Cardiovascular Muscle
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
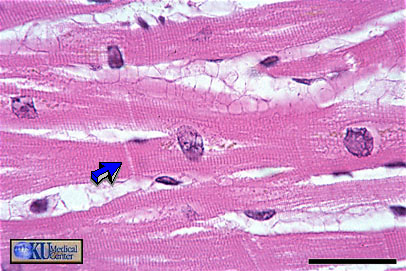
Cardiac Muscle: Longitudinal cardiac muscle can be identified by centrally placed round to oblong nuclei, striations, branching, and intercalated discs (arrow).
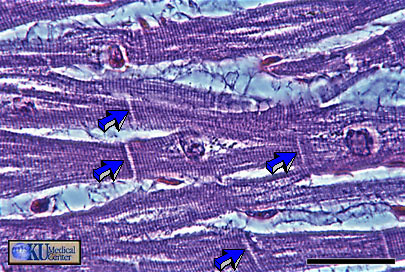
Cardiac Muscle: This photomicrograph of the same tissue taken in phase shows the striations and intercalated disks (arrows) more clearly.
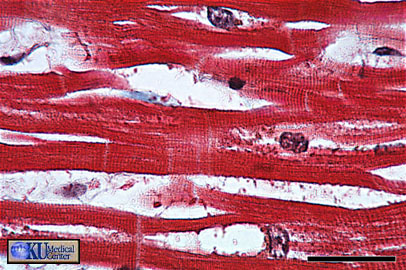
Cardiac Muscle: The trichrome stain also shows the characteristics of longitudinal cardiac muscle.
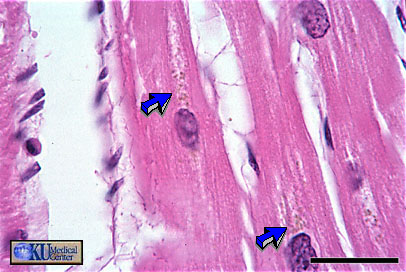
Cardiac Muscle: the arrows mark organelles of the cardiac myocyte. Specific organelles cannot be distinguished.
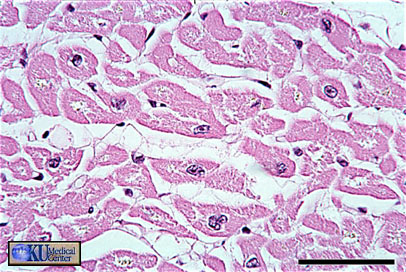
Cardiac Muscle: In cross section, cardiac muscle is identified by central nuclei and a large ring of surrounding cytoplasm.
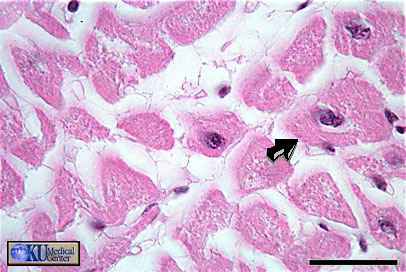
Cardiac Muscle: A closer look shows the large ring of cytoplasm that is at least twice the size of the smooth muscle ring.
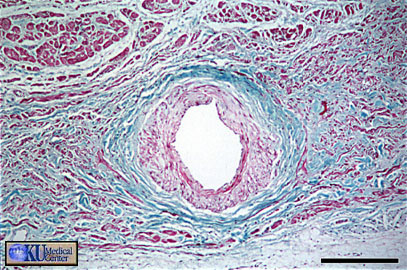
Sino-atrial Node: surrounds the nodal artery from which it receives a rich blood supply. These smaller, modified muscle cells generate the electrical signal that controls the heart.
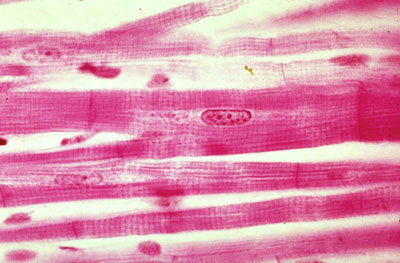
What type of muscle tissue is this?
Cardiac muscle
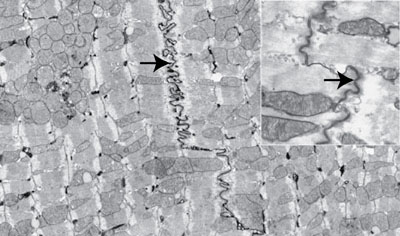
What is the function of this structure? What protein complexes mediate those functions
Physical connection of the cells and rapid spread of excitation impulse via its high electrical conductance. Desmosomes mediate physical connections and gap junctions mediate spread of action potentials.