Anatomy, Cells & Tissues
1/75
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
76 Terms
Epithelial tissue (cells)
Squamous cells
Columnar cells
Cuboid cells
(what type of tissue?)
epithelial tissue (def)
lines the cavities and surfaces of structures throughout the body, and also form many glands.
Functions: protection, secretion, absorption
simple squamous cells
one cell thick, very thin, permeable
found in protected regions where absorption takes place, such as: alveoli (lungs-air sacs), wall of capillary, lining of kidney
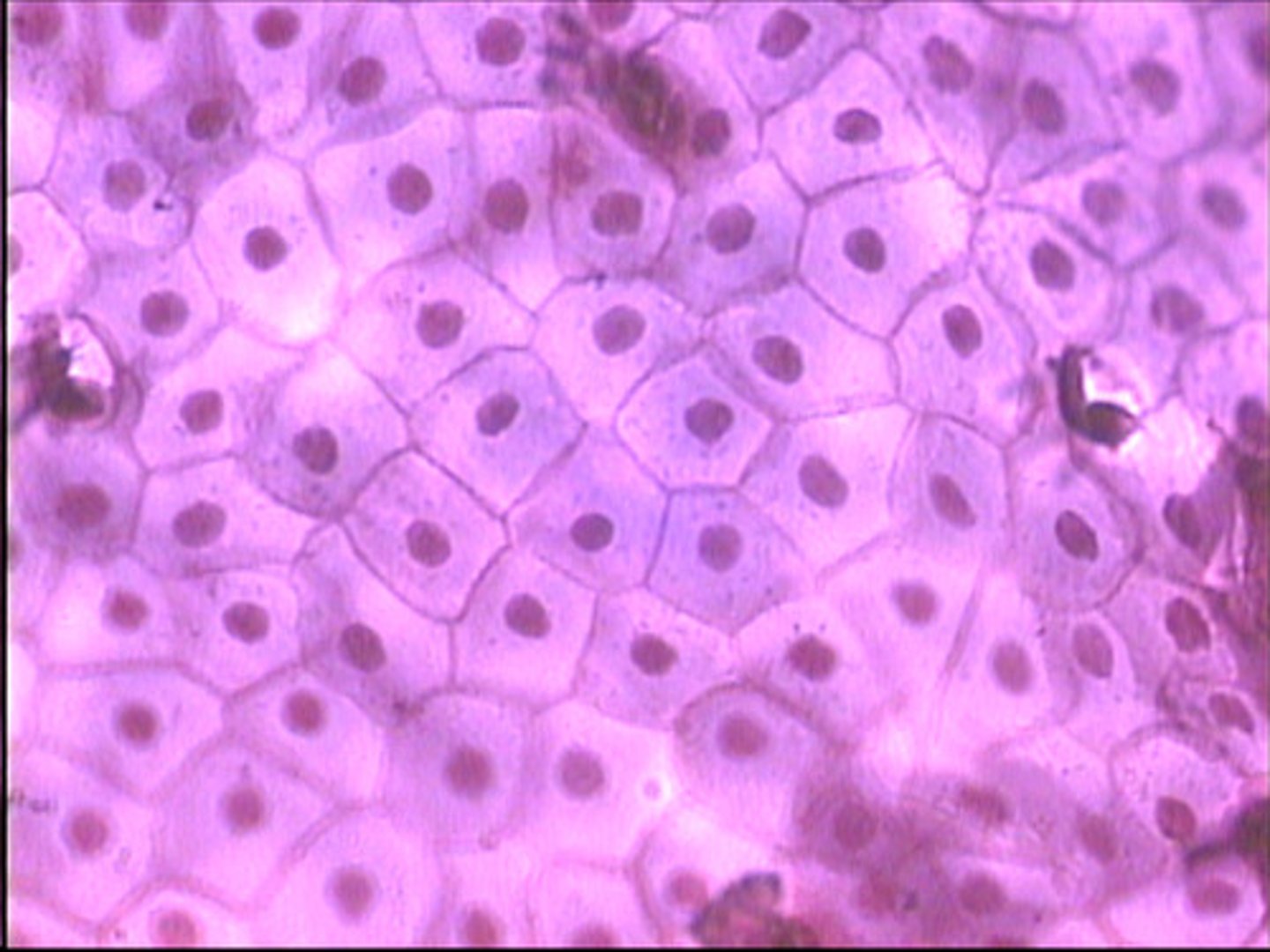
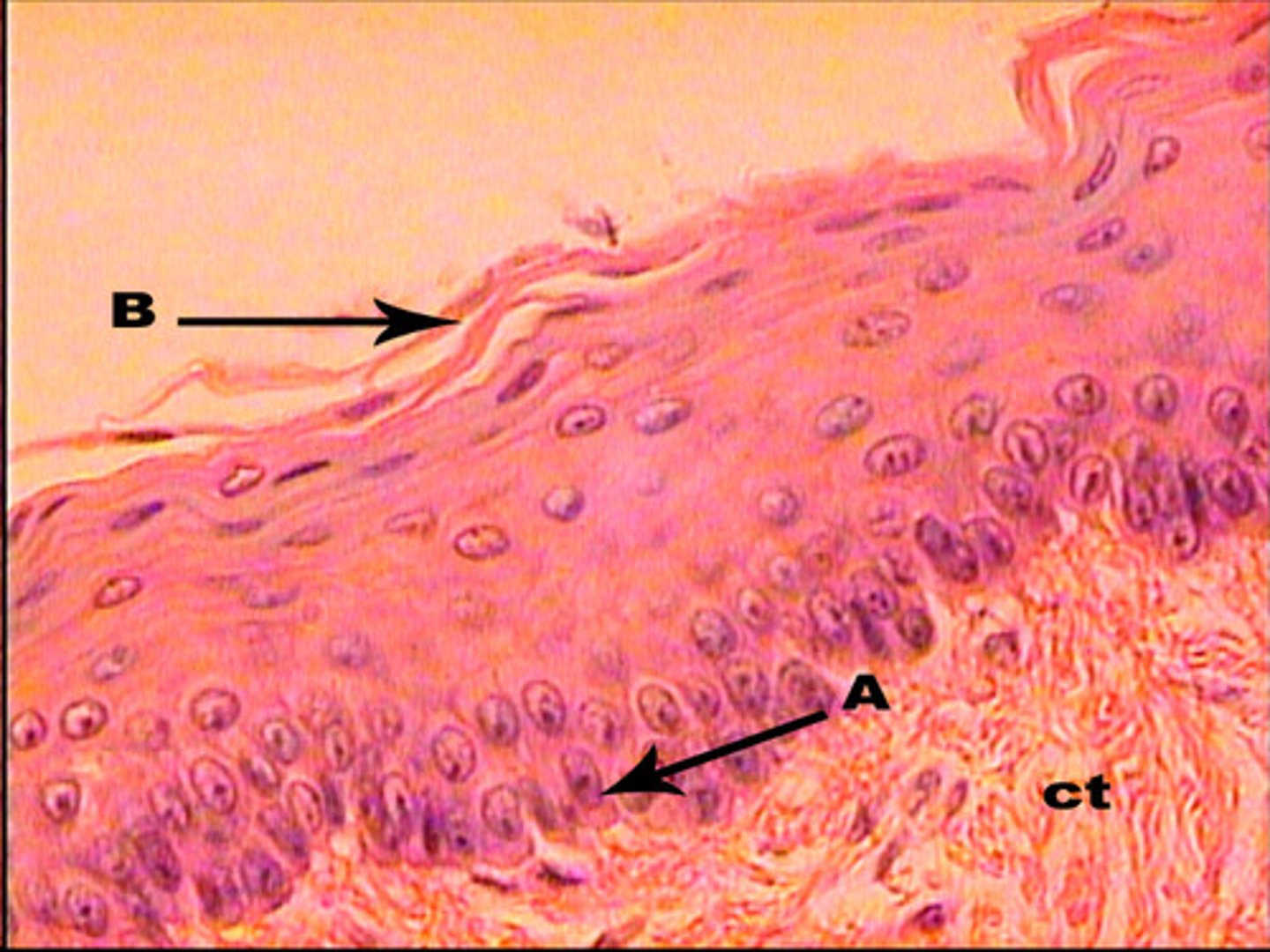
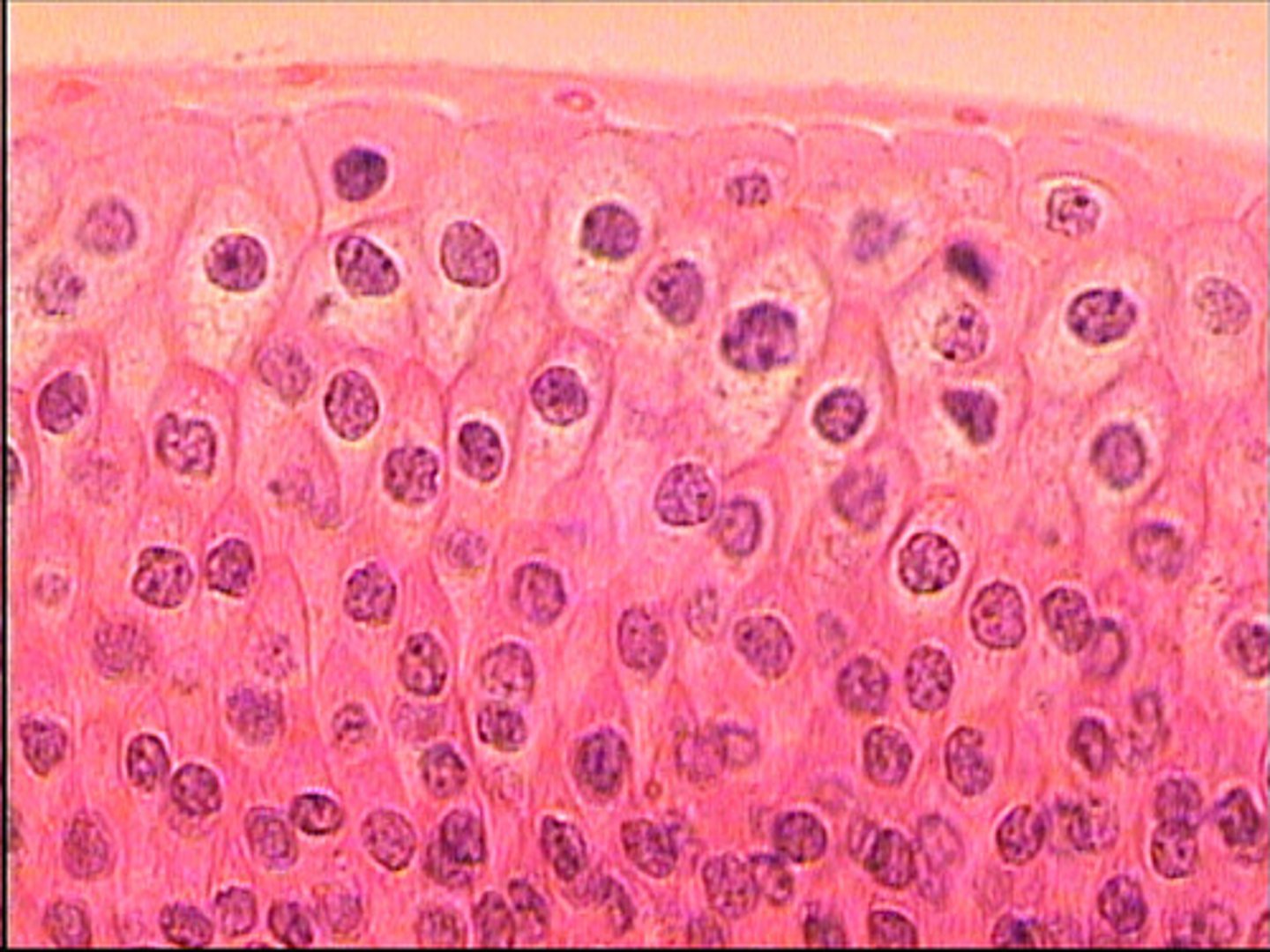
Stratified squamous cells
in layers, flat, scale-like, surface cells are shed and replaced
keratinized-packed with keratin, makes cells tough and water resistant
found in epidermis (surface layer of skin), mucous membranes (line body openings-mouth, throat, esophagus, rectum, vagina, anus)
(deeper cells are cuboid or columnar)
Simple Columnar cells
single layer of column shaped cells.
Nucleaus is near base
some have cilia
lines the GI tract, resp. tubes, ovarian tubes
function: provide protection, secrete and absorb products

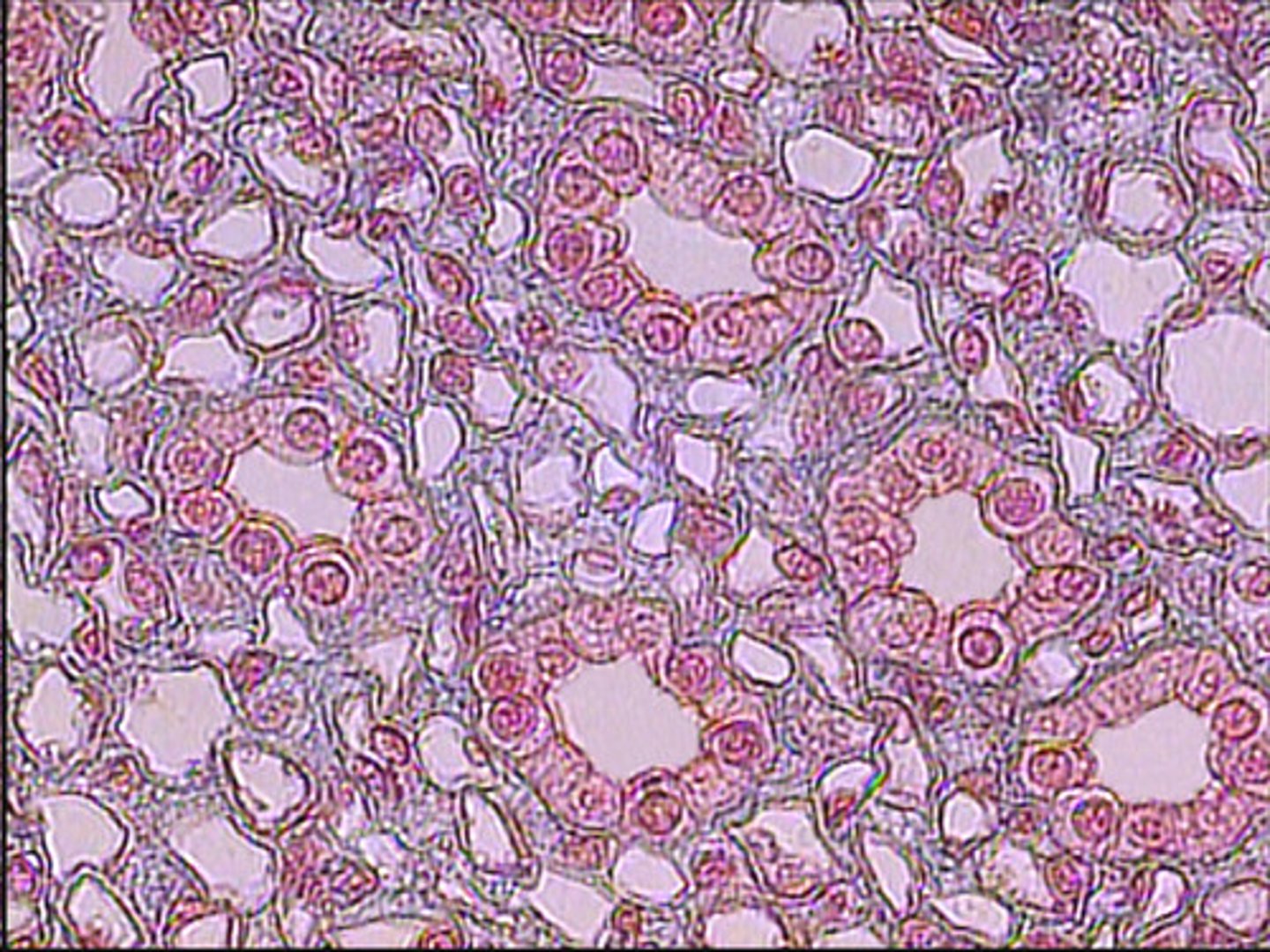
simple cuboidal cells
square (cube) shape
make up the lining of the urinary tubules and some glands, kidney tubules, thyroid gland
function: secret and absorb products
Muscular Tissue cells (types)
smooth muscle cells
skeletal muscle cells
cardiac muscle cells
(what type of tissue?)
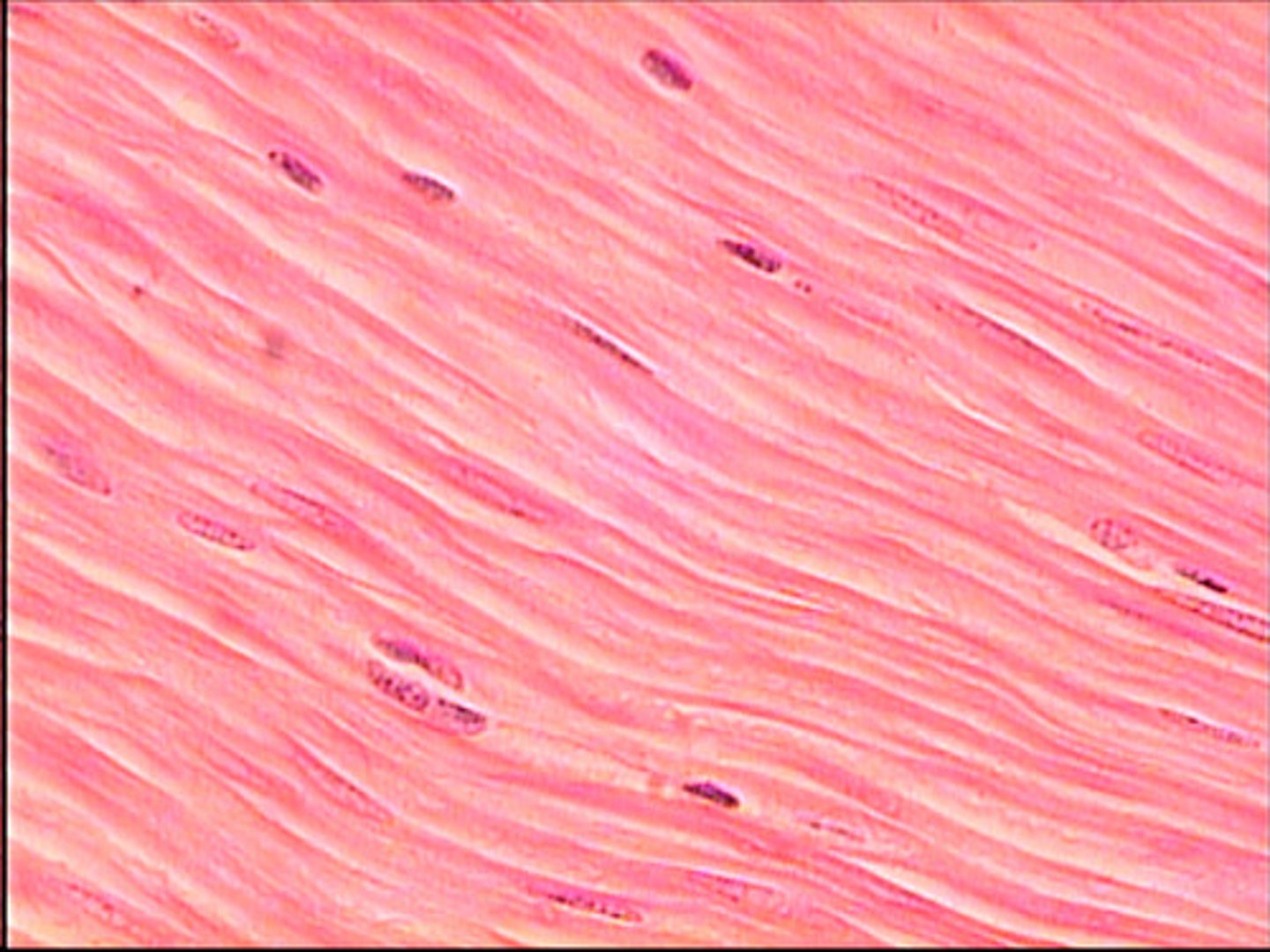
Smooth muscle cells
elongated cells, tapered at both ends (spindle shaped)
No striations
more responsive to chemical stimuli than nerve
myogenic-can initiate own contraction
slowest response
ofund in: GI tract, resp tract, urinary tract, capillary sphincters (regulate blood pressure) and also the myometrium of the uterus
function: provide involuntary contraction
Skeletal muscle cells
cylindrical, elongated cells, multinucleated and striated (caused by filaments actin and myocin)
called muscle "fiber"
neurogenic-normally stimulated by nerve impulse
fastest response of musle types
make up skeletal muscles such as biceps brachii
function: provide voluntary contraction
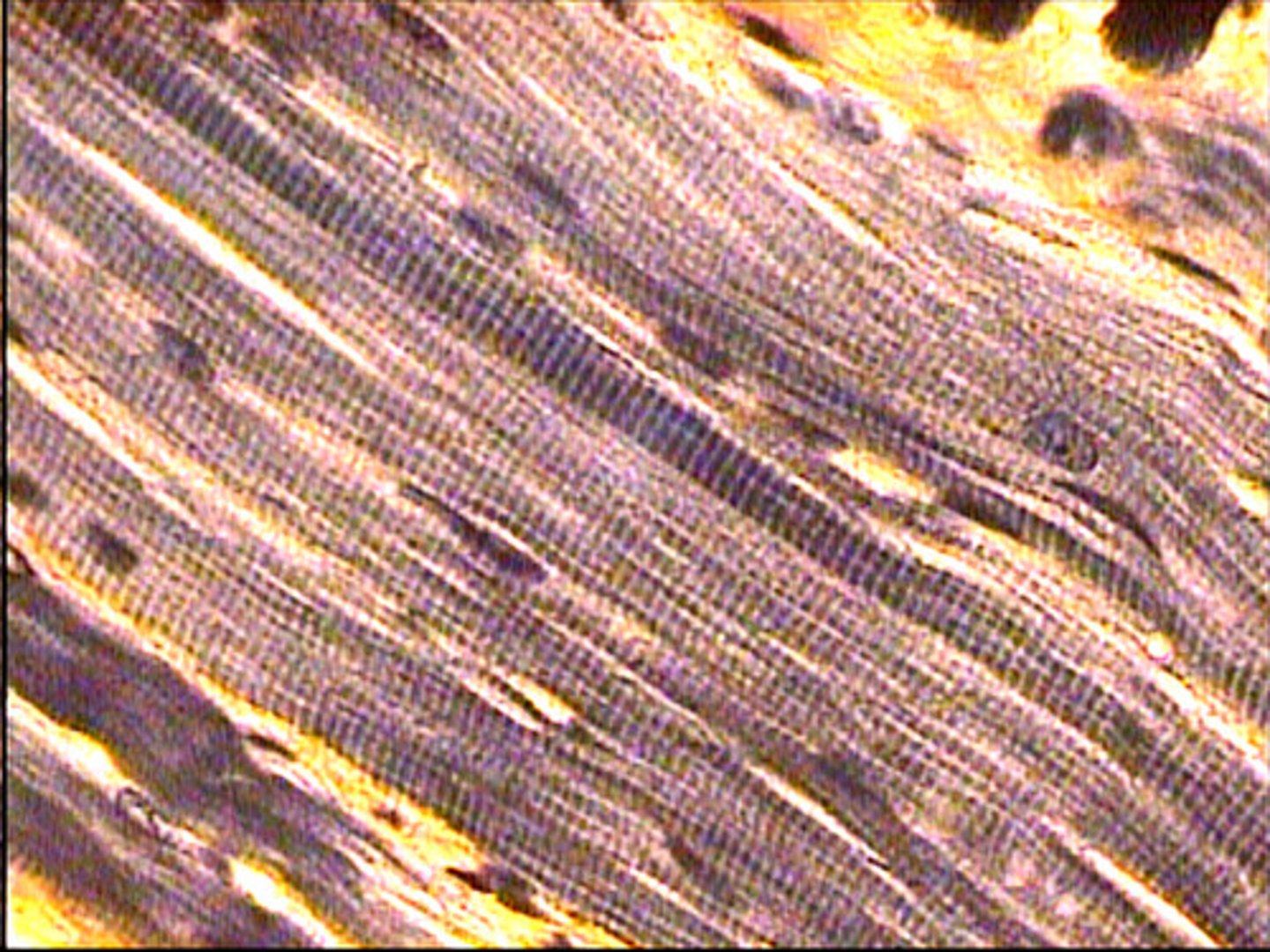
Cardiac muscle cells
striated, branched fibers
intercalated discs
myogenic-can initiate own contraction
found only in the heart
function: provide rhythmic contractions
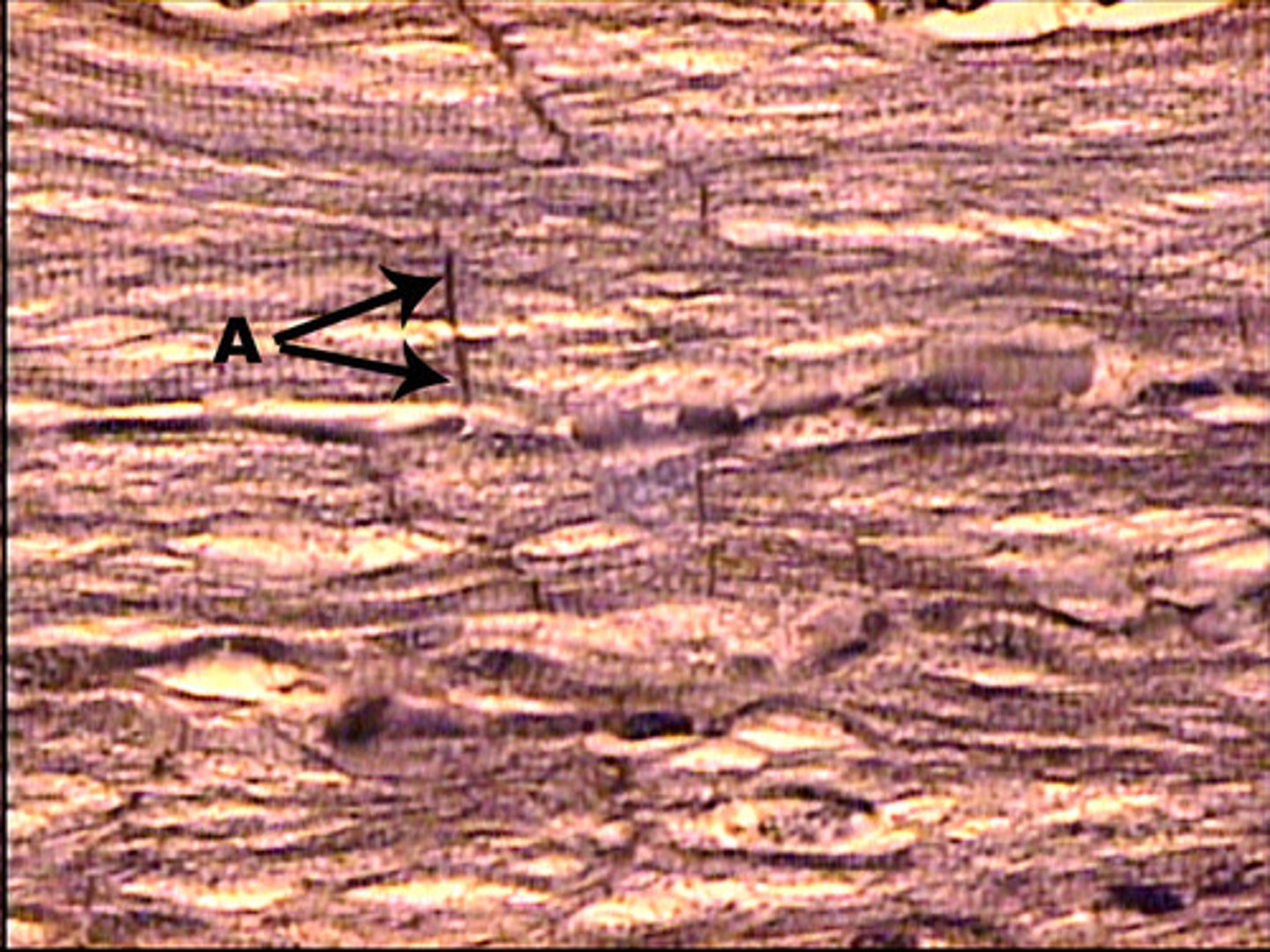
Neural Tissue cell types
Neuron cells
Glial cells
Neuron cells
soma-body
axon-larger branch-transmits impulse from soma
myelin sheath-surrounds some axons-protective coating made of cholesterol
dendrites-carry impulse to soma
synapse-gap between neurons
found in all nerve tissue, such as brain and spinal cord
function: conduct an impulse
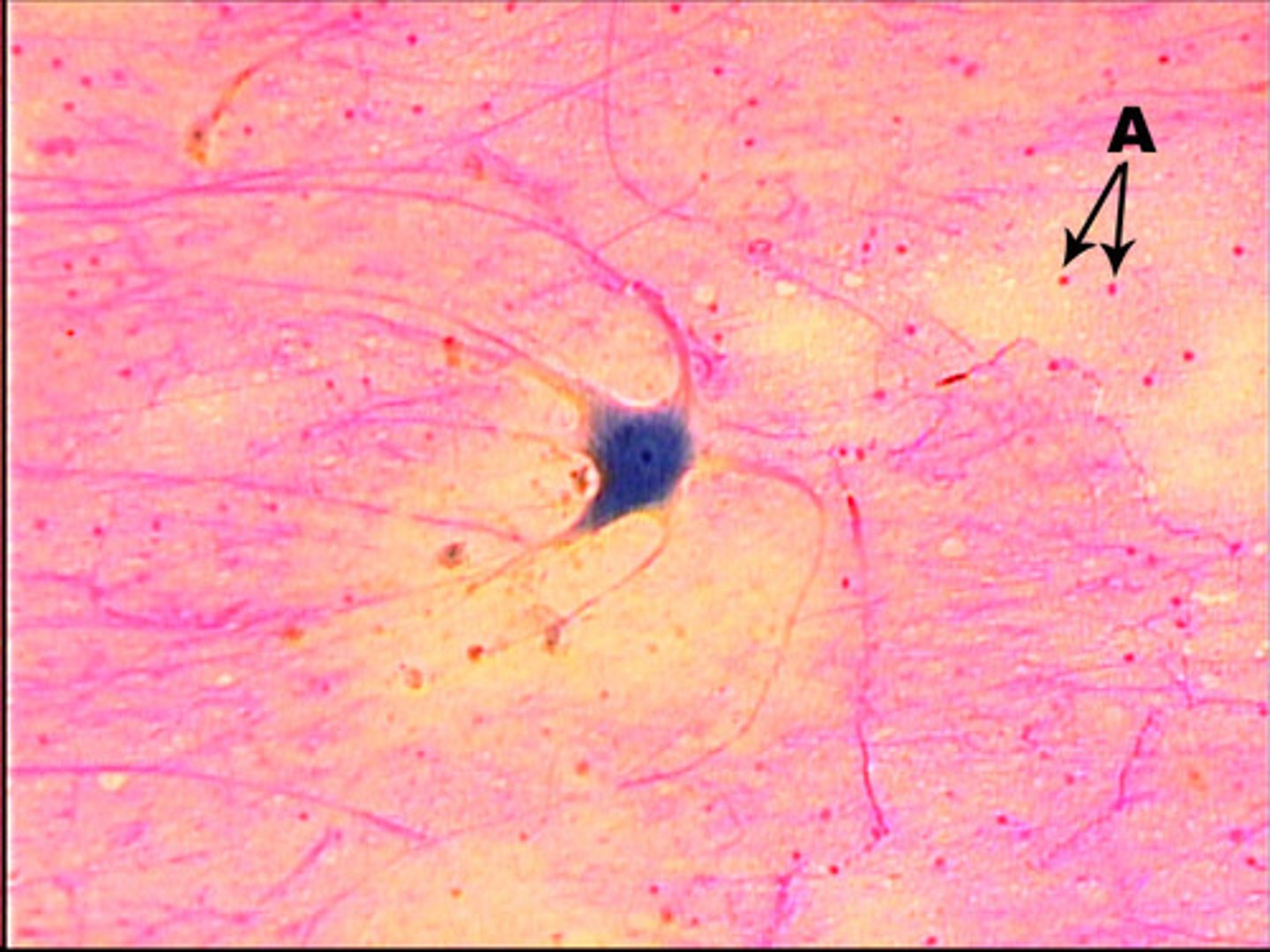
Glial cells (nurse cells)
supportive cells to neural cells
many appear as small cells located near neurons
several types:
oliglodendrocyts-produce myelin
microaglia-phagocytic-found in nervous tissue
astrocytes (most numerous)-growth & repair of neurons
some cells surround the axon of a neuron
some cells attach parallel nerves together
some cells are located between different nerves
function: provide protection for the neuron and or nervous system
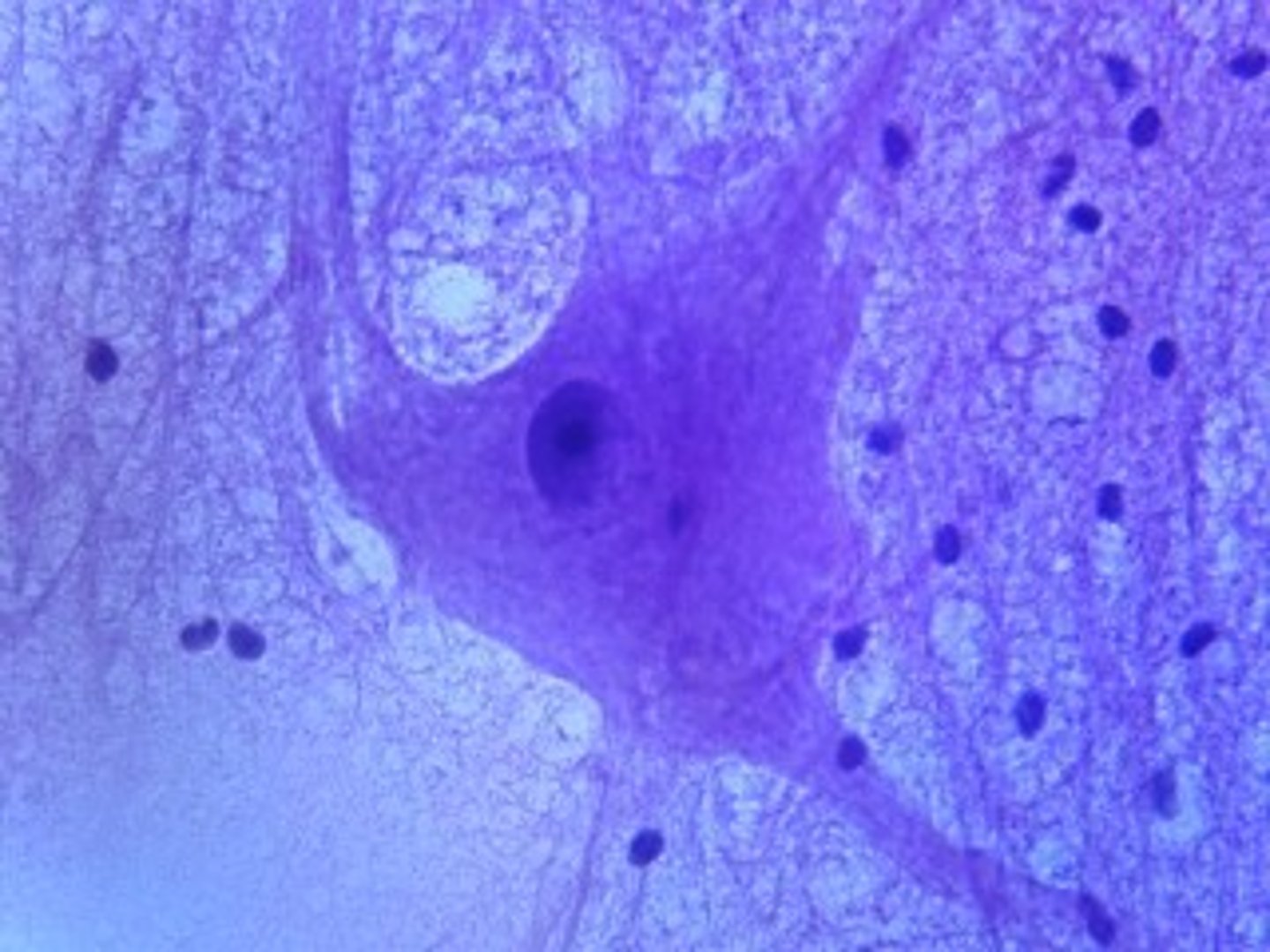
Connective Tissue cells
mucous
Adipose
Areloar
Blood
Bone
Cartilage
Dense
Reticular
(what type of tissue)
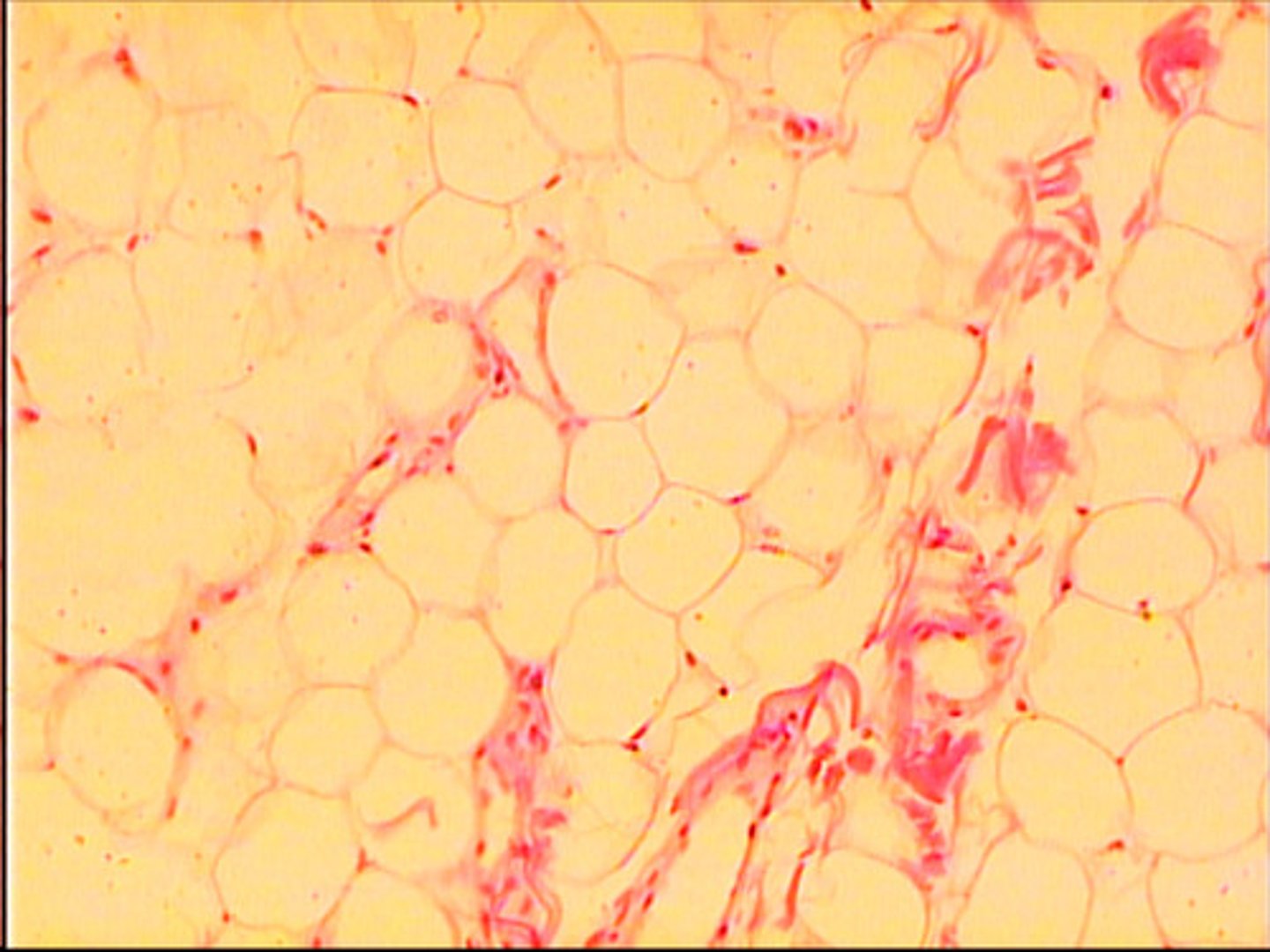
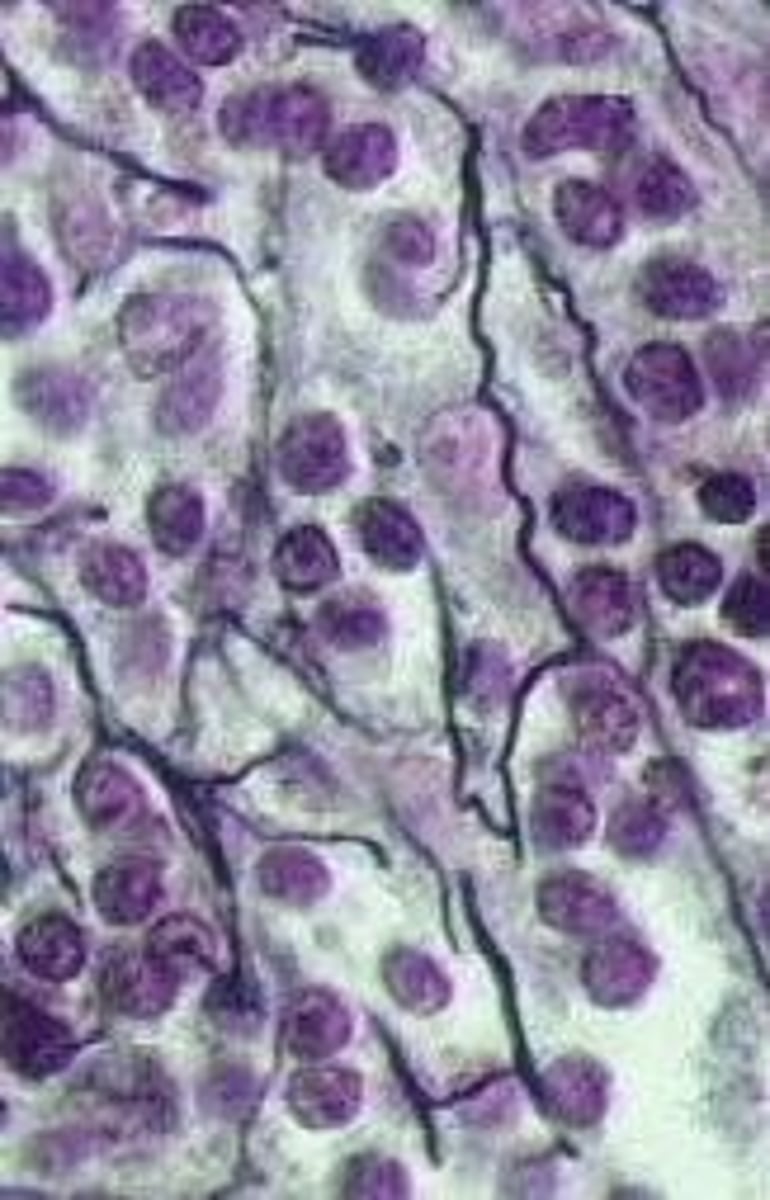
Adipose cells
round cells, give the appearance of being empty, nucleus is pushed off to one side
found surrounding body organs
provide insulation (fat)
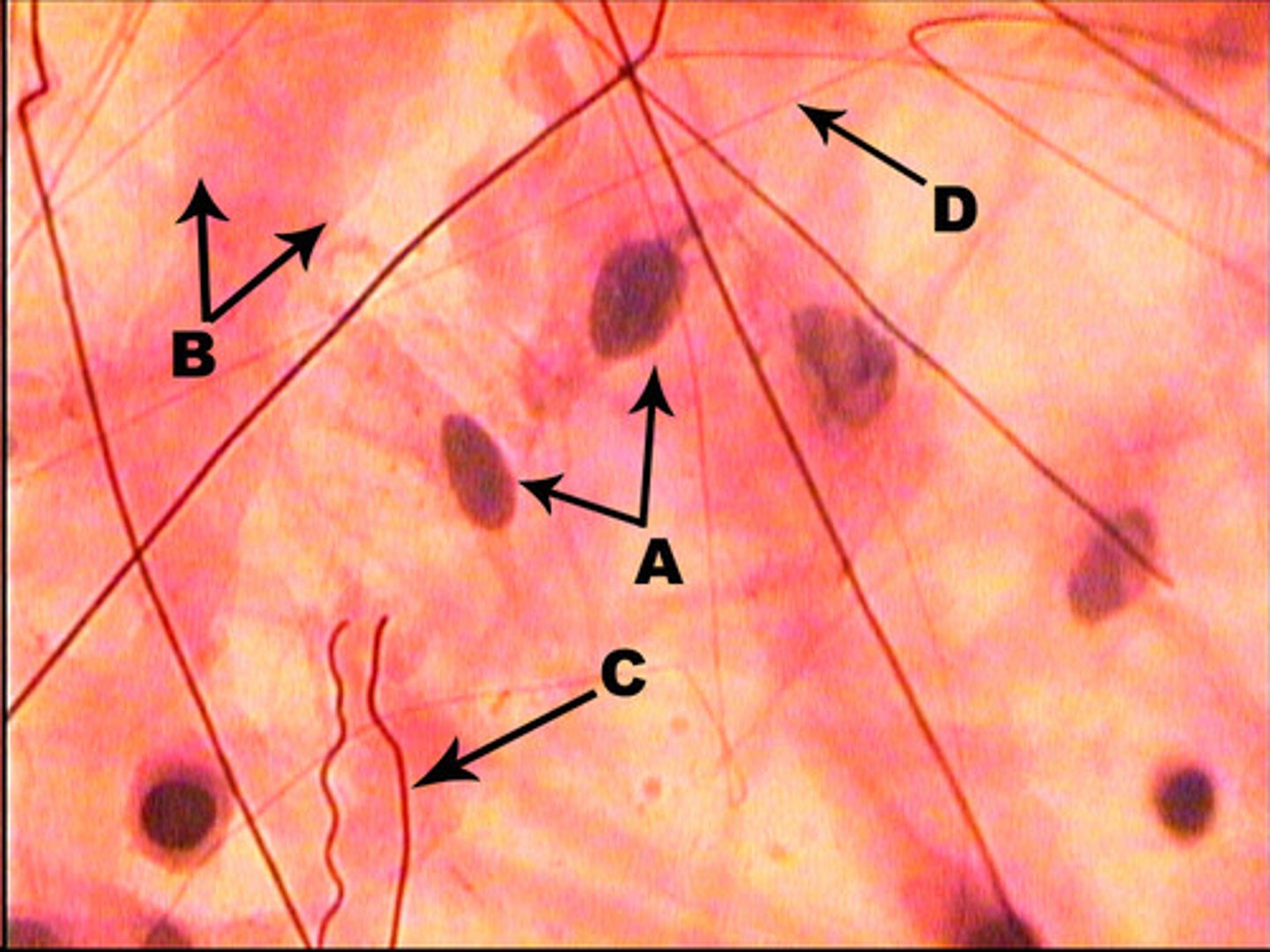
Areolar cells
small, have numerous fibers (elastic & collagenous) coursing between cells
found between the skin and muscle
function: attach skin to muscle
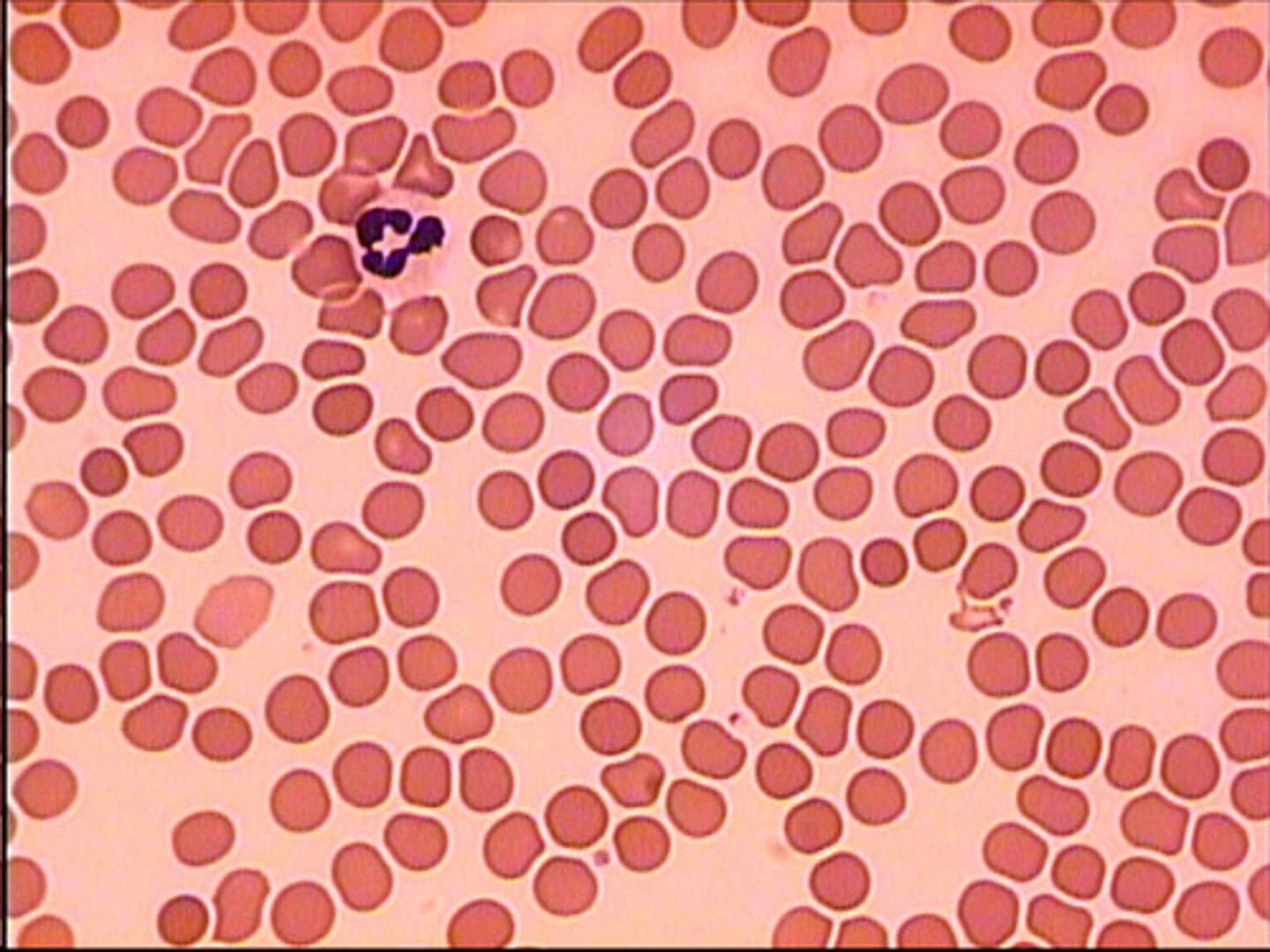
Blood cells
has watery matrix - plasma
cells form concentric rings around central canal.
found in circulatory system
function: transports cells, dissolved nutrients, dissolved waste material, come CO2, chemicals (hormones, enzymes, etc.)
Blood cells (types)
Erythrocytes (red blood cells)
Leukocytes (white blood cells)
platelets
erythrocytes
red blood cells
biconcave discs, no nucleus when mature
transport oxygen and carbon dioxide
C cells
cells sit in a lacuna.
found within joints
function: reduce friction that might occur within a joint
Dense regular cells
mostly collagenous fibers are parallel and packed tightly together
contains fibrocytes
found making up our tendons, ligaments and aponeurosis
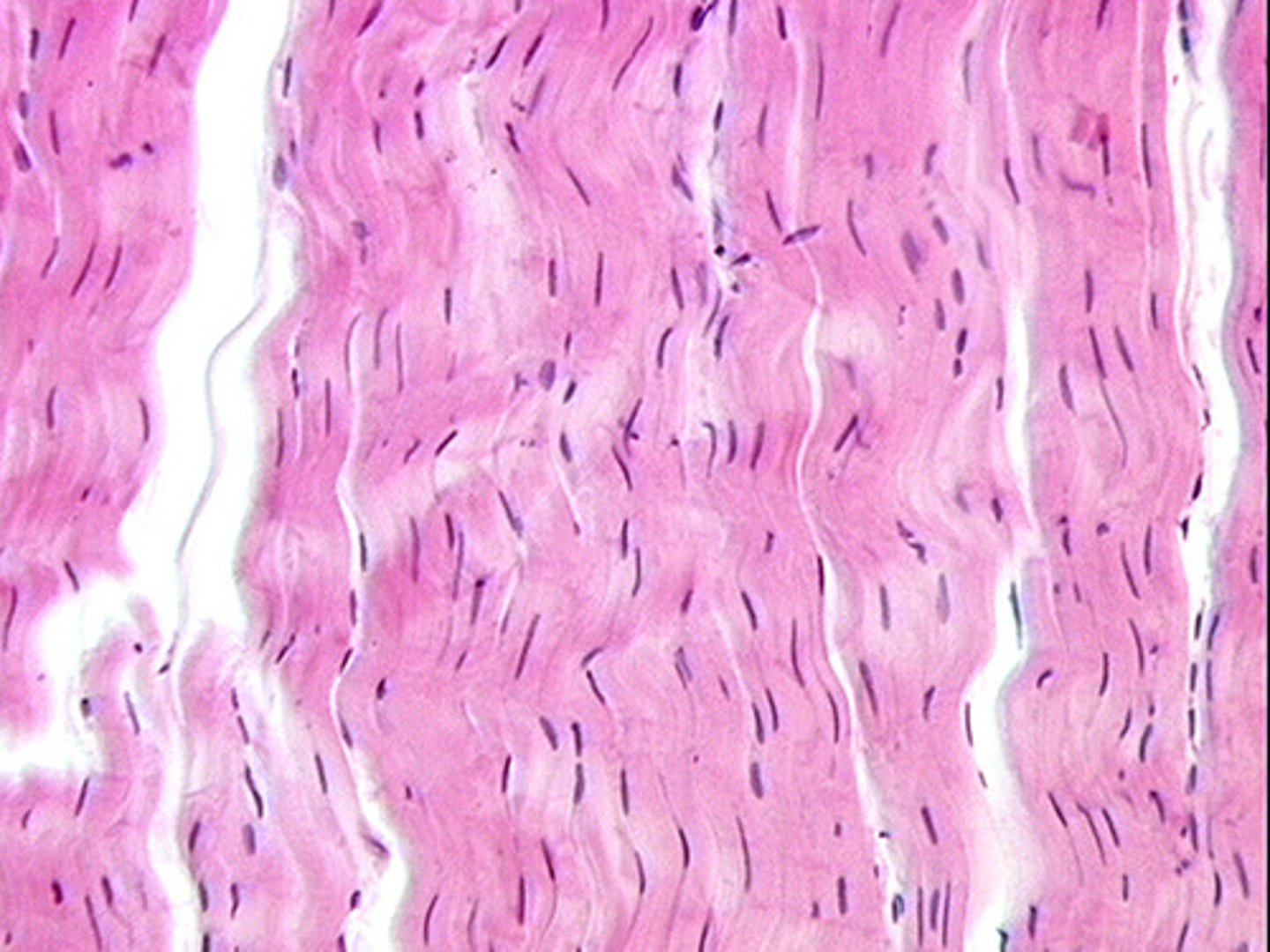
Reticular cells
small cells that have fibers passing between them. Fibers are short and thick
found making up the main portions of the liver, spleen, appendix, tonsils and lymph nodes
function: involved in making up the "framework" of the liver, spleen, appendix, tonsils and lymph nodes
Bone cells
cells found in our skeleton
provide support
Osteocytes
individual bone cells that form concentric rings around the central canal (major component of an Osteon)
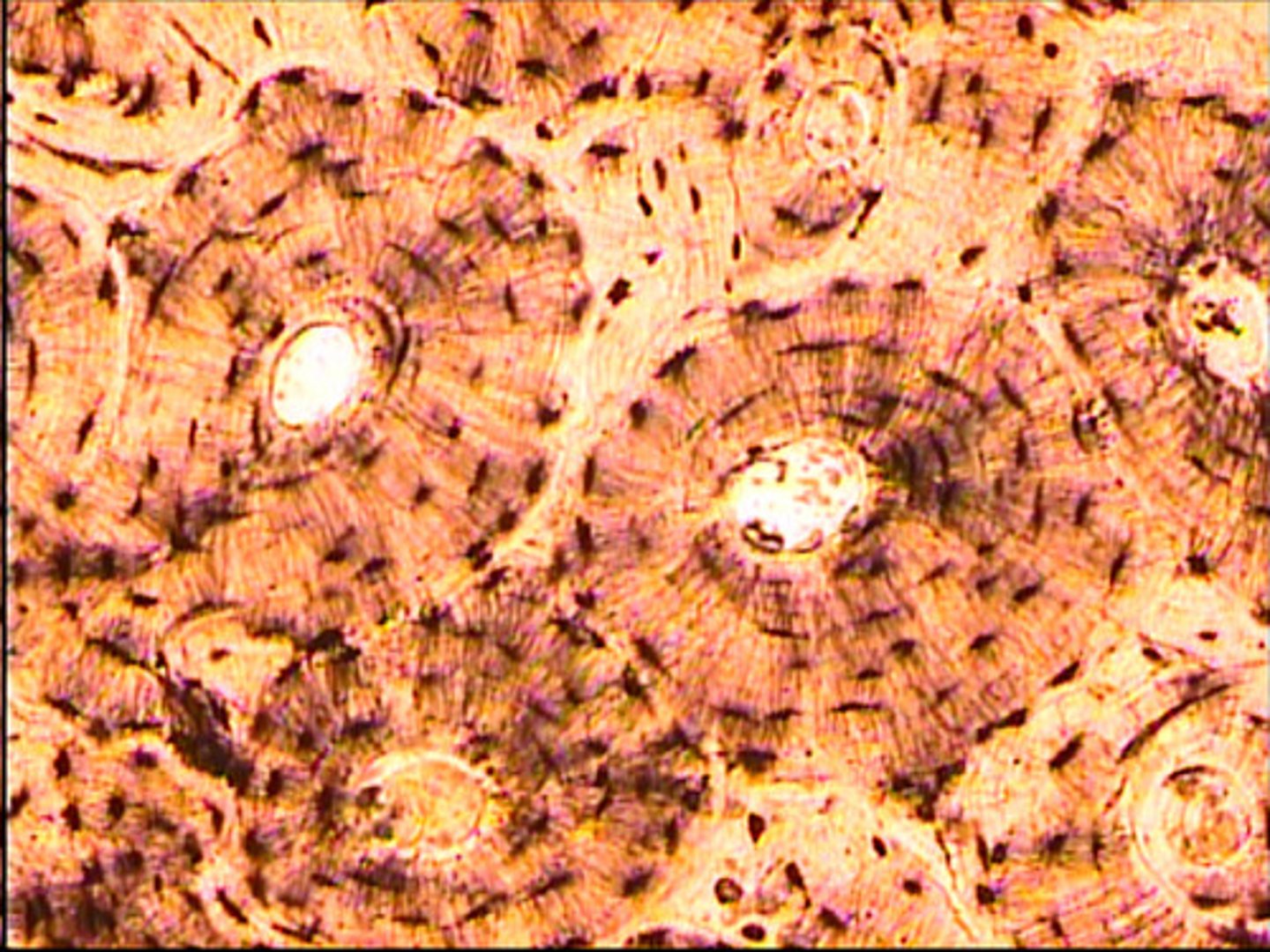
Central canal
consists of blood vessels, which supply nutrients to osteocytes (major component of an osteon)
Canaliculi
Transports nutrients from the blood vessels to the stationary osteocytes (major component of an osteon)
Lacuna
the depression in the bone in which osteocytes sit
(major component of an osteon)
Lamella
the matrix of the bone through which the canaliculi pass
Dense cells (types)
tendons
ligaments
aponeurosis
Epithelial tissue
-Tissue covers surfaces (outside [skin] and inside [organs])
-Cellularity-cells bound closely together, little to no space between
-Attached to basal lamina
-Arranged in sheets or layers
-Avascularity-does not contain blood vessels-must obtain nutrients by diffusion or absorption
-Regeneration-damaged/lost cells are replaced through division of stem cells
function: protection, secretion, absorption
Connective tissue
tissue with greatest variety of cells
function:
protection & support (cart. & bone)
transport (fluids/chemicals)
store energy (fat)
cellular & chemical defense
Types of fibers
Collagenous fibers (white fibers)
Reticular fibers
Elastic fibers (yellow fibers)
pseudostratified ciliated columnar cells
single layer of irregular shaped cells (different heights)
nuclei are at different levels
found in lower pharynx, trachea, primary bronchi
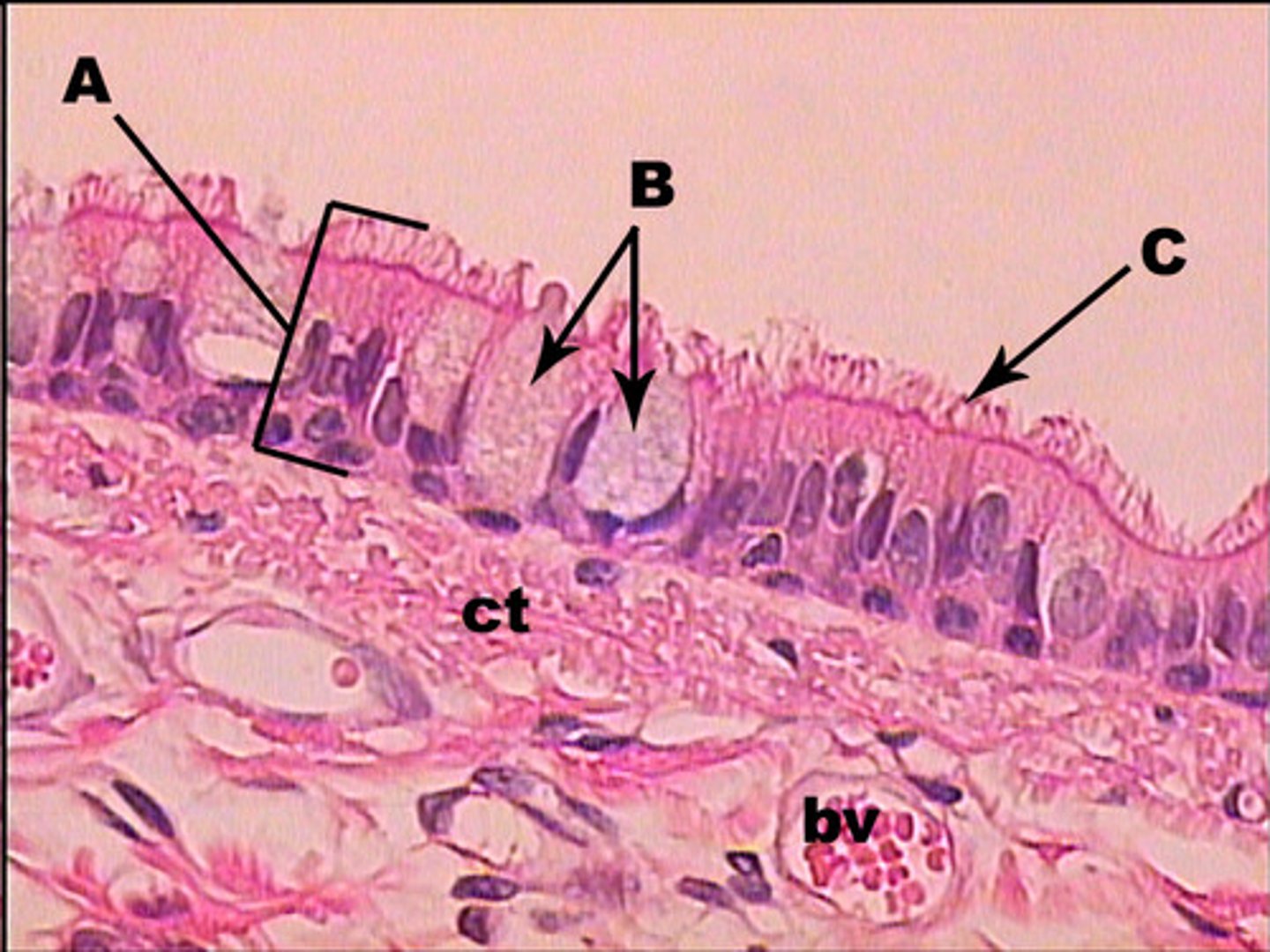
goblet cells
unicellular mucous glands, randomly distributed among some columnar cells, can appear as an empty space
found in digestive tract (keep from digesting self)
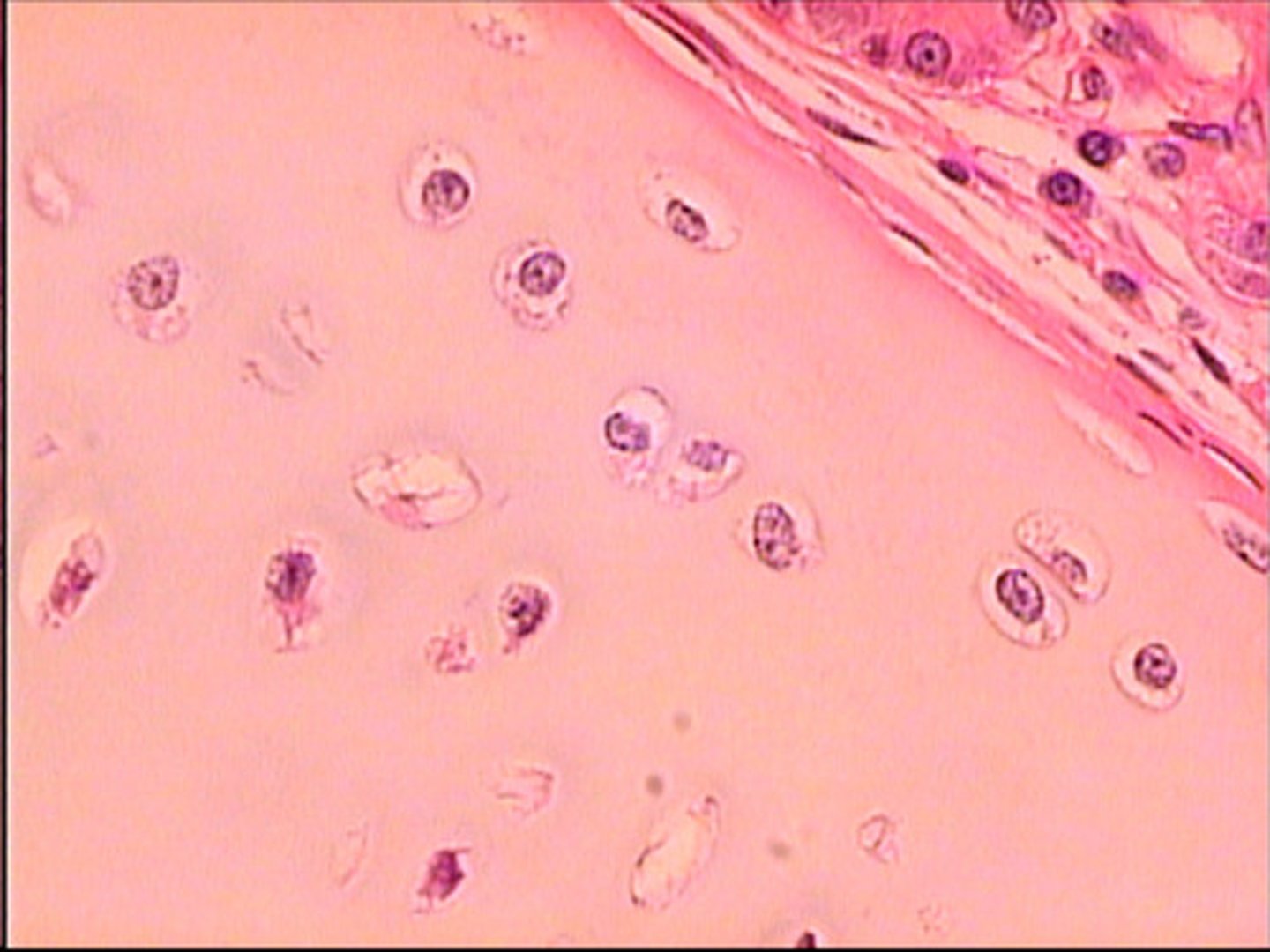
Elastic Cartilage cells
cell has chondrocytes in lacuna but also has fibers in matrix
found in pinna, epigottis, thyroid cart (located above gland)
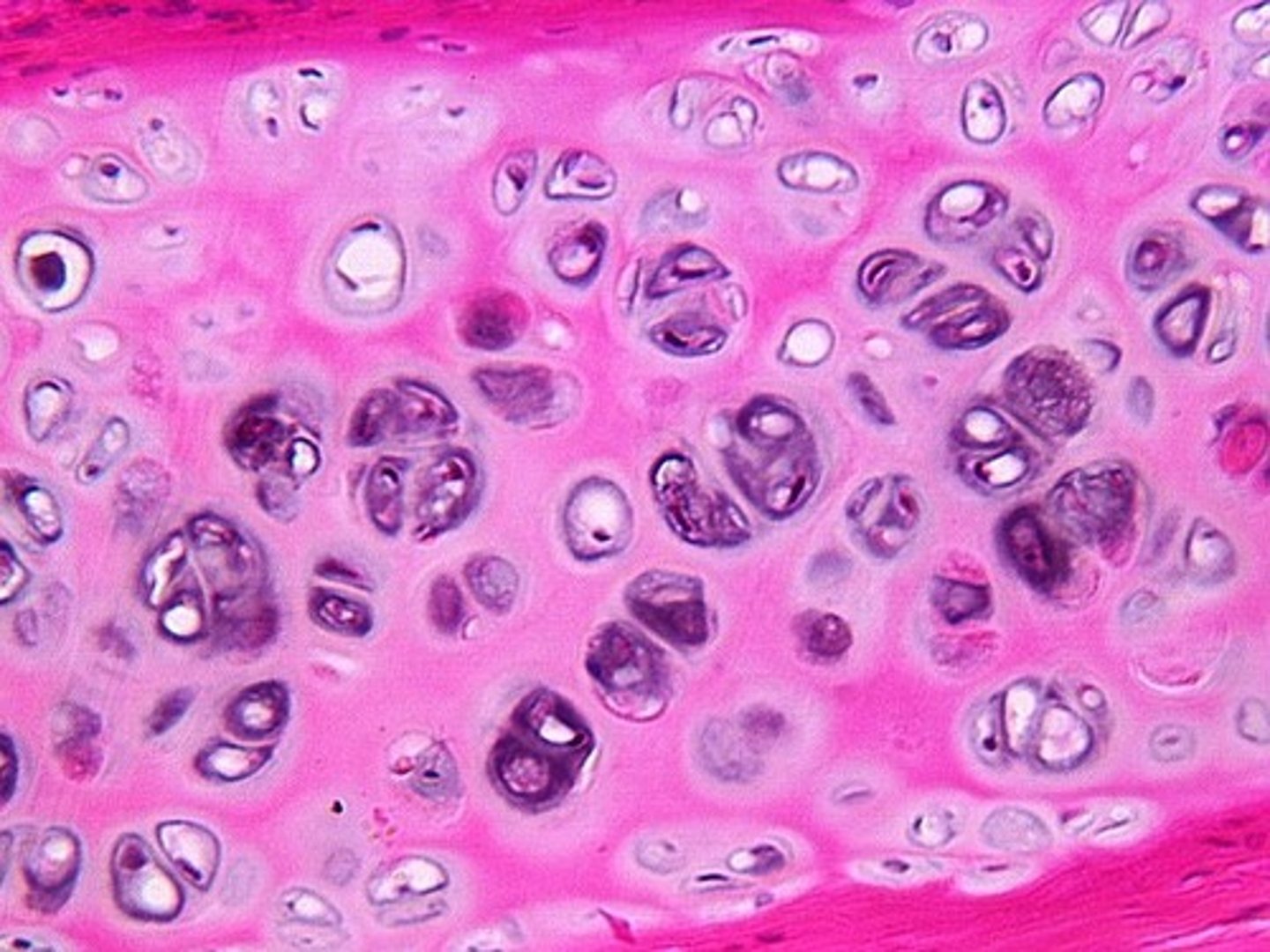
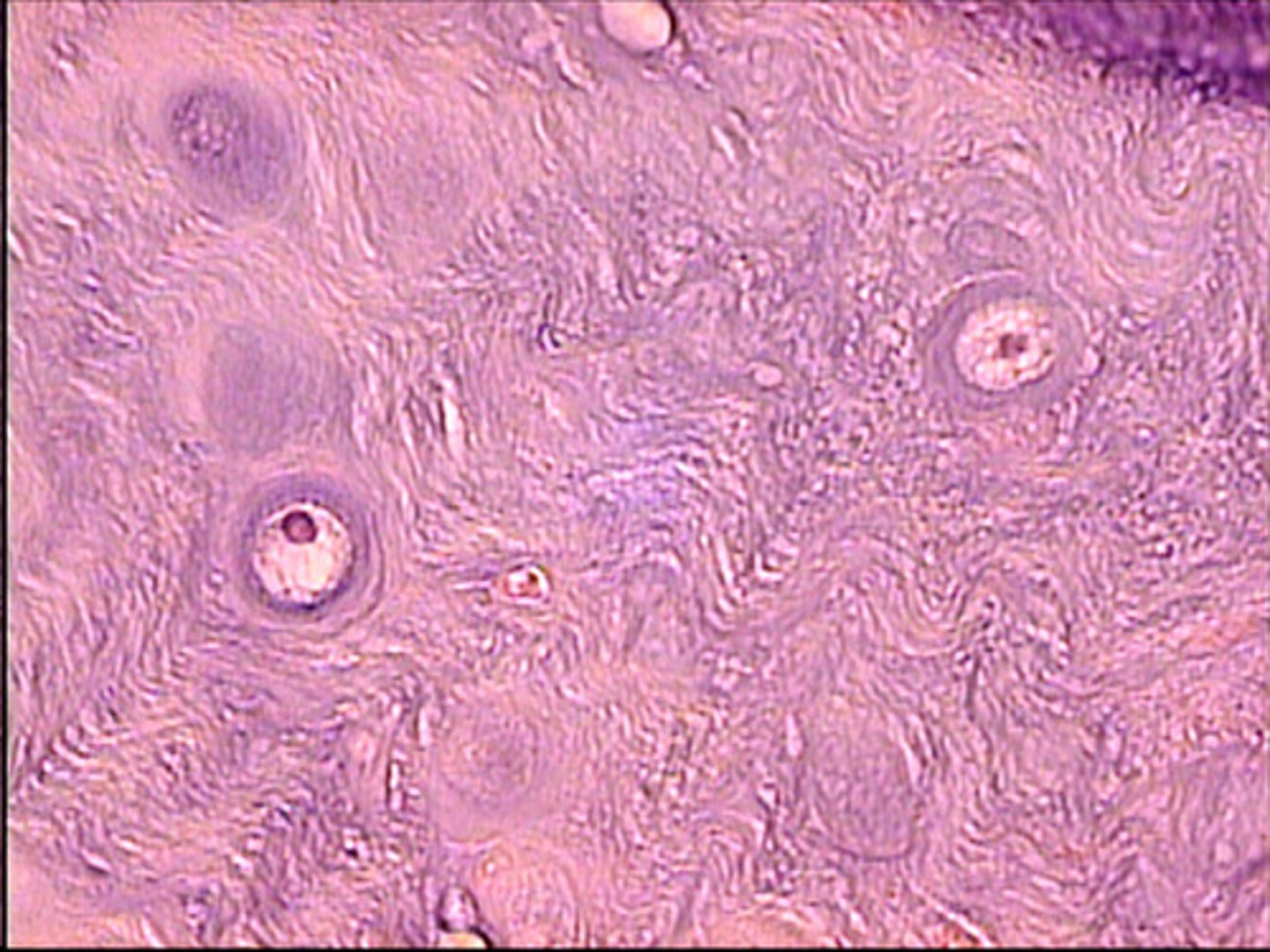
Hyaline cartilage
cell has homogeneous matrix (same throughout, glassy)
chondrocyte in lacuna
found in articulating surfaces of bones (joint surface)
nasal cart.
costal cart (attach ribs to sternum)
trachea & bronchi (hold trac/bronch open)
entire embryonic skeleton
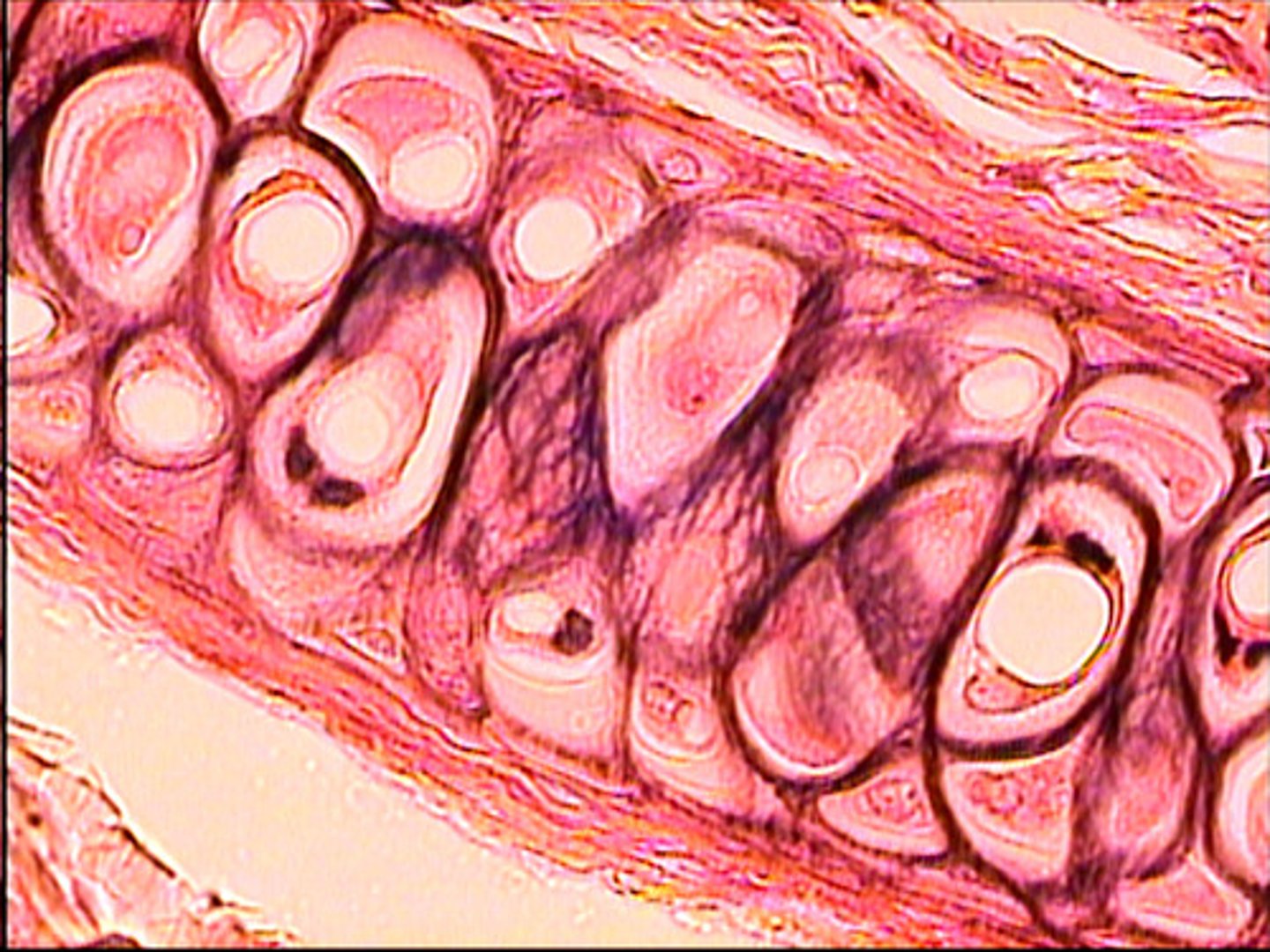
Fibrocartilage
cell has collagenous fibers (tougher/stronger)
found in intervertebral discs, pubic symphisis (joint btwn left & rt pubices)
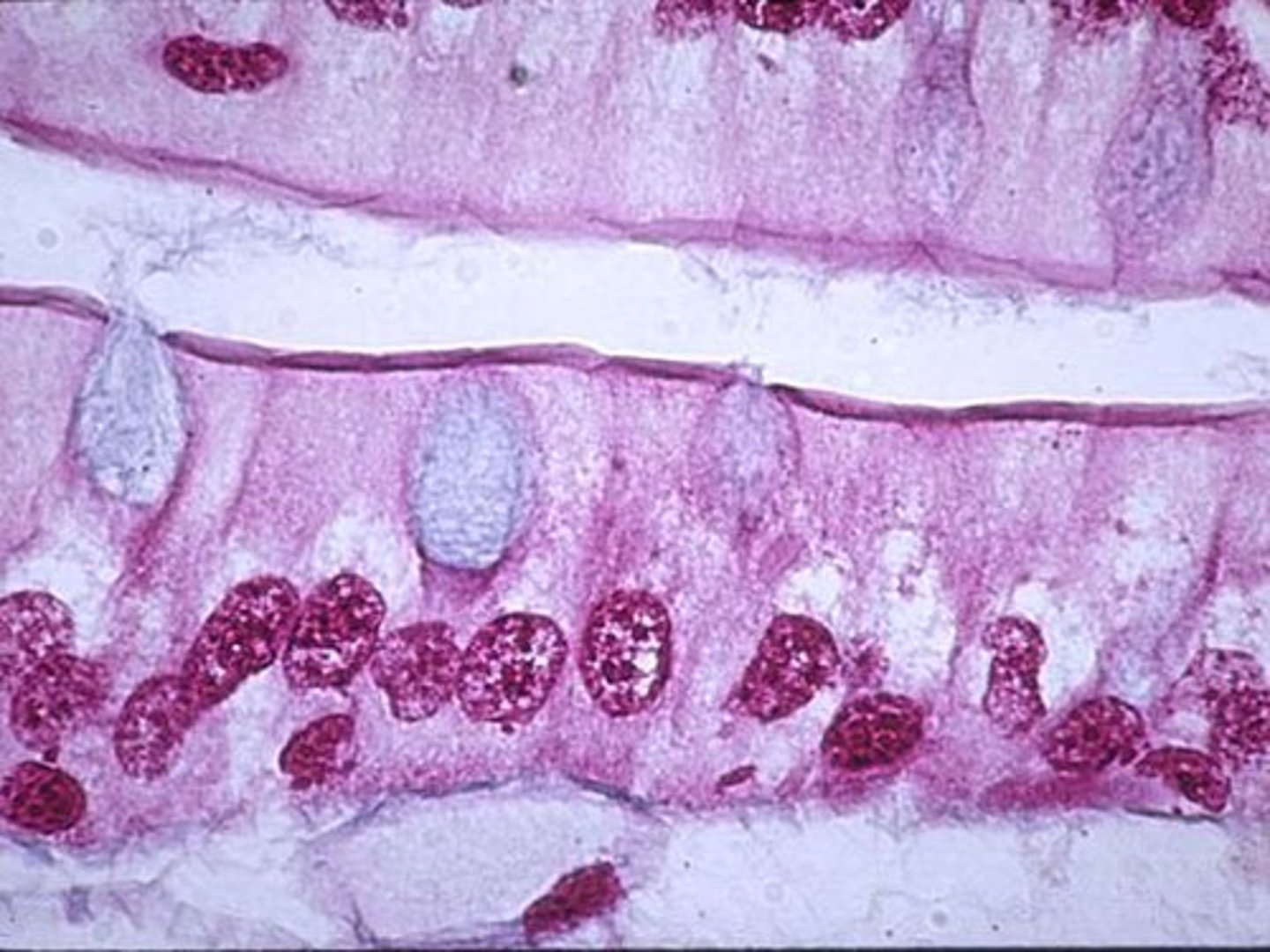
Simple epithelium
single layer of cells
thin and fragile
found only in protected areas of body:
ventral body cavities
blood vessels
lining of intestines
gas exchange surfaces of lungs
stratified epithelium
2 or more layers
thick and sturdy
found in areas subject to mechanical or chemical stress:
surface of skin
lining of mouth
Connective Tissue Cells (functions)
establish structural framework for body
transportation
protection
support/surround/interconnect other tissue types
store lipids
defend against microorganisms
Loose Connective Tissue types
Areolar
Adipose
Reticular
Dense Connective Tissue Types
Dense Regular
Dense Irregular
Fluid Connective Tissue Types
Blood
lymph
Supporting Connective Tissue Types
Cartilage: Hyaline, Elastic, Fibrous
Bone
Muscle Tissue Types
skeletal
cardiac
smooth
transitional cells
combination of stratified squamous, cuboidal, and columnar cells (modified cuboidal cells)
lines urinary bladder
have ability to stretch
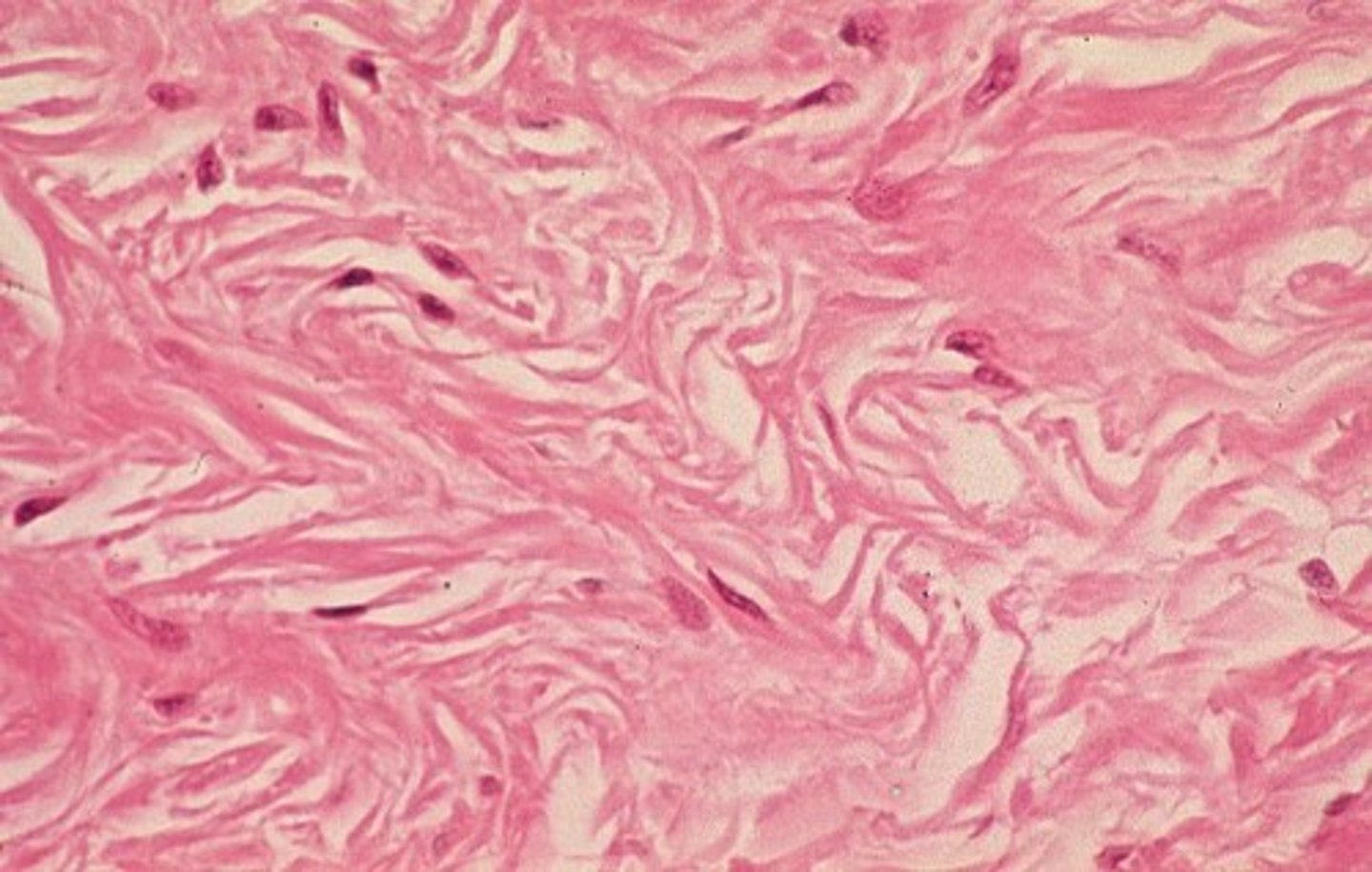
dense irregular cells
shorter fibers, not parallel
found: dermis, periostenum (membrane surrounding bone), perichondrium (membrane surrounding cartilage)
axon
largest branch of the neural cell.
transmits impulse from the body of the cell (soma)
sometimes covered in a myelin sheath made of cholesterol (insulation)
Nodes of Ranvier-bumps on myelin sheath
dendrite
branch of the neural cell, each cell has several
carries impulse to soma
synapse
gap between neurons
chemical (seratonin) released by end brush of axon is received by receptor on dendrite
nodes of ranvier
bumps on myelin sheath covering axon
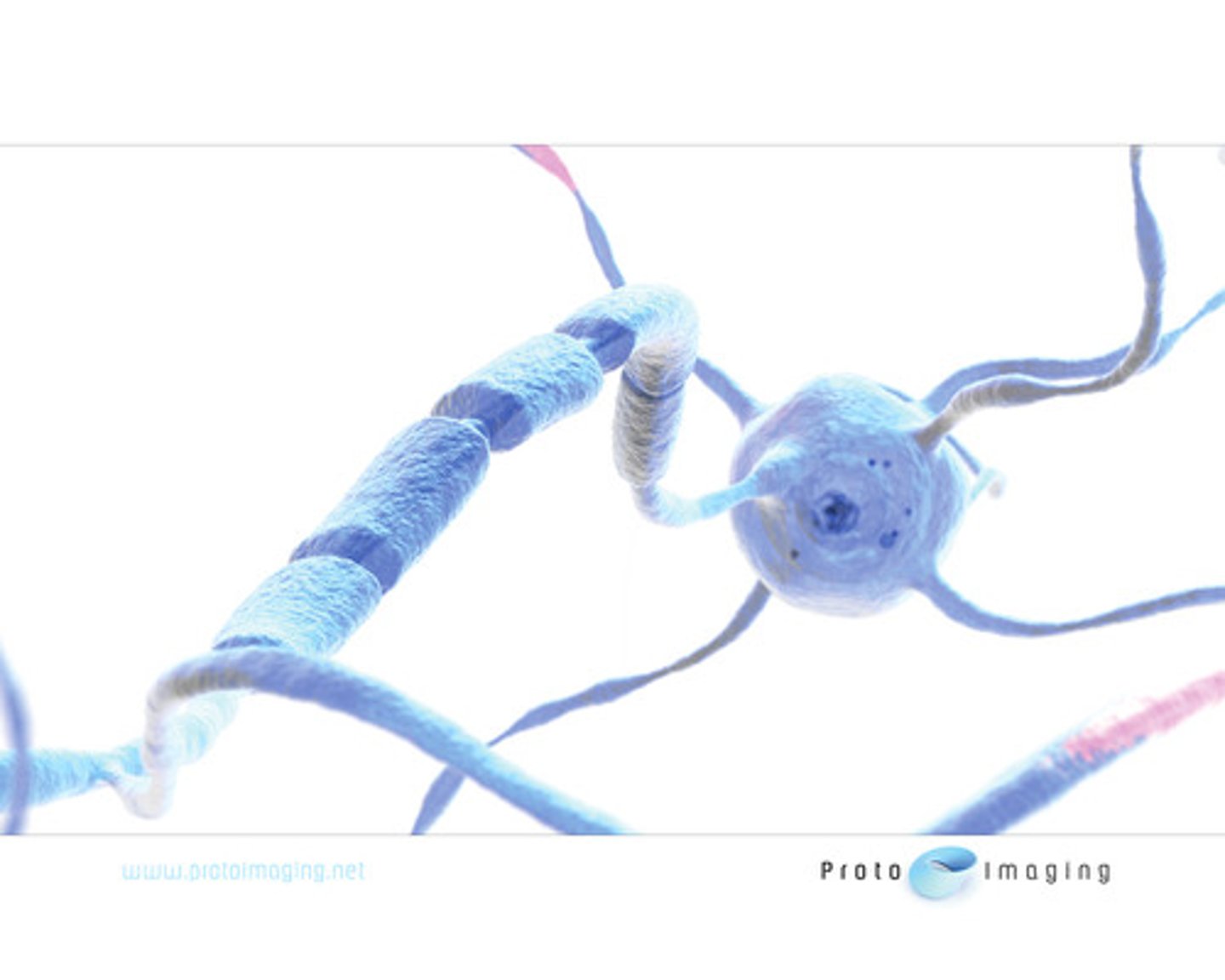
myelin sheath
insulation covering the axon
made of cholesterol (HDL)
creates white matter
contains nodes of Ranvier
oligodendrocytes
type of glial cell that produces myelin
microglia
type of glial cell that is phagocytic
found in nervous tissue
astrocytes
most numerous type of glial cell
concerned with growth & repair (regeneration) of neurons
cranial & spinal cavity lining
dura mater
arachnoid
pia mater
dura mater
outermost lining of cranial & spinal cavities
durable, tough, superficial
arachnoid
lines subdural space of cranial & spinal cavities
web-like membrane
pia mater
lines subarachnal space of cranial & spinal cavities
deepest layer, delicate, thin
located right next to brain or spinal cord
simple squamous (location)
alveoli (lung air sacs)
wall of capillary
inner lining of cornea
stratified squamous (location)
epidermis
mucous membranes (mouth, throat, esophagus, rectum, anus, vagina)
cuboidal (location)
glands
ducts (pancreatic, bile, renal tubules)
smallest bronchi (bronchioles)
transitional epithellium (location)
bladder
simple columnar (location)
stomach
small intestines
colon (lg intestine)
ciliated columnar (location)
uterus
uterine tubes
secondary bronchi
pseudostratified ciliated columnar (location)
lower pharynx
trachea
primary bronchi
areolar (location)
between skin and muscle
adipose (location)
hypodermis
greater omentum (membrane in abdomen)
fatty appendages on colon
dense regular (location)
ligaments
tendons
aponeuroses
dense irregular (location)
dermis
peristenum (membrane surrounding bone)
perichondrium (membrane surrounding cartilage)
reticluar (location)
liver
spleen
kidney
lymph nodes
hyaline cartilage (location)
joint surface
nasal cartilage
costal cartilage
trachea & bronchi (hold open)
entire embryonic skeleton
elastic cartilage (location)
pinna
epiglottis
fibrocartilage (location)
intervertebral discs (btwn vertebrae)
pubic symphysis (joint btwn left/right pubices)
blood (location)
circulatory system
smooth muscle (location)
GI tract
respiratory tract
urinary tract
capillary sphincters