mutations
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
define mutation
change in normal DNA sequence.
usually neutral — no affect on organism’s fitness
harmful — responsible for many disorders
beneficial mutations
mutants better adapted to environment → evolution via natural selection
point mutations
change in 1 nucleotide/base pair in a gene
can be substitution, insertion, or deletion
only causes problems in exons
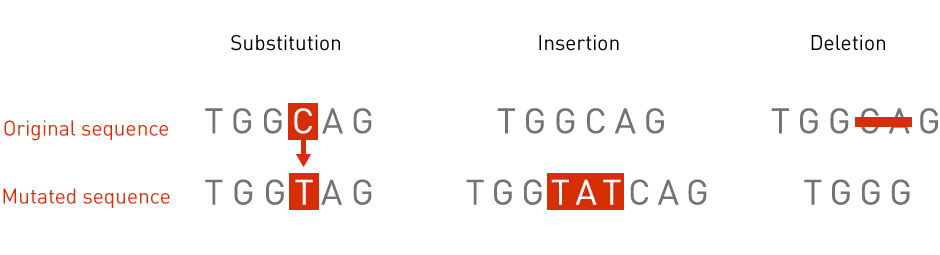
how are point mutations occuring/fixed
errors are from uncorrected mistake in DNA replication
insertions fixed by exonucleases
deletions are rarely reversible
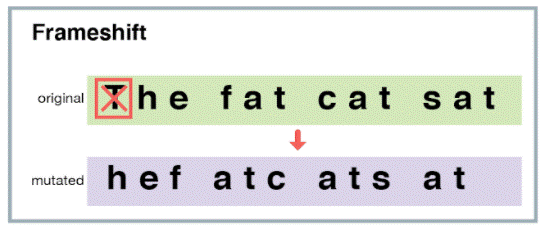
frameshift mutations
caused by insertion/deletion that’s not factor of 3 nucleotides
entire “reading frame'“ (codon) altered
silent mutations
codes for the same amino acid, substitution of nucleotide doesn’t change anything, thus “silent”
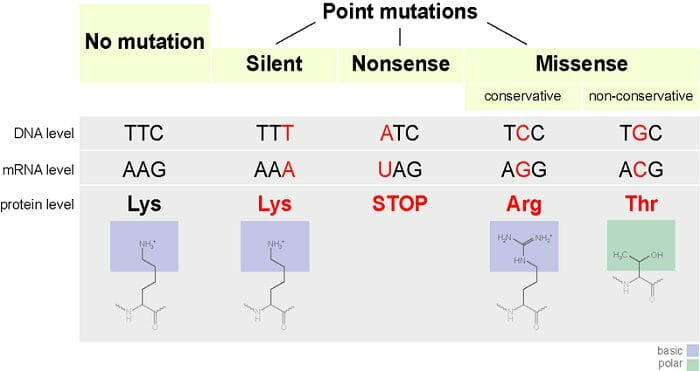
missense mutations
codes for a different amino acid
sickle cell anemia caused by single base pair substitution (missense)
beneficial in creating new proteins like antibodies to fight new infections

nonsense mutations
codes for a premature stop codon
can be lethal to the cell, usually very harmful to the organism
change to chromosome number is…
always detrimental, if not lethal, to an organism
mutations can also involve [_____] which may affect [____] and thus [__] synthesis
mutations can also involve [rearrangement of genetic material which may affect several genes & chromosomes and thus protein synthesis
chromosomal deletion
loss of genes
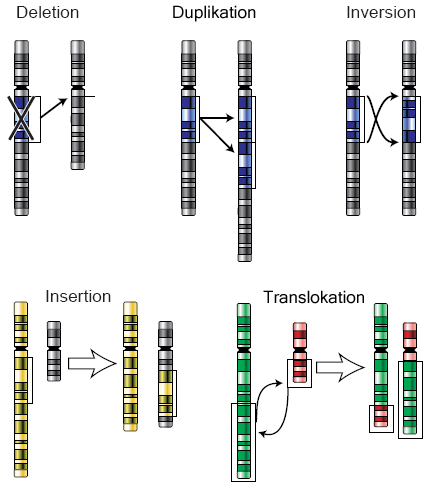
chromosomal duplications
multiple copies of genes/chromosomes
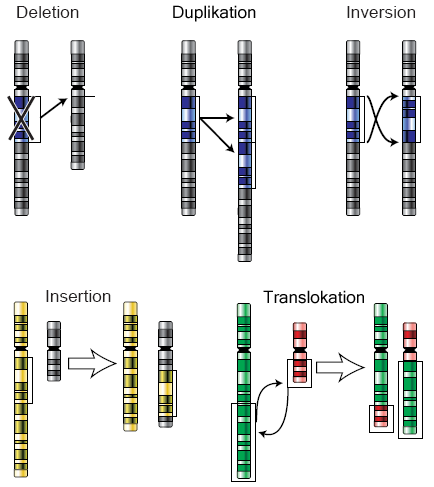
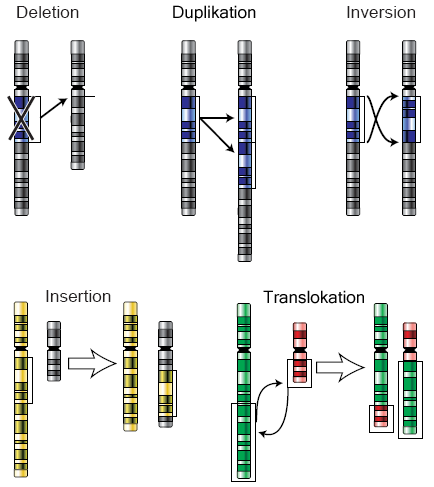
chromosomal inversion
segment of DNA in a chromosome gets inverted
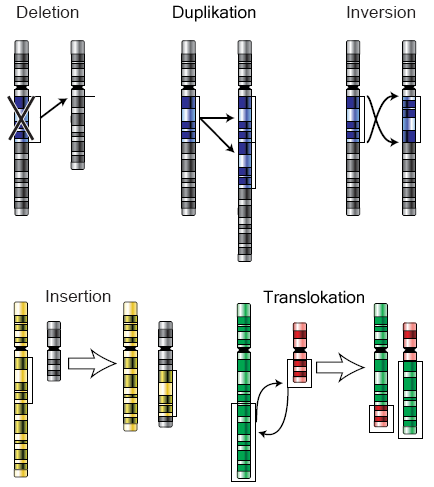
chromosomal translocation
trading of chromosomal segments between 2 different chromosomes
usually not the same size segment being traded
some forms of cancer are caused by translocation
cause of spontaneous mutations
happen naturally
cause of induced mutations
environmental factors
cause of spontaneous mutation
DNA rep. errors
DNA transposition: movement of specific DNA sequences (transposable elements)
mutagen/mutagenic agent
substance/event that increases rate of mutations
induced mutations — physical mutagen
cause physical dmg to DNA
X-Ray — point mutations and chromosomal deletions
UV radiation — causes reactions between adjacent pyrimidine bases (dimers)
chemical mutagen
react chemically with DNA to cause a nucleotide substitution/frameshift mutation. Most are carcinogenic
may also have a similar structure to a nucleotide but with different base pairing properties
nitrites
gasoline fumes
cigarette smoke
mutations that accumulate too rapidly or are very harmful do not provide a [__]
mutations that accumulate too rapidly or are very harmful do not provide a selective advantage
DNA pol can repair…
errors made in DNA rep
mismatch repair by…
Mut proteins, help reduce replication errors
DNA repair (2 ways)
photorepair — correct UV dmg, a photolyase uses visible light to cleave the bond made between adjacent pyrimidines
excision repair enzymes — recognizes & remove many diff forms of dmg, DNA pol rebuild the removed segment