Chapter 6: Adipose Tissue
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
60 Terms
Large, fat-storing cells that differentiate from mesenchymal stem cells.
What are adipocytes?
Poor conductor of heat; provides thermal insulation.
What role does adipose tissue play in body insulation?
15–20%
What percentage of body weight does adipose tissue normally make up in men?
High caloric density (9.3 kcal/g) and insoluble in water (no osmotic stress).
Why are triglycerides an efficient form of energy storage?
Around small blood vessels where mesenchymal cells are abundant.
Where do new adipocytes usually form?
White adipose tissue (WAT).
What is the most common type of adipose tissue?
One large lipid droplet, nucleus flattened against membrane (signet-ring appearance).
Describe the structure of a unilocular adipocyte.
By the 14th week of gestation.
When do humans first develop stores of white adipose tissue?
Mitochondria, small Golgi, few RER cisternae, free polyribosomes.
What cytoplasmic organelles are found near the nucleus of WAT cells?
Reticular fibers.
What fibers support white adipose tissue structure?
Carotenoids dissolved in the lipid.
What gives freshly dissected WAT its white-to-yellow color?
Leptin.
What hormone is secreted by WAT to regulate appetite?
Lipoma.
What type of tumor is a benign proliferation of adipocytes?
Obesity.
What condition is linked to chronic mild inflammation from excess white fat?
Because both adipocyte size and number increase (hyperplasia).
In childhood obesity, why is weight loss harder long-term?
Lipoprotein complexes transporting dietary fats from intestines.
What are chylomicrons?
Lipoproteins transporting triglycerides synthesized in the liver.
What are VLDLs?
Lipoprotein lipase.
What enzyme hydrolyzes triglycerides in capillaries?
Norepinephrine via cAMP system.
What activates hormone-sensitive lipase for fat mobilization?
Albumin.
What protein binds free fatty acids in blood transport?
Stimulates glucose uptake and triglyceride formation.
How does insulin affect adipocytes?
Stimulates lipase activity and lipid mobilization.
How does growth hormone affect adipocytes?
Acts as a satiety factor, regulates appetite and adipose formation.
What is leptin’s role?
2–5%.
What percentage of body weight does brown fat make up in newborns?
Back, neck, and shoulders.
Where is brown adipose tissue located in newborns?
Abundant mitochondria with cytochromes + rich blood supply.
What feature gives brown fat its color?
Cells contain many small lipid droplets.
Why is brown adipose tissue called multilocular?
Heat production (non-shivering thermogenesis).
What is the main function of brown adipose tissue?
Uncoupling protein-1 (UCP1, thermogenin).
What protein in mitochondria is essential for heat generation in BAT?
Sympathetic innervation via norepinephrine.
What stimulates BAT activity?
Mesenchymal stem cells (mesoderm).
From what embryonic layer are adipocytes derived?
Precursors resembling fibroblasts with cytoplasmic lipid droplets.
What are preadipocytes?
Beige adipocytes share features of both white and brown fat; can convert to brown during cold adaptation.
What is the difference between white and beige adipocytes?
Earlier than white fat.
When does brown adipose tissue appear in fetal development?
They shift to functional brown adipocytes.
What happens to beige cells during cold adaptation?
Autonomic nerves stimulate differentiation and prevent apoptosis.
How does the nervous system affect brown adipocyte differentiation?
Reticular fibers and connective tissue septa.
What supports adipose tissue structurally?
Dietary fats (chylomicrons), liver-synthesized fats (VLDLs), locally synthesized fatty acids.
How do adipocytes store lipids? (3 sources)
Norepinephrine.
What hormone activates lipase in adipocytes for lipid mobilization?
Diabetes and cardiovascular disease.
What diseases are strongly linked to increased visceral fat?
1. Epicardial adipose tissue
2. Ectopic hepatic lipids
3. Visceral adipose tissue
4. Subcutaneous adipose tissue
5. Perivascular adipose tissue
What do you call the adipose tissue located on the ff. location?
1. Surface of the heart.
2. Liver
3. Around small intestines
4. Near the surface of the body
5. Surrounding the blood vessels
Around small blood vessels
Undifferentiated mesenchymal cells are most abundant
By filling of existing adipocytes until around age 10, followed by period of new fat cell differentiation that lasts through adolescence.
How does adipose tissue increases?
Sex hormones
WAT exists in breasts and thighs, too. What regulates this?
Caveolae
This is responsible for th lipid trafficking, and formation of the large triglyceride storage droplet.
Hibernomas
Fetal lipomas of brown fat are called
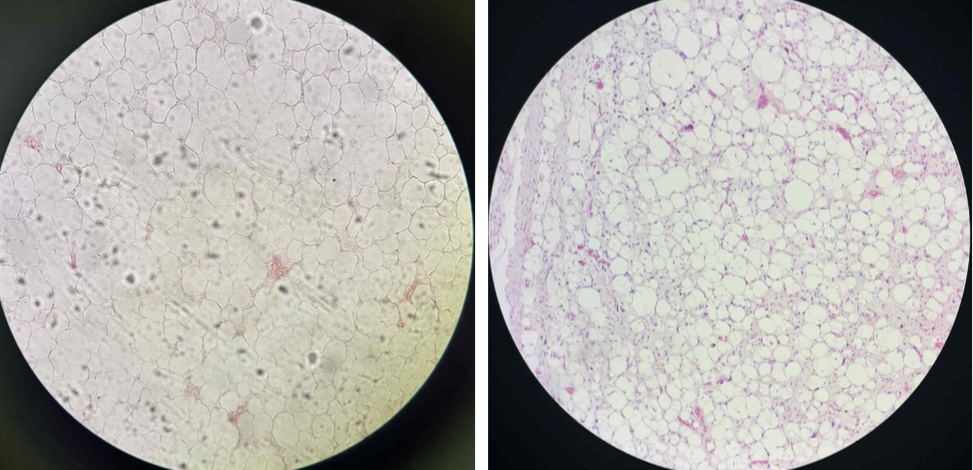
Both are unilocular adipocytes. Lipomas are benign tumors and liposarcomas are malignant adipose tumors.
Differentiate lipomas and liposrcomas
Starvation
During this, adipocytes can lose nearly all their fat and become polyhedral or spindle-shaped cells with only very small lipid droplets
insufficient or defective receptors or post-receptor signal transduction
In most obese humans, adipocytes produce adequate or excess quantities of leptin, but target cells are not responsive due apparently to
hypertrophy
It is present in adult-onset obesity. Mainly involves increasing the size of existing adipocytes also called as
depletion of chylomicrons
Clinical tests for circulating levels of lipoproteins routinely measure blood lipids after fasting to allow
active transport and diffusion
Free Fatty and Acids and Glycerols enter the adipocytes by both
Kidneys, adrenal glands, aorta, and mediastinum
Where do brown fats occur in adults?
Promote brown adipocyte differentiation and prevent apoptosis in mature fat cells.
Besides stimulating thermogenic activity, what other functions does autonomic nerves do?
20%
White adipose tissue is found in many organs throughout the body, typically forming about … of the body weight in adults
Leptin
is a polypeptide hormone with target cells in the hypothalamus that is released from white adipocytes and helps regulate eating behavior
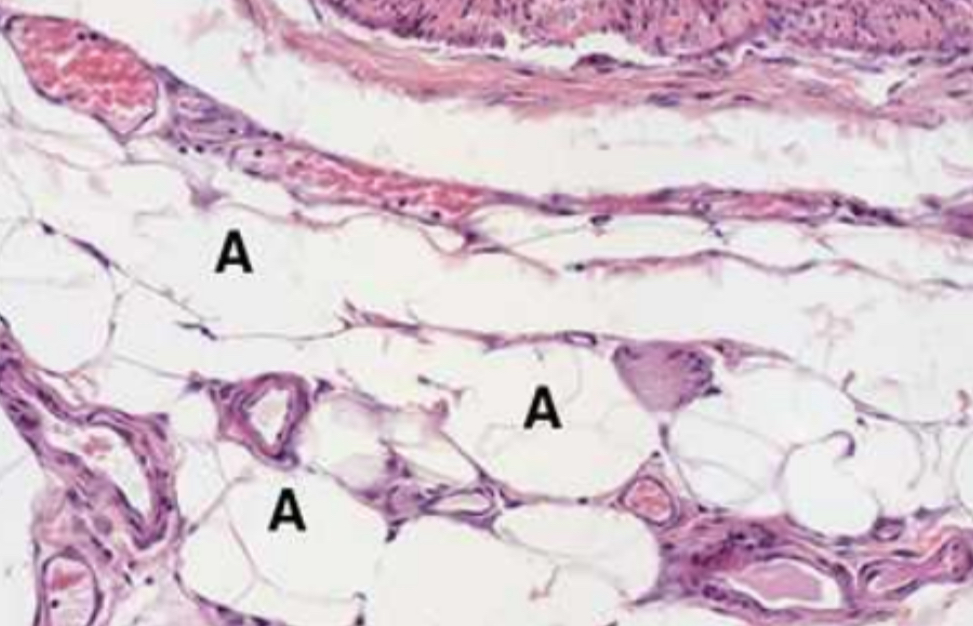
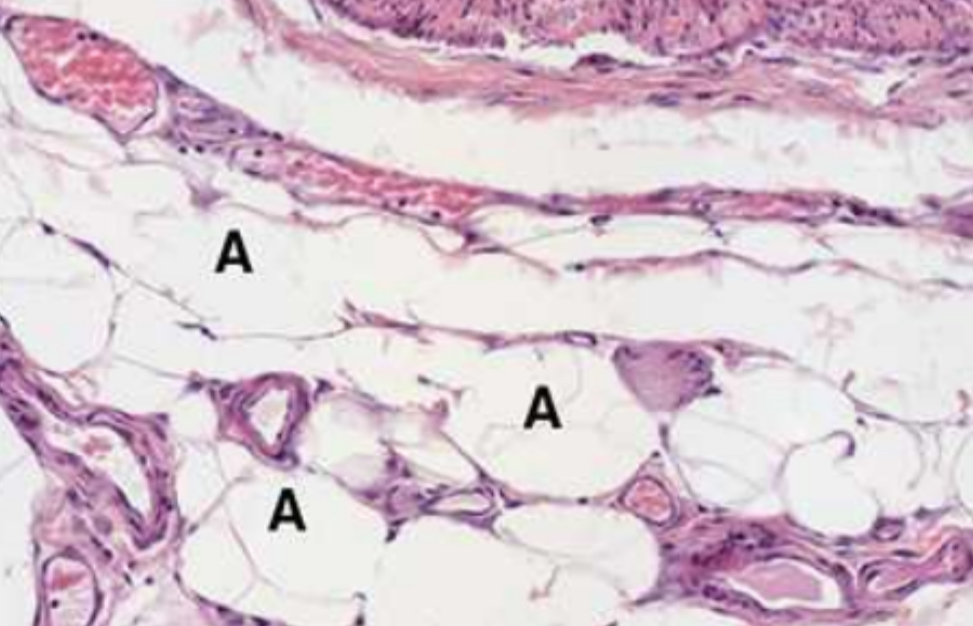
1. White or Unilocular Adipose Tissue
2. Large adipocytes associate with small blood vessels.
3. Lipid was dissolved away in slide preparation
1. Specimen?
2. Describe the specimen.
3. Why are fat cells empty?
1. A: Lipoma; B: Liposarcoma
1. Specimen A and B?
1. Brown Adipose Tissue
2. Slightly smaller than WAT, has small lipid droplets, and central spherical nuclei.
1. Specimen?
2. Describe and compare to the other type.
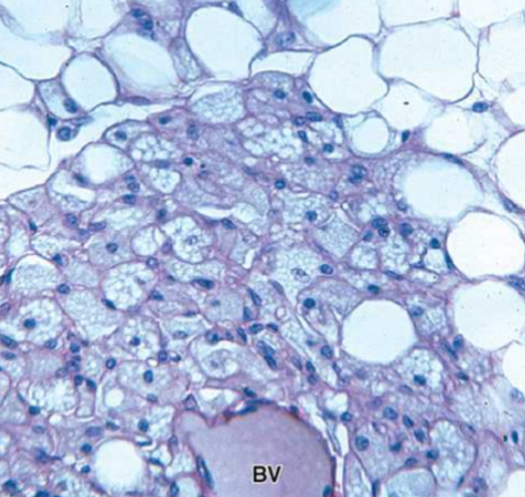
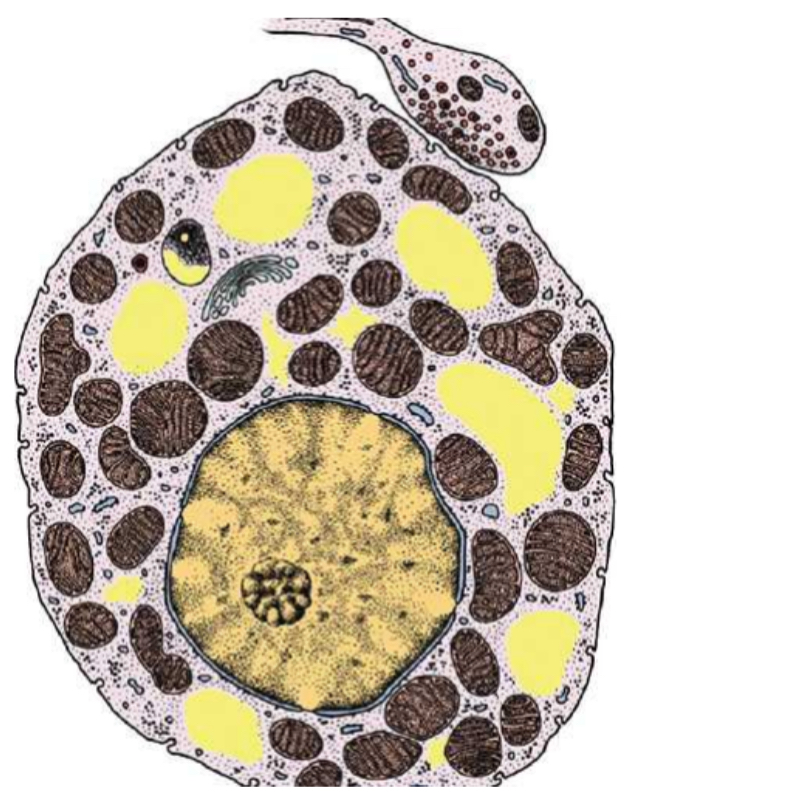
1. Brown Adipose Tissue
2. Yellow: small lipid droplets; Brown: Numerous mitochondria
3. Sympathetic nerve. Releases norepinephrine. To stimulate mitochondrial production of heat.
1. Specimen?
2. What are the yellow and brown?
3. What is the one attached to it outside? What does it do and why?