Chemistry Level 3 External - 3.5 Organic Chemistry
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
66 Terms
Condensation (substitution)
Two molecules are joined together and a small molecule (H2O or HCl) is released.
Hydrolysis (Esters & Amides)
Water is used to break the amide/ester bond with one part gaining a H and the other an OH.
Structural feature required for optical isomerism
Chiral carbon
Chiral carbon
A carbon bonded to 4 different atoms or groups
Enantiomer
Different forms of an optical isomer
Features of enantiomers
Have a chiral carbon Mirror images Non-superimposable Behave differently in living organisms
How to distinguish between different enantiomers
They rotate the plane of plane-polarised light in opposite directions
Soluble functional groups (1-4 C's)
Alcohols incl diols Amines Carboxylic acids Salts of amines/ carboxylic acids
Br2
Alkene/ alkyne: rapid decolourisation from orange to colourless All other alkyl groups: slow decolourisation from orange to colourless only in the presence of UV light.
MnO4-
Purple → brown ppt
MnO4- / H+
Purple → colourless
Cr2O72- / H+
Orange → green
Amine + damp litmus
Blue stays blue Red turns blue
Carboxylic acid + damp litmus
Blue turns red Red stays red
Carboxylic acid + metal
Fizzing (H2 gas)
Carboxylic acid + metal carbonate/Carboxylic acid + metal bicarbonate
Fizzing (CO2 gas)
Structural (Constitutional) isomers
Two substances with the same molecular formula (number and type of atom) but different structural formula (bond order).
Primary alcohol/ haloalkane
The C directly bonded to the -OH/ -X is bonded to 1 other C
Secondary alcohol/ haloalkane
The C directly bonded to the -OH/ -X is bonded to 2 other C's
Tertiary alcohol/ haloalkane
The C directly bonded to the -OH/ -X is bonded to 3 other C's
Requirements for geometric (cis/trans) isomerism
A C=C Two different atoms or groups bonded to each of the C's of the C=C
C=C required for geometric isomerism
It prevents rotation of the attached atoms (or groups), stopping the two isomers from interconverting.
Two different atoms bonded to each C of the C=C required for geometric isomerism
So that different arrangements in space are possible.
*Markovnikoff addition* Major product explanation
The major product forms when hydrogen is bonded to the less substituted C of the double bond.
*Markovnikoff addition* Conditions required
The alkene is unsymmetrical as there is a different number of H's bonded to each of the C's of the C=C. The addend is also unsymmetrical.
Elimination
Atoms (or groups of atoms) are removed from adjacent carbons, with a double bond forming between those carbons. The molecule changes from saturated to unsaturated.
*Saytzeff elimination* Major product explanation
The major product forms when the hydrogen is removed from the more substituted C.
*Saytzeff elimination* Conditions required
There are two different C's (with different numbers of H's) adjacent to the C bonded to the Cl, Br, OH
Oxidation
Gain O/ increase ON/ lose H/ lose e-
Reduction
Lose O/ decrease ON/ gain H/ gain e-
Acid/Base (NOT neutralisation)
There is a transfer of protons. The acid (_____) is a proton donor and the base (_____) is a proton acceptor.
Polymerisation Definition
The joining together (bonding) of many smaller molecules (monomers).
Substitution
An atom (or group of atoms) are removed from a molecule and a different atom (or group) bonds in its place.
Addition
A C to C double bond (C=C) is broken and atoms (or groups) bond to those C's. The molecule changes from unsaturated to saturated.
Alkane naming
-ane
C-C (fnl gp)
Alkane
Alkene naming
-ene
C=C (fnl gp)
Alkene
Alkyne naming
-yne
Alkyne (fnl gp)
C triple bonded to C
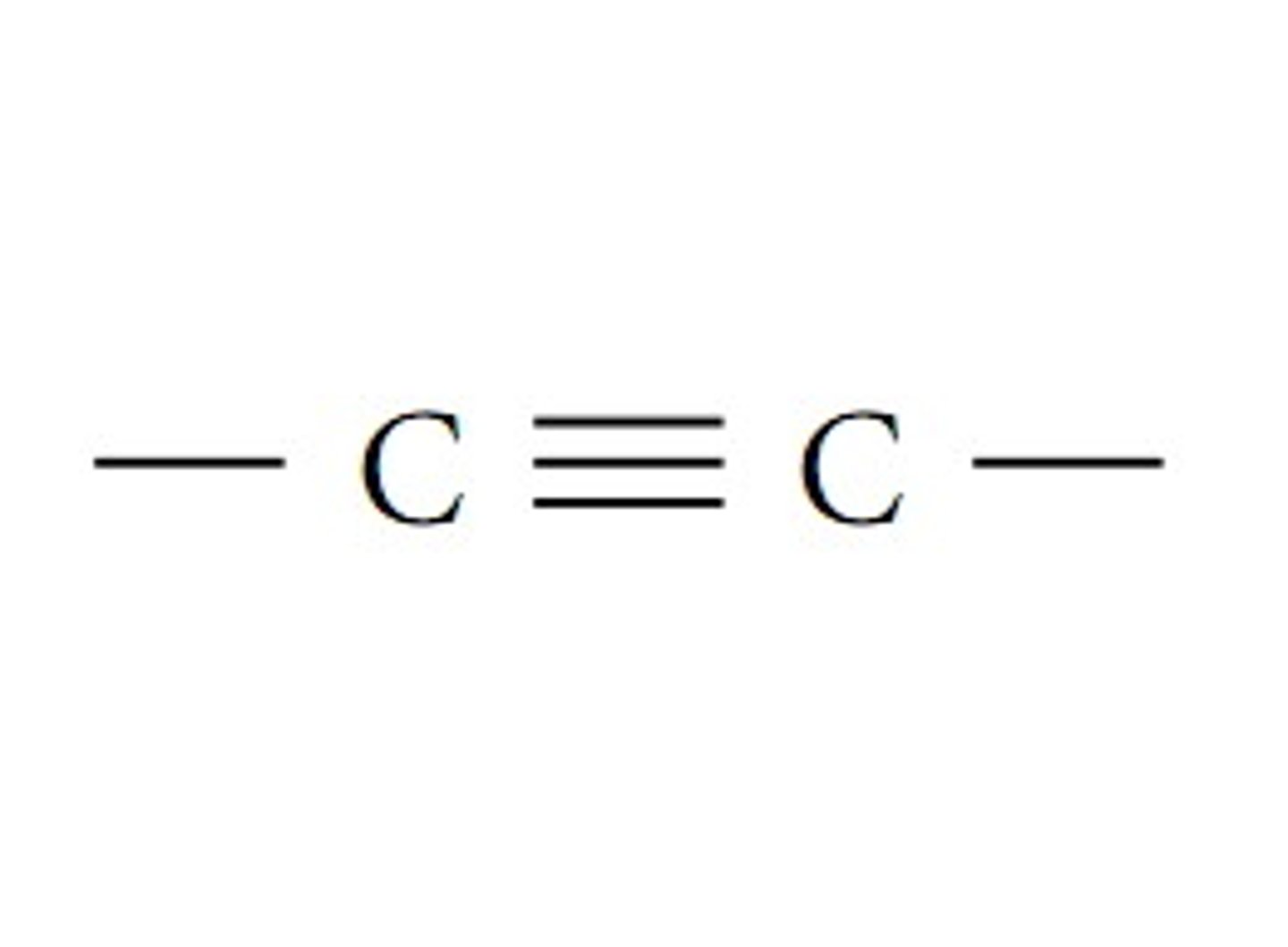
haloalkane naming
fluoro- chloro- bromo- iodo-
-F -Cl -Br -I (fnl gp)
haloalkane
alcohol naming
-anol
-OH (fnl gp)
alcohol
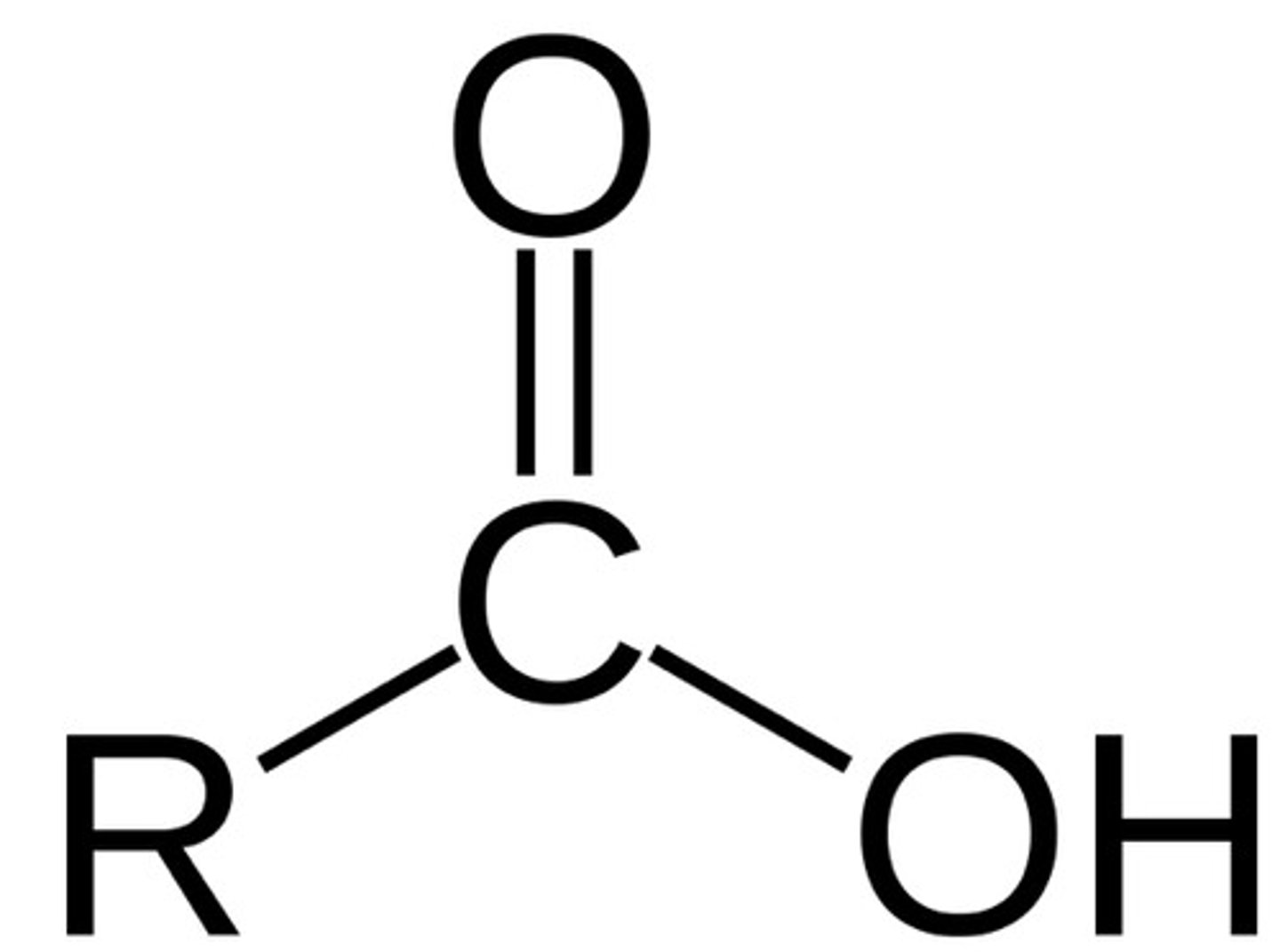
Carboxylic acid naming
-anoic acid
carboxylic acid (fnl gp)
C double bonded to O and single bonded to OH
Amine naming
amino- or -amine
-NH2 (fnl gp)
amine
8C
oct-
7C
hept-
6C
hex-
5C
pent-
4C
but-
3C
prop-
2C
eth-
1C
meth-
ketone (fnl gp)
C double bonded to O
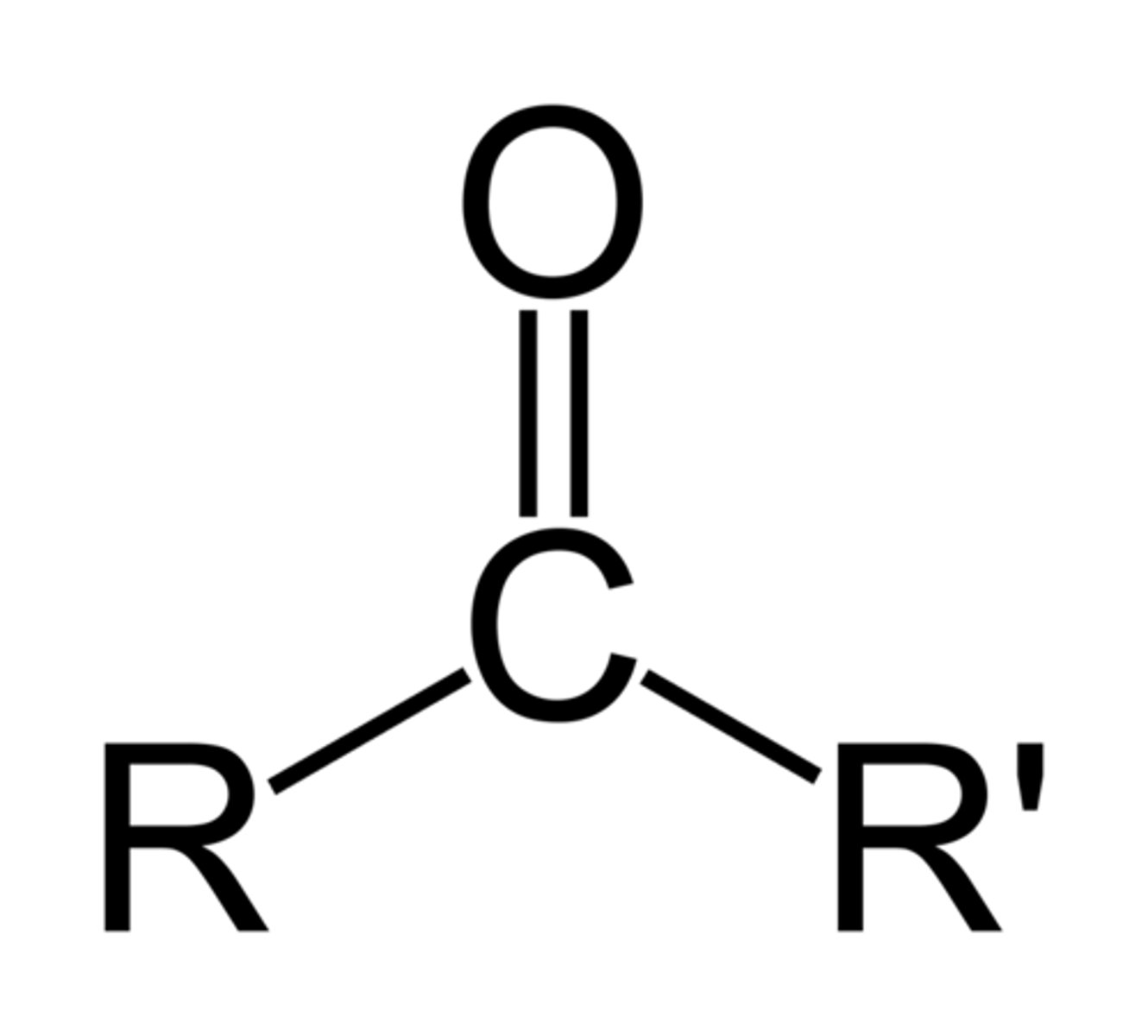
Ketone naming
-anone (number required if >4 C's)
aldehyde (fnl gp)
C double bonded to O and single bonded to H
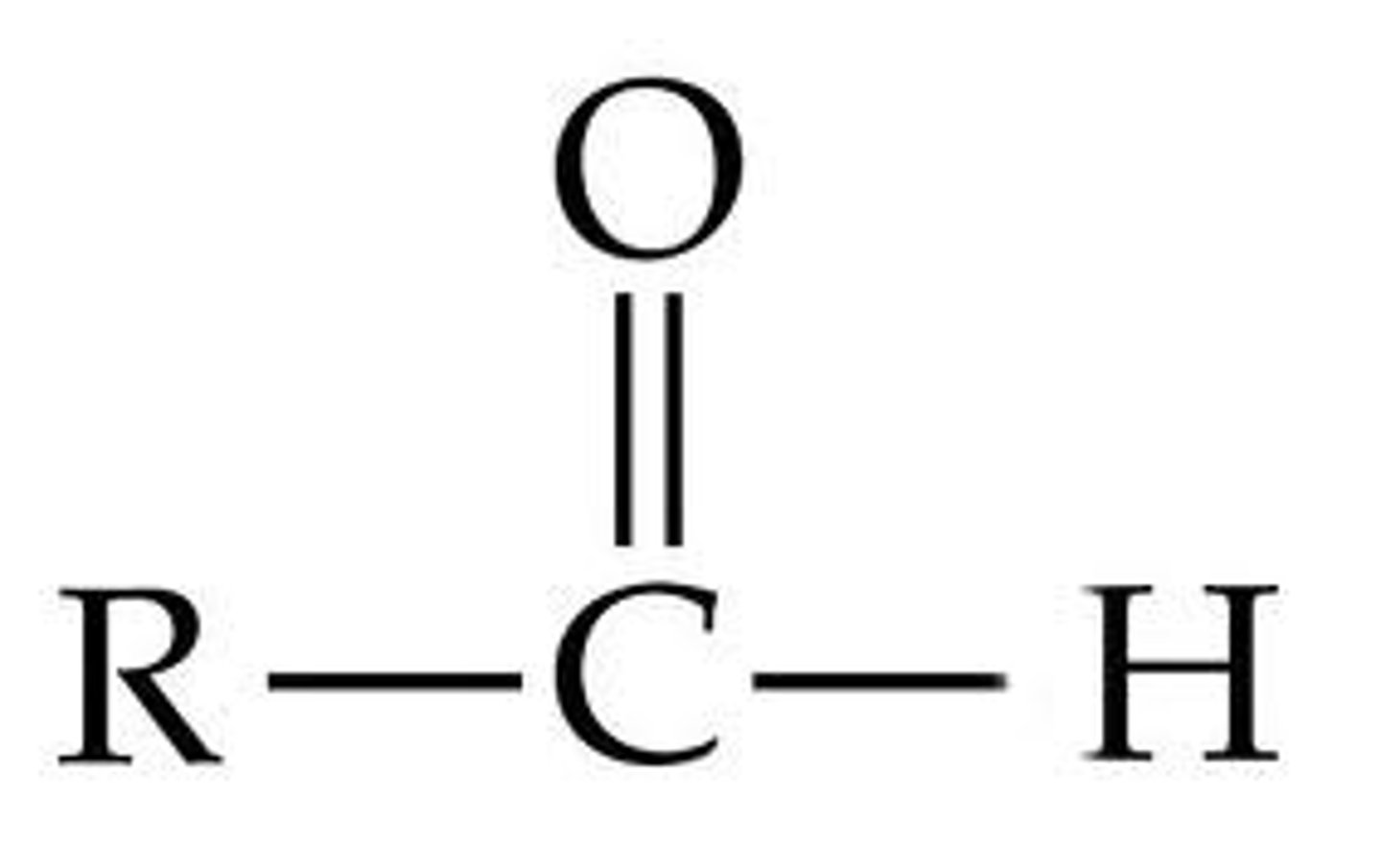
Aldehyde naming
-anal (no number required)
Amide (fnl gp)
C double bonded to O and single bonded to NH2
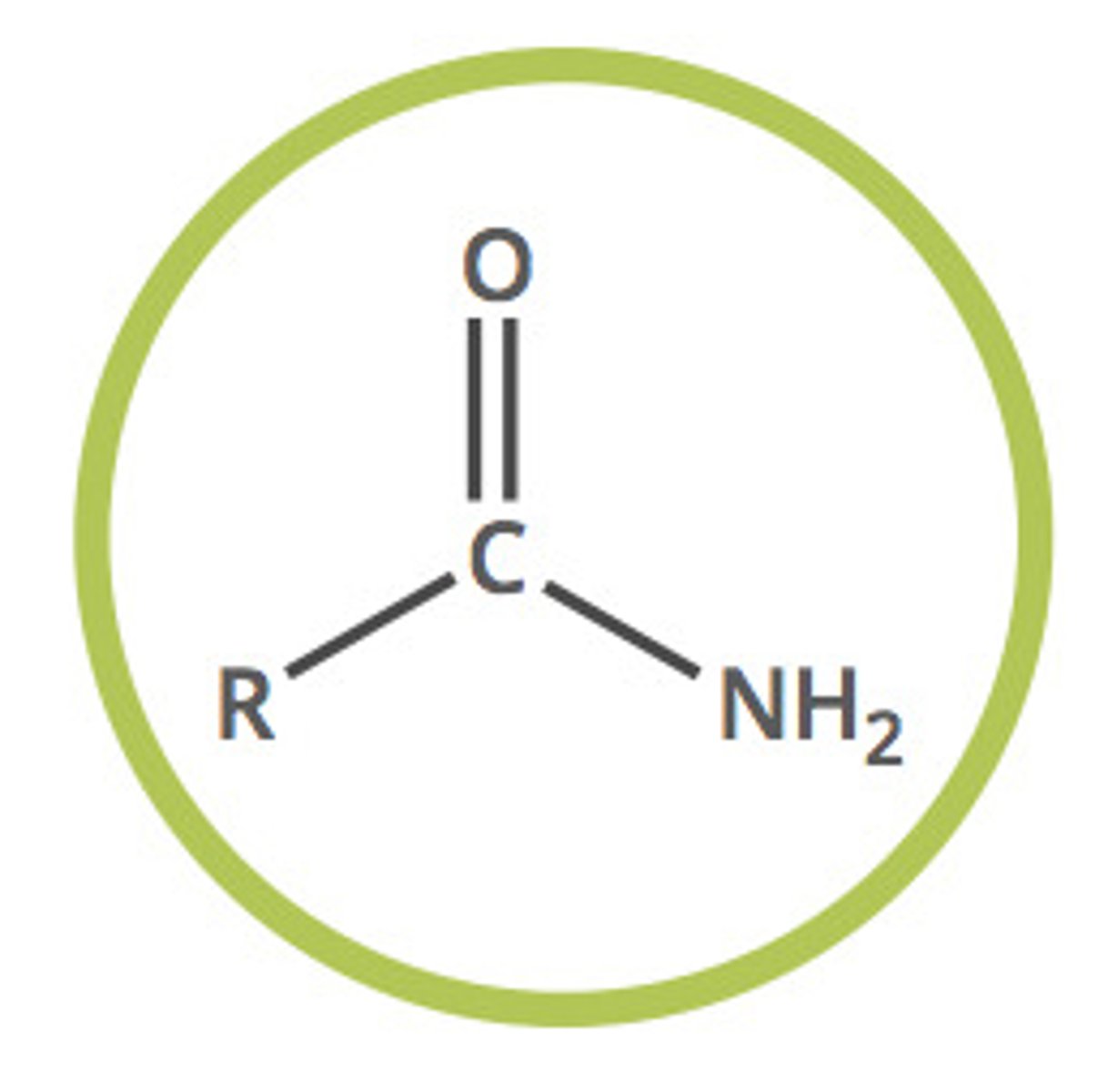
Amide naming
-anamide (no number required)
acid chloride (fnl gp)
C double bonded to O and single bonded to Cl
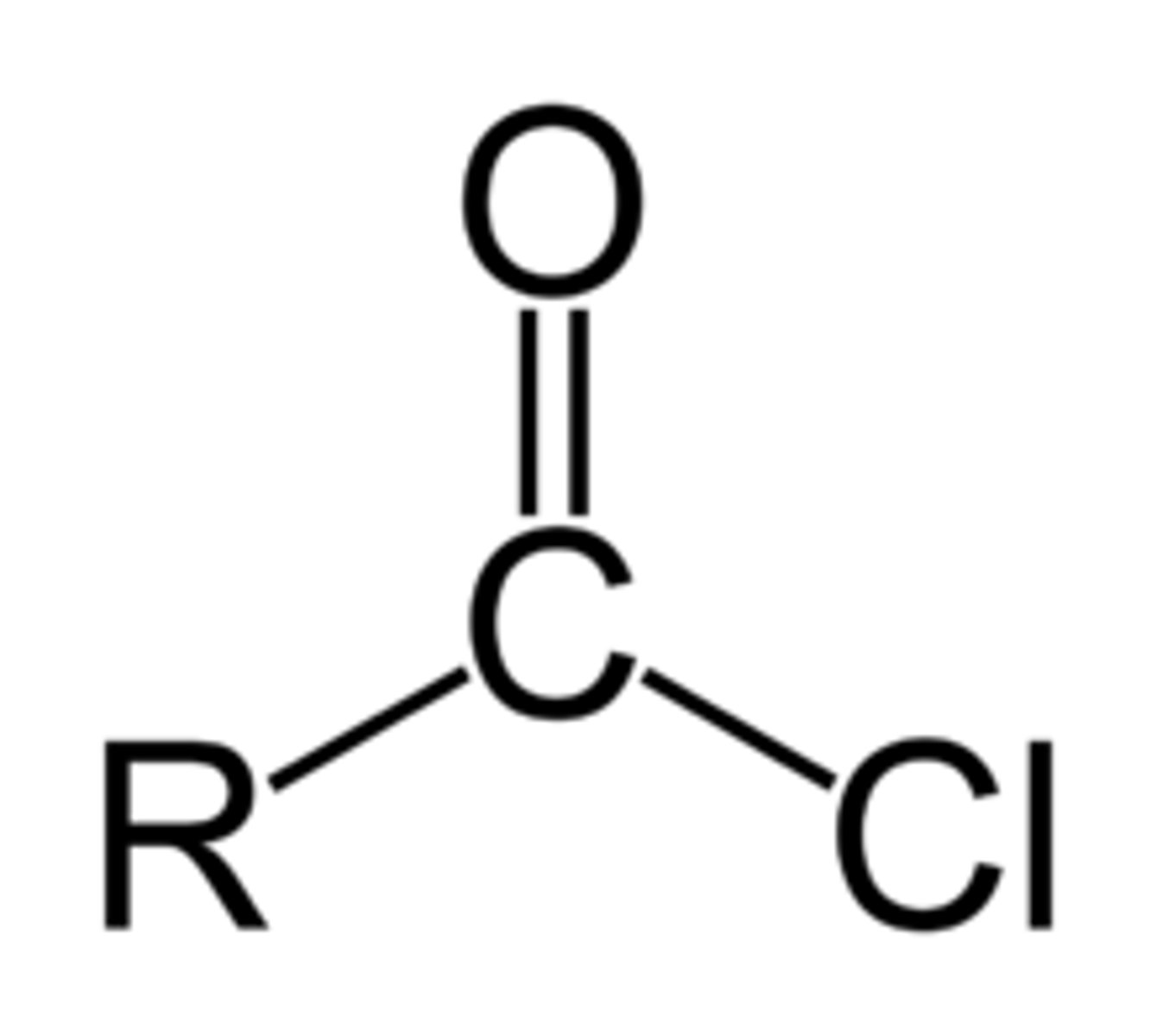
Acid chloride naming
-anoyl chloride (no number required)
ester (fnl gp)
C double bonded to O and single bonded to OR'
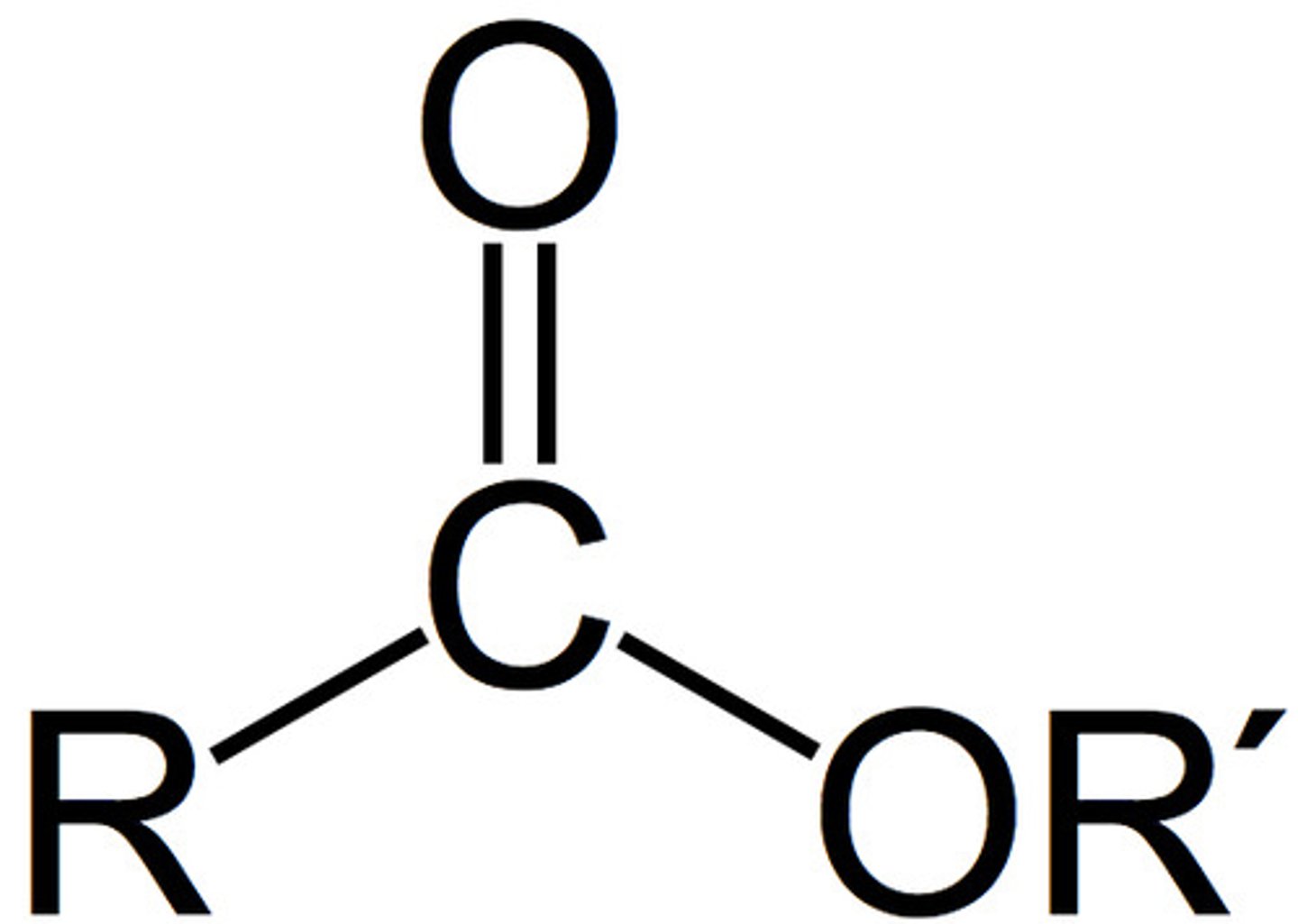
Ester naming
-anoyl carboxylate (no number required)