Management Accounting and its environment I
1/14
Earn XP
Description and Tags
These flashcards cover essential concepts from the lecture on management accounting and organizational structures, aimed at reinforcing key vocabulary and definitions relevant to the exam.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
Management Accounting
support decision-making and aid managers in the planning and control of operations.
Internal job to support internal decision-making having external impact.
accounting
The process of identifying, measuring, and communicating economic information to provide information for decision-making.
Management
Involves planning, decision-making, organizing, leading, motivating, and controlling resources to achieve objectives.

Management Functions
Key activities in management including planning, decision-making, controlling, and organizing efforts towards objectives.
Management Accountant
In the beginning (1950s), responsible for gathering, processing and providing information and emphasis on past performance and control in the short-run only.
changed in recent times because of, Rise of Enterprise Resource Planning systems, Automation through new technology and More emphasis on ethics in business.
Managers make decisions —— Management accountants support the decision-making.
Organisation
A series of activities of people aimed at achieving common goals through division of labor and a hierarchy of authority.
People working together to get things done.
why to manage organisation?
To manage conflicting interests
To maximise organisational objectives
To ensure smooth functioning of the organisations
Types of organisation
Generally:
Manufacturing company
Merchandizing company
Service company
Legal status:
Sole proprietorship
Partnership
Corporation
Purpose-wise:
For-profits
Non-profits
Dual purpose [new development]
principles of organisations
1. Hierarchy refers to how the organisation is structured. What different levels of management are there. It can be tall or flat.
2. Span of control means the number of employees directly reporting to a manager. It can be wide or narrow.
3. Chain of command refers to the number of different levels in the structure. It can be long or short.
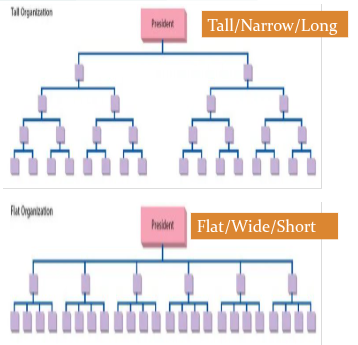
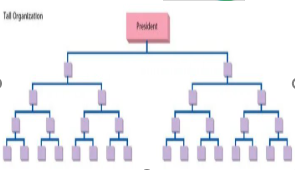
tall organisational structure
More hierarchical, with several layers of management, from executives at the top to low level employees at the bottom. Here each manager has a narrower span of control with less subordinates.
advantages: clearer communication, better supervision, and specialized roles.
disadvantages: slower decision-making and increased costs.
flat organisational structure
few layers of management with wider span of control with more employees.
advantages: faster decision-making, better communication, and increased employee autonomy.
disadvantages: may lead to overburdened managers, less supervision, and potential for role confusion.
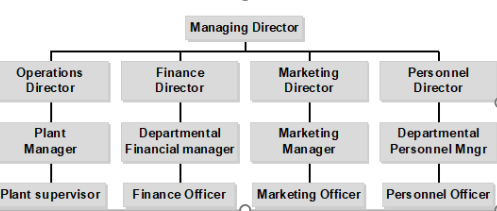
functional organisational structure
groups employees based on their job roles, utilising there specialisation and efficiency within specific areas such as marketing, finance, or production.
advantages: increased efficiency, clear career paths, and effective management of specialists.
disadvantages: potential for poor inter-departmental communication, and rigidity in adapting to changes.
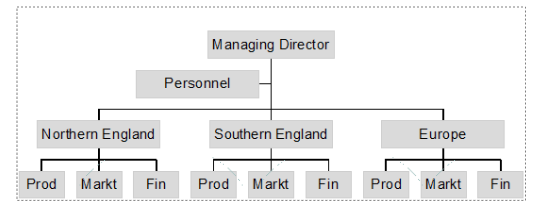
geographical organisational structure
An organizational design that arranges employees based on geographic regions or locations, allowing for tailored strategies and operations in different markets.
advantages: include localized decision-making, better customer responsiveness, and adaptation to regional preferences.
Disadvantages: may involve redundancy of roles, increased costs, and potential inconsistency across regions.
matrix organisational structure
employees report to multiple managers, typically a functional manager (for their department) and a project manager (for a specific project).
advantages: improved flexibility, enhanced collaboration, and better resource allocation.
disadvantages: potential for confusion in authority, increased complexity in management, and conflict between managers.
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP)
Integrated management software that organizations use to collect, store, manage, and interpret data from various business activities.