Balance of payments
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
What does the balance of payments consist of?
Current account, financial account, capital account.
What is the current account?
What does the current account consist of?
It is the payment for the purchase and sale of all goods and services and the flow of income
Trade of goods like raw materials and manufactured
Trade of services like tourism and banking
Income like interest payments
Current transfers like govt to govt payments
Whats the financial account and what does it consist of?
flow of money associated with savings and investment
Portfolio investment like buying and selling shares/bonds
Foreign direct investment
Forex reserve
Whats the capital account and whats it consist of?
Its the transfer of ownership products
Like patens or trade marks
How are the 3 components of the BoP linked?
they must equal to 0
if theres a CA deficit the FA and CA must be in surplus
What is a current account deficit?
What causes it?
When there are more imports than exports
Exchange rate: if the currency appreciates then imports will be cheaper and increase. Exports will decrease cus they’ll be more expensive for foreigners.
if the currency depreciates, imports will be more expensive and decrease, thus making CA deficit better. Exports will also be more attractive for foreigners.
Domestic inflation: if there’s inflation, people will import more as a substitute.
What is the link between the financial account and the exchange rate?
Inflow of financial assets increases the demand for a currency leading to appreciation. Outflow of financial assets increases the supply, causing depreciation.
A strong ER makes investment in a country attractive
Whereas weak does opposite
What are the pros and cons of a current account deficit?
Cons:
Debt because the deficit is payed for by the financial account. This is bad in the LR because of dependence on countries loans.
Depreciation due to a lower demand for domestic currency as they’re buying imports from foreign currencies and a increase in supply of foreign currency due to the buying of imports
Depreciation leads to loss of standards of living and import inflation cus its more expensive relative to before
Causes interest rates to go up cus of less confidence in borrowers
Credit crunch because a country is borrowing to sustain the huge amount of imports, which decreases investors confidence leading to them leaving or increasing interest rates, leading to credit crunch, defined as a decrease in available loans.
Pros:
Imported capital leads to growth of a country and LR growth.
Supports consumption and increase in AD
Evaluation: SR good LR bad
What are the pros and cons of a current account surplus?
Pros:
Makes the ER strong
Attracts foreign investment
Goods are cheaper for consumption
Low import inflation
High future incomes
Cons:
Lack of imports causes inefficiency due to less competition with foreign firms.
Appreciation cus of increased demand for domestic currency decreased supply.
EV: SR bad LR good
What are the 3 methods to correct a persistent current account deficit? Evaluate them.
Expenditure switching: shifting consumption from imports to exports
Protectionism like tariffs and quotas
Evaluation: Harms consumers cus they pay more and leads to retaliation
Exchange rate manipulation: Supply your own currency to make it depreciate to make goods cheaper and increase exports.
Evaluation: less imports which makes life worse but it decreases unemployment cus of exports
Expenditure reducing: reducing overall spending to lower import demand.
Contractionary fiscal policy (less govt spending) and contractionary monetary policy (IR) to shift AD left to decrease imports.
Evaluation: increased unemployment and less government spending on merit goods
Supply side policy: Increase exports competitiveness by increasing economic productivity
Shifting LRAS right through SS policy like govt provision or decreased taes
Evaluation: costs money, may be inefficent cus it dont work, time lag.
However has good LR benefits.
What does the J curve show and then draw it.
It shows the time lag of depreciation fixing a current account deficit by increasing exports.
It happens because firms and consumers take time to respond to price changes in exports.
It takes long for them to be certain that the currency will stay depreciated
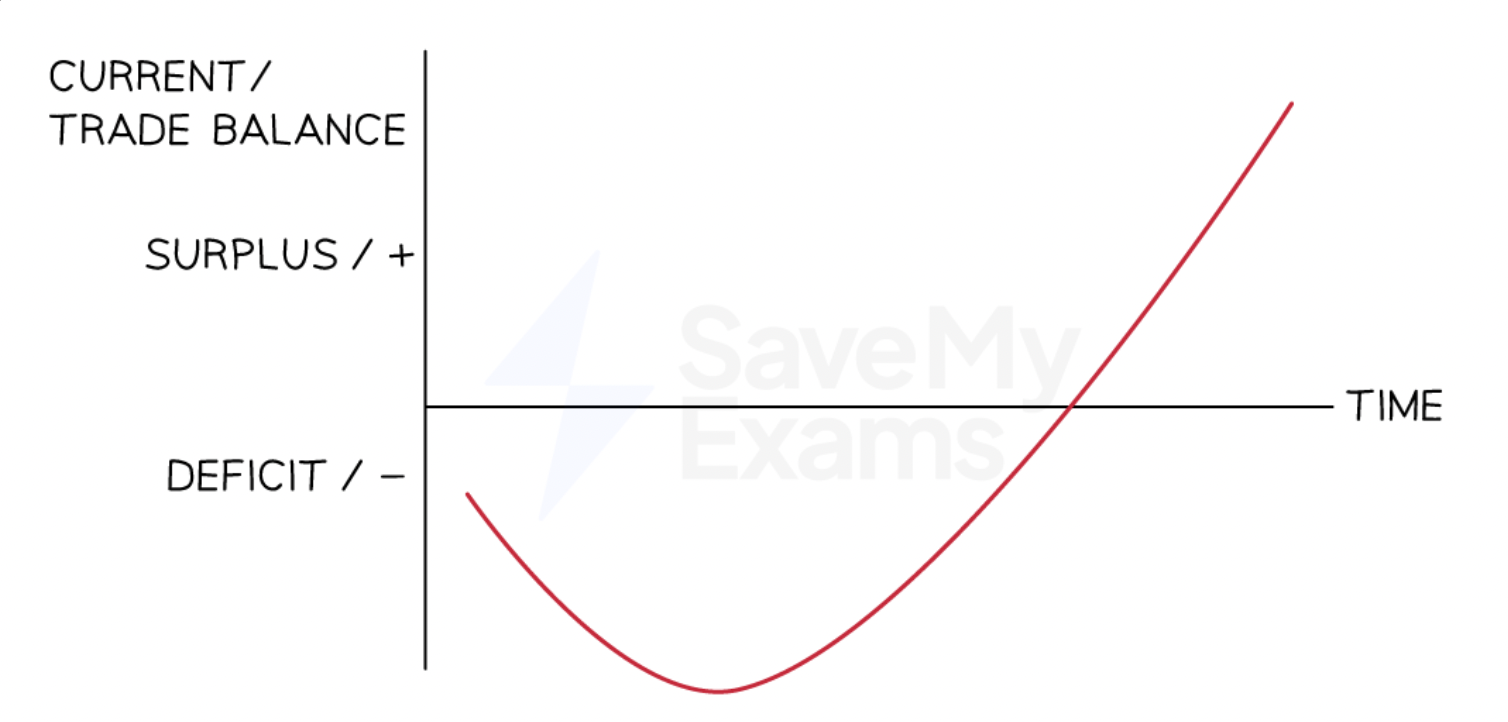
In the SR, demand for imports and exports is inelastic so firms have contracts and imperfect knowledge of the depreciation, meaning the current account deficit doesn’t improve but actually get worse.
In the LR, demand for imports and exports is elastic because firms are out of contracts and have better information, thus CA deficit impproves.
What is the marshall lerner condition?
It is a condition which means that depreciating the exchange rate only improves the CA deficit if it is met.
It happens when the PED for imports and exports is elastic or greater than 1.
If its met depreciation helps CA deficit
If its not met depreciation worsens the CA deficit.
impacts of a persistent current account surplus
Increased investment as exporting firms are making profit and higher profits increases consumption
Appreciating exchange rate due to increased demand for the domestic currency as more foreigners are buying exported goods.
This appreciation deters investment cus its expensive.
Inflation due to AD shift right
Unemployment falls
Export competitiveness falls