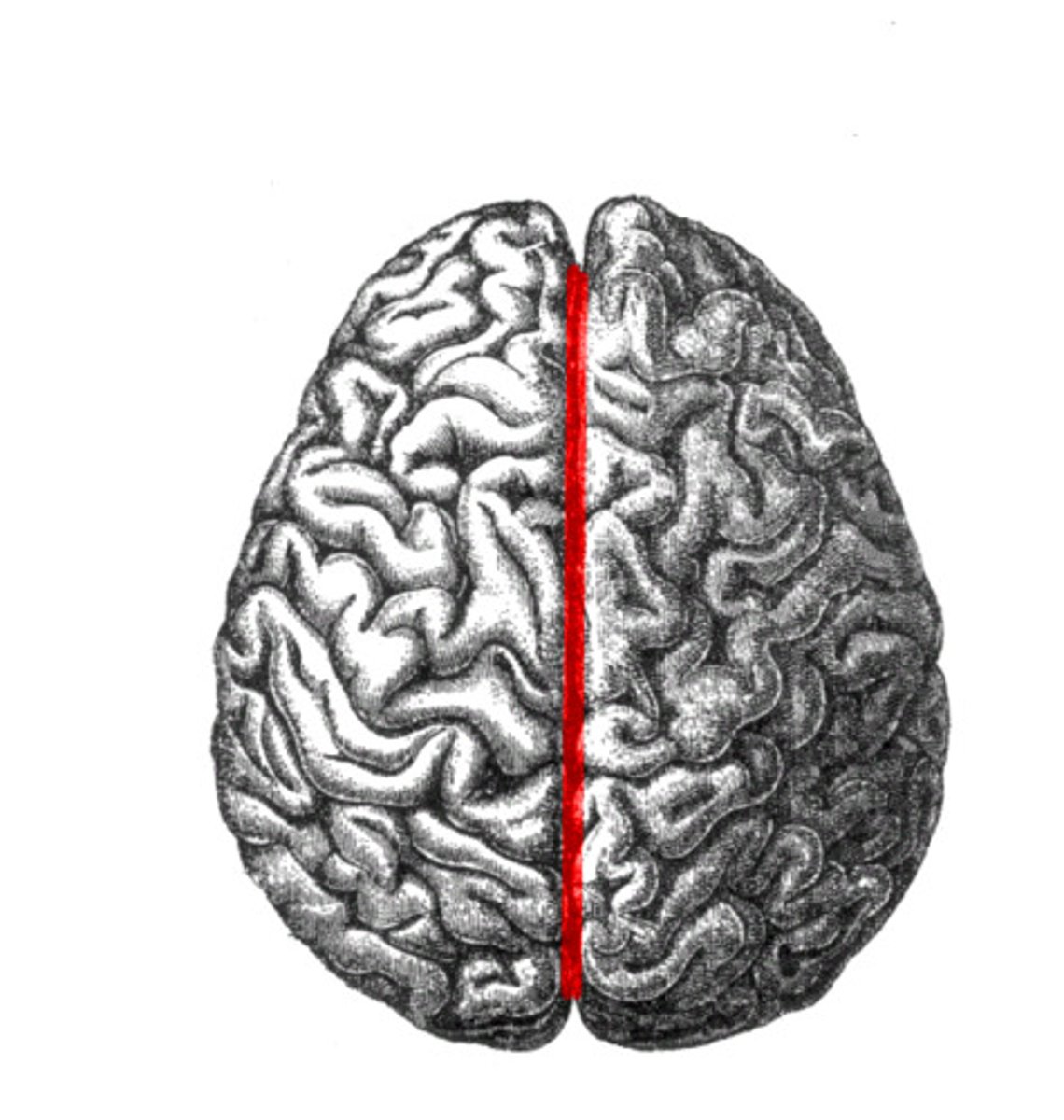
longitudinal fissure
separates cerebral hemispheres
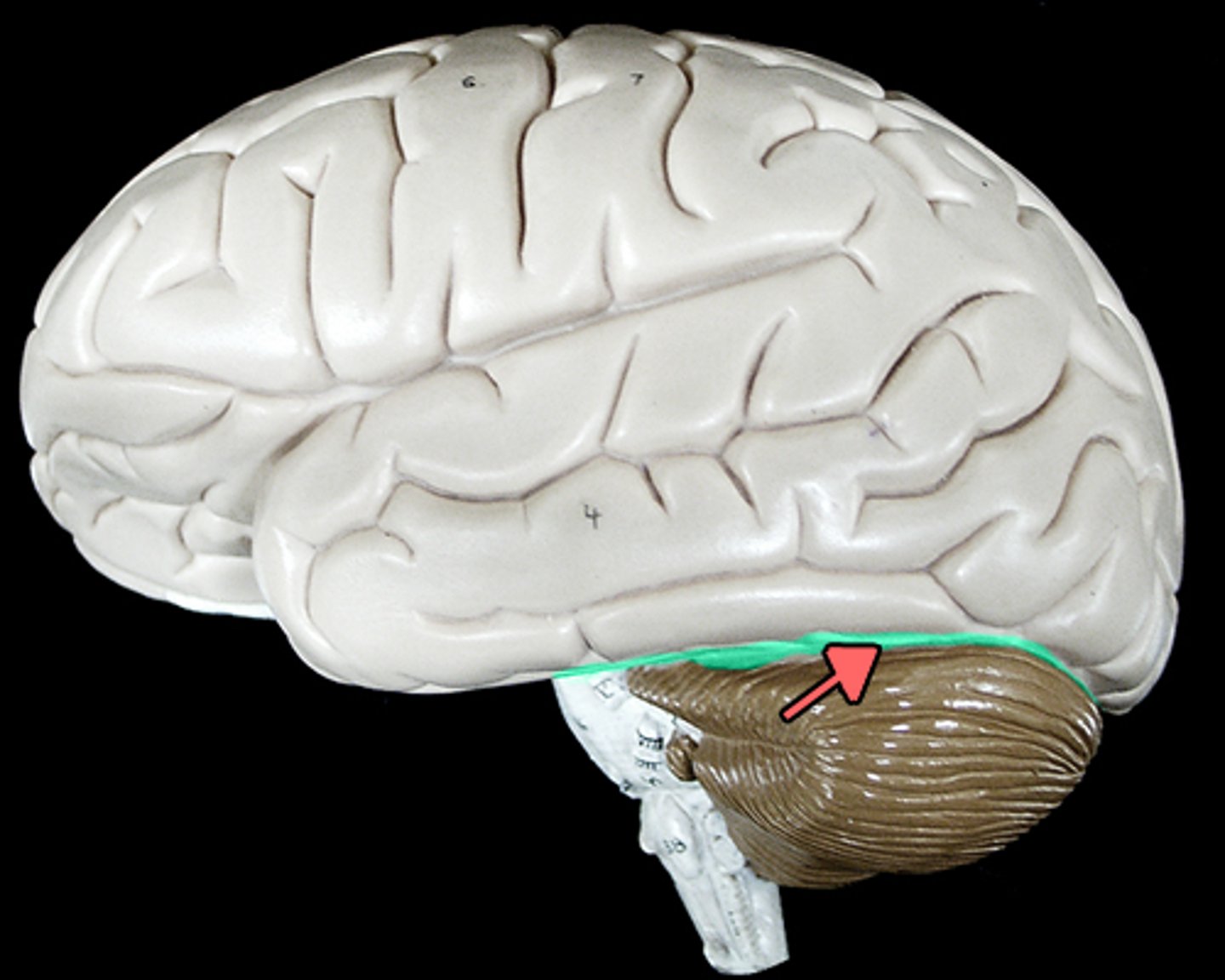
transverse fissure
separates cerebrum from cerebellum
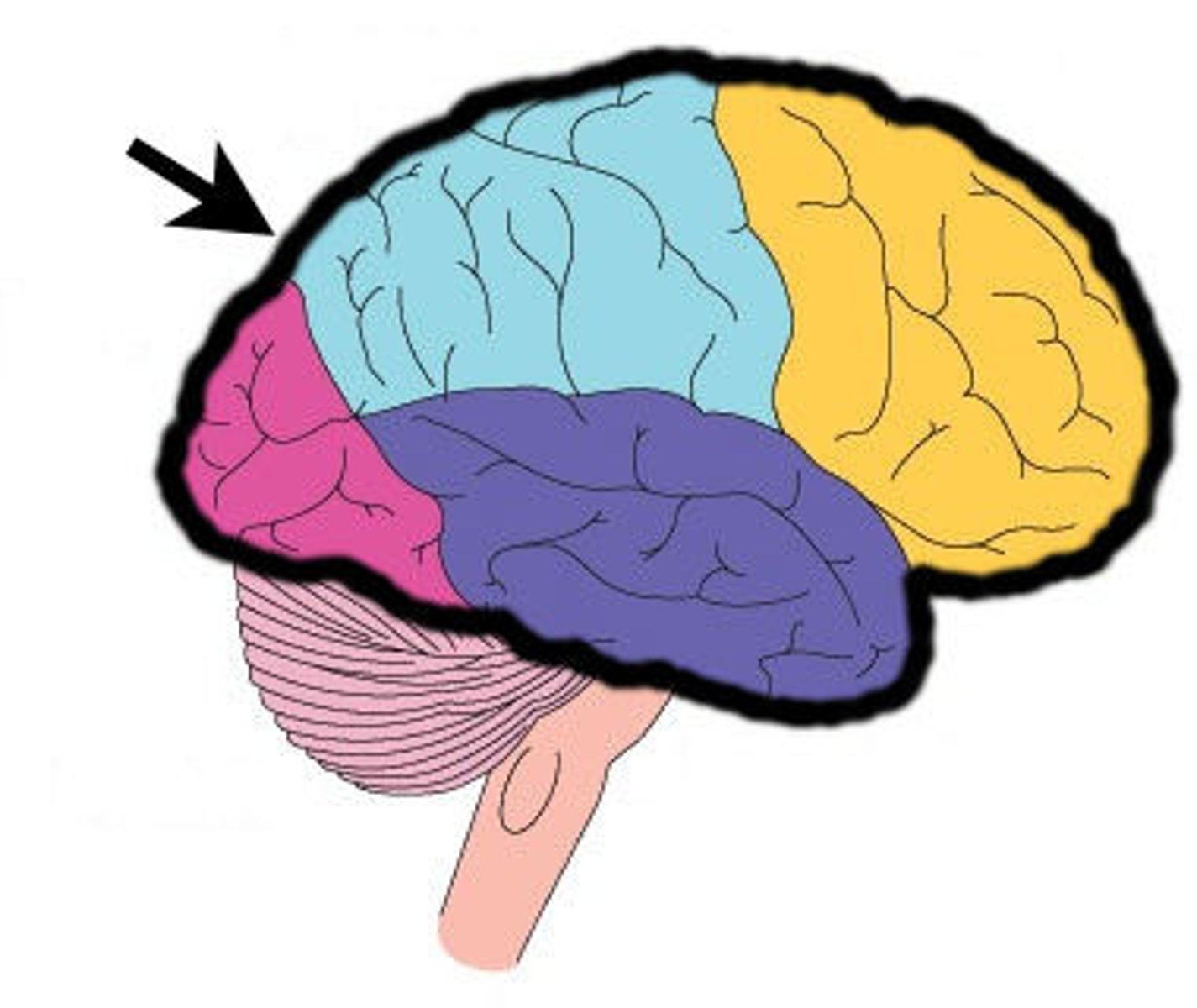
frontal lobe
associated with social cues, personality, planning, movement, emotions, and problem solving - contains primary motor cortex
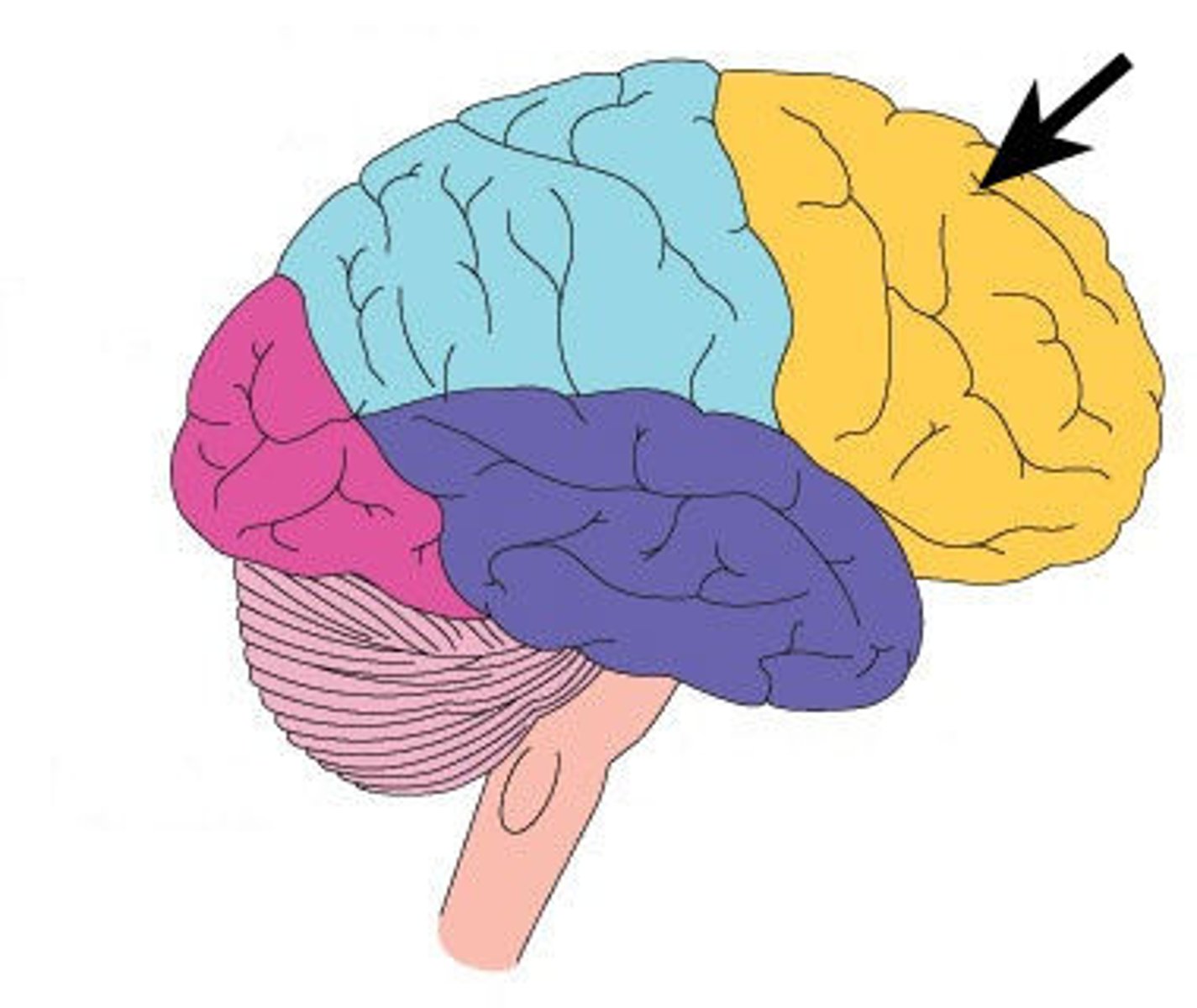
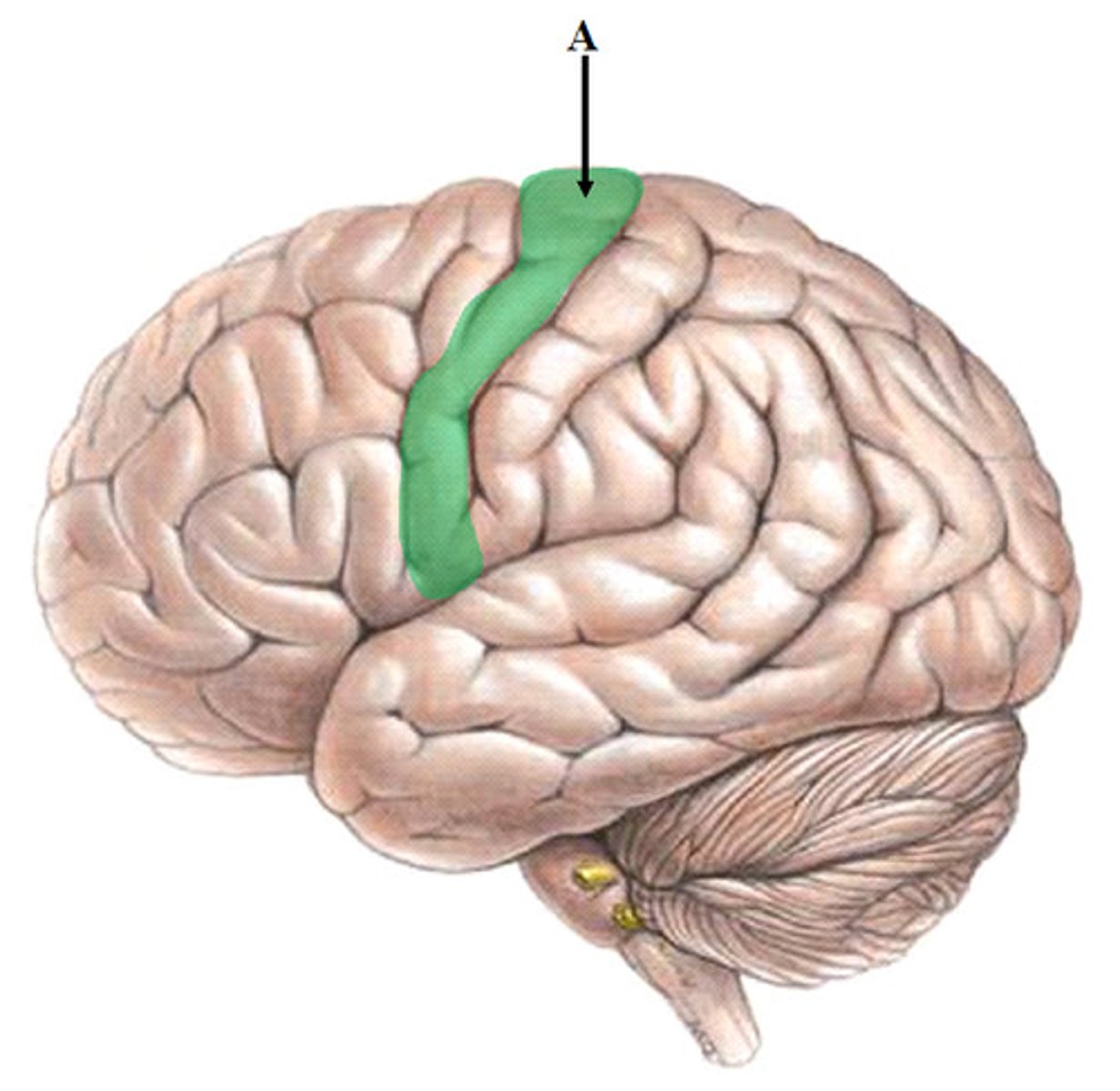
precentral gyrus
primary motor cortex
parietal lobe
A region of the cerebral cortex whose functions include processing information about touch, contains primary somatosensory cortex
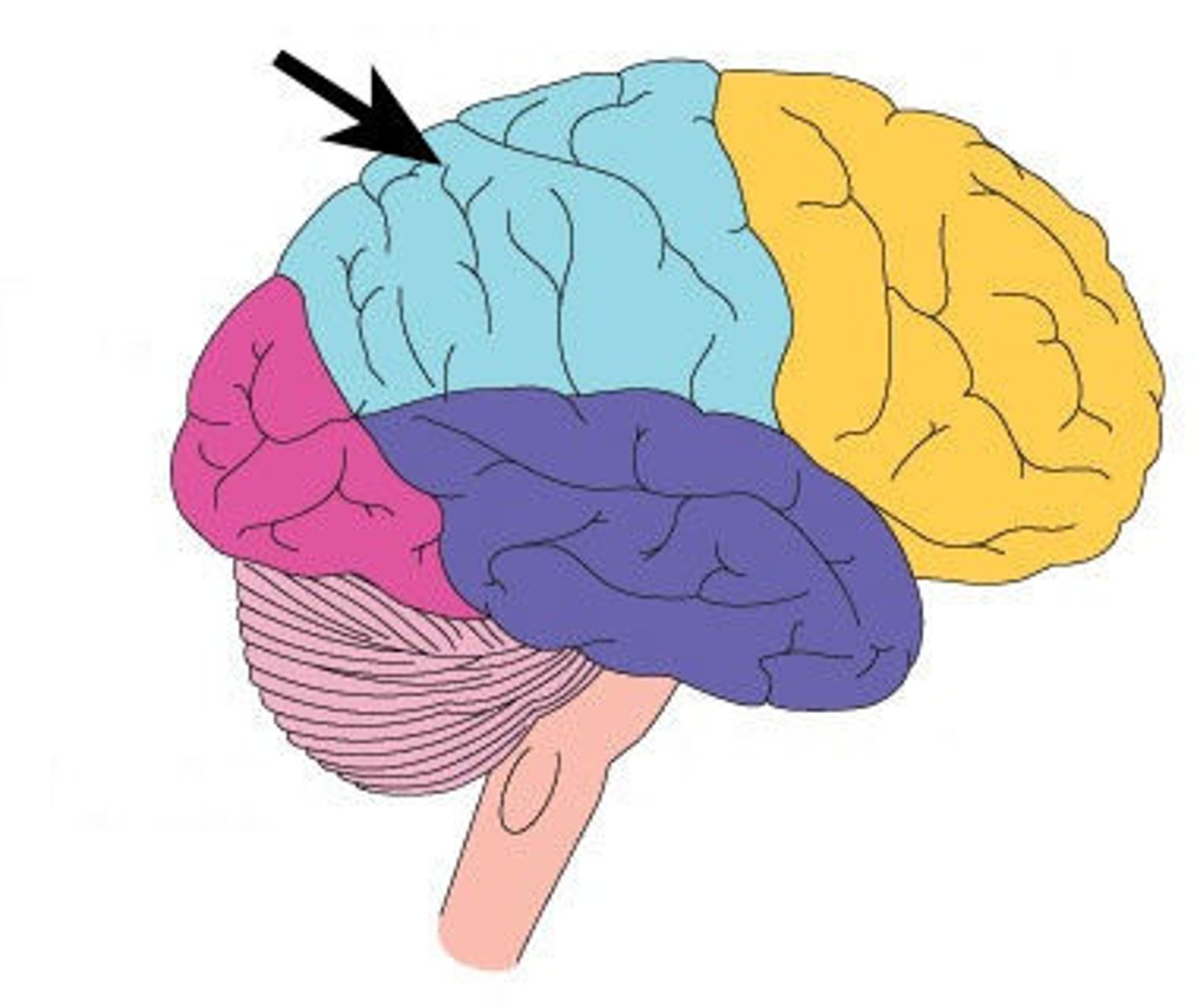
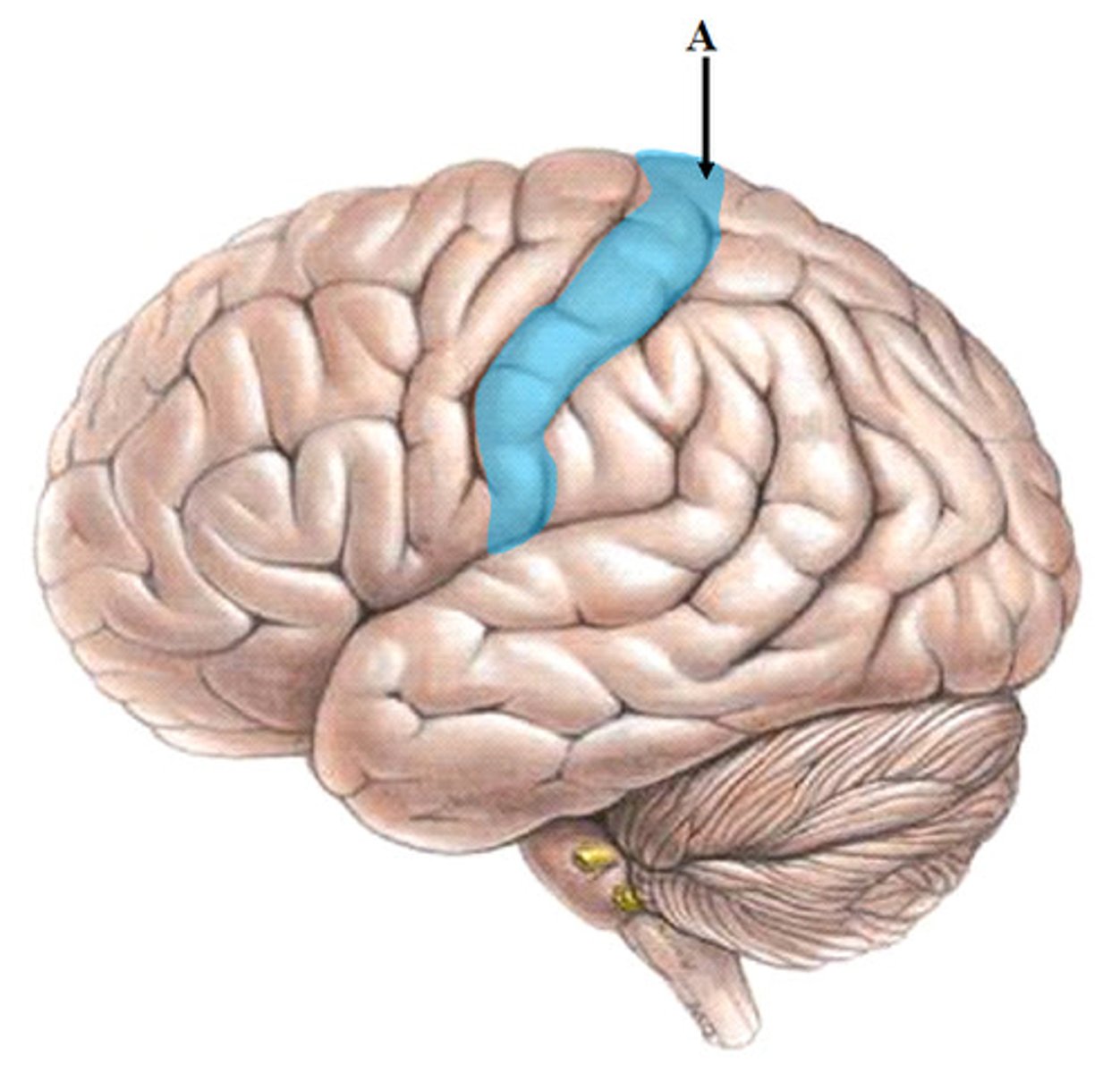
postcentral gyrus
primary somatosensory cortex
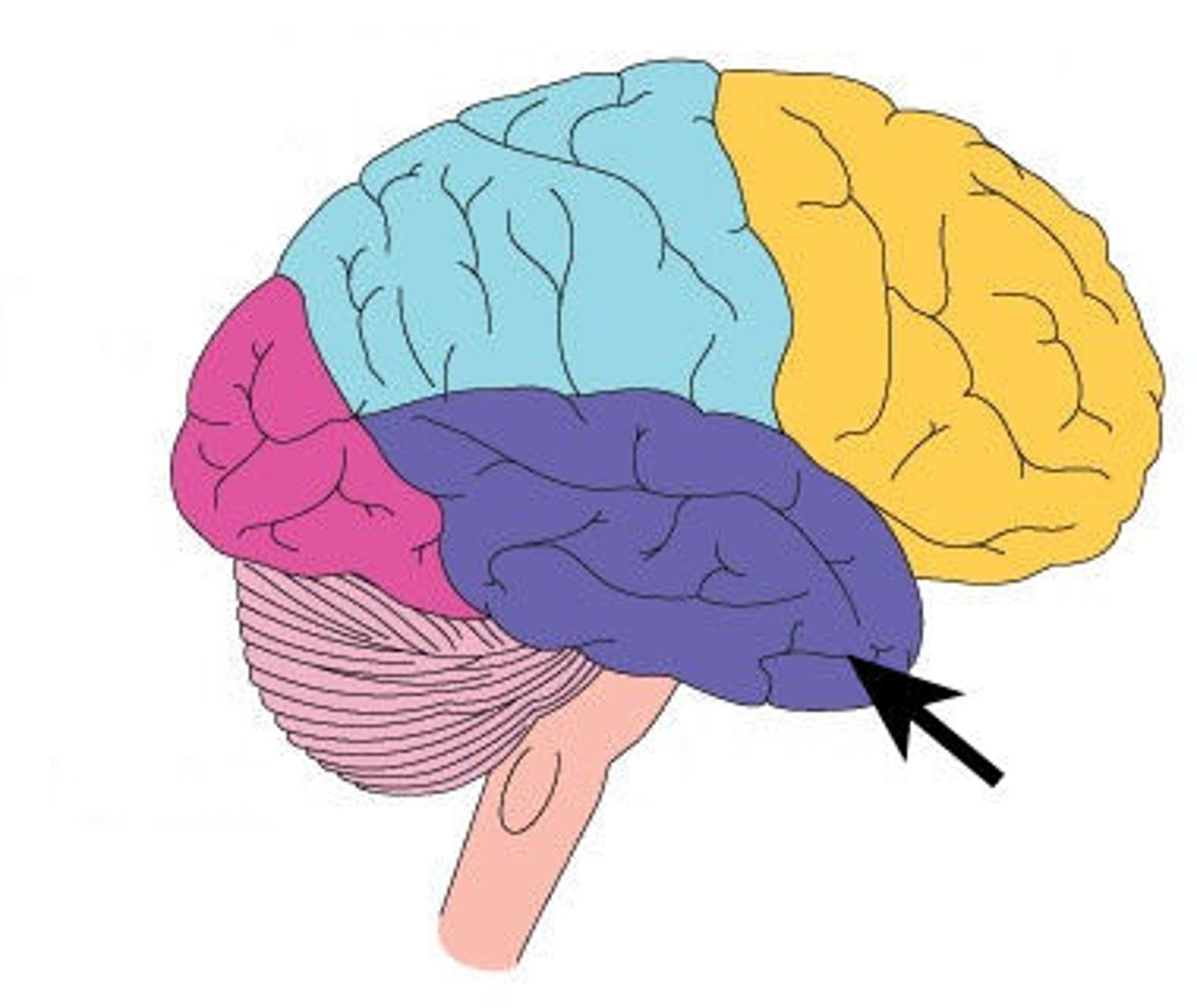
occipital lobe
visual center
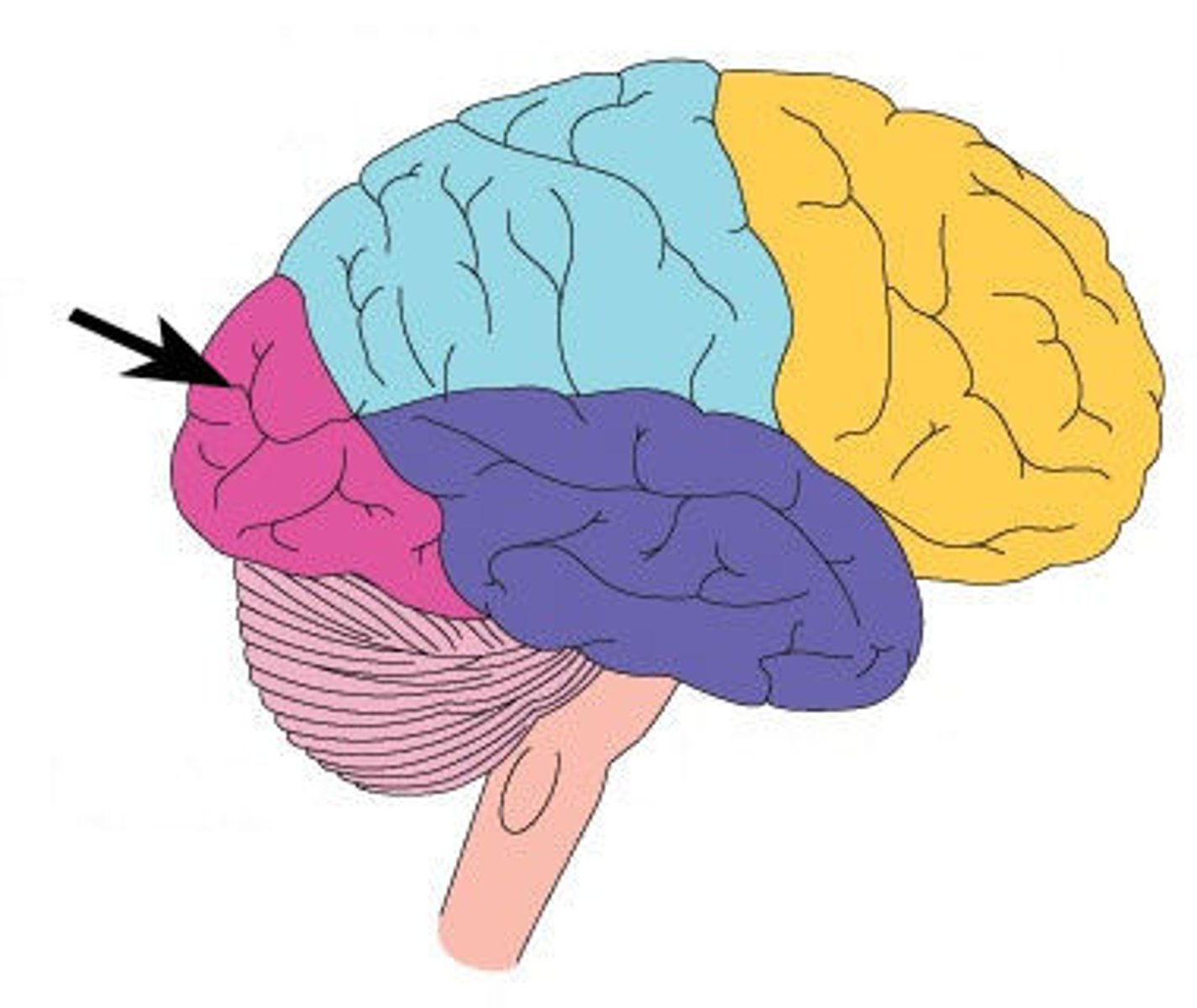
temporal lobe
language centers, auditory processing, olfactory
I. Olfactory nerve
sensory
origin: olfactory mucosa of nasal cavity
function: smell