XRD Diffraction Theory
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
What does the x-axis represent in an X-ray diffraction pattern?
The diffraction angle 2θ, corresponding to the Bragg angle for lattice planes.
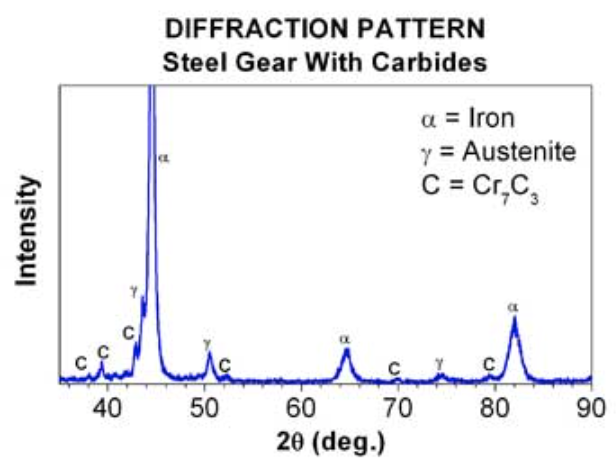
What does the y-axis represent in an X-ray diffraction pattern?
The diffracted X-ray intensity (counts) from crystallographic planes.
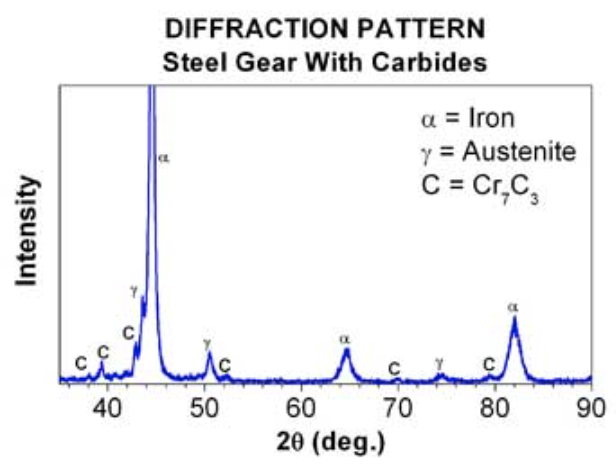
What causes the position of peaks along the 2θ axis?
The interplanar spacing (d) of lattice planes.
n\lambda = 2d\sin\theta
d = interplanar spacing
\theta = Bragg angle
What does a shift of peaks to lower 2θ values indicate?
An increase in d-spacing, usually due to lattice expansion or larger unit cell parameters.
What does peak intensity depend on in an XRD pattern?
The structure factor,
atomic positions,
atomic scattering factors,
and preferred orientation.
How does a single crystal XRD pattern differ from a powder XRD pattern?
A single crystal shows few sharp peaks,
while a powder shows many peaks from all orientations.
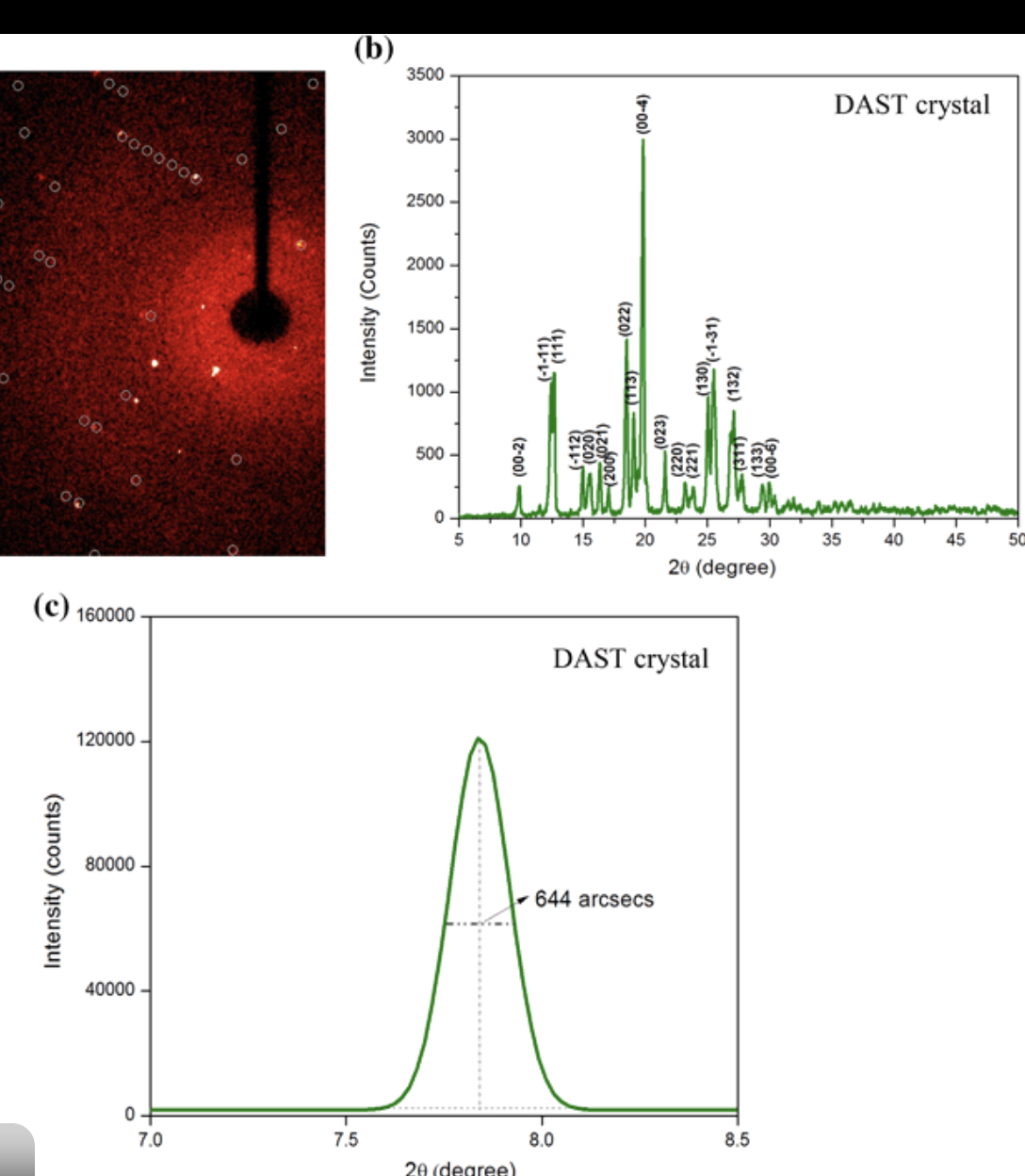
Why does a powder XRD pattern contain many diffraction peaks?
Because randomly oriented crystallites allow all possible (hkl) planes to satisfy Bragg’s law.
How does preferred orientation affect an XRD pattern?
It causes abnormally intense peaks and missing reflections.
What feature of an XRD pattern indicates nanocrystalline material?
Broad diffraction peaks due to small crystallite size.
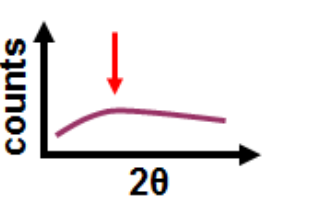
What causes peak broadening in XRD besides small crystallite size?
Lattice strain,
defects,
and instrumental broadening.
What is FWHM in an XRD peak?
The Full Width at Half Maximum, measuring peak broadness.
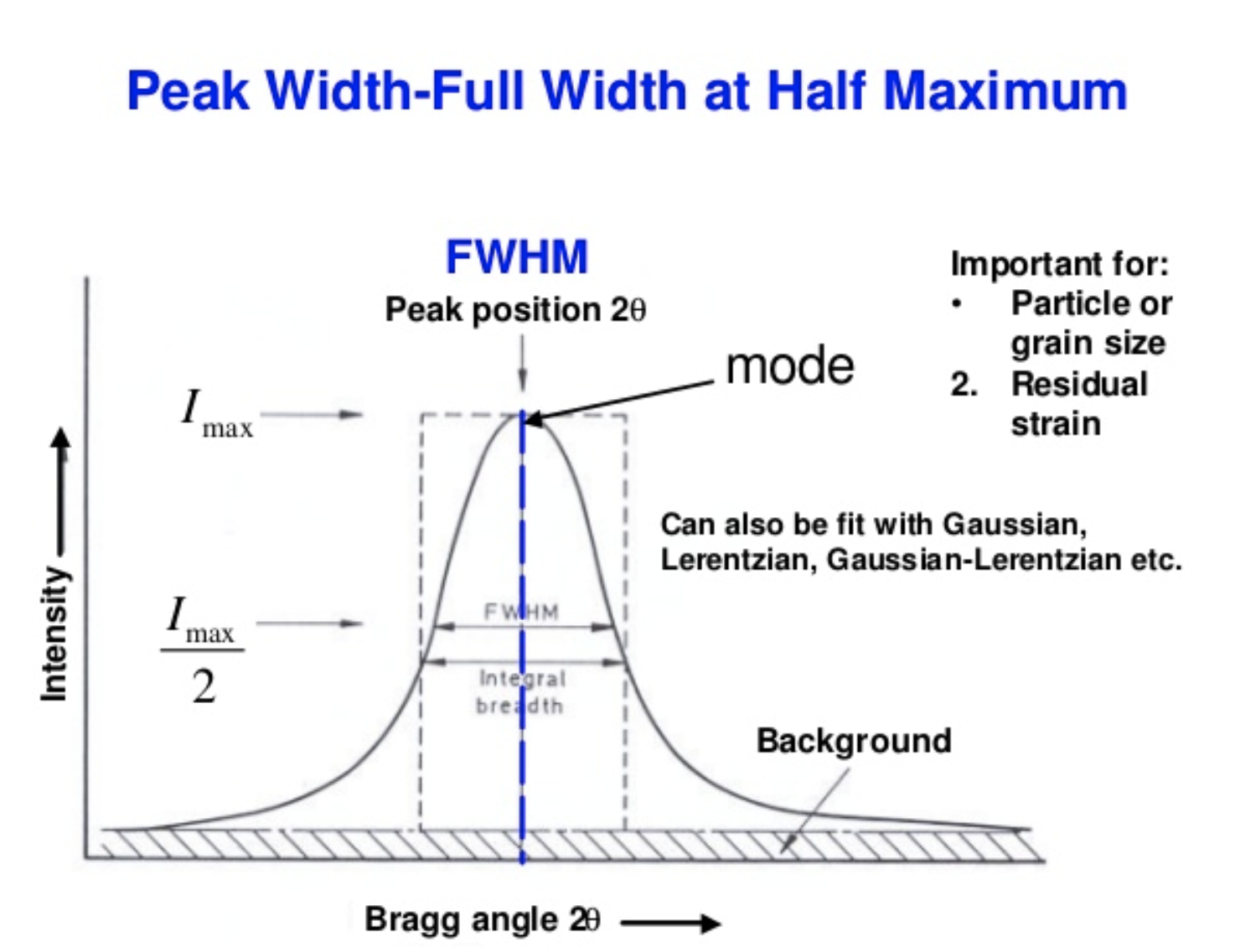
How is crystallite size calculated from an XRD peak?
Using the Scherrer equation.
t = \frac{K\lambda}{B\cos\theta}
t = crystallite size
K = shape factor
\lambda = X-ray wavelength
B = FWHM (radians)
\theta = Bragg angle
How can anisotropy be identified from XRD peak data?
Different crystallite sizes calculated from different peaks.
How do FCC and BCC lattices differ in diffraction patterns?
They show systematic absences due to lattice centering.
What reflection condition applies to FCC lattices?
Only reflections where h, k, l are all even or all odd appear.
What reflection condition applies to BCC lattices?
Only reflections where h + k + l is even appear.
What information does peak spacing (Δ2θ) provide?
It reflects lattice symmetry and allows indexing of diffraction patterns.
How does an amorphous material appear in an XRD pattern?
A broad diffuse hump with no sharp Bragg peaks.
How does a thin film XRD pattern differ from bulk powder?
It shows fewer peaks due to strong orientation effects.
Why do higher angle peaks often appear weaker?
Because intensity decreases with increasing sinθ/λ and atomic scattering factors.
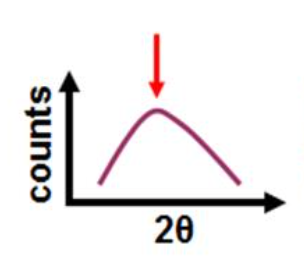
Identify the types of sample that gives rise to the following XRD pattern
Completely amorphous / essentially no crystalline order
Just background no diffraction peaks
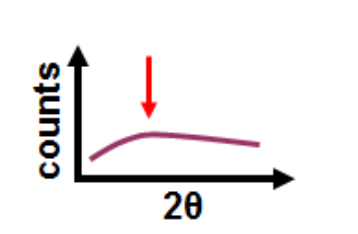
Identify the types of sample that gives rise to the following XRD pattern
Poorly crystalline / semi crystalline
May be nano crystalline or semicrystalline material
a very weak, broad, “bump” instead of sharp peaks
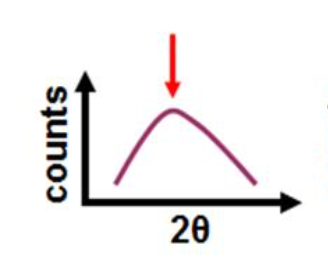
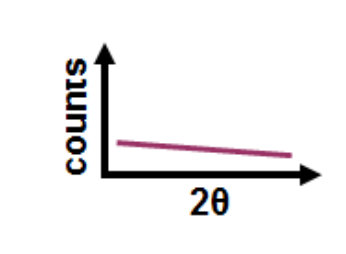
Identify the types of sample that gives rise to the following XRD pattern
Amorphous (glassy/ polymer- like) material
a broad diffuse hump = “amorphous halo” from short-range order
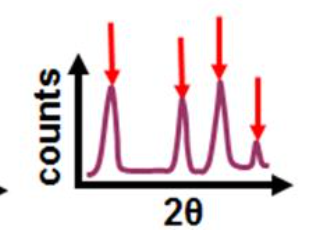
Identify the types of sample that gives rise to the following XRD pattern
Highly crystalline polycrystalline (powder) sample
multiple sharp bragg peaks